



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 23297. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023297 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023297
文诗嘉1,2( ), 邓敏学1,2(
), 邓敏学1,2( ), 吴丁2, 王志勇1, 任宗昕3,*(
), 吴丁2, 王志勇1, 任宗昕3,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-21
接受日期:2023-11-22
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-11-28
通讯作者:
*E-mail: renzongxin@mail.kib.ac.cn
基金资助:
Shijia Wen1,2( ), Minxue Deng1,2(
), Minxue Deng1,2( ), Ding Wu2, Zhiyong Wang1, Zongxin Ren3,*(
), Ding Wu2, Zhiyong Wang1, Zongxin Ren3,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-08-21
Accepted:2023-11-22
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-11-28
Contact:
*E-mail: renzongxin@mail.kib.ac.cn
摘要:
花蜜的分泌特征在种间、种内以及植株内不同花朵间的变异决定了花朵对访花动物的吸引和访花模式, 进而影响传粉效率和植物繁殖成功。然而, 我们对花蜜分泌特征变异性的认识还不够深入, 缺乏野外实验数据。研究选取龙胆科獐牙菜属(Swertia) 4种同域分布的植物, 即獐牙菜(S. bimaculata)、西南獐牙菜(S. cincta)、贵州獐牙菜(S. kouitchensis)和紫红獐牙菜(S. punicea)为研究对象, 开展花蜜特征及其变异性的研究。通过比较种内套袋24 h和自然状况下花朵的3个花蜜特征, 即花蜜体积、糖浓度和含糖量(重量)的异同, 以及同一植株不同花朵间花蜜特征的差异, 试图阐明花蜜特征在种间、种内植株间和个体内的变异性。结果显示獐牙菜属4种植物的花蜜特征有显著差异; 套袋24 h处理和自然状态花朵的花蜜特征大多有显著差异, 仅有獐牙菜和贵州獐牙菜的糖浓度在两种处理间差异不显著; 相邻两朵花的糖浓度都具有显著正相关, 然而, 花蜜体积和糖含量在相邻花朵间的相似性较低; 相邻两朵花花蜜特征的正相关在套袋处理花中高于自然状态, 显示自然状态下花蜜特征的高变异性。研究结果表明花蜜的变异性包括: (1)花蜜的种间差异可能与传粉昆虫类群有关; (2)同一植株相邻花朵间花蜜糖浓度显著相关, 表明花蜜体积和含糖量相互调节使得花蜜糖浓度保持在相似区间内; (3)花蜜特征在个体间和花朵间较高的变异性可促使传粉者在植株间访问, 从而提升植物繁殖成功率。
文诗嘉, 邓敏学, 吴丁, 王志勇, 任宗昕 (2024) 獐牙菜属四种植物花蜜特征的比较. 生物多样性, 32, 23297. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023297.
Shijia Wen, Minxue Deng, Ding Wu, Zhiyong Wang, Zongxin Ren (2024) Comparative floral nectar attributes in four Swertia species (Gentianaceae). Biodiversity Science, 32, 23297. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023297.
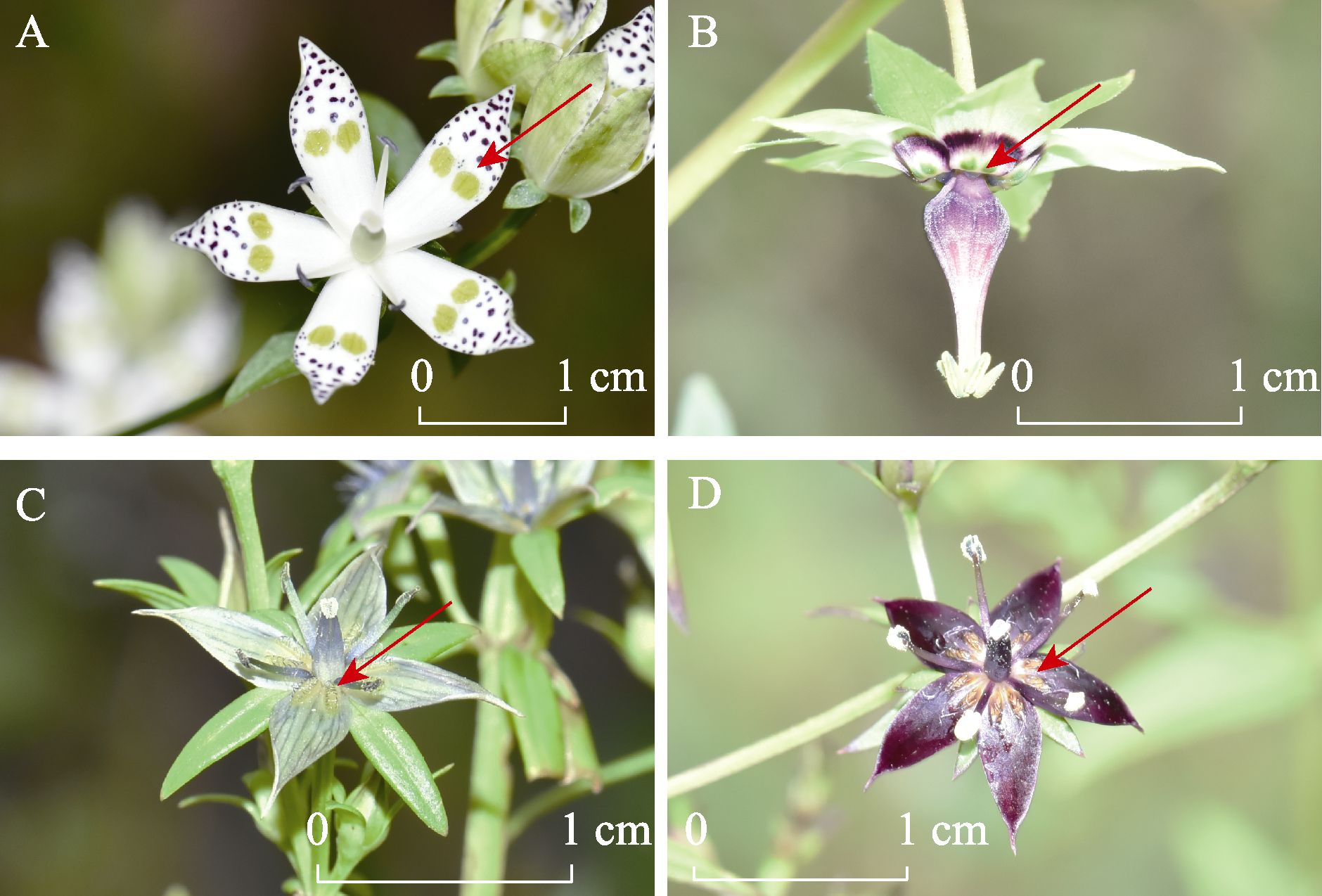
图1 4种獐牙菜属植物的花部特征。A: 獐牙菜; B: 西南獐牙菜; C: 贵州獐牙菜; D: 紫红獐牙菜。箭头所指为蜜腺。
Fig. 1 Floral characteristics of four species in the genus Swertia. The arrows indicate nectaries. A, Swertia bimaculata; B, S. cincta; C, S. kouitchensis; D, S. punicea.
| 种名 Species | 蜜腺特征 Floral nectaries | 花期 Flowering phenology | 生境 Habitats |
|---|---|---|---|
| 獐牙菜 S. bimaculata | 蜜腺斑点黄绿色、裸露于花冠裂片表面 Nectary spots yellow-green, exposed on the surface of corolla lobes | 9-11月 Sep. to Nov. | 林下、灌丛中 Under the woods and underbrush |
| 西南獐牙菜 S. cincta | 开口朝上的马蹄形腺窝, 位于花冠裂片基部 A horseshoe shaped nectary with an upward opening, located at the base of corolla lobes | 8-11月 Aug. to Nov. | 潮湿山坡、林下、灌丛中 Wet hillside, under the woods, and underbrush |
| 贵州獐牙菜 S. kouitchensis | 腺窝黄绿色, 具流苏覆盖 The nectaries are yellow-green and covered with tassels | 8-10月 Aug. to Oct. | 山坡草地、灌丛中 Hillside meadow and underbrush |
| 紫红獐牙菜 S. punicea | 腺窝紫红色, 具流苏覆盖 The nectaries are purple-red and covered with tassels | 9-11月 Sep. to Nov. | 林下、草地、灌丛中 Under the woods, grassland, and underbrush |
表1 獐牙菜属4种植物的蜜腺特征、花期和生境比较
Table 1 Floral nectaries, flowering phenology and habitats of four species in the genus Swertia
| 种名 Species | 蜜腺特征 Floral nectaries | 花期 Flowering phenology | 生境 Habitats |
|---|---|---|---|
| 獐牙菜 S. bimaculata | 蜜腺斑点黄绿色、裸露于花冠裂片表面 Nectary spots yellow-green, exposed on the surface of corolla lobes | 9-11月 Sep. to Nov. | 林下、灌丛中 Under the woods and underbrush |
| 西南獐牙菜 S. cincta | 开口朝上的马蹄形腺窝, 位于花冠裂片基部 A horseshoe shaped nectary with an upward opening, located at the base of corolla lobes | 8-11月 Aug. to Nov. | 潮湿山坡、林下、灌丛中 Wet hillside, under the woods, and underbrush |
| 贵州獐牙菜 S. kouitchensis | 腺窝黄绿色, 具流苏覆盖 The nectaries are yellow-green and covered with tassels | 8-10月 Aug. to Oct. | 山坡草地、灌丛中 Hillside meadow and underbrush |
| 紫红獐牙菜 S. punicea | 腺窝紫红色, 具流苏覆盖 The nectaries are purple-red and covered with tassels | 9-11月 Sep. to Nov. | 林下、草地、灌丛中 Under the woods, grassland, and underbrush |
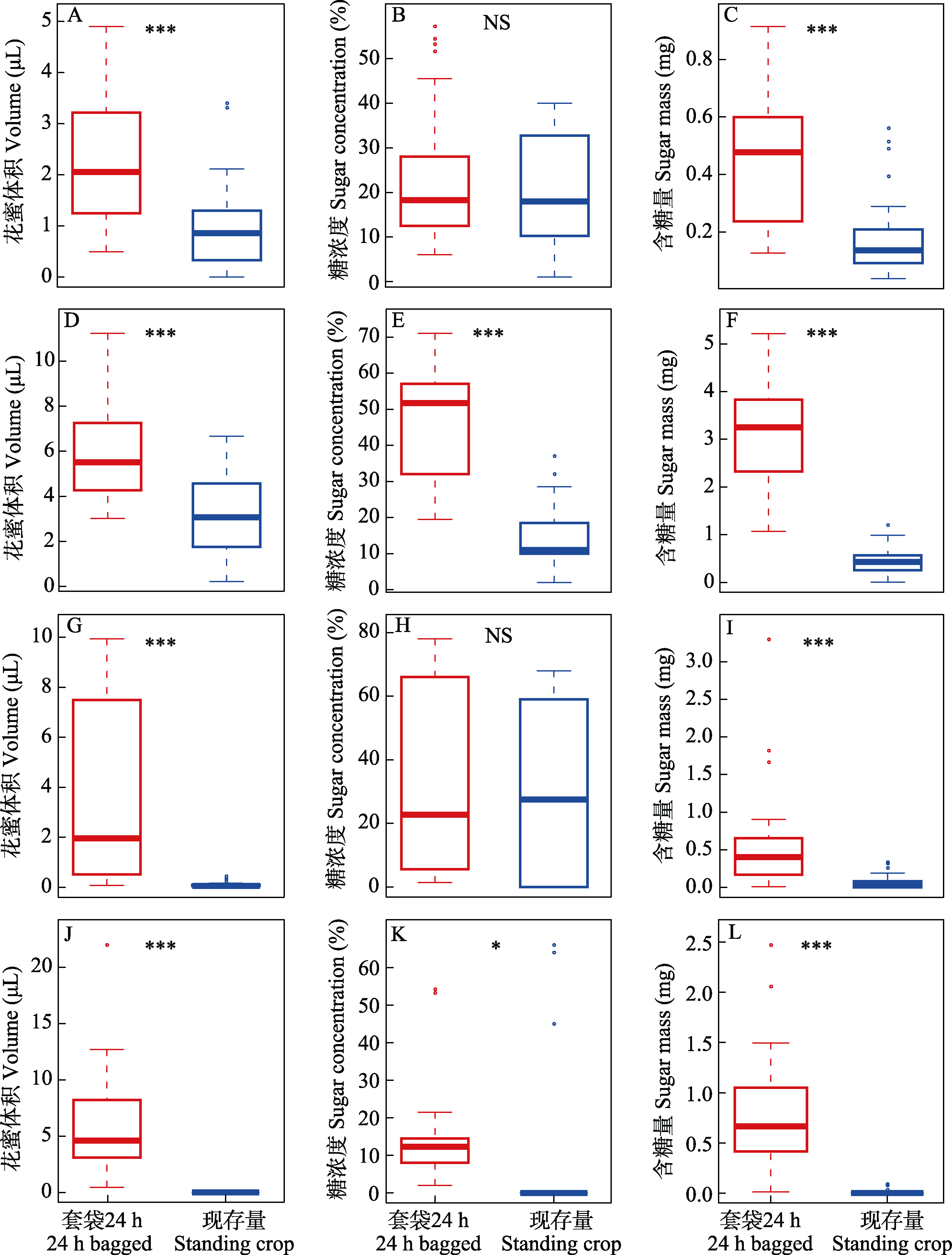
图2 獐牙菜属植物花朵套袋24 h花蜜储存量和自然状态现存量的比较。花蜜特征包括: 花蜜体积(μL)、糖浓度(%)、含糖量(mg)的方差分析。A-C: 獐牙菜; D-F: 西南獐牙菜; G-I: 贵州獐牙菜; J-L: 紫红獐牙菜。NS, P > 0.05; * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001。
Fig. 2 Comparison of floral nectar attributes (nectar volume, sugar concentration and sugar mass) for 24 h bagged flowers and flowers in natural conditions among four Swertia species. A-C, S. bimaculata; D-F, S. cincta; G-I, S. kouitchensis; J-L, S. punicea. NS, P > 0.05; * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
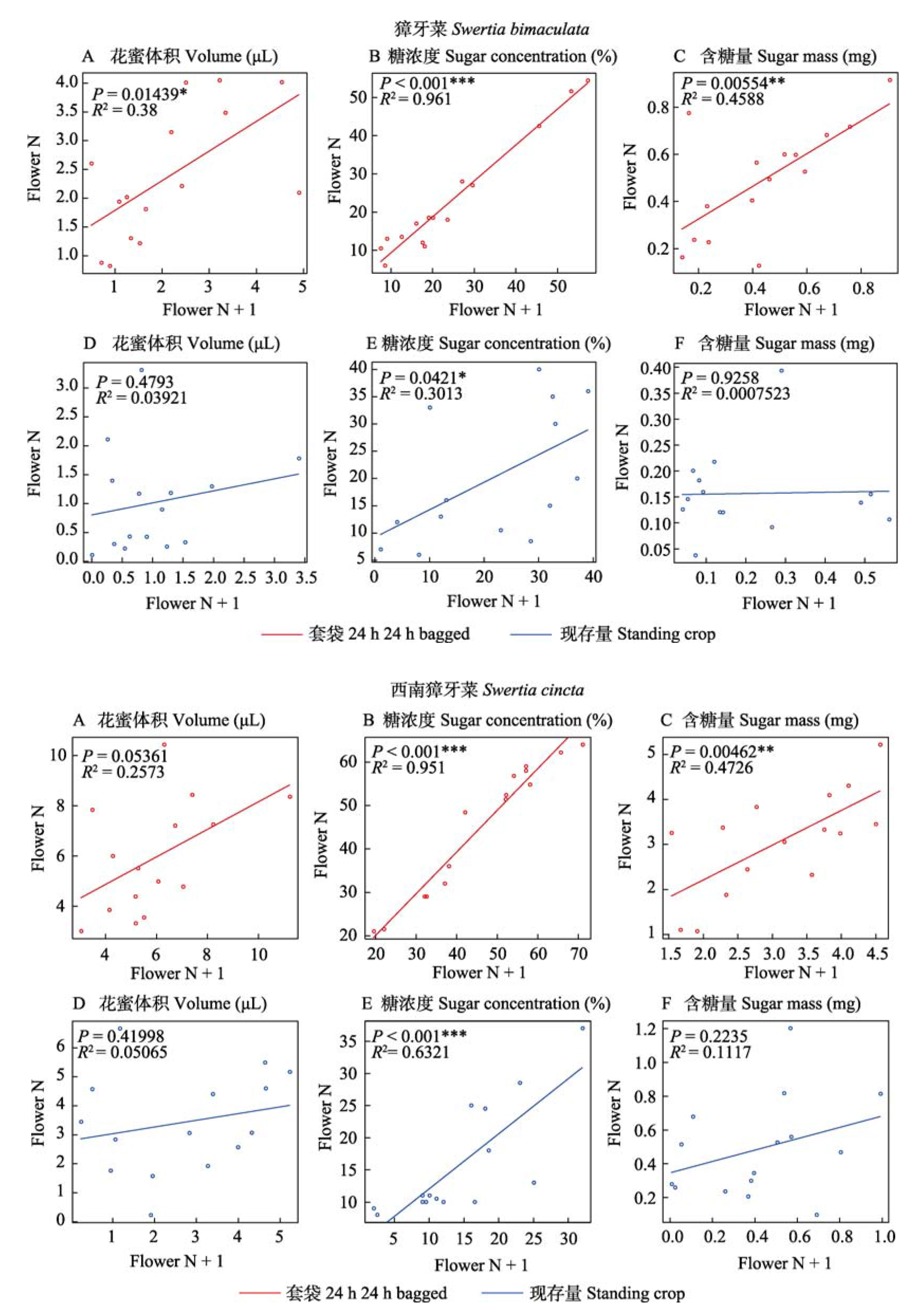
图3-4 獐牙菜(图3)、西南獐牙菜(图4)相邻两朵花花蜜特征(花蜜体积、糖浓度、含糖量)相关性的回归分析。A-C: 套袋24 h的储存量; D-F: 现存量。Flower N和Flower N + 1分别为同一株植物上不同的两朵花。* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001。
Fig. 3-4 Correlation of floral nectar attributes (nectar volume, sugar concentration and sugar mass) between two neighbored flowers in Swertia bimaculata (Fig. 3) and S. cincta (Fig. 4). A-C, Flowers bagged for 24 hours; D-F, Standing crops under the natural conditions. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
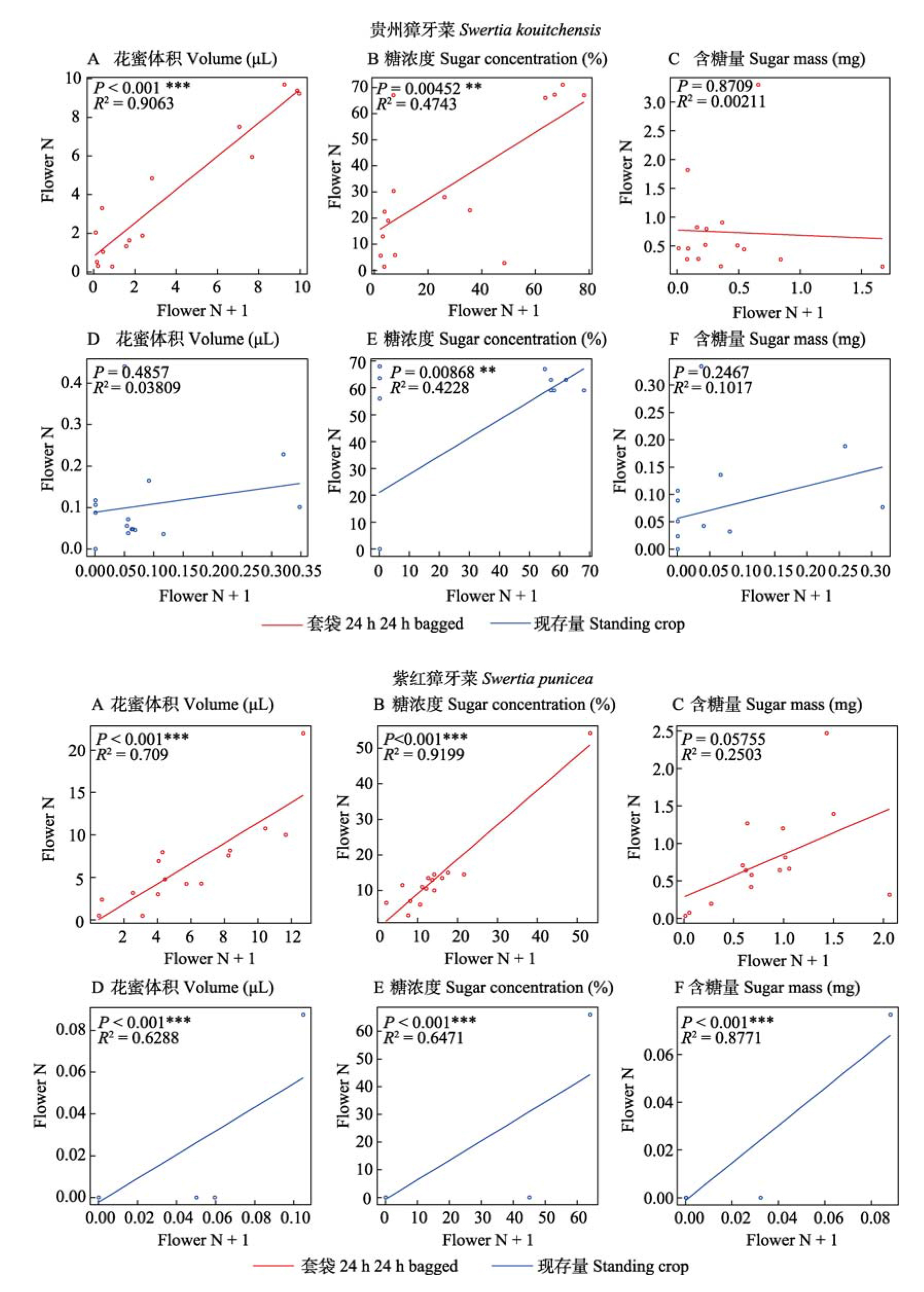
图5-6 贵州獐牙菜、紫红獐牙菜相邻两朵花花蜜特征(花蜜体积、糖浓度、含糖量)相关性的回归分析。A-C: 套袋24 h的储存量; D-F: 现存量。Flower N和Flower N + 1分别为同一株植物上不同的两朵花。* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001。
Fig. 5-6 Correlation of floral nectar attributes (nectar volume, sugar concentration and sugar mass) between two neighbored flowers in Swertia kouitchensis (Fig. 5) and S. punicea (Fig. 6). A-C, Flowers bagged for 24 hours; D-F, Standing crops under the natural conditions. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
| [1] |
Burquez A, Corbet SA (1991) Do flowers reabsorb nectar? Functional Ecology, 5, 369-379.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Liu CQ, Niu Y, Peng DL, Sun H (2018) Are superior ovaries damaged by the bills of flower-visiting birds and does this preclude adaptation to bird pollinators? Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 187, 499-511.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Lunau K, Ren ZX, Fan XQ, Trunschke J, Pyke GH, Wang H (2020) Nectar mimicry: A new phenomenon. Scientific Reports, 10, 7039.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Luo EY, Ogilvie JE, Thomson JD (2014) Stimulation of flower nectar replenishment by removal: A survey of eleven animal-pollinated plant species. Journal of Pollination Ecology, 12, 52-62.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Luyt R, Johnson SD (2002) Postpollination nectar reabsorption and its implications for fruit quality in an epiphytic orchid. Biotropica, 34, 442-446.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Nepi M, Stpiczynska M (2008) Do plants dynamically regulate nectar features through sugar sensing? Plant Signaling & Behavior, 3, 874-876. |
| [7] |
Nicolson SW, Nepi M (2005) Dilute nectar in dry atmospheres: Nectar secretion patterns in Aloe castanea (Asphodelaceae). International Journal of Plant Sciences, 166, 227-233.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Ollerton J (2021) Pollinators and Pollination:Nature and Society. Pelagic Publishing, Exeter, UK. |
| [9] |
Ordano M, Ornelas JF (2005) The cost of nectar replenishment in two epiphytic bromeliads. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 21, 541-547.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Plos C, Stelbrink N, Römermann C, Knight TM, Hensen I (2023) Abiotic conditions affect nectar properties and flower visitation in four herbaceous plant species. Flora, 303, 152279.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Pyke GH, Kalman JRM, Bordin DM, Blanes L, Doble PA (2020a) Patterns of floral nectar standing crops allow plants to manipulate their pollinators. Scientific Reports, 10, 1660.
DOI |
| [12] |
Pyke GH, Ren ZX (2023) Floral nectar production: What cost to a plant? Biological Reviews, 98, 2078-2090.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Pyke GH, Ren ZX, Trunschke J, Lunau K, Wang H (2020b) Salvage of floral resources through re-absorption before flower abscission. Scientific Reports, 10, 15960.
DOI |
| [14] |
Pyke GH, Waser NM (1981) The production of dilute nectars by hummingbird and honeyeater flowers. Biotropica, 13, 260-270.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Pyke GH (2016a) Floral nectar: Pollinator attraction or manipulation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 339-341.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Pyke GH (2016b) Plant-pollinator co-evolution: It’s time to reconnect with Optimal Foraging Theory and Evolutionarily Stable Strategies. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 19, 70-76.
DOI URL |
| [17] | R Core Team (2022) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. (accessed on 2023-08-01) |
| [18] |
Stpiczyńska M (2003) Nectar resorption in the spur of Platanthera chlorantha Custer (Rchb.) Orchidaceae— Structural and microautoradiographic study. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 238, 119-126.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Wang S, Fu WL, Du W, Zhang Q, Li Y, Lyu YS, Wang XF (2018) Nectary tracks as pollinator manipulators: The pollination ecology of Swertia bimaculata (Gentianaceae). Ecology and Evolution, 8, 3187-3207.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Wickham H (2016) ggplot2:Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [21] | Xue CY, He TN, Li DZ (2002) Floral nectaries in Swertia: Anatomy and morphology. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 24, 359-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [薛春迎, 何廷农, 李德铢 (2002) 獐牙菜属植物花蜜腺形态及解剖学. 云南植物研究, 24, 359-369.] | |
| [22] |
Zhang FP, Cai XH, Wang H, Ren ZX, Larson-Rabin Z, Li DZ (2012) Dark purple nectar as a foraging signal in a bird- pollinated Himalayan plant. New Phytologist, 193, 188-195.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Zhang HP, Wen SJ, Wang H, Ren ZX (2023) Floral nectar reabsorption and a sugar concentration gradient in two long-spurred Habenaria species (Orchidaceae). BMC Plant Biology, 23, 331.
DOI |
| [1] | 李艳朋, 盘李军, 陈洁, 许涵, 杨立新. 亚热带人工混交林叶功能性状对森林演替的响应规律及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24049-. |
| [2] | 吕晓琴, 李杨, 王顺雨, 姚仁秀, 王晓月. 中甸乌头总状花序不同位置花粉和花蜜的化学性状没有显著差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23371-. |
| [3] | 程继铭, 何慧敏, 牛红玉, 张洪茂. 鼠类种内个性差异对种子传播影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22446-. |
| [4] | 姚仁秀, 陈燕, 吕晓琴, 王江湖, 杨付军, 王晓月. 海拔及环境因子影响杜鹃属植物的表型特征和化学性状[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22259-. |
| [5] | 张世航, 陶冶, 陈玉森, 郭浩, 陆永兴, 郭星, 刘朝红, 周晓兵, 张元明. 准噶尔荒漠土壤多功能性的空间变异特征及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22097-. |
| [6] | 李艳朋, 倪云龙, 许涵, 练琚愉, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林植物功能性状变异与不同垂直层次个体生长的关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1186-1197. |
| [7] | 陈俊, 姚兰, 艾训儒, 朱江, 吴漫玲, 黄小, 陈思艺, 王进, 朱强. 基于功能性状的水杉原生母树种群生境适应策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 296-302. |
| [8] | 翁茁先, 黄佳琼, 张仕豪, 余锴纯, 钟福生, 黄勋和, 张彬. 利用线粒体COI基因揭示中国乌骨鸡遗传多样性和群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 667-676. |
| [9] | 王晓月,朱鑫鑫,杨娟,刘云静,汤晓辛. 梅花个体内花柱长度的变异及其对繁殖成功的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(2): 159-167. |
| [10] | 张入匀, 李艳朋, 倪云龙, 桂旭君, 练琚愉, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林叶功能性状沿群落垂直层次的种内变异[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(12): 1279-1290. |
| [11] | 杜新宇, 卢金梅, 李德铢. 石松类和蕨类植物质体基因组结构演化研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(11): 1172-1183. |
| [12] | 芦伟, 余建平, 任海保, 米湘成, 陈建华, 马克平. 古田山中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落物种多样性的空间变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 1023-1028. |
| [13] | 盛芳, 陈淑英, 田嘉, 李鹏, 秦雪, 罗淑萍, 李疆. 新疆准噶尔山楂不同居群的遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(5): 518-530. |
| [14] | 童浩杰, 张凯龙, 刘宇航, 张立勋, 赵伟, 金园庭. 基底颜色对两种沙蜥体色变异的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(9): 1039-1044. |
| [15] | 唐青青, 黄永涛, 丁易, 臧润国. 亚热带常绿落叶阔叶混交林植物功能性状的种间和种内变异[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(3): 262-270. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()