



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 25160. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025160 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025160
熊欢1( ), 刘雪艳1, 吴燕芳1, 陈红州1(
), 刘雪艳1, 吴燕芳1, 陈红州1( ), 马妍1, 胡星月1, 张静宜1, 夏瑨宇1, 吴伟泽2, 陈伟1,*(
), 马妍1, 胡星月1, 张静宜1, 夏瑨宇1, 吴伟泽2, 陈伟1,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-29
接受日期:2025-10-02
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-12-26
通讯作者:
陈伟
基金资助:
Huan Xiong1( ), Xueyan Liu1, Yanfang Wu1, Hongzhou Chen1(
), Xueyan Liu1, Yanfang Wu1, Hongzhou Chen1( ), Yan Ma1, Xingyue Hu1, Jingyi Zhang1, Jinyu Xia1, Weize Wu2, Wei Chen1,*(
), Yan Ma1, Xingyue Hu1, Jingyi Zhang1, Jinyu Xia1, Weize Wu2, Wei Chen1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2025-04-29
Accepted:2025-10-02
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-12-26
Contact:
Wei Chen
Supported by:摘要:
山地因独特的环境特征(地形地貌、气候和海拔等)和高度丰富的物种组成, 被认为是研究生物多样性分布格局及群落构建的热点地区。截至目前, 尚未有针对南北气候过渡带区域(如皖西大别山区)的山地两栖类物种多样性分布格局及其群落构建机制的报道。因此, 本文于2024年采用标准样线调查法, 在不同海拔梯度、生境类型和季节尺度上, 对皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类展开调查, 并对其alpha多样性与beta多样性进行分析, 结合气候、地形、生境及人为干扰等环境因素, 探讨其多样性格局及其影响因素。Alpha多样性的结果显示: 该区域共有无尾两栖类6科12属18种, 且物种丰富度与海拔呈显著负相关, 而Pielou均匀度指数则显示了相反的海拔变异规律; 此外, 该区域内无尾两栖类的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson优势度指数和Pielou均匀度指数在不同生境类型间表现出显著差异(农田生境高于其他生境), 其中Shannon-Wiener多样性指数也呈现出显著的季节性差异(夏季高于春季), 同时发现年降水量是影响物种丰富度、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数和Simpson优势度指数的主要因素。Beta多样性的研究表明, Bray-Curtis相异性指数和Sørensen相异性指数表现出周转组分高于嵌套组分且年均温是影响beta多样性指数及其周转组分的主要因素。本研究阐明了处于气候过渡带的皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类多样性格局及其影响因素, 为该区域生物多样性保护提供了数据支撑和理论依据。
熊欢, 刘雪艳, 吴燕芳, 陈红州, 马妍, 胡星月, 张静宜, 夏瑨宇, 吴伟泽, 陈伟 (2025) 皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类alpha和beta多样性格局及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 33, 25160. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025160.
Huan Xiong, Xueyan Liu, Yanfang Wu, Hongzhou Chen, Yan Ma, Xingyue Hu, Jingyi Zhang, Jinyu Xia, Weize Wu, Wei Chen (2025) The alpha and beta diversity and their influencing factors of Anurans in Dabie Mountains, Anhui Province. Biodiversity Science, 33, 25160. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025160.
| 物种 Species | 保护等级 Protection level | 中国生物多样性红色名录 China’s Red List of Biodiversity | 区系 Fauna | 优势度 Dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叉舌蛙科 Dicroglossidae | ||||
| 棘胸蛙属 Quasipaa | ||||
| 叶氏隆肛蛙 Q. yei | II | VU | OR | 0.0006 |
| 虎纹蛙属 Hoplobatrachus | ||||
| 虎纹蛙 H. chinensis | II | EN | OR | 0.0001 |
| 陆蛙属 Fejervarya | ||||
| 泽陆蛙 F. multistriata | LC | WS | 0.4559 | |
| 蛙科 Ranidae | ||||
| 蛙属 Rana | ||||
| 中国林蛙 R. chensinensis | LC | WS | 0.0201 | |
| 大别山林蛙 R. dabieshanensis | LC | OR | 0.0003 | |
| 侧褶蛙属 Pelophylax | ||||
| 黑斑侧褶蛙 P. nigromaculatus | NT | WS | 0.2056 | |
| 金线侧褶蛙 P. plancyi | NT | WS | 0.0073 | |
| 水蛙属 Hylarana | ||||
| 阔褶水蛙 H. latouchii | LC | WS | 0.0856 | |
| 树蛙科 Rhacophoridae | ||||
| 张树蛙属 Zhangixalus | ||||
| 安徽树蛙 Z. zhoukaiyae | DD | OR | 0.0079 | |
| 大树蛙 Z. dennysi | LC | OR | 0.0012 | |
| 泛树蛙属 Polypedates | ||||
| 布氏泛树蛙 P. braueri | LC | OR | 0.0224 | |
| 蟾蜍科 Bufonidae | ||||
| 蟾蜍属 Bufo | ||||
| 中华蟾蜍 B. gargarizans | LC | WS | 0.0671 | |
| 姬蛙科 Microhylidae | ||||
| 姬蛙属 Microhyla | ||||
| 饰纹姬蛙 M. fissipes | LC | OR | 0.0863 | |
| 大别山姬蛙 M. dabieshanensis | DD | OR | 0.0005 | |
| 合征姬蛙 M. mixtura | LC | OR | 0.0367 | |
| 小弧斑姬蛙 M. heymonsi | LC | OR | 0.0020 | |
| 狭口蛙属 Kaloula | ||||
| 北方狭口蛙 K. borealis | LC | PR | 0.0001 | |
| 雨蛙科 Hylidae | ||||
| 雨蛙属 Hyla | ||||
| 大别山雨蛙 H. dabieshanensis | LC | OR | 0.0003 |
表1 皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类名录
Table 1 List of Anurans in the Dabie Mountains of western Anhui Province
| 物种 Species | 保护等级 Protection level | 中国生物多样性红色名录 China’s Red List of Biodiversity | 区系 Fauna | 优势度 Dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叉舌蛙科 Dicroglossidae | ||||
| 棘胸蛙属 Quasipaa | ||||
| 叶氏隆肛蛙 Q. yei | II | VU | OR | 0.0006 |
| 虎纹蛙属 Hoplobatrachus | ||||
| 虎纹蛙 H. chinensis | II | EN | OR | 0.0001 |
| 陆蛙属 Fejervarya | ||||
| 泽陆蛙 F. multistriata | LC | WS | 0.4559 | |
| 蛙科 Ranidae | ||||
| 蛙属 Rana | ||||
| 中国林蛙 R. chensinensis | LC | WS | 0.0201 | |
| 大别山林蛙 R. dabieshanensis | LC | OR | 0.0003 | |
| 侧褶蛙属 Pelophylax | ||||
| 黑斑侧褶蛙 P. nigromaculatus | NT | WS | 0.2056 | |
| 金线侧褶蛙 P. plancyi | NT | WS | 0.0073 | |
| 水蛙属 Hylarana | ||||
| 阔褶水蛙 H. latouchii | LC | WS | 0.0856 | |
| 树蛙科 Rhacophoridae | ||||
| 张树蛙属 Zhangixalus | ||||
| 安徽树蛙 Z. zhoukaiyae | DD | OR | 0.0079 | |
| 大树蛙 Z. dennysi | LC | OR | 0.0012 | |
| 泛树蛙属 Polypedates | ||||
| 布氏泛树蛙 P. braueri | LC | OR | 0.0224 | |
| 蟾蜍科 Bufonidae | ||||
| 蟾蜍属 Bufo | ||||
| 中华蟾蜍 B. gargarizans | LC | WS | 0.0671 | |
| 姬蛙科 Microhylidae | ||||
| 姬蛙属 Microhyla | ||||
| 饰纹姬蛙 M. fissipes | LC | OR | 0.0863 | |
| 大别山姬蛙 M. dabieshanensis | DD | OR | 0.0005 | |
| 合征姬蛙 M. mixtura | LC | OR | 0.0367 | |
| 小弧斑姬蛙 M. heymonsi | LC | OR | 0.0020 | |
| 狭口蛙属 Kaloula | ||||
| 北方狭口蛙 K. borealis | LC | PR | 0.0001 | |
| 雨蛙科 Hylidae | ||||
| 雨蛙属 Hyla | ||||
| 大别山雨蛙 H. dabieshanensis | LC | OR | 0.0003 |
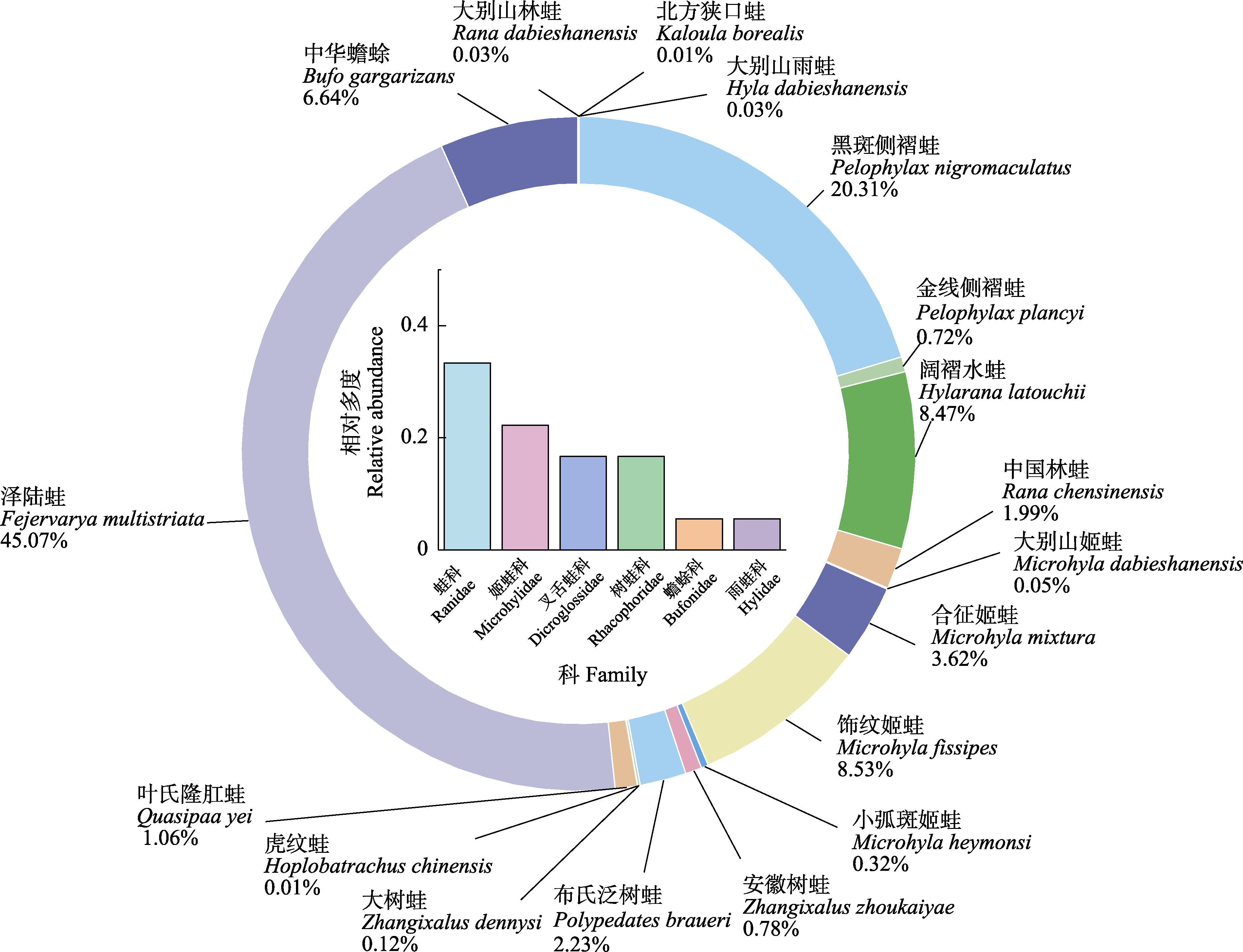
图2 皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类物种组成及相对多度。环形图: 各物种个体数量占总个体数的比例; 柱状图: 各科的物种相对多度。
Fig. 2 Species composition and relative abundance of Anurans in the Dabie Mountains of western Anhui Province. The pie chart shows the proportion of individuals for each species, and the bar chart shows the relative abundance of each family.
| Alpha多样性指数 Alpha diversity index | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | Mann-Whitney U test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | 0.811 ± 0.056 | 0.951 ± 0.041 | U = 1,193; P = 0.043 |
| Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index | 0.471 ± 0.031 | 0.520 ± 0.022 | U = 1,386; P = 0.374 |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index | 0.487 ± 0.026 | 0.507 ± 0.020 | U = 1,366; P = 0.607 |
表2 皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类alpha多样性的季节差异
Table 2 Seasonal differences in alpha diversity of Anurans in the Dabie Mountains of western Anhui Province
| Alpha多样性指数 Alpha diversity index | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | Mann-Whitney U test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | 0.811 ± 0.056 | 0.951 ± 0.041 | U = 1,193; P = 0.043 |
| Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index | 0.471 ± 0.031 | 0.520 ± 0.022 | U = 1,386; P = 0.374 |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index | 0.487 ± 0.026 | 0.507 ± 0.020 | U = 1,366; P = 0.607 |
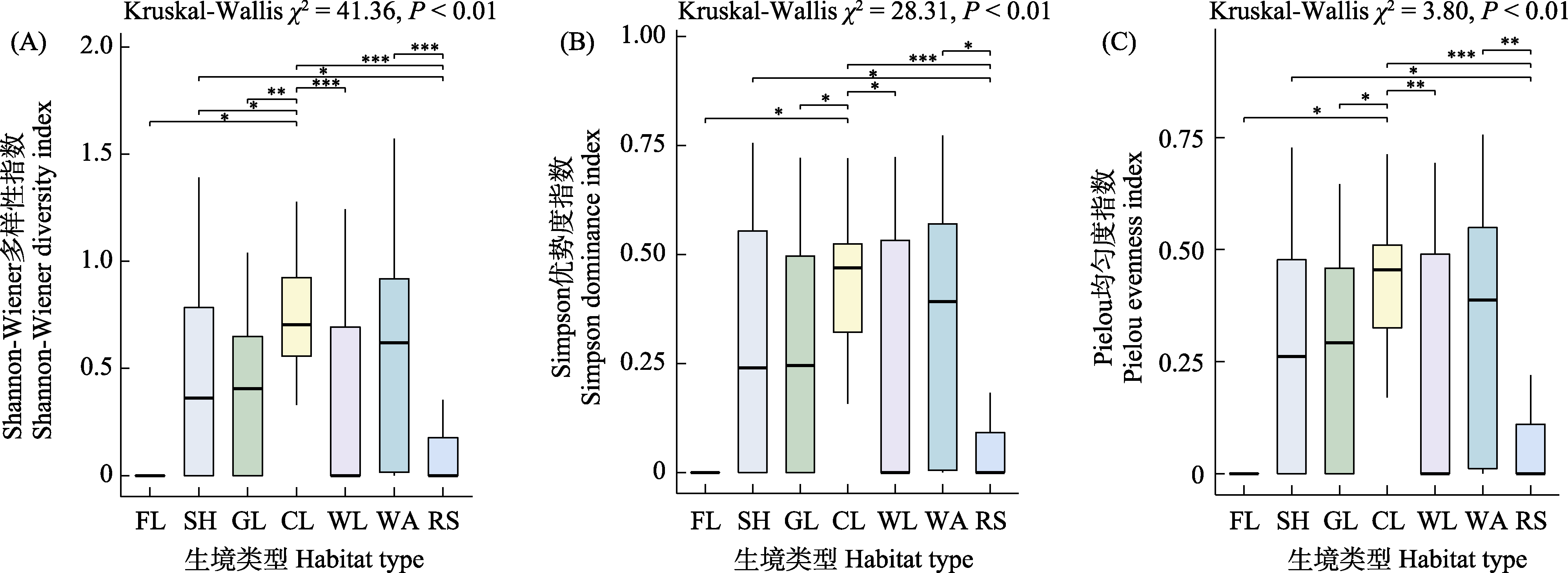
图3 不同生境类型无尾两栖类alpha多样性。FL: 林地; SH: 灌丛; GL: 草地; CL: 农田; WL: 荒地; WA: 水域; RS: 居民区。* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001。
Fig. 3 Alpha diversity of Anurans of different habitat types. FL, Forest land; SH, Shrub; GL, Grassland; CL, Farmland; WL, Wasteland; WA, Water area; RS, Residential area. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
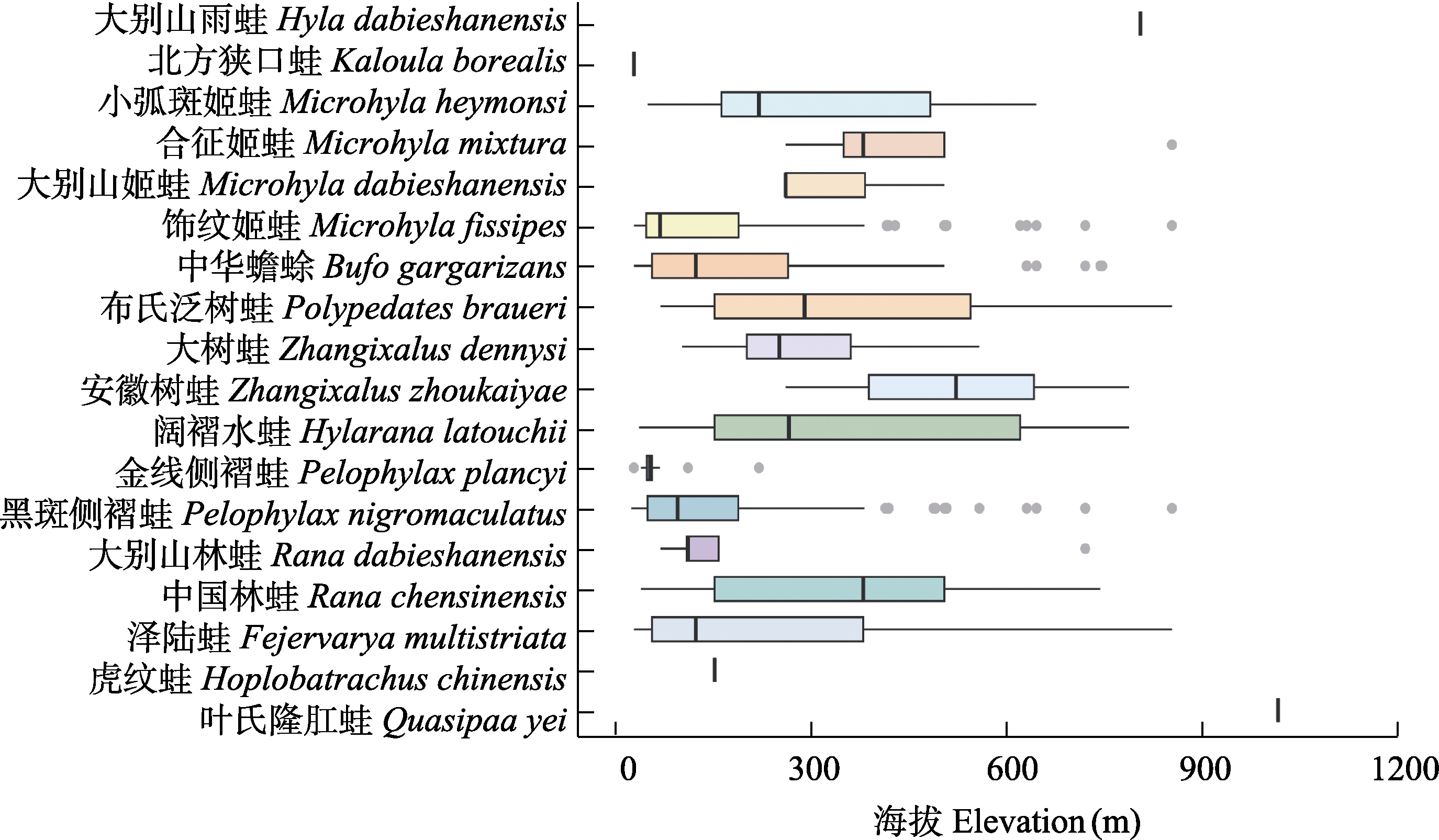
图4 皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类的海拔分布格局。箱体表示四分位距(IQR), 箱内粗线为中位数, 上下须线表示位于1.5倍四分位距范围内的最小值和最大值, 灰色圆点为离群值。
Fig. 4 Elevational distribution patterns of anuran species in the Dabie Mountains, western Anhui Province, China. Boxes indicate interquartile ranges (IQR), thick lines within boxes show medians, whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values within 1.5 × IQR, and grey dots denote outliers.
| Alpha多样性指数 Alpha diversity index | 环境因子 Environmental factors | 估计值M | 相对重要性Wi | 标准误SE | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | 年降水量 Annual precipitation | 0.001 | 1.00 | 0.001 | 0.010 |
| 生境类型 Habitat type | 0.045 | 0.52 | 0.003 | 0.454 | |
| 归一化植被指数 Normalized difference vegetation index | -0.001 | 0.63 | 0.001 | 0.356 | |
| 距道路距离 Distance to road | -0.301 | 0.32 | 0.683 | 0.662 | |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.001 | 0.07 | 0.003 | 0.879 | |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.001 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 0.896 | |
| Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index | 年降水量 Annual precipitation | 0.001 | 1.00 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| 生境类型 Habitat type | 0.008 | 0.40 | 0.014 | 0.561 | |
| 归一化植被指数 Normalized difference vegetation index | -0.001 | 0.47 | 0.001 | 0.488 | |
| 距道路距离 Distance to road | -0.112 | 0.27 | 0.321 | 0.730 | |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 年降水量 Annual precipitation | 0.001 | 0.90 | 0.001 | 0.047 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.006 | 0.34 | 0.002 | 0.219 | |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.001 | 0.33 | 0.001 | 0.231 | |
| 归一化植被指数 Normalized difference vegetation index | -0.001 | 0.47 | 0.001 | 0.899 |
表3 皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类alpha多样性95%置信区间内各参数的模型平均化估计值(M)、标准误(SE)、相对重要性(Wi)和P值
Table 3 Model-averaged estimates (M), standard errors (SE), model weights (Wi), and P values for parameters influencing the alpha diversity of Anurans within 95% confidence intervals in the Dabie Mountains of western Anhui Province
| Alpha多样性指数 Alpha diversity index | 环境因子 Environmental factors | 估计值M | 相对重要性Wi | 标准误SE | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | 年降水量 Annual precipitation | 0.001 | 1.00 | 0.001 | 0.010 |
| 生境类型 Habitat type | 0.045 | 0.52 | 0.003 | 0.454 | |
| 归一化植被指数 Normalized difference vegetation index | -0.001 | 0.63 | 0.001 | 0.356 | |
| 距道路距离 Distance to road | -0.301 | 0.32 | 0.683 | 0.662 | |
| 坡度 Slope | -0.001 | 0.07 | 0.003 | 0.879 | |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.001 | 0.07 | 0.001 | 0.896 | |
| Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index | 年降水量 Annual precipitation | 0.001 | 1.00 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| 生境类型 Habitat type | 0.008 | 0.40 | 0.014 | 0.561 | |
| 归一化植被指数 Normalized difference vegetation index | -0.001 | 0.47 | 0.001 | 0.488 | |
| 距道路距离 Distance to road | -0.112 | 0.27 | 0.321 | 0.730 | |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 年降水量 Annual precipitation | 0.001 | 0.90 | 0.001 | 0.047 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.006 | 0.34 | 0.002 | 0.219 | |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.001 | 0.33 | 0.001 | 0.231 | |
| 归一化植被指数 Normalized difference vegetation index | -0.001 | 0.47 | 0.001 | 0.899 |
| Sørensen相异性指数 Sørensen index | Bray-Curtis相异性指数 Bray-Curtis index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 嵌套 Nestedness | 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 嵌套 Nestedness | |
| R2 | 0.320*** | 0.257*** | 0.054 | 0.190*** | 0.179** | 0.051 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.020 | 0.026* | -0.006 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.013 |
| 年均温 Annual mean temperature | 0.094*** | 0.081** | 0.013 | 0.074*** | 0.119*** | -0.045* |
| 年降水量 Annual precipitation | 0.043* | 0.026 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.000 |
| 地理距离 Geographic distance | -0.001* | -0.001* | 0.001 | 0.001* | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 生境类型 Habitat type | 0.020 | 0.031** | -0.011 | 0.034** | 0.028 | 0.005 |
| 人类足迹 Human footprint | 0.004 | 0.011 | -0.007 | -0.016 | -0.022 | 0.006 |
| 归一化植被指数 Normalized difference vegetation index | 0.020 | -0.032 | 0.007 | -0.010 | -0.003 | -0.007 |
| 距河流距离 Distance to river | -0.005 | -0.012 | 0.007 | 0.001 | -0.011 | 0.012 |
| 距道路距离 Distance to road | 0.003 | -0.003 | 0.006 | 0.015 | -0.002 | 0.017 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.001 | 0.020 | -0.019* | -0.008 | -0.028 | 0.020 |
表4 皖西大别山地区无尾两栖类群落beta多样性及其组分的影响因素
Table 4 Factors influencing the beta diversity and its components of Anurans communities in the Dabie Mountains of western Anhui Province
| Sørensen相异性指数 Sørensen index | Bray-Curtis相异性指数 Bray-Curtis index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 嵌套 Nestedness | 总体 Total | 周转 Turnover | 嵌套 Nestedness | |
| R2 | 0.320*** | 0.257*** | 0.054 | 0.190*** | 0.179** | 0.051 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 0.020 | 0.026* | -0.006 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.013 |
| 年均温 Annual mean temperature | 0.094*** | 0.081** | 0.013 | 0.074*** | 0.119*** | -0.045* |
| 年降水量 Annual precipitation | 0.043* | 0.026 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.000 |
| 地理距离 Geographic distance | -0.001* | -0.001* | 0.001 | 0.001* | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 生境类型 Habitat type | 0.020 | 0.031** | -0.011 | 0.034** | 0.028 | 0.005 |
| 人类足迹 Human footprint | 0.004 | 0.011 | -0.007 | -0.016 | -0.022 | 0.006 |
| 归一化植被指数 Normalized difference vegetation index | 0.020 | -0.032 | 0.007 | -0.010 | -0.003 | -0.007 |
| 距河流距离 Distance to river | -0.005 | -0.012 | 0.007 | 0.001 | -0.011 | 0.012 |
| 距道路距离 Distance to road | 0.003 | -0.003 | 0.006 | 0.015 | -0.002 | 0.017 |
| 坡度 Slope | 0.001 | 0.020 | -0.019* | -0.008 | -0.028 | 0.020 |
| [1] |
Baselga A (2010) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 134-143.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Becker CG, Fonseca CR, Haddad CFB, Prado PI (2010) Habitat split as a cause of local population declines of amphibians with aquatic larvae. Conservation Biology, 24, 287-294.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Benton TG, Vickery JA, Wilson JD (2003) Farmland biodiversity: Is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 182-188.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Bickford D, Howard SD, Ng DJJ, Sheridan JA (2010) Impacts of climate change on the amphibians and reptiles of Southeast Asia. Biodiversity and Conservation, 19, 1043-1062.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bray JR, Curtis JT (1957) An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecological Monographs, 27, 325-349.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Burger IJ, Carter ET, Magner LM, Muñoz MM, Sears MW, Fitzpatrick BM, Riddell EA (2024) Assessing hybrid vigour using the thermal sensitivity of physiological trade-offs in tiger salamanders. Functional Ecology, 38, 143-152.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2004) Multimodel inference: Understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociological Methods & Research, 33, 261-304. |
| [8] |
Čengić M, Šunje E, Bonato L, Van Damme R, Lenders RHJ, Huijbregts MAJ, Lukić Bilela L, Schipper AM (2024) A multi-modelling approach for informing the conservation of a cold-adapted terrestrial amphibian in the face of climate change. Journal of Biogeography, 51, 2469-2483.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Cheng SY, Li YJ, Liu SF (2010) Geomorphology features of the Dabie Orogenic Belt based on DEM data. Journal of East China Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 33, 270-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程三友, 李英杰, 刘少峰 (2010) 基于DEM的大别山地区地貌特征研究. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 33, 270-275.] | |
| [10] |
Connell JH (1978) Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science, 199, 1302-1310.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Cushman SA (2006) Effects of habitat loss and fragmentation on amphibians: A review and prospectus. Biological Conservation, 128, 231-240.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Dai WY, Wu ZN, Yu BY, Liu YZ, Wang JC (2025) Research progress on the situation and causes of amphibian decline and its implications for conservation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 45, 3593-3613. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴文昱, 吴朝宁, 余博洋, 刘耘志, 王结臣 (2025) 两栖类衰退研究进展. 生态学报, 45, 3593-3613.] | |
| [13] |
Dalpasso A, Seglie D, Eusebio Bergò P, Ciracì A, Compostella M, Laddaga L, Manica M, Marino G, Pandolfo I, Soldato G, Falaschi M (2023) Effects of temperature and precipitation changes on shifts in breeding phenology of an endangered toad. Scientific Reports, 13, 14573.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Dinno A (2015) Nonparametric pairwise multiple comparisons in independent groups using Dunn’s test. The Stata Journal: Promoting Communications on Statistics and Stata, 15, 292-300.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Duan RY, Kong XQ, Huang MY, Varela S, Ji X (2016) The potential effects of climate change on amphibian distribution, range fragmentation and turnover in China. PeerJ, 4, e2185. |
| [16] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Tian WS, Jiang JP, Wu GF, Li J, Wang YS (2009) Fauna Sinica∙Amphibia (Vol. 2):Anura. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 田婉淑, 江建平, 吴贯夫, 李健, 王宜生 (2009) 中国动物志∙两栖纲(中卷): 无尾目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] | Fei L, Ye CY, Jiang JP (2012) Colored Atlas of Chinese Amphibians and Their Distributions. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 叶昌媛, 江建平 (2012) 中国两栖动物及其分布彩色图鉴. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [18] | Gan JM, Li Y, Wan YQ, Li JQ, Zhang BW (2021) The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Rana dabieshanensis (Anura: Ranidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B, Resources, 6, 2418-2419. |
| [19] |
García-Rodríguez A, Velasco JA, Villalobos F, Parra-Olea G (2021) Effects of evolutionary time, speciation rates and local abiotic conditions on the origin and maintenance of amphibian montane diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30, 674-684.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Godoy O, Gómez-Aparicio L, Matías L, Pérez-Ramos IM, Allan E (2020) An excess of niche differences maximizes ecosystem functioning. Nature Communications, 11, 4180.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Goslee S, Urban D (2022) ecodist: Dissimilarity-based Functions for Ecological Analysis. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ecodist/. (accessed on 2023-10-30) |
| [22] |
Graham MH (2003) Confronting multicollinearity in ecological multiple regression. Ecology, 84, 2809-2815.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Gray MJ, Smith LM, Brenes R (2004) Effects of agricultural cultivation on demographics of southern high plains amphibians. Conservation Biology, 18, 1368-1377.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Harrell FE Jr, Dupont C (2025) Hmisc: Harrell Miscellaneous. https://hbiostat.org/R/Hmisc/. (accessed on 2025-04-25) |
| [25] | Henry DAW, Cumming GS (2016) Spatial and environmental processes show temporal variation in the structuring of waterbird metacommunities. Ecosphere, 7, e01451. |
| [26] | Hijmans RJ (2019) Introduction to the geosphere package (Version 1.5- 10). https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/geosphere/index.html. (accessed on 2024-10-14) |
| [27] |
Hong F, Pang DP, Lin XJ, Huang WX, Fang J, Li WB (2025) Diversity and distribution patterns of amphibians in the Huangshan Mountain Region: The roles of climate and human activities. Animals, 15, 938.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Hu JH, Xie F, Li C, Jiang JP (2011) Elevational patterns of species richness, range and body size for spiny frogs. PLoS ONE, 6, e19817. |
| [29] |
Ibáñez R, Condit R, Angehr G, Aguilar S, GarcÍa T, MartÍnez R, Sanjur A, Stallard R, Wright SJ, Rand AS, Heckadon S (2002) An ecosystem report on the Panama Canal: Monitoring the status of the forest communities and the watershed. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 80, 65-95.
PMID |
| [30] |
Isbell F, Craven D, Connolly J, Loreau M, Schmid B, Beierkuhnlein C, Bezemer TM, Bonin C, Bruelheide H, de Luca E, Ebeling A, Griffin JN, Guo QF, Hautier Y, Hector A, Jentsch A, Kreyling J, Lanta V, Manning P, Meyer ST, Mori AS, Naeem S, Niklaus PA, Polley HW, Reich PB, Roscher C, Seabloom EW, Smith MD, Thakur MP, Tilman D, Tracy BF, van der Putten WH, van Ruijven J, Weigelt A, Weisser WW, Wilsey B, Eisenhauer N (2015) Biodiversity increases the resistance of ecosystem productivity to climate extremes. Nature, 526, 574-577.
DOI |
| [31] | Jiang JP, Xie F, Li C, Wang B (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity∙Vertebrates (Vol. IV): Amphibians. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [ 江建平, 谢锋, 李成, 王斌 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录∙脊椎动物(第四卷): 两栖动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [32] |
Jiang JP, Xie F, Zang CX, Cai L, Li C, Wang B, Li JT, Wang J, Hu JH, Wang Y, Liu JY (2016) Assessing the threat status of amphibians in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 588-597. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 江建平, 谢锋, 臧春鑫, 蔡蕾, 李成, 王斌, 李家堂, 王杰, 胡军华, 王燕, 刘炯宇 (2016) 中国两栖动物受威胁现状评估. 生物多样性, 24, 588-597.]
DOI |
|
| [33] |
Khatiwada JR, Zhao T, Chen YH, Wang B, Xie F, Cannatella DC, Jiang JP (2019) Amphibian community structure along elevation gradients in eastern Nepal Himalaya. BMC Ecology, 19, 19.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Koleff P, Gaston KJ, Lennon JJ (2003) Measuring beta diversity for presence-absence data. Journal of Animal Ecology, 72, 367-382.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Li C, Xie F, Che J, Jiang JP (2017) Monitoring and research of amphibians and reptiles diversity in key areas of China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 246-254. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 李成, 谢锋, 车静, 江建平 (2017) 中国关键地区两栖爬行动物多样性监测与研究. 生物多样性, 25, 246-254.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Liang G (1998) The characteristics of the herpetofauna in Qinling area and the strategies for sustainable development. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 28, 545-549. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 梁刚 (1998) 秦岭地区两栖爬行动物区系组成特点及持续发展对策. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 28, 545-549.] | |
| [37] | Liao ZY, Zhang WY, Guo ZG, Qian Q, He YX, Xiao Q, Wu N, Shi XQ, Liu ZD, Liang LW, Fan HZ, Chen YH (2025) Energy availability and spatial effect determine the multi-scale distributional patterns of multi-dimensional diversity of amphibians in China. Journal of Biogeography, 52, e15085. |
| [38] |
Liu MX, Yang CL, Miao LL, Xiao YD, Wang QY, Wang M (2024) Rare and common species contribute disproportionately to alpine meadow community construction and functional variation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 31, 24881-24893.
DOI |
| [39] | Liu P, Wu GF (1994) Study on floral characteristics and forest vegetation of the Dabie Mountains. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (1), 76-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘鹏, 吴国芳 (1994) 大别山植物区系的特点和森林植被的研究. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (1), 76-81.] | |
| [40] |
Luedtke JA, Chanson J, Neam K, Hobin L, Maciel AO, Catenazzi A, Borzée A, Hamidy A, Aowphol A, Jean A, Sosa-Bartuano Á, Fong GA, de Silva A, Fouquet A, Angulo A, Kidov AA, Muñoz Saravia A, Diesmos AC, Tominaga A, Shrestha B, Gratwicke B, Tjaturadi B, Martínez Rivera CC, Vásquez Almazán CR, Señaris C, Chandramouli SR, Strüssmann C, Cortez Fernández CF, Azat C, Hoskin CJ, Hilton-Taylor C, Whyte DL, Gower DJ, Olson DH, Cisneros-Heredia DF, Santana DJ, Nagombi E, Najafi-Majd E, Quah ESH, Bolaños F, Xie F, Brusquetti F, Álvarez FS, Andreone F, Glaw F, Castañeda FE, Kraus F, Parra-Olea G, Chaves G, Medina-Rangel GF, González-Durán G, Ortega-Andrade HM, Machado IF, Das I, Dias IR, Urbina-Cardona JN, Crnobrnja-Isailović J, Yang JH, Jiang JP, Wangyal JT, Rowley JJL, Measey J, Vasudevan K, Chan KO, Gururaja KV, Ovaska K, Warr LC, Canseco-Márquez L, Toledo LF, Díaz LM, Khan MMH, Meegaskumbura M, Acevedo ME, Napoli MF, Ponce MA, Vaira M, Lampo M, Yánez-Muñoz MH, Scherz MD, Rödel MO, Matsui M, Fildor M, Kusrini MD, Ahmed MF, Rais M, Kouamé NG, García N, Gonwouo NL, Burrowes PA, Imbun PY, Wagner P, Kok PJR, Joglar RL, Auguste RJ, Brandão RA, Ibáñez R, May RV, Hedges SB, Biju SD, Ganesh SR, Wren S, Das S, Flechas SV, Ashpole SL, Robleto-Hernández SJ, Loader SP, Incháustegui SJ, Garg S, Phimmachak S, Richards SJ, Slimani T, Osborne-Naikatini T, Abreu-Jardim TPF, Condez TH, De Carvalho TR, Cutajar TP, Pierson TW, Nguyen TQ, Kaya U, Yuan ZY, Long B, Langhammer P, Stuart SN (2023) Ongoing declines for the world’s amphibians in the face of emerging threats. Nature, 622, 308-314.
DOI |
| [41] | Ma KP (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 1). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 162-168. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法.I. α多样性的测度方法(上). 生物多样性, 2, 162-168.] | |
| [42] |
Ma KP (2016) Hot topics for biodiversity science. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1-2. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[ 马克平 (2016) 生物多样性科学的热点问题. 生物多样性, 24, 1-2.]
DOI |
|
| [43] | Ma KP, Liu YM (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平, 刘玉明 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| [44] |
Matavelli R, Oliveira JM, Soininen J, Ribeiro MC, Bertoluci J (2022) Altitude and temperature drive anuran community assembly in a Neotropical mountain region. Biotropica, 54, 607-618.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
McKinney ML (2006) Urbanization as a major cause of biotic homogenization. Biological Conservation, 127, 247-260.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Medina D, Ibáñez R, Lips KR, Crawford AJ (2019) Amphibian diversity in Serranía de Majé, an isolated mountain range in eastern Panamá. ZooKeys, 859, 117-130.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | Mi CR, Huettmann F, Li XH, Jiang ZW, Du WG, Sun BJ (2022) Effects of climate and human activity on the current distribution of amphibians in China. Conservation Biology, 36, e13964. |
| [48] | Mittermeier RA, Turner WR, Larsen FW, Brooks TM, Gascon C (2011) Global biodiversity conservation:The critical role of hotspots. In: Biodiversity Hotspots: Distribution and Protection of Conservation Priority Areas (eds Zachos FE, Habel JC), pp.3-22. Springer, Berlin. |
| [49] |
Ochoa-Ochoa LM, Rodríguez P, Mora F, Flores-Villela O, Whittaker RJ (2012) Climate change and amphibian diversity patterns in Mexico. Biological Conservation, 150, 94-102.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Oksanen JF, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Wagner H (2011) Vegan: Community Ecology Package. https://github.com/vegandevs/vegan. (accessed on 2024-04-25) |
| [51] | Pan T, Zhang YN, Wang H, Wu J, Kang X, Qian LF, Li K, Zhang Y, Chen JY, Rao DQ, Jiang JP, Zhang BW (2017) A new species of the genus Rhacophorus (Anura: Rhacophoridae) from Dabie Mountains in East China. Asian Herpetological Research, 8, 1-13. |
| [52] | Pan T, Zhou WL, Shi WB, Zhao K, Chen JY, Wang WG, Chu J, Pu FG, Gu CM, Zhang BW (2014) Species richness of amphibians and reptiles in Dabie Mountains, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 49, 195-206. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 潘涛, 周文良, 史文博, 赵凯, 陈锦云, 汪文革, 储俊, 蒲发光, 顾长明, 张保卫 (2014) 大别山地区两栖爬行动物区系调查. 动物学杂志, 49, 195-206.] | |
| [53] |
Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2007) A latitudinal gradient in large-scale beta diversity for vascular plants in North America. Ecology Letters, 10, 737-744.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | Qian YQ, MA KP (1994) Principles and Methods of Biodiversity Research. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 钱迎倩, 马克平 (1994) 生物多样性研究的原理与方法. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [55] |
Rahbek C, Borregaard MK, Antonelli A, Colwell RK, Holt BG, Nogues-Bravo D, Rasmussen CMØ, Richardson K, Rosing MT, Whittaker RJ, Fjeldså J (2019) Building mountain biodiversity: Geological and evolutionary processes. Science, 365, 1114-1119.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Raz T, Allison A, Avila LJ, Bauer AM, Böhm M, de O Caetano GH, Colli G, Doan TM, Doughty P, Grismer L, Itescu Y, Kraus F, Martins M, Morando M, Murali G, Nagy ZT, de C Nogueira C, Novosolov M, Oliver PM, Passos P, Pincheira- Donoso D, Sindaco R, Slavenko A, Torres-Carvajal O, Uetz P, Wagner P, Zimin A, Roll U, Meiri S (2024) Diversity gradients of terrestrial vertebrates—Substantial variations about a common theme. Journal of Zoology, 322, 126-140.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Santos-Pereira M, Rocha CFD (2025) Anuran altitudinal distribution in an Atlantic Forest hill: Band area and Rapoport effect driving it. Herpetological Journal, 35, 89-98. |
| [58] | Shao WJ, Song XQ, Chen C, Zhao L, Jin L, Liao WB (2022) Diversity and distribution pattern of amphibians and reptiles in Yingjing area of the Giant Panda National Park. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 57, 707-721. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邵威杰, 宋心强, 陈川, 赵丽, 金龙, 廖文波 (2022) 大熊猫国家公园荥经片区两栖爬行动物多样性及海拔分布格局. 动物学杂志, 57, 707-721.] | |
| [59] |
Soininen J, Heino J, Wang JJ (2018) A meta-analysis of nestedness and turnover components of beta diversity across organisms and ecosystems. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 96-109.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Sørensen T (1948) A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. Biologiske Skrifter, 5, 1-34. |
| [61] |
Trisos CH, Merow C, Pigot AL (2020) The projected timing of abrupt ecological disruption from climate change. Nature, 580, 496-501.
DOI |
| [62] |
VanderWaal KL, Obanda V, Omondi GP, McCowan B, Wang H, Fushing H, Isbell LA (2016) The “strength of weak ties” and helminth parasitism in giraffe social networks. Behavioral Ecology, 27, 1190-1197.
DOI URL |
| [63] | Wang XY, Yang SN, Guo CP, Tang K, Jiang JP, Hu JH (2020) Amphibian diversity and conservation along an elevational gradient on Mount Emei, southwestern China. Amphibian & Reptile Conservation, 14, 46-56. |
| [64] |
Wang XY, Zhong MJ, Yang SN, Jiang JP, Hu JH (2022a) Multiple β-diversity patterns and the underlying mechanisms across amphibian communities along a subtropical elevational gradient. Diversity and Distributions, 28, 2489-2502.
DOI URL |
| [65] | Wang XY, Zhong MJ, Zhang J, Si XF, Yang SN, Jiang JP, Hu JH (2022b) Multidimensional amphibian diversity and community structure along a 2600 m elevational gradient on the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Zoological Research, 43, 40-51. |
| [66] | Welsh HH Jr, Ollivier LM (1998) Stream amphibians as indicators of ecosystem stress: A case study from California’s redwoods. Ecological Applications, 8, 1118-1132. |
| [67] |
Whitfield SM, Lips KR, Donnelly MA (2016) Amphibian decline and conservation in central America. Copeia, 104, 351-379.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Wu Q, Chen X, Cao Q, Chen YT, Yue W (2022) Variation characteristics of agricultural climatic resources in area of Dabie Mountains in China from 1961 to 2020. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 51(2), 75-85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [ 伍琼, 陈曦, 曹强, 陈砚涛, 岳伟 (2022) 1961-2020年大别山区农业气候资源变化特征分析. 河南农业科学, 51(2), 75-85.] | |
| [69] | Xia SS, Ji XL, Meng L, Zhou LZ (2025) Functional diversity of wintering waterbird enhanced by restored wetland in the lakeshore of Chaohu Lake. Ecology and Evolution, 15, e71751. |
| [70] | Xu HG, Wu J, Wu YQ, Guo WB, He YX, Li JQ, Li JN, Chen MM, Cai L (2018) Progress in construction of China Amphibian Diversity Observation Network (China BON-Amphibians). Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 34, 20-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐海根, 吴军, 吴延庆, 郭伟波, 何玉晓, 李佳琦, 李建南, 陈萌萌, 蔡蕾 (2018) 全国两栖动物多样性观测网络(China BON-Amphibians)建设进展. 生态与农村环境学报, 34, 20-26.] | |
| [71] | Xu JP, Wang H, Wu Q, Wang J, Xu X (2021) Climatic variation characteristics of Dabie Mountains in western Anhui during 1961-2019. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 49(4), 131-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐建鹏, 王晖, 伍琼, 王杰, 徐祥 (2021) 1961-2019年皖西大别山区的气候变化特征. 贵州农业科学, 49(4), 131-137.] | |
| [72] | Xu XX, Zhao WG, Liu P (2018) Effect of environmental temperature on body temperature during reproductive period and embryonic development in different geographic populations of Rana dybowskii. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 2965-2973. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐骁骁, 赵文阁, 刘鹏 (2018) 环境温度对东北林蛙不同地理种群繁殖期体温和胚胎发育的影响. 生态学报, 38, 2965-2973.] | |
| [73] |
Zancolli G, Steffan-Dewenter I, Rödel MO (2014) Amphibian diversity on the roof of Africa: Unveiling the effects of habitat degradation, altitude and biogeography. Diversity and Distributions, 20, 297-308.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Zhang CW, Chen C, Zhang MH, Wang ZY, Ma HH, Sun RL, Jiang JP, Zhang BW (2022) A new species of the genus Microhyla (Amphibia: Anura: Microhylidae) from the Dabie Mountains, China. Animals, 12, 2894.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Zhang CW, Zhang Y, Cai YF, Yu L, Pang DP, Jiang QY, Ding J, Gong DJ, Zhang BW (2025) A new species of the genus Hyla (Amphibia: Anura: Hylidae) from the Dabie Mountains, Anhui, China. Zoological Research: Diversity and Conservation, 2, 42-54.
DOI URL |
| [76] | Zhang MY, Wang ZQ, Qiu ZX, Wu HY, Zhang TX, Zhang Y, Han WJ, Huang XF (2025) Diversity and distribution patterns of amphibians and reptiles in Xinyu City, Jiangxi Province. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 41, 904-911. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张曼玉, 王臻褀, 仇志欣, 吴怀远, 张天祥, 张阳, 韩卫杰, 黄晓凤 (2025) 江西新余市两栖爬行动物多样性及保护空缺研究. 生态与农村环境学报, 41, 904-911.] | |
| [77] | Zhang RZ (2011) Chinese Zoogeography. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张荣祖 (2011) 中国动物地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [78] | Zhang YG (1989) Effect of temperature on the early embryonic development of Rana japonica Guenther. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 14(3), 74-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张耀光 (1989) 温度对日本林蛙早期胚胎发育的影响. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 14(3), 74-79.] | |
| [79] |
Zheng Z, Gong DJ, Sun CX, Li XJ, Li WJ (2014) Elevational pattern of amphibian and reptile diversity in Qinling Range and explanation. Biodiversity Science, 22, 596-607. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 郑智, 龚大洁, 孙呈祥, 李晓军, 李万江 (2014) 秦岭两栖、爬行动物物种多样性海拔分布格局及其解释. 生物多样性, 22, 596-607.]
DOI |
|
| [80] | Zhu WB, Zhao CL, Liao CL, Zou B, Xu D, Zhu W, Zhao T, Jiang JP (2020) Spatial and temporal patterns of amphibian species richness on Tianping Mountain, Hunan Province, China. Zoological Research, 41, 182-187. |
| [81] |
Zu KL, Wang ZH (2022) Research progress on the elevational distribution of mountain species in response to climate change. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21451. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 祖奎玲, 王志恒 (2022) 山地物种海拔分布对气候变化响应的研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 21451.]
DOI |
| [1] | 程晓帆, 李青媛, 李媛辉, 张明祥. 外来入侵物种治理政策体系的困境与出路[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(2): 25332-. |
| [2] | 陈璐露, 汤皓婷, 冷红, 袁青, 杨昕悦. 城市街区建成环境对生物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(2): 25286-. |
| [3] | 高雯琪, 向景荣, 赵耀, 范灵霜, 谷圆, 邵韦涵, 李高俊, 赵光军, 陈明斌, 蔡杏伟, 陈凯. 海南热带雨林国家公园黎母山和尖峰岭溪流鱼类群落特征及其对土地利用的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(2): 25374-. |
| [4] | 卢晓强, 芮丹, 张江峰, 尹冰鑫, 王雨露, 岑雨婷, 崔怡晨, 杨万霞. 氮输入驱动的关键生态过程对生物多样性的影响及其管理启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(2): 25368-. |
| [5] | 谭廷鸿, 高帆, 杨雨, 肖群英, 吴春芳, 邱娜, 赵宁宁, 周敏, 康公平, 卢志宏, 高健强, 杨红, 杨传东, 邓春英. 中国西南喀斯特地区大型真菌区系与物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(2): 25281-. |
| [6] | 谢将剑, 朱梦坤, 蒋爱伍, 肖治术. 聆听生物多样性的未来:声景自动评估方法的局限性与发展方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(2): 25296-. |
| [7] | 刘海鸥, 郝志明, 杜乐山, 刘文慧, 李子圆, 刘蕾. 全球生物多样性框架基金运行进展、挑战与启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(2): 25463-. |
| [8] | 王也, 王茜璐, 关婧, 王迎. 《生物多样性公约》现行资金机制及其替代方案研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(1): 25353-. |
| [9] | 杨方义, 靳彤, 申小莉, 张立, 杨彪. 生物多样性公益捐赠对中国生物多样性保护战略与行动计划(2023‒2030年)的贡献[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(1): 25269-. |
| [10] | 田璐瑶, 尹豪. 国外生物多样性抵消研究现状和对策研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(1): 25187-. |
| [11] | 蒙仁嘉, 秦涛, 汤心萌. 企业生物多样性保护驱动路径与模式[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(1): 25246-. |
| [12] | 秦洋, 吾买尔江·艾山, 魏文涛, 迪丽尼嘎·沙木沙克. A股上市公司生物多样性信息披露对供应链韧性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(1): 25342-. |
| [13] | 黎明, 秦响玲, 朱玉茹, 熊文. 自然保护区生物多样性抵消价值实现的理论框架与运行机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(1): 25241-. |
| [14] | 吴春莹, Viorel D. Popescu, 季吟秋. 生物多样性评估挑战的层级占有率模型解决路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(1): 25386-. |
| [15] | 王茜璐, 王禹兮, 王也, 赵阳, 王新. 生物多样性信用机制: 中外实践比较与启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2026, 34(1): 25299-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()