



生物多样性 ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (6): 654-664. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.11073 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.11073
收稿日期:2012-03-22
接受日期:2012-05-23
出版日期:2012-11-20
发布日期:2013-01-04
通讯作者:
刘文耀
作者简介:* E-mail: Liuwy@xtbg.ac.cn** 同等贡献作者
基金资助:
Yuanlin Yao1,2, Wenyao Liu1,*( ), Wenzhang Ma3, Liang Song1,2
), Wenzhang Ma3, Liang Song1,2
Received:2012-03-22
Accepted:2012-05-23
Online:2012-11-20
Published:2013-01-04
Contact:
Wenyao Liu
About author:First author contact:** The two authors contributed equally to this work
摘要:
对环境变化敏感的附生苔藓植物是亚热带潮湿生境山地森林生态系统的重要组分之一。为了解不同类型植物群落间过渡带附生苔藓植物多样性与分布特征, 我们对哀牢山徐家坝地区中山湿性常绿阔叶林(也称为原生林) 与3类不同类型森林(苔藓矮林、次生的栎类萌生林和滇山杨(Populus bonatii)林)之间的过渡带内树干附生植物的物种组成、多样性、生活型等进行了调查研究。结果表明: 原生林与苔藓矮林过渡带的物种丰富度(68)和Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(3.46)低于其相邻的原生林(分别为85和3.69)和苔藓矮林(分别为92和3.98)。而在原生林与栎类萌生林、滇山杨林两类次生林的过渡带上, 物种的丰富程度高于各自的次生森林但低于原生林。有些物种的分布仅限于过渡带, 如亮叶光萼苔(Porella nitens)和细枝刺枝藓(Wijkia surcularis)的分布仅限于原生林-滇山杨林过渡带, 狭叶厚角藓(Gammiella tonkinensis)仅出现于原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带, 具有一定的保护价值。我们认为边缘效应产生高生物多样性这一特征对于过渡带树干附生苔藓植物群落而言并不符合。
姚元林, 刘文耀, 马文章, 宋亮 (2012) 云南哀牢山国家保护区几个过渡带树干附生苔藓的物种组成与多样性. 生物多样性, 20, 654-664. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.11073.
Yuanlin Yao, Wenyao Liu, Wenzhang Ma, Liang Song (2012) Species composition and diversity of epiphytes of several ecotones in Ailao Mountain National Nature Reserve, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 20, 654-664. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.11073.
| 生态交错带及其相邻群落 Ecotone and its adjacent communities | 胸径 DBH (cm) | 宿主株树 No. of hosts |
|---|---|---|
| 原生林 OGF | 29.60 ± 3.60 | 51 |
| 原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带 EOO | 30.51 ± 1.75 | 36 |
| 苔藓矮林 ODMF | 14.59 ± 0.84 | 30 |
| 原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带 EOSl | 27.01 ± 1.62 | 36 |
| 50年栎类萌生林 SLF | 23.81 ± 1.76 | 36 |
| 原生林-滇山杨林过渡带 EOSp | 31.70 ± 2.82 | 36 |
| 滇山杨林 SPF | 29.90 ± 2.40 | 38 |
表1 各过渡带及其相邻群落调查宿主的平均胸径
Table 1 Mean DBH of hosts surveyed among each ecotone and its adjacent communities
| 生态交错带及其相邻群落 Ecotone and its adjacent communities | 胸径 DBH (cm) | 宿主株树 No. of hosts |
|---|---|---|
| 原生林 OGF | 29.60 ± 3.60 | 51 |
| 原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带 EOO | 30.51 ± 1.75 | 36 |
| 苔藓矮林 ODMF | 14.59 ± 0.84 | 30 |
| 原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带 EOSl | 27.01 ± 1.62 | 36 |
| 50年栎类萌生林 SLF | 23.81 ± 1.76 | 36 |
| 原生林-滇山杨林过渡带 EOSp | 31.70 ± 2.82 | 36 |
| 滇山杨林 SPF | 29.90 ± 2.40 | 38 |
| 过渡带或群落的优势种类 Dominant species of ectone or community | 宿主数 Host No. | 重要值 IV | 生活型 Life form |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原生林 OGF | |||
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 43 | 25.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 刀叶树平藓 H. scalpellifolium | 41 | 24.9 | 扇型 Fan |
| 阿萨羽苔 Plagiochila assamica | 17 | 10.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 羽枝羽苔 P. fruticosa | 12 | 8.4 | 扇型 Fan |
| 疏叶丝带藓 Floribundaria walker | 26 | 7.1 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 21 | 6.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 网藓 Syrrhopodon gardneri | 10 | 5.1 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 扁平棉藓原变种 Plagiothecium neckeroideum var. neckeroideum | 12 | 4.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 疏叶美喙藓 Eurhynchium laxirete | 16 | 4.8 | 粗平铺型 Rough mat |
| 狭叶羽苔 Plagiochila trabeculata | 16 | 4.5 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带 EOO | |||
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 22 | 27.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 刀叶树平藓 H. scalpellifolium | 20 | 20.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 落叶细鳞苔 Lejeunea subacuta | 30 | 19.0 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 短叶毛锦藓 Pylaisiadelpha yokohamae | 20 | 9.5 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 14 | 8.2 | 扇型 Fan |
| 南方小锦藓 Brotherella henonii | 12 | 8.2 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 阿萨羽苔 Plagiochila assamica | 10 | 8.2 | 扇型 Fan |
| 卷叶鞭苔 Bazzania yoshinagana | 6 | 5.6 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 扁平棉藓原变种 Plagiothecium neckeroideum var. neckeroideum | 13 | 5.4 | 扇型 Fan |
| 平叉苔 Metzgeria conjugata | 15 | 5.2 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 苔藓矮林 ODMF | |||
| 弯叶刺枝藓 Wijkia deflexifolia | 19 | 10.5 | 粗平铺型 Rough mat |
| 喜马拉雅鞭苔 Bazzania himalayana | 8 | 10.1 | 交织型 Weft |
| 刀叶树平藓 Homaliodendron scalpellifolium | 13 | 10.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 树平藓 H. flabellatum | 15 | 9.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 狭叶剪叶苔 Herbertus angustissimus | 11 | 8.4 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 9 | 8.4 | 扇型 Fan |
| 阿萨羽苔 P. assamica | 8 | 8.2 | 扇型 Fan |
| 平叉苔 Metzgeria conjugata | 18 | 6.6 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 粗仰叶垂藓 Sinskea phaea | 14 | 5.3 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 拟扭叶藓卷叶变种 Trachypodopsis serrulata var. crispatula | 4 | 5.2 | 树型 Dendroid |
| 原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带 EOSl | |||
| 阿萨羽苔 Plagiochila assamica | 10 | 20.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 16 | 15.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 喜马拉雅鞭苔 Bazzania himalayana | 13 | 15.3 | 交织型 Weft |
| 刀叶树平藓 Homaliodendron scalpellifolium | 17 | 14.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 落叶细鳞苔 Lejeunea subacuta | 24 | 14.1 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 弯叶刺枝藓 Wijkia deflexifolia | 22 | 12.7 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 14 | 12.6 | 扇型 Fan |
| 桧叶白发藓 Leucobryum juniperoideum | 12 | 6.2 | 垫状型 Cushion |
| 刺叶羽苔 Plagiochila sciophila | 11 | 5.8 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 小叶鞭苔 Bazzania ovistipula | 4 | 4.4 | 粗平铺型 Rough mat |
| 50年栎类萌生林 SLF | |||
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 26 | 23.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 落叶细鳞苔 Lejeunea subacuta | 32 | 16.3 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 16 | 10.9 | 扇型 Fan |
| 过渡带或群落的优势种类 Dominant species of ectone or community | 宿主数 Host No. | 重要值 IV | 生活型 Life-form |
| 疏叶羽苔 P. secretifolia | 17 | 10.8 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 阿萨羽苔 P. assamica | 12 | 10.0 | 扇型 Fan |
| 狭叶羽苔 P. trabeculata | 18 | 9.6 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 平叉苔 Metzgeria conjugata | 29 | 9.3 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 刀叶树平藓 Homaliodendron scalpellifolium | 12 | 8.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 南方小锦藓 Brotherella henonii | 17 | 7.8 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 青毛藓 Dicranodontium denudatum | 19 | 6.4 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 原生林-滇山杨林过渡带 EOSp | |||
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 29 | 23.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 刀叶树平藓 H. scalpellifolium | 18 | 15.3 | 扇型 Fan |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 20 | 13.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 疏叶丝带藓 Floribundaria walkeri | 16 | 11.0 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 落叶细鳞苔 Lejeunea subacuta | 21 | 9.9 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 齿叶平藓 Neckera crenulata | 10 | 8.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 狭叶羽苔 Plagiochila trabeculata | 13 | 8.6 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 皱萼苔 Ptychanthus striatus | 10 | 6.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 大羽藓 Thuidium cymbifolium | 10 | 5.9 | 交织型 Weft |
| 短叶毛锦藓 Pylaisiadelpha yokohamae | 12 | 5.0 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 滇山杨林 SPF | |||
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 23 | 24.9 | 扇型 Fan |
| 皱萼苔 Ptychanthus striatus | 17 | 15.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 疏叶丝带藓 Floribundaria walkeri | 13 | 12.0 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 黄松萝藓 Papillaria fuscescens | 13 | 12.0 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 大羽藓 Thuidium cymbifolium | 12 | 11.7 | 交织型 Weft |
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 14 | 10.3 | 扇型 Fan |
| 狭叶羽苔 Plagiochila trabeculata | 10 | 8.8 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 侧枝匍灯藓 Plagiomnium maximoviczii | 12 | 8.3 | 粗平铺型 Rough mat |
| 轮叶波叶藓 Himantocladium cyclophyllum | 10 | 8.0 | 扇型 Fan |
| 大耳羽苔 Plagiochila subtropica | 8 | 6.9 | 扇型 Fan |
表2 各过渡带及其相邻群落附生苔藓重要值居前10位的优势物种
Table 2 Top 10 dominant epiphytic bryophytes ranked by importance value (IV) across all ecotones and communities
| 过渡带或群落的优势种类 Dominant species of ectone or community | 宿主数 Host No. | 重要值 IV | 生活型 Life form |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原生林 OGF | |||
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 43 | 25.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 刀叶树平藓 H. scalpellifolium | 41 | 24.9 | 扇型 Fan |
| 阿萨羽苔 Plagiochila assamica | 17 | 10.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 羽枝羽苔 P. fruticosa | 12 | 8.4 | 扇型 Fan |
| 疏叶丝带藓 Floribundaria walker | 26 | 7.1 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 21 | 6.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 网藓 Syrrhopodon gardneri | 10 | 5.1 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 扁平棉藓原变种 Plagiothecium neckeroideum var. neckeroideum | 12 | 4.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 疏叶美喙藓 Eurhynchium laxirete | 16 | 4.8 | 粗平铺型 Rough mat |
| 狭叶羽苔 Plagiochila trabeculata | 16 | 4.5 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带 EOO | |||
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 22 | 27.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 刀叶树平藓 H. scalpellifolium | 20 | 20.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 落叶细鳞苔 Lejeunea subacuta | 30 | 19.0 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 短叶毛锦藓 Pylaisiadelpha yokohamae | 20 | 9.5 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 14 | 8.2 | 扇型 Fan |
| 南方小锦藓 Brotherella henonii | 12 | 8.2 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 阿萨羽苔 Plagiochila assamica | 10 | 8.2 | 扇型 Fan |
| 卷叶鞭苔 Bazzania yoshinagana | 6 | 5.6 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 扁平棉藓原变种 Plagiothecium neckeroideum var. neckeroideum | 13 | 5.4 | 扇型 Fan |
| 平叉苔 Metzgeria conjugata | 15 | 5.2 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 苔藓矮林 ODMF | |||
| 弯叶刺枝藓 Wijkia deflexifolia | 19 | 10.5 | 粗平铺型 Rough mat |
| 喜马拉雅鞭苔 Bazzania himalayana | 8 | 10.1 | 交织型 Weft |
| 刀叶树平藓 Homaliodendron scalpellifolium | 13 | 10.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 树平藓 H. flabellatum | 15 | 9.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 狭叶剪叶苔 Herbertus angustissimus | 11 | 8.4 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 9 | 8.4 | 扇型 Fan |
| 阿萨羽苔 P. assamica | 8 | 8.2 | 扇型 Fan |
| 平叉苔 Metzgeria conjugata | 18 | 6.6 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 粗仰叶垂藓 Sinskea phaea | 14 | 5.3 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 拟扭叶藓卷叶变种 Trachypodopsis serrulata var. crispatula | 4 | 5.2 | 树型 Dendroid |
| 原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带 EOSl | |||
| 阿萨羽苔 Plagiochila assamica | 10 | 20.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 16 | 15.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 喜马拉雅鞭苔 Bazzania himalayana | 13 | 15.3 | 交织型 Weft |
| 刀叶树平藓 Homaliodendron scalpellifolium | 17 | 14.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 落叶细鳞苔 Lejeunea subacuta | 24 | 14.1 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 弯叶刺枝藓 Wijkia deflexifolia | 22 | 12.7 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 14 | 12.6 | 扇型 Fan |
| 桧叶白发藓 Leucobryum juniperoideum | 12 | 6.2 | 垫状型 Cushion |
| 刺叶羽苔 Plagiochila sciophila | 11 | 5.8 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 小叶鞭苔 Bazzania ovistipula | 4 | 4.4 | 粗平铺型 Rough mat |
| 50年栎类萌生林 SLF | |||
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 26 | 23.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 落叶细鳞苔 Lejeunea subacuta | 32 | 16.3 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 16 | 10.9 | 扇型 Fan |
| 过渡带或群落的优势种类 Dominant species of ectone or community | 宿主数 Host No. | 重要值 IV | 生活型 Life-form |
| 疏叶羽苔 P. secretifolia | 17 | 10.8 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 阿萨羽苔 P. assamica | 12 | 10.0 | 扇型 Fan |
| 狭叶羽苔 P. trabeculata | 18 | 9.6 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 平叉苔 Metzgeria conjugata | 29 | 9.3 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 刀叶树平藓 Homaliodendron scalpellifolium | 12 | 8.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 南方小锦藓 Brotherella henonii | 17 | 7.8 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 青毛藓 Dicranodontium denudatum | 19 | 6.4 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 原生林-滇山杨林过渡带 EOSp | |||
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 29 | 23.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 刀叶树平藓 H. scalpellifolium | 18 | 15.3 | 扇型 Fan |
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 20 | 13.7 | 扇型 Fan |
| 疏叶丝带藓 Floribundaria walkeri | 16 | 11.0 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 落叶细鳞苔 Lejeunea subacuta | 21 | 9.9 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 齿叶平藓 Neckera crenulata | 10 | 8.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 狭叶羽苔 Plagiochila trabeculata | 13 | 8.6 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 皱萼苔 Ptychanthus striatus | 10 | 6.8 | 扇型 Fan |
| 大羽藓 Thuidium cymbifolium | 10 | 5.9 | 交织型 Weft |
| 短叶毛锦藓 Pylaisiadelpha yokohamae | 12 | 5.0 | 细平铺型 Smooth mat |
| 滇山杨林 SPF | |||
| 树形羽苔 Plagiochila arbuscula | 23 | 24.9 | 扇型 Fan |
| 皱萼苔 Ptychanthus striatus | 17 | 15.1 | 扇型 Fan |
| 疏叶丝带藓 Floribundaria walkeri | 13 | 12.0 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 黄松萝藓 Papillaria fuscescens | 13 | 12.0 | 悬垂型 Pendant |
| 大羽藓 Thuidium cymbifolium | 12 | 11.7 | 交织型 Weft |
| 树平藓 Homaliodendron flabellatum | 14 | 10.3 | 扇型 Fan |
| 狭叶羽苔 Plagiochila trabeculata | 10 | 8.8 | 丛集型 Turf |
| 侧枝匍灯藓 Plagiomnium maximoviczii | 12 | 8.3 | 粗平铺型 Rough mat |
| 轮叶波叶藓 Himantocladium cyclophyllum | 10 | 8.0 | 扇型 Fan |
| 大耳羽苔 Plagiochila subtropica | 8 | 6.9 | 扇型 Fan |
| 过渡带或群落 Ectones or communities | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson 指数 Simpson index | 物种丰富度 Richness |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原生林 OGF | 3.69 | 0.95 | 85 |
| 原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带 EOO | 3.46 | 0.95 | 68 |
| 苔藓矮林 ODMF | 3.98 | 0.97 | 92 |
| 原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带 EOSl | 3.49 | 0.95 | 65 |
| 50年栎类萌生林 SLF | 3.47 | 0.95 | 63 |
| 原生林-滇山杨林过渡带 EOSp | 3.61 | 0.96 | 73 |
| 滇山杨林 SPF | 3.44 | 0.95 | 54 |
表3 各过渡带及其相邻群落附生苔藓的Simpson和Shannon-Wiener多样性指数以及物种丰富度
Table 3 Simpson diversity index, Shannon-Wiener diversity index and species richness among all ecotones and communities of epiphytic bryophytes
| 过渡带或群落 Ectones or communities | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson 指数 Simpson index | 物种丰富度 Richness |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原生林 OGF | 3.69 | 0.95 | 85 |
| 原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带 EOO | 3.46 | 0.95 | 68 |
| 苔藓矮林 ODMF | 3.98 | 0.97 | 92 |
| 原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带 EOSl | 3.49 | 0.95 | 65 |
| 50年栎类萌生林 SLF | 3.47 | 0.95 | 63 |
| 原生林-滇山杨林过渡带 EOSp | 3.61 | 0.96 | 73 |
| 滇山杨林 SPF | 3.44 | 0.95 | 54 |
| 过渡带与其相邻的群落之间 Between ecotone and its adjacent communities | 相似性系数 Similarity coefficient | 共有种数 Number of common species | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原生林与原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带 OGF-EOO | 0.60 | 46 | |
| 原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带与苔藓矮林 EOO-ODMF | 0.63 | 50 | |
| 原生林与原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带 OGF-EOSl | 0.48 | 36 | |
| 原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带与50年栎类萌生林 EOSl-SLF | 0.69 | 44 | |
| 原生林与原生林-滇山杨林过渡带 OGF-EOSp | 0.58 | 46 | |
| 原生林-滇山杨林过渡带与滇山杨林 EOSp-SPF | 0.43 | 27 | |
表4 各过渡带与其相邻群落附生苔藓的相似性系数和共有种数
Table 4 Number of common species and S?rensen’s similarity coefficient of epiphytic bryophytes among different ecotones and its adjacent communities
| 过渡带与其相邻的群落之间 Between ecotone and its adjacent communities | 相似性系数 Similarity coefficient | 共有种数 Number of common species | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原生林与原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带 OGF-EOO | 0.60 | 46 | |
| 原生林-苔藓矮林过渡带与苔藓矮林 EOO-ODMF | 0.63 | 50 | |
| 原生林与原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带 OGF-EOSl | 0.48 | 36 | |
| 原生林-50年栎类萌生林过渡带与50年栎类萌生林 EOSl-SLF | 0.69 | 44 | |
| 原生林与原生林-滇山杨林过渡带 OGF-EOSp | 0.58 | 46 | |
| 原生林-滇山杨林过渡带与滇山杨林 EOSp-SPF | 0.43 | 27 | |
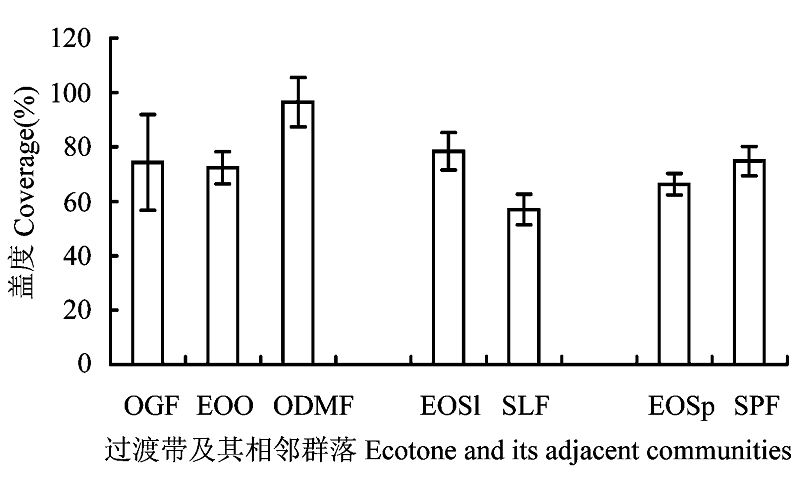
图2 过渡带及其相邻群落附生苔藓的盖度(过渡带或群落代号同表1)
Fig. 2 Mean coverage of epiphytic bryophytes among each ecotone and its adjacent communities. Ecotone or community codes see Table 1.
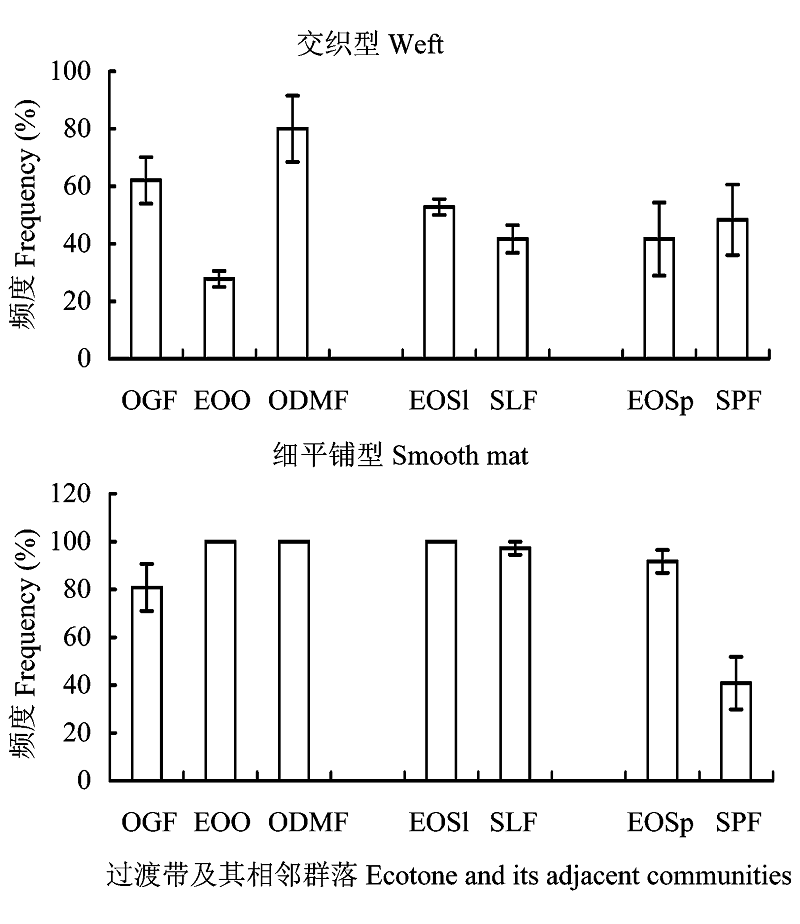
图3 过渡带及其相邻群落附生苔藓植物各生活型的分布频度(过渡带或群落代号同表1)
Fig. 3 Frequencies of each life-form among each ecotone and its adjacent communities. Ecotone or community codes see Table 1.
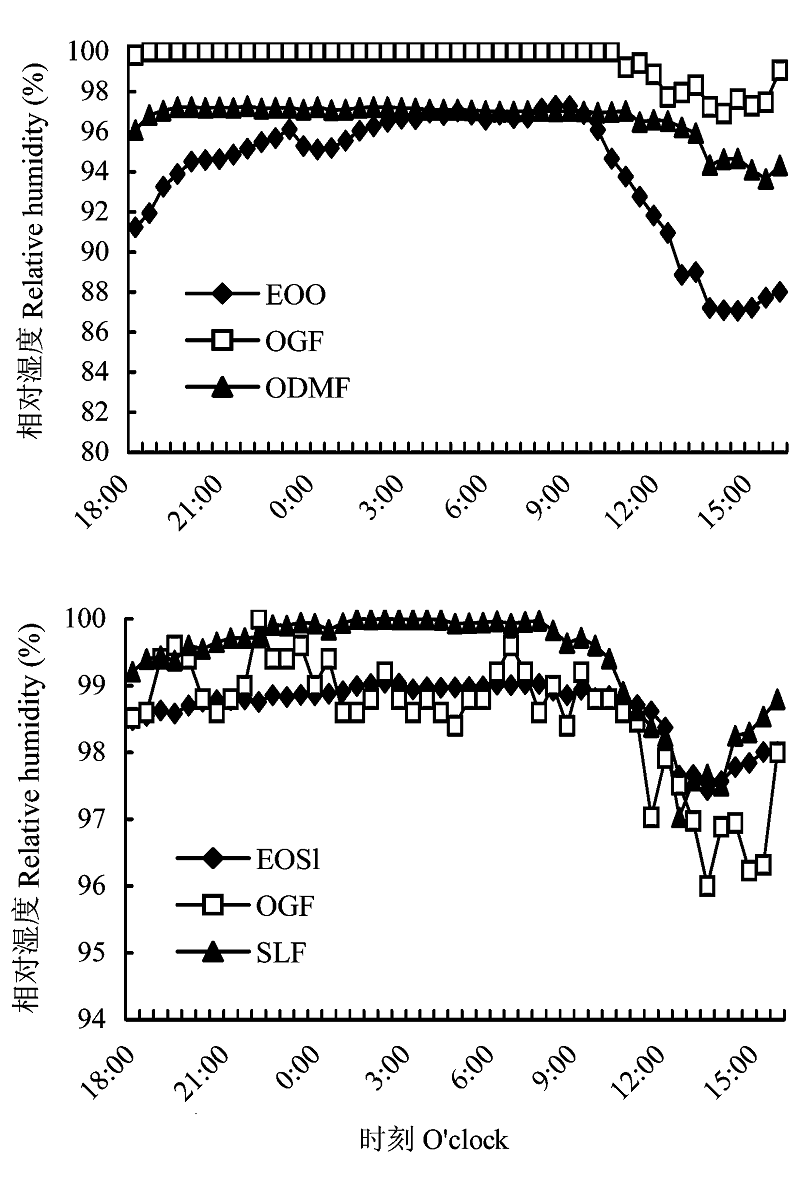
图4 各过渡带及其相邻群落空气相对湿度日变化曲线(过渡带或群落代号同表1)
Fig. 4 Relative humidity (hourly means) of atmosphere in ecotones and its adjacent communities. Ecotone or community codes see Table 1.
| [1] | Acebey A, Gradstein SR, Krömer T (2003) Species richness and habitat diversification of bryophytes in submontane rain forest and fallows of Bolivia. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 19, 9-18. |
| [2] | Bates JW (1998) Is ‘life-form’ a useful concept in bryophyte ecology? Oikos, 82, 223-237. |
| [3] | Burley ST, Harper KA, Lundholm JT (2010) Vegetation composition, structure and soil properties across coastal forest-barren ecotones. Plant Ecology, 211, 279-296. |
| [4] | Cao T (曹同), Guo SL (郭水良) (2000) A study on bryophytes diversity in the main ecosystems in Changbai Mountain. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 8, 50-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | During HJ, van Tooren BF (1987) Recent developments in bryophyte population ecology. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 2, 89-93. |
| [6] | Dutoit T, Buisson E, Gerbaud E, Roche P, Tatoni T (2007) The status of transitions between cultivated fields and their boundaries: ecotones, ecoclines or edge effects? Acta Oecologica, 31, 127-136. |
| [7] | Enroth J (1990) Altitudinal zonation of bryophytes on the Huon Peninsula, Papua New Guinea. A floristic approach, with phytogeographic considerations. Tropical Bryology, 2, 61-90. |
| [8] | Gao Q (高谦), Cao T (曹同) (2000) Flora Yunnanica, Tomus 17, Bryophyta: Hepaticae, Anthocerotae (云南植物志第十七卷, 苔藓植物: 苔纲、角苔纲). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Gosz JR, Sharpe PJH (1989) Broad-scale concepts for interactions of climate, topography, and biota at biome transitions. Landscape Ecology, 3, 229-243. |
| [10] | Gradstein SR (1992) Threatened bryophytes of the neotropical rain forest: a status report. Tropical Bryology, 6, 83-93. |
| [11] | Gradstein SR, Nadkarni NM, Krömer T, Holz I, Nöske N (2003) A protocol for rapid and representative sampling of vascular and non-vascular epiphyte diversity of tropical rain forests. Selbyana, 24, 105-111. |
| [12] | Gradstein SR, van Reenen GB, Griffin D III (1989) Species richness and origin of the bryophyte flora of the Colombian Andes. Acta Botanica Neerlandica, 38, 439-448. |
| [13] | Grytnes JA, Heegaard E, Ihlen PG (2006) Species richness of vascular plants, bryophytes, and lichens along an altitudinal gradient in western Norway. Acta Oecologica, 29, 241-246. |
| [14] | Guo SL (郭水良), Han SJ (韩士杰), Cao T (曹同) (1999) Indicative value of bryophytes on forest eco-boundary. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 10, 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Guo ZG (郭正刚), Wang GX (王根绪), Shen YY (沈禹颖), Cheng GD (程国栋) (2004) Plant species diversity of grassland plant communities in permafrost regions of the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 24, 149-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Hedenås H, Bolyukh VO, Jonsson BG (2003) Spatial distribution of epiphytes on Populus tremula in relation to dispersal mode. Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 233-242. |
| [17] | Hietz P (1998) Diversity and conservation of epiphytes in a changing environment. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 70, 2114-2125. |
| [18] | Hietz-Seifert U, Hietz P, Guevara S (1996) Epiphyte vegetation and diversity on remnant trees after forest clearance in southern Veracruz, Mexico. Biological Conservation, 75, 103-111. |
| [19] | Holland MM (1988) SCOPE/MAB technical consultations on landscape boundaries: report of a SCOPE/MAB workshop on ecotones. Biology International, 17(Special issue), 47-106. |
| [20] | Karger DN, Kluge J, Abrahamczyk S, Salazar L, Homeier J, Lehnert M, Amoroso VB, Kessler M (2012) Bryophyte cover on trees as proxy for air humidity in the tropics. Ecological Indicators, 20, 277-281. |
| [21] | Krebs CJ (1999) Ecological Methodology, 2nd edn. Addison-Welsey Publishers, Menlo Park, California. |
| [22] | León-Vargas Y, Engwald S, Proctor MCF (2006) Microclimate, light adaptation and desiccation tolerance of epiphytic bryophytes in two Venezuelan cloud forests. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 901-913. |
| [23] | Leuschner C, Lendzion J (2009) Air humidity, soil moisture and soil chemistry as determinants of the herb layer composition in European beech forests. Journal of Vegetation Science, 20, 288-298. |
| [24] | Li XJ (黎兴江) (2002) Flora Yunnanica, Tomus 18, Bryophyta: Musci (云南植物志第十八卷, 苔藓植物: 藓纲). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [25] | Li XJ (黎兴江) (2005) Flora Yunnanica, Tomus 19, Bryophyta: Musci (云南植物志第十九卷, 苔藓植物: 藓纲). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [26] | Ma WZ (马文章) (2009) The Composition and Biomass of Epiphytic Materials and Their Relationships with Ecological Factors in Xujiaba Region from Ailao Mountains, Yunnan (云南哀牢山徐家坝地区附生植物的物种组成、生物量及其与生态因子的关系). PhD dissertation, Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Ma WZ, Liu WY, Li XJ (2009) Species composition and life forms of epiphytic bryophytes in old-growth and secondary forests in Mt. Ailao, SW China. Cryptogamie Bryologie, 30, 477-500. |
| [28] | Ma WZ (马文章), Liu WY (刘文耀), Yang LP (杨礼攀), Yang GP (杨国平) (2008) Edge effects on epiphytes in montane moist evergreen broad-leaved forest. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16, 245-254. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Nadkarni MN (1992) The conservation of epiphyte and their habitats: summary of discussion at the international symposium on the biology and conservation of epiphytes. Selbyana, 13, 140-142. |
| [30] | Neilson RP (1993) Transient ecotone response to climatic change: some conceptual and modelling approaches. Ecological Applications, 3, 385-395. |
| [31] | Nöske NM, Hilt N, Werner FA, Brehm G, Fiedler K, Sipman HJM, Gradstein SR (2008) Disturbance effects on diversity of epiphytes and moths in a montane forest in Ecuador. Basic and Applied Ecology, 9, 4-12. |
| [32] | Odum EP (1983) Basic Ecology. Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia. |
| [33] | Peshkova NV, Andreyashkina NI (2009) Structural-functional organization of lower vegetation layers in tree communities of the upper timberline ecotone in the Polar Urals. Russian Journal of Ecology, 40, 44-47. |
| [34] | Peters RL, Darling JDS (1985) The greenhouse effect and nature reserves. BioScience, 35, 707-717. |
| [35] | Qiu XZ (邱学忠), Xie SC (谢寿昌) (1998) Research of Forest Ecosystem in Ailao Mountains, Yunnan (哀牢山森林生态系统研究). Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [36] | Risser PG (1993) Ecotones at local to regional scales from around the world. Ecological Applications, 3, 367-368. |
| [37] | Risser PG (1995) The status of the science examining ecotones. BioScience, 45, 318-326. |
| [38] | Schilthuizen M (2000) Ecotone: speciation-prone. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15, 130-131. |
| [39] | Shi JP (施济普), Zhao CJ (赵崇奖), Zhu H (朱华) (2007) Characteristics and species composition of main vegetation types on west slope of the Ailao Mountains in Yunnan. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (应用与环境生物学报), 11, 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [40] | Shmida A, Ellner S (1984) Coexistence of plant species with similar niches. Vegetatio, 58, 29-55. |
| [41] | Song L, Liu WY, Ma WZ, Tan ZH (2011) Bole epiphytic bryophytes on Lithocarpus xylocarpus (Kurz) Markgr. in the Ailao Mountains, SW China. Ecological Research, 26, 351-363. |
| [42] | Stowe CJ, Kissling WD, Ohlemuller R, Wilson JB (2003) Are ecotone properties scale-dependent? A test from a Nothofagus treeline in southern New Zealand. Community Ecology, 4, 35-42. |
| [43] | Wolf JHD (1993) Diversity patterns and biomass of epiphytic bryophytes and lichens along an altitudinal gradient in the northern Andes. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 80, 928-960. |
| [44] | Wolf JHD (2005) The response of epiphytes to anthropogenic disturbance of pine-oak forests in the highlands of Chiapas, Mexico. Forest Ecology and Management, 212, 376-393. |
| [45] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1983) Research on Forest Ecosystem in Ailao Mountains, Yunnan (云南哀牢山森林生态系统研究). Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [46] | Xu HQ (徐海清), Liu WY (刘文耀) (2005) Species diversity and distribution of epiphytes in the montane moist evergreen broad-leaved forest in Ailao Mountain, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 13, 137-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] | Yu SL (于顺利), Liu CR (刘灿然), Ma KP (马克平) (2000) A study on the ecotones between Quercus mongolica community and other communities. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 8, 277-283. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [48] | Zartman CE, Nascimento HEM (2006) Are habitat-tracking metacommunities dispersal limited? Inferences from abundance-occupancy patterns of epiphylls in Amazonian forest fragments. Biological Conservation, 127, 46-54. |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn