



生物多样性 ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (1): 59-65. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.07160 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.07160
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
陈颖1,2, 李肖肖3, 应娇妍2,*( ), 梁存柱1, 白永飞2
), 梁存柱1, 白永飞2
收稿日期:2011-09-13
接受日期:2012-01-12
出版日期:2012-01-20
发布日期:2012-02-14
通讯作者:
应娇妍
作者简介:*E-mail: yingjy@ibcas.ac.cn基金资助:
Ying Chen1,2, Xiaoxiao Li3, Jiaoyan Ying2,*( ), Cunzhu Liang1, Yongfei Bai2
), Cunzhu Liang1, Yongfei Bai2
Received:2011-09-13
Accepted:2012-01-12
Online:2012-01-20
Published:2012-02-14
Contact:
Jiaoyan Ying
摘要:
为了分析不同植物群落组成对内蒙古典型草原土壤微生物群落组成的影响, 本研究利用植物功能群剔除处理实验平台, 采用荧光定量PCR(real-time PCR)和自动核糖体间隔区基因分析(automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis, ARISA)技术, 对不同植物功能群组成的非根际土壤和常见物种的根际土壤中细菌和真菌的数量及群落结构进行了分析。结果表明, 在非根际土壤中, 不同植物功能群组成对细菌数量有显著影响, 而对真菌数量及细菌和真菌的群落结构影响不明显; 在根际土壤中, 不同植物物种对细菌、真菌的数量都有显著影响。此外, 聚类分析表明, 不同物种的根际土中细菌和真菌的群落结构也有所不同, 尤其以细菌的群落结构变化较为明显。研究结果表明不同植物物种可以通过根系影响土壤微生物群落组成。
陈颖, 李肖肖, 应娇妍, 梁存柱, 白永飞 (2012) 内蒙草原不同植物功能群及物种对土壤微生物组成的影响. 生物多样性, 20, 59-65. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.07160.
Ying Chen, Xiaoxiao Li, Jiaoyan Ying, Cunzhu Liang, Yongfei Bai (2012) Effects of plant functional groups and plant species on soil microbial composition in a Inner Mongolian grassland. Biodiversity Science, 20, 59-65. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.07160.
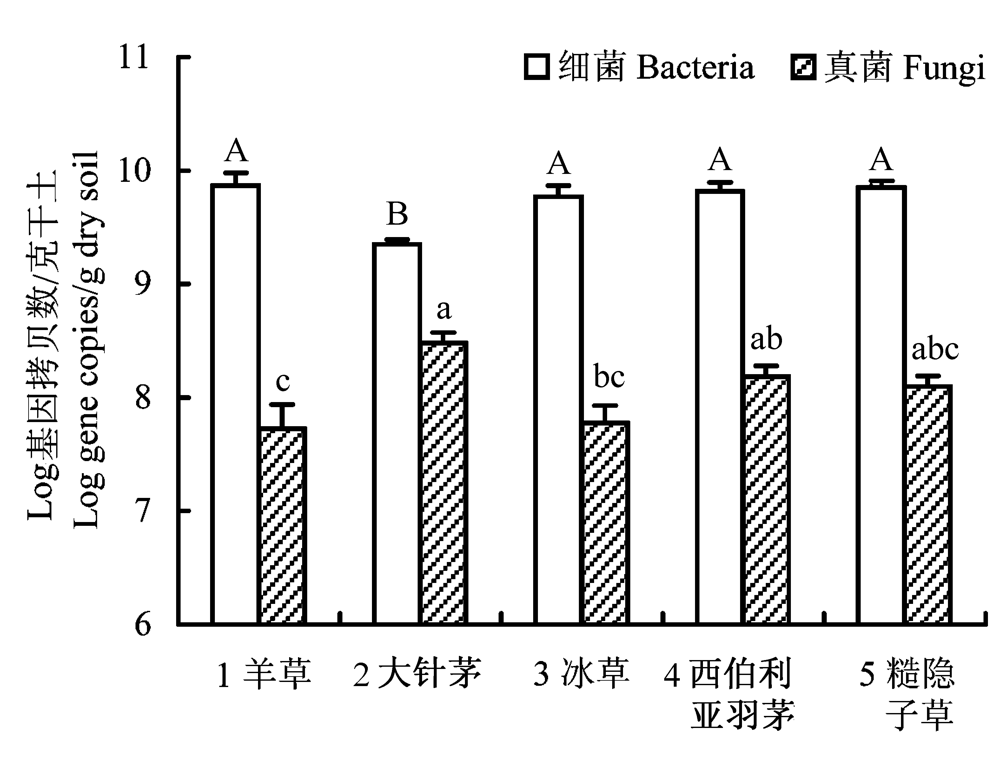
图1 不同植物物种根际土中细菌、真菌的数量。误差线上方的字母分别表示细菌、真菌不同处理间的显著性差异, P < 0.05。
Fig. 1 Abundance of bacteria and fungi in rhizosphere soil of different grass species. Letters above bars indicate significance (P < 0.05) among different treatments 1, Leymus chinensis; 2, Stipa grandis; 3, Agropyron cristatum; 4, Achnatherum sibiricum; 5, Cleistogenes squarrosa.
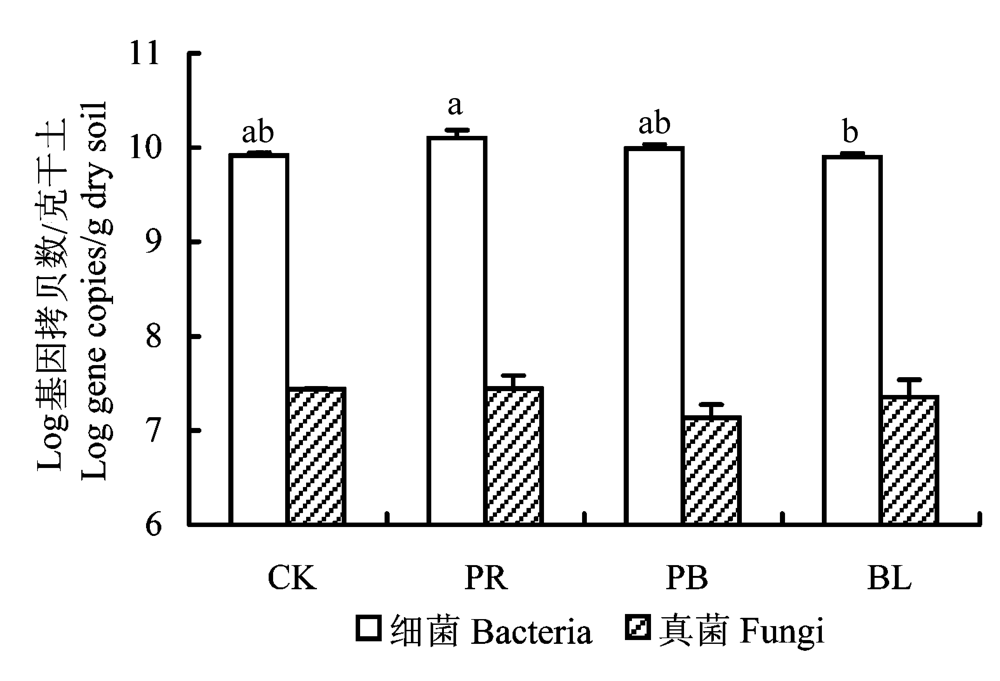
图2 不同功能群剔除处理下土壤中细菌和真菌的数量。CK: 不剔除; PR: 保留多年生根茎禾草; PB: 保留多年生丛生禾草; BL: 剔除所有植物。误差线上方的字母表示不同处理间的显著性差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 2 Abundance of bacteria and fungi under different plant functional group removal treatments. CK, No removal; PR, The remaining group is perennial rhizome forbs; PB, The remaining group is perennial bunch-grass; BL, All the plants were removed. Letters above bars indicate significance (P< 0.05) among treatments.
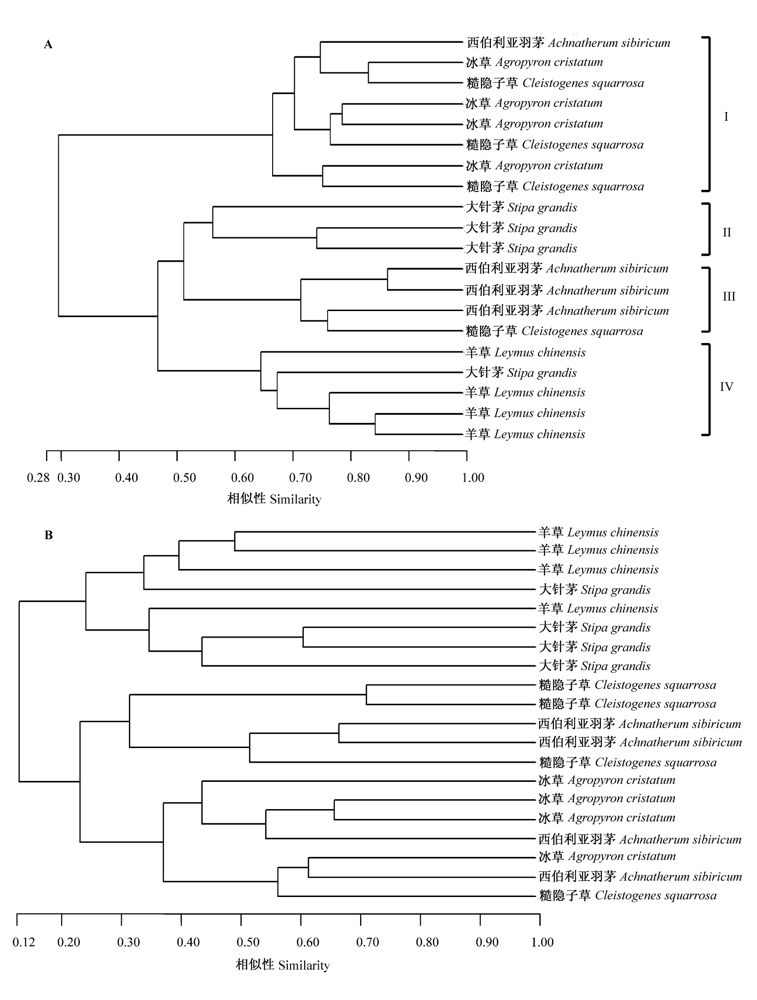
图3 不同植物物种根际土中细菌群落(A)和真菌群落(B)的ARISA数据的聚类分析
Fig. 3 Cluster analysis of soil bacterial (A) and fungal(B) community structure in rhizosphere soil of different grass species based on ARISA data.
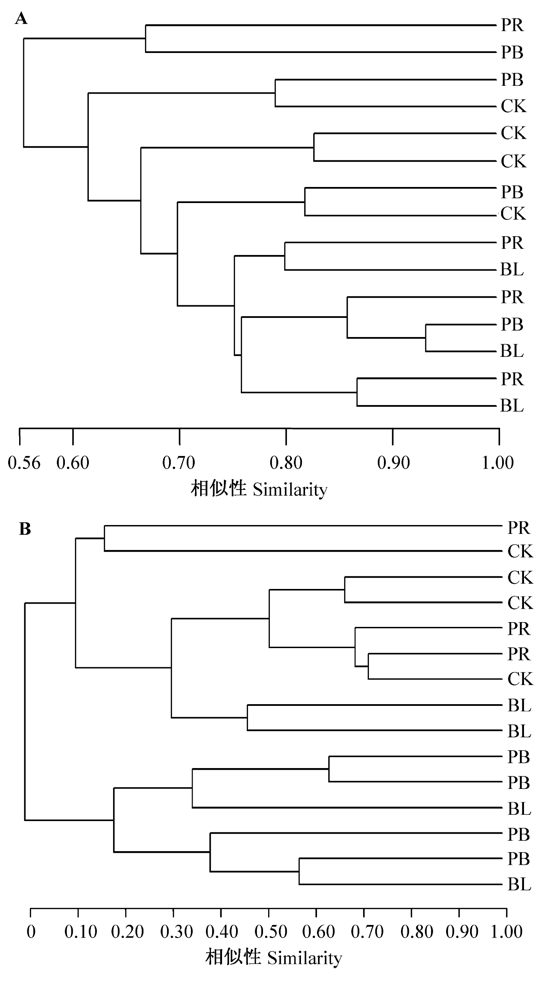
图4 不同功能群剔除小区细菌(A)和真菌(B)群落ARISA数据的聚类分析。CK: 不剔除; PR: 保留多年生根茎禾草; PB: 保留多年生丛生禾草; BL: 剔除所有植物。
Fig. 4 Cluster analysis of soil bacterial (A) and fungal (B) community structure under different functional group removal treatments based on ARISA data. CK, No removal; PR, The remaining group was perennial rhizome forbs; PB, The remaining group was perennial bunch-grass; BL, All the plants were removed.
| [1] | Bai YF, Wu JG, Pan QM, Huang JH, Wang QB, Li FS, Buyantuyev A, Han XG (2007) Positive linear relationship between productivity and diversity: evidence from the Eurasian Steppe. Journal of Applied Ecology, 44,1023-1034. |
| [2] |
Berg G, Smalla K (2009) Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 68,1-13.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] | Cardinale M, Brusetti L, Quatrini P, Borin S, Puglia AM, Rizzi A, Zanardini E, Sorlini C, Corselli C, Daffonchio D (2004) Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70,6147-6156. |
| [4] | Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103,626-631. |
| [5] |
Gao Z, Li BL, Zheng CC, Wang GY (2008) Molecular detection of fungal communities in the Hawaiian marine sponges Suberites zeteki and Mycale armata. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74,6091-6101.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Garbeva P, van Veen JA, van Elsas JD (2004) Microbial diversity in soil: selection of microbial populations by plant and soil type and implications for disease suppressiveness. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 42,243-270.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Girvan MS, Bullimore J, Ball AS, Pretty JN, Osborn AM (2004) Responses of active bacterial and fungal communities in soils under winter wheat to different fertilizer and pesticide regimens. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70,2692-2701.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Jones DL, Hodge A, Kuzyakov Y (2004) Plant and mycorrhizal regulation of rhizodeposition. New Phytologist, 163,459-480. |
| [9] | Jones DL, Nguyen C, Finlay RD (2009) Carbon flow in the rhizosphere: carbon trading at the soil-root interface. Plant and Soil, 321,5-33. |
| [10] |
Kielak A, Pijl AS, van Veen JA, Kowalchuk GA (2008) Differences in vegetation composition and plant species identity lead to only minor changes in soil-borne microbial communities in a former arable field. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 63,372-382.
URL PMID |
| [11] |
Klamer M, Roberts MS, Levine LH, Drake BG, Garland JL (2002) Influence of elevated CO2on the fungal community in a coastal scrub oak forest soil investigated with terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68,4370-4376.
URL PMID |
| [12] |
Kowalchuk GA, Buma DS, de Boer W, Klinkhamer PGL, van Veen JA (2002) Effects of above-ground plant species composition and diversity on the diversity of soil-borne microorganisms. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 81,509-520.
URL PMID |
| [13] | Lambers H, Chapin FS III, Pons TL (2008) Plant Physiological Ecology, 2nd edn. Springer, New York. |
| [14] | Lambers H, Mougel C, Jaillard B, Hinsinger P (2009) Plant-microbe-soil interactions in the rhizosphere: an evolutionary perspective. Plant and Soil, 321,83-115. |
| [15] |
Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75,5111-5120.
URL PMID |
| [16] |
Lemanceau P, Corberand T, Gardan L, Latour X, Laguerre G, Boeufgras JM, Alabouvette C (1995) Effect of two plant species, flax ( Linumusitatissinum L.) and tomato ( Lycope-rsicon esculentum Mill.), on the diversity of soilborne populations of Fluorescent pseudomonads. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61,1004-1012.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] | Marschner P, Crowley D, Yang CH (2004) Development of specific rhizosphere bacterial communities in relation to plant species, nutrition and soil type. Plant and Soil, 261,199-208. |
| [18] |
May LA, Smiley B, Schmidt MG (2001) Comparative denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of fungal communities associated with whole plant corn silage. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 47,829-841.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] | Miethling R, Wieland G, Backhaus H, Tebbe CC (2000) Variation of microbial rhizosphere communities in response to crop species, soil origin, and inoculation with Sinorhizobium meliloti L33. Microbial Ecology, 40,43-56. |
| [20] |
Schmidt TM (2006) The maturing of microbial ecology. International Microbiology, 9,217-223.
URL PMID |
| [21] |
Schwarzenbach K, Enkerli J, Widmer F (2007) Objective criteria to assess representativity of soil fungal community profiles. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 68,358-366.
URL PMID |
| [22] |
Smalla K, Wieland G, Buchner A, Zock A, Parzy J, Kaiser S, Roskot N, Heuer H, Berg G (2001) Bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities studied by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis: plant-dependent enrichment and seasonal shifts revealed. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67,4742-4751.
URL PMID |
| [23] |
Suzuki MT, Taylor LT, Delong EF (2000) Quantitative analysis of small-subunit rRNA genes in mixed microbial populations via 5′-nuclease assays. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66,4605-4614.
URL PMID |
| [24] |
van der Heijden MGA, Bardgett RD, van Straalen NM (2008) The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 11,296-310.
URL PMID |
| [25] |
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setälä H, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science, 304,1629-.
URL PMID |
| [26] | White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications (eds Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ), pp.315-324. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [27] |
Yergeau E, Newsham KK, Pearce DA, Kowalchuk GA (2007) Patterns of bacterial diversity across a range of Antarctic terrestrial habitats. Environmental Microbiology, 9,2670-2682.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [2] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [3] | 连佳丽, 陈婧, 杨雪琴, 赵莹, 罗叙, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 李建平. 荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24044-. |
| [4] | 万凤鸣, 万华伟, 张志如, 高吉喜, 孙晨曦, 王永财. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的应用潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| [5] | 张乃鹏, 梁洪儒, 张焱, 孙超, 陈勇, 王路路, 夏江宝, 高芳磊. 土壤类型和地下水埋深对黄河三角洲典型盐沼植物群落空间分异的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [6] | 蒋陈焜, 郁文彬, 饶广远, 黎怀成, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. 植物系统发生海报——以演化视角介绍植物多样性的科教资料项目[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [7] | 韩赟, 迟晓峰, 余静雅, 丁旭洁, 陈世龙, 张发起. 青海野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [8] | 陈又生, 宋柱秋, 卫然, 罗艳, 陈文俐, 杨福生, 高连明, 徐源, 张卓欣, 付鹏程, 向春雷, 王焕冲, 郝加琛, 孟世勇, 吴磊, 李波, 于胜祥, 张树仁, 何理, 郭信强, 王文广, 童毅华, 高乞, 费文群, 曾佑派, 白琳, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 张步云, 杜思怡. 西藏维管植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23188-. |
| [9] | 宋柱秋, 叶文, 董仕勇, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 王震, 张步云, 徐晔春, 陈文俐, 李世晋, 姚纲, 徐洲锋, 廖帅, 童毅华, 曾佑派, 曾云保, 陈又生. 广东省高等植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23177-. |
| [10] | 梁彩群, 陈玉凯, 杨小波, 张凯, 李东海, 江悦馨, 李婧涵, 王重阳, 张顺卫, 朱子丞. 海南省野生维管植物编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23067-. |
| [11] | 李仕裕, 张奕奇, 邹璞, 宁祖林, 廖景平. 广东省植物园植物多样性迁地保护现状及发展建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22647-. |
| [12] | 吴浩, 余玉蓉, 王佳钰, 赵媛博, 高娅菲, 李小玲, 卜贵军, 薛丹, 吴林. 低水位增加灌木多样性和生物量但降低土壤有机碳含量: 以鄂西南贫营养泥炭地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22600-. |
| [13] | 肖翠, 刘冰, 吴超然, 马金双, 叶建飞, 夏晓飞, 林秦文. 北京维管植物编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 22064-. |
| [14] | 林秦文, 肖翠, 马金双. 中国外来植物数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 22127-. |
| [15] | 吴仁武, 南歆格, 晏海, 杨凡, 史琰, 包志毅. 梅耶(Frank Nicholas Meyer)在亚欧国家引种植物的路线和种类调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22063-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn