



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 89-100. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014213 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014213
陈小林1, 陈光杰1,*( ), 卢慧斌1, 刘晓东2, 张虎才1
), 卢慧斌1, 刘晓东2, 张虎才1
收稿日期:2014-10-09
接受日期:2014-12-26
出版日期:2015-01-20
发布日期:2015-05-04
通讯作者:
陈光杰
作者简介:E-mail: guangjiechen@gmail.com基金资助:
Xiaolin Chen1, Guangjie Chen1,*( ), Huibin Lu1, Xiaodong Liu2, Hucai Zhang1
), Huibin Lu1, Xiaodong Liu2, Hucai Zhang1
Received:2014-10-09
Accepted:2014-12-26
Online:2015-01-20
Published:2015-05-04
Contact:
Guangjie Chen
摘要:
目前国内对生产力-生物多样性关系(productivity-diversity relationship, PDR)的研究主要集中于陆地生态系统和空间尺度, 少量关于湖泊系统的研究也主要集中于现代调查, 缺乏较长时间尺度上的模式探讨。本文应用沉积物色素记录重建了抚仙湖和滇池初级生产力变化历史, 对硅藻群落的主成分分析(PCA)表明两个湖泊的初级生产力都是驱动硅藻群落变化的主要环境梯度。进一步分析硅藻群落α与β多样性响应湖泊生产力水平的模式, 发现滇池硅藻群落表现为随着系统生产力的上升物种丰富度减少, β多样性降低, 而抚仙湖呈现相反的变化模式。两个湖泊β多样性与生产力平均水平的关系均表现出与α多样性相似的特征, 但在与生产力变化幅度的关系上, 滇池表现出显著的负相关, 而抚仙湖则没有显著的变化。滇池硅藻群落生产力随硅藻多样性的降低显著增加(R 2 = 0.597, P < 0.01), 而在抚仙湖无显著变化, 表明了滇池群落多样性的维持对群落生产力的影响较弱, 如与营养盐富集的促进作用相比。滇池明显的富营养化过程与强烈的人类扰动带来的环境异质性降低可能对群落多样性-生产力的关系产生了明显的控制作用。
陈小林, 陈光杰, 卢慧斌, 刘晓东, 张虎才 (2015) 抚仙湖和滇池硅藻生物多样性与生产力关系的时间格局. 生物多样性, 23, 89-100. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014213.
Xiaolin Chen, Guangjie Chen, Huibin Lu, Xiaodong Liu, Hucai Zhang (2015) Long-term diatom biodiversity responses to productivity in lakes of Fuxian and Dianchi. Biodiversity Science, 23, 89-100. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014213.
| 湖泊 Lake | 水域面积 Surface area (km2)* | 最大水深 Maximal depth (m)# | 平均水深 Mean depth (m)# | pH | 总氮 TN (μg/L) | 总磷 TP (μg/L) | 叶绿素a Chl-a (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抚仙湖 Fuxian Lake | 216.6 | 155 | 89.7 | 9.0 | 136.7 | 10.0 | 1.4 |
| 滇池 Dianchi Lake | 298.0 | 6.5 | 2.9 | 9.1 | 3,548.0 | 192.0 | 62.0 |
表1 抚仙湖和滇池湖泊学基本特征
Table 1 Summary of key limnological features for Fuxian and Dianchi lakes
| 湖泊 Lake | 水域面积 Surface area (km2)* | 最大水深 Maximal depth (m)# | 平均水深 Mean depth (m)# | pH | 总氮 TN (μg/L) | 总磷 TP (μg/L) | 叶绿素a Chl-a (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抚仙湖 Fuxian Lake | 216.6 | 155 | 89.7 | 9.0 | 136.7 | 10.0 | 1.4 |
| 滇池 Dianchi Lake | 298.0 | 6.5 | 2.9 | 9.1 | 3,548.0 | 192.0 | 62.0 |
图1 抚仙湖与滇池采样点分布图。轮廓图中的黑点表示采样点位置。
Fig. 1 Site maps showing the coring locations at Fuxian Lake and Dianchi Lake. Coring sites are labeled as black circles.
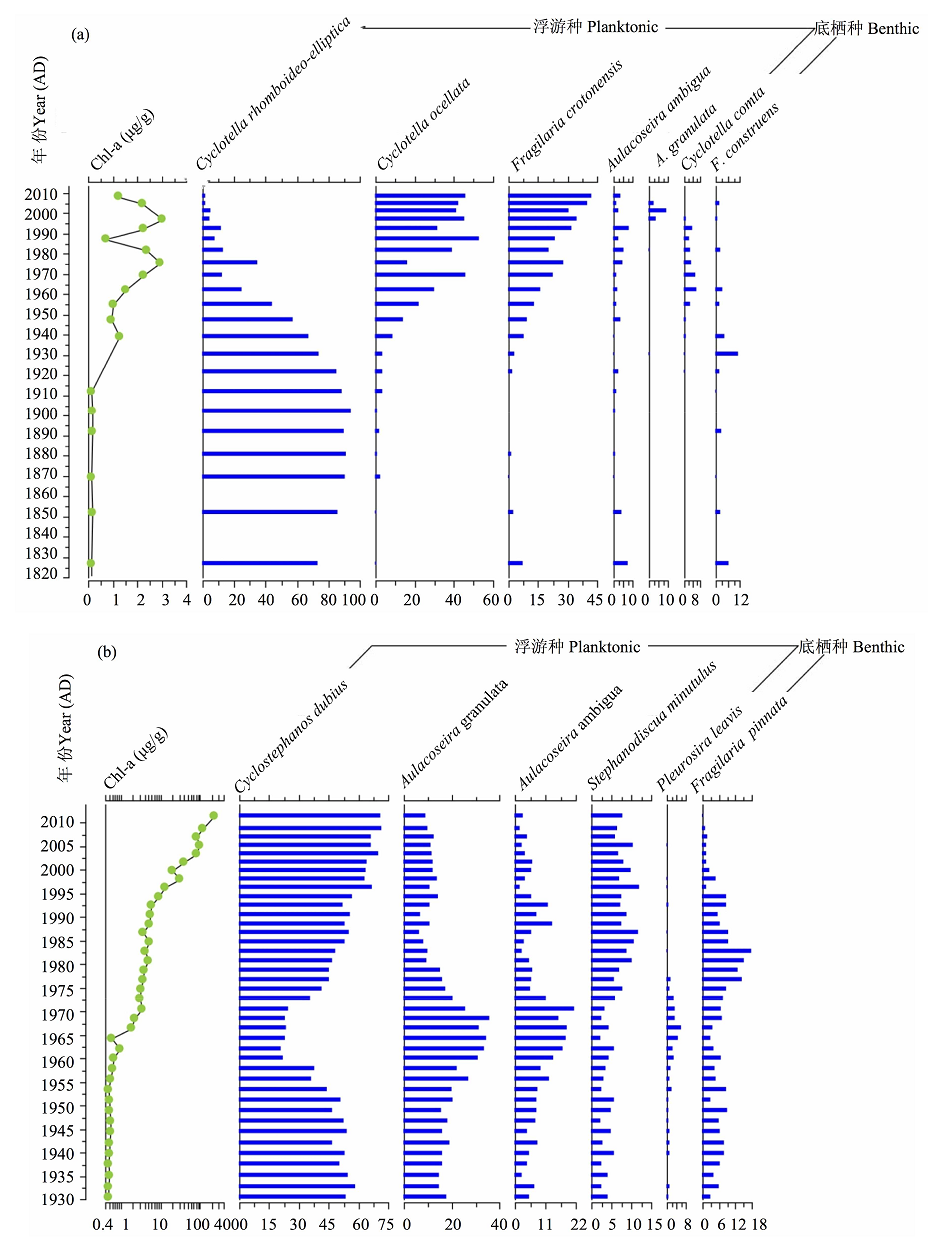
图2 抚仙湖(a)和滇池(b)硅藻群落变化(相对丰度)的时间序列。硅藻地层图仅包括物种相对丰度不低于5%的属种。
Fig. 2 Stratigraphic plots showing sedimentary pigment and diatom community (relative abundance) changes at Fuxian Lake (a) and Dianchi Lake (b). Only diatom taxa with relative abundance not less than 5% were shown.
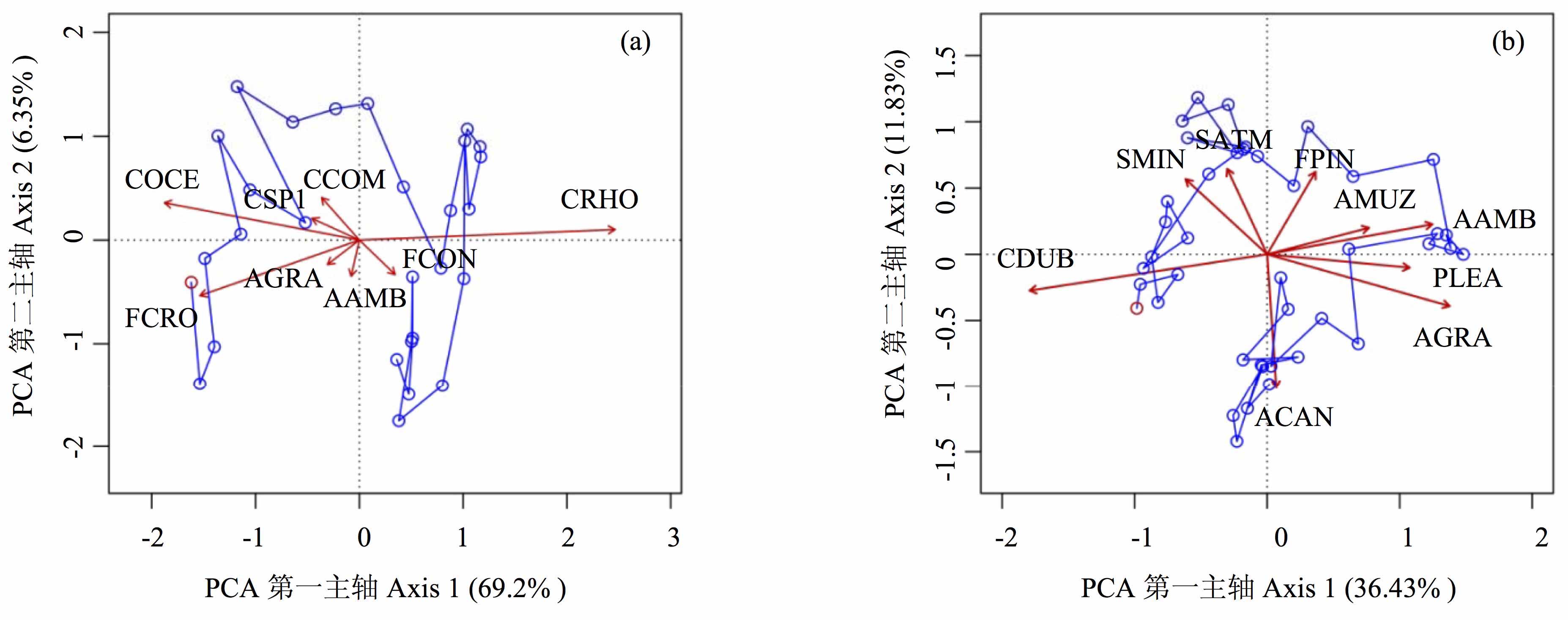
图3 抚仙湖(a)和滇池(b)硅藻群落的主成分分析(PCA)双图。箭头表示的是硅藻不同的种, 圆圈表示的是样品点。硅藻属种的全称如下:CRHO: Cyclotella rhomboideo-elliptica; CCOM: Cyclotella comta; CSP1: Cyclotella sp.1(主要分类学特征与C. stelligera相似); COCE: Cyclotella ocelata; FCRO: Fragilaria crotonensis; AGRA: Aulacoseira granulate; AAMB: Aulacoseira ambigua; FCON: Fragilaria construens; AMUZ: Aulacoseira amuzzensis; FPIN: Frailaria pinnata; SATM: Stephanodiscus atmosphere; SMIN: Stephanodiscus minutulus; CDUB: Cyclostephanos dubius; ACAN: Aulacoseira canadensis; PLEA: Plerosira leavis。
Fig. 3 PCA biplots of diatom assemblages for Fuxian (a) and Dianchi (b) lakes. Arrows and circles represent dominant diatom taxa and samples, respectively. Full names for the abbreviated diatom taxa are listed above.
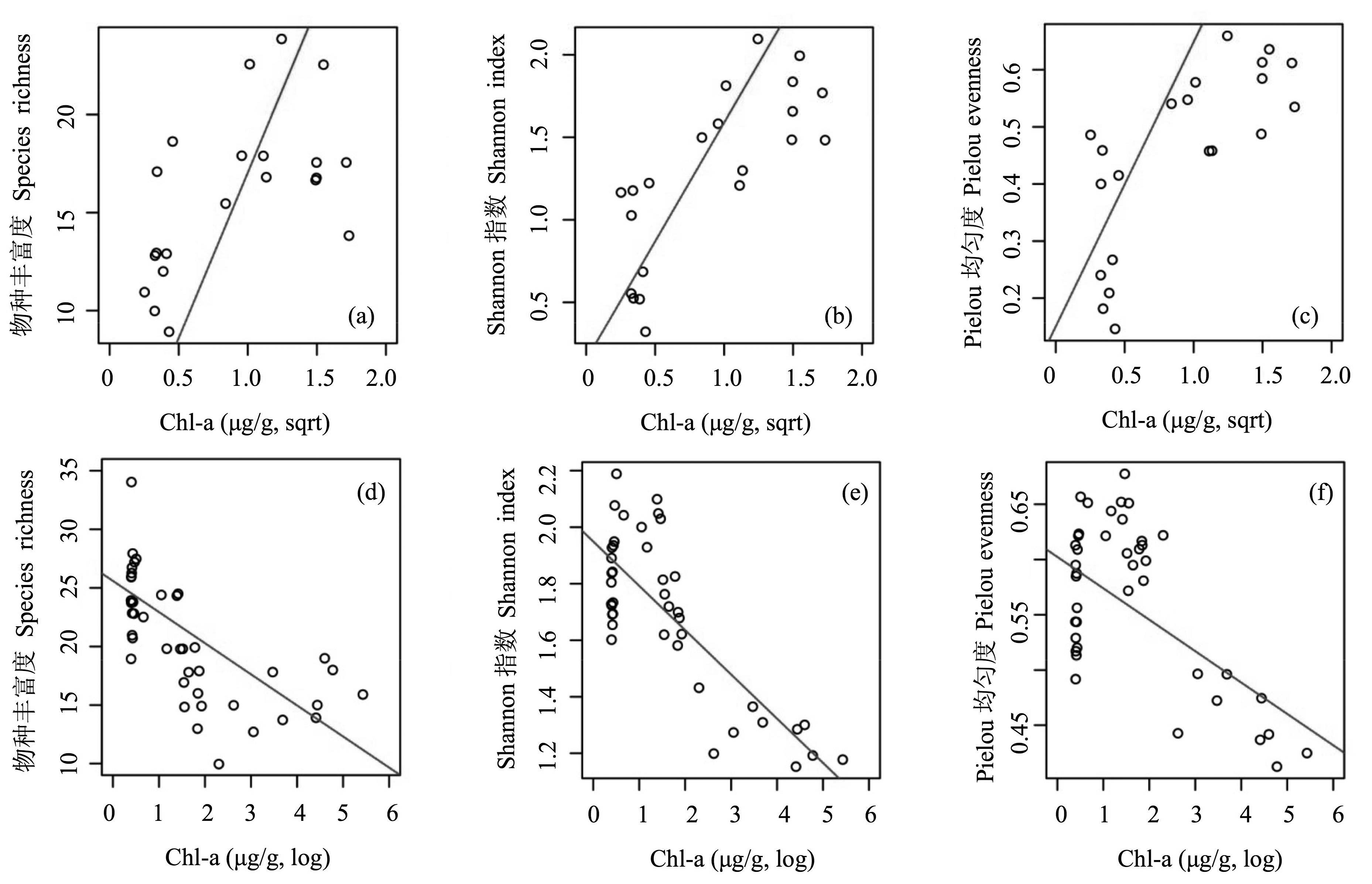
图4 抚仙湖(a, b, c)和滇池(d, e, f)中硅藻α多样性3个指标与Chl-a浓度长期变化关系的散点图
Fig. 4 Scatter plots showing the relationships among the three indices of diatom α diversity and sedimentary Chl-a concentrations at Fuxian Lake (a, b, c) and Dianchi Lake (d, e, f), respectively
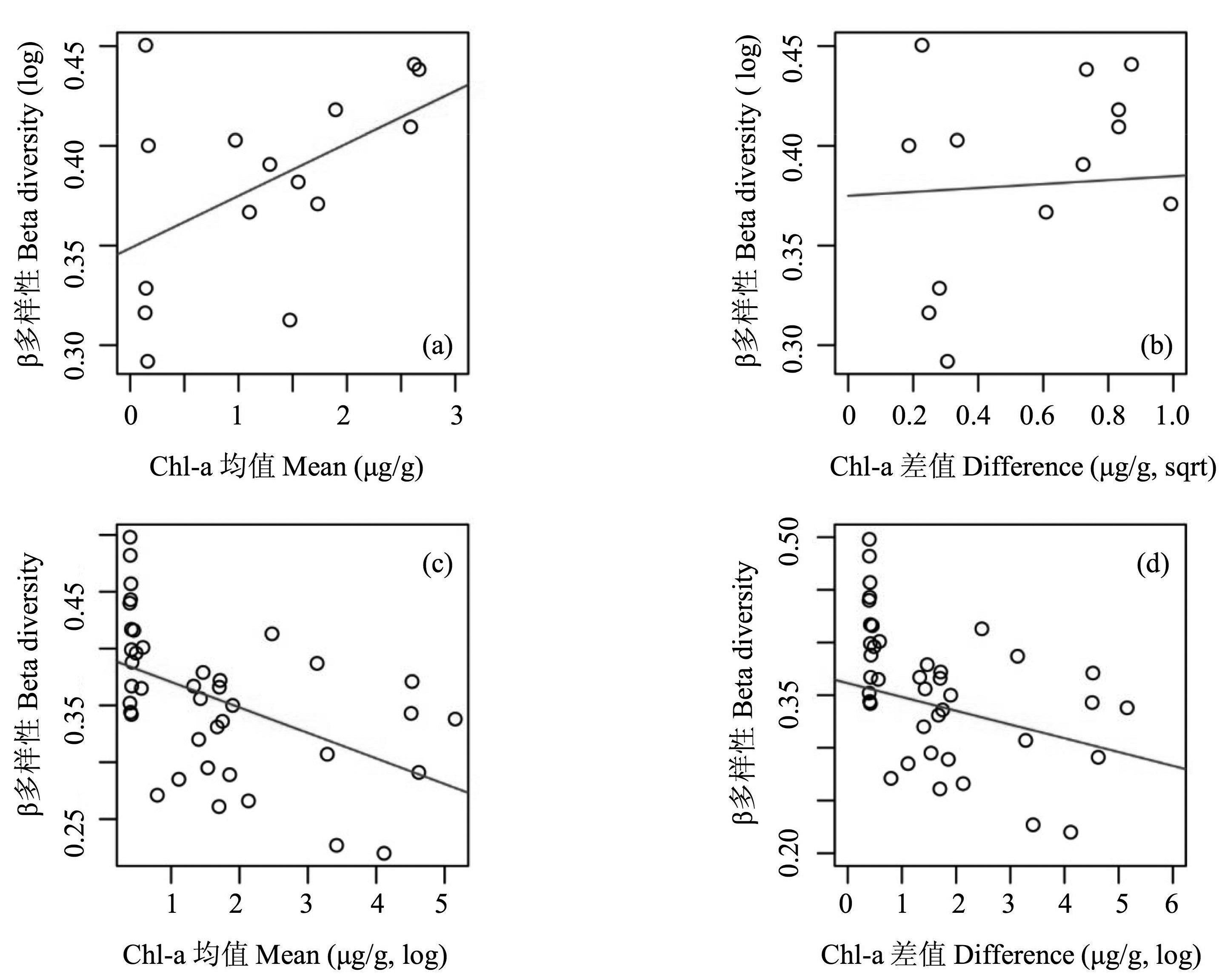
图5 抚仙湖(a, b)和滇池(c, d)硅藻β多样性指数响应Chl-a平均浓度与变化幅度的散点图
Fig. 5 Scatter plots showing the relationships between diatom β diversity and mean Chl-a levels and magnitude of sedimentary Chl-a changes at Fuxian Lake (a, b) and Dianchi Lake (c, d), respectively
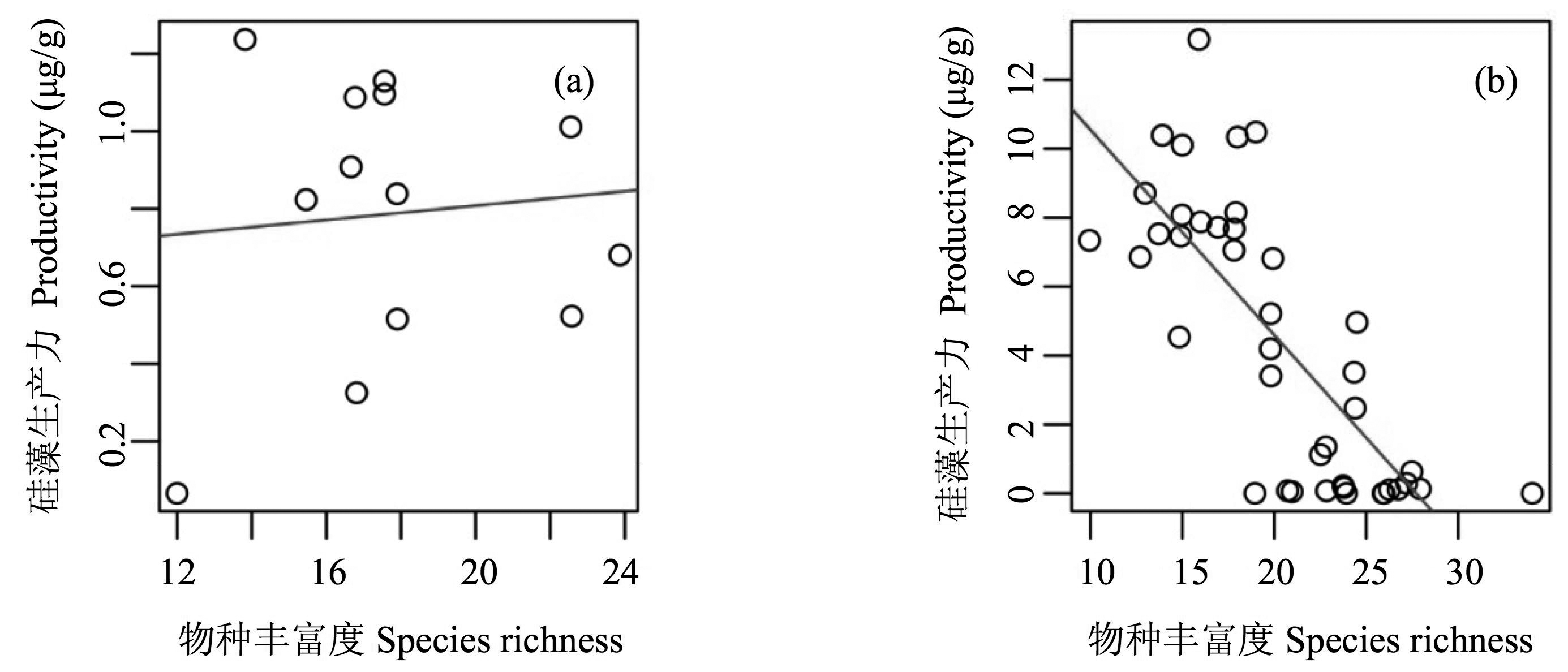
图6 抚仙湖(a)和滇池(b)硅藻物种丰富度与硅藻群落生产力长期关系的散点图
Fig. 6 Scatter plots showing the long-term relationships between diatom species richness and diatoxanthin concentrations at Fuxian Lake (a) and Dianchi Lake (b), respectively
| 1 |
Adler PB, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Hillebrand H, Hautier Y, Hector A, Harpole WS, O’Halloran LR, Grace JB, Anderson TM, Bakker JD, Biederman LA, Brown CS, Buckley YM, Calabrese LB, Cheng JC, Cleland EE, Collins SL, Cottingham KL, Crawley MJ, Damschen EI, Davies KF, DeCrappeo NM, Fay PA, Firn J, Frater P, Gasarch EI, Gruner DS, Hagenah N, Lambers JHR, Humphries H, Jin VL, Kay AD, Kirkman KP, Klein JA, Knops JMH, Pierre KJL, Lambrinos JG, Li W, Dougall ASM, Culley RLM, Melbourne BA, Mitchell CE, Moore JL, Morgan JW, Mortensen B, Orrock JL, Prober SM, Pyke DA, Risch AC, Schuetz M, Smith MD, Stevens CJ, Sullivan LL, Wang G, Wragg PD, Wright JP, Yang LH ( 2011) Productivity is a poor predictor of plant species richness. Science, 333, 1750-1753.
DOI URL PMID |
| 2 | Appleby PG ( 2001) Chronostratigraphic techniques in recent sediments. In: Basin Analysis, Coring, and Chronological Techniques (eds Last WM, Smol JP), pp. 171-202. Springer-Verlag, Dordrecht. |
| 3 | Bai LF ( 白龙飞 ) ( 2012) Research on the Development of Ecological Environment in Dianchi Lake Basin and Kunming City’s Social Development During 1949-2009 (当代滇池流域生态环境变迁与昆明城市发展研究(1949-2009)). PhD dissertation, Institute of Humanities, Yunnan University, Kunming. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 4 | Battarbee RW, Jones VJ, Flower RJ, Cameron NG, Bennion H, Carvalho L, Juggins S ( 2001) Diatoms. In: Terrestrial, Algal, and Siliceous Indicators (eds Smol JP, Birks HJB, Last WM), pp. 155-202. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht. |
| 5 |
Cardinale BJ ( 2011) Biodiversity improves water quality through niche partitioning. Nature, 472, 86-89.
DOI URL PMID |
| 6 |
Chase MA, Leibold JM ( 2002) Spatial scale dictates the productivity-diversity relationship. Nature, 416, 427-430.
DOI URL PMID |
| 7 |
Chase MA, Ryberg WA ( 2004) Connectivity, scale-depend- ence, and the productivity-diversity relationship. Ecology Letters, 7, 676-683.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Chen GJ, Talbot ES, Selbie DT, Brown E, Schindler DE, Bunting L, Leavitt PR, Finney BP, Eaves IG ( 2011) Salmon- derived nutrients drive diatom beta-diversity patterns. Freshwater Biology, 56, 292-306.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Das B, Nordin R, Mazumder A ( 2008) Relationship between phytoplankton paleoproduction and diversity in contrasting trophic states. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management, 11, 78-90.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Declerck S, Vanderstukken M, Pals A, Muylaert K, De Meester L ( 2007) Plankton biodiversity along a gradient of productivity and its mediation by macrophytes. Ecology, 88, 2199-2210.
DOI URL PMID |
| 11 | Dillon PJ, Rigler FH ( 1974) The phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 20, 767-773. |
| 12 |
Dodson SI, Arnott SE, Cottingham KL ( 2000) The relationship in lake communities between primary productivity and species richness. Ecology, 80, 2662-2679.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Donohue I, Jackson AL, Pusch MT, Irvine K ( 2009) Nutrient enrichment homogenizes lake benthic assemblages at local and regional scales. Ecology, 90, 3470-477.
DOI URL PMID |
| 14 |
Dornlas M, Gotelli NJ, McGill B, Shimadzu H, Moyes F, Sievers C, Magurran AE ( 2014) Assemblage time series reveal biodiversity change but not systematic loss. Science, 344, 296-299.
DOI URL PMID |
| 15 |
Gao W ( 高伟), Chen Y ( 陈岩), Xu M ( 徐敏), Guo HC ( 郭怀成), Xie YC ( 谢阳村 ) ( 2013) Trend and driving factors of water quality change in Lake Fuxian (1980-2011). Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 25, 635-642. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Gong ZJ, Li YL, Shen J, Xie P ( 2009) Diatom community succession in the recent history of a eutrophic Yunnan Plateau lake, Lake Dianchi, in subtropical China. Limnology, 10, 247-253.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Gregory-Eaves I, Beisner BE ( 2011) Palaeolimnological insights for biodiversity science: an emerging field. Freshwater Biology, 56, 2653-2661.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Hobbs JPA, Frisch AJ, Allen GR, Van Herwerden L ( 2009) Marine hybrid hotspot at Indo-Pacific biogeographic border. Biology Letters, 5, 258-261.
DOI URL PMID |
| 19 |
Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ, Byrnes JEK, Hungate BA, Matulich KL, Gonzalez A, Duffy JE, Gamfeldt L, O’Connor MI ( 2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature, 486, 105-108.
DOI URL PMID |
| 20 | Huston MA ( 1994) Biological Diversity: The Coexsitence of Species on Changing Landscapes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| 21 |
Korhonen JJ, Wang JJ, Soininen J ( 2011) Productivity-diversity relationships in lake plankton communities. PLoS ONE, 6, e22041.
DOI URL PMID |
| 22 | Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H ( 1986-1991) Bacillariophyceae. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg and Berlin. |
| 23 | Leavitt PR, Hodgson DA ( 2001) Sedimentary pigments. In: Terrestrial, Algal, and Siliceous Indicators (eds Smol JP, Birks HJB, Last WM), pp. 295-325. Springer-Verlag, Dordrecht. |
| 24 |
Li YL, Gong ZJ, Xia WL, Shen J ( 2011) Effects of eutrophication and fish yield on the diatom community in Lake Fuxian, a deep oligotrophic lake in southwest China. Diatom Research, 26, 51-56.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Li YL, Gong ZJ, Shen J ( 2012) Effects of eutrophication and temperature on Cyclotella rhomboideo-elliptica Skuja, endemic diatom to China. Phycological Research, 60, 288-296.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Li YX ( 李荫玺), Wang L ( 王林), Qi YK ( 祁云宽), Tang F ( 唐芳 ) ( 2007) Studies on the phytoplankton development trend in Lake Fuxian, China. Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 19, 223-226. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Li ZJ ( 李中杰), Zheng YX ( 郑一新), Zhang DW ( 张大为), Ni JB ( 倪金碧 ) ( 2012) Impacts of 20-year socio-economic development on quatic environment of Lake Dianchi Basin. Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 24, 875-882. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA ( 2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: current knowledge and future challenges. Science, 294, 804-808.
DOI URL PMID |
| 29 | Lotter AF ( 2001) The effect of eutrophication on diatom diversity: examples from six Swiss lakes. In: Lange-Bertalot- Festschrift: Studies on Diatoms (eds Jahn R, Kociolek JP, Witkowski A, Compere P), pp. 416-432. A. R. G. Gantner Verlag K.G., Florida. |
| 30 |
Ma WH, He JS, Yang YH, Wang XP, Liang CZ, Mohammat A, Zeng H, Fang JY, Bernhard S ( 2010) Environmental factors covary with plant diversity environmental relationships among Chinese grassland sites. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 233-243.
DOI URL |
| 31 | Magurran AE ( 2004) Measuring Biological Diversity. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford. |
| 32 | Pan JZ ( 潘继征), Xiong F ( 熊飞), Li WC ( 李文朝), Ke F ( 柯凡 ) ( 2009) Structure, distribution and impact factors of phytoplankton community in Fuxian Lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 29, 5376-5385. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 33 | Proulx M, Mazmuder A ( 1998) Reversal of grazing impact on plant species richness in nutrient-poor vs. nutrient-rich ecosystems. Ecology, 79, 2581-2592. |
| 34 | Qu WC ( 瞿文川), Wu RJ ( 吴瑞金), Wang SM ( 王苏民), Zhang ZK ( 张振克 ) ( 2000) Sedimentary pigment and its environmental signification of east Juyanhai in Inner Mongolia since the past 2600 years. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica (沉积学报), 18, 13-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Reynolds CS ( 2006) Ecology of Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| 36 | Rosenzweig ML ( 1995) Species Diversity in Space and Time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| 37 |
Rusak JA, Leavitt PR, McGowan S, Chen GM, Olson O, Wunsam S, Cumming BF ( 2004) Millennial-scale relationships of diatom species richness and production in two prairie lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 49, 1290-1299.
DOI URL |
| 38 |
Scheffer M, Carpenter S, Foley JA, Folke C, Walker B ( 2001) Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature, 413, 591-596.
DOI URL PMID |
| 39 |
Schindler DW ( 1978) Factors regulating phytoplankton production and standing crop in world’s lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 23, 478-486.
DOI URL |
| 40 |
Seehausen O, Bouton N ( 1997) Microdistribution and fluctuations in niche overlap in a rocky shore cichlid community in Lake Victoria. Ecology of Freshwater Fish, 6, 59-66.
DOI URL |
| 41 | Shen J ( 沈吉), Xue B ( 薛滨), Wu JL ( 吴敬禄), Wu YH ( 吴艳宏), Liu XQ ( 刘兴起) , Yang XD ( 羊向东), Liu J ( 刘健), Wang SM ( 王苏民 ) ( 2010) Lake Sediments and Environmental Evolution (湖泊沉积与环境演化). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 42 | Smol JP, Wolfe AP, Birks HJB, Douglas MSV, Jones VJ, Korhola A, Pienitz R, Ruhland K, Sorvari S, Antoniades D, Brooks SJ, Fallu MA, Hughes M, Keatley BE, Laing TE, Michelutti N, Nazarova L, Nyman M, Paterson AM, Perren B, Quinlan R, Rautio M, Saulnier-Talbot E, Siitonen S, Solovieva N, Weckstrom J ( 2005) Climate-driven regime shifts in the biological communities of arctic lakes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 4397-4402. |
| 43 | Smol JP ( 2008) Pollution of Lakes and Rivers: A Paleoenvironmental Perspective, 2nd edn. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford. |
| 44 | Stoermer EF, Smol J ( 1999) The Diatoms: Applications for the Environmental and Earth Sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| 45 |
Svensson JR, Lindegarth M, Siccha M, Lenz M, Molis M, Wahl M, Pavia H ( 2007) Maximum species richness at intermediate frequencies of disturbance: consistency among levels of productivity. Ecology, 88, 830-838.
DOI URL PMID |
| 46 |
Tillman D ( 1982) Phytoplankton community ecology: the role of limiting nutrients. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 13, 349-372.
DOI URL |
| 47 |
Velghe K, Vermaire JC, Gregory-Eaves I ( 2012) Declines in littoral species richness across both spatial and temporal nutrient gradients: a palaeolimnological study of two taxonomic groups. Freshwater Biology, 57, 2378-2389.
DOI URL |
| 48 |
Violle C, Pu Z, Jiang L ( 2010) Experimental demonstration of the importance of competition under disturbance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 107, 12925-12929.
DOI URL |
| 49 |
Virtanen R, Grytnes JA, Lenoir J, Luoto M, Oksanen J, Oksanen L, Svenning JC ( 2013) Productivity-diversity patterns in arctic tundra vegetation. Ecography, 36, 331-341.
DOI URL |
| 50 |
Vyverman W, Verleyen E, SABBE K, Vanhoutte K, Sterken M, Hodgson DA, Mann DG, Juggins S, Vijver BV, Jones V, Flower R, Roberts D, Chepurnov VA, Kilroy C, Vanormenlingen P, Wever AD ( 2007) Historical processes constrain patterns in global diatom diversity. Ecology, 88, 1924-1931.
DOI URL PMID |
| 51 |
Wang R, Dearing JA, Langdon PG, Zhang EL, Yang XD, Dakos V, Scheffer M ( 2012) Flickering gives early warning signals of a critical transition to an eutrophic lake state. Nature, 492, 419-422.
DOI URL PMID |
| 52 | Wang SM ( 王苏民), Dou HS ( 窦鸿身 ) ( 1998) The Lakes of China (中国湖泊志). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 53 |
Wang SH, Wang J, Li MB, Du F, Yang YM, Lassoie JP, Hassan MZ ( 2013) Six decades of changes in vascular hydrophyte and fish species in three plateau lakes in Yunnan, China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 22, 3197-3221.
DOI URL |
| 54 | Wang Z, Brown J H, Tang Z, Fang J ( 2009) Temperature dependence, spatial scale, and tree species diversity in eastern Asia and North America. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 13388-13392. |
| 55 |
Watson SB, McCauley E, Downing JA ( 1997) Patterns in phytoplankton taxonomic composition across temperature lakes of differing nutrient status. Limnology and Oceanography, 42, 487-495.
DOI URL |
| 56 | Wei ZH ( 卫志宏), Zhang LX ( 张利仙), Yang SK ( 杨四昆), Lü XJ ( 吕兴菊), Zhu J ( 朱江), Dou JS ( 窦嘉顺 ) ( 2012) Community structure and seasonal succession of phytoplankton in Erhai Lake. Journal of Hydroecology (水生态学杂志), 33(4), 21-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 57 | Yang DG ( 杨德广 ) ( 2011) Diatom Based Inference of Change in Climate and Biodiversity in Erlongwan Maar Lake, Northeastern China (400年来吉林省二龙湾玛珥湖硅藻组合及生物多样性). PhD dissertation, Institute of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 58 | Yu GY ( 余国营), Zhang XH ( 张小华), Liang XM ( 梁小民), Xu XQ ( 徐小清 ) ( 2000) Biogeochemical characteristics of metal elements in water-plant system of Lake Dianchi. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica (水生生物学报), 24, 172-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 59 | Yuan G ( 袁刚), Ru HJ ( 茹辉军), Liu XQ ( 刘学勤 ) ( 2010) Fish diversity and fishery resources in lakes of Yunnan Plateau during 2007-2008. Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 22, 837-841. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 60 | Zhang M ( 张民), Yu Y ( 于洋), Qian SQ ( 钱善勤), Li DM ( 李大命), Kong FX ( 孔繁翔 ) ( 2010) Phytoplankton community structure and biodiversity in summer Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau lakes. Journal of Lake Sciences (湖泊科学), 22, 829-836. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 61 | Zhang M ( 张梅), Li Y ( 李原), Wang RN ( 王若南 ) ( 2006) Dynamic variation for the species of phytoplankton in Dianchi Lake, China. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences) ( 云南大学学报(自然科学版)), 28(1), 73-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()