



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 23364. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023364 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023364
收稿日期:2023-09-26
接受日期:2023-12-20
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2024-01-24
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Xiangzhang Wu1, Fumin Lei1, Yiyi Shan1, Jing Yu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-26
Accepted:2023-12-20
Online:2024-02-20
Published:2024-01-24
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要:
城市公园的生物多样性十分丰富, 在生物多样性保护方面具有重要价值。苔藓植物是公园生物多样性的重要组成成分, 但因其体型小、难以鉴定等, 容易被人们所忽略, 因此对其多样性的研究和保护也相对薄弱。本文基于文献资料和生态调查数据, 整合上海市中心城区和郊区共35个样点的苔藓植物名录, 应用聚类分析对公园进行分组, 比较了市区和郊区两个区域的苔藓植物相似性; 采用典范对应分析(CCA)及层次分割的方法, 定量研究环境因子与城市公园苔藓植物多样性分布格局的关系。结果表明, 35个公园共有苔藓植物34科74属164种, 包括苔类7科8属9种、藓类27科66属155种, 其中有12种中国特有种和4种近危种。根据聚类分析结果, 35个公园可划分为两组, 主要与人口密度、与市中心距离、与主干道距离及公园面积等因素有关。市区和郊区两个区域的科、属、种的Jaccard相似性系数分别为0.94、0.89和0.30, 表明两个区域的物种组成各有特点。层次分割结果显示, 环境因子对城市公园苔藓植物多样性分布格局的解释率从高到低分别为人口密度、公园年龄、与市中心距离、与主干道距离、森林覆盖率、湖泊覆盖率及公园面积。整体上, 上海城市公园苔藓植物物种多样性较高, 而且市区公园和郊区公园物种组成存在一定差异, 两个区域对于苔藓植物多样性保护都具有重要价值。本研究揭示了人口密度、与主干道距离和森林覆盖率等不同环境因子对城市公园苔藓植物多样性分布格局的影响, 有助于对城市苔藓植物多样性的全面认识, 促进城市生态系统及苔藓植物多样性的保护。
吴相獐, 雷富民, 单壹壹, 于晶 (2024) 上海城市公园苔藓植物多样性分布格局及其环境影响因子. 生物多样性, 32, 23364. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023364.
Xiangzhang Wu, Fumin Lei, Yiyi Shan, Jing Yu (2024) Distribution pattern of bryophyte diversity and environmental impact factors in urban parks of Shanghai. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23364. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023364.
| 优势科 Dominant families | 种数 No. of species | 物种比例 Proportion of species (%) | 优势属 Dominant genera | 种数 No. of species | 物种比例 Proportion of species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丛藓科 Pottiaceae | 32 | 19.5 | 青藓属 Brachythecium | 13 | 7.9 |
| 青藓科 Brachytheciaceae | 27 | 16.5 | 真藓属 Bryum | 10 | 6.1 |
| 真藓科 Bryaceae | 15 | 9.1 | 绢藓属 Entodon | 9 | 5.5 |
| 薄罗藓科 Leskeaceae | 14 | 8.5 | 丝瓜藓属 Pohlia | 7 | 4.3 |
| 提灯藓科 Mniaceae | 10 | 6.1 | 墙藓属 Tortula | 6 | 3.7 |
| 总计 Total | 98 | 59.8 | 总计 Total | 45 | 27.4 |
表1 上海城市公园苔藓植物优势科和优势属
Table 1 The dominant families and genera of bryophytes in Shanghai urban parks
| 优势科 Dominant families | 种数 No. of species | 物种比例 Proportion of species (%) | 优势属 Dominant genera | 种数 No. of species | 物种比例 Proportion of species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丛藓科 Pottiaceae | 32 | 19.5 | 青藓属 Brachythecium | 13 | 7.9 |
| 青藓科 Brachytheciaceae | 27 | 16.5 | 真藓属 Bryum | 10 | 6.1 |
| 真藓科 Bryaceae | 15 | 9.1 | 绢藓属 Entodon | 9 | 5.5 |
| 薄罗藓科 Leskeaceae | 14 | 8.5 | 丝瓜藓属 Pohlia | 7 | 4.3 |
| 提灯藓科 Mniaceae | 10 | 6.1 | 墙藓属 Tortula | 6 | 3.7 |
| 总计 Total | 98 | 59.8 | 总计 Total | 45 | 27.4 |
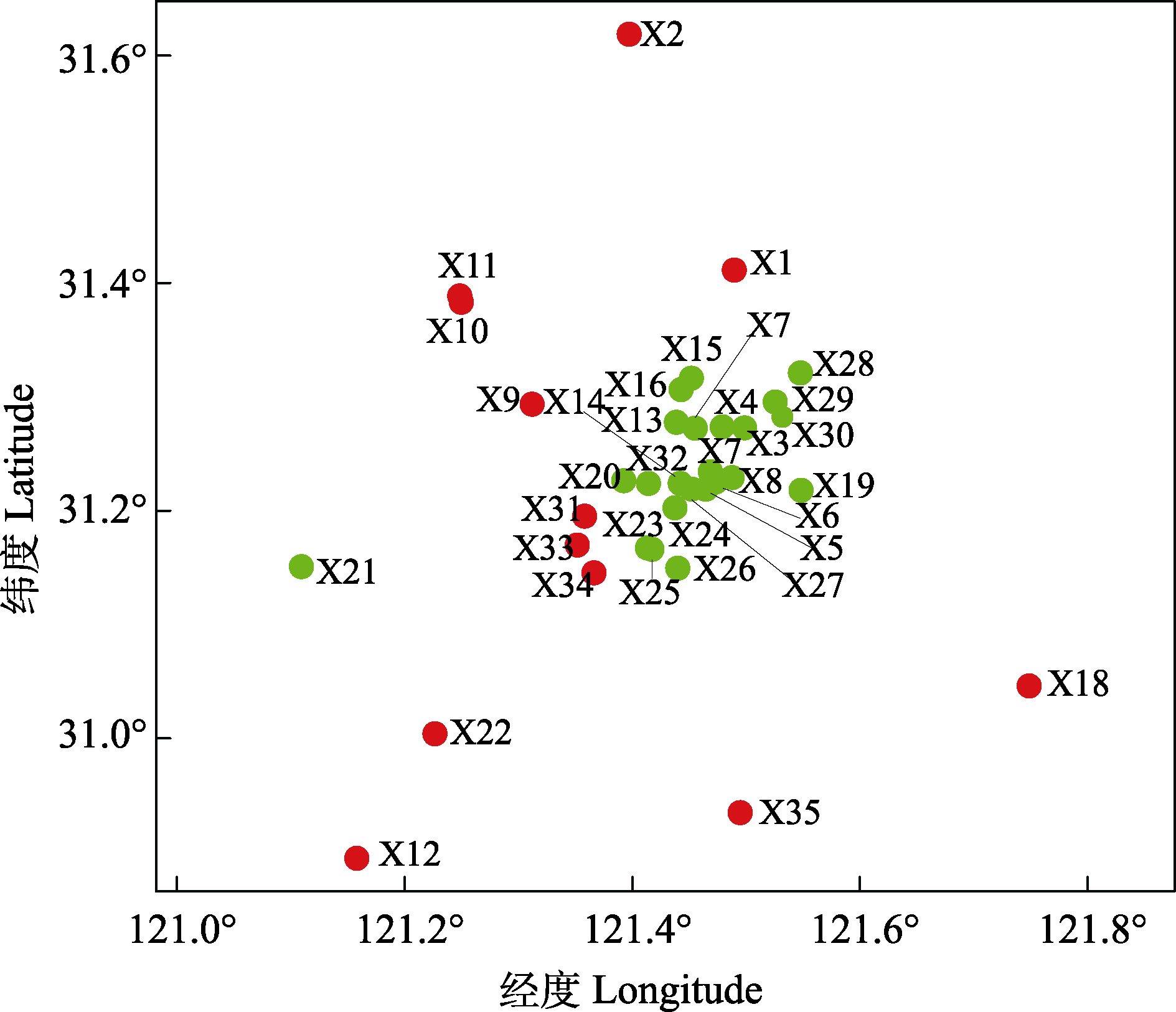
图2 上海市35个城市公园的聚类分析(基于物种有无矩阵)。红色圆点为组1,绿色圆点为组2。X1‒X35: 样点编号(详见附录1)。
Fig. 2 Cluster analysis of 35 urban parks in Shanghai based on the species matrix. The red dots are group 1, and the green dots are group 2; X1‒X35, Sample point code (See Appendix 1 for details).
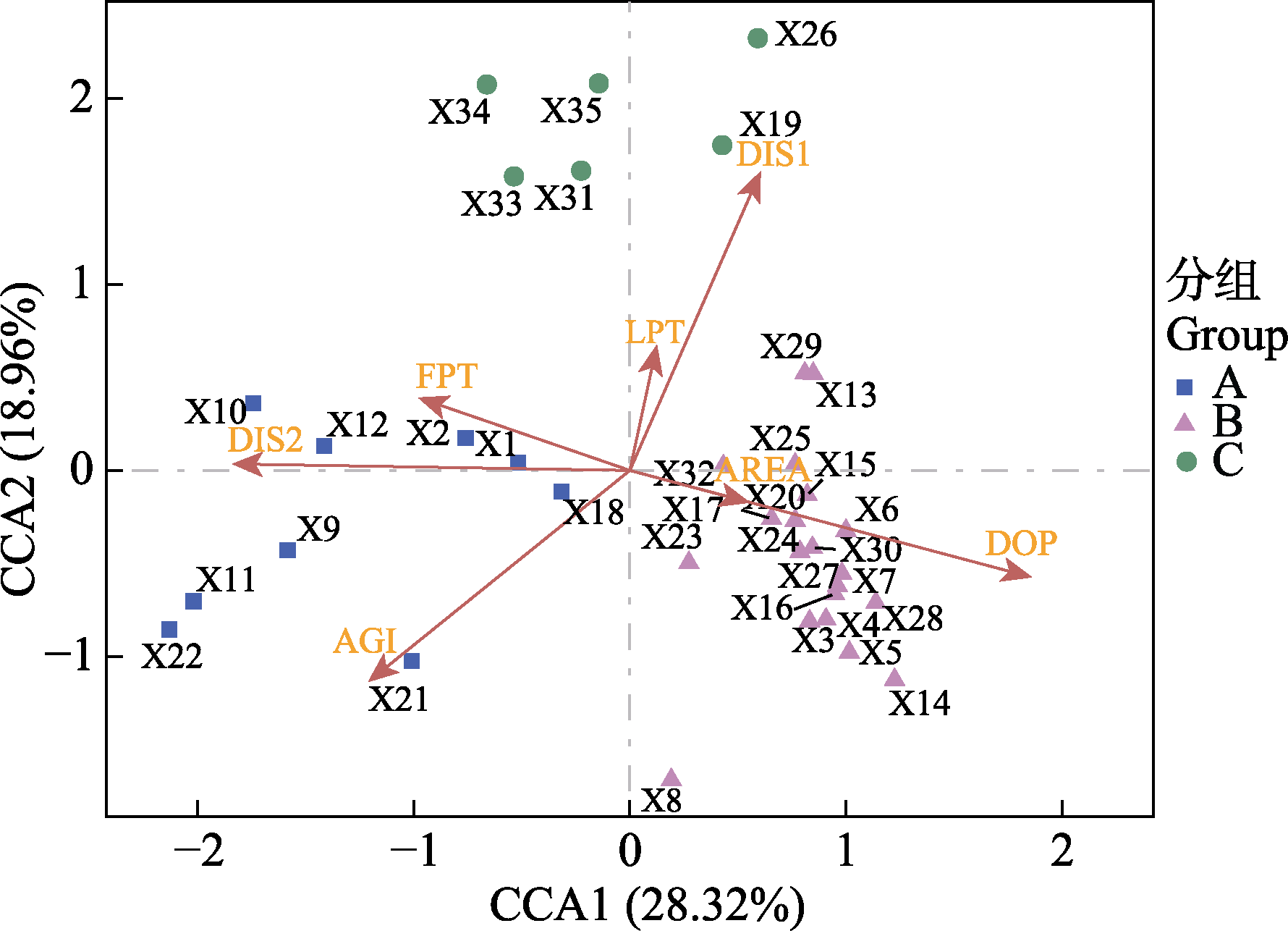
图3 样点和环境因子的典范对应分析(CCA)二维排序图。AGI: 公园年龄; AREA: 公园面积; DIS1: 与主干道距离; DIS2: 与市中心距离; DOP: 人口密度; FPT: 森林覆盖率; LPT: 湖泊覆盖率。X1‒X35: 样点编号(详见附录1)。
Fig. 3 CCA two-dimensional ordination diagram of sample points and environmental factors. AGI, Age of the park; AREA, Park area; DIS1, Distance to the primary highway; DIS2, Distance to the city center; DOP, Population density; FPT, Proportion of forest area to park area; LPT, Proportion of lake area to park area. X1‒X35, Sample points code (See Appendix 1 for details).
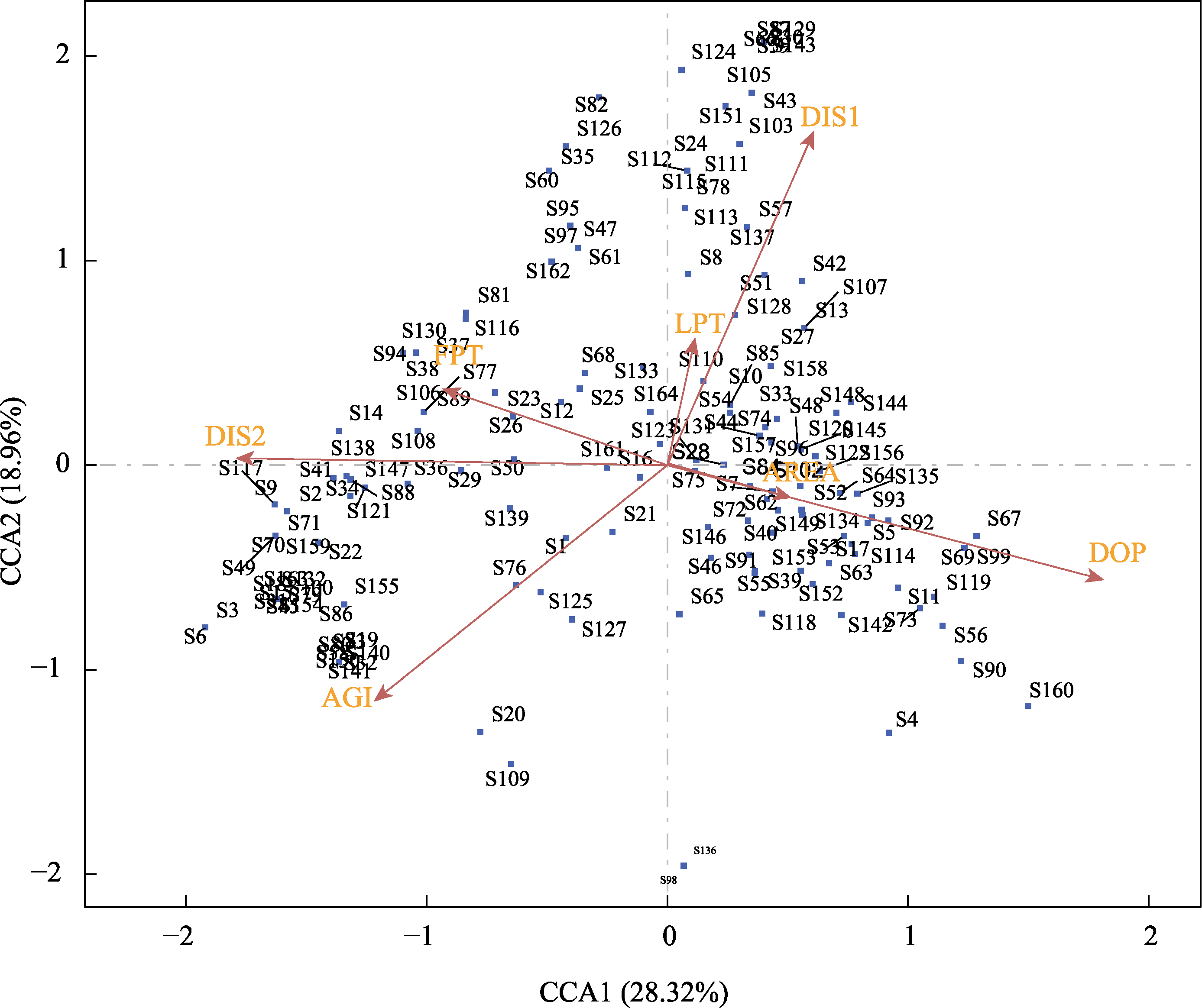
图4 物种和环境因子的典范对应分析(CCA)二维排序图。AGI: 公园年龄; AREA: 公园面积; DIS1: 与主干道距离; DIS2: 与市中心距离; DOP: 人口密度; FPT: 森林覆盖率; LPT: 湖泊覆盖率。S1‒S164: 物种编号(详见附录2)。
Fig. 4 CCA two-dimensional ordination diagram of species and environmental factors. AGI, Age of the park; AREA, Park area; DIS1, Distance to the primary highway; DIS2, Distance to the city center; DOP, Population density; FPT, Proportion of forest area to park area; LPT, Proportion of lake area to park area. S1‒S164, Species code (See Appendix 2 for details).
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 第一轴 Axis1 | 第二轴 Axis2 |
|---|---|---|
| 与主要干道距离 Distance to the primary highway (DIS1) | 0.59 | 1.58 |
| 公园年龄 Age of the park (AGI) | -1.18 | -1.12 |
| 公园面积 Park area (AREA) | 0.46 | -0.15 |
| 与市中心距离 Distance to the city center (DIS2) | -1.74 | 0.03 |
| 人口密度 Population density (DOP) | 1.76 | -0.54 |
| 森林占比 Proportion of forest area to park area (FPT) | -0.89 | 0.35 |
| 湖泊占比 Proportion of lake area to park area (LPT) | 0.10 | 0.56 |
表2 环境因子与典范对应分析(CCA)前两个排序轴的相关系数
Table 2 Correlation coefficients between environmental factors of the first two axes of CCA
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 第一轴 Axis1 | 第二轴 Axis2 |
|---|---|---|
| 与主要干道距离 Distance to the primary highway (DIS1) | 0.59 | 1.58 |
| 公园年龄 Age of the park (AGI) | -1.18 | -1.12 |
| 公园面积 Park area (AREA) | 0.46 | -0.15 |
| 与市中心距离 Distance to the city center (DIS2) | -1.74 | 0.03 |
| 人口密度 Population density (DOP) | 1.76 | -0.54 |
| 森林占比 Proportion of forest area to park area (FPT) | -0.89 | 0.35 |
| 湖泊占比 Proportion of lake area to park area (LPT) | 0.10 | 0.56 |
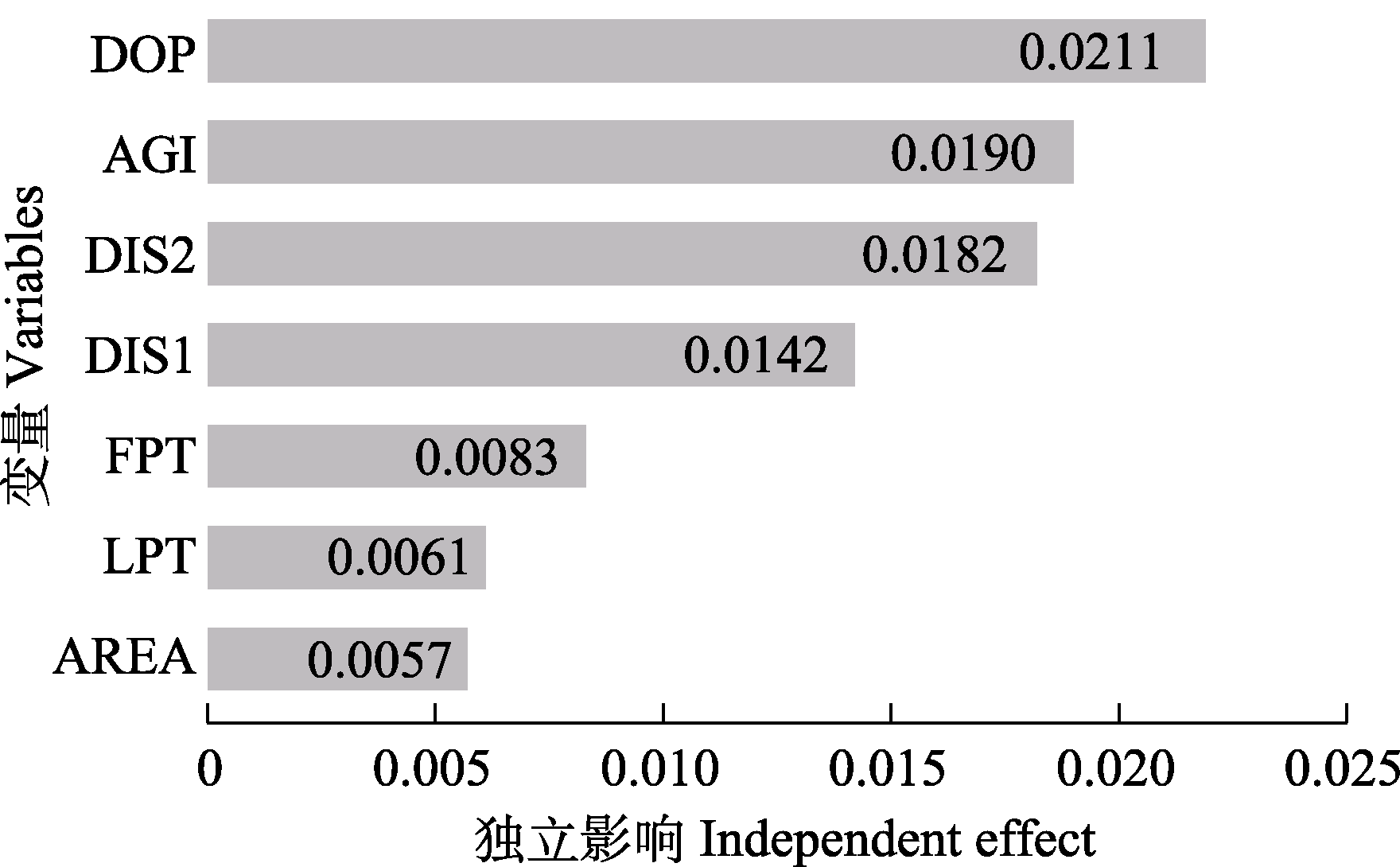
图5 7个环境因子的层次分割结果。AGI: 公园年龄; AREA: 公园面积; DIS1: 与主干道距离; DIS2: 与市中心距离; DOP: 人口密度; FPT: 森林覆盖率; LPT: 湖泊覆盖率。
Fig. 5 Hierarchical partitioning results of seven environmental factors. AGI, Age of the park; AREA, Park area; DIS1, Distance to the primary highway; DIS2, Distance to the city center; DOP, Population density; FPT, Proportion of forest area to park area; LPT, Proportion of lake area to park area.
| [1] | Bai XL, Zhao LM, Sun W, Sun WG (1998) A preliminary study on the species diversity, phytomass and ecological effect of bryophytes in Helan Mountain, China. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Neimongol, 29, 118-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [白学良, 赵连梅, 孙维, 孙卫国 (1998) 贺兰山苔藓植物物种多样性、生物量及生态学作用的研究. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 29, 118-124.] | |
| [2] |
Berisha S, Skudnik M, Vilhar U, Sabovljević M, Zavadlav S, Jeran Z (2017) Trace elements and nitrogen content in naturally growing moss Hypnum cupressiforme in urban and peri-urban forests of the Municipality of Ljubljana (Slovenia). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 4517-4527.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Cao T, Chen Y, Yu J, Song GY (2004) Distribution patterns of moss species in Shanghai city. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15, 1785-1791. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曹同, 陈怡, 于晶, 宋国元 (2004) 上海市地面藓类植物的分布格局分析. 应用生态学报, 15, 1785-1791.] | |
| [4] | Cao T, Zhao Q, Yu J, Song GY (2002) Biodiversity and distribution pattern of the bryophytes of the main parks in Shanghai. In: Proceedings of the Fifth National Symposium on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biodiversity in China, pp. 237-252. China Meteorological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [曹同, 赵青, 于晶, 宋国元 (2002) 上海市主要公园的苔藓植物多样性及其分布格局. 见: 第五届全国生物多样性保护与持续利用研讨会论文集, 237-252页. 气象出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Chamizo S, Serrano-Ortiz P, López-Ballesteros A, Sánchez-Cañete EP, Vicente-Vicente JL, Kowalski AS (2017) Net ecosystem CO2 exchange in an irrigated olive orchard of SE Spain: Influence of weed cover. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 239, 51-64. |
| [6] |
Chandra S, Chandra D, Barh A, Pankaj, Pandey RK, Sharma IP (2016) Bryophytes: Hoard of remedies, an ethno-medicinal review. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 7, 94-98.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Chang CR, Chen MC, Su MH (2021) Natural versus human drivers of plant diversity in city parks and the anthropogenic species-area hypotheses. Landscape and Urban Planning, 208, 104023.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Chen L, Wu YH, Li W, Gao Q (2009) Distribution patterns of floor bryophytes in Shenyang and the influence of environmental factors. Ecological Science, 28, 206-211. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈龙, 吴玉环, 李微, 高谦 (2009) 沈阳市地面苔藓植物的分布及对环境因子的响应. 生态科学, 28, 206-211.] | |
| [9] |
Chen X, Tu SW, Dai Z, Gao S, Wang YF, Xing SC, Wei BJ, Tang LY, Shi RP, Wang XR, Liu YY, Zhao DP, Tang X, Zhao MY, Wu HX, Qi XB, Zhang J, Li M, Wang J (2023) Bryophytes diversity of Tianmushan National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22649. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈星, 涂淑雯, 戴尊, 高爽, 王幼芳, 邢诗晨, 魏博嘉, 唐录艳, 师瑞萍, 王晓蕊, 刘永英, 赵东平, 唐霞, 赵明永, 吴晗星, 祁祥斌, 张健, 李敏, 王健 (2023) 浙江天目山国家级自然保护区苔藓植物多样性. 生物多样性, 31, 22649.]
DOI |
|
| [10] |
DeCandido R (2004) Recent changes in plant species diversity in urban Pelham Bay Park, 1947-1998. Biological Conservation, 120, 129-136.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Fahim A, Tan QM, Bhatti U, Ali Nawaz S, Kaleri AH (2022) Urban diversity impact on plant Species due to environmental conditions. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 31, 1617-1623.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Fan M, Wu YP, Hu RG, Jiang YB (2017) Diversity and distribution of bryophytes and their relationship with environmental factors in Wuhan. Plant Science Journal, 35, 825-834. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [范苗, 伍玉鹏, 胡荣桂, 姜炎彬 (2017) 武汉市城区苔藓植物多样性和分布及与环境因子的关系. 植物科学学报, 35, 825-834.] | |
| [13] | Flores PMC, Fernandez AI, Orozco KJU, Endino RMC, Garces JJC (2020) Ornamental plant diversity richness and composition in city parks: Studies in Metro Cebu Philippines. Environmental and Experimental Biology, 18, 183-192. |
| [14] |
Fudali E (2019) Distribution of epiphytic bryophytes in Wroclaw in relation to urban-use complexes. Biodiversity Research and Conservation, 54, 11-21.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Giordano S, Adamo P, Spagnuolo V, Tretiach M, Bargagli R (2013) Accumulation of airborne trace elements in mosses, lichens and synthetic materials exposed at urban monitoring stations: Towards a harmonisation of the moss-bag technique. Chemosphere, 90, 292-299.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
He XL, He KS, Hyvönen J (2016) Will bryophytes survive in a warming world? Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 19, 49-60.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Jiang YB, Fan M, Hu RG, Zhao JS, Wu YP (2018) Mosses are better than leaves of vascular plants in monitoring atmospheric heavy metal pollution in urban areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 1105.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Jiao YH, Ye J (2006) Utilization status of bryophyta in the garden city. Journal of Biology, 23(2), 48-49, 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [焦云红, 叶嘉 (2006) 苔藓植物在园林城市建设中的应用现状分析. 生物学杂志, 23(2), 48-49, 34.] | |
| [19] |
Jing L, Lu JG, Xia W (2018) Diversity of bryophytes in urban area of Nanjing, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29, 1797-1804. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[景蕾, 芦建国, 夏雯 (2018) 南京市主城区苔藓植物多样性及其与环境的关系. 应用生态学报, 29, 1797-1804.]
DOI |
|
| [20] |
Lai JS, Zou Y, Zhang JL, Peres-Neto PR (2022) Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 13, 782-788.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Lei JR, Song XQ, Chen ZZ (2017) Analysis on plant community diversity in Haikou city parks. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 37(1), 88-93, 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [雷金睿, 宋希强, 陈宗铸 (2017) 海口城市公园植物群落多样性研究. 西南林业大学学报, 37(1), 88-93, 103.] | |
| [22] | Li JF, Wang ZH, Zhang ZH (2013) Bryophyte diversity and the effect of soil formation along with water conservation in Karst rocky desertification region. Research of Environmental Sciences, 26, 759-764. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李军峰, 王智慧, 张朝晖 (2013) 喀斯特石漠化山区苔藓多样性及水土保持研究. 环境科学研究, 26, 759-764.] | |
| [23] |
Liu G, Wang XR (2022) Bryophyte diversity and environmental response in university campuses in Karst mountainous regions: A case study of Guizhou University. Subtropical Plant Science, 51, 198-206. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [刘果, 王秀荣 (2022) 喀斯特山地高校苔藓植物多样性及环境响应——以贵州大学为例. 亚热带植物科学, 51, 198-206.] | |
| [24] | Liu XC, Shao XM, Jiang YB, Sun Y, Hu WY (2010) Relationship between bryophytes distribution and environmental factors in urban Beijing. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 28, 171-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘欣超, 邵小明, 姜炎彬, 孙宇, 胡伟毅 (2010) 北京市区苔藓植物空间分布与环境关系的研究. 武汉植物学研究, 28, 171-178.] | |
| [25] | Liu Y, Cao T, Lou YX (2008a) Effect of environmental change on species diversity of bryophytes: A case study in Xujiahui (Zi ka Wei) area, Shanghai. Biodiversity Science, 16, 181-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘艳, 曹同, 娄玉霞 (2008a) 环境变化对苔藓植物物种多样性的影响: 以上海徐家汇地区为例. 生物多样性, 16, 181-184.] | |
| [26] | Liu Y, Cao T, Wang J, Cao Y (2008b) Relationships between distribution of soil-born bryophytes in urban area of Hangzhou and related ecological factors. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 19, 775-781. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘艳, 曹同, 王剑, 曹阳 (2008b) 杭州市区土生苔藓植物分布与生态因子的关系. 应用生态学报, 19, 775-781.] | |
| [27] | Liu Y, Pi CY, Tian S (2015) Relationships between characteristics of ground bryophyte communities and environmental factors in urban area of Chongqing, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26, 3145-3152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘艳, 皮春燕, 田尚 (2015) 重庆主城区地面苔藓植物群落特征及其与环境的关系. 应用生态学报, 26, 3145-3152.] | |
| [28] | Liu Y, Qiao GJ (2016) Water holding capacities of bryophytes under different habitats in Jin-Yun-Shan National Nature Reserve. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science), 33(4), 150-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘艳, 乔光军 (2016) 缙云山国家级自然保护区不同生境下苔藓植物持水能力研究. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 33(4), 150-153.] | |
| [29] |
Lloret F, González-Mancebo JM (2011) Altitudinal distribution patterns of bryophytes in the Canary Islands and vulnerability to climate change. Flora, 206, 769-781.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Lu JG, Jing L (2019) Biodiversity and characteristics of ground bryophytes in 11 parks of Nanjing. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 36, 486-493. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [芦建国, 景蕾 (2019) 南京市公园绿地苔藓植物多样性及特点. 浙江农林大学学报, 36, 486-493.] | |
| [31] | Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China and Chinese Academy of Sciences (2023) Released the Red List of Biodiversity in China: Higher Plants (2020). (in Chinese) |
| [生态环境部和中国科学院 (2023) 关于发布《中国生物多样性红色名录——高等植物卷(2020)》的公告.] https://www.mee.gov.cn/xgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/202305/t20230522_1030745.html. (accessed on 2023-05-18) | |
| [32] | Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2020) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R packages version 2.5-7. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan. (accessed on 2020-11-28) |
| [33] | Qin YF, Liu T, Cui X, Liu F, Zheng XM, Zhou LM (2017) Temporal and spatial distribution of trace elements in Haplocladium of urban parks in Shanghai. Environmental Chemistry, 36, 1785-1794. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [秦艺帆, 刘婷, 崔鑫, 刘飞, 郑祥民, 周立旻 (2017) 上海市公园绿地小羽藓中微量元素时空分布特征. 环境化学, 36, 1785-1794.] | |
| [34] | Rao Y, Bao WK, Yan XL (2010) Monitoring of tail gas from vehicles using mosses in the Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage Site in northern Sichuan, China. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 16, 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [饶瑶, 包维楷, 闫晓丽 (2010) 苔藓植物监测机动车尾气中元素排放量研究——以九寨沟世界自然遗产地原始林景点为例. 应用与环境生物学报, 16, 23-27.] | |
| [35] |
Sabovljević MS, Sabovljević AD, Ikram NKK, Peramuna A, Bae H, Simonsen HT (2016) Bryophytes—An emerging source for herbal remedies and chemical production. Plant Genetic Resources, 14, 314-327.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Sun SQ, Wu YH, Wang GX, Zhou J, Yu D, Bing HJ, Luo J (2013) Bryophyte species richness and composition along an altitudinal gradient in Gongga Mountain, China. PLoS ONE, 8, e58131. |
| [37] |
Tangney RS, Wilson JB, Mark AF (1990) Bryophyte island biogeography: A study in Lake Manapouri, New Zealand. Oikos, 59, 21.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Trujillo-González JM, Zapata-Muñoz YL, Torres-Mora MA, García-Navarro FJ, Jiménez-Ballesta R (2020) Assessment of urban environmental quality through the measurement of lead in bryophytes: Case study in a medium-sized city. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42, 3131-3139.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Virtanen R, Johnston AE, Crawley MJ, Edwards GR (2000) Bryophyte Biomass and Species Richness on the Park Grass Experiment, Rothamsted, UK. Plant Ecology, 151, 129-141.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Wang J, Cao T, Wang M, Wei HF (2008) Floristic analysis of bryophytes from urban area of Suzhou. Journal of Shanghai Normal University (Natural Sciences), 37(1), 105-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王剑, 曹同, 王敏, 韦海峰 (2008) 苏州市区苔藓植物区系分析. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 37(1), 105-110.] | |
| [41] | Wei PJ, Sun B, He XR, Liu C, Hu SK, Fei YJ (2019) Analysis on plant community diversity in Jingzhou city parks. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 47(3), 106-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏普杰, 孙兵, 贺心茹, 刘畅, 胡胜科, 费永俊 (2019) 荆州城市公园植物群落多样性研究. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 47(3), 106-113.] | |
| [42] |
Werner FA, Gradstein SR (2009) Diversity of dry forest epiphytes along a gradient of human disturbance in the tropical Andes. Journal of Vegetation Science, 20, 59-68.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Wu Q, Lu ZH, Li CN, Jiang W, Zhou YH, Gao SP, Zhou YH, Yu XF (2019) Research on the bryophytes’ diversity and microhabitat in Wenjiang Park of Sichuan Province. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 34, 458-465. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [伍青, 卢子豪, 李春浓, 蒋伟, 周亚辉, 高素萍, 周永红, 余小芳 (2019) 四川温江公园苔藓植物多样性及微生境调查研究. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 34, 458-465.] | |
| [44] | Xie JS, Cai LP, Huang RZ, Chen YX, Yang YS (2002) A study on N and P cycling in soil and water conservation forest composed of P. massoniana and shrubs. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 26(5), 27-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[谢锦升, 蔡丽平, 黄荣珍, 陈银秀, 杨玉盛 (2002) 水土保持乔灌混交林N、P养分循环的研究. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 26(5), 27-31.]
DOI |
|
| [45] |
Xing SC, Tang LY, Dai Z, Tu SW, Chen X, Zhang AZ, Li HQ, Peng T, Wang J (2022) Bryophyte diversity in Shitai County and Qingyang County, Anhui Province. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[邢诗晨, 唐录艳, 戴尊, 涂淑雯, 陈星, 张建行, 李宏庆, 彭涛, 王健 (2022) 安徽石台县与青阳县苔藓植物多样性. 生物多样性, 30, 21186.]
DOI |
|
| [46] | Zhang QF, Xu Y (2016) Approaches for the biodiversity conservation of urban forest. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 14(3), 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张庆费, 许源 (2016) 城市森林生物多样性保育途径探讨. 中国城市林业, 14(3), 1-5.] | |
| [47] |
Zhu RL, Ma XY, Cao C, Cao ZY (2022) Advances in research on bryophyte diversity in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22378. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[朱瑞良, 马晓英, 曹畅, 曹子寅 (2022) 中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22378.]
DOI |
|
| [48] | Zhuang Q, Zhou RL (2006) Ecological function of bryophytes and its application in gardens. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 20(3), 92-95. (in Chinese) |
| [庄强, 周瑞玲 (2006) 苔藓植物的生态功能及其在园林中的应用. 林业科技开发, 20(3), 92-95.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()