



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 24370. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024370 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024370
尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-18
接受日期:2024-12-03
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-02-21
通讯作者:
*E-mail: wanghb@caf.ac.cn
基金资助:
Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-08-18
Accepted:2024-12-03
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-02-21
Contact:
*E-mail: wanghb@caf.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要: 为明确我国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布特征, 本文基于构建的中国杨树害虫物种分布数据库, 对杨树害虫物种组成、危害类型及地理分布等进行综合分析。结果表明, 我国已知杨树害虫9目126科1,674种, 以鳞翅目、鞘翅目和半翅目为主要类群。在危害类型上, 叶部害虫的物种数量最多, 达1,058种, 而苗圃及根部害虫物种数量最少, 仅173种, 但其物种组成分布较为均匀且多样性最丰富。从栖息寄主角度看, 白杨派的害虫物种数量最多, 达1,258种, 但其物种多样性和均匀度最低, 大叶杨派和胡杨派害虫物种数量较少, 分别为20种和44种, 但其物种多样性和均匀度较高。在地理分布广度上, 杨树害虫物种的数量随着省区数量的增加而逐渐减少, 超过70%的害虫仅分布在全国不到一半的省区, 而易造成毁灭危害的主要害虫种类则几乎遍布全国。总体而言, 杨树害虫的分布格局呈现出明显的地域差异, 华东地区及“胡焕庸线”东侧的省区害虫物种数量较多。聚类分析表明, 杨树害虫的地理分布可划分为6个类群, 且不同类群之间表现出较强的地域相似性。本研究为今后杨树害虫科学精准防控提供了基础理论数据支持。
尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌 (2025) 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布. 生物多样性, 33, 24370. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024370.
Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin (2025) Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24370. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024370.
| 杨树派系 Poplar factions | 害虫数量 Pest number | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou’s evenness index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目 Order | 科 Family | 种 Species | ||||
| 白杨派 Leuce | 9 | 115 | 1,258 | 1.14 | 0.61 | 0.52 |
| 黑杨派 Aigeiros | 9 | 84 | 388 | 1.26 | 0.63 | 0.57 |
| 青杨派 Tacamahaca | 8 | 54 | 171 | 1.19 | 0.64 | 0.61 |
| 胡杨派 Turanga | 5 | 27 | 44 | 1.24 | 0.66 | 0.77 |
| 大叶杨派 Leucoides | 5 | 16 | 20 | 1.25 | 0.69 | 0.90 |
| 未分派系 Unclassified | 4 | 29 | 75 | / | / | / |
表1 不同杨树派系害虫物种数量及多样性指数
Table 1 Number and diversity indices of pest species in different poplar factions
| 杨树派系 Poplar factions | 害虫数量 Pest number | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou’s evenness index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目 Order | 科 Family | 种 Species | ||||
| 白杨派 Leuce | 9 | 115 | 1,258 | 1.14 | 0.61 | 0.52 |
| 黑杨派 Aigeiros | 9 | 84 | 388 | 1.26 | 0.63 | 0.57 |
| 青杨派 Tacamahaca | 8 | 54 | 171 | 1.19 | 0.64 | 0.61 |
| 胡杨派 Turanga | 5 | 27 | 44 | 1.24 | 0.66 | 0.77 |
| 大叶杨派 Leucoides | 5 | 16 | 20 | 1.25 | 0.69 | 0.90 |
| 未分派系 Unclassified | 4 | 29 | 75 | / | / | / |
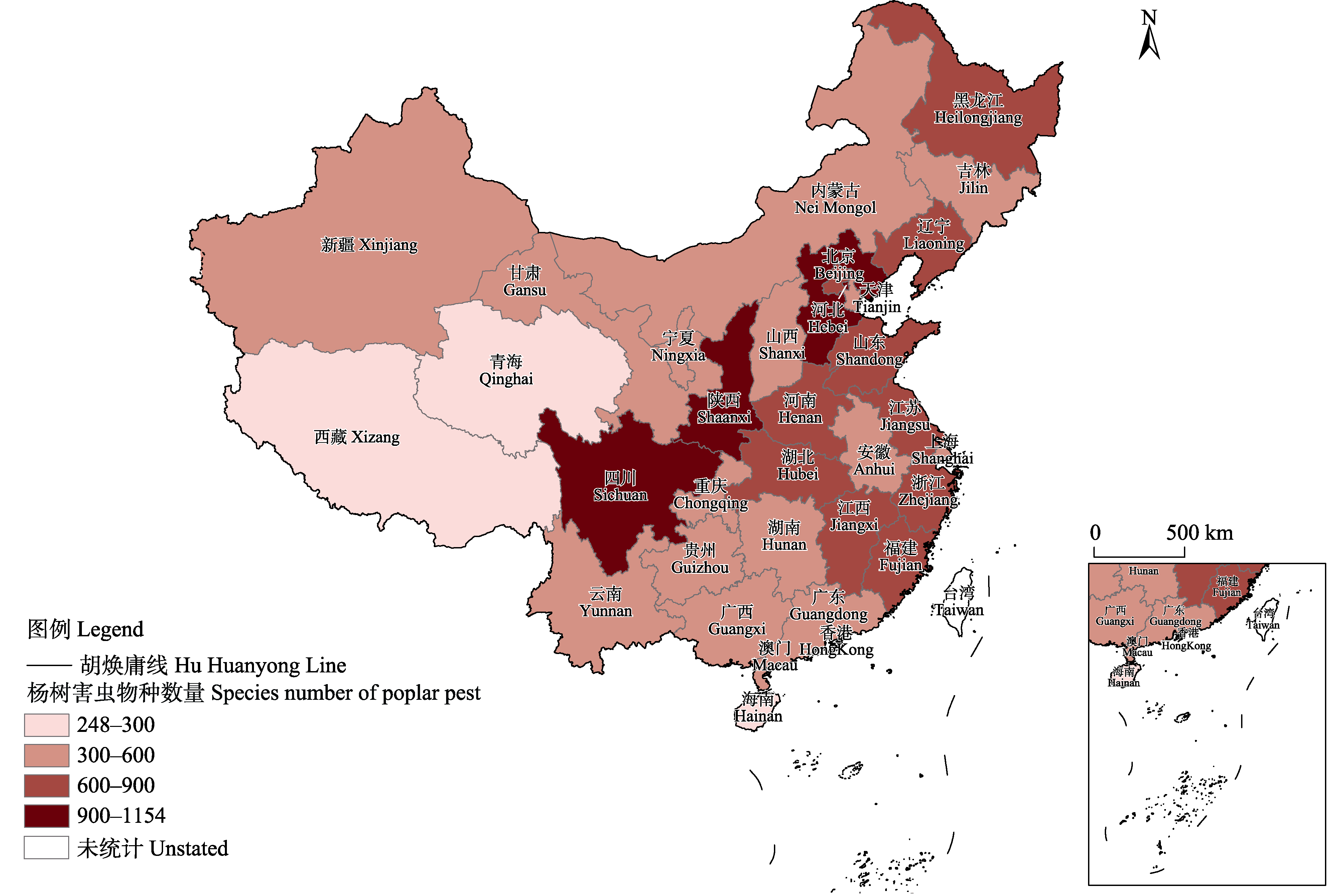
图5 杨树害虫在我国各省的分布趋势(缺少台湾、香港、澳门的数据)
Fig. 5 The distribution trend of poplar pests in China’s provinces (Absence of data from Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau)
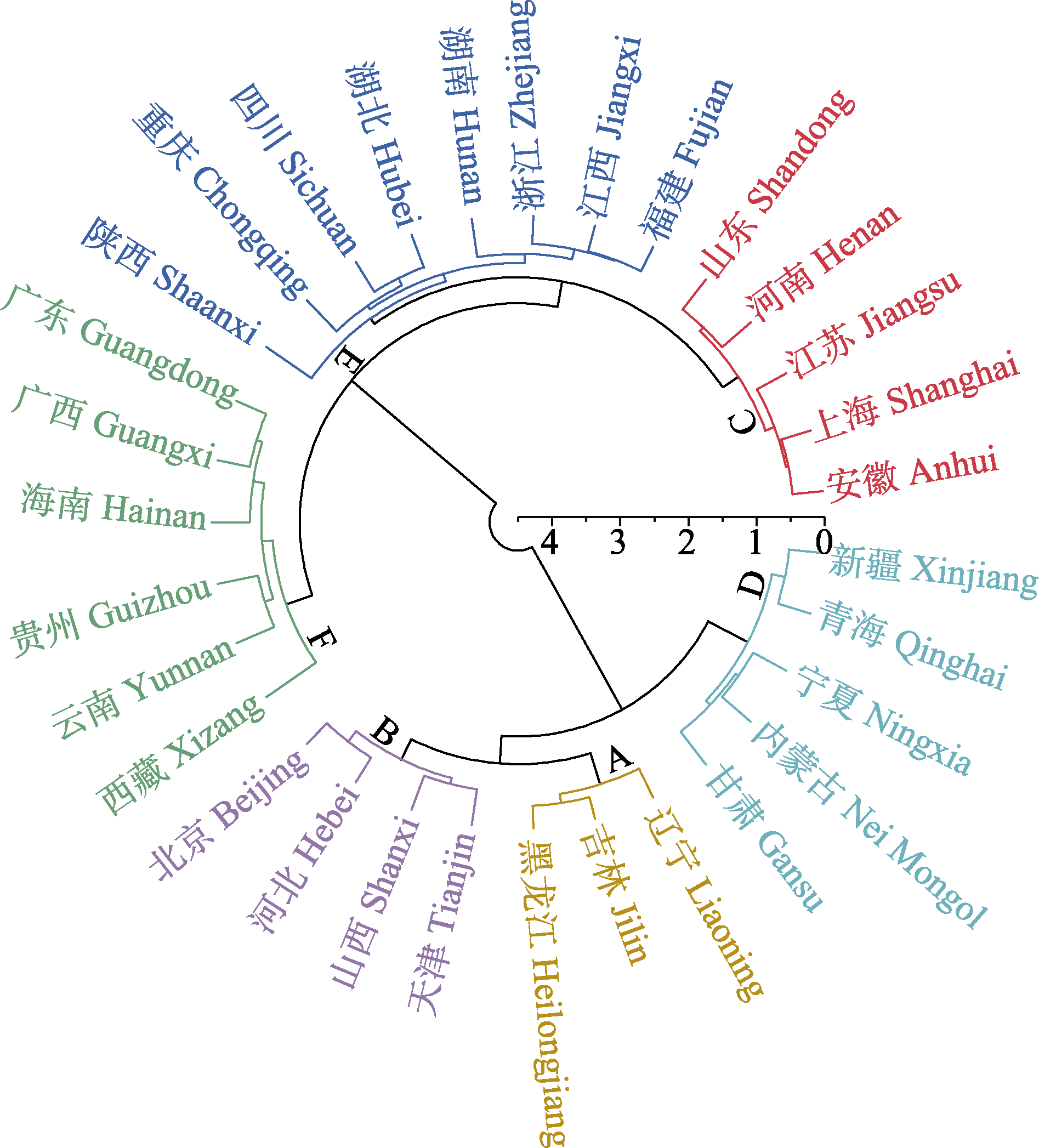
图6 基于各省区杨树害虫分布相似性的聚类分析(缺少台湾、香港、澳门的数据)
Fig. 6 Cluster analysis based on the distribution similarity of poplar pests in each province (Absence of data from Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau)
| [1] | Bale JS, Masters GJ, Hodkinson ID, Awmack C, Bezemer TM, Brown VK, Butterfield J, Buse AL, Coulson JC, Farrar J, Good JEG, Harrington R, Hartley S, Jones TH, Lindroth RL, Press MC, Symrnioudis I, Watt AD, Whittaker JB (2002) Herbivory in global climate change research:Direct effects of rising temperature on insect herbivores. Global Change Biology, 8, 1-16. |
| [2] | Dang YQ, Wang XY, Yang ZQ, Zhang YA (2022) Research progress on the biological control of forest insect pests in China. Forest Pest and Disease, 41(5), 6-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 党英侨, 王小艺, 杨忠岐, 张永安 (2022) 中国林业害虫生物防治研究进展. 中国森林病虫, 41(5), 6-13.] | |
| [3] | Wang Z (1984) Salicaceae. In: Flora Reipublicae Polularies Sinicae, Tomus 20(2) (ed. Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academicae Sinicae Edita). Science Press. Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王战 (1984) 杨柳科. 见: 中国植物志, 第20卷第二分册(杨柳科) ( 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [4] |
Fang CL, Li GD, Qi W, Sun SA, Cui XG, Ren YF (2023) Unbalanced trend of urban and rural development on the east and west sides of Hu Huanyong Line and micro-breakthrough strategy along the Bole-Taipei Line. Acta Geographica Sinica, 78, 443-455. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 方创琳, 李广东, 戚伟, 孙思奥, 崔学刚, 任宇飞 (2023) “胡焕庸线”东西部城乡发展不平衡趋势及沿博台线微突破策略. 地理学报, 78, 443-455.]
DOI |
|
| [5] | Gao RT (2003) Research on integrated control of poplar pests. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 高瑞桐 (2003) 杨树害虫综合防治研究. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Gao Y, Xie CX (2012) Feeding preference of Micromelalopha troglodyta to 4 poplar varieties. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 32(1), 61-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高悦, 解春霞 (2012) 杨小舟蛾对4个杨树品种叶片取食的选择性. 西南林业大学学报, 32(1), 61-63.] | |
| [7] | General Station of Forest and Grassland Pest Management, National Forestry and Grassland Administration.(2019) Forestry Pests in China: Results of National Forestry Pest Survey in 2014-2017. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家林业和草原局森林和草原病虫害防治总站 (2019) 中国林业有害生物: 2014-2017年全国林业有害生物普查成果. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | General Station of Forest Pest Control, State Forestry Administration (2010) Forestry Pest Control Calendar. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家林业局森林病虫害防治总站 (2010) 林业有害生物防治历. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Hou ZE, Wen JB, Xia NB (2000) Isozyme analysis in three poplars’ resistance to Anoplophora glabripennis. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 22(1), 91-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 侯仲娥, 温俊宝, 夏乃斌 (2000) 同工酶分析在三种杨树对光肩星天牛抗性上的应用. 北京林业大学学报, 22(1), 91-94.] | |
| [10] |
Hu JJ, Yang MS, Lu MZ (2010) Advances in biosafety studies on transgenic insect-resistant poplars in China. Biodiversity Science, 18, 336-345. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 胡建军, 杨敏生, 卢孟柱 (2010) 我国抗虫转基因杨树生态安全性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 336-345.]
DOI |
|
| [11] | Jaccard P (1901) Distribution de la Flore Alpine dans le Bassin des Dranses et dans quelque regions voisines. Bulletin de la Societe Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles, 37, 241-272. |
| [12] | Lei ZR, Guo YY, Li SF (2014) Catalogue of Pests on Major Crops in China. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 雷仲仁, 郭予元, 李世访 (2014) 中国主要农作物有害生物名单. 中国农业科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [13] | Li HP, Wang ZG, Yang MS, Zhang YG, Huang DZ, Zhang SH (2003) The relation between tannin and phenol constituents and resistance to Anoplophora glabripennis of various poplar tree species. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 26(1), 36-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李会平, 王志刚, 杨敏生, 张彦广, 黄大庄, 张世红 (2003) 杨树单宁与酚类物质种类及含量与光肩星天牛危害之间关系的研究. 河北农业大学学报, 26(1), 36-39.] | |
| [14] | Li Y, Wu JG, Xie LY, Zhou QF (2012) Relationship between the geographic distribution patterns of typical agricultural and forest pest species with climatic factors in China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 25, 533-542. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李艳, 吴建国, 谢立勇, 周巧富 (2012) 典型农林害虫分布与气候要素的关系. 环境科学研究, 25, 533-542.] | |
| [15] | Li YJ (1983) Poplar Pests in China. Liaoning Forestry Science and Technology House, Shenyang. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李亚杰 (1983) 中国杨树害虫. 辽宁科学技术出版社, 沈阳.] | |
| [16] | Liu D, Shen WS, Zhu SX, Zou CX, Xie HJ, Ouyang Y, Lin NF (2014) Spatial patterns of agricultural and forest pests in China and the impact factors. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33, 3322-3331. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘冬, 沈渭寿, 朱四喜, 邹长新, 谢浩京, 欧阳琰, 林乃峰 (2014) 中国农林业害虫分布特征及其影响因素. 生态学杂志, 33, 3322-3331.] | |
| [17] | Liu KL, Zhao WX (2002) Characteristics of forest biological disasters and sustainable control strategies in northwest China. World Forestry Research, 15(5), 41-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘开玲, 赵文霞 (2002) 我国西北地区森林生物灾害发生特点及可持续控制策略. 世界林业研究, 15(5), 41-48.] | |
| [18] | Liu XP, Zhang WJ, Cao JS, Yang B, Cai YJ (2018) Carbon sequestration of plantation in Beijing-Tianjin sand source areas. Journal of Mountain Science, 15, 2148-2158. |
| [19] | Luo YQ, Liu RG, Xu ZC, Sun CC, Wen JB (2002) Theories and technologies of ecologically regulating poplar longhorned beetle disaster in shelter forest. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, (Z1), 164-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 骆有庆, 刘荣光, 许志春, 孙长春, 温俊宝 (2002) 防护林杨树天牛灾害的生态调控理论与技术. 北京林业大学学报, (Z1), 164-168.] | |
| [20] | Mei AH, Chen JY, Wu GY, Du XS, Luo FS (1998) Investigation on species of poplar pests in Jianghan Plain, occurrence causes and control countermeasures of main pests. Forest Pest and Disease, (2), 35-37. (in Chinese) |
| [ 梅爱华, 陈京元, 吴高云, 杜夕森, 罗福世 (1998) 江汉平原杨树害虫种类调查、发生原因及主要害虫防治对策. 森林病虫通讯, (2), 35-37.] | |
| [21] | Niu ZT, Zhang QW, Peng ZH, Li JH, Sun ZY (2006) Advances in research on fast-growing mechanism and ideotypes of Populus. World Forestry Research, (2), 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 牛正田, 张绮纹, 彭镇华, 李金花, 孙振元 (2006) 国外杨树速生机制与理想株型研究进展. 世界林业研究, (2), 23-27.] | |
| [22] | Qi W, Liu SH, Zhao MF, Liu Z (2016) China’s different spatial patterns of population growth based on the “Hu Line”. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 26, 1611-1625. |
| [23] | Shang HD, Wang M, Li GH, Wang HB (2024) List of poplar pest species in China, V1. China Scientific Data, https://doi.org/10.11922/11-6035.csd.2024.0138.zh. (in Chinese) |
| [ 尚华丹, 王梅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌 (2024) 中国杨树害虫物种名录数据集, V1. 中国科学数据(中英文网络版). https://doi.org/10.11922/11-6035.csd.2024.0138.zh.] | |
| [24] | Shen XC, Zhang SJ, Shen Q, Hu GL, Lu JQ (2021) Multivariate similarity clustering analysis: A new method regarding biogeography and its application in global insects. Integrative Zoology, 16, 390-403. |
| [25] | Wang F, Xiong Z, Yan XD, Dai XG, Wang LB, Li YF (2018) Geographical distribution pattern of species diversity of the genus Populus L. in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 282-290. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王芳, 熊喆, 延晓冬, 戴新刚, 王磊斌, 李亚飞 (2018) 杨属物种多样性在中国的地理分布格局. 生态学报, 38, 282-290.] | |
| [26] |
Wang GY, Dong Y, Liu XJ, Yao GS, Yu XY, Yang MS (2018) The current status and development of insect-resistant genetically engineered poplar in China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1408.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Wang YJ (1991) Overview of poplar pest control research in China. Journal of Jiangsu Forestry Science & Technology, 18(1), 47-48, 26. (in Chinese) |
| [ 汪永俊 (1991) 我国杨树害虫防治研究概述. 江苏林业科技, 18(1), 47-48, 26.] | |
| [28] | Xiao GR (2020) Chinese Forest Insects, 3rd edn. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 萧刚柔 (2020) 中国森林昆虫(第三版). 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] | Xu MG, Chen YJ, Liu JZ, Wang D, Liu YQ (2016) The distribution pattern dynamics of Populus euphratica are influenced by hydrology in the middle reaches of Tarim River. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 2646-2655. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐梦辰, 陈永金, 刘加珍, 王丹, 刘亚琦 (2016) 塔里木河中游水文影响下的胡杨种群格局动态. 生态学报, 36, 2646-2655.] | |
| [30] | Yan YW, Wang YC, Feng CC, Wan PM, Chang KT (2017) Potential distributional changes of invasive crop pest species associated with global climate change. Applied Geography, 82, 83-92. |
| [31] | Yang XY, Wu J (1981) List of Forest Insects in China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨秀云, 吴坚 (1981) 中国森林昆虫名录. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [32] | Yang ZQ (2018) Research progress on biological control of major forest pests in China (1). Forest Science and Technology, (4), 40-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨忠岐 (2018) 我国重大林木害虫生物防治研究进展(一). 林业科技通讯, (4), 40-43.] | |
| [33] | Zou Y, Zhang LJ, Ge XZ, Guo SW, Li X, Chen LH, Wang T, Zong SX (2019) Prediction of the long-term potential distribution of Cryptorhynchus lapathi (L.) under climate change. Forests, 11, 5-5. |
| [34] | Zhao XY, Ma KF, Shen YB, Zhang M, Li KY, Wu RL, Zhang ZY (2012) Characteristic variation and selection of forepart hybrid clones of Sect. Populus. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 34(2), 45-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵曦阳, 马开峰, 沈应柏, 张明, 李奎友, 邬荣领, 张志毅 (2012) 白杨派杂种无性系植株早期性状变异与选择研究. 北京林业大学学报, 34(2), 45-51.] | |
| [35] | Zhu W, Wang YF, Qu GB, Xi BY, Jia LM (2024) Cultivar and tree size, but not climate, are principal factors affecting stem quality of Populus tomentosa plantations in the North China Plain. Forest Ecology and Management, 573, 122348. |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [5] | 陈丁松, 刘子恺, 贺子洋, 陈伟东. 缓步动物多样性、分布特征和生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24406-. |
| [6] | 张颂琪, 陆义, 陈炳耀, 杨光, 王彦平, 陈传武. 全球鲸豚类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24442-. |
| [7] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [8] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [9] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [10] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [11] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [12] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [13] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [14] | 韩思成, 陆道炜, 韩宇辰, 栗若寒, 杨晶, 孙戈, 杨陆, 钱俊伟, 方翔, 罗述金. 北京近郊浅山地区的野生豹猫分布及环境影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24138-. |
| [15] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn