



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 863-874. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016114 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016114
王月霞1, 金毅1, 吴初平1,2, 翁东明3, 叶立新4, 陈德良5, 余建平6, 刘金亮1, 仲磊1, 于明坚1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2016-04-29
接受日期:2016-08-10
出版日期:2016-08-20
发布日期:2016-09-02
通讯作者:
于明坚
基金资助:
Yuexia Wang1, Yi Jin1, Chuping Wu1,2, Dongming Wong3, Lixing Ye4, Deliang Chen5, Jianping Yu6, Jinliang Liu1, Lei Zhong1, Mingjian Yu1,*( )
)
Received:2016-04-29
Accepted:2016-08-10
Online:2016-08-20
Published:2016-09-02
Contact:
Yu Mingjian
摘要:
了解不同森林群落类型的物种和谱系水平的α和β多样性, 有助于指导森林经营和生物多样性保护。本研究比较了浙江省内不同地点主要森林类型(包括常绿阔叶林、常绿落叶阔叶混交林、落叶阔叶林和针阔叶混交林)的物种α多样性和谱系α多样性, 以及物种β多样性和谱系β多样性。研究表明, 该地区主要森林类型的物种和谱系α多样性均存在较大差异, 但控制了空间和地形因子的作用后, 差异几乎全部消失; 森林类型内部及相互间的物种和谱系β多样性均存在显著差异, 同种森林类型内部的物种和谱系β多样性分别小于不同森林类型之间的物种和谱系β多样性, 且在控制了空间和地形因子的作用后, 以上差异仍然显著。本研究表明影响亚热带主要森林群落类型物种和谱系水平的α和β多样性的因素存在差异: α多样性可能主要受到空间和地形因子等的影响, 而β多样性则可能受到森林类型的重要影响。
王月霞, 金毅, 吴初平, 翁东明, 叶立新, 陈德良, 余建平, 刘金亮, 仲磊, 于明坚 (2016) 浙江省主要亚热带森林群落类型物种和谱系水平的α和β多样性比较. 生物多样性, 24, 863-874. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016114.
Yuexia Wang, Yi Jin, Chuping Wu, Dongming Wong, Lixing Ye, Deliang Chen, Jianping Yu, Jinliang Liu, Lei Zhong, Mingjian Yu (2016) Taxonomic and phylogenetic α and β diversities of major subtropical forest community types in Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 24, 863-874. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016114.
图1 研究地点的地理分布图。WYL: 乌岩岭; BSZ: 百山祖; FYS: 凤阳山; JLS: 九龙山; GTS: 古田山; QLF: 清凉峰; TMS: 天目山; LWS: 龙王山。
Fig. 1 Geographic locations of the studied reserves. WYL, Wuyanling (119.641º-119.691º E, 27.667º-27.728º N); BSZ, Baishanzu (119.129º-119.322º E, 27.629º-27.842º N); FYS, Fengyangshan (119.100º-119.250º E, 27.767º-27.967 N); JLS, Jiulongshan (118.817º-118.917º E, 28.317º-28.400º N); GTS, Gutianshan (118.064º-118.187º E, 29.172º-29.295º N); TMS, Tianmushan (119.403º-119.453º E, 30.308º-30.360º N); QLF, Qingliangfeng (118.867º-119.183º E, 30.083º-30.283º N); LWS, Longwangshan (119.404º-119.438º E, 30.375º-30.417º N).
| 变量类型 Variable type | 描述 Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 分类变量 Categorical variable | 类别 Category | |
| 森林类型 Forest type | 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest (EBLF) 常绿落叶阔叶混交林 Evergreen deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest (EDBLF) 落叶阔叶林 Deciduous broad-leaved forest (DBLF) 针阔叶混交林 Coniferous broad-leaved mixed forest (CBLF) | |
| 连续变量 Continuous variable (unit) | 范围 Range | 平均值 Mean |
| 经度 Longitude (°) | 118.06-119.67 | 119.63 |
| 纬度 Latitude (°) | 27.54-30.40 | 28.95 |
| 海拔 Elevation (m) | 363-1,54 | 974.08 |
| 坡度 Slope (°) | 10.2-45 | 30.36 |
| 坡向 Aspect (°) | 5.0-358.6 | 172.5 |
表1 本研究所使用参数汇总
Table 1 Summary of the variables used in this study
| 变量类型 Variable type | 描述 Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 分类变量 Categorical variable | 类别 Category | |
| 森林类型 Forest type | 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest (EBLF) 常绿落叶阔叶混交林 Evergreen deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest (EDBLF) 落叶阔叶林 Deciduous broad-leaved forest (DBLF) 针阔叶混交林 Coniferous broad-leaved mixed forest (CBLF) | |
| 连续变量 Continuous variable (unit) | 范围 Range | 平均值 Mean |
| 经度 Longitude (°) | 118.06-119.67 | 119.63 |
| 纬度 Latitude (°) | 27.54-30.40 | 28.95 |
| 海拔 Elevation (m) | 363-1,54 | 974.08 |
| 坡度 Slope (°) | 10.2-45 | 30.36 |
| 坡向 Aspect (°) | 5.0-358.6 | 172.5 |
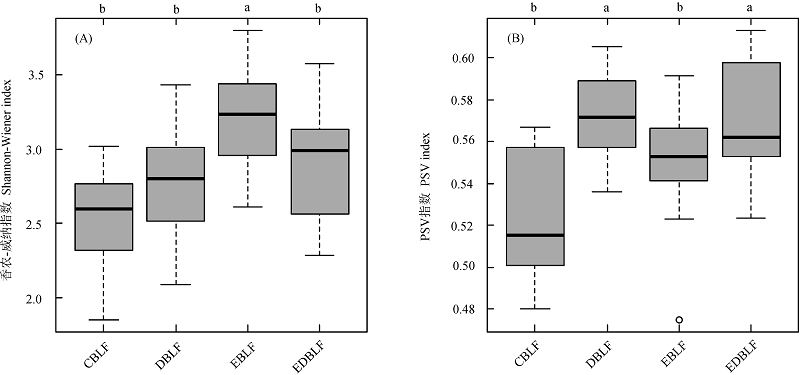
图2 不同森林类型间物种(A)与谱系(B) α多样性比较。不同小写字母表示组间差异显著(P < 0.05)。CBLF、DBLF、EBLF和EDBLF的含义见表1。
Fig. 2 Comparisons of taxonomic (A) and phylogenetic (B) α diversities among forest types. Different lower case letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). PSV, Phylogenetic species variability. See Table 1 for the key to CBLF, DBLF, EBLF and EDBLF.
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | PSV指数 PSV index | |
|---|---|---|
| 常绿阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林 EBLF vs. EDBLF | -0.128 | -0.019 |
| 常绿阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林 EBLF vs. DBLF | -0.042 | -0.042* |
| 常绿阔叶林vs.针阔叶混交林 EBLF vs. CBLF | 0 | -0.031 |
| 常绿落叶阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林 EDBLF vs. DBLF | -0.111 | 0.006 |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.针阔叶混交林 EDBLF vs. CBLF | 0.278 | 0.027 |
| 落叶阔叶林vs.针阔叶混交林 DBLF vs. CBLF | 0.328 | 0.019 |
表2 不同森林类型间物种和谱系α多样性差异的线性混合效应模型结果
Table 2 Linear mixed effects model results for the differences in taxonomic and phylogenetic α diversities among forest types
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | PSV指数 PSV index | |
|---|---|---|
| 常绿阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林 EBLF vs. EDBLF | -0.128 | -0.019 |
| 常绿阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林 EBLF vs. DBLF | -0.042 | -0.042* |
| 常绿阔叶林vs.针阔叶混交林 EBLF vs. CBLF | 0 | -0.031 |
| 常绿落叶阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林 EDBLF vs. DBLF | -0.111 | 0.006 |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.针阔叶混交林 EDBLF vs. CBLF | 0.278 | 0.027 |
| 落叶阔叶林vs.针阔叶混交林 DBLF vs. CBLF | 0.328 | 0.019 |
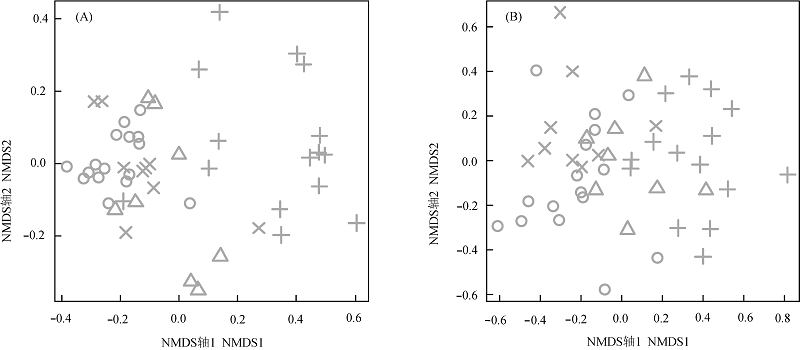
图3 研究区森林物种(A)和谱系(B) β多样性的非度量多维标度排序(NMDS)排序结果。○表示常绿阔叶林, △表示常绿落叶阔叶混交林, ×表示针阔叶混交林, +表示落叶阔叶林。
Fig. 3 Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling (NMDS) result of taxonomic (A) and phylogenetic (B) β diversities of the studied forests. ○, Evergreen broad-leaved forest (EBLF); △, Evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest (EDBLF); ×, Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest (CBLF); +, Deciduous broad-leaved forest (DBLF).
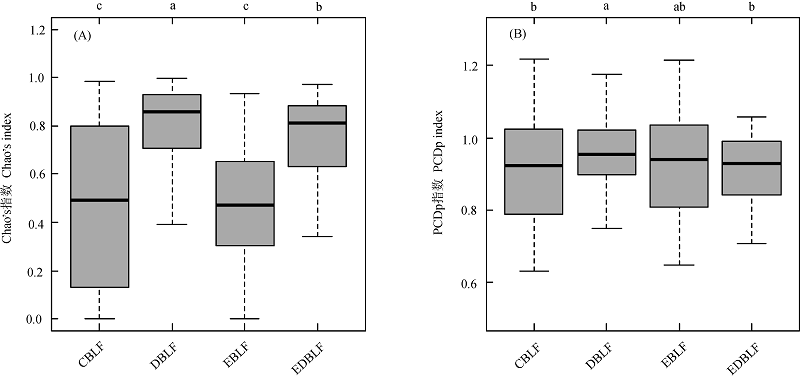
图4 同种森林类型内部的物种(A)与谱系(B) β多样性。不同小写字母表示组间差异显著(P < 0.05)。CBLF、DBLF、EBLF和EDBLF的含义见表1。
Fig. 4 Taxonomic (A) and phylogenetic (B) β diversities within forest types. Different lower case letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). PCDp, Phylogenetic community dissimilarity among nonshared species. See Table 1 for the key to CBLF, DBLF, EBLF and EDBLF.
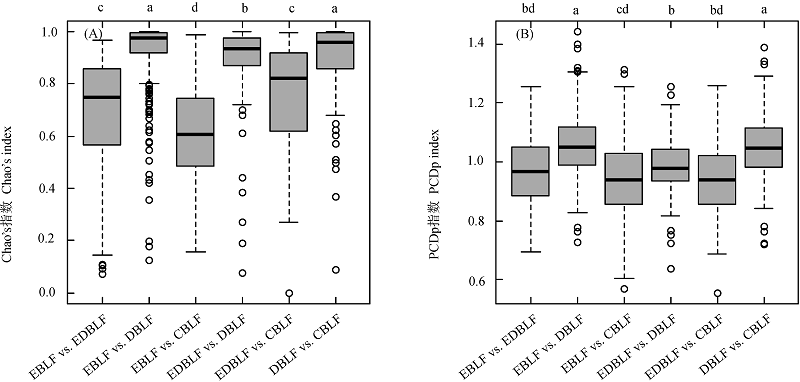
图5 不同森林类型之间的物种(A)与谱系(B) β多样性比较。不同小写字母表示组间差异显著(P < 0.05)。“vs.”表示前后两种森林类型间的β多样性。CBLF、DBLF、EBLF和EDBLF的含义见表1。
Fig. 5 Comparisons of the taxonomic (A) and phylogenetic (B) β diversities between forest types. Different lower case letter indicate significant difference (P < 0.05). “vs.” indicates the β diversity between forest types on its both sides. See Table 1 for the key to CBLF, DBLF, EBLF and EDBLF. PCDp, Phylogenetic community dissimilarity among nonshared species.
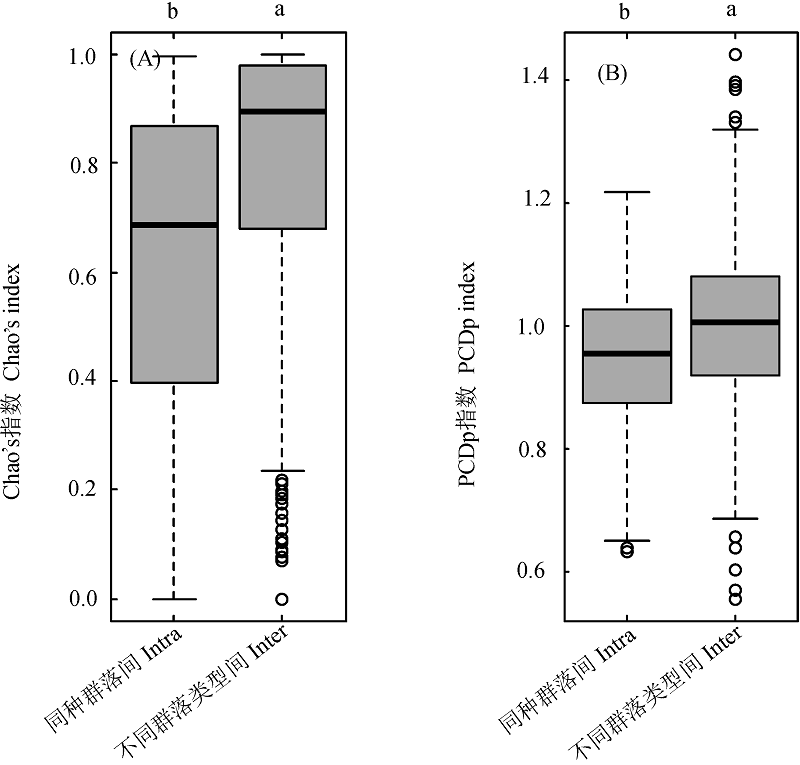
图6 森林群落类型内部及相互间的物种(A)与谱系(B) β多样性比较。使用线性混合效应模型控制了空间和环境因素的影响后, 两个组间的差异仍然显著(P < 0.05)。柱形上方若不存在相同英文字母, 表示组间有显著差异(P < 0.05)。“同种群落间”指同种森林群落间的β多样性, “不同群落类型间”指不同森林群落类型之间的β多样性。
Fig. 6 Comparisons of the taxonomic (A) and phylogenetic (B) β diversities within and between forest types. When the spatial and environmental variables effects were controlled in linear mixed effects model, differences between the two paired groups were still significant (P < 0.05 in both cases). Boxes with different lower case letter indicate significant difference (P < 0.05). “Intra” represents β diversity between communities from the same forest type, “Inter” represents β diversity between communities from different forest types. PCDp, Phylogenetic community dissimilarity among nonshared species.
| Chao’s指数 Chao’s index | PCDp指数 PCDp index | |
|---|---|---|
| 常绿阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林 EBLF vs. EDBLF | -0.073 | 0.006 |
| 常绿阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林 EBLF vs. DBLF | -0.256*** | -0.018* |
| 常绿阔叶林vs.针阔叶混交林 EBLF vs. CBLF | -0.038 | -0.129* |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.落叶阔叶林 EDBLF vs. DBLF | -0.13* | -0.067** |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.针阔叶混交林 EDBLF vs. CBLF | 0.244** | -0.044 |
| 落叶阔叶林vs.针阔叶混交林 DBLF vs. CBLF | 0.315*** | 0.02 |
表3 同种森林类型内部物种和谱系β多样性差异的线性混合效应模型结果
Table 3 Mixed effects model results for the differences in taxonomic and phylogenetic β diversities within forest types
| Chao’s指数 Chao’s index | PCDp指数 PCDp index | |
|---|---|---|
| 常绿阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林 EBLF vs. EDBLF | -0.073 | 0.006 |
| 常绿阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林 EBLF vs. DBLF | -0.256*** | -0.018* |
| 常绿阔叶林vs.针阔叶混交林 EBLF vs. CBLF | -0.038 | -0.129* |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.落叶阔叶林 EDBLF vs. DBLF | -0.13* | -0.067** |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.针阔叶混交林 EDBLF vs. CBLF | 0.244** | -0.044 |
| 落叶阔叶林vs.针阔叶混交林 DBLF vs. CBLF | 0.315*** | 0.02 |
| Chao’s指数 Chao’s index | PCDp指数 PCDp index | |
|---|---|---|
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. EBLF / DBLF | -0.135*** | -0.09*** |
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. EBLF / CBLF | 0.06 | 0.063** |
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. EDBLF / DBLF | 0.146*** | -0.021 |
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. EDBLF / CBLF | -0.052 | 0.033 |
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | -0.154*** | -0.012 |
| 常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林vs.常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / DBLF vs. EBLF / CBLF | 0.052* | 0.115*** |
| 常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林 EBLF / DBLF vs. EDBLF / DBLF | -0.021* | 0.059*** |
| 常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / DBLF vs. EDBLF / CBLF | 0.055* | 0.114*** |
| 常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / DBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | 0.019 | 0.01 |
| 常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林 EBLF / CBLF vs. EDBLF / DBLF | -0.141*** | -0.056* |
| 常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / CBLF vs. EDBLF / CBLF | -0.063** | -0.01 |
| 常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / CBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | -0.192*** | -0.132*** |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林 EDBLF / DBLF vs. EDBLF / CBLF | 0.064* | 0.067** |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EDBLF / DBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | 0.064* | -0.005 |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EDBLF / CBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | -0.079** | -0.112*** |
表4 不同森林类型之间物种和谱系β多样性差异的线性混合效应模型结果
Table 4 Linear mixed effects model results for the differences in taxonomic and phylogenetic β diversities between forest types
| Chao’s指数 Chao’s index | PCDp指数 PCDp index | |
|---|---|---|
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. EBLF / DBLF | -0.135*** | -0.09*** |
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. EBLF / CBLF | 0.06 | 0.063** |
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. EDBLF / DBLF | 0.146*** | -0.021 |
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. EDBLF / CBLF | -0.052 | 0.033 |
| 常绿阔叶林/常绿落叶阔叶混交林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / EDBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | -0.154*** | -0.012 |
| 常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林vs.常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / DBLF vs. EBLF / CBLF | 0.052* | 0.115*** |
| 常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林 EBLF / DBLF vs. EDBLF / DBLF | -0.021* | 0.059*** |
| 常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / DBLF vs. EDBLF / CBLF | 0.055* | 0.114*** |
| 常绿阔叶林/落叶阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / DBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | 0.019 | 0.01 |
| 常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林 EBLF / CBLF vs. EDBLF / DBLF | -0.141*** | -0.056* |
| 常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / CBLF vs. EDBLF / CBLF | -0.063** | -0.01 |
| 常绿阔叶林/针阔叶混交林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EBLF / CBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | -0.192*** | -0.132*** |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林vs.常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林 EDBLF / DBLF vs. EDBLF / CBLF | 0.064* | 0.067** |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林/落叶阔叶林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EDBLF / DBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | 0.064* | -0.005 |
| 常绿落叶阔叶混交林/针阔叶混交林vs.落叶阔叶林/针阔叶混交林 EDBLF / CBLF vs. DBLF / CBLF | -0.079** | -0.112*** |
| [1] | Arellano G, Tello JS, Jørgensen PM, Fuentes AF, Loza MI, Torrez V, Macía MJ (2015) Disentangling environmental and spatial processes of community assembly in tropical forests from local to regional scales. Oikos, 51, 327-335. |
| [2] | Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67, 1-48. |
| [3] | Beckage B, Osborne B, Gavin DG, Pucko C, Siccama T, Perkins T (2008) A rapid upward shift of a forest ecotone during 40 years of warming in the green mountains of Vermont. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 4197-4202. |
| [4] | Bolker BM, Brooks ME, Clark CJ, Geange SW, Poulsen JR, Stevens MHH, White JSS (2009) Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 24, 127-135. |
| [5] | Bruelheide H, Böhnke M, Both S, Fang T, Assmann T, Baruffol M, Bauhus J, Buscot F, Chen XY, Ding BY, Durka W, Erfmeier A, Fischer M, Geißler C, Guo DL, Guo LD, Härdtle W, He JS, Hector A, Kröber W, Kühn P, Lang AC, Nadrowski K, Pei KQ, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Shi XZ, Scholten T, Schuldt A, Trogisch S, von Oheimb G, Welk E, Wirth C, Wu YT, Yang XF, Zeng XQ, Zhang SR, Zhou HZ, Ma KP, Schmid B (2011) Community assembly during secondary forest succession in a Chinese subtropical forest. Ecological Monographs, 81, 25-41. |
| [6] | Cayuela L, Oksanen J (2016) Taxonstand: Taxonomic Standardization of Plant Species Names. R package Version 1.8. (accessed on 2016-04-14) |
| [7] | Chao A, Chazdon RL, Colwell RK, Shen TJ (2006) Abundance-based similarity indices and their estimation when there are unseen species in samples. Biometrics, 62, 361-371. |
| [8] | Chave J (2009) Spatial variation in tree species composition across tropical forests: pattern and process. In: Tropical Forest Community Ecology (eds Carson WP, Schnitzer S), pp. 11-30. Wiley/Blackwell, Hoboken, NJ, USA. |
| [9] | Chen LZ, Chen QL, Liu WH (1997) Forest Diversity and Its Geographical Distribution in China. Science Press, Beijing. |
| [陈灵芝, 陈清朗, 刘文华 (1997) 中国森林多样性及其地理分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Cheng QB, Wu MX, Chen HT (1996) Comprehensive observations report on Fengyangshan-Baishanzu Nature Reserve of Zhejiang. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 16(6), 1-7. (in Chinese) |
| [程秋波, 吴鸣翔, 陈豪庭 (1996) 浙江凤阳山-百山祖自然保护区综合考察报告. 浙江林业科技, 16(6), 1-7.] | |
| [11] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and A Comparison with Other Plots. Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin, Germany. |
| [12] | Cun YZ, Wang XQ (2010) Plant recolonization in the Himalaya from the Southeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: geographical isolation contributed to high population differentiation. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56, 972-982. |
| [13] | de Cáceres M, Legendre P, Valencia R, Cao M, Chang LW, Chuyong G, Condit R, Hao ZQ, Hsieh CF, Hubbell S, Kenfack D, Ma KP, Mi XC, Noor MNS, Kassim AR, Ren HB, Su SH, Sun IF, Thomas D, Ye WH, He FL (2012) The variation of tree beta diversity across a global network of forest plots. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1191-1202. |
| [14] | Ding HB, Wu ZL, Lü DP, Wu QJ, Shan MY, Bai HT, Luo K (2015) Community phylogenetic structural characteristics of various secondary forests in mountainous Eastern Yunnan. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 2720-2726. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁洪波, 吴兆录, 吕东蓬, 武秋君, 单梦颖, 白皓天, 罗康 (2015) 云南东部山区不同类型次生林群落谱系结构特征. 生态学杂志, 34, 2720-2726.] | |
| [15] | Fang JY, Ohsawa M, Kira T (1996) Vertical vegetation zones along 30° N latitude in humid East Asia. Plant Ecology, 126, 135-149. |
| [16] | Feng G, Svenning JC, Mi XC, Jia Q, Rao MD, Ren HB, Bebber D, Ma KP (2014) Anthropogenic disturbance shapes phylogenetic and functional tree community structure in a subtropical forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 313, 188-198. |
| [17] | Helmus MR, Bland TJ, Williams CK, Ives AR (2007) Phylogenetic measures of biodiversity. The American Naturalist, 169, E68-E83. |
| [18] | Ives AR, Helmus MR (2010) Phylogenetic metrics of community similarity. The American Naturalist, 176, 559-559. |
| [19] | Jin Y, Qian H, Yu MJ (2015) Phylogenetic structure of tree species across different life stages from seedlings to canopy trees in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. PLoS ONE, 10, e0131162. |
| [20] | Jones MM, Tuomisto H, Borcard D, Legendre P, Clark DB, Olivas PC (2008) Explaining variation in tropical plant community composition: influence of environmental and spatial data quality. Oecologia, 155, 593-604. |
| [21] | Kembel SW, Hubbell SP (2006) The phylogenetic structure of a neotropical forest tree community. Ecology, 87, S86-S99. |
| [22] | Kembel SW, Cowan PD, Helmus MR, Cornwell WK, Morlon H, Ackerly DD, Blomberg SP, Webb CO (2010) Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics, 26, 1463-1464. |
| [23] | Kira T (1991) Forest ecosystems of East and Southeast Asia in a global perspective. Ecological Research, 6, 185-200. |
| [24] | Legendre P, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP, Yu MJ, Sun IF, He FL (2009) Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China. Ecology, 90, 663-674. |
| [25] | Letcher SG (2010) Phylogenetic structure of angiosperm communities during tropical forest succession. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 277, 97-104. |
| [26] | Liu XJ, Swenson NG, Wright SJ, Zhang LW, Song K, Du YJ, Zhang JL, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2012) Covariation in plant functional traits and soil fertility within two species-rich forests. PLoS ONE, 7, e34767. |
| [27] | Liu XJ, Swenson NG, Zhang JW, Ma KP (2013) The environment and space, not phylogeny, determine trait dispersion in a subtropical forest. Functional Ecology, 27, 264-272. |
| [28] | Liu YL, Guo RQ, Sun SC (2010) Variations in the vertical vegetation zonation of subtropical Chinese mountains: the importance of climatic seasonality. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 3912-3922. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘亚兰, 郭汝清, 孙书存 (2010) 中国亚热带山地植被垂直带分布对气候季节性的响应. 生态学报, 30, 3912-3922.] | |
| [29] | López-Martínez JO, Hernández-Stefanoni JL, Dupuy JM, Meave JA (2013) Partitioning the variation of woody plant β-diversity in a landscape of secondary tropical dry forests across spatial scales. Journal of Vegetation Science, 24, 33-45. |
| [30] | Lu P, Jin Y, Chen JH, Li MH, Yu MJ (2013) Influences of geographical distance and topographic difference on β diversity of two large-scale forest dynamics plots. Biodiversity Science, 21, 554-563. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢品, 金毅, 陈建华, 李铭红, 于明坚 (2013) 地理距离和地形差异对两个大型森林动态样地β多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 21, 554-563.] | |
| [31] | Myers JA, Chase JM, Jiménez I, Jørgensen PM, Araujo- Murakami A, Paniagua-Zambrana N, Seidel R (2013) Beta-diversity in temperate and tropical forests reflects dissimilar mechanisms of community assembly. Ecology Letters, 16, 151-157. |
| [32] | Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2016) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package Version 2.3-4. (accessed on 2016-06-25) |
| [33] | Qian H, Jin Y (2016) An updated megaphylogeny of plants, a tool for generating plant phylogenies and an analysis of phylogenetic community structure. Journal of Plant Ecology, 9, 233-239. |
| [34] | Qian H, Hao ZQ, Zhang J (2014) Phylogenetic structure and phylogenetic diversity of angiosperm assemblages in forests along an elevational gradient in Changbaishan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 7, 154-165. |
| [35] | R Core Team (2016) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [36] | Shen GC, He FL, Waagepetersen R, Sun IF, Hao ZQ, Chen ZS, Yu MJ (2013) Quantifying effects of habitat heterogeneity and other clustering processes on spatial distributions of tree species. Ecology, 94, 2436-2443. |
| [37] | Silvertown J, Dodd M, Gowing D, Lawson C, Mcconway K (2006) Phylogeny and the hierarchical organization of plant diversity. Ecology, 87, S39-S49. |
| [38] | Singmann H, Bolker B, Westfall J, Aust F, Højsgaard S, Fox J, Lawrence MA, Mertens U (2016) afex: Analysis of Factorial Experiments. R Package Version 0.16-1. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=afex (accessed on 2016-04-14) |
| [39] | Song K, Mi XC, Jia Q, Ren HB, Bebber D, Ma KP (2011) Variation in phylogenetic structure of forest communities along a human disturbance gradient in Gutianshan forest, China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 190-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋凯, 米湘成, 贾琪, 任海保, Bebber D, 马克平 (2011) 不同程度人为干扰对古田山森林群落谱系结构的影响. 生物多样性, 19, 190-196.] | |
| [40] | Song YC (1999) Perspective of the vegetation zonation of forest region in Eastern China. Acta Botanica Sinica, 41, 541-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋永昌 (1999) 中国东部森林植被带划分之我见. 植物学报, 41, 541-552.] | |
| [41] | Song YC (2013) Evergreen Broad-leaved Forests in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [宋永昌(2013) 中国常绿阔叶林. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] | State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) (1998) China’s Biodiversity: A Country Study. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中华人民共和国国家环境保护局(1998) 中国生物多样性国情研究报告. 中国环境科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] | Tello JS, Myers JA, Macía MJ, Fuentes AF, Cayola L, Arellano G, Loza MI, Torrez V, Cornejo, Miranda TB, Jørgensen PM (2015) Elevational gradients in β-diversity reflect variation in the strength of local community assembly mechanisms across spatial scales. PLoS ONE, 10, e0121458. |
| [44] | Webb CO, Ackerly DD, Kembel SW (2008) Phylocom: software for the analysis of phylogenetic community structure and trait evolution. Bioinformatics, 24, 2098-2100. |
| [45] | Whittaker RH, Niering WA (1965) Vegetation of the Santa Catalina Mountains, Arizona: a gradient analysis of the south slope. Ecology, 46, 429-452. |
| [46] | Wiens JJ, Graham CH (2005) Niche conservatism: integrating evolution, ecology, and conservation biology. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution & Systematics, 36, 519-539. |
| [47] | Wu ZY (1995) Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒 (1995) 中国植被. 科学出版社, 北京] | |
| [48] | Xiang QY (Jenny), Zhang WH, Ricklefs RE, Qian H, Chen ZD, Wen J, Li JH (2004) Regional differences in rates of plant speciation and molecular evolution: a comparison between eastern Asia and eastern North America. Evolution, 58, 2175-2184. |
| [49] | Yu MJ, Hu ZH, Yu JP, Ding BY, Fang T (2001) Forest vegetation types in Gutianshan Nature Reserve in Zhejiang. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Science), 27, 375-380. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于明坚, 胡正华, 余建平, 丁炳扬, 方腾 (2001) 浙江古田山自然保护区森林植被类型. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 27, 375-380.] | |
| [50] | Zanne AE, Tank DC, Cornwell WK, Eastman JM, Smith SA, Fitzjohn RG, McGlinn DJ, O’Meara BC, Moles AT, Reich PB, Royer DL, Soltis DE, Stevens PF, Westoby M, Wright IJ, Aarssen L, Bertin RI, Calaminus A, Govaerts R, Hemmings F, Leishman MR, Oleksyn J, Soltis PS, Swenson NG, Warman L, Beaulieu JM (2015) Three keys to the radiation of angiosperms into freezing environments. Nature, 521, 89-92. |
| [51] | Zhao TQ, Ouyang ZY, Zheng H, Wang XK, Miao H (2004) Forest ecosystem services and their valuation in China. Journal of Natural Resources, 19, 480-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵同谦, 欧阳志云, 郑华, 王效科, 苗鸿 (2004) 中国森林生态系统服务功能及其价值评价. 自然资源学报, 19, 480-491.] | |
| [52] | Zheng CZ (2005) Key of Seed Plants in Zhejiang Province. Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [郑朝宗 (2005) 浙江种子植物检索鉴定手册. 浙江科学技术出版社, 杭州.] |
| [1] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [2] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [3] | 李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦. 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [4] | 王启蕃, 刘小慧, 朱紫薇, 刘磊, 王鑫雪, 汲旭阳, 周绍春, 张子栋, 董红雨, 张明海. 黑龙江北极村国家级自然保护区鸟类与兽类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [5] | 所翟, 俞渃茜, 李媛辉, 徐基良. 基于实证分析中国自然保护区地方立法问题检视和优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [6] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [7] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [8] | 陈明苗, 张楚然, 邓云, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 魏兆喆, 张彩彩, 林露湘. 地形因子对亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物萌生特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24282-. |
| [9] | 熊松, 淦江, 谢彦军, 邓晰朝, 覃国乐, 彭晚霞, 曾馥平, 占志立, 谭卫宁, 黄国勤, 杜虎. 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林凋落物产量动态及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24248-. |
| [10] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [11] | 毛锐锐, 沈拓, 李慧, 田琳楚, 谭海蓉, 卢李荣, 吴小刚, 范宗骥, 伍国仪, 李杰, 吴勇, 朱弼成, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区无尾两栖类动物鸣声特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [12] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [13] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [14] | 邓婷婷, 魏岩, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林地形和林分结构对林下草本植物物种多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22671-. |
| [15] | 陈本平, 陈建武, 凌征文, 杨旭, 陈鑫, 李生强, 杨彪. 四川老君山国家级自然保护区林下鸟兽多样性及动态变化数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22566-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn