



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 22679. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022679 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022679
景昭阳1, 程可光1, 舒恒2,3, 马永鹏2, 刘平丽1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-12
接受日期:2023-02-08
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-03-21
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Zhaoyang Jing1, Keguang Cheng1, Heng Shu2,3, Yongpeng Ma2, Pingli Liu1,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-12
Accepted:2023-02-08
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-03-21
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
全球生物多样性的急剧下降促使人们对生物多样性的保护日益重视。保护遗传学是濒危物种保护研究的重要手段, 它极大地促进了人们对保护生物学多个领域的认知。然而, 保护生物学的一些重大科学问题, 包括濒危植物的演化历史、濒危原因和过程以及适应性演化机制等仍有待进一步深入研究。近年来, 高通量测序技术和保护遗传学思想的交叉融合, 促进了保护基因组学的产生, 为深入探讨这些重要问题提供了新的方法和思路。本文简要综述了组学方法中的全基因组重测序方法在濒危植物保护研究中取得的一些重要进展, 以期推动我国濒危植物保护生物学的进一步发展。全基因组重测序作为目前保护基因组学方法中具有最高分辨力的一种方法, 在研究濒危植物系统发育和种群遗传结构、基因组多样性、种群演化历史、适应性演化和近交衰退等方面取得了一些重要进展, 这些研究确定了一些濒危物种的分类地位和种群保护单元, 揭示了它们的进化历史、濒危原因和过程, 阐明了部分适应性进化和近交衰退的遗传机制。由于重测序方法可以更加深入地窥探保护生物学的诸多问题, 随着测序技术进一步发展和费用的降低, 它必将成为保护生物学研究的主要技术手段。
景昭阳, 程可光, 舒恒, 马永鹏, 刘平丽 (2023) 全基因组重测序方法在濒危植物保护中的应用. 生物多样性, 31, 22679. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022679.
Zhaoyang Jing, Keguang Cheng, Heng Shu, Yongpeng Ma, Pingli Liu (2023) Whole genome resequencing approach for conservation biology of endangered plants. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22679. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022679.
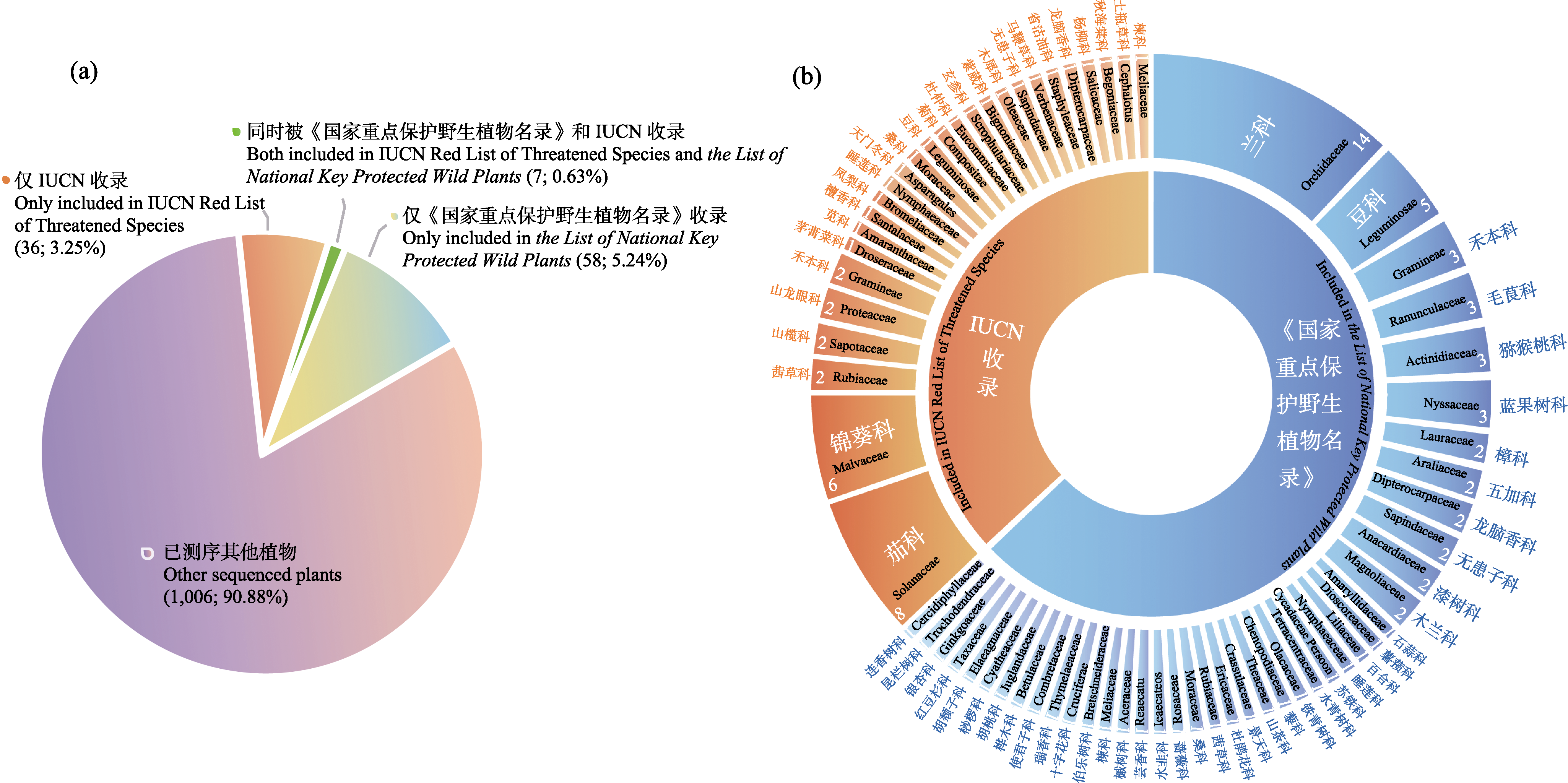
图1 全基因组从头测序的受威胁植物统计。(a)已经全基因组测序的受威胁植物饼图。括号中的数字分别表示已经全基因组测序的受威胁植物物种数量及其所占总测序植物物种数量的比例。(b)《世界自然保护联盟红皮书》和2021年发布的《国家重点保护野生植物名录》收录的受威胁植物所属科统计图。图中的数字表示物种的数量。
Fig. 1 The species statistics with de novo whole-genome sequencing. (a) Comparison of threatened plant species and other plant species with de novo whole-genome sequencing. Values in bracket indicate the number of threatened plant species with de novo whole genome sequencing and its proportion to the total plant species with de novo whole genome sequencing. (b) The distribution of species with de novo whole-genome sequencing included in IUCN Red List of Threatened Species and the List of National Key Protected Wild Plants (2021) in different family. Values indicate the number of species in each family.
| 学名 Scientific name | 濒危等级 Endangered category | 保护等级 Protection level | θπ | 样本量 Sample size | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生稻 Oryza rufipogon | 极危 CR | Ⅱ级 Class II | 0.003000 | 446 | Huang et al, |
| 天目铁木 Ostrya rehderiana | 极危 CR | I级 Class I | 0.001660 | 13 | Yang et al, |
| 野生莲 Nelumbo nucifera | - | II级 Class II | 0.002177 | 7 | Huang et al, |
| 鹅掌楸 Liriodendron chinense | - | II级 Class II | 0.001280 | 14 | Chen et al, 2019 |
| 银杏 Ginkgo biloba | 极危 CR | I级 Class I | 0.002110 | 545 | Zhao et al, |
| 水青树 Tetracentron sinense | II级 Class II | 0.012800 | 55 | Liu et al, | |
| 细叶杨 Populus ilicifolia | 易危 VU | - | 0.000830 | 19 | Chen Z et al, |
| 珙桐 Davidia involucrate | - | I级 Class I | 0.005850 | 10 | Chen Y et al, |
| 连香树 Cercidiphyllum japonicum | - | II级 Class II | 0.001100 | 82 | Zhu et al, |
| 小粒咖啡 Coffea arabica | 濒危 EN | - | 0.003810 | 48 | Huang et al, |
| 朱红大杜鹃 Rhododendron griersonianum | 极危 CR | - | 0.001940 | 31 | Ma et al, |
| 胡桃 Juglans regia | 易危 VU | II级 Class II | 0.000500 | 55 | Bernard et al, |
| 斧翅沙芥 Pugionium dolabratum | - | II级 Class II | 0.013000 | 20 | Hu et al, |
| 茶 Camellia sinensis | - | II级 Class II | 0.006100 | 120 | Lu et al, |
| 野生荔枝 Litchi chinensis | - | II级 Class II | 0.008300 | 38 | Hu et al, |
| 漾濞槭 Acer yangbiense | 濒危 EN | - | 0.003130 | 105 | Ma et al, |
| 芒苞草 Acanthochlamys bracteata | 易危 VU | - | 0.000460 | 14 | Xu et al, |
| 野大豆 Glycine soja | - | II级 Class II | 0.001220 | 40 | Wang et al, |
表1 受威胁植物核酸多样性
Table 1 Nucleic acid diversity of threatened plant species
| 学名 Scientific name | 濒危等级 Endangered category | 保护等级 Protection level | θπ | 样本量 Sample size | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 野生稻 Oryza rufipogon | 极危 CR | Ⅱ级 Class II | 0.003000 | 446 | Huang et al, |
| 天目铁木 Ostrya rehderiana | 极危 CR | I级 Class I | 0.001660 | 13 | Yang et al, |
| 野生莲 Nelumbo nucifera | - | II级 Class II | 0.002177 | 7 | Huang et al, |
| 鹅掌楸 Liriodendron chinense | - | II级 Class II | 0.001280 | 14 | Chen et al, 2019 |
| 银杏 Ginkgo biloba | 极危 CR | I级 Class I | 0.002110 | 545 | Zhao et al, |
| 水青树 Tetracentron sinense | II级 Class II | 0.012800 | 55 | Liu et al, | |
| 细叶杨 Populus ilicifolia | 易危 VU | - | 0.000830 | 19 | Chen Z et al, |
| 珙桐 Davidia involucrate | - | I级 Class I | 0.005850 | 10 | Chen Y et al, |
| 连香树 Cercidiphyllum japonicum | - | II级 Class II | 0.001100 | 82 | Zhu et al, |
| 小粒咖啡 Coffea arabica | 濒危 EN | - | 0.003810 | 48 | Huang et al, |
| 朱红大杜鹃 Rhododendron griersonianum | 极危 CR | - | 0.001940 | 31 | Ma et al, |
| 胡桃 Juglans regia | 易危 VU | II级 Class II | 0.000500 | 55 | Bernard et al, |
| 斧翅沙芥 Pugionium dolabratum | - | II级 Class II | 0.013000 | 20 | Hu et al, |
| 茶 Camellia sinensis | - | II级 Class II | 0.006100 | 120 | Lu et al, |
| 野生荔枝 Litchi chinensis | - | II级 Class II | 0.008300 | 38 | Hu et al, |
| 漾濞槭 Acer yangbiense | 濒危 EN | - | 0.003130 | 105 | Ma et al, |
| 芒苞草 Acanthochlamys bracteata | 易危 VU | - | 0.000460 | 14 | Xu et al, |
| 野大豆 Glycine soja | - | II级 Class II | 0.001220 | 40 | Wang et al, |
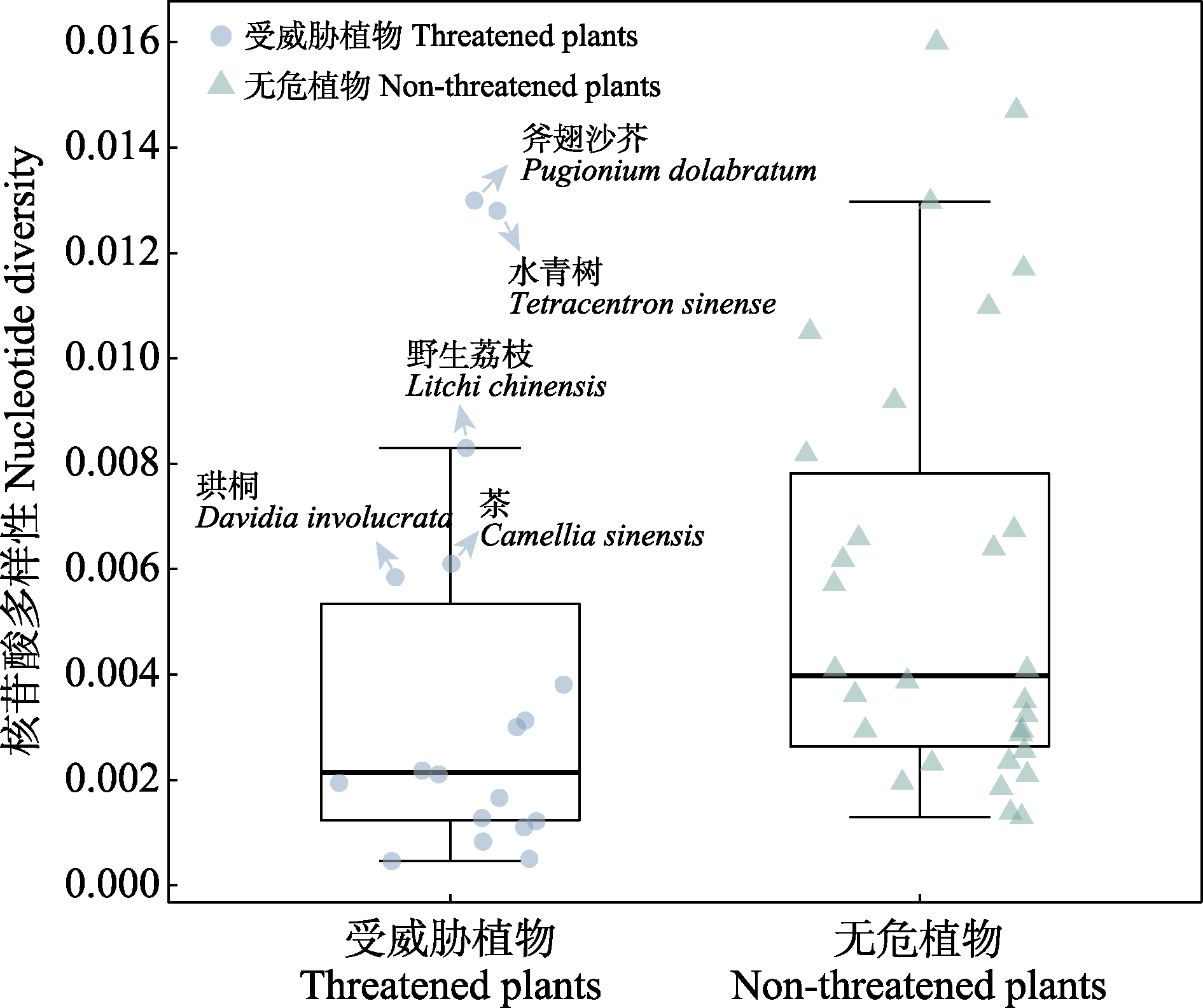
图2 受威胁植物和无危植物的基因组多样性(π)统计。图中只显示遗传多样性最高的5种受威胁植物的名称。
Fig. 2 Genome-wide nucleotide diversity (π). Only species names of five threatened species with the highest genetic diversity are shown.
| [1] |
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nature Methods, 7, 248-249.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Allendorf FW (2017) Genetics and the conservation of natural populations: Allozymes to genomes. Molecular Ecology, 26, 420-430.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Allendorf FW, Hohenlohe PA, Luikart G (2010) Genomics and the future of conservation genetics. Nature Reviews Genetics, 11, 697-709.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Andrews KR, Good JM, Miller MR, Luikart G, Hohenlohe PA (2016) Harnessing the power of RADseq for ecological and evolutionary genomics. Nature Reviews Genetics, 17, 81-92.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Avise JC (2010) Perspective: Conservation genetics enters the genomics era. Conservation Genetics, 11, 665-669.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bao WQ, Ao D, Wuyun T, Wang L, Bai Y (2020) Development of 85 SNP markers for the endangered plant species Prunus mira (Rosaceae) based on restriction site-associated DNA sequencing (RAD-seq). Conservation Genetics Resources, 12, 525-527.
DOI |
| [7] | Beaumont MA, Nichols RA (1996) Evaluating loci for use in the genetic analysis of population structure. Proceedings: Biological Sciences, 263, 1619-1626. |
| [8] |
Bernard A, Crabier J, Donkpegan ASL, Marrano A, Lheureux F, Dirlewanger E (2021) Genome-wide association study reveals candidate genes involved in fruit trait variation in Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.). Frontiers in Plant Science, 11, 607213.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Bongaarts J (2019) Summary for policymakers of the global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Population and Development Review, 45, 680-681. |
| [10] | Cai CN, Xiao JH, Ci XQ, Conran JG, Li J (2021) Genetic diversity of Horsfieldia tetratepala (Myristicaceae), an endangered Plant Species with Extremely Small Populations to China: Implications for its conservation. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 307, 50. |
| [11] | Ceballos G, Ehrlich PR, Raven PH (2020) Vertebrates on the brink as indicators of biological annihilation and the sixth mass extinction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 117, 13596-13602. |
| [12] |
Chen JH, Hao ZD, Guang XM, Zhao CX, Wang PK, Xue LJ, Zhu QH, Yang LF, Sheng Y, Zhou YW, Xu HB, Xie HQ, Long XF, Zhang J, Wang ZR, Shi MM, Lu Y, Liu SQ, Guan LH, Zhu QH, Yang LM, Ge S, Cheng TL, Laux T, Gao Q, Peng Y, Liu N, Yang SH, Shi JS (2018) Liriodendron genome sheds light on angiosperm phylogeny and species-pair differentiation. Nature Plants, 5, 18-25.
DOI |
| [13] |
Chen Y, Ma T, Zhang LS, Kang MH, Zhang ZY, Zheng ZY, Sun PC, Shrestha N, Liu JQ, Yang YZ (2020) Genomic analyses of a “living fossil”: The endangered dove-tree. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20, 756-769.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Chen ZY, Ai FD, Zhang JL, Ma XZ, Yang WL, Wang WW, Su YT, Wang MC, Yang YZ, Mao KS, Wang QF, Lascoux M, Liu JQ, Ma T (2020) Survival in the tropics despite isolation, inbreeding and asexual reproduction: Insights from the genome of the world’s southernmost poplar (Populus ilicifolia). The Plant Journal, 103, 430-442.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Chong ZC, Ruan J, Wu CI (2012) Rainbow: An integrated tool for efficient clustering and assembling RAD-seq reads. Bioinformatics, 28, 2732-2737.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Clarke J, Wu HC, Jayasinghe L, Patel A, Reid S, Bayley H (2009) Continuous base identification for single-molecule nanopore DNA sequencing. Nature Nanotechnology, 4, 265-270.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Combosch DJ, Lemer S, Ward PD, Landman NH, Giribet G (2017) Genomic signatures of evolution in Nautilus—An endangered living fossil. Molecular Ecology, 26, 5923-5938.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Eaton DAR (2014) PyRAD: Assembly of de novo RADseq loci for phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics, 30, 1844-1849.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Forester BR, Murphy M, Mellison C, Petersen J, Pilliod DS, Van Horne R, Harvey J, Funk WC (2022) Genomics- informed delineation of conservation units in a desert amphibian. Molecular Ecology, 31, 5249-5269.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Frichot E, Schoville SD, Bouchard G, François O (2013) Testing for associations between loci and environmental gradients using latent factor mixed models. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 1687-1699.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Fuentes-Pardo AP, Ruzzante DE (2017) Whole-genome sequencing approaches for conservation biology: Advantages, limitations and practical recommendations. Molecular Ecology, 26, 5369-5406.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Funk WC, McKay JK, Hohenlohe PA, Allendorf FW (2012) Harnessing genomics for delineating conservation units. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 27, 489-496.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Goodwin S, McPherson JD, McCombie WR (2016) Coming of age: Ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nature Reviews Genetics, 17, 333-351.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Hao YB, Jin H, Yang L, Li KX, Hu YB (2022) Research advances in conservation genetics and genomics of snow leopard (Panthera uncia). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 42, 508-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[郝宇波, 金红, 杨林, 李可欣, 胡义波 (2022) 雪豹保护遗传学和基因组学研究进展. 兽类学报, 42, 508-518.]
DOI |
|
| [25] |
Hohenlohe PA, Funk WC, Rajora OP (2021) Population genomics for wildlife conservation and management. Molecular Ecology, 30, 62-82.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Hu GB, Feng JT, Xiang X, Wang JB, Salojärvi J, Liu CM, Wu ZX, Zhang JS, Liang XM, Jiang ZD, Liu W, Ou LX, Li JW, Fan GY, Mai YX, Chen CJ, Zhang XT, Zheng JK, Zhang YQ, Peng HX, Yao LX, Wai CM, Luo XP, Fu JX, Tang HB, Lan TY, Lai B, Sun JH, Wei YZ, Li HL, Chen JZ, Huang XM, Yan Q, Liu X, McHale LK, Rolling W, Guyot R, Sankoff D, Zheng CF, Albert VA, Ming R, Chen HB, Xia R, Li JG (2022) Two divergent haplotypes from a highly heterozygous lychee genome suggest independent domestication events for early and late-maturing cultivars. Nature Genetics, 54, 73-83. |
| [27] | Hu Q, Ma Y, Mandakova T, Shi S, Chen C, Sun P, Zhang L, Feng L, Zheng Y, Feng X, Yang W, Jiang J, Li T, Zhou P, Yu Q, Wan D, Lysak MA, Xi Z, Nevo E, Liu J (2021) Genome evolution of the psammophyte Pugionium for desert adaptation and further speciation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 118, e2025711118. |
| [28] |
Huang LF, Wang XY, Dong YP, Long YZ, Hao CY, Yan L, Shi T (2020) Resequencing 93 accessions of coffee unveils independent and parallel selection during Coffea species divergence. Plant Molecular Biology, 103, 51-61.
DOI |
| [29] |
Huang LY, Yang M, Li L, Li H, Yang D, Shi T, Yang PF (2018) Whole genome re-sequencing reveals evolutionary patterns of sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 60, 2-15.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Huang XH, Kurata N, Wei XH, Wang ZX, Wang AH, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu KY, Lu HY, Li WJ, Guo YL, Lu YQ, Zhou CC, Fan DL, Weng QJ, Zhu CR, Huang T, Zhang L, Wang YC, Feng L, Furuumi H, Kubo T, Miyabayashi T, Yuan XP, Xu Q, Dong GJ, Zhan QL, Li CY, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Lu TT, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li JY, Han B (2012) A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature, 490, 497-501.
DOI |
| [31] |
Jones MR, Good JM (2016) Targeted capture in evolutionary and ecological genomics. Molecular Ecology, 25, 185-202.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Joost S, Bonin A, Bruford MW, Després L, Conord C, Erhardt G, Taberlet P (2007) A spatial analysis method (SAM) to detect candidate loci for selection: Towards a landscape genomics approach to adaptation. Molecular Ecology, 16, 3955-3969.
PMID |
| [33] | Lewin HA, Robinson GE, Kress WJ, Baker WJ, Coddington J, Crandall KA, Durbin R, Edwards SV, Forest F, Gilbert MTP, Goldstein MM, Grigoriev IV, Hackett KJ, Haussler D, Jarvis ED, Johnson WE, Patrinos A, Richards S, Castilla-Rubio JC, van Sluys MA, Soltis PS, Xu X, Yang HM, Zhang GJ (2018) Earth BioGenome Project: Sequencing life for the future of life. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 115, 4325-4333. |
| [34] |
Li A, Ge S (2002) Advances in plant conservation genetics. Biodiversity Science, 10, 61-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李昂, 葛颂 (2002) 植物保护遗传学研究进展. 生物多样性, 10, 61-71.]
DOI |
|
| [35] |
Liu HL, Harris AJ, Wang ZF, Chen HF, Li ZA, Wei X (2022) The genome of the Paleogene relic tree Bretschneidera sinensis: Insights into trade-offs in gene family evolution, demographic history, and adaptive SNPs. DNA Research, 29, dsac003.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Liu PL, Zhang X, Mao JF, Hong YM, Zhang RG, E YL, Nie S, Jia K, Jiang CK, He J, Shen W, He Q, Zheng W, Abbas S, Jewaria PK, Tian X, Liu CJ, Jiang X, Yin Y, Liu B, Wang L, Jin B, Ma Y, Qiu Z, Baluska F, Samaj J, He X, Niu S, Xie J, Xie L, Xu H, Kong H, Ge S, Dixon RA, Jiao Y, Lin J (2020) The Tetracentron genome provides insight into the early evolution of eudicots and the formation of vessel elements. Genome Biology, 21, 291.
DOI |
| [37] |
Liu SL, Qiu N, Zhang SY, Zhao ZN, Zhou X (2022) Application of genomics technology in biodiversity conservation research. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22441. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘山林, 邱娜, 张纾意, 赵竹楠, 周欣 (2022) 基因组学技术在生物多样性保护研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 30, 22441.]
DOI |
|
| [38] |
Lu LT, Chen HF, Wang XJ, Zhao YC, Yao XZ, Xiong B, Deng YL, Zhao DG (2021) Genome-level diversification of eight ancient tea populations in the Guizhou and Yunnan regions identifies candidate genes for core agronomic traits. Horticulture Research, 8, 190.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Ma H, Liu YB, Liu DT, Sun WB, Liu XF, Wan YM, Zhang XJ, Zhang RG, Yun QZ, Wang JH, Li ZH, Ma YP (2021a) Chromosome-level genome assembly and population genetic analysis of a critically endangered Rhododendron provide insights into its conservation. The Plant Journal, 107, 1533-1545.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Ma YP, Liu DT, Wariss HM, Zhang RG, Tao LD, Milne RI, Sun WB (2022) Demographic history and identification of threats revealed by population genomic analysis provide insights into conservation for an endangered maple. Molecular Ecology, 31, 767-779.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Ma YP, Wariss HM, Liao RL, Zhang RG, Yun QZ, Olmstead RG, Chau JH, Milne RI, Van de Peer Y, Sun WB (2021b) Genome-wide analysis of butterfly bush (Buddleja alternifolia) in three uplands provides insights into biogeography, demography and speciation. New Phytologist, 232, 1463-1476.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Meyer JY, Pouteau R, Vincent F (2022) Assessing habitat suitability for the translocation of Ochrosia tahitensis (Apocynaceae), a critically endangered endemic plant from the island of Tahiti (South Pacific). Journal for Nature Conservation, 68, 126198.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Ng PC, Henikoff S (2003) SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 3812-3814.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Niu ZT, Zhu F, Fan YJ, Li C, Zhang BH, Zhu SY, Hou ZY, Wang MT, Yang JP, Xue QY, Liu W, Ding XY (2021) The chromosome-level reference genome assembly for Dendrobium officinale and its utility of functional genomics research and molecular breeding study. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 11, 2080-2092.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Primmer CR (2009) From conservation genetics to conservation genomics. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1162, 357-368. |
| [46] |
Qi YX, Liu YB, Rong WH (2011) RNA-Seq and its applications: A new technology for transcriptomics. Hereditas (Beijing), 33, 1191-1202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [祁云霞, 刘永斌, 荣威恒 (2011) 转录组研究新技术: RNA-Seq及其应用. 遗传, 33, 1191-1202.] | |
| [47] |
Schuster SC (2008) Next-generation sequencing transforms today’s biology. Nature Methods, 5, 16-18.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Shear W, Werth A (2014) The evolutionary truth about living fossils. The American Scientist, 102, 434.
DOI URL |
| [49] | Tan XX, Li M (2018) From conservation genetics to conservation genomics. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Science Edition), 42, 22-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谭鑫鑫, 李明 (2018) 从保护遗传学到保护基因组学. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 42, 22-28.] | |
| [50] |
Vitalis R, Dawson K, Boursot P (2001) Interpretation of variation across marker loci as evidence of selection. Genetics, 158, 1811-1823.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Wang GT, Wang ZF, Wang RJ, Liang D, Jiang GB (2019) Development of microsatellite markers for a monotypic and globally endangered species, Glyptostrobus pensilis (Cupressaceae). Applications in Plant Sciences, 7, e01217. |
| [52] |
Wang J, Hu ZB, Liao XL, Wang ZY, Li W, Zhang PP, Cheng H, Wang Q, Bhat JA, Wang H, Liu B, Zhang HY, Huang F, Yu DY (2022) Whole-genome resequencing reveals signature of local adaptation and divergence in wild soybean. Evolutionary Applications, 15, 1820-1833.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Warr A, Robert C, Hume D, Archibald A, Deeb N, Watson M (2015) Exome sequencing: Current and future perspectives. 3G (Genes|Genomes|Genetics), 5, 1543-1550. |
| [54] |
Wei FW, Huang GP, Fan HZ, Hu YB (2021) Research advances and perspectives of conservation genomics and meta-genomics of threatened mammals in China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 41, 581-590. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[魏辅文, 黄广平, 樊惠中, 胡义波 (2021) 中国濒危兽类保护基因组学和宏基因组学研究进展与展望. 兽类学报, 41, 581-590.]
DOI |
|
| [55] |
Xu B, Liao M, Deng HN, Yan CC, Lv YY, Gao YD, Ju WB, Zhang JY, Jiang LS, Li X, Gao XF (2022) Chromosome- level de novo genome assembly and whole-genome resequencing of the threatened species Acanthochlamys bracteata (Velloziaceae) provide insights into alpine plant divergence in a biodiversity hotspot. Molecular Ecology Resources, 22, 1582-1595.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Yang YZ, Ma T, Wang ZF, Lu ZQ, Li Y, Fu CX, Chen XY, Zhao MS, Olson MS, Liu JQ (2018) Genomic effects of population collapse in a critically endangered ironwood tree Ostrya rehderiana. Nature Communications, 9, 5449.
DOI |
| [57] |
Zhao YP, Fan GY, Yin PP, Sun S, Li N, Hong XN, Hu G, Zhang H, Zhang FM, Han JD, Hao YJ, Xu QW, Yang XW, Xia WJ, Chen WB, Lin HY, Zhang R, Chen J, Zheng XM, Lee SMY, Lee J, Uehara K, Wang J, Yang HM, Fu CX, Liu X, Xu X, Ge S (2019) Resequencing 545 ginkgo genomes across the world reveals the evolutionary history of the living fossil. Nature Communications, 10, 4201.
DOI |
| [58] |
Zhu SS, Chen J, Zhao J, Comes HP, Li P, Fu CX, Xie X, Lu RS, Xu WQ, Feng Y, Ye WQ, Sakaguchi S, Isagi Y, Li LF, Lascoux M, Qiu YX (2020) Genomic insights on the contribution of balancing selection and local adaptation to the long-term survival of a widespread living fossil tree, Cercidiphyllum japonicum. New Phytologist, 228, 1674-1689.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 罗瑞, 陈娅, 张汉马. 芸薹属植物全基因组重测序研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23237-. |
| [2] | 张光富, 熊天石, 孙婷, 李恺頔, 邵丽鸳. 江苏珍稀濒危植物的多样性、分布及保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21335-. |
| [3] | 陈小红, 陈浩杰, 王雅竹, 肖书礼, 衡小琴, 赵安玖. 濒危植物峨眉含笑的种内、种间竞争[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22003-. |
| [4] | 王婷, 夏增强, 舒江平, 张娇, 王美娜, 陈建兵, 王慷林, 向建英, 严岳鸿. 全基因组复制事件的绝对定年揭示莲座蕨属植物的迟滞演化[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 722-734. |
| [5] | 刘忠成, 张忠, 兰勇, 赵万义, 刘佳, 陈春泉, 廖文波, 王蕾. 罗霄山脉珍稀濒危重点保护野生植物的生存状况及保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(7): 867-875. |
| [6] | 张玲玲, 刘子玥, 王瑞江. 广东兰科植物多样性保育现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(7): 787-795. |
| [7] | 李媛媛, 刘超男, 王嵘, 罗水兴, 农寿千, 王静雯, 陈小勇. 分子标记在濒危物种保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 367-375. |
| [8] | 任海. 植物园与植物回归[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(9): 945-950. |
| [9] | 陈玉凯, 杨小波, 李东海, 龙文兴. 海南岛维管植物物种多样性的现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(8): 948-956. |
| [10] | 杨文忠, 向振勇, 张珊珊, 康洪梅, 史富强. 极小种群野生植物的概念及其对我国野生植物保护的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 419-425. |
| [11] | 张荣京, 赵哲, 苏文拔, 邢福武. 海南甘什岭保护区珍稀濒危植物的分布与评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(1): 11-17. |
| [12] | 李长昊, 程涛, 董文攀, 周世良. “中国珍稀濒危植物DNA条形码鉴定平台”简介[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(1): 110-110. |
| [13] | 王蕾, 施诗, 廖文波, 陈春泉, 李贞. 井冈山地区珍稀濒危植物及其生存状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(2): 163-169. |
| [14] | 黄宏文, 张征. 中国植物引种栽培及迁地保护的现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(5): 559-571. |
| [15] | 周翔, 高江云. 珍稀濒危植物的回归: 理论和实践[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(1): 97-105. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()