



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 21431. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021431 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021431
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全; 昆虫多样性与生态功能
李正飞1, 蒋小明2, 王军3, 孟星亮1, 张君倩1, 谢志才1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-10-29
接受日期:2022-01-08
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2022-01-09
通讯作者:
谢志才
作者简介:* E-mail: gxf005@hotmail.com基金资助:
Zhengfei Li1, Xiaoming Jiang2, Jun Wang3, Xingliang Meng1, Junqian Zhang1, Zhicai Xie1,*( )
)
Received:2021-10-29
Accepted:2022-01-08
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-01-09
Contact:
Zhicai Xie
摘要:
雅鲁藏布江流域维系着丰富而独特的生物资源, 是全球生物多样性研究的热点区域。然而, 该流域底栖动物多样性的调查却极不充分。本文于2015年10月和2016年3月对雅鲁藏布江干流(朗县至墨脱段)和主要支流的底栖动物进行了调查, 并采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)和典范对应分析(canonical correspondence analysis)等对群落多样性格局进行解析。共采集到底栖动物270种, 隶属于5门8纲20目92科, 包括昆虫纲246种, 寡毛纲14种, 腹足纲4种, 其他动物6种。春季和秋季分别采集到底栖动物184种和214种, 优势种均以喜清洁和冷水的水生昆虫为主, 包括四节蜉属一种(Baetis sp.)、花翅蜉属一种(Baetiella sp.)、蚋属一种(Simulium sp.)、小突摇蚊属一种(Micropsetra sp.)和短石蛾属一种(Brachycentrus sp.)等。全流域平均密度为939.1 ind./m2,sp.)等。平均生物量为5.44 g/m2。底栖动物的物种组成、密度和多样性在季节和区域之间存在一定差异, 支流的多样性显著高于干流。典范对应分析显示, 海拔、流速、河宽和底质类型等环境因子是影响雅鲁藏布江流域底栖动物群落结构的关键环境因素, 而大峡谷地区多变的气候类型和地理阻隔是造成群落变化的根本原因。本研究可为雅鲁藏布江流域底栖动物多样性评估和环境监测提供重要的基础和参考。
李正飞, 蒋小明, 王军, 孟星亮, 张君倩, 谢志才 (2022) 雅鲁藏布江中下游底栖动物物种多样性及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 30, 21431. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021431.
Zhengfei Li, Xiaoming Jiang, Jun Wang, Xingliang Meng, Junqian Zhang, Zhicai Xie (2022) Species diversity and driving factors of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the middle and lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21431. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021431.
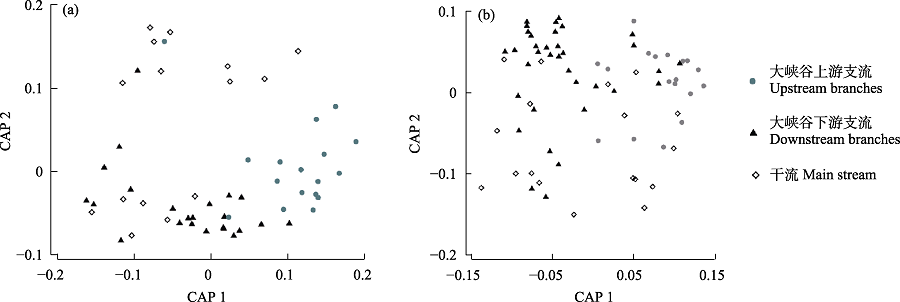
图3 雅鲁藏布江各区域底栖动物群落差异的CAP排序图。(a)春季; (b)秋季。
Fig. 3 Canonical analysis of principal coordinates (CAP) ordination diagrams of benthic macroinvertebrates in different reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. (a) Spring; (b) Autumn.
| 时期 Periods | 干流 Main stream | 大峡谷上游支流 Upstream branches | 大峡谷下游支流 Downstream branches | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 密度 Density (ind./m2) | 春季 Spring | 477.5 ± 465.6a | 1,402.2 ± 1,080.6b | 1,075.7 ± 1,319.4b | 6.741 | 0.005 |
| 秋季 Autumn | 327.1 ± 301.7a | 1,219.2 ± 1,008.3b | 1,321.9 ± 864.6b | 5.945 | 0.007 | |
| 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 春季 Spring | 2.12 ± 3.69a | 7.05 ± 4.36ab | 8.24 ± 7.28b | 4.114 | 0.028 |
| 秋季 Autumn | 2.89 ± 4.68 | 5.71 ± 7.50 | 3.37 ± 2.31 | 0.872 | 0.428 |
表1 雅鲁藏布江干支流断面底栖动物密度与生物量的比较
Table 1 Comparison of density and biomass of macroinvertebrates in different reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River
| 时期 Periods | 干流 Main stream | 大峡谷上游支流 Upstream branches | 大峡谷下游支流 Downstream branches | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 密度 Density (ind./m2) | 春季 Spring | 477.5 ± 465.6a | 1,402.2 ± 1,080.6b | 1,075.7 ± 1,319.4b | 6.741 | 0.005 |
| 秋季 Autumn | 327.1 ± 301.7a | 1,219.2 ± 1,008.3b | 1,321.9 ± 864.6b | 5.945 | 0.007 | |
| 生物量 Biomass (g/m2) | 春季 Spring | 2.12 ± 3.69a | 7.05 ± 4.36ab | 8.24 ± 7.28b | 4.114 | 0.028 |
| 秋季 Autumn | 2.89 ± 4.68 | 5.71 ± 7.50 | 3.37 ± 2.31 | 0.872 | 0.428 |
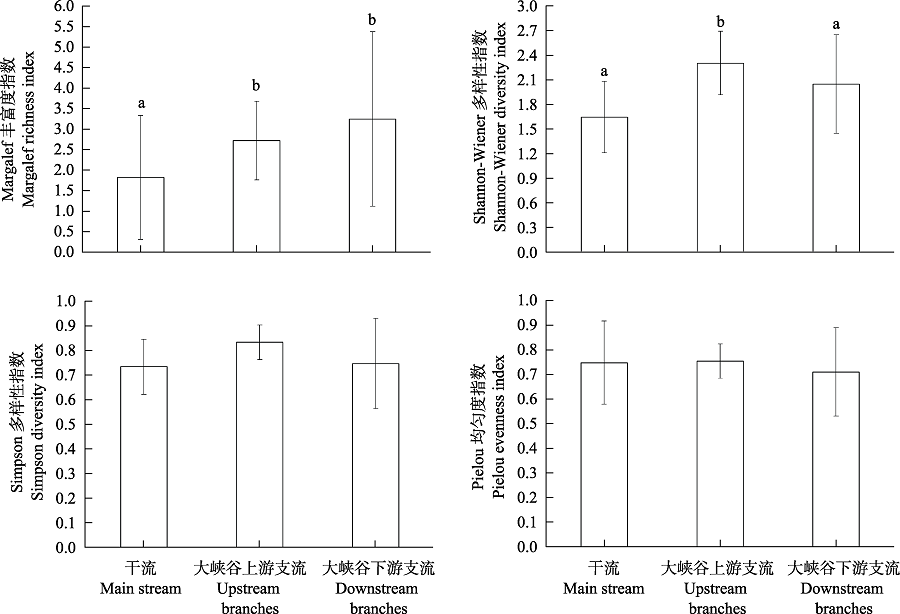
图4 雅鲁藏布江春季干支流河段底栖动物多样性指数的差异。不同字母表示存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 4 Comparation of diversity index of benthic macroinvertebrates in different reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River in spring. Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).
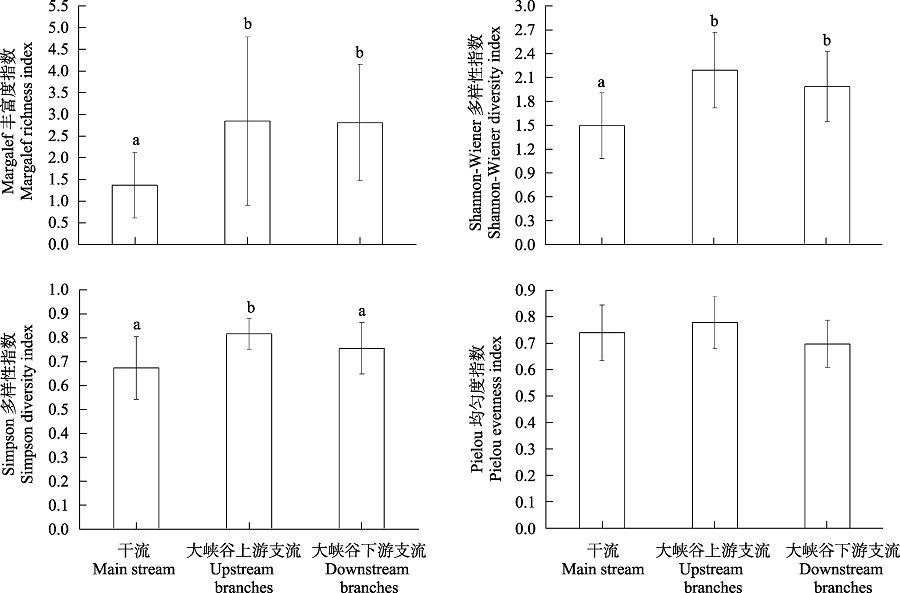
图5 雅鲁藏布江秋季干支流河段底栖动物多样性指数的差异。不同字母表示存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 5 Comparation of diversity index of macroinvertebrates in different regions of the Yarlung Zangbo River in autumn. Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).
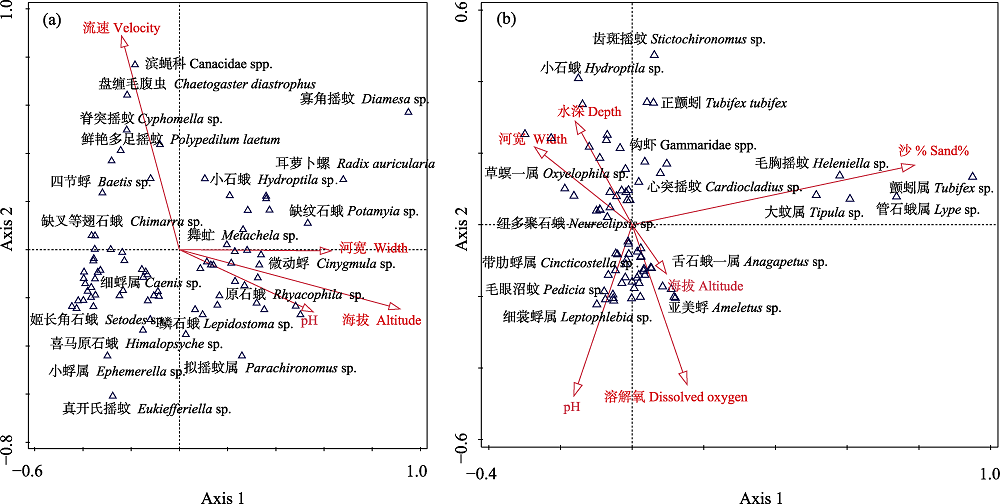
图6 雅鲁藏布江春季(a)和秋季(b)底栖动物物种与环境因子的典范对应分析排序图
Fig. 6 Canonical correspondence analysis ordination diagram of benthic macroinvertebrate communities with significant environmental variables in spring (a) and autumn (b)
| 获取的关键因子 Key factors selected | 与排序轴的相关系数 Correlation coefficients with the axes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | ||
| 春季 Spring | 海拔 Altitude | 1.60 | 0.001 | 0.762 | -0.183 | -0.408 | -0.182 |
| 河宽 Depth | 1.93 | 0.001 | 0.643 | 0.019 | 0.121 | 0.164 | |
| pH | 1.23 | 0.064 | 0.485 | -0.405 | 0.292 | 0.097 | |
| 流速 Velocity | 1.25 | 0.080 | -0.325 | 0.175 | 0.454 | -0.606 | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 海拔 Altitude | 1.78 | 0.001 | 0.070 | 0.266 | 0.612 | -0.521 |
| 沙% Sand% | 1.89 | 0.004 | 0.682 | 0.243 | -0.339 | -0.015 | |
| pH | 1.61 | 0.004 | -0.165 | -0.205 | -0.226 | -0.478 | |
| 溶解氧 Dissolved oxygen | 1.67 | 0.004 | -0.406 | 0.453 | -0.168 | 0.226 | |
| 水深 Depth | 1.46 | 0.052 | 0.289 | 0.123 | 0.551 | 0.244 | |
| 河宽 Width | 1.48 | 0.021 | 0.203 | -0.268 | 0.194 | -0.047 | |
表2 雅鲁藏布江底栖动物群落结构与环境因子关系的典范对应分析结果汇总表
Table 2 The key environmental factors affecting macroinvertebrate communities in the Yarlung Zangbo River based on canonical correspondence analysis
| 获取的关键因子 Key factors selected | 与排序轴的相关系数 Correlation coefficients with the axes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | ||
| 春季 Spring | 海拔 Altitude | 1.60 | 0.001 | 0.762 | -0.183 | -0.408 | -0.182 |
| 河宽 Depth | 1.93 | 0.001 | 0.643 | 0.019 | 0.121 | 0.164 | |
| pH | 1.23 | 0.064 | 0.485 | -0.405 | 0.292 | 0.097 | |
| 流速 Velocity | 1.25 | 0.080 | -0.325 | 0.175 | 0.454 | -0.606 | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 海拔 Altitude | 1.78 | 0.001 | 0.070 | 0.266 | 0.612 | -0.521 |
| 沙% Sand% | 1.89 | 0.004 | 0.682 | 0.243 | -0.339 | -0.015 | |
| pH | 1.61 | 0.004 | -0.165 | -0.205 | -0.226 | -0.478 | |
| 溶解氧 Dissolved oxygen | 1.67 | 0.004 | -0.406 | 0.453 | -0.168 | 0.226 | |
| 水深 Depth | 1.46 | 0.052 | 0.289 | 0.123 | 0.551 | 0.244 | |
| 河宽 Width | 1.48 | 0.021 | 0.203 | -0.268 | 0.194 | -0.047 | |
| [1] | Allan JD (1995) Stream Ecology. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| [2] |
Anderson MJ (2008) Animal-sediment relationships re-visited: Characterising species’ distributions along an environmental gradient using canonical analysis and quantile regression splines. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 366, 16-27.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Barbour MT, Gerritsen J, Snyder BD (1999) Rapid Bioassessment for Use in Streams and Wadeable Rivers: Periphyton, Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish, 2nd edn. Environment Protection Agency, Office of Water, Washington, DC, USA. |
| [4] | Beckmann L, Thomas DC, Fischer C, Chang-Claude J (2005) Haplotype sharing analysis using mantel statistics. BMC Genetics, 59, 67-78. |
| [5] |
Beisel JN, Usseglio-Polatera P, Moreteau JC (2000) The spatial heterogeneity of a river bottom, a key factor determining macroinvertebrate communities. Hydrobiologia, 422/423, 163-171.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Berger E, Haase P, Schäfer RB, Sundermann A (2018) Towards stressor-specific macroinvertebrate indices: Which traits and taxonomic groups are associated with vulnerable and tolerant taxa? Science of the Total Environment, 619/620, 144-154.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Brinkhurst RO (1986) Guide to the freshwater aquatic microdrile oligochaetes on North America. Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 84, 1-259. |
| [8] | Chaves ML, Rieradevall M, Chainho P, Costa JL, Costa MJ, Prat N (2008) Macroinvertebrate communities of non-glacial high altitude intermittent streams. Freshwater Biology, 53, 55-76. |
| [9] |
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) A further biodiversity index Applicable to species lists: Variation in taxonomic distinctness. Marine Ecology Progress, 216, 265-278.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Ding JH, Zhou LZ, Deng DG (2017) Community structure of macrozoobenthos and biological evaluation of water quality in the mainstream of Huai River. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 26, 1875-1883. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁建华, 周立志, 邓道贵 (2017) 淮河干流大型底栖动物群落结构及水质生物学评价. 长江流域资源与环境, 26, 1875-1883.] | |
| [11] | Duan XH, Wang ZY, Cheng DS (2007) Benthic macroinvertebrates communities and biodiversity in various stream substrata. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27, 1664-1672. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [段学花, 王兆印, 程东升 (2007) 典型河床底质组成中底栖动物群落及多样性. 生态学报, 27, 1664-1672.] | |
| [12] | Epler JH (2001) Identification Manual for the Larval Chironomidae (Diptera) of North and South Carolina. America: EPA Grant X984l70-97. |
| [13] |
Gallardo B, Gascon S, García-Antón M, Comín FA (2009) Testing the response of macroinvertebrate functional structure and biodiversity to flooding and confinement. Journal of Limnology, 68, 315-326.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Guo B, Xie C, Qi L, Qi P, Wu C, Abbas K (2010) Assessment of the genetic diversity among Glyptosternum maculatum, an endemic fish of Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibet, China using SSR markers. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 38, 1116-1121.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Heino J (2013) Environmental heterogeneity, dispersal mode, and co-occurrence in stream macroinvertebrates. Ecology and Evolution, 3, 344-355.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Jacobsen D, Rostgaard S, Vásconez JJ (2003) Are macroinvertebrates in high altitude streams affected by oxygen deficiency? Freshwater Biology, 48, 2025-2032.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Jian D, Huang DM, Chang XL, Zhang Q, Xie S, Chen F, Chen S (2015) Zoobenthos community structure in the middle and lower reaches of Lhasa River. Journal of Hydroecology, 36, 40-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [简东, 黄道明, 常秀岭, 张庆, 谢山, 陈峰, 陈胜 (2015) 拉萨河中下游底栖动物群落结构特征分析. 水生态学杂志, 36, 40-46.] | |
| [18] |
Jiang X, Xie Z, Chen Y (2014) Longitudinal patterns of macroinvertebrate communities in relation to environmental factors in a Tibetan-Plateau River system. Quaternary International, 304, 107-114.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
La Q, Zhaxi C, Zhu WD, Xu M, Zhong Y (2014) Plant species-richness and association with environmental factors in the riparian zone of the Yarlung Zangbo River of Tibet, China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 337-347. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[拉琼, 扎西次仁, 朱卫东, 许敏, 钟扬 (2014) 雅鲁藏布江河岸植物物种丰富度分布格局及其环境解释. 生物多样性, 22, 337-347.]
DOI |
|
| [20] |
Laursen SK, Hamerlik L, Moltesen K, Christoffersen K, Jacobsen D (2015) Diversity and composition of macroinvertebrate assemblages in high-altitude Tibetan streams. Inland Waters, 5, 263-274.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Lencioni V, Maiolini B, Marziali L, Lek S, Rossaro B (2007) Macroinvertebrate assemblages in glacial stream systems, a comparison of linear multivariate methods with artificial neural networks. Ecological Modelling, 203, 119-131.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Li C, Xu WL, Li QK, Wang JS (2021) Community structure and diversity distribution pattern of sandy plants in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 12, 11-21. |
| [23] |
Li FQ, Tonkin JD, Haase P (2018) Dispersal capacity and broad-scale landscape structure shape benthic invertebrate communities along stream networks. Limnologica, 71, 68-74.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Li ZF, Jiang XM, Wang J, Meng XL, Heino J, Xie ZC (2019a) Multiple facets of stream macroinvertebrate alpha diversity are driven by different ecological factors across an extensive altitudinal gradient. Ecology and Evolution, 9, 1306-1322.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Li ZF, Wang J, Meng XL, Heino J, Sun MQ, Jiang XM, Xie ZC (2019b) Disentangling the effects of dispersal mode on the assembly of macroinvertebrate assemblages in a heterogeneous highland region. Freshwater Science, 38, 170-182.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Li ZF, Wang J, Xie ZC, Ding CZ, Jiang XM (2016) Relationship between zoobenthos biodiversity and environmental factors in Nanla River. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 3364-3373. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李正飞, 王军, 谢志才, 丁城志, 蒋小明 (2016) 南腊河底栖动物多样性与环境因子的关系. 生态学杂志, 35, 3364-3373. ] | |
| [27] |
Liu HP, Ye SW, Yang XF, Zhang LS, Zhong GH, He YP, Basang, Li ZJ (2014) Macrozoobenthos. Journal of Lake Sciences, 26, 154-160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [刘海平, 叶少文, 杨雪峰, 张良松, 钟国辉, 何勇平, 巴桑, 李钟杰 (2014) 西藏尼洋河水生生物群落时空动态及与环境因子关系. 3. 大型底栖动物. 湖泊科学, 26, 154-160.] | |
| [28] | Liu TC (1999) Hydrological characteristics of Yarlung Zangbo River. Acta Geographica Sinica, 54, 157-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[刘天仇 (1999) 雅鲁藏布江水文特征. 地理学报, 54, 157-164.]
DOI |
|
| [29] | Liu YY, Zhang WZ, Wang YX, Wang EY (1979) Freshwater Mollusk:Economic Fauna of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [刘月英, 张文珍, 王跃先, 王恩义 (1979) 中国经济动物: 淡水软体动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Ma BS, Xie CX, Yang XF, Huo B (2012) A preliminary study on periphyton and zoobenthos in the Xaitongmoin reach of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 21, 942-950. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马宝珊, 谢从新, 杨学峰, 霍斌 (2012) 雅鲁藏布江谢通门江段着生生物和底栖动物资源初步研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 21, 942-950.] | |
| [31] |
Madsen PB, Morabowen A, Andino P, Espinosa R, Cauvy- Fraunié S, Dangles O, Jacobsen D (2015) Altitudinal distribution limits of aquatic macroinvertebrates: An experimental test in a tropical alpine stream. Ecological Entomology, 40, 629-638.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Maiolini B, Lencioni V (2001) Longitudinal distribution of macroinvertebrate assemblages in a glacially influenced stream system in the Italian Alps. Freshwater Biology, 46, 1625-1639.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Margalef R (1958) Information theory in ecology. General Systems, 3, 36-71. |
| [34] |
Meng XL, Jiang XM, Xiong X, Wu CX, Xie ZC (2016) Mediated spatio-temporal patterns of macroinvertebrate assemblage associated with key environmental factors in the Qinghai Lake area, China. Limnologica, 56, 14-22.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Milesi SV, Dolédec S, Melo AS (2016) Substrate heterogeneity influences the trait composition of stream insect communities: An experimental in situ study. Freshwater Science, 35, 1321-1329.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Milner AM, Brittain JE, Castella E, Petts GE (2001) Trends of macroinvertebrate community structure in glacier-fed rivers in relation to environmental conditions: A synthesis. Freshwater Biology, 46, 1833-1847.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Morse JC, Yang LF, Tian LX (1994) Aquatic Insects of China Useful for Monitoring Water Quality. Hohai University Press, Nanjing. |
| [38] | Nie N, Zhang WC, Deng C (2012) Spatial and temporal climate variations from 1978 to 2009 and their trend projection over the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 34, 64-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [聂宁, 张万昌, 邓财 (2012) 雅鲁藏布江流域1978-2009年气候时空变化及未来趋势研究. 冰川冻土, 34, 64-71.] | |
| [39] |
Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 13, 131-144.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. The Bell System Technical Journal, 27, 379-423.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature, 163, 688-688.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Su BZ, Li WX, Lai ZX (1989) A survey on benthic macroinvertebrates in the Pearl River basin (Guangdong reach). Chinese Journal of Zoology, 24(3), 15-19. (in Chinese) |
| [苏炳之, 黎伟新, 赖泽兴 (1989) 珠江水系(广东江段)底栖动物调查. 动物学杂志, 24(3), 15-19.] | |
| [43] | ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2002) CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (version 4.5). Section on Permutation Methods Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, New York. |
| [44] |
Tonkin JD, Altermatt F, Finn DS, Heino J, Olden JD, Pauls SU, Lytle DA (2018) The role of dispersal in river network metacommunities: Patterns, processes, and pathways. Freshwater Biology, 63, 141-163.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Vannote RL, Minshall GW, Cummins KW, Sedell JR, Cushing CE (1980) The river continuum concept. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 37, 130-137.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Vieira NK, Poff N, Carlisle DM, Moulton S, Koski ML, Kondratieff BC (2006) A database of lotic invertebrate traits for North America. US Geological Survey Data Series, 187, 1-15. |
| [47] |
Wallace JB, Webster JR (1996) The role of macroinvertebrates in stream ecosystem function. Annual Review of Entomology, 41, 115-139.
PMID |
| [48] | Wang J (2018) Macroinvertebrate Diversity and Its Application in Health Bioassessment in the Chishui River. PhD dissertation, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王军 (2018) 赤水河大型无脊椎动物多样性与河流生态系统健康评价. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院水生生物研究所, 武汉.] | |
| [49] |
Wang JJ, Soininen J, Zhang Y, Wang BX, Yang XD, Shen J (2010) Contrasting patterns in elevational diversity between microorganisms and macroorganisms. Journal of Biogeography, 38, 595-603.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Wang Y, Zuo YF, Feng Q, Li BL, Kong DX, Zhang XY, Lu H, Wang S (2021) Assessment of macrozoobenthos habitat suitability in the upper and middle reaches of the Heihe River. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40, 1116-1127. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王昱, 左一锋, 冯起, 李宝龙, 孔德星, 张昕雨, 卢晗, 汪双 (2021) 黑河中上游大型底栖动物栖息地适宜度评估. 生态学杂志, 40, 1116-1127.] | |
| [51] | Wu YF, Wu CZ (1992) The Fishes of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [武云飞, 吴翠珍 (1992) 青藏高原鱼类. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [52] | Xie JC (2001) Water pollution and aquatic animal. Bulletin of Biology, 36(6), 10-11. (in Chinese) |
| [谢建春 (2001) 水体污染与水生动物. 生物学通报, 36(6), 10-11.] | |
| [53] |
Xing Y, Wu XP, Ouyang S, Zhang JQ, Xu J, Yin SL, Xie ZC (2019) Assessment of macrobenthos biodiversity and potential human-induced stressors in the Ganjiang River system. Biodiversity Science, 27, 648-657. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[邢圆, 吴小平, 欧阳珊, 张君倩, 徐靖, 银森录, 谢志才 (2019) 赣江水系大型底栖动物多样性与受胁因子初探. 生物多样性, 27, 648-657.]
DOI |
|
| [54] |
Xu MZ, Wang ZY, Pan BZ, Gong TL, Liu L (2012) Research on assemblage characteristics of macroinvertebrates in the Yalu Tsangpo River Basin. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 2351-2360. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [徐梦珍, 王兆印, 潘保柱, 巩同梁, 刘乐 (2012) 雅鲁藏布江流域底栖动物多样性及生态评价. 生态学报, 32, 2351-2360.] | |
| [55] | Yu S, Jia NE, Zhang ZX, Li K, Sun DD, Yang HJ (2017) Community structure and environmental determinants of macroinvertebrates in Ili River. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 41, 1062-1070. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于帅, 贾娜尔·阿汗, 张振兴, 李昆, 孙东东, 杨海军 (2017) 新疆伊犁河不同生境大型底栖动物群落及其影响因素. 水生生物学报, 41, 1062-1070.] | |
| [56] |
Zhang Y, Cheng L, Tolonen KE, Yin HB, Gao JF, Zhang ZM, Li KY, Cai YJ (2018) Substrate degradation and nutrient enrichment structuring macroinvertebrate assemblages in agriculturally dominated Lake Chaohu Basins, China. Science of the Total Environment, 627, 57-66.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Zhao WH, Liu XQ (2010) Preliminary study on macrozoobenthos in Yarlung Zangbo River and its branches around Xiongcun, Tibet, China. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 19, 281-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵伟华, 刘学勤 (2010) 西藏雅鲁藏布江雄村河段及其支流底栖动物初步研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 19, 281-286.] | |
| [58] |
Zhao YJ, Li H, Wang T, Liu Y, Liu QG, Liu J, Hao ZC, Zhu XQ, Shen JZ (2011) Community structure of benthic macroinvertebrates in Lake Ulungur in Xinjiang. Journal of Lake Sciences, 23, 974-981. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [赵永晶, 李鸿, 王腾, 刘宇, 刘其根, 刘军, 郝志才, 朱湘强, 沈建忠 (2011) 新疆乌伦古湖大型底栖无脊椎动物的群落结构. 湖泊科学, 23, 974-981.] | |
| [59] | Zhou CF, Gui H, Zhou KY (2003) Larval Key to Families of Ephemeroptera from China (Insecta). Journal of Nanjing Normal University, 26(2), 65-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周长发, 归鸿, 周开亚 (2003) 中国蜉蝣目稚虫科检索表(昆虫纲). 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 26(2), 65-68.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 宋远昊, 龚吕, 李贲, 胡阳, 李秀珍. 辽河口不同退塘还湿方式对大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [8] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [9] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [10] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [11] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [12] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [13] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [14] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [15] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()