



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 23282. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023282 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023282
所属专题: 美丽中国建设
刘彩莲1( ), 张雄2, 樊恩源3, 王松林4, 姜艳1, 林柏岸1(
), 张雄2, 樊恩源3, 王松林4, 姜艳1, 林柏岸1( ), 房璐4, 李玉强4, 刘乐彬4, 刘敏1,*(
), 房璐4, 李玉强4, 刘乐彬4, 刘敏1,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-04
接受日期:2023-12-05
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2024-01-10
通讯作者:
*E-mail: minliuxm@xmu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Cailian Liu1( ), Xiong Zhang2, Enyuan Fan3, Songlin Wang4, Yan Jiang1, Baian Lin1(
), Xiong Zhang2, Enyuan Fan3, Songlin Wang4, Yan Jiang1, Baian Lin1( ), Lu Fang4, Yuqiang Li4, Lebin Liu4, Min Liu1,*(
), Lu Fang4, Yuqiang Li4, Lebin Liu4, Min Liu1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-08-04
Accepted:2023-12-05
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2024-01-10
Contact:
*E-mail: minliuxm@xmu.edu.cn
摘要:
濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约(CITES)于2002年将海马属(Hippocampus)所有物种列入附录II进行国际贸易监管。2021年2月, 农业农村部和国家林业和草原局联合公布了调整后的《国家重点保护野生动物名录》, 明确将中国海域海马属所有物种(野外种群)列为国家二级重点保护动物。尽管我国高度重视海马保护工作, 但目前仍缺乏对各海区海马物种多样性以及重要生态学信息的汇总。本文通过文献资料整理, 提供了最新的中国海域分布的16种海马名录, 总结了其分布区域、栖息生境、繁殖特征等生态信息, 并归纳了不同物种的濒危等级和主要威胁因素。在16种海马中, 莫氏海马(H. mohnikei, 又名日本海马)分布范围最为广泛, 从渤海至南海均有出现。台湾、海南、广东、福建及广西沿岸海域的海马物种多样性较高。海马营底层生活, 其栖息生境十分多样化, 包括珊瑚礁、海草床、海藻场、红树林、碎石及砂泥质海床等。目前, 海马野外种群所面临的主要威胁来自于渔业兼捕及栖息地破坏。为更好地保护海马野外种群, 建议管理部门关注海马作为旗舰物种在海洋生态环境保护工作中的影响力, 建立以海马及其栖息生境为主要保护目标的国家级自然保护区或采取其他有效的区域保护措施; 加强海马保护公众宣传, 着力解决海马兼捕问题; 尽快启动全国范围的海马栖息地调查及种群数量评估工作, 识别海马关键栖息地; 提升贸易监管能力, 规范海马利用管理, 建立鉴别野生和养殖海马群体的关键技术, 以期促进对我国海马野外种群的有效保护。
刘彩莲, 张雄, 樊恩源, 王松林, 姜艳, 林柏岸, 房璐, 李玉强, 刘乐彬, 刘敏 (2024) 中国海域海马的物种多样性、生态特征及保护建议. 生物多样性, 32, 23282. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023282.
Cailian Liu, Xiong Zhang, Enyuan Fan, Songlin Wang, Yan Jiang, Baian Lin, Lu Fang, Yuqiang Li, Lebin Liu, Min Liu (2024) Species diversity, ecological characteristics and conservation measures of seahorses (Hippocampus) in China’s waters. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23282. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023282.
| 序号No. | 中文名/英文名 Common name in Chinese and Englisha | 拉丁学名 Latin name | 全球分布 Global distributionb | 中国海域分布 Domestic distributionc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 印度洋 Indian Ocean | 太平洋 Pacific Ocean | 渤海 Bo Hai | 黄海 Yellow Sea | 东海 East China Sea | 南海 South China Sea | |||
| 1 | 巴博海马(鲍氏海马) Barbour’s seahorse | Hippocampus barbouri | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | |||
| 2 | 巴氏海马(巴氏豆丁海马) Pygmy seahorse | H. bargibanti | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | ||
| 3 | 北部湾海马 Beibu Bay seahorse | H. casscsio | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅北部湾 Only recorded in Beibu Bay) | ||||
| 4 | 克里蒙氏海马(科氏海马) Coleman’s pygmy seahorse* | H. colemani | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | |||
| 5 | 虎尾海马 Tiger tail seahorse | H. comes | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | |||
| 6 | 冠海马 Crowned seahorse | H. coronatus | $\checkmark$ (西北部 Northwest) | $\checkmark$ | ||||
| 7 | 丹尼斯海马(丹尼斯豆丁海马或橘色海马) Denise’s pygmy seahorse* | H. denise | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | ||||
| 8 | 日本豆丁海马 Japanese pygmy seahorse* | H. japapigu | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$(仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | ||||
| 9 | 刺海马 Thorny seahorse | H. histrix | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | ||
| 10 | 克氏海马(大海马) Kellog’s seahorse | H. kelloggi | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | ||
| 11 | 库达海马 Spotted seahorse | H. kuda | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | ||
| 12 | 莫氏海马(日本海马) Japanese seahorse | H. mohnikei | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ |
| 13 | 彭氏海马 Pontoh’s pygmy seahorse* | H. pontohi | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | |||
| 14 | 花海马 Shiho’s seahorse | H. sindonis | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | ||||
| 15 | 棘海马 Hedgehog seahorse | H. spinosissimus | $\checkmark$ (东北部 Northeast) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | ||
| 16 | 三斑海马(斑海马) Longnose seahorse | H. trimaculatus | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | |
表1 中国海域分布的16种海马
Table 1 Sixteen seahorse species recorded in China’s waters
| 序号No. | 中文名/英文名 Common name in Chinese and Englisha | 拉丁学名 Latin name | 全球分布 Global distributionb | 中国海域分布 Domestic distributionc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 印度洋 Indian Ocean | 太平洋 Pacific Ocean | 渤海 Bo Hai | 黄海 Yellow Sea | 东海 East China Sea | 南海 South China Sea | |||
| 1 | 巴博海马(鲍氏海马) Barbour’s seahorse | Hippocampus barbouri | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | |||
| 2 | 巴氏海马(巴氏豆丁海马) Pygmy seahorse | H. bargibanti | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | ||
| 3 | 北部湾海马 Beibu Bay seahorse | H. casscsio | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅北部湾 Only recorded in Beibu Bay) | ||||
| 4 | 克里蒙氏海马(科氏海马) Coleman’s pygmy seahorse* | H. colemani | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | |||
| 5 | 虎尾海马 Tiger tail seahorse | H. comes | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | |||
| 6 | 冠海马 Crowned seahorse | H. coronatus | $\checkmark$ (西北部 Northwest) | $\checkmark$ | ||||
| 7 | 丹尼斯海马(丹尼斯豆丁海马或橘色海马) Denise’s pygmy seahorse* | H. denise | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | ||||
| 8 | 日本豆丁海马 Japanese pygmy seahorse* | H. japapigu | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$(仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | ||||
| 9 | 刺海马 Thorny seahorse | H. histrix | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | ||
| 10 | 克氏海马(大海马) Kellog’s seahorse | H. kelloggi | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | ||
| 11 | 库达海马 Spotted seahorse | H. kuda | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | ||
| 12 | 莫氏海马(日本海马) Japanese seahorse | H. mohnikei | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ |
| 13 | 彭氏海马 Pontoh’s pygmy seahorse* | H. pontohi | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | |||
| 14 | 花海马 Shiho’s seahorse | H. sindonis | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ (仅台湾海域 Only recorded in Taiwan) | ||||
| 15 | 棘海马 Hedgehog seahorse | H. spinosissimus | $\checkmark$ (东北部 Northeast) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | ||
| 16 | 三斑海马(斑海马) Longnose seahorse | H. trimaculatus | $\checkmark$ (东部 East) | $\checkmark$ (西部 West) | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | $\checkmark$ | |
| 中文名/英文名 Common name in Chinese and English | 全球栖息地记录 Global habitat recordsa | 中国栖息地记录 Habitat records in Chinab | 水深 Water depth (m)a | 繁殖季节 Breeding seasonc | 寿命 Lifespan (year)d | 初次性成熟体高 Height at first maturity (cm)d | 每胎产幼体数 Number of juvenile per pouchb | 主要食性喜好 Main dietsa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巴博海马 Barbour’s seahorse | 海草床、珊瑚礁 Seagrass beds and coral reefs | - | 0-10 | - | - | 8.0 | - | 哲水蚤桡足类、甲壳类幼虫等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as calanoid copepods and decapod larvae | |||||||
| 巴氏海马 Pygmy seahorse | 柳珊瑚(小尖柳珊瑚属种类) Gorgonian corals (Muricella spp.) | 柳珊瑚(小尖柳珊瑚属种类) Gorgonian corals (Muricella spp.) | 15-40 | 全年繁殖 Breeding year-round | - | 1.3 | - | 钩虾、猛水蚤等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as gammarid amphipods and harpacticoid copepods | |||||||
| 北部湾海马 Beibu Bay seahorse | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 克里蒙氏海马 Coleman’s pygmy seahorse | 粗砂质底及海草床(鳗草、喜盐草) Coarse sand and seagrass beds (Zostera spp. and Halophilia spp.) | 粗砂粒及藻类丰富浅海区 Shallow waters with coarse sand and seaweeds rich | 0-5 | - | - | - | - | 钩虾、猛水蚤、糠虾等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as gammarid amphipods, harpacticoid copepods and mysids | |||||||
| 虎尾海马 Tiger tail seahorse | 珊瑚礁、海绵、海藻场、海草床 Coral reefs, sponges, seaweed beds and seagrass beds | 0-20 | 全年繁殖(菲律宾) Breeding year-round in central Philippines | - | 8.1 | - | - | ||||||||
| 冠海马 Crowned seahorse | 海藻场(马尾藻)、海草床(鳗草) Seaweed beds (Sargassum spp.) and seagrass beds (Zostera spp.) | 近海多海藻区 Nearshore waters with abundant seaweeds | 0-20 | 6-7月繁殖(日本) Breeding season June to July in Japan | 3-5 | 6.0 | - | 钩虾、桡足类等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as gammarid amphipods and copepods | |||||||
| 丹尼斯海马 Denise’s pygmy seahorse | 柳珊瑚(小尖柳珊瑚属、刺柳珊瑚属等种类) Gorgonian corals (e.g. Muricella spp. and Annella spp.) | 柳珊瑚(刺柳珊瑚属种类* Gorgonian corals (Annella spp.) | 5-100 | 全年繁殖(印度尼西亚) Breeding year-round in Indonesia | - | 1.1 | - | - | |||||||
| 日本豆丁海马 Japanese pygmy seahorse | 岩礁、软珊瑚、仙掌藻属种类及水螅 Rocky reefs, soft corals, Halimeda spp., and hydroids | 仙掌藻属种类* Halimeda spp. | 0-20* | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 刺海马 Thorny seahorse | 岩礁、海草床、软珊瑚、海绵 Rocky reefs, seagrass beds, soft corals and sponges | 岩礁、海藻场 Rocky reefs and seaweed beds | 5-80 | - | - | 7.9 | - | 猛水蚤、哲水蚤、糠虾等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as harpacticoid and cyclopoid copepods, and mysids | |||||||
| 克氏海马Kellog’s seahorse | 柳珊瑚、海鞭 Gorgonian corals and sea whips | 砂泥海床、具海藻的岩礁、海藻场 Muddy or sandy bottoms, weedy rocky reefs and seaweed beds | 20-150 | - | - | 15.0 | - | 猛水蚤、哲水蚤、钩虾等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as harpacticoid and cyclopoid copepods, and gammarid amphipods | |||||||
| 库达海马 Spotted seahorse | 砂泥海床、岩礁、海草床、红树林及河口区 Muddy or sandy bottoms, rocky reefs, seagrass beds, mangrove meadows and estuaries | 砂泥海床、具海 藻的岩礁、海藻场、海草床、珊瑚礁及河口区 Muddy or sandy bottoms, weedy rocky reefs, seagrass beds, seaweed beds, coral reefs and estuaries | 0-70 | 全年繁殖(越南) Breeding year-round in Vietnam | - | 14.0 | 200-1,200 | 小型浮游动物 Small zooplankton | |||||||
| 莫氏海马 Japanese seahorse | 海草床(大叶藻、卵叶喜盐草、泰来草、海菖蒲等)、红树林 Seagrass beds (Zostera spp., Halophila ovalis, Thalassia hemprichii, Enhalus acoroides) and mangroves | 砂泥海床、海藻场、海草床及河口区Muddy and sandy bottoms, seaweed beds, seagrass beds and estuaries | 0-40** | 7-9月(中国)** July to September in China | - | 5.5 | 10-400 | 枝角类、短尾类等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as Penilia avirostris and species of Brachyura | |||||||
| 彭氏海马 Pontoh’s pygmy seahorse | 仙掌藻属种类、 软珊瑚、柏状羽螅 Halimeda spp., soft corals and the Aglaophenia cupressina | 仙掌藻属种类、 柏状羽螅 Halimeda spp. and Aglaophenia cupressina | 10-25 | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 花海马 Shiho’s seahorse | 海藻场、海草床、珊瑚 Seaweed beds, seagrass beds and corals | 具海藻场的岩礁 Weedy rocky reefs | 0-20 | - | - | 4.0 | - | - | |||||||
| 棘海马 Hedgehog seahorse | 软珊瑚、海藻场、 海草床、珊瑚礁 Soft corals, seaweed beds, seagrass beds and coral reefs | 砂泥海床、海藻场、海草床、具海藻的岩礁 Muddy or sandy bottoms, seaweed beds, seagrass beds and weedy rocky reefs | 5-70 | 全年繁殖, 高峰5-10月(越南) Breeding year-round and peaking May to October in Vietnam | - | 10.4 | - | - | |||||||
| 三斑海马 Longnose seahorse | 砾石及砂泥海床、海藻场、软珊瑚 Muddy, sandy or gravel bottoms, seaweed beds and soft corals | 砂泥海床、海藻场、岩礁、红树林及河口区 Muddy or sandy bottoms, seaweed beds, rocky reefs, mangroves and estuaries | 10-100 | 全年繁殖, 高峰3-5月和10月(越南) Breeding year-round and peaking March to May and October in Vietnam | 3 | 14.0 | 300-1,200 | 端足类、磷虾等小型浮游甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as amphipoda and euphausiid | |||||||
表2 中国海域16种海马的生态信息
Table 2 Ecological information of the sixteen seahorse species recorded in China’s waters
| 中文名/英文名 Common name in Chinese and English | 全球栖息地记录 Global habitat recordsa | 中国栖息地记录 Habitat records in Chinab | 水深 Water depth (m)a | 繁殖季节 Breeding seasonc | 寿命 Lifespan (year)d | 初次性成熟体高 Height at first maturity (cm)d | 每胎产幼体数 Number of juvenile per pouchb | 主要食性喜好 Main dietsa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巴博海马 Barbour’s seahorse | 海草床、珊瑚礁 Seagrass beds and coral reefs | - | 0-10 | - | - | 8.0 | - | 哲水蚤桡足类、甲壳类幼虫等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as calanoid copepods and decapod larvae | |||||||
| 巴氏海马 Pygmy seahorse | 柳珊瑚(小尖柳珊瑚属种类) Gorgonian corals (Muricella spp.) | 柳珊瑚(小尖柳珊瑚属种类) Gorgonian corals (Muricella spp.) | 15-40 | 全年繁殖 Breeding year-round | - | 1.3 | - | 钩虾、猛水蚤等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as gammarid amphipods and harpacticoid copepods | |||||||
| 北部湾海马 Beibu Bay seahorse | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 克里蒙氏海马 Coleman’s pygmy seahorse | 粗砂质底及海草床(鳗草、喜盐草) Coarse sand and seagrass beds (Zostera spp. and Halophilia spp.) | 粗砂粒及藻类丰富浅海区 Shallow waters with coarse sand and seaweeds rich | 0-5 | - | - | - | - | 钩虾、猛水蚤、糠虾等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as gammarid amphipods, harpacticoid copepods and mysids | |||||||
| 虎尾海马 Tiger tail seahorse | 珊瑚礁、海绵、海藻场、海草床 Coral reefs, sponges, seaweed beds and seagrass beds | 0-20 | 全年繁殖(菲律宾) Breeding year-round in central Philippines | - | 8.1 | - | - | ||||||||
| 冠海马 Crowned seahorse | 海藻场(马尾藻)、海草床(鳗草) Seaweed beds (Sargassum spp.) and seagrass beds (Zostera spp.) | 近海多海藻区 Nearshore waters with abundant seaweeds | 0-20 | 6-7月繁殖(日本) Breeding season June to July in Japan | 3-5 | 6.0 | - | 钩虾、桡足类等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as gammarid amphipods and copepods | |||||||
| 丹尼斯海马 Denise’s pygmy seahorse | 柳珊瑚(小尖柳珊瑚属、刺柳珊瑚属等种类) Gorgonian corals (e.g. Muricella spp. and Annella spp.) | 柳珊瑚(刺柳珊瑚属种类* Gorgonian corals (Annella spp.) | 5-100 | 全年繁殖(印度尼西亚) Breeding year-round in Indonesia | - | 1.1 | - | - | |||||||
| 日本豆丁海马 Japanese pygmy seahorse | 岩礁、软珊瑚、仙掌藻属种类及水螅 Rocky reefs, soft corals, Halimeda spp., and hydroids | 仙掌藻属种类* Halimeda spp. | 0-20* | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 刺海马 Thorny seahorse | 岩礁、海草床、软珊瑚、海绵 Rocky reefs, seagrass beds, soft corals and sponges | 岩礁、海藻场 Rocky reefs and seaweed beds | 5-80 | - | - | 7.9 | - | 猛水蚤、哲水蚤、糠虾等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as harpacticoid and cyclopoid copepods, and mysids | |||||||
| 克氏海马Kellog’s seahorse | 柳珊瑚、海鞭 Gorgonian corals and sea whips | 砂泥海床、具海藻的岩礁、海藻场 Muddy or sandy bottoms, weedy rocky reefs and seaweed beds | 20-150 | - | - | 15.0 | - | 猛水蚤、哲水蚤、钩虾等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as harpacticoid and cyclopoid copepods, and gammarid amphipods | |||||||
| 库达海马 Spotted seahorse | 砂泥海床、岩礁、海草床、红树林及河口区 Muddy or sandy bottoms, rocky reefs, seagrass beds, mangrove meadows and estuaries | 砂泥海床、具海 藻的岩礁、海藻场、海草床、珊瑚礁及河口区 Muddy or sandy bottoms, weedy rocky reefs, seagrass beds, seaweed beds, coral reefs and estuaries | 0-70 | 全年繁殖(越南) Breeding year-round in Vietnam | - | 14.0 | 200-1,200 | 小型浮游动物 Small zooplankton | |||||||
| 莫氏海马 Japanese seahorse | 海草床(大叶藻、卵叶喜盐草、泰来草、海菖蒲等)、红树林 Seagrass beds (Zostera spp., Halophila ovalis, Thalassia hemprichii, Enhalus acoroides) and mangroves | 砂泥海床、海藻场、海草床及河口区Muddy and sandy bottoms, seaweed beds, seagrass beds and estuaries | 0-40** | 7-9月(中国)** July to September in China | - | 5.5 | 10-400 | 枝角类、短尾类等小型甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as Penilia avirostris and species of Brachyura | |||||||
| 彭氏海马 Pontoh’s pygmy seahorse | 仙掌藻属种类、 软珊瑚、柏状羽螅 Halimeda spp., soft corals and the Aglaophenia cupressina | 仙掌藻属种类、 柏状羽螅 Halimeda spp. and Aglaophenia cupressina | 10-25 | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 花海马 Shiho’s seahorse | 海藻场、海草床、珊瑚 Seaweed beds, seagrass beds and corals | 具海藻场的岩礁 Weedy rocky reefs | 0-20 | - | - | 4.0 | - | - | |||||||
| 棘海马 Hedgehog seahorse | 软珊瑚、海藻场、 海草床、珊瑚礁 Soft corals, seaweed beds, seagrass beds and coral reefs | 砂泥海床、海藻场、海草床、具海藻的岩礁 Muddy or sandy bottoms, seaweed beds, seagrass beds and weedy rocky reefs | 5-70 | 全年繁殖, 高峰5-10月(越南) Breeding year-round and peaking May to October in Vietnam | - | 10.4 | - | - | |||||||
| 三斑海马 Longnose seahorse | 砾石及砂泥海床、海藻场、软珊瑚 Muddy, sandy or gravel bottoms, seaweed beds and soft corals | 砂泥海床、海藻场、岩礁、红树林及河口区 Muddy or sandy bottoms, seaweed beds, rocky reefs, mangroves and estuaries | 10-100 | 全年繁殖, 高峰3-5月和10月(越南) Breeding year-round and peaking March to May and October in Vietnam | 3 | 14.0 | 300-1,200 | 端足类、磷虾等小型浮游甲壳类 Small crustaceans, such as amphipoda and euphausiid | |||||||
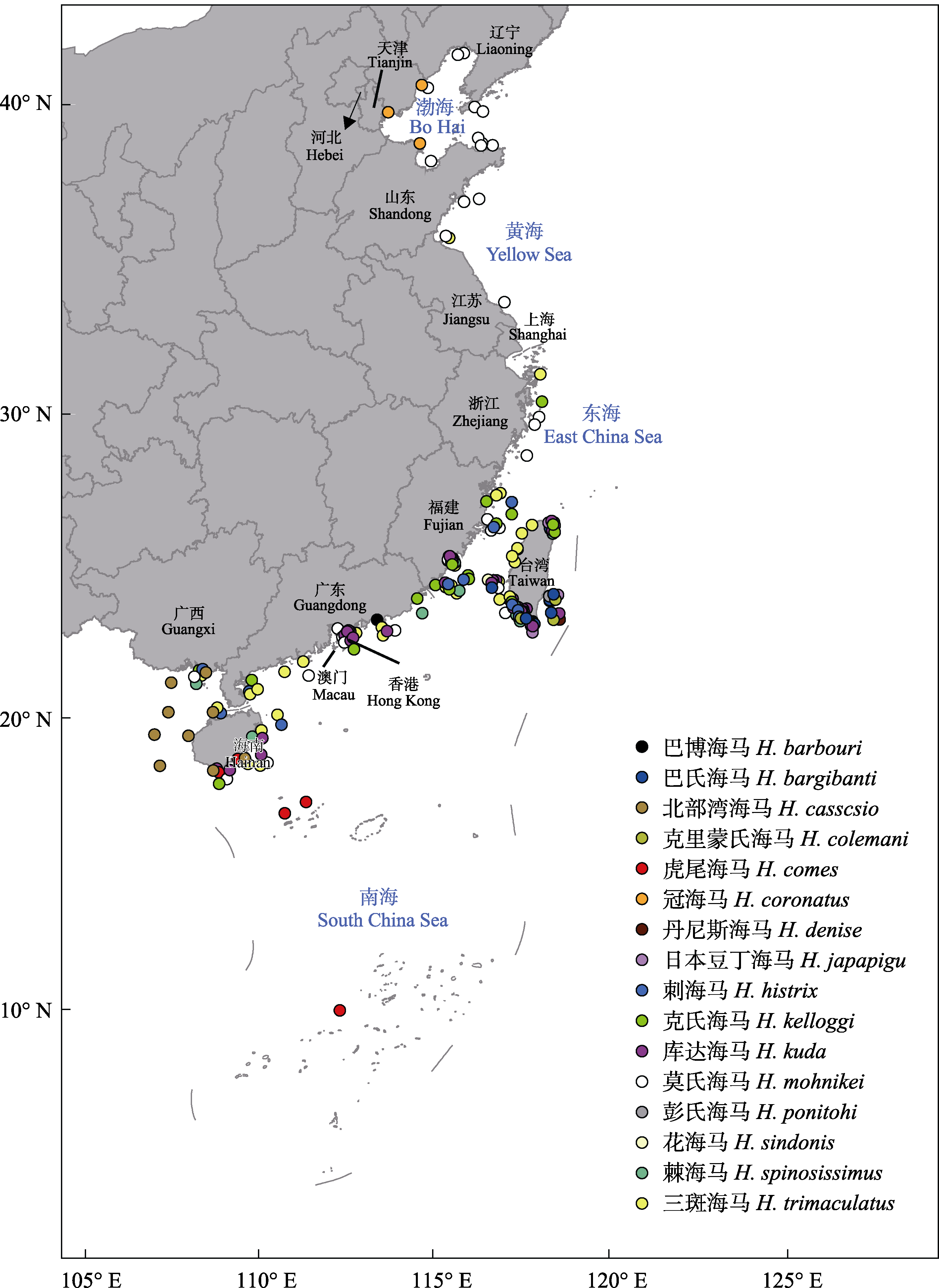
图1 中国海域有记录的海马采集点或观测点(重复点仅算1次)分布图
Fig. 1 The collection sites or the observation sites (only counted once among repeated sites) for Hippocampus species in China’s waters
| 物种中文名/英文名 Common species name in Chinese and English | IUCN红色名录等级及评估时间 IUCN Red List category (assessed year)a | 全球种群趋势 Global population trenda | 主要威胁 Main threatsa | 中国物种红 色名录 China Species Red Listb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巴博海马 Barbour’s seahorse | 易危 VU (2017) | 下降 Decreasing | 目标种捕捞、兼捕、栖息地(海草床)丧失 Targeted fishery, bycatch, and habitat (seagrass beds) loss | 未评估 NE |
| 巴氏海马 Pygmy seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2016) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(珊瑚礁)破坏和丧失 Habitat (coral reefs) destruction and loss | 未评估 NE |
| 北部湾海马 Beibu Bay seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2017) | 未知 Unknown | 未知 Unknown | 未评估 NE |
| 克里蒙氏海马 Coleman’s pygmy seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2016) | 未知 Unknown | 未知 Unknown | 未评估 NE |
| 虎尾海马 Tiger tail seahorse | 易危 VU (2013) | 下降 Decreasing | 目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏、兼捕 Targeted fishery, habitat destruction, and bycatch | 未评估 NE |
| 冠海马 Crowned seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2015) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(海草床)破坏 Habitat (seagrass beds) destruction | 濒危 EN |
| 丹尼斯海马 Denise’s pygmy seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2015) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(珊瑚礁)破坏 Habitat (coral reefs) destruction | 未评估 NE |
| 日本豆丁海马 Japanese pygmy seahorse | 未评估 NE | 未知 Unknown | 未知 Unknown | 未评估 NE |
| 刺海马 Thorny seahorse | 易危 VU (2017) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕、目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏 Bycatch, targeted fishery, and habitat destruction | 濒危 EN |
| 克氏海马 Kellog’s seahorse | 易危 VU (2017) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕、目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏 Bycatch, targeted fishery, and habitat destruction | 濒危 EN |
| 库达海马 Spotted seahorse | 易危 VU (2012) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕、目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏 Bycatch, targeted fishery, and habitat destruction | 濒危 EN |
| 莫氏海马 Japanese seahorse | 易危 VU (2016) | 下降 Decreasing | 目标种捕捞、兼捕、栖息地(海草床、红树林)丧失 Targeted fishery, bycatch, and habitat (seagrass and mangrove) loss | 易危 VU |
| 彭氏海马 Pontoh’s pygmy seahorse | 无危 LC (2016) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(珊瑚藻属的海藻场)丧失 Habitat (seaweed beds of Halimeda spp.) loss | 未评估 NE |
| 花海马 Shiho’s seahorse | 无危 LC (2016) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(珊瑚礁、海草床)破坏和丧失、目标种捕捞、兼捕 Habitat (coral reef and seagrass beds) destruction and loss, targeted fishery, and bycatch | 未评估 NE |
| 棘海马 Hedgehog seahorse | 易危 VU (2016) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕 Bycatch | 未评估 NE |
| 三斑海马 Longnose seahorse | 易危 VU (2012) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕、目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏 Bycatch, targeted fishery, and habitat destruction | 濒危 EN |
表3 中国海域16种海马的濒危等级及主要威胁
Table 3 Threatened categories of the sixteen seahorse species recorded in China’s waters and their main threats
| 物种中文名/英文名 Common species name in Chinese and English | IUCN红色名录等级及评估时间 IUCN Red List category (assessed year)a | 全球种群趋势 Global population trenda | 主要威胁 Main threatsa | 中国物种红 色名录 China Species Red Listb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巴博海马 Barbour’s seahorse | 易危 VU (2017) | 下降 Decreasing | 目标种捕捞、兼捕、栖息地(海草床)丧失 Targeted fishery, bycatch, and habitat (seagrass beds) loss | 未评估 NE |
| 巴氏海马 Pygmy seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2016) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(珊瑚礁)破坏和丧失 Habitat (coral reefs) destruction and loss | 未评估 NE |
| 北部湾海马 Beibu Bay seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2017) | 未知 Unknown | 未知 Unknown | 未评估 NE |
| 克里蒙氏海马 Coleman’s pygmy seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2016) | 未知 Unknown | 未知 Unknown | 未评估 NE |
| 虎尾海马 Tiger tail seahorse | 易危 VU (2013) | 下降 Decreasing | 目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏、兼捕 Targeted fishery, habitat destruction, and bycatch | 未评估 NE |
| 冠海马 Crowned seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2015) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(海草床)破坏 Habitat (seagrass beds) destruction | 濒危 EN |
| 丹尼斯海马 Denise’s pygmy seahorse | 数据不足 DD (2015) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(珊瑚礁)破坏 Habitat (coral reefs) destruction | 未评估 NE |
| 日本豆丁海马 Japanese pygmy seahorse | 未评估 NE | 未知 Unknown | 未知 Unknown | 未评估 NE |
| 刺海马 Thorny seahorse | 易危 VU (2017) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕、目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏 Bycatch, targeted fishery, and habitat destruction | 濒危 EN |
| 克氏海马 Kellog’s seahorse | 易危 VU (2017) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕、目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏 Bycatch, targeted fishery, and habitat destruction | 濒危 EN |
| 库达海马 Spotted seahorse | 易危 VU (2012) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕、目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏 Bycatch, targeted fishery, and habitat destruction | 濒危 EN |
| 莫氏海马 Japanese seahorse | 易危 VU (2016) | 下降 Decreasing | 目标种捕捞、兼捕、栖息地(海草床、红树林)丧失 Targeted fishery, bycatch, and habitat (seagrass and mangrove) loss | 易危 VU |
| 彭氏海马 Pontoh’s pygmy seahorse | 无危 LC (2016) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(珊瑚藻属的海藻场)丧失 Habitat (seaweed beds of Halimeda spp.) loss | 未评估 NE |
| 花海马 Shiho’s seahorse | 无危 LC (2016) | 未知 Unknown | 栖息地(珊瑚礁、海草床)破坏和丧失、目标种捕捞、兼捕 Habitat (coral reef and seagrass beds) destruction and loss, targeted fishery, and bycatch | 未评估 NE |
| 棘海马 Hedgehog seahorse | 易危 VU (2016) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕 Bycatch | 未评估 NE |
| 三斑海马 Longnose seahorse | 易危 VU (2012) | 下降 Decreasing | 兼捕、目标种捕捞、栖息地破坏 Bycatch, targeted fishery, and habitat destruction | 濒危 EN |
| [1] |
Alfaro-Shigueto J, Alfaro-Cordova E, Mangel JC (2022) Review of threats to the Pacific seahorse Hippocampus ingens (Girard 1858) in Peru. Journal of Fish Biology, 100, 1327-1334.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Aylesworth L, Phoonsawat R, Vincent ACJ (2018) Effects of indiscriminate fisheries on a group of small data-poor species in Thailand. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 75, 642-652.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Bruno JF, Selig ER (2007) Regional decline of coral cover in the Indo-Pacific: Timing, extent, and subregional comparisons. PLoS ONE, 2, e711. |
| [4] | Cai YH, Zhang HB, Xiang YT (2005) Discussion on the construction and management of marine special protected areas. Ocean Development and Management, 22(3), 55-57. (in Chinese) |
| [蔡燕红, 张海波, 项有堂 (2005) 海洋特别保护区的建设与管理问题探讨. 海洋开发与管理, 22(3), 55-57.] | |
| [5] |
Chang CH, Jang-Liaw NH, Lin YS, Fang YC, Shao KT (2013) Authenticating the use of dried seahorses in the traditional Chinese medicine market in Taiwan using molecular forensics. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 21, 310-316.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Chen CQ (1983) Ben Cao Shi Yi (Collated by Shang ZJ). Wannan Medical College, Wuhu, Anhui. (in Chinese) |
| [陈藏器 (1983) 本草拾遗(尚志钧辑校). 皖南医学院, 安徽芜湖.] | |
| [7] | Chen DG, Zhang MZ (2016) Marine Fishes of China. China Ocean University Press, Qingdao, Shandong. (in Chinese) |
| [陈大刚, 张美昭 (2016) 中国海洋鱼类. 中国海洋大学出版社, 山东青岛.] | |
| [8] |
Chen L, Wang XY, Huang BK (2015) The genus Hippocampus—A review on traditional medicinal uses, chemical constituents and pharmacological properties. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 162, 104-111.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Chen XZ, Zeng YY (2020) Analysis of species and identification techniques of seahorses. China Port Science and Technology, (12), 48-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈信忠, 曾韵颖 (2020) 海马种类及其鉴定技术分析. 中国口岸科学技术, (12), 48-54.] | |
| [10] | Cheng QT (1997) Fishes of Shandong Province:Gasterosteiformes. Shandong Science and Technology Press, Jinan. (in Chinese) |
| [成庆泰 (1997) 山东鱼类志: 刺鱼目. 山东科学技术出版社, 济南.] | |
| [11] | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2020) Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. China Medical Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [国家药典委员会 (2020) 中华人民共和国药典. 中国医药科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [12] | CITES Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (2005) Trade in Seahorses. https://cites.org/sites/default/files/eng/notif/2005/014.pdf. (accessed on 2022-11-22) |
| [13] | Cohen FPA, Valenti WC, Planas M, Calado R (2017) Seahorse aquaculture, biology and conservation: Knowledge gaps and research opportunities. Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture, 25, 100-111. |
| [14] | Correia MJT (2014) Trends in Seahorse Abundance in the Ria Formosa, South Portugal: Recent Scenario and Future Prospects. PhD dissertation, Universidade do Algarve, Algarve, |
| [15] | Dong SX, Li WD, Wang PZ, Jiang FY, Wu YT (2017) Species identification of Hippocampus and analysis of population genetic diversity. Technology and Market, 24(12), 126-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董世雄, 李卫东, 王沛政, 姜芳燕, 武耀廷 (2017) 海马种类鉴定及群体遗传多样性分析. 技术与市场, 24(12), 126-128.] | |
| [16] | Evanson M, Foster SJ, Wiswedel S, Vincent ACJ (2011) Tracking the international trade of seahorses (Hippocampus species). The Frisheries Centre, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada. |
| [17] | Fan ZY (2005) National Report—China. In:The Proceedings of the International Workshop on CITES Implementation for Seahorse Conservation and Trade. https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/456/noaa_456_DS1.pdf. (accessed on 2022-11-22) |
| [18] |
Foster SJ, Kuo TC, Wan A, Vincent ACJ (2019) Global seahorse trade defies export bans under CITES action and national legislation. Marine Policy, 103, 33-41.
DOI |
| [19] |
Foster SJ, Wiswedel S, Vincent ACJ (2016) Opportunities and challenges for analysis of wildlife trade using CITES data—Seahorses as a case study. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 26, 154-172.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Foster SJ (2016) Seahorses (Hippocampus spp.) and the CITES Review of Significant Trade. Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada. |
| [21] |
Foster SJ, Justason T, Magera AM, Vincent ACJ (2022) CITES makes a measurable difference to the trade in live marine fishes: The pioneering case of seahorses. Biological Conservation, 272, 109653.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Foster SJ, Kuo TC, Wan AKY, Vincent ACJ (2018) Global seahorse trade defies export bans under CITES action and national legislation. Marine Policy, 103, 33-41.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Foster SJ, Vincent ACJ (2004) Life history and ecology of seahorses: Implications for conservation and management. Journal of Fish Biology, 65, 1-61. |
| [24] | Foster SJ, Vincent ACJ (2021) Holding governments accountable for their commitments: CITES review of significant trade for a very high-volume taxon. Global Ecology and Conservation, 27, e01572. |
| [25] |
Han SY, Kim JK, Kai Y, Senou H (2017) Seahorses of the Hippocampus coronatus complex: Taxonomic revision, and description of Hippocampus haema, a new species from Korea and Japan (Teleostei, Syngnathidae). ZooKeys, 712, 113-139.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Harasti D, Martin-Smith K, Gladstone W (2014) Does a no-take marine protected area benefit seahorses? PLoS ONE, 9, e105462. |
| [27] |
Heard J, Chen JP, Wen CKC (2019) Citizen science yields first records of Hippocampus japapigu and Hippocampus denise (Syngnathidae) from Taiwan: A hotspot for pygmy seahorse diversity. ZooKeys, 883, 83-90.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Holt WV, Fazeli A, Otero-Ferrer F (2021) Sperm transport and male pregnancy in seahorses: An unusual model for reproductive science. Animal Reproduction Science, 246, 106854.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Jiang C, Shan F, Yuan Y, Liu FY, Zhan ZL, Jin Y, Zhao YY, Huang LQ (2017) Exploration and thoughts about zoological origin and macroscopical identification of Chinese material medica “Haima” in China Pharmacopoeia. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 42, 3836-3842. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI PMID |
| [蒋超, 单锋, 袁媛, 刘富艳, 詹志来, 金艳, 赵玉洋, 黄璐琦 (2017) 《中国药典》收载中药海马的基原与性状探讨. 中国中药杂志, 42, 3836-3842.] | |
| [30] | Jin XB (1984) The Fishes of Fujian Province (Part I):Gasterosteiformes. Fujian Science and Technology Press, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [金鑫波 (1984) 福建鱼类志(上卷), 刺鱼目. 福建科学技术出版社, 福州.] | |
| [31] |
Koldewey HJ, Martin-Smith KM (2010) A global review of seahorse aquaculture. Aquaculture, 302, 131-152.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Koning S, Hoeksema BW (2021) Diversity of seahorse species (Hippocampus spp.) in the international aquarium trade. Diversity, 13, 187.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Kuiter RH (2001) Revision of the Australian seahorses of the genus Hippocampus (Syngnathiformes: Syngnathidae) with descriptions of nine new species. Records of the Australian Museum, 53, 293-340.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Lawson JM, Foster SJ, Lim ACO, Chong VC, Vincent ACJ (2015) Novel life-history data for threatened seahorses provide insight into fishery effects. Journal of Fish Biology, 86, 1-15.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Lee SC (1993) Fishes of Taiwan: Syngnathiformes. Department of Zoology, Taiwan University, Taipei. (in Chinese) |
| [李信徹 (1993) 台湾鱼类志: 海龙目. 台湾大学动物学系, 台北.] | |
| [36] | Li SZ (1965) Compendium of Materia Medica. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李时珍 (1965) 本草纲目. 人民卫生出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] | Lin Q (2012) Conservation and aquaculture status of seahorse resources in China. In:The 10th National Congress and Symposium of the Chinese Society of Oceanology and Limnology. The Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academic of Sciences, Qingdao, Shandong. (in Chinese) |
| [林强 (2012) 中国近海海马资源保护及养殖现状. 中国海洋湖沼学会第十次全国会员代表大会暨学术研讨会论文集. 中国科学院海洋研究所, 山东青岛.] | |
| [38] |
Lin Q, Lu JY, Gao YL, Shen L, Cai J, Luo JN (2006) The effect of temperature on gonad, embryonic development and survival rate of juvenile seahorses, Hippocampus kuda Bleeker. Aquaculture, 254, 701-713.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Lin TT, Liu X, Zhang D (2021) Does the female seahorse still prefer her mating partner after a period of separation? Journal of Fish Biology, 99, 1613-1621.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Liu YL, Qu M, Jiang H, Schneider R, Qin G, Luo W, Yu HY, Zhang B, Wang X, Zhang YH, Zhang HX, Zhang ZX, Wu YL, Zhang YY, Yin JP, Zhang S, Venkatesh B, Roth O, Meyer A, Lin Q (2022) Immunogenetic losses co-occurred with seahorse male pregnancy and mutation in tlx1 accompanied functional asplenia. Nature Communications, 13, 7610.
DOI |
| [41] | Lourie SA (2006) Spatial Genetic Patterns in the Hippocampus barbouri Species Group (Teleostei:Syngnathidae) across the Coral Triangle. Proceedings 10th International Coral Reef Symposium, Okinawa, Japan. |
| [42] | Lourie SA, Foster SJ, Cooper EW, Vincent ACJ (2004) A Guide to the Identification of Seahorses. https://project seahorse.org/resource/a-guide-to-the-identification-of-seahorses/. (accessed on 2022-11-22) |
| [43] |
Lourie SA, Pollom RA, Foster SJ (2016) A global revision of the Seahorses Hippocampus Rafinesque 1810 (Actinopterygii: Syngnathiformes): Taxonomy and biogeography with recommendations for further research. Zootaxa, 4146, 1-66.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Martín J, Puig P, Palanques A, Giamportone A (2014) Commercial bottom trawling as a driver of sediment dynamics and deep seascape evolution in the Anthropocene. Anthropocene, 7, 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Meeuwig JJ, Hoang DH, Ky TS, Job SD, Vincent ACJ (2006) Quantifying non-target seahorse fisheries in central Vietnam. Fisheries Research, 81, 149-157.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Morgan S, Bull C (2005) Potential Techniques for Marking and Tagging Seahorses. Project Seahorse Technical Report No. 7, Version 1.0. Project Seahorse, Fisheries Centre, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada. |
| [47] | Nelson JS, Grande TC, Wilson MV (2016) Fishes of the World, 5th edn. John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, USA. |
| [48] |
Novelli B, Socorro JA, Caballero MJ, Otero-Ferrer F, Segade-Botella A, Molina Domínguez L (2015) Development of seahorse (Hippocampus reidi, Ginsburg 1933): Histological and histochemical study. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 41, 1233-1251.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Perry AL, Lunn KE, Vincent ACJ (2010) Fisheries, large-scale trade, and conservation of seahorses in Malaysia and Thailand. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 20, 464-475.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Qin G, Johnson C, Zhang Y, Zhang HX, Yin JP, Miller G, Turingan RG, Guisbert E, Lin Q (2018) Temperature- induced physiological stress and reproductive characteristics of the migratory seahorse Hippocampus erectus during a thermal stress simulation. Biology Open, 7, bio032888. |
| [51] |
Qin G, Zhang YH, Ho ALFC, Zhang Y, Lin Q (2017) Seasonal distribution and reproductive strategy of seahorses. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 74, 2170-2179.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Reijnen BT, van der Meij SET, van Ofwegen LP (2011) Fish, fans and hydroids: Host species of pygmy seahorses. ZooKeys, 103, 1-26.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Segaran TC, Aouissi HA, Noor MIM, Wahid MEA, Lananan F, Petrisor AI, Azra MN (2023) Assessing the state of seahorse research through scientometric analysis: An update. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 33, 1237-1262.
DOI |
| [54] |
Shokri MR, Gladstone W, Jelbart J (2009) The effectiveness of seahorses and pipefish (Pisces: Syngnathidae) as a flagship group to evaluate the conservation value of estuarine seagrass beds. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 19, 588-595.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Short G, Claassens L, Smith R, De Brauwer M, Hamilton H, Stat M, Harasti D (2020) Hippocampus nalu, a new species of pygmy seahorse from South Africa, and the first record of a pygmy seahorse from the Indian Ocean (Teleostei, Syngnathidae). ZooKeys, 934, 141-156.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Short G, Smith R, Motomura H, Harasti D, Hamilton H (2018) Hippocampus japapigu, a new species of pygmy seahorse from Japan, with a redescription of H. pontohi (Teleostei, Syngnathidae). ZooKeys, 779, 27-49.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Stocks AP, Foster SJ, Bat NK, Ha NM, Vincent ACJ (2019) Local fishers’ knowledge of target and incidental seahorse catch in southern Vietnam. Human Ecology, 47, 397-408.
DOI |
| [58] |
Vaidyanathan T, Zhang X, Balakrishnan R, Vincent ACJ (2021) Catch and trade bans for seahorses can be negated by non-selective fisheries. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 31, 43-59.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Verissimo D, MacMillan DC, Smith RJ (2011) Toward a systematic approach for identifying conservation flagships. Conservation Letters, 4, 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Vincent ACJ (1990) Reproductive Ecology of Seahorses. PhD dissertation, University of Cambridge, Cambridge. |
| [61] |
Vincent ACJ, Evans KL, Marsden AD (2005) Home range behaviour of the monogamous Australian seahorse, Hippocampus whitei. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 72, 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Vincent ACJ, Foster SJ, Koldewey HJ (2011) Conservation and management of seahorses and other Syngnathidae. Journal of Fish Biology, 78, 1681-1724.
DOI PMID |
| [63] | Vincent ACJ, Koldewey HJ (2006) An Uncertain Future for Seahorse Aquaculture in Conservation and Economic Contexts. Aquaculture Department, Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center, Tigbauan, Iloilo. |
| [64] |
Walpole MJ, Leader-Williams N (2002) Tourism and flagship species in conservation. Biodiversity and Conservation, 11, 543-547.
DOI URL |
| [65] | Wan Z (1911) Nan Zhou Yi Wu Zhi (Collated by Chen YR). Yuelu Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [万震 (1911) 南州异物志(陈运溶辑校). 岳麓书社, 长沙.] | |
| [66] | Wang S, Xie Y (2009) China Species Red List (Vol. II):Vertebrates (Part 1). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [汪松, 解焱 (2009) 中国物种红色名录(第二卷): 脊椎动物(上册). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [67] | Wen LL, Li JD, Wan DG, Ren Y, Guo JL (2013) Market survey and identification of Hippocampus (Haima). China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 38, 969-972. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [温珑莲, 李军德, 万德光, 任艳, 国锦琳 (2013) 海马市场调查与基原动物鉴定研究. 中国中药杂志, 38, 969-972.] | |
| [68] | Wiswedel S. (2015) Hippocampus trimaculatus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T10087A17252219.en. (accessed on 2022-11-22) |
| [69] |
Woods CMC, Martin-Smith KM (2004) Visible implant fluorescent elastomer tagging of the big-bellied seahorse, Hippocampus abdominalis. Fisheries Research, 66, 363-371.
DOI URL |
| [70] | Wu HL, Shao KT, Lai CF, Zhuang DH, Lin PL (2017) Latin-Chinese Dictionary of Fish Names by Classification System. China Ocean University Press, Qingdao, Shandong. (in Chinese) |
| [伍汉霖, 邵广昭, 赖春福, 庄棣华, 林沛立 (2017) 拉汉世界鱼类系统名典. 中国海洋大学出版社, 山东青岛.] | |
| [71] |
Xie JS, Bu LF, Jin S, Wang XY, Zhao QS, Zhou SM, Xu YJ (2020) Outbreak of vibriosis caused by Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio alginolyticus in farmed seahorse Hippocampus kuda in China. Aquaculture, 523, 735168.
DOI URL |
| [72] | Xie PF, Gu YB, Sui WN, Tao GF, Sun SY (2019) Big data challenges for species distribution models in predicting potential distribution of marine species. Marine Information, 34, 51-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [解鹏飞, 顾炎斌, 隋伟娜, 陶冠峰, 孙淑艳 (2019) 物种分布模型在海洋物种潜在分布预测中面临的大数据挑战. 海洋信息, 34, 51-61.] | |
| [73] |
Xu YJ, Li J, Bo Y, Wang RP (2023) Comparison of feeding behaviour characteristics between wild-caught and captive-reared Hippocampus kuda Bleeker. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 259, 105850.
DOI URL |
| [74] | Xu YJ, Lu HX, Lu GM (2011) Study on the artificial eco-aquaculture of the three-spot seahorse, Hippocampus trimaculatus Leach. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 32(5), 38-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐永健, 陆慧贤, 卢光明 (2011) 三斑海马的人工生态养殖. 渔业科学进展, 32(5), 38-43.] | |
| [75] | Xu YM, Chen JW, Guo X (1994) Studies on the phospholipids and fatty acids in traditional Chinese medicinal materials Hippocampus and Syngnathus. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, (1), 14-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [许益民, 陈建伟, 郭戌 (1994) 海马和海龙中磷脂成分与脂肪酸的分析研究. 中国海洋药物, (1), 14-18.] | |
| [76] | Yan BL, Wu HL (2006) Fishes of Jiangsu Province:Gasterosteiformes. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [阎斌伦, 伍汉霖 (2006) 江苏鱼类志: 刺鱼目. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [77] |
Yasué M, Nellas A, Vincent ACJ (2012) Seahorses helped drive creation of marine protected areas, so what did these protected areas do for the seahorses? Environmental Conservation, 39, 183-193.
DOI URL |
| [78] | Yiu SKF, Chow CF, Tsang SHT, Zhang X, Chung JTH, Sin SYT, Chow WK, Chan LL (2022) New record of the Japanese seahorse Hippocampus mohnikei Bleeker, 1853 (Syngnathiformes: Syngnathidae) in Hong Kong waters. Check List, 8, 455-461. |
| [79] |
Zeng L, Armani A, Wen J, Lin HJ, Xu YH, Fan SG, Sun YL, Yang CG, Chen ZM, Chen DH, Zhao J, Li XY (2019) Molecular identification of seahorse and pipefish species sold as dried seafood in China: A market-based survey to highlight the actual needs for a proper trade. Food Control, 103, 175-181.
DOI URL |
| [80] | Zhang CL (1963) Fishes in East China Sea:Syngnathiformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春霖 (1963) 东海鱼类志: 海龙目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [81] | Zhang CL, Cheng QT, Zheng BS, Li SZ, Zheng WL, Wang WY (1955) Report of Fish Survey in Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea:Syngnathiformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春霖, 成庆泰, 郑葆珊, 李思忠, 郑文莲, 王文滨 (1955) 黄渤海鱼类调查报告: 海龙目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [82] | Zhang CL, Zhang YW (1962) Fishes in South China Sea:Syngnathiformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春霖, 张有为 (1962) 南海鱼类志: 海龙目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [83] | Zhang F (1997) A study on the histology of digestive system of larval seahorse. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 4, 92-94. (in Chinese) |
| [张峰 (1997) 日本海马仔鱼消化系统的组织学研究. 中国水产科学, 4, 92-94.] | |
| [84] | Zhang F, Wang GE (1991) The observation of hitology of the pituitary gland of seahorse(Hippocampus japonicus). Journal of Dalian Fisheries College, 3, 28-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张峰, 王国恩 (1991) 日本海马(Hippocampus japonicus)脑垂体的组织学观察. 大连水产学院学报, 3, 28-34.] | |
| [85] |
Zhang X, Vincent ACJ (2017) Integrating multiple datasets with species distribution models to inform conservation of the poorly-recorded Chinese seahorses. Biological Conservation, 211, 161-171.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Zhang X, Vincent ACJ (2018) Predicting distributions, habitat preferences and associated conservation implications for a genus of rare fishes, seahorses (Hippocampus spp.). Diversity and Distributions, 24, 1005-1017.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
Zhang X, Vincent ACJ (2019a) Using cumulative human-impact models to reveal global threat patterns for seahorses. Conservation Biology, 33, 1380-1391.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Zhang X, Vincent ACJ (2019b) Conservation prioritization for seahorses (Hippocampus spp.) at broad spatial scales considering socioeconomic costs. Biological Conservation, 235, 79-88.
DOI URL |
| [89] | Zhang YH, Pham NK, Zhang HX, Lin JD, Lin Q (2014) Genetic variations in two seahorse species (Hippocampus mohnikei and Hippocampus trimaculatus): Evidence for Middle Pleistocene population expansion. PLoS ONE, 9, e105494. |
| [90] | Zhang YH, Qin G, Wang X, Lin Q (2016) A new species of seahorse (Teleostei: Syngnathidae) from the South China Sea. Zootaxa, 4170, 384-392. |
| [91] |
Zhang YH, Qin G, Zhang HX, Wang X, Lin Q (2017) DNA barcoding reflects the diversity and variety of brooding traits of fish species in the family Syngnathidae along China’s coast. Fisheries Research, 185, 137-144.
DOI URL |
| [92] | Zhang ZH, Xu GJ, Xu LS, Wang Q (1994) Inhibitory effects of Hippocampus spp. extracts on L-glutamic acid induced Ca2+ influx in rats’ neurons. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 13(4), 6-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张朝晖, 徐国钧, 徐珞珊, 王强 (1994) 五种海马提取物对L-谷氨酸致大鼠神经元钙内流的拮抗作用. 中国海洋药物, 13(4), 6-9.] | |
| [93] | Zhang ZH, Xu GJ, Xu LS, Wang Q (1995) Research progress of domestic medicinal fishes of Syngnathidae. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 14(4), 26-29. (in Chinese) |
| [张朝晖, 徐国钧, 徐珞珊, 王强 (1995) 国产海龙科药用鱼类研究进展. 中国海洋药物, 14(4), 26-29.] | |
| [94] | Zheng BS, Zhang YW (1957) Seahorse. Bulletin of Biology, (7), 30-34. (in Chinese) |
| [郑葆珊, 张有为 (1957) 海马. 生物学通报, (7), 30-34.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 康燕 干靓 俞霖琳 何晨静 张理卿 吴婧彬. 基于自然解决方案的城市小微栖息地营造与网络构建模式:以上海市长宁区生境花园为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24528-. |
| [3] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [4] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [5] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [6] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [7] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [8] | 陈丁松, 刘子恺, 贺子洋, 陈伟东. 缓步动物多样性、分布特征和生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24406-. |
| [9] | 张颂琪, 陆义, 陈炳耀, 杨光, 王彦平, 陈传武. 全球鲸豚类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24442-. |
| [10] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [11] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [12] | 邓洪, 钟占友, 寇春妮, 朱书礼, 李跃飞, 夏雨果, 武智, 李捷, 陈蔚涛. 基于线粒体全基因组揭示斑鳠的种群遗传结构与演化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24241-. |
| [13] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [14] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [15] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()