



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (3): 303-309. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08339 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.08339
赵永强, 曾江宁, 高爱根, 陈全震*( ), 廖一波, 寿鹿
), 廖一波, 寿鹿
收稿日期:2008-12-22
接受日期:2009-03-30
出版日期:2009-05-20
发布日期:2009-05-20
通讯作者:
陈全震
作者简介:*E-mail: chenqz6509@126.com基金资助:
Yongqiang Zhao, Jiangning Zeng, Aigen Gao, Quanzhen Chen*( ), Yibo Liao, Lu Shou
), Yibo Liao, Lu Shou
Received:2008-12-22
Accepted:2009-03-30
Online:2009-05-20
Published:2009-05-20
Contact:
Quanzhen Chen
摘要:
为了解椒江口滩涂大型底栖动物群落格局与多样性, 揭示其对环境变化的响应规律, 作者于2007年10月、2008年1月、4月和7月在椒江口南岸和北岸潮间带, 沿河流到海洋方向共布设6条采样断面进行大型底栖动物调查。分析了大型底栖动物种类组成、栖息密度和生物量的时空变化特征, 在此基础上运用α,β和γ多样性测度方法对大型底栖动物多样性进行分析, 同时探讨了大型底栖动物群落结构对环境变化的响应方向及程度, 结果显示: (1) 6条断面共记录到大型底栖动物78种, 总种数随季节变化显著, 在空间上沿河流到海洋方向呈升高趋势; (2) 栖息密度的季节变化不显著(P=0.145>0.05), 但空间变化显著(P=0.017<0.05), 生物量的季节变化显著(P=0.012<0.05), 空间变化极显著(P=0.004<0.01); (3)β和γ多样性指数定量显示了椒江河口区域滩涂环境的多变性和大型底栖动物群落的多样性和更替性。
赵永强, 曾江宁, 高爱根, 陈全震, 廖一波, 寿鹿 (2009) 椒江口滩涂大型底栖动物群落格局与多样性. 生物多样性, 17, 303-309. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08339.
Yongqiang Zhao, Jiangning Zeng, Aigen Gao, Quanzhen Chen, Yibo Liao, Lu Shou (2009) Community pattern and diversity of macrozoobenthos in an intertidal flat, Jiaojiang Estuary. Biodiversity Science, 17, 303-309. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08339.
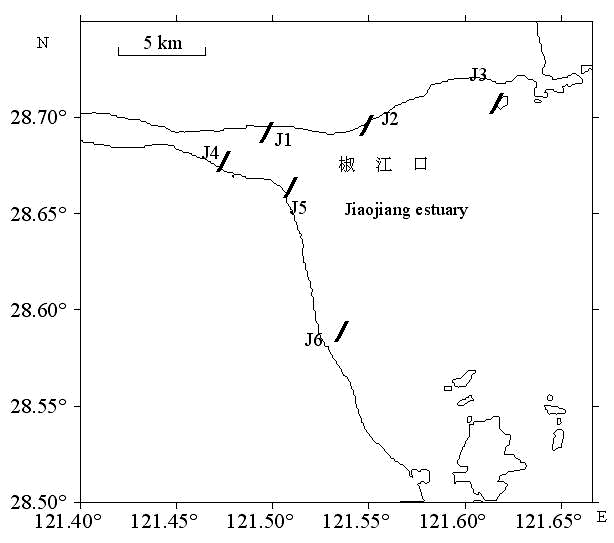
图1 研究区域与采样断面。J1-J6分别代表里西潭、杜下浦闸、涂岙、岩头、三甲九塘与三甲八塘6条采样断面。
Fig. 1 Study area and sampling transect. J1-J6 stand for the sampling transect Lixitan, Duxiapuzha, Tuao, Yantou, Sanjiajiutang and Sanjiabatang, respectively.
| 采样断面Sampling transect | 类群 Group | 物种数 Species number | 栖息密度 Density(ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季Winter | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季Winter | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | ||||
| J1 | 软体类 Mollusca | 4 | 5 | 9 | 4 | 798 | 181 | 68 | 6 | 15.25 | 16.13 | 9.37 | 0.84 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.90 | 0.00 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 110 | 17 | 27 | 0.06 | 1.85 | 0.39 | 0.38 | |||
| 其他 Others | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |||
| 总计 Total | 5 | 6 | 13 | 6 | 804 | 291 | 92 | 34 | 15.31 | 17.98 | 11.67 | 1.23 | |||
| J2 | 软体类 Mollusca | 2 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 210 | 4 | 22 | 3 | 7.76 | 1.79 | 4.81 | 0.55 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 4 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 27 | 7 | 0 | 1.49 | 3.38 | 3.22 | 0.25 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 9 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.12 | |||
| 其他 Others | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.00 | |||
| 总计 Total | 8 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 223 | 31 | 35 | 10 | 9.36 | 5.17 | 8.49 | 0.92 | |||
| J3 | 软体类 Mollusca | 3 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 48 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 2.77 | 0.15 | 0.91 | 0.20 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 3 | 5 | 12 | 4 | 60 | 401 | 8 | 185 | 3.54 | 4.71 | 1.31 | 2.18 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 8 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 131 | 3 | 5 | 12 | 3.29 | 0.01 | 1.62 | 0.44 | |||
| 其他 Others | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.23 | |||
| 总计 Total | 16 | 9 | 23 | 12 | 256 | 406 | 20 | 201 | 9.87 | 4.89 | 3.87 | 3.05 | |||
| J4 | 软体类 Mollusca | 3 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 2,632 | 2,733 | 940 | 4,014 | 32.81 | 317.00 | 532.89 | 14.84 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 42 | 7 | 0.53 | 1.42 | 1.38 | 0.14 | |||
| 其他 Others | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||
| 总计 Total | 6 | 8 | 13 | 4 | 2,647 | 2,781 | 982 | 4,022 | 33.36 | 319.90 | 534.27 | 14.99 | |||
| J5 | 软体类 Mollusca | 9 | 8 | 12 | 3 | 1,079 | 1,299 | 68 | 5 | 19.44 | 21.21 | 10.05 | 1.59 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 18 | 6 | 20 | 0.00 | 2.69 | 3.16 | 1.66 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 75 | 7 | 4 | 11 | 0.91 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.41 | |||
| 其他 Others | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.10 | |||
| 总计 Total | 12 | 15 | 20 | 9 | 1,156 | 1,327 | 80 | 41 | 20.37 | 24.29 | 13.53 | 3.75 | |||
| J6 | 软体类 Mollusca | 8 | 8 | 12 | 8 | 68 | 296 | 495 | 36 | 8.25 | 15.29 | 33.32 | 3.50 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 22 | 84 | 27 | 38 | 0.18 | 20.38 | 13.42 | 1.46 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 9 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 129 | 58 | 6 | 4 | 2.26 | 1.25 | 0.25 | 1.15 | |||
| 其他 Others | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 17 | 1 | 4 | 0.12 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.86 | |||
| 总计 Total | 21 | 18 | 22 | 16 | 229 | 455 | 529 | 82 | 10.80 | 37.29 | 47.04 | 6.97 | |||
| 平均值 Mean | 11 | 10 | 17 | 9 | 886 | 882 | 290 | 732 | 16.51 | 68.25 | 103.15 | 5.15 | |||
| 标准误 SE | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 385 | 420 | 159 | 659 | 3.78 | 50.58 | 86.45 | 2.16 | |||
表1 椒江口滩涂大型底栖动物种类、栖息密度和生物量时空变化特征
Table 1 Temporal and spatial distribution of species number, density and biomass of macrozoobenthos in an intertidal flat of Jiaojiang estuary
| 采样断面Sampling transect | 类群 Group | 物种数 Species number | 栖息密度 Density(ind./m2) | 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季Winter | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季Winter | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | ||||
| J1 | 软体类 Mollusca | 4 | 5 | 9 | 4 | 798 | 181 | 68 | 6 | 15.25 | 16.13 | 9.37 | 0.84 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.90 | 0.00 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 110 | 17 | 27 | 0.06 | 1.85 | 0.39 | 0.38 | |||
| 其他 Others | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |||
| 总计 Total | 5 | 6 | 13 | 6 | 804 | 291 | 92 | 34 | 15.31 | 17.98 | 11.67 | 1.23 | |||
| J2 | 软体类 Mollusca | 2 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 210 | 4 | 22 | 3 | 7.76 | 1.79 | 4.81 | 0.55 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 4 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 27 | 7 | 0 | 1.49 | 3.38 | 3.22 | 0.25 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 9 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.12 | |||
| 其他 Others | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.00 | |||
| 总计 Total | 8 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 223 | 31 | 35 | 10 | 9.36 | 5.17 | 8.49 | 0.92 | |||
| J3 | 软体类 Mollusca | 3 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 48 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 2.77 | 0.15 | 0.91 | 0.20 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 3 | 5 | 12 | 4 | 60 | 401 | 8 | 185 | 3.54 | 4.71 | 1.31 | 2.18 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 8 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 131 | 3 | 5 | 12 | 3.29 | 0.01 | 1.62 | 0.44 | |||
| 其他 Others | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 17 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.23 | |||
| 总计 Total | 16 | 9 | 23 | 12 | 256 | 406 | 20 | 201 | 9.87 | 4.89 | 3.87 | 3.05 | |||
| J4 | 软体类 Mollusca | 3 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 2,632 | 2,733 | 940 | 4,014 | 32.81 | 317.00 | 532.89 | 14.84 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 42 | 7 | 0.53 | 1.42 | 1.38 | 0.14 | |||
| 其他 Others | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||
| 总计 Total | 6 | 8 | 13 | 4 | 2,647 | 2,781 | 982 | 4,022 | 33.36 | 319.90 | 534.27 | 14.99 | |||
| J5 | 软体类 Mollusca | 9 | 8 | 12 | 3 | 1,079 | 1,299 | 68 | 5 | 19.44 | 21.21 | 10.05 | 1.59 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 18 | 6 | 20 | 0.00 | 2.69 | 3.16 | 1.66 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 75 | 7 | 4 | 11 | 0.91 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.41 | |||
| 其他 Others | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.10 | |||
| 总计 Total | 12 | 15 | 20 | 9 | 1,156 | 1,327 | 80 | 41 | 20.37 | 24.29 | 13.53 | 3.75 | |||
| J6 | 软体类 Mollusca | 8 | 8 | 12 | 8 | 68 | 296 | 495 | 36 | 8.25 | 15.29 | 33.32 | 3.50 | ||
| 甲壳类 Crustacean | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 22 | 84 | 27 | 38 | 0.18 | 20.38 | 13.42 | 1.46 | |||
| 多毛类 Polychaetes | 9 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 129 | 58 | 6 | 4 | 2.26 | 1.25 | 0.25 | 1.15 | |||
| 其他 Others | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 17 | 1 | 4 | 0.12 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 0.86 | |||
| 总计 Total | 21 | 18 | 22 | 16 | 229 | 455 | 529 | 82 | 10.80 | 37.29 | 47.04 | 6.97 | |||
| 平均值 Mean | 11 | 10 | 17 | 9 | 886 | 882 | 290 | 732 | 16.51 | 68.25 | 103.15 | 5.15 | |||
| 标准误 SE | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 385 | 420 | 159 | 659 | 3.78 | 50.58 | 86.45 | 2.16 | |||
| [1] | An CG (安传光), Zhao YL (赵云龙), Lin L (林凌), Lü GT (吕敢堂), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿) (2007) Primary investigation of seasonal characters of macrobenthic communities distribution in tidalflats of Jiuduansha wetland of Yangtze River estuary. Journal of Fisheries of China (水产学报), 31(Suppl.),52-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [2] | Cai LZ (蔡立哲), Li HM (厉红梅), Lin P (林鹏), Liu JJ (刘俊杰) (2001) Analysis of environmental effect and polychaete quantitative variations on intertidal mudflat in Shenzhen estuary. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science) (厦门大学学报(自然科学版)), 40,741-750. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Cai RX (蔡如星) (1991) Fauna of Zhejiang: Mollusks(浙江动物志: 软体动物). Zhejiang Science and Technology Publishing House, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | García-Arberas L, Rallo A (2002) The intertidal soft-bottom infaunal macrobenthos in three basque estuaries (Gulf of Biscay): a feeding guild approach. Hydrobiologia, 475/476,457-468. |
| [5] | Gaudêncio MJ, Cabral HN (2007) Trophic structure of macrobenthos in the Tagus estuary and adjacent coastal shelf. Hydrobiologia, 587,241-251. |
| [6] |
Gray JS (2000) The measurement of marine species diversity, with an application to the benthic fauna of the Norwegian continental shelf. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 250,23-49.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Lin KM (林开敏), Huang BL (黄宝龙) (2001) Studies on β-diversity index of undergrowth plant in Chinese fir plantation. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 9,157-161. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Lui TH, Lee SY, Sadovy Y (2002) Macrobenthos of a tidal impoundment at the Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve, Hong Kong. Hydrobiologia, 468,193-212. |
| [9] | Ma KP (马克平), Liu CR (刘灿然), Liu YM (刘玉明) (1995) Measurement of biotic community diversity. II. β diversity. Chinese Biodiversity (生物多样性), 3,38-43. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | McLusky DS (1987) Intertidal habitats and benthic macrofauna of the Forth estuary, Scotland. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 93,389-399. |
| [11] |
Ricotta C (2008) Computing additive β-diversity from presence and absence scores: A critique and alternative parameters. Theoretical Population Biology, 73,244-249.
URL PMID |
| [12] | Yang DJ (杨德渐), Sun RP (孙瑞平) (1988) Polychaetous Annelids of the Chinese Coast (中国近海多毛环节动物). China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | Sun RP (孙瑞平), Yang DJ (杨德渐) (2002) Fauna Sinica: Invertebrata (中国动物志: 无脊椎动物), 33. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [14] | Sun T (孙涛), Yang ZF (杨志峰) (2004) Studies on the evaluating index system for estuarine ecosystem restoration and its application. China Environmental Science (中国环境科学), 24,381-384. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Tang ZY (唐志尧), Fang JY (方精云), Zhang L (张玲) (2004) Patterns of woody plant species diversity along environmental gradients on Mt. Taibai, Qinling Mountains. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 12,115-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Tian HZ (田怀珍), Xing FW (邢福武) (2008) Elevational diversity patterns of orchids in Nanling National Nature Reserve, northern Guangdong Province. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 16,75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Wang YM (王益鸣), Zhang FY (张凤英), Xu ZP (许贞平), Sun Y (孙毅), Tang JL (唐静亮), Liu SX (刘世贤), Ren SJ (任世军) (2005) Assessment on the situation of ecological environment quality in Jiaojiang Estuary. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science) (浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版)), 24,221-226. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Wilson MV, Shmida A (1984) Measuring beta diversity with presence-absence data. Journal of Ecology, 72,1055-1064. |
| [19] | Whittaker RH (1972) Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon, 21,213-251. |
| [1] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | 孙智闲, 田晨, 王鑫, 方雨田, 李博, 赵亚辉. 热带沿海城市土著鱼类面临的威胁: 以海南省三亚市为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24165-. |
| [3] | 陈瑶琪, 郭晶晶, 蔡国俊, 葛依立, 廖宇, 董正, 符辉. 近七十年(1954-2021)长江中下游湖泊沉水植物群落多样性演变特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23319-. |
| [4] | 王巍伟, 米湘成, 王宁宁, 任海保, 唐治喜, 张主宁, 马克平, 陈磊. 2005-2020年浙江古田山24 ha亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地植物多样性数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24417-. |
| [5] | 陈晓澄, 张鹏展, 康斌, 刘林山, 赵亮. 基于中国科学院西北高原生物研究所馆藏标本分析青藏高原雀形目鸟类物种和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22638-. |
| [6] | 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 杨涛, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张秋雨, 张洪强, 张旭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性格局与环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [7] | 张菁, 白煜, 黄子强, 张正旺, 李东来. 盐地碱蓬盐沼与相邻泥质滩涂湿地迁徙期鸻鹬类的群落组成及行为差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 351-360. |
| [8] | 宋博,陈琳琳,闫朗,姜少玉,刘春云,李秉钧,李宝泉. 山东东营和烟台潮间带海草床食物网结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(9): 984-992. |
| [9] | 张田田, 王璇, 任海保, 余建平, 金毅, 钱海源, 宋小友, 马克平, 于明坚. 浙江古田山次生与老龄常绿阔叶林群落特征的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1069-1080. |
| [10] | 翁昌露,张田田,巫东豪,陈声文,金毅,任海保,于明坚,罗媛媛. 古田山10种主要森林群落类型的α和β多样性格局及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(1): 33-41. |
| [11] | 葛美玲, 徐勤增, 范士亮, 王宗兴, 张学雷. 中国近海多毛纲底栖类群目与科水平的分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 998-1003. |
| [12] | 宋云峰, 陈声文, 王薇, 余建平, 钱海源, 王云泉, 陈磊, 米湘成, 任海保, 叶铎, 陈建华, 马克平. 负密度制约和生境过滤对古田山幼苗功能多样性年际变化的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(9): 959-965. |
| [13] | 张敬怀, 高阳, 时小军, 吕向立. 大亚湾底拖网海洋生物种类组成及物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(9): 1019-1030. |
| [14] | 徐勇, 李新正, 王洪法, 张宝琳, 帅莲梅. 长江口邻近海域丰水季大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(7): 811-819. |
| [15] | 李晓静, 周政权, 陈琳琳, 李宝泉. 山东烟台大沽夹河河口及邻近海域大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 157-165. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn