



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (6): 764-769. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06164 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.06164
所属专题: 中国的海洋生物多样性
收稿日期:2011-09-15
接受日期:2011-12-07
出版日期:2011-11-20
发布日期:2011-12-19
通讯作者:
刘静
作者简介:*E-mail: jliu@qdio.ac.cn基金资助:Received:2011-09-15
Accepted:2011-12-07
Online:2011-11-20
Published:2011-12-19
Contact:
Jing Liu
摘要:
本文根据中国科学院海洋研究所标本馆馆藏标本、采集记录及相关文献资料, 分析了黄海鱼类的种类组成、区系特征和历史变迁。结果表明: 黄海海域共出现鱼类113科321种。从适温类型来看, 暖温性种类最多, 有139种; 暖水性种类次之, 107种; 冷温性种类70种; 冷水性种类5种。从栖所类型来看, 绝大多数为大陆架浅水底层鱼类, 有193种, 大陆架岩礁性、大陆架浅水中上层、大陆架浅水中底层、大陆架大洋洄游性中上层和大洋深水底层鱼类分别为41、34、29、15和9种。纵观历史文献资料, 发现黄海鱼类群落结构和数量发生了很大变化, 目前以鳀鱼占绝对优势, 传统经济鱼类如小黄鱼(Larimichthys polyactis)、太平洋鳕(Gadus macrocephalus)、太平洋鲱(Clupea pallasii)、蓝点马鲛(Scomberomorus niphonius)、鲐(Scomber japonicus)、带鱼(Trichiurus lepturus)、镰鲳(Pampus echinogaster)、鲆鲽类等在渔获物中所占的比例降低, 昔日占优势的大型经济鱼类, 逐渐被小黄鱼幼鱼、皮氏叫姑鱼(Johnius belangerii)、六丝钝尾虾虎鱼(Amblychaeturichthys hexanema)、细纹狮子鱼(Liparis tanakae)、方氏云鳚(Pholis fangi)、玉筋鱼(Ammodytes personatus)等经济价值较低的种类所取代, 鱼类物种多样性和资源量呈下降趋势。因此, 加强黄海渔业资源管理和多样性保护工作显得尤为重要。
刘静, 宁平 (2011) 黄海鱼类组成、区系特征及历史变迁. 生物多样性, 19, 764-769. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06164.
Jing Liu, Ping Ning (2011) Species composition and faunal characteristics of fishes in the Yellow Sea. Biodiversity Science, 19, 764-769. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06164.
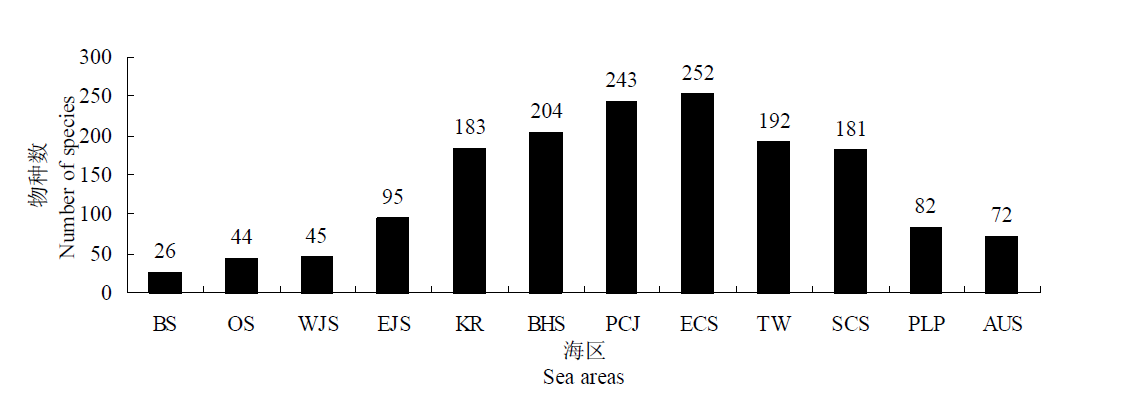
图1 黄海和邻近海域共有种数BS: 白令海; OS: 鄂霍茨克海; WJS: 日本海西岸; EJS: 日本海东岸; KR: 朝鲜半岛; BHS: 渤海; PCJ: 日本太平洋沿岸; ECS: 东海; TW: 台湾; SCS: 南海; PLP: 菲律宾; AUS: 澳大利亚。
Fig. 1 The common fish species in number shared by the Yellow Sea and its adjacent waters. BS, Bering Sea; OS, Okhotsk Sea; WJS, Western Coastal Waters of Japan Sea; EJS, Eastern Coastal Waters of Japan Sea; KR, Korean Peninsula; BHS, Bohai Sea; PCJ, Pacific Coastal Waters of Japan; ECS, East China Sea; TW, Taiwan; SCS, South China Sea; PLP, Philippines; AUS, Australia.
| [1] | Chen CH (陈昌海) (1997) The fishery resources in the deeper area of the middle Yellow Sea and its conservation. Marine Fisheries Research (海洋水产研究), 18(1), 47-53. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Chen DG (陈大刚), Jiao Y (焦燕) (1997) Comparative study of marine fishes and their distribution in the China and Japan seas. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao (青岛海洋大学学报), 27(3), 305-312. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | Cheng QT (成庆泰) (1959) Notes on the economic fish fauna of Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 2, 53-60. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | Cheng QT (成庆泰), Zheng BS (郑葆珊) (1987) Systematic Synopsis of Chinese Fishes (中国鱼类系统检索). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | Choi Y, Kim JH, Park JP (2002) Marine Fishes of Korea. Kyo-Hak Publishing Co. Ltd, Seoul. (in Korean with English abstract) |
| [6] | Ding GW (丁耕芜), Chen JK (陈介康), Shi YR (施友仁), Wang H (王辉) (1980) A supplemental checklist of fishes of the Bohai and Yellow Sea. Chinese Journal of Zoology (动物学杂志), 15(3), 36-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Froese R, Pauly D (2011) FishBase. http://www.fishbase.org. |
| [8] | Huang ZG (黄宗国) (1994) The Species and Distribution of Marine Organisms of China (中国海洋生物种类与分布). Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院动物研究所), Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院海洋研究所), Shanghai Fisheries University (上海水产学院) (1962) The Fishes of the South China Sea (南海鱼类志). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | Jin XS (金显仕), Zhao XY (赵宪勇), Meng TX (孟田湘), Cui Y (崔毅) (2005) The Fishery Resources and the Environment of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea (黄渤海生物资源与栖息环境). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [11] | Lindberg GU, Legeza MI (1989) Fishes of the Sea of Japan and the Adjacent Areas of the Sea of 011,K. D.C. English abstractg:Okhotsk and the Yellow Sea. Part 4. Smithsonian Institution Libraries and National Science Foundation, Washington, DC. |
| [12] | Liu J (刘静) (2008) Subphylum of Vertebrata (脊椎动物亚门). In: Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas (中国海洋生物名录)(ed. Liu RY (刘瑞玉)), pp. 886-1066. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | Liu JY (刘瑞玉) (2004) On sustainable exploitation of marine biological resources in China. Science & Technology Review (科技导报), 22(11), 28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Liu JY (刘瑞玉) (2008) Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas (中国海洋生物名录). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [15] | Liu XS (刘效舜) (1990) Marine Fishery Divisions of China (中国海洋渔业区划). Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [16] | Nakabo T (2002) Fishes of Japan with Pictorial Keys to the Species. Tokai University Press, Tokyo. |
| [17] | Nelson JS (2006) Fishes of the World, 4th edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [18] | Shao KT (2011) The Fish Database of Taiwan. http://fishdb. sinica. edu.tw. |
| [19] | Tang QS (唐启升) (2006) The Living Marine Resources and Habitat of Exclusive Economic Zone of China (中国专属经济区海洋生物资源与栖息环境). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [20] | Tian MC (田明诚), Sun BL (孙宝龄), Yang JM (杨纪明) (1993) Analysis of the fish fauna of the Bohai Sea. Studia Marina Sinica (海洋科学集刊), 34, 157-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Team of compiler of “The Marine Fishery Environment of China” ( 中国海洋渔业环境编写组) (1991) The Marine Fishery Environment of China (中国海洋渔业环境). Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [22] | Team of compiler of “The Marine Fishery Resources of China” ( 中国海洋渔业资源编写组) (1990) The Marine Fisheries Resources of China (中国海洋渔业资源). Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Xu BD (徐宾铎), Jin XS (金显仕), Liang ZL (梁振林) (2005) Calculation of hierarchical diversity of fish in the Huanghai and Bohai seas. Periodical of Ocean University of China (中国海洋大学学报), 35, 25-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Yang JM (杨纪明) (1988) Status of fishery resources development in the western Huanghai Sea. Marine Sciences (海洋科学), 12(4), 70-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Zhang CL (张春霖), Cheng QT (成庆泰), Zheng BS (郑葆珊), Li SZ (李思忠), Zheng WL (郑文莲), Wang WB (王文滨) (1955) The Survey Report of the Fishes of Bohai and Yellow Sea (黄渤海鱼类调查报告). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [26] | Zhu YD (朱元鼎), Wang YH (王幼槐) (1964) On the geographical distribution and faunal characteristics of the chondrichthian fishes of China. Acta Zoologica Sinica (动物学报), 4, 674-689. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Zhu YD (朱元鼎), Zhang CL (张春霖), Cheng QT (成庆泰) (1963) The Fishes of the East China Sea (东海鱼类志). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [10] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [11] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [14] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [15] | 徐伟强, 苏强. 分形模型与一般性物种多度分布关系的检验解析:以贝类和昆虫群落为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
