



生物多样性 ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (3): 227-232. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.227 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.227
收稿日期:2009-10-19
接受日期:2009-12-16
出版日期:2010-05-20
发布日期:2012-02-08
通讯作者:
张大明
作者简介: E-mail: zhangdm@ibcas.ac.cnReceived:2009-10-19
Accepted:2009-12-16
Online:2010-05-20
Published:2012-02-08
Contact:
Daming Zhang
摘要:
本文调查研究了野生稻群体内及群体间的DNA甲基化多样性。选取与亚洲栽培稻近缘的两个野生种Oryza nivara和O. rufipogon作为研究对象, 采用改进的MSAP (methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism)技术对其基因组CCGG位点的甲基化多样性进行了分析。结果表明: 在同一个IRGC(the International Rice Germplasm Center)编号群体内的不同个体间, 基因组甲基化条带高度一致; 而在不同编号群体间, 甲基化条带表现为多态。其中后者又可以分为两类: 条带模式高度一致的Class I和条带模式呈多态性的Class II。将上述两类甲基化片段的编码基因与栽培稻粳稻(O. sativaL. subsp. japonica)和籼稻(O. sativa L. subsp. indica)两个亚种的同源基因进行序列比对发现, 在进化趋势上Class I表现得比较保守, 而Class II较为活跃。DNA甲基化多样性作为标志遗传多样性的一种信息来源, 其在群体分化及物种进化过程中的作用还需要进一步探讨。
崔影影, 张大明 (2010) 野生稻Oryza nivara和O. rufipogon DNA甲基化多样性. 生物多样性, 18, 227-232. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.227.
Yingying Cui, Daming Zhang (2010) Surveying DNA methylation diversity in the wild rice, Oryza nivaraand O. rufipogon. Biodiversity Science, 18, 227-232. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.227.
| 序号 Index | IRGC编号 IRGC No. | 来源地 Geographic origin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O. nivara | ||||||||
| N1 | 103407 | 斯里兰卡 Sri LanKa | ||||||
| N2 | 105431 | 斯里兰卡 Sri LanKa | ||||||
| N3 | 105391 | 泰国 Thailand | ||||||
| N4 | 106345 | 缅甸 Myanmar | ||||||
| N5 | 106185 | 印度 India | ||||||
| O. rufipogon | ||||||||
| R1 | 106515 | 越南 Vietnam | ||||||
| R2 | 82000 | 巴布亚新几内亚 Papua New Guinea | ||||||
| R3 | 103423 | 斯里兰卡 Sri LanKa | ||||||
| R4 | 105958 | 印度尼西亚 Indonesia | ||||||
| R5 | 106036 | 马来西亚 Malaysia | ||||||
表1 研究所用Oryza nivara和O. rufipogon材料
Table 1 Oryza nivaraand O. rufipogon accessions studied
| 序号 Index | IRGC编号 IRGC No. | 来源地 Geographic origin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O. nivara | ||||||||
| N1 | 103407 | 斯里兰卡 Sri LanKa | ||||||
| N2 | 105431 | 斯里兰卡 Sri LanKa | ||||||
| N3 | 105391 | 泰国 Thailand | ||||||
| N4 | 106345 | 缅甸 Myanmar | ||||||
| N5 | 106185 | 印度 India | ||||||
| O. rufipogon | ||||||||
| R1 | 106515 | 越南 Vietnam | ||||||
| R2 | 82000 | 巴布亚新几内亚 Papua New Guinea | ||||||
| R3 | 103423 | 斯里兰卡 Sri LanKa | ||||||
| R4 | 105958 | 印度尼西亚 Indonesia | ||||||
| R5 | 106036 | 马来西亚 Malaysia | ||||||
| 引物与接头 Primer and adapter | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| 接头 Adapter | |
| EcoRI-adapter I | CTGGTAGACTGCGTACC |
| EcoRI-adapter II | AATTGGTACGCAGTC |
| 预扩增引物 Preselective primer | |
| EcoRI + A | GACTGCGTACCAATTCA |
| EcoRI + C | GACTGCGTACCAATTCC |
| 选择性扩增引物 Selective primer | |
| EcoRI + AA | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAA |
| EcoRI + AT | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAT |
| EcoRI + AC | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAC |
| EcoRI + AG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAG |
| EcoRI + CT | GACTGCGTACCAATTCCT |
| EcoRI + CG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCCG |
| EcoRI + CA | GACTGCGTACCAATTCCA |
表2 MSAP所用的接头和选择性扩增引物序列
Table 2 Sequences of adapter and primer used for MSAP analysis
| 引物与接头 Primer and adapter | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| 接头 Adapter | |
| EcoRI-adapter I | CTGGTAGACTGCGTACC |
| EcoRI-adapter II | AATTGGTACGCAGTC |
| 预扩增引物 Preselective primer | |
| EcoRI + A | GACTGCGTACCAATTCA |
| EcoRI + C | GACTGCGTACCAATTCC |
| 选择性扩增引物 Selective primer | |
| EcoRI + AA | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAA |
| EcoRI + AT | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAT |
| EcoRI + AC | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAC |
| EcoRI + AG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCAG |
| EcoRI + CT | GACTGCGTACCAATTCCT |
| EcoRI + CG | GACTGCGTACCAATTCCG |
| EcoRI + CA | GACTGCGTACCAATTCCA |
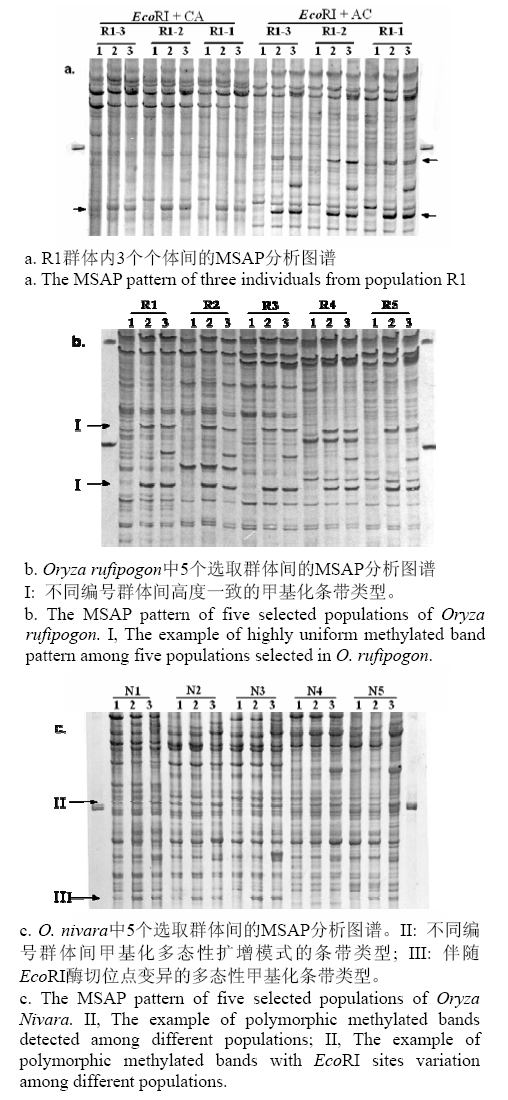
图1 MSAP分析Oryza nivara和O. rufipogon的DNA甲基化部分电泳图。泳道1, 2, 3分别表示同一样品的3种酶切扩增产物(1:EcoRI/MspI; 2:EcoRI/HpaII; 3:EcoRI )。箭头指示含有CCGG甲基化位点的片段。
Fig. 1 Part of electrophoretic profiles obtained using MSAP in the wild rice, Oryza nivara and O. Rufipogon.Lanes 1-3 show three digestion and amplification production (1, EcoRI / MspI; 2, EcoRI /HpaII and 3:EcoRI), respectively. The arrowheads indicate fragments containing the methylated CCGG sites.
| 种 Species | 大小 Size (bp) | E值 E value | 基因库 GenBank | 染色体 Chromosome | 检索结果 Result of BLAST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | |||||
| O. nivara | 494 | 0 | AP008217 | 11,12 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.9) |
| 644 | 0 | AP008217 | 11,12 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.9) | |
| O. rufipogon | 615 | 0 | AP005531 | 8 | RNA-binding region RNP-1containing protein (BAD05783) |
| 640 | 0 | AP008218 | 11,12 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.85) | |
| 548 | 0 | AP008212 | 6 | Putative mitochondrial phosphate transporter (BAD35704.1) | |
| 282 | 6.00E-13 | AC104322 | 3 | Putative polyprotein (AAR89842.1) | |
| Class II | |||||
| O. nivara | 742 | 0 | AP008216.1 | 2,10 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.97/ 0.89) |
| 630 | 0 | AP005563 | 9 | TPR-like domain containing protein (BAD19882.1) | |
| 218 | 4.00E-61 | AL731583 | 4 | Ribonuclease HI (CAE 05186.2) | |
| O. rufipogon | 366 | 0 | AP008210 | 4 | Kinesin, motor region domain containing protein (CAE04590.2) |
| 563 | 7.00E-56 | AP008213 | 7 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.99) | |
| Class III | |||||
| O. nivara | 569 | 0 | AC120529 | 3 | Near the centromere, the internal region of putative protein and retrotransposon |
| 305 | 2.00E-11 | AP008208.1 | 2 | Inetrnal region of a pseudo gene | |
| 681 | 0 | AP008209 | 3 | Snabo-1 miniature inverted repeat transposable element/ the intron of pseudo gene | |
| 615 | 0 | AC120529 | 3 | Near the centromere, the internal region of putative protein and retrotransposon | |
| O. rufipogon | 478 | 0 | AC120529 | 3 | Near the centromere, the internal region of putative protein and retrotransposon |
| 599 | 0 | AP004364.4 | 11,12 | Internal region of two hypotetical protein | |
| 514 | 0 | AP008209.1 | 3 | Near the centromere, the internal region of putative protein and retrotransposon |
表3 甲基化片段测序后BLAST(The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool)结果
Table 3 BLAST (short of The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) search results for sequenced methylated fragments
| 种 Species | 大小 Size (bp) | E值 E value | 基因库 GenBank | 染色体 Chromosome | 检索结果 Result of BLAST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | |||||
| O. nivara | 494 | 0 | AP008217 | 11,12 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.9) |
| 644 | 0 | AP008217 | 11,12 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.9) | |
| O. rufipogon | 615 | 0 | AP005531 | 8 | RNA-binding region RNP-1containing protein (BAD05783) |
| 640 | 0 | AP008218 | 11,12 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.85) | |
| 548 | 0 | AP008212 | 6 | Putative mitochondrial phosphate transporter (BAD35704.1) | |
| 282 | 6.00E-13 | AC104322 | 3 | Putative polyprotein (AAR89842.1) | |
| Class II | |||||
| O. nivara | 742 | 0 | AP008216.1 | 2,10 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.97/ 0.89) |
| 630 | 0 | AP005563 | 9 | TPR-like domain containing protein (BAD19882.1) | |
| 218 | 4.00E-61 | AL731583 | 4 | Ribonuclease HI (CAE 05186.2) | |
| O. rufipogon | 366 | 0 | AP008210 | 4 | Kinesin, motor region domain containing protein (CAE04590.2) |
| 563 | 7.00E-56 | AP008213 | 7 | Internal region of two genes; predicted as promoter region (0.99) | |
| Class III | |||||
| O. nivara | 569 | 0 | AC120529 | 3 | Near the centromere, the internal region of putative protein and retrotransposon |
| 305 | 2.00E-11 | AP008208.1 | 2 | Inetrnal region of a pseudo gene | |
| 681 | 0 | AP008209 | 3 | Snabo-1 miniature inverted repeat transposable element/ the intron of pseudo gene | |
| 615 | 0 | AC120529 | 3 | Near the centromere, the internal region of putative protein and retrotransposon | |
| O. rufipogon | 478 | 0 | AC120529 | 3 | Near the centromere, the internal region of putative protein and retrotransposon |
| 599 | 0 | AP004364.4 | 11,12 | Internal region of two hypotetical protein | |
| 514 | 0 | AP008209.1 | 3 | Near the centromere, the internal region of putative protein and retrotransposon |
| 类型 Class | 序列号 Accession no. | 注释 Note | 编码区长度 Coding region (bp) | 同源序列比对 Sequence contrast | 非同义突变位点 Non synonymy mutation sites | 同义突变位点 Synonymy mutation sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | Os08g0190200 | RNA recognition motif | 391 | rufipogon-japonica rufipogon-indica | 1 0 | 0 2 |
| Os06g0210500 | Putative mitochondrial phosphate transporter | 150 | rufipogon-japonica rufipogon-indica | 0 0 | 0 0 | |
| OSJNBa0024F18.68 | Putative polyprotein | 281 | rufipogon-japonica rufipogon-indica | 0 0 | 4 5 | |
| Class II | Os09g0124100 | TPR-like domain containing protein | 128 | nivara-japonica nivara-indica | 1 1 | 0 0 |
| OSJNBb0069N01.4 | Ribonuclease HI | 207 | nivara-japonica nivara-indica | 11 11 | 6 7 | |
| Os04g0375900 | Kinesin, motor region domain containing protein | 241 | rufipogon-japonica rufipogon-indica | 0 4 | 0 1 |
表4 6条部分外显子区同栽培稻2个亚种变异位点的比较结果
Table 4 Comparisons of partial exon sequences of six genes with the corresponding sequences of japonica and indica
| 类型 Class | 序列号 Accession no. | 注释 Note | 编码区长度 Coding region (bp) | 同源序列比对 Sequence contrast | 非同义突变位点 Non synonymy mutation sites | 同义突变位点 Synonymy mutation sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | Os08g0190200 | RNA recognition motif | 391 | rufipogon-japonica rufipogon-indica | 1 0 | 0 2 |
| Os06g0210500 | Putative mitochondrial phosphate transporter | 150 | rufipogon-japonica rufipogon-indica | 0 0 | 0 0 | |
| OSJNBa0024F18.68 | Putative polyprotein | 281 | rufipogon-japonica rufipogon-indica | 0 0 | 4 5 | |
| Class II | Os09g0124100 | TPR-like domain containing protein | 128 | nivara-japonica nivara-indica | 1 1 | 0 0 |
| OSJNBb0069N01.4 | Ribonuclease HI | 207 | nivara-japonica nivara-indica | 11 11 | 6 7 | |
| Os04g0375900 | Kinesin, motor region domain containing protein | 241 | rufipogon-japonica rufipogon-indica | 0 4 | 0 1 |
| [1] |
Alexandre CM, Hennig L (2008) FLC or not FLC: the other side of vernalization. Journal of Experimental Botany, 59, 1127-1135.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Ashikawa I (2001) Surveying CpG methylation at 5'-CCGG in the genomes of rice cultivars. Plant Molecular Biology, 45, 31-39.
DOI URL PMID |
| [3] |
Cervera MT, Ruiz-García L, Martínez-Zapater JM (2002) Analysis of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana based on methylation-sensitive AFLP markers. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 268, 543-552.
URL PMID |
| [4] |
Chan SW, Henderson IR, Jacobsen SE (2005) Gardening the genome: DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature Reviews Genetics, 6, 351-360.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Cubas P, Vincent C, Coen E (1999) An epigenetic mutation responsible for natural variation in floral symmetry. Nature, 401, 157-161.
URL PMID |
| [6] |
Gruenbaum Y, Naveh-Many T, Ceder H, Razin A (1981) Sequence specificity of methylation in higher plant DNA. Nature, 292, 860-862.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Kaeppler SM, Kaeppler HF, Rhee Y (2000) Epigenetic aspects of somaclonal variation in plants. Plant Molecular Biology, 43, 179-188.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] | Keyte AL, Percififld R, Liu B, Wendel JF (2006) Intraspecific DNA methylation polymorphism in cotton ( Gossypim hir- sutum L.). Journal of Heredity, 97, 444-450. |
| [9] |
Knox MR, Ellis THN (2001) Stability and inheritance of methylation states at PstI sites in Pisum. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 265, 497-507.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 8, 4321-4325.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | Nelson M, McClelland M (1991) Site-specific methylation: effect on DNA modification methyltransferases and restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Research, 19S, 2045-2071. |
| [12] |
Susan K, Michael DP (2004) Epialleles via DNA methylation: consequences for plant evolution. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 19, 309-314.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 24, 4876-4882. |
| [14] |
Tran RK, Henikoff JG, Zilberman D, Ditt RF, Jacobsen SE, Henikoff S (2005) DNA methylation profiling identifies CG methylation clusters in Arabidopsis genes. Current Biology, 15, 154-159.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
Wang YM, Lin XY, Dong B, Wang YD, Liu B (2004) DNA methylation polymorphism in a set of elite rice cultivars and its possible contribution to inter-cultivar differential gene expression. Cellular and Molecular Biology Letters, 9, 543-556.
URL PMID |
| [16] |
Xiong LZ, Xu CG, Saghai Maroof MA, Zhang Q (1999) Patterns of cytosine methylation in an elite rice hybrid and its parental lines, detected by a methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism technique. Molecular and General Genetics, 261, 439-446.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Zilberman D (2008) The evolving functions of DNA methylation. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 11, 554-559.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 陈楠, 张全国. 实验进化研究途径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [2] | 何花, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 被子植物隐性雌雄异株性系统的多样性、系统演化及进化意义[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24149-. |
| [3] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [4] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [5] | 沈诗韵, 潘远飞, 陈丽茹, 土艳丽, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草原产地和入侵地种群的植物-土壤反馈差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22436-. |
| [6] | 俄广旭, 白天天, 朱振宇, 郭雪峰. 动物消化道微生物多样性与宿主协同进化关系的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23214-. |
| [7] | 戚海迪, 张定海, 单立山, 陈国鹏, 张勃. 昆虫病原真菌感染昆虫宿主的机制和宿主昆虫的防御策略研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23273-. |
| [8] | 葛颂. 中国植物系统和进化生物学研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22385-. |
| [9] | 王芸芸, 郝占庆. 被子植物性系统的多样性、生态功能及分布规律[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22065-. |
| [10] | 薛成, 李波卡, 雷天宇, 山红艳, 孔宏智. 生物多样性起源与进化研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22460-. |
| [11] | 王少鹏, 罗明宇, 冯彦皓, 储诚进, 张大勇. 生物多样性理论最新进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22410-. |
| [12] | 邓铭先, 黄河燕, 沈诗韵, 吴纪华, 拉琼, 斯确多吉, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草在青藏高原对模拟增温的可塑性: 引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1198-1205. |
| [13] | 陈旸康, 王益, 李家亮, 王文韬, 冯端宇, 毛康珊. 主流分子钟定年方法的原理、误差来源和使用建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 629-646. |
| [14] | 黄河燕, 朱政财, 吴纪华, 拉琼, 周永洪, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对模拟全天增温的可塑性: 引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 419-427. |
| [15] | 孙思邈, 陈吉欣, 冯炜炜, 张昶, 黄凯, 管铭, 孙建坤, 刘明超, 冯玉龙. 植物氮形态利用策略及对外来植物入侵性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 72-80. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
