



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 23427. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023427 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023427
高欣1,5( ), 赵亚辉2(
), 赵亚辉2( ), 田菲3(
), 田菲3( ), 王晓爱4(
), 王晓爱4( ), 黎明政1,5(
), 黎明政1,5( ), 林鹏程1,5(
), 林鹏程1,5( ), 常涛1,5, 俞丹1,5(
), 常涛1,5, 俞丹1,5( ), 刘焕章1,5,*(
), 刘焕章1,5,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-08
接受日期:2023-12-27
出版日期:2023-12-20
发布日期:2024-01-05
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Xin Gao1,5( ), Yahui Zhao2(
), Yahui Zhao2( ), Fei Tian3(
), Fei Tian3( ), Xiaoai Wang4(
), Xiaoai Wang4( ), Mingzheng Li1,5(
), Mingzheng Li1,5( ), Pengcheng Lin1,5(
), Pengcheng Lin1,5( ), Tao Chang1,5, Dan Yu1,5(
), Tao Chang1,5, Dan Yu1,5( ), Huanzhang Liu1,5,*(
), Huanzhang Liu1,5,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-11-08
Accepted:2023-12-27
Online:2023-12-20
Published:2024-01-05
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要:
内陆水体鱼类多样性监测专项网(简称鱼类监测网)是我国建立的第一个全国范围的内陆水体鱼类多样性监测网络。本文阐述了鱼类监测网的监测工作和研究进展, 提出了对鱼类多样性监测和研究工作的展望和建议。鱼类监测网在长江、黄河、澜沧江、怒江、塔里木河、青海湖、黑龙江和珠江等八大水系开展了鱼类早期资源、个体生物学、种群和群落的监测和研究, 建立了我国第一个全国性的内陆鱼类多样性数据库, 收集和保藏鱼类样本上万尾和重要流域1997-2022年的鱼类多样性数据。主要研究结果显示, 过度捕捞、水利水电工程建设和外来物种入侵等导致重要流域鱼类群落结构发生了稳态变化; 中华鲟(Acipenser sinensis)繁殖主要受到水温和流量的影响, 长江干流大型水利水电工程造成下泄水温滞后和流量减小, 严重影响中华鲟的繁殖活动, 导致其野生种群数量急剧减少, 物种极度濒危; 长江四大家鱼呈现2000年前后减少, 近期资源增加的格局, 水温和流量日变化是影响四大家鱼繁殖的主要环境因素, 放流亲鱼对四大家鱼资源恢复有重要作用; 获得了圆口铜鱼(Coreius guichenoti)、长鳍吻鮈(Rhinogobio ventralis)、岩原鲤(Procypris rabaudi)等11种特有鱼类的生长、食性、繁殖特征等基础生物学数据。监测网的监测数据和研究结果为三峡工程生态影响评估、长江十年禁渔、赤水河生态环境保护、中华鲟物种保护等重要国家任务的完成和政策制定提供了数据基础和科学依据。为了完善全国性的监测网络建设, 建议加大投入, 建设观测台站; 推动数据共享和区域合作; 开展新技术、新方法的研究和应用。
高欣, 赵亚辉, 田菲, 王晓爱, 黎明政, 林鹏程, 常涛, 俞丹, 刘焕章 (2023) 中国内陆水体鱼类多样性监测专项网的监测和研究进展. 生物多样性, 31, 23427. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023427.
Xin Gao, Yahui Zhao, Fei Tian, Xiaoai Wang, Mingzheng Li, Pengcheng Lin, Tao Chang, Dan Yu, Huanzhang Liu (2023) Progress of monitoring and research of China Inland Water Fish Biodiversity Observation Network. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23427. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023427.
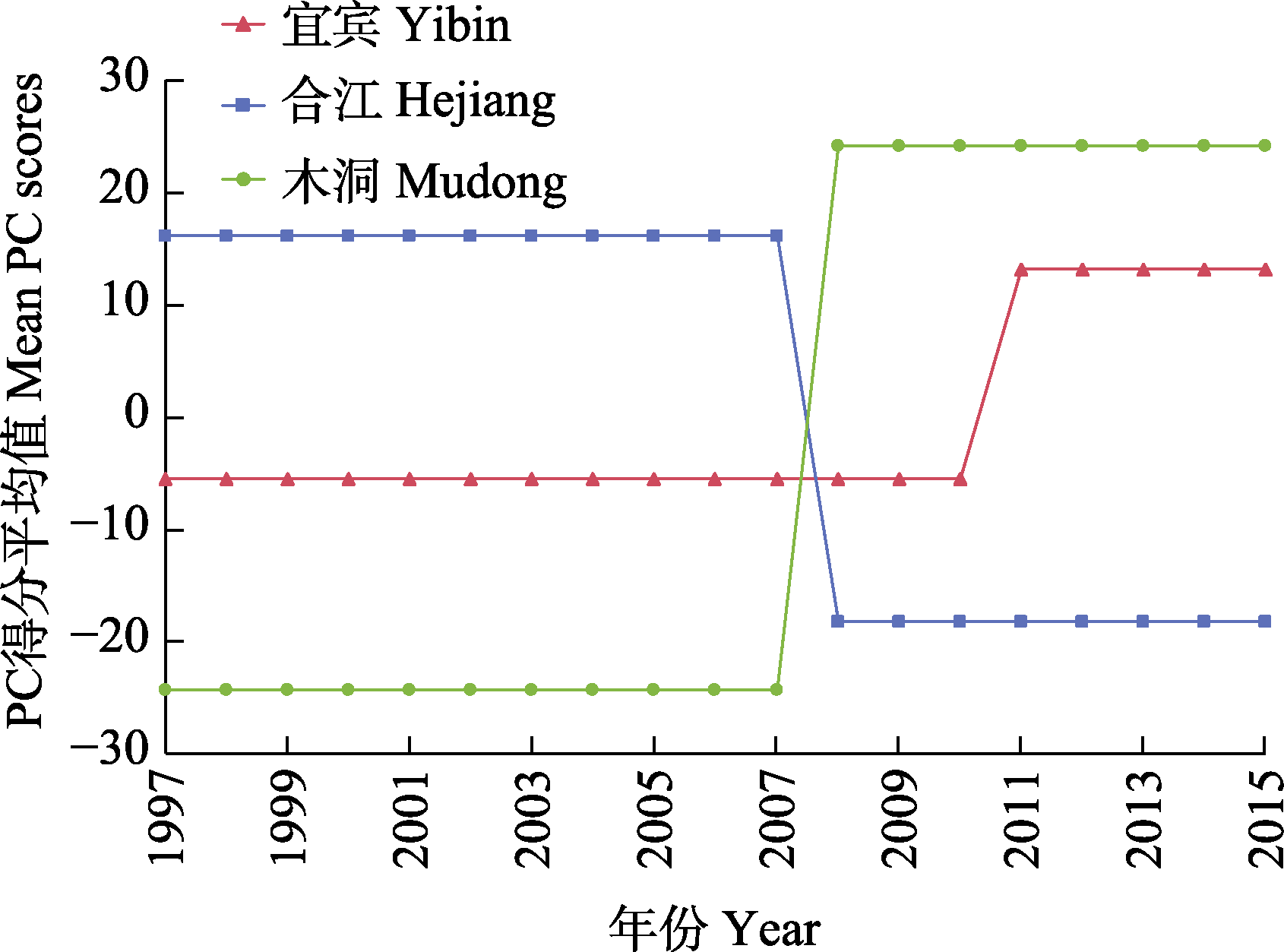
图1 三峡工程蓄水后长江上游干流江段鱼类群落发生稳态转换, 木洞和合江江段稳态转换发生在2008年, 宜宾江段稳态转换发生在2011年。改编自Gao等(2019)。
Fig. 1 Regime shifts of the time series for fish assemblage after impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir. The shifts in Mudong and Hejiang reaches occurred in 2008 and the shift in Yibin reach occurred in 2011. Adapted from Gao et al (2019).
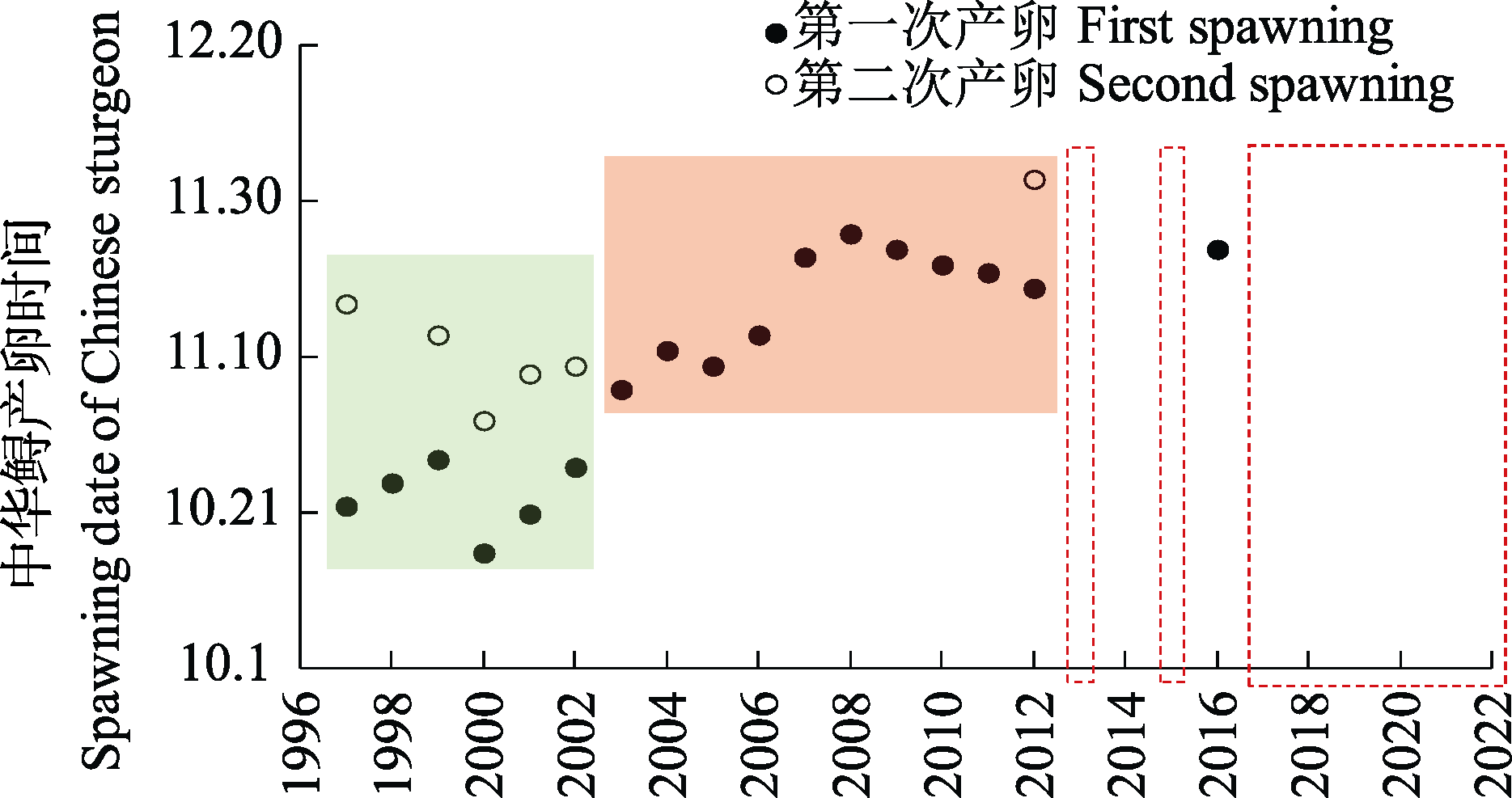
图4 1997-2022年葛洲坝下游宜昌江段中华鲟产卵时间发生变化(数据来源于中国科学院水生生物研究所监测数据和Gao et al, 2016)
Fig. 4 Changes in spawning dates of Chinese sturgeon in the Yichang reach below the Gezhou Dam from 1997 to 2022 (The data sourced from the monitoring data of the Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Gao et al, 2016)
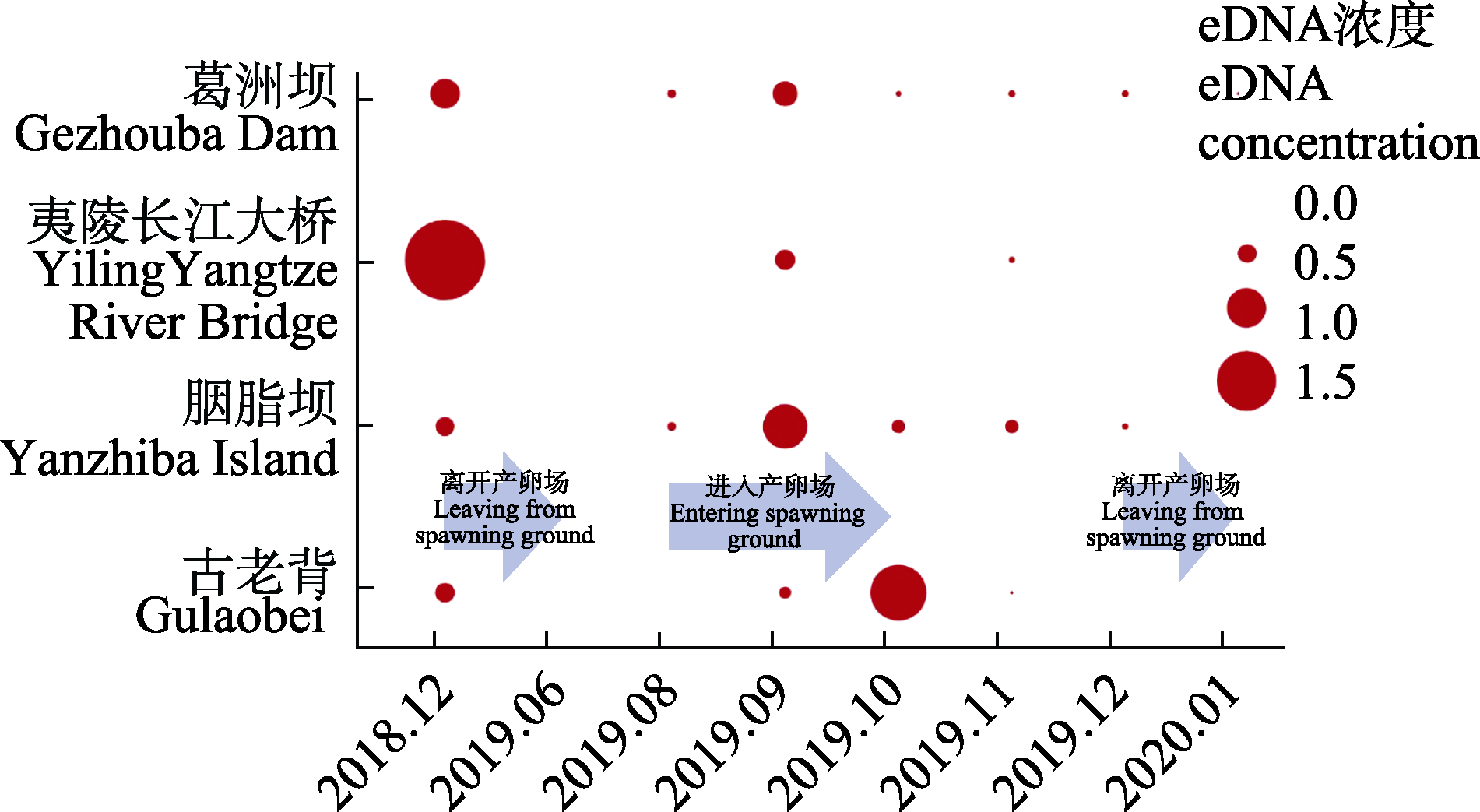
图5 2018年12月至2021年1月葛洲坝下游中华鲟保护区中华鲟eDNA浓度的时空分布特征(数据来源于中国科学院水生生物研究所监测数据和Yu et al, 2021)
Fig. 5 Spatiotemporal distribution of Chinese sturgeon eDNA concentration at four sampling sites in the protection area of Chinese sturgeon below Gezhouba Dam from December 2018 to January 2021 (The data sourced from the monitoring data of the Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Yu et al, 2021)
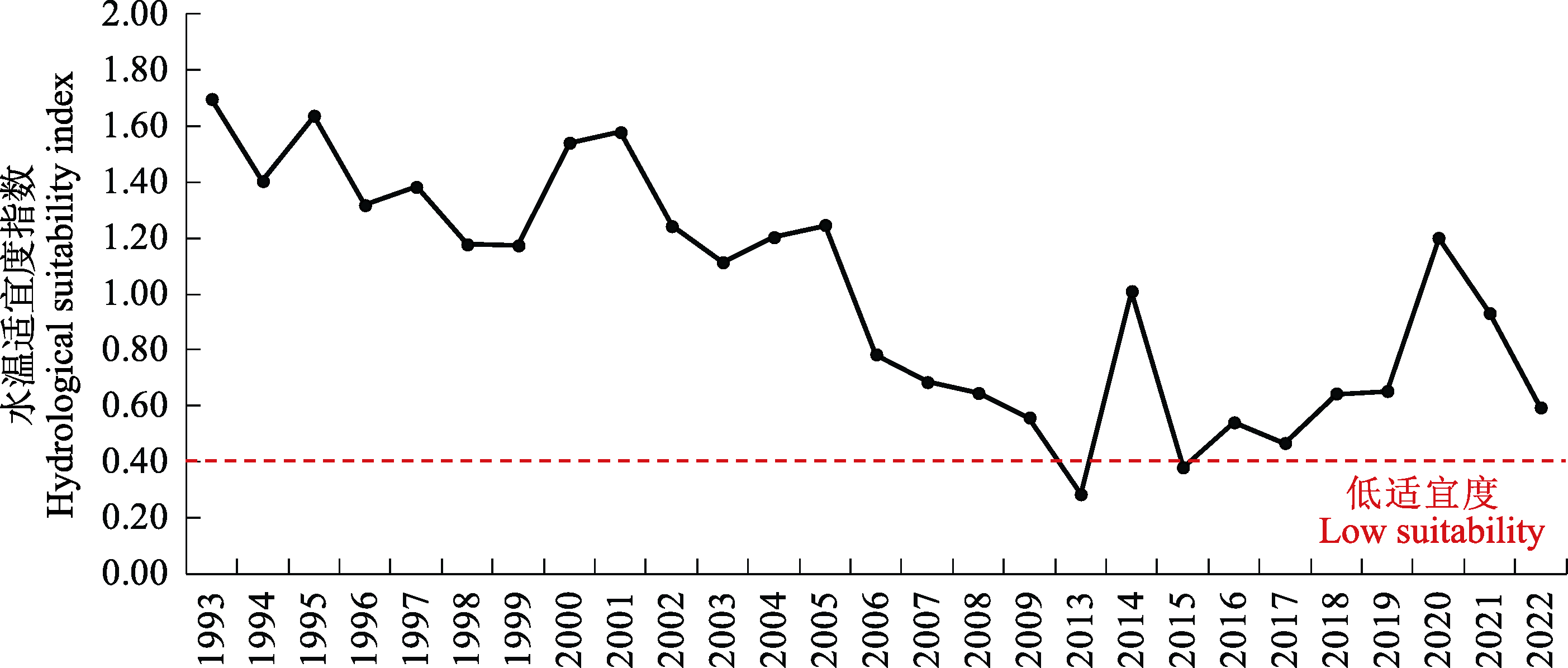
图6 1993-2022年中华鲟产卵场水文适宜度指数的时间变(数据来源于中国科学院水生生物研究所监测数据和Chang et al, 2021)
Fig. 6 Annual variation of the hydrological suitability index for Chinese sturgeon (The data sourced from the monitoring data of the Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chang et al, 2021)
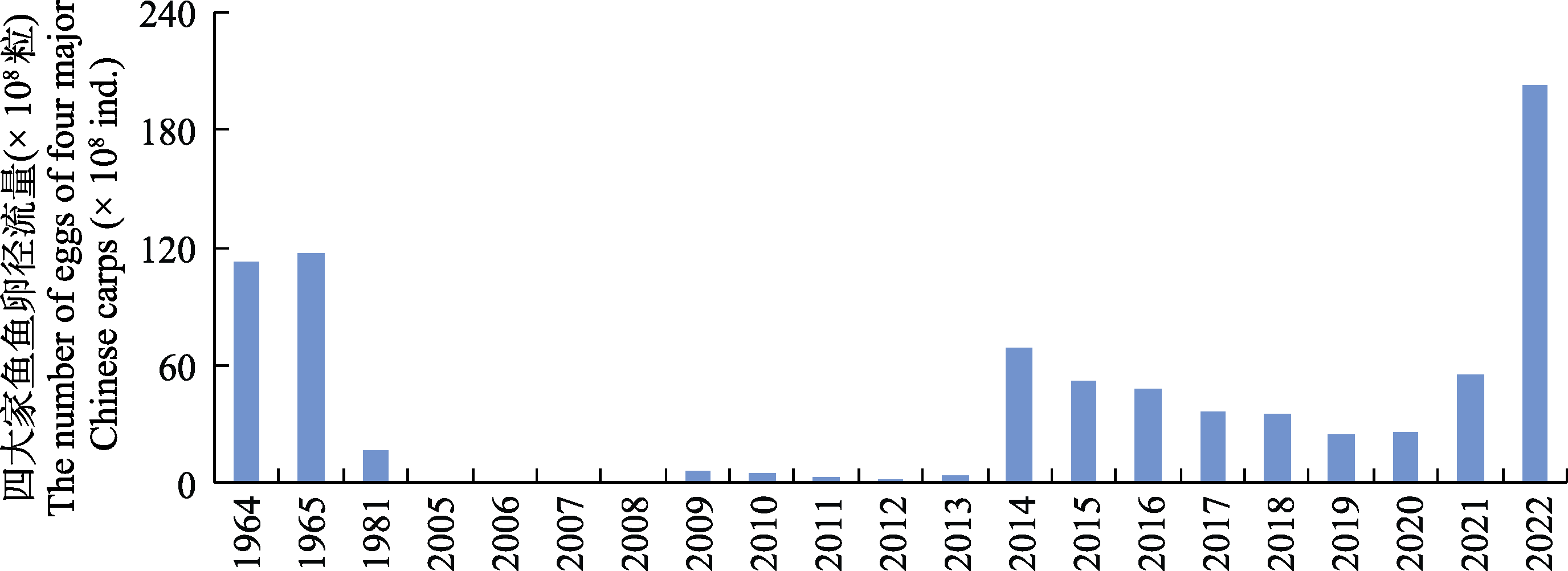
图7 1964-2022年长江中游宜昌江段四大家鱼产卵规模变化。数据来源于中国科学院水生生物研究所监测数据、长江四大家鱼产卵场调查队(1982)和易伯鲁等(1988)。
Fig. 7 Changes in egg abundance of four major Chinese carps in the Yichang reach from 1964 to 2022. The data sourced from the monitoring data of the Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Survey Team of Spawning Grounds of Domestic Fishes in Chanjiang River et al (1982) and Yi et al (1988).
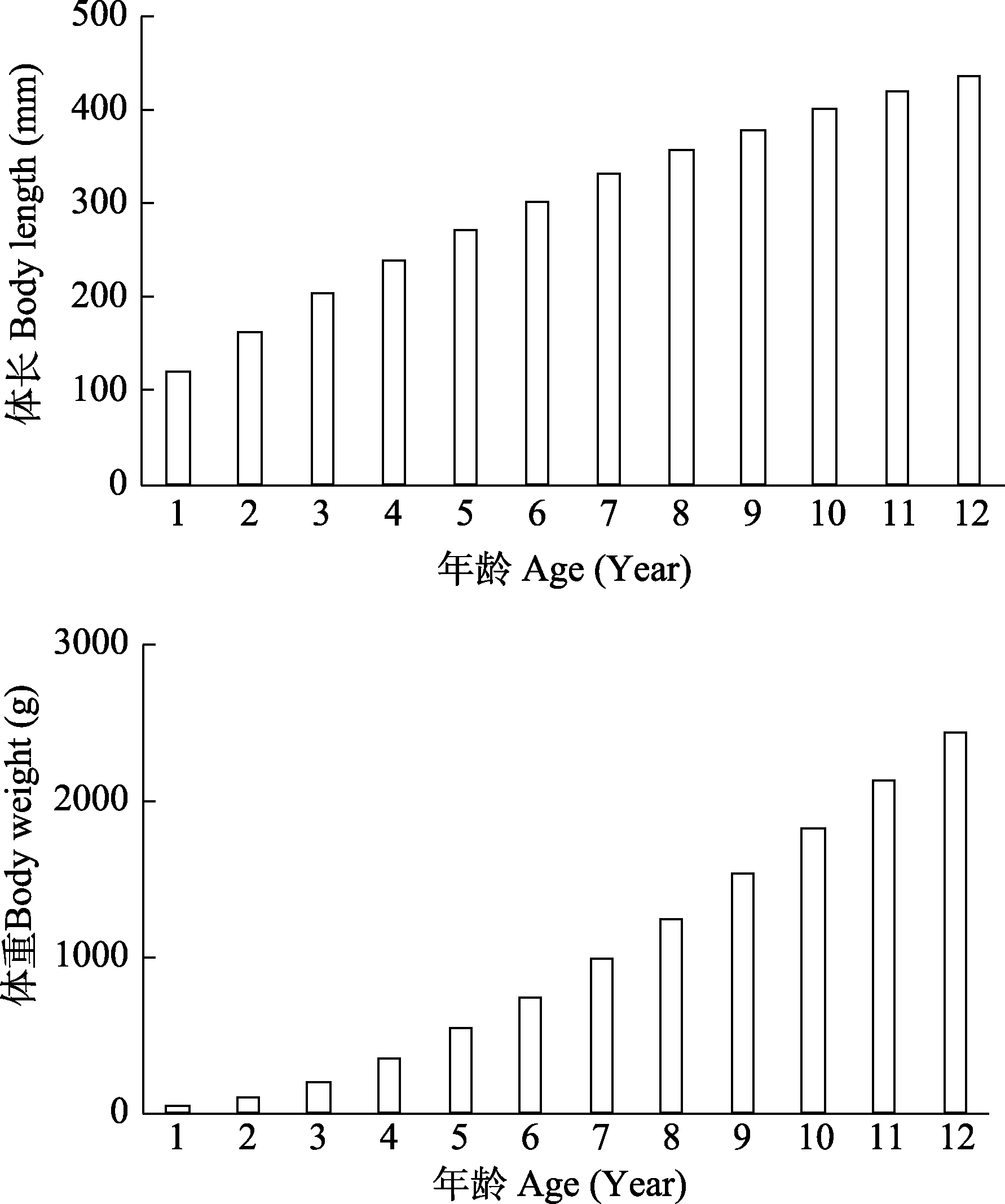
图8 2014-2017年赤水河长江上游特有鱼类岩原鲤的生长特征。改编自刘焕章等(2023)。
Fig. 8 Growth characteristics based on the von Bertalanffy growth curve estimated by standard length at age observed from scales of rock carp Procypris rabaudi from 2014 to 2017. Adapted from Liu et al (2023).
| [1] | Cao L, Shao WH, Yi WJ, Zhang E (2023) A review of conservation status of freshwater fish diversity in China. Journal of Fish Biology, doi: 10.1111/jfb.15606. |
| [2] | Cao WX, Chang JB, Qiao Y, Duan ZH (2007) Fish Resources of Early Life History Stages in Yangtze River. China Water Power Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 曹文宣, 常剑波, 乔晔, 段中华 (2007) 长江鱼类早期资源. 中国水利水电出版社, 北京.] | |
| [3] |
Carey MP, Wahl DH (2011) Determining the mechanism by which fish diversity influences production. Oecologia, 167, 189-198.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Chang JB, Cao WX (1999) History and prospect of conservation on Chinese sturgeon in the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 23, 712-720. (in Chinese) |
| [常剑波, 曹文宣 (1999) 中华鲟物种保护的历史与前景. 水生生物学报, 23, 712-720.] | |
| [5] | Chang T, Duan ZH, Li MZ (2021) Dynamic of fish eggs assemblage in the middle Yangtze River after the impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 30, 137-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [常涛, 段中华, 黎明政 (2021) 三峡水库蓄水后长江中游宜昌江段鱼类早期资源群聚动态. 长江流域资源与环境, 30, 137-146.] | |
| [6] |
Chang T, Gao X, Danley PD, Lin PC, Li MZ, Liu HZ (2017a) Longitudinal and temporal water temperature patterns in the Yangtze River and its influence on spawning of the Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis Gray 1835). River Research and Applications, 33, 1445-1451.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Chang T, Gao X, Liu HZ (2021) Potential hydrological regime requirements for spawning success of the Chinese sturgeon Acipenser sinensis in its present spawning ground of the Yangtze River. Ecohydrology, 14, e2339. |
| [8] |
Chang T, Lin PC, Gao X, Liu F, Duan ZH, Liu HZ (2017b) Using adaptive resolution imaging sonar to investigate Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis Gray, 1835) behaviour on its only spawning ground in the Yangtze River. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 33, 681-688.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Chen C, Li MZ, Gao X, Jiang W, Liu HZ, Duan ZH, Cao WX (2020) The status of the early-stage fish resources and hydrologic influencing conditions in the Yichang section in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 44, 1055-1063. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈诚, 黎明政, 高欣, 姜伟, 刘焕章, 段中华, 曹文宣 (2020) 长江中游宜昌江段鱼类早期资源现状及水文影响条件. 水生生物学报, 44, 1055-1063.] | |
| [10] | Froese R, Pauly D (2023) FishBase. World Wide Web (Electronic Publication). https://www.fishbase.org. (accessed on 2023-11-08) . |
| [11] |
Gao X, Fujiwara M, Winemiller KO, Lin PC, Li MZ, Liu HZ (2019) Regime shift in fish assemblage structure in the Yangtze River following construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Scientific Reports, 9, 4212.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Gao X, Fujiwara M, Zhang WW, Lin PC, Liu HZ (2022) The impact of dams on the population viability of a migratory fish in the Yangtze River, China. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 32, 1509-1519.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Gao X, Li MZ, Lin PC, Duan ZH, Liu HZ (2013) Environmental cues for natural reproduction of the Chinese sturgeon, Acipenser sinensis Gray, 1835, in the Yangtze River, China. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 29, 1389-1394.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Gao X, Lin PC, Chang T, Liu HZ (2021) Ecological and environmental assessment index in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River based on the spawning population size of Chinese sturgeon. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 45, 1396-1399. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高欣, 林鹏程, 常涛, 刘焕章 (2021) 基于中华鲟繁殖群体数量的长江中、下游生态环境考核指标. 水生生物学报, 45, 1396-1399.] | |
| [15] |
Gao X, Lin PC, Li MZ, Duan ZH, Liu HZ (2014) Effects of water temperature and discharge on natural reproduction time of the Chinese sturgeon, Acipenser sinensis, in the Yangtze River, China and impacts of the impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Zoological Science, 31, 274-278.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Gao X, Lin PC, Li MZ, Duan ZH, Liu HZ (2016) Impact of the Three Gorges Dam on the spawning stock and natural reproduction of Chinese sturgeon in Changjiang River, China. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 34, 894-901.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Gao X, Wang JW, Brosse S (2009) Threatened fishes of the world: Acipenser sinensis Gray, 1834 (Acipenseriformes: Acipenseridae). Environmental Biology of Fishes, 84, 183-184.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Gao X, Zeng Y, Wang JW, Liu HZ (2010) Immediate impacts of the second impoundment on fish communities in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 87, 163-173.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Guan XH, Cao WX (2007) Study on the hatch date and growth of juvenile grass carp from middle reaches of the Yangtze River using daily increment technology. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 31, 18-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [管兴华, 曹文宣 (2007) 利用耳石日轮技术研究长江中游草鱼幼鱼的孵化期及生长. 水生生物学报, 31, 18-23.] | |
| [20] | Jiang W (2009) Studies on Fish Early Resources in the Main Stream of State-level Natural Protection Area for Rare and Endemic Fishes in the Upper Yangtze River. PhD dissertation, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜伟 (2009) 长江上游珍稀特有鱼类国家级自然保护区干流江段鱼类早期资源研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院水生生物研究所, 武汉.] | |
| [21] | Li GG, Feng CG, Tang YT, Zhang RY, Zhao K (2017) Survey of native fish resources in inland river system in Xinjiang. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 52, 22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李国刚, 冯晨光, 汤永涛, 张仁意, 赵凯 (2017) 新疆内陆河土著鱼类资源调查. 甘肃农业大学学报, 52, 22-27.] | |
| [22] |
Li MZ, Duan ZH, Gao X, Cao WX, Liu HZ (2016) Impact of the Three Gorges Dam on reproduction of four major Chinese carps species in the middle reaches of the Changjiang River. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 34, 885-893.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Li MZ, Duan ZH, Jiang W, Liu HZ (2011) Preliminary analysis on the diel drifting behavior of fish eggs and larvae in different sections of main stream of the Yangtze River. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 20, 957-962. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黎明政, 段中华, 姜伟, 刘焕章 (2011) 长江干流不同江段鱼卵及仔鱼漂流特征昼夜变化的初步分析. 长江流域资源与环境, 20, 957-962.] | |
| [24] |
Li MZ, Gao X, Yang SR, Duan ZH, Cao WX, Liu HZ (2013) Effects of environmental factors on natural reproduction of the four major Chinese carps in the Yangtze River, China. Zoological Science, 30, 296-303.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Li MZ, Jiang W, Gao X, Duan ZH, Liu HZ (2010) Status quo of early life history stages at Wuxue cross-section of the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 34, 1211-1217. (in Chinese) |
| [黎明政, 姜伟, 高欣, 段中华, 刘焕章 (2010) 长江武穴江段鱼类早期资源现状. 水生生物学报, 34, 1211-1217.] | |
| [26] | Li WJ, Wang JW, Xie CX, Tan DQ (2007a) Age structure and growth characteristics of Megalobrama pellegrini—An endemic fish living only in upper reaches of Yangtze River. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 14, 215-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李文静, 王剑伟, 谢从新, 谭德清 (2007a) 厚颌鲂的年龄结构及生长特性. 中国水产科学, 14, 215-222.] | |
| [27] | Li WJ, Wang JW, Xie CX, Tan DQ (2007b) Reproductive biology and spawning habitats of Megalobrama pellegrini an endemic fish in upper-reaches of Yangtze River basin. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27, 1917-1925. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李文静, 王剑伟, 谢从新, 谭德清 (2007b) 厚颌鲂(Megalobrama pellegrini)的繁殖生物学特征. 生态学报, 27, 1917-1925.] | |
| [28] |
Lin PC, Gao X, Liu F, Li MZ, Liu HZ (2019) Long-term monitoring revealed fish assemblage zonation in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 37, 1258-1267.
DOI |
| [29] | Lin PC, Liu F, Li MZ, Gao X, Liu HZ (2018) Spatial pattern of fish assemblages along the river-reservoir gradient caused by the Three Gorge Reservoir (TGD). Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 42, 1124-1134. |
| [30] |
Liu CC, Gao X, Wang HS, Liu HZ, Cao WX, Danley PD (2013) Reproductive characteristics of Ancherythroculter nigrocauda, an endemic fish in the upper Yangtze River, China. Fisheries Science, 79, 799-806.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Liu F, Dan SG, Wang JW, Cao WX (2012) Feeding habits of Coreius guichenoti (Sauvage et Dabry) in the Upper Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 36, 1081-1086. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [刘飞, 但胜国, 王剑伟, 曹文宣 (2012) 长江上游圆口铜鱼的食性分析. 水生生物学报, 36, 1081-1086.] | |
| [32] |
Liu F, Wang J, Zhang FB, Liu HZ, Wang JW (2020) Spatial organisation of fish assemblages in the Chishui River, the last free-flowing tributary of the upper Yangtze River, China. Ecology of Freshwater Fish, 30, 48-60.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Liu F, Wang X, Wang MR, Liu HZ, Wang JW (2019) Diet partitioning and trophic guild structure of fish assemblages in Chishui River, the last undammed tributary of the Upper Yangtze River, China. River Research and Applications, 35, 1530-1539.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Liu F, Wang ZX, Xia ZJ, Wang JW, Liu HZ (2023) Changes in fish resources 5 years after implementation of the 10-year fishing ban in the Chishui River, the first river with a complete fishing ban in the Yangtze River Basin. Ecological Processes, 12, 51. |
| [35] | Liu F, Wu JM, Wang JW (2011) Growth and reproductive characteristics of Ancherythroculter kurematsui Kimura. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 35, 586-595. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘飞, 吴金明, 王剑伟 (2011) 高体近红鲌的生长与繁殖. 水生生物学报, 35, 586-595.] | |
| [36] |
Liu F, Yu FD, Xia ZJ, Qin Q, Xu CS, Wang JW, Liu HZ (2021) Changes in fish assemblages following the implementation of a complete fishing closure in the Chishui River. Fisheries Research, 243, 106099.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Liu HZ, Liu F, Chen YB (2023) A Study on the Biology of Fish in Chishui River. China Three Gorges Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 刘焕章, 刘飞, 陈永柏 (2023) 赤水河鱼类生物学研究. 中国三峡出版社, 北京.] | |
| [38] |
Liu HZ, Yang JX, Liu SW, Gao X, Chen YS, Zhang CG, Zhao K, Li XH, Liu W (2016) Theory and methods on fish diversity monitoring with an introduction to the inland water fish diversity observation in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1227-1233. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘焕章, 杨君兴, 刘淑伟, 高欣, 陈宇顺, 张春光, 赵凯, 李新辉, 刘伟 (2016) 鱼类多样性监测的理论方法及中国内陆水体鱼类多样性监测. 生物多样性, 24, 1227-1233.]
DOI |
|
| [39] | Ministry of Water Resources, National Bureau of Statistics (2013) Bulletin of First National Census for Water. China Water Resources and Hydropower Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [水利部, 国家统计局 (2013) 第一次全国水利普查公报. 中国水利水电出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] | Mu HX (2014) Study on Fish Early Resources at the End of Three Gorges Reservoir and blow the Three Gorges Dam. PhD dissertation, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [母红霞 (2014) 长江三峡水库库尾江段及三峡坝下鱼类早期资源生态学研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院水生生物研究所, 武汉.] | |
| [41] | Mu HX, Sun BZ, Cao WX, Dan SG, Tan DQ (2011) Analysis on the feeding habits of Hemiculter tchangi. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 35, 373-378. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [母红霞, 孙宝柱, 曹文宣, 但胜国, 谭德清 (2011) 张氏䱗的食性分析. 水生生物学报, 35, 373-378.] | |
| [42] | Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2023) Chinese Lake Ecological Environment Series: Research Report on the Ecological Environment of Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所 (2023) 中国湖泊生态环境丛书: 中国湖泊生态环境研究报告. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] | Pimm SL, Jenkins CN, Abell R, Brooks TM, Gittleman JL, Joppa LN, Raven PH, Roberts CM, Sexton JO (2014) The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science, 344, 1246752. |
| [44] |
Radinger J, Britton JR, Carlson SM, Magurran AE, Alcaraz-Hernández JD, Almodóvar A, Benejam L, Fernández-Delgado C, Nicola GG, Oliva-Paterna FJ, Torralva M, García-Berthou E (2019) Effective monitoring of freshwater fish. Fish and Fisheries, 20, 729-747.
DOI |
| [45] | Sun BZ, Li J, Dan SG, Tan DQ (2010a) Age structure and growth characteristics of Hemiculter tchangi Fang. Freshwater Fisheries, 40(2), 3-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙宝柱, 李晋, 但胜国, 谭德清 (2010a) 张氏䱗的年龄结构及生长特性. 淡水渔业, 40(2), 3-8.] | |
| [46] | Sun BZ, Li J, Dan SG, Tan DQ (2010b) Studies on the reproductive biology of Hemiculter tchangi Fang. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 34, 998-1003. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙宝柱, 李晋, 但胜国, 谭德清 (2010b) 张氏䱗的繁殖生物学特性. 水生生物学报, 34, 998-1003.] | |
| [47] | Survey Team of Spawning Grounds of Domestic Fishes in Chanjiang River (1982) A survey on the spawning grounds of the “four famous Chinese carps” in the Changjiang River after dammed by the key water control project at Gezhouba. Journal of Fisheries of China, 6, 287-305. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 长江四大家鱼产卵场调查队 (1982) 葛洲坝水利枢纽工程截流后长江四大家鱼产卵场调查. 水产学报, 6(4), 287-305.] | |
| [48] | Tian F, Liu SJ, Shi JQ, Qi HF, Zhao K, Xie BS (2019) Transcriptomic profiling reveals molecular regulation of seasonal reproduction in Tibetan highland fish, Gymnocypris przewalskii. BMC Genomics, 20, 2. |
| [49] |
Tittensor DP, Walpole M, Hill SLL, Boyce DG, Britten GL, Burgess ND, Butchart SHM, Leadley PW, Regan EC, Alkemade R, Baumung R, Bellard C, Bouwman L, Bowles-Newark NJ, Chenery AM, Cheung WWL, Christensen V, Cooper HD, Crowther AR, Dixon MJR, Galli A, Gaveau V, Gregory RD, Gutierrez NL, Hirsch TL, Höft R, Januchowski-Hartley SR, Karmann M, Krug CB, Leverington FJ, Loh J, Lojenga RK, Malsch K, Marques A, Morgan DHW, Mumby PJ, Newbold T, Noonan-Mooney K, Pagad SN, Parks BC, Pereira HM, Robertson T, Rondinini C, Santini L, Scharlemann JPW, Schindler S, Sumaila UR, Teh LSL, van Kolck J, Visconti P, Ye YM (2014) A mid-term analysis of progress toward international biodiversity targets. Science, 346, 241-244.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Topor ZM, Rasher DB, Duffy JE, Brandl SJ (2019) Marine protected areas enhance coral reef functioning by promoting fish biodiversity. Conservation Letters, 12, e12638. |
| [51] |
Wang J, Liu F, Zhang X, Cao WX, Liu HZ, Gao X (2014) Reproductive biology of Chinese minnow Hemiculterella sauvagei Warpachowski, 1888 in the Chishui River, China. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 30, 314-321.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Wang J, Wang MR, Dan SG, Cao WX, Liu HZ (2012) Age and growth of Hemiculterella sauvagei from the Chishui River in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 31, 713-719. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王俊, 王美荣, 但胜国, 曹文宣, 刘焕章 (2012) 赤水河半䱗年龄与生长. 四川动物, 31, 713-719.] | |
| [53] |
Wang MR, Yang SR, Liu F, Li MZ, Dan SG, Liu HZ (2012) Age and growth of Rhinogobio cylindricus Günther in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 36, 262-269. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [王美荣, 杨少荣, 刘飞, 黎明政, 但胜国, 刘焕章 (2012) 长江上游圆筒吻鮈年龄与生长的研究. 水生生物学报, 36, 262-269.] | |
| [54] |
Wang T, Fujiwara M, Gao X, Liu HZ (2019) Minimum viable population size and population growth rate of freshwater fishes and their relationships with life history traits. Scientific Reports, 9, 3612.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Wang T, Gao X, Wang J, Jakovlić I, Dan SG, Liu HZ (2015) Life history traits and implications for conservation of rock carp Procypris rabaudi Tchang, an endemic fish in the upper Yangtze River, China. Fisheries Science, 81, 515-523.
DOI URL |
| [56] | WWF World Wide Fund for Nature or World Wildlife Fund (2022) Living Planet Report 2022—Building A Nature-positive Society (eds Almond REA, Grooten M, Juffe BD, Petersen T), WWF, Gland, Switzerland. |
| [57] | Xin JF, Yang YF, Liu HZ (2010) Study on the age and growth of Rhinogobio ventralis in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 29, 352-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [辛建峰, 杨宇峰, 刘焕章 (2010) 长江上游长鳍吻鮈年龄与生长的研究. 四川动物, 29, 352-356.] | |
| [58] | Yang ML, Jiang WS, Wang WY, Pan XF, Kong DP, Han FH, Chen XY, Yang JX (2016) Fish assemblages and diversity in three tributaries of the Irrawaddy River in China: Changes, threats and conservation perspectives. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems, 417, 9. |
| [59] | Yang SR, Ma BS, Kong Y, Zhou C, Liu HZ (2010) Growth features of juvenile Coreius guichenoti and its conservation in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 19(S2), 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨少荣, 马宝珊, 孔焰, 周灿, 刘焕章 (2010) 三峡库区木洞江段圆口铜鱼幼鱼的生长特征及资源保护. 长江流域资源与环境, 19(S2), 52-57.] | |
| [60] | Yi BL, Yu ZT, Liang ZS (1988) Gezhouba Water Control Project and Four Famous Fishes in Yangtze River. Hubei Science and Technology Press, Wuhan. (in Chinese) |
| [易伯鲁, 余志堂, 梁秩燊 (1988) 葛洲坝水利枢纽与长江四大家鱼. 湖北科学技术出版社, 武汉.] | |
| [61] |
Yu D, Gao X, Shen ZY, Fujiwara M, Yang P, Chang T, Zhang FT, Wu XH, Duan ZH, Liu HZ (2023) Novel insights into the reproductive strategies of wild Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) populations based on the kinship analysis. Water Biology and Security, 2, 100134.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Yu D, Shen ZY, Chang T, Li S, Liu HZ (2021) Using environmental DNA methods to improve detectability in an endangered sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) monitoring program. BMC Ecology and Evolution, 21, 216.
DOI |
| [63] |
Zhang C, Fujiwara M, Pawluk M, Liu HZ, Cao WX, Gao X (2020) Changes in taxonomic and functional diversity of fish communities after catastrophic habitat alteration caused by construction of Three Gorges Dam. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 5829-5839.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Zhang C, Liu F, Liu HZ, Wang CL, Lin PC, Gao X (2022) Temporal changes in taxonomic and functional diversity of fish assemblages in the upper Yangtze River after impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 875789.
DOI URL |
| [65] | Zhang CG, Zhao YH (2016) Species and Distribution of Inland Fish in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春光, 赵亚辉 (2016) 中国内陆水体鱼类与物种分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [66] | Zhang E, Cao WX (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity·Vertebrates (Vol. Ⅴ):Freshwater Fishes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [张鹗, 曹文宣 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录·脊椎动物(第五卷): 淡水鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [67] |
Zhang FB, Liu F, Qin Q, Liu HZ, Cao WX, Gao X (2018) Diet composition and trophic guild structure of fish assemblage in headwaters of the Chishui River, a tributary of the upper Yangtze River, China. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 101, 1235-1248.
DOI |
| [68] |
Zhao YH, Xing YC, Lü BB, Zhou CJ, Yang WB, Zhao K (2020) Species diversity and conservation of freshwater fishes in the Yellow River Basin. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1496-1510. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [赵亚辉, 邢迎春, 吕彬彬, 周传江, 杨文波, 赵凯 (2020) 黄河流域淡水鱼类多样性和保护. 生物多样性, 28, 1496-1510.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [6] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [7] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [8] | 易木荣, 卢萍, 彭勇, 汤勇, 许久恒, 尹浩萍, 张路杨, 翁晓东, 底明晓, 雷隽, 卢宸祺, 曹如君, 戴年华, 占德洋, 童媚, 楼智明, 丁永刚, 柴静, 车静. 北潦河金家水支流江西大鲵野外种群现状及栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [9] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [10] | 李沫潼, 何拓, 李薇, 廖菁, 曾岩. 从CITES的术语看野生动植物国际贸易监管规则[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24545-. |
| [11] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [12] | 刘志禹, 吉鑫, 隋国辉, 杨定, 李轩昆. 北京首都国际机场野牛草与杂草草坪无脊椎动物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [13] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [14] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [15] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()