



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 959-965. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017053 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017053
宋云峰1,3#, 陈声文2#, 王薇3, 余建平2, 钱海源2, 王云泉3, 陈磊3, 米湘成3,*( ), 任海保3, 叶铎1, 陈建华1,*(
), 任海保3, 叶铎1, 陈建华1,*( ), 马克平3
), 马克平3
收稿日期:2017-02-21
接受日期:2017-06-08
出版日期:2017-09-20
发布日期:2017-10-04
通讯作者:
米湘成,陈建华
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Yunfeng Song1,3#, Shengwen Chen2#, Wei Wang3, Jianping Yu2, Haiyuan Qian2, Yunquan Wang3, Lei Chen3, Xiangcheng Mi3,*( ), Haibao Ren3, Duo Ye1, Jianhua Chen1,*(
), Haibao Ren3, Duo Ye1, Jianhua Chen1,*( ), Keping Ma3
), Keping Ma3
Received:2017-02-21
Accepted:2017-06-08
Online:2017-09-20
Published:2017-10-04
Contact:
Mi Xiangcheng,Chen Jianhua
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
生物多样性的维持机制一直是群落生态学研究的核心内容。目前利用负密度制约和生境过滤分别解释群落多样性空间分布格局的研究较多, 但结合这两种机制来解释功能多样性格局年际变化的研究还很少。本文以古田山亚热带常绿阔叶林24 ha动态监测样地的木本植物幼苗为研究对象, 利用2006年和2007年的幼苗动态监测数据, 比较了幼苗功能α和β多样性随时间推移而变化的趋势。结果表明: 2006-2007年间, 随着时间的变化, 幼苗群落内与木质密度、比叶面积、叶片氮含量、叶片磷含量4种功能性状相关的功能α多样性显著增加, 与气孔密度相关的α多样性变化不显著; 幼苗群落间基于5种功能性状的β多样性均呈显著增加趋势。综合分析表明, 负密度制约能够促进古田山木本植物幼苗群落内的功能α多样性, 而生境过滤只能在一定程度上解释群落的功能β多样性。该结论还需要更长期的调查数据来验证。
宋云峰, 陈声文, 王薇, 余建平, 钱海源, 王云泉, 陈磊, 米湘成, 任海保, 叶铎, 陈建华, 马克平 (2017) 负密度制约和生境过滤对古田山幼苗功能多样性年际变化的影响. 生物多样性, 25, 959-965. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017053.
Yunfeng Song, Shengwen Chen, Wei Wang, Jianping Yu, Haiyuan Qian, Yunquan Wang, Lei Chen, Xiangcheng Mi, Haibao Ren, Duo Ye, Jianhua Chen, Keping Ma (2017) Effects of negative density dependence and habitat filtering on the functional diversity of seedlings in the subtropical forest of Gutianshan. Biodiversity Science, 25, 959-965. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017053.
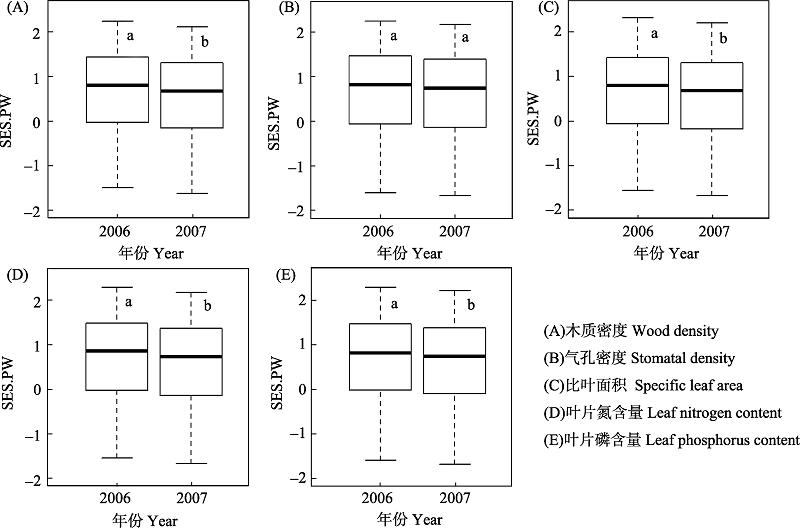
图1 2006年和2007年古田山24 ha森林动态监测样地幼苗的成对功能性状关系指数(SES.PW) (α多样性)的变化趋势。不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.01)。
Fig.1 Changes of pairwise trait dispersion (SES.PW) (α diversity) within seedling community in the 24 ha Gutianshan forest dynamics plot in 2006 and 2007. Different letters indicate significant difference (P < 0.01).
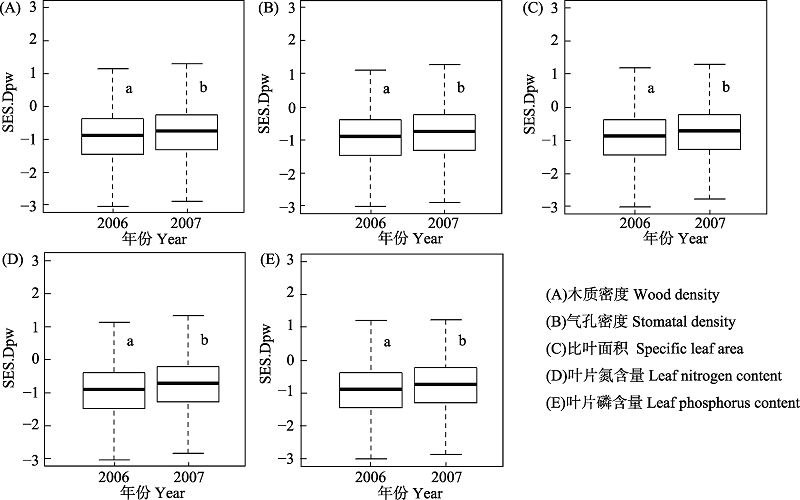
图2 古田山24 ha森林动态监测样地幼苗2006和2007年样方间成对功能性状关系指数(SES.Dpw) (β多样性)的变化趋势。不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.01)。
Fig. 2 Changes of mean pairwise distance (SES.Dpw) (β diversity) within seedling community in the 24 ha Gutianshan forest dynamics plot in 2006 and 2007. Different letters indicate significant difference (P < 0.01).
| [1] |
Beckage B, Clark JS (2003) Seedling survival and growth of three forest tree species: the role of spatial heterogeneity. Ecology, 84, 1849-1861.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Cao K, Rao MD, Yu JZ, Liu XJ, Mi XC, Chen JH (2013) The phylogenetic signal of functional traits and their effects on community structure in an evergreen broad-leaved forest. Biodiversity Science, 21, 564-571. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曹科, 饶米德, 余建中, 刘晓娟, 米湘成, 陈建华 (2013) 古田山木本植物功能性状的系统发育信号及其对群落结构的影响. 生物多样性, 21, 564-571.] | |
| [3] |
Cavender-Bares J, Ackerly DD, Baum DA, Bazzaz FA (2004) Phylogenetic overdispersion in Floridian oak communities. The American Naturalist, 163, 823-843.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
Chen L, Mi XC, Comita LS, Zhang L, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Community-level consequences of density dependence and habitat association in a subtropical broad-leaved forest. Ecology Letters, 13, 695-704.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin. |
| [6] |
Fortunel C, Valencia R, Wright SJ, Garwood NC, Kraft NJB (2016) Functional trait differences influence neighbourhood interactions in a hyperdiverse Amazonian forest. Ecology Letters, 19, 1062-1070.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Gilbert GS, Harms KE, Hamill DN, Hubbell SP (2001) Effects of seedling size, El Ni?o drought, seedling density, and distance to nearest conspecific adult on 6-year survival of Ocoteawhitei seedlings in Panamá. Oecologia, 127, 509-516.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
Gonzalez MA, Roger A, Courtois EA, Jabot F, Norden N, Paine CET, Baraloto C, Thebaud C, Chave J (2010) Shifts in species and phylogenetic diversity between sapling and tree communities indicate negative density dependence in a lowland rain forest. Journal of Ecology, 98, 137-146.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Graham CH, Fine PV (2008) Phylogenetic beta diversity: linking ecological and evolutionary processes across space in time. Ecology Letters, 11, 1265-1277.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Grime JP, Hodgson JG, Hunt R (2006) Comparative Plant Ecology. Castlepoint Press, Dalbeattie, UK. |
| [11] |
Guevara JE, Damasco G, Baraloto C, Fine PVA, Penuela MC, Castilho C, Vincentini A, Cardenas D, Wittmann F, Targhetta N, Phillips O, Stropp J, Amaral I, Maas P, Monteagudo A, Jimenez EM, Thomas R, Brienen R, Duque A, Magnusson W, Ferreira C, Honorio E, Matos FA, Arevalo FR, Engel J, Petronelli P, Vasquez1 R, Steege H (2016) Low phylogenetic beta diversity and geographic neo-endemism in Amazonian white-sand forests. Biotropica, 48, 34-46.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Hardy OJ, Senterre B (2007) Characterizing the phylogenetic structure of communities by an additive partitioning of phylogenetic diversity. Journal of Ecology, 95, 493-506.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Hu ZH, Yu MJ, Ding BY, Fang T, Qian HY, Chen QC (2003) Types of evergreen broad-leaved forests and their species diversity in Gutian Mountain National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Applied Environmental Biology, 9, 341-345. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[胡正华, 于明坚, 丁炳扬, 方腾, 钱海源, 陈启瑺 (2003) 古田山国家级自然保护区常绿阔叶林类型及其群落物种多样性研究. 应用与环境生物学报, 9, 341-345.]
DOI URL |
|
| [14] |
Hulshof CM, Swenson NG (2010) Variation in leaf functional trait values within and across individuals and species: an example from a Costa Rican dry forest. Functional Ecology, 24, 217-223.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kraft NJB, Adler PB, Godoy O, James EC, Fuller S, Levine JM (2015) Community assembly, coexistence and the environmental filtering metaphor. Functional Ecology, 29, 592-599.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Lebrija-Trejos E, Pérez-García EA, Meave JA, Bongers F, Poorter L (2010) Functional traits and environmental filtering drive community assembly in a species-rich tropical system. Ecology, 91, 386-398.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] | Liu XJ, Ma KP (2015) Plant functional traits—concepts, applications and future directions. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 45, 325-339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晓娟, 马克平 (2015) 植物功能性状研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 45, 325-339.] | |
| [18] |
Liu XJ, Swenson NG, Wright SJ, Zhang LW, Song K, Du YJ, Zhang JL, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2012) Covariation in plant functional traits and soil fertility within two species-rich forests. PLoS ONE, 7, e34767.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Reich PB (2014) The world-wide “fast-slow” plant economics spectrum: a traits manifesto. Journal of Ecology, 102, 275-301.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Shen Y, Yu SX, Lian JY, Shen H, Cao HL, Lu HP, Ye WH (2016) Inferring community assembly processes from trait diversity across environmental gradients. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 32, 290-299.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Silvertown J (2004) Plant coexistence and the niche. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 605-611.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Stubbs WJ, Wilson JB (2004) Evidence for limiting similarity in a sand dune community. Journal of Ecology, 92, 557-567.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Swenson NG, Enquist BJ (2009) Opposing assembly mechanisms in a Neotropical dry forest: implications for phylogenetic and functional community ecology. Ecology, 90, 2161-2170.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Swenson NG, Erickson DL, Mi XC, Bourg NA, Forero- Montana J, Ge XJ, Howe R, Lake JK, Liu XJ, Ma KP, Pei NC, Thompson J, Uriarte M, Wolf A, Wright SJ, Ye WH, Zhang JL, Zimmerman JK, Kress WJ (2012) Phylogenetic and functional alpha and beta diversity in temperate and tropical tree communities. Ecology, 93, S112-S125.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Uriarte M, Swenson NG, Chazdon RL, Comita LS, Kress WJ, Erickson D, Forero-Montana J, Zimmerman JK, Thompson J (2010) Trait similarity, shared ancestry and the structure of neighbourhood interactions in a subtropical wet forest: implications for community assembly. Ecology Letters, 13, 1503-1514.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Wang W, Rao MD, Chen SW, Zhu DH, Mi XC, Zhang JT (2014) Effects of negative density dependence and habitat filtering on temporal variation in phylogenetic community structure of seedlings in a mid-subtropical forest. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 1844-1850. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王薇, 饶米德, 陈声文, 朱大海, 米湘成, 张金屯 (2014) 负密度制约和生境过滤对古田山幼苗系统发育多样性时间变化的影响. 科学通报, 59, 1844-1850.] | |
| [27] |
Wang XG, Wiegand T, Kraft NJB, Swenson NG, Davies SJ, Hao ZQ, Howe R, Lin YC, Ma KP, Mi XC, Su SH, Sun IF, Wolf A (2016) Stochastic dilution effects weaken deterministic effects of niche-based processes in species rich forests. Ecology, 97, 347-360.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] |
Webb CO (2000) Exploring the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities: an example for rain forest trees. The American Naturalist, 156, 145-155.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M, Ackerly DD, Baruch Z, Bongers F, Cavender-Bares J, Chapin T, Cornelissen JHC, Diemer M, Flexas J, Garnier E, Groom PK, Gulias J, Hikosaka K, Lamont BB, Lee T, Lee1 W, Lusk C, Midgley JJ, Navas ML, Niinemets U, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Poot P, Prior L, Pyankov VI, Roumet C, Thomas SC, Tjoelker MG, Veneklaas EJ, Villar R (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature, 428, 821-827.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
Wright SJ (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: a review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia, 130, 1-14.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
Wright SJ, Kitajima K, Kraft NJB, Reich PB, Wright IJ, Bunker DE, Condit R, Dalling JW, Davies SJ, Díaz S, Engelbrecht BMJ, Harms KE, Hubbell SP, Marks CO, Ruiz-Jaen MC, Salvador CM, Zanne AE (2010) Functional traits and the growth-mortality trade-off in tropical trees. Ecology, 91, 3664-3674.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
Zheng SX, Shangguan ZP (2004) Stomata-density changes of the plants in the Loess Plateau of China over last century. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 2457-2464. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[郑淑霞, 上官周平 (2004) 近一世纪黄土高原区植物气孔密度变化规律. 生态学报, 24, 2457-2464.]
DOI URL |
|
| [33] |
Zhu Y, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Density dependence is prevalent in a heterogeneous subtropical forest. Oikos, 119, 109-119.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Zhu Y, Zhao GF, Zhang LW, Shen GC, Mi XC, Ren HB, Yu MJ, Chen JH, Chen SW, Fang T, Ma KP (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祝燕, 赵谷风, 张俪文, 沈国春, 米湘成, 任海保, 于明坚, 陈建华, 陈声文, 方腾, 马克平 (2008) 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地—群落组成与结构. 植物生态学报, 32, 262-273.] |
| [1] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [2] | 郑梦瑶, 李媛, 王雪蓉, 张越, 贾彤. 芦芽山不同植被类型土壤原生动物群落构建机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23419-. |
| [3] | 吴琪, 张晓青, 杨雨婷, 周艺博, 马毅, 许大明, 斯幸峰, 王健. 浙江钱江源-百山祖国家公园庆元片区叶附生苔多样性及其时空变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24010-. |
| [4] | 徐智超, 朱美慧, 毛子昆, 王绪高. 氮添加对东北温带阔叶红松林幼苗动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24255-. |
| [5] | 徐凯伦, 陈小荣, 张敏华, 于婉婉, 吴素美, 朱志成, 陈定云, 兰荣光, 董舒, 刘宇. 演替和地形共同影响浙江百山祖森林群落的性系统多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24338-. |
| [6] | 杨胜娴, 杨清, 李晓东, 巢欣, 刘惠秋, 魏蓝若雪, 巴桑. 确定性过程主导高原典型河流浮游植物地理分布格局和群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23092-. |
| [7] | 陈声文, 任海保, 童光蓉, 王宁宁, 蓝文超, 薛建华, 米湘成. 钱江源国家公园木本植物物种多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22587-. |
| [8] | 杜芳, 荣晓莹, 徐鹏, 尹本丰, 张元明. 降水对古尔班通古特沙漠细菌群落多样性和构建过程的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22492-. |
| [9] | 董建宇, 孙昕, 詹启鹏, 张宇洋, 张秀梅. 莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落beta多样性格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21388-. |
| [10] | 王寅, 王健铭, 曲梦君, 李景文. 干旱内陆河流域植物群落构建过程及其关键驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21419-. |
| [11] | 雍青措姆, 习新强, 牛克昌. 高寒草甸植物物种丧失对草原毛虫的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22069-. |
| [12] | 米湘成, 王绪高, 沈国春, 刘徐兵, 宋晓阳, 乔秀娟, 冯刚, 杨洁, 毛子昆, 徐学红, 马克平. 中国森林生物多样性监测网络: 二十年群落构建机制探索的回顾与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22504-. |
| [13] | 高程, 郭良栋. 微生物物种多样性、群落构建与功能性状研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22429-. |
| [14] | 王少鹏, 罗明宇, 冯彦皓, 储诚进, 张大勇. 生物多样性理论最新进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22410-. |
| [15] | 康佳鹏, 韩路, 冯春晖, 王海珍. 塔里木荒漠河岸林不同生境群落物种多度分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 875-886. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn