



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 21274. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021274 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021274
• 研究报告: 植物多样性 • 下一篇
佘丹琦1, 张喜亭1, 肖路2, 仲召亮1, 王慧梅1, 王文杰1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-11
接受日期:2021-11-15
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-01-30
通讯作者:
王文杰
作者简介:*E-mail: wwj225@nefu.edu.cn基金资助:
Danqi She1, Xiting Zhang1, Lu Xiao2, Zhaoliang Zhong1, Huimei Wang1, Wenjie Wang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-11
Accepted:2021-11-15
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-01-30
Contact:
Wenjie Wang
摘要:
自然保护区如何设置才能够最大程度保护生物多样性, 是保护生物学的研究热点; 阐明beta多样性特征、组分格局及其影响因素是保护生物学的重要基础。本研究选取小兴安岭凉水国家级自然保护区不同功能区(核心区、缓冲区、实验区)及毗邻地区(保护区外)共80块样方作为研究对象, 调查每块样方的保护位置(经纬度、海拔、坡位、坡度、坡向)和群落结构(郁闭度、林龄、乔木树高、胸径、灌木树高、地径), 并采集0-20 cm土壤样品, 测定土壤理化性质(有机碳、全氮、pH值、电导率、含水量、容重)。将样方间的beta多样性分解为物种周转和物种多度差异两种组分, 通过Mantel分析、冗余分析和方差分解分析解析非生物因子(地理地形、保护强度、土壤因子)和生物因子(群落结构)对beta多样性及其组分的影响。结果表明: (1)乔、灌、草3层中, 物种周转组分对于beta多样性的贡献均占主导地位(65%-73%), 物种多度差异贡献较小。(2) Mantel检验结果表明, 乔、灌、草3层beta多样性及其组分与地理地形指标显著相关的因子最多; 土壤因子只对乔木层和灌木层beta多样性及组分有影响, 对草本层影响不大。其中坡位、坡度、乔木树高和保护强度均与保护区乔、灌、草3层beta多样性显著正相关(P < 0.05)。(3)植物整体beta多样性受地理地形影响最大, 但存在乔、灌、草差异。乔木层beta多样性受生物因子影响最大; 灌木层的土壤因子解释力分别为地理地形和生物因子的2倍; 而草本层主要受地理地形的影响, 其解释力分别是土壤和生物因子的26倍和3倍。乔木胸径对植物beta多样性差异具有最大的解释作用。本研究结果表明, 未来保护区设置需要根据保护植物的类型, 选择适当的林分结构、土壤和地理地形等, 以增强保护区植物多样性保护的效果。
佘丹琦, 张喜亭, 肖路, 仲召亮, 王慧梅, 王文杰 (2022) 小兴安岭凉水国家级自然保护区植物beta多样性及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 30, 21274. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021274.
Danqi She, Xiting Zhang, Lu Xiao, Zhaoliang Zhong, Huimei Wang, Wenjie Wang (2022) Plant beta diversity and its influence factors in the Liangshui National Nature Reserve in the central region of the Xiaoxing’an Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21274. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021274.
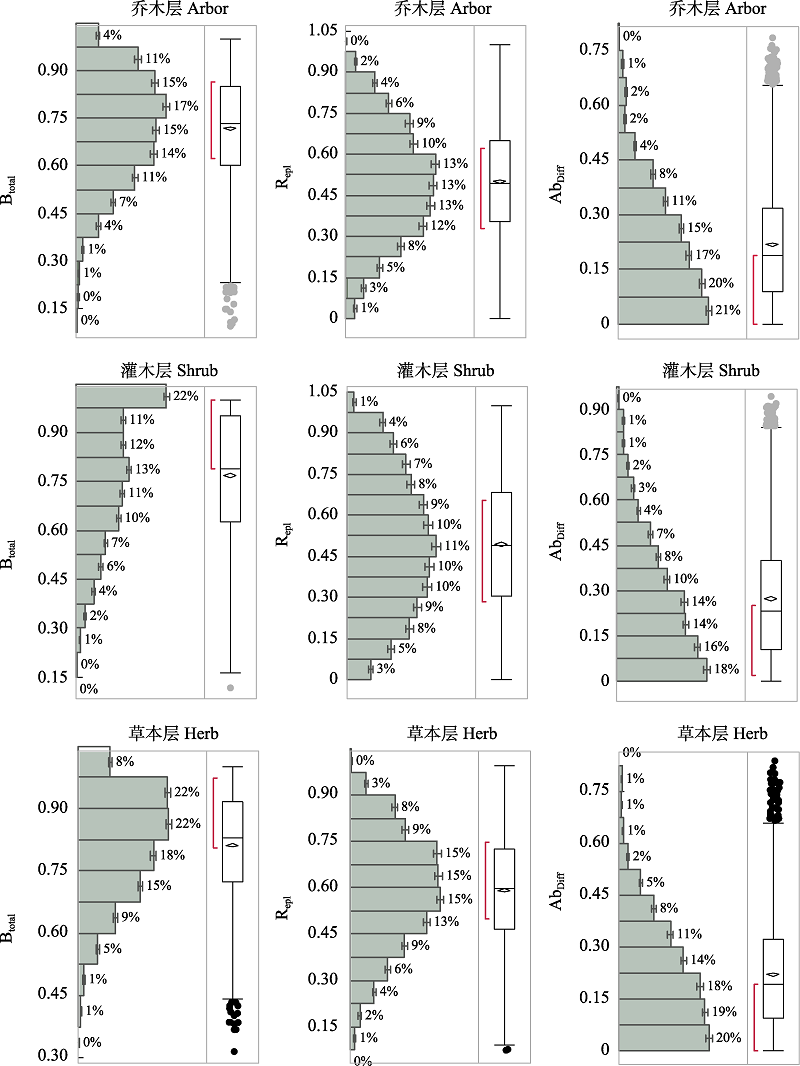
图1 Beta多样性(Btotal)及其物种周转组分(Repl)和物种多度差异组分(AbDiff)特征频率分布箱线图
Fig. 1 The relationship of taxonomic and functional trait beta diversity and its components (turnover and nestedness) of macrobenthic communities with difference in geographic distance
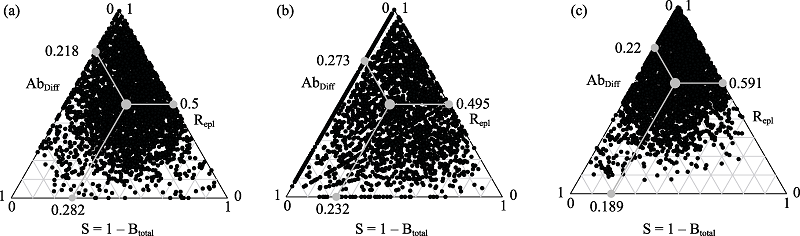
图2 乔木层(a)、灌木层(b)、草本层(c) beta多样性(Btotal)及其物种周转组分(Repl)和物种多度差异组分(AbDiff)三角图。图中每个黑点表示一个样方对, 其位置由物种组成相似性(S = 1 - Btotal)、Repl和AbDiff决定, 三者之和等于1。灰色大点表示平均值。
Fig. 2 Triangle figures for arbor (a), shrub (b), and herb (c) of plant beta diversity (Btotal), and its components of species turnover (Repl) and abundance differences (AbDiff). Each black dot represents a pair of sites. Their positions were determined by a triplet of values from the species composition similarity (S = 1 - Btotal), Repl, and AbDiff; each triplet sums to 1. The larger grey dots represent the mean values.
| | 乔木层 Arbor layer | 灌木层 Shrub layer | 草本层 Herb layer | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sørensen index | AbDiff | Repl | Sørensen index | AbDiff | Repl | Sørensen index | AbDiff | Repl | |||
| 地理地形 Geography and terrain | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 0.079** | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | -0.06 | 0.1** | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.21*** | 0.21* | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.07 | <0.001 | 0.18*** | 0.06 | 0.07 | ||
| 坡度 Slope | 0.2*** | -0.01 | 0.174** | 0.18** | 0.03 | 0.12* | 0.3*** | 0.05 | 0.16*** | ||
| 坡位 Slope position | 0.35*** | 0.14*** | 0.182*** | 0.18*** | 0.09* | 0.08** | 0.13*** | 0.05 | 0.05* | ||
| 坡向 Aspect | -0.08 | 0.02 | -0.08 | -0.07 | -0.08 | 0.01 | -0.01 | -0.04 | 0.03 | ||
| 保护强度 Protection intensity | 0.14*** | 0.12*** | 0.02 | 0.1** | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.08** | -0.01 | 0.07** | ||
| 土壤因子 Soil factors | 有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 0.03 | -0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.09 | -0.03 | -0.01 | -0.01 | <0.001 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.16** | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||
| C : N | -0.06 | 0.004 | -0.05 | 0.01 | -0.06 | 0.06 | -0.02 | <0.001 | -0.01 | ||
| pH | 0.05 | 0.13* | -0.06 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.05 | -0.04 | <0.001 | -0.03 | ||
| 电导率 Electroconductibility | 0.05 | -0.08 | 0.02 | -0.003 | 0.11 | -0.09 | -0.01 | -0.01 | <0.001 | ||
| 容重 Soil bulk density | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.003 | 0.13* | 0.11 | 0.02 | -0.003 | -0.01 | 0.01 | ||
| 含水量 Soil water content | 0.09* | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.21** | -0.01 | 0.18* | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||
| 生物因子 Biological factors | 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.06* | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.008 | -0.04 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |
| 林龄 Forest age | 0.28*** | 0.42*** | -0.1 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.004 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||
| 乔木树高 Tree height | 0.24*** | -0.01 | 0.21*** | 0.14** | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.11* | -0.06 | 0.13*** | ||
| 乔木胸径 Tree DBH | 0.18*** | 0.45*** | -0.21 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.09* | 0.03 | 0.03 | ||
| 灌木树高 Shrub height | 0.05 | 0.04 | -0.01 | 0.12* | 0.14* | -0.02 | -0.03 | 0.01 | -0.03 | ||
| 灌木地径 Shrub ground diameter | 0.02 | -0.02 | 0.03 | 0.16** | 0.17* | 0.01 | -0.08 | <0.001 | -0.06 | ||
表1 Beta多样性(Btotal)及其物种周转组分(Repl)和物种多度差异组分(AbDiff)与地理地形、保护强度、土壤因子、生物因子相关性的Mantel检验
Table 1 Mantel correlations analysis between beta diversity (Btotal), its components of species turnover (Repl) and abundance differences (AbDiff) and geography and terrain, protection intensity, soil factors and biological factors
| | 乔木层 Arbor layer | 灌木层 Shrub layer | 草本层 Herb layer | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sørensen index | AbDiff | Repl | Sørensen index | AbDiff | Repl | Sørensen index | AbDiff | Repl | |||
| 地理地形 Geography and terrain | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 0.079** | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | -0.06 | 0.1** | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.21*** | 0.21* | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.07 | <0.001 | 0.18*** | 0.06 | 0.07 | ||
| 坡度 Slope | 0.2*** | -0.01 | 0.174** | 0.18** | 0.03 | 0.12* | 0.3*** | 0.05 | 0.16*** | ||
| 坡位 Slope position | 0.35*** | 0.14*** | 0.182*** | 0.18*** | 0.09* | 0.08** | 0.13*** | 0.05 | 0.05* | ||
| 坡向 Aspect | -0.08 | 0.02 | -0.08 | -0.07 | -0.08 | 0.01 | -0.01 | -0.04 | 0.03 | ||
| 保护强度 Protection intensity | 0.14*** | 0.12*** | 0.02 | 0.1** | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.08** | -0.01 | 0.07** | ||
| 土壤因子 Soil factors | 有机碳 Soil organic carbon | 0.03 | -0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.09 | -0.03 | -0.01 | -0.01 | <0.001 | |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.16** | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||
| C : N | -0.06 | 0.004 | -0.05 | 0.01 | -0.06 | 0.06 | -0.02 | <0.001 | -0.01 | ||
| pH | 0.05 | 0.13* | -0.06 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.05 | -0.04 | <0.001 | -0.03 | ||
| 电导率 Electroconductibility | 0.05 | -0.08 | 0.02 | -0.003 | 0.11 | -0.09 | -0.01 | -0.01 | <0.001 | ||
| 容重 Soil bulk density | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.003 | 0.13* | 0.11 | 0.02 | -0.003 | -0.01 | 0.01 | ||
| 含水量 Soil water content | 0.09* | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.21** | -0.01 | 0.18* | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||
| 生物因子 Biological factors | 郁闭度 Canopy density | 0.06* | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.008 | -0.04 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |
| 林龄 Forest age | 0.28*** | 0.42*** | -0.1 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.004 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||
| 乔木树高 Tree height | 0.24*** | -0.01 | 0.21*** | 0.14** | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.11* | -0.06 | 0.13*** | ||
| 乔木胸径 Tree DBH | 0.18*** | 0.45*** | -0.21 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.09* | 0.03 | 0.03 | ||
| 灌木树高 Shrub height | 0.05 | 0.04 | -0.01 | 0.12* | 0.14* | -0.02 | -0.03 | 0.01 | -0.03 | ||
| 灌木地径 Shrub ground diameter | 0.02 | -0.02 | 0.03 | 0.16** | 0.17* | 0.01 | -0.08 | <0.001 | -0.06 | ||
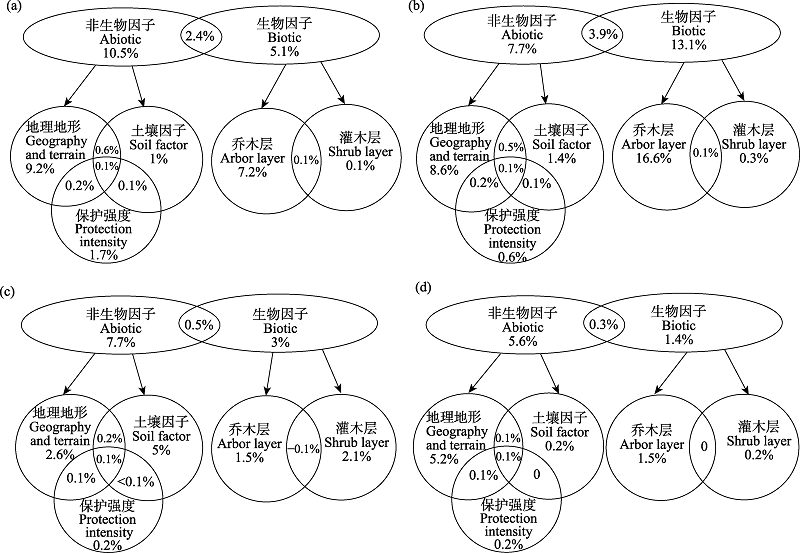
图3 地理地形、保护强度、群落结构与土壤因子对beta多样性特征解释力的方差分解分析。(a)乔、灌、草整体; (b)乔木; (c)灌木; (d)草本。
Fig. 3 Using variation partitioning to analysis the effect of geography and terrain, protection intensity, community characteristics and soil factor on beta diversity characteristics. (a) Arbor-shrub-herb; (b) Arbor; (c) Shrub; (d) Herb.
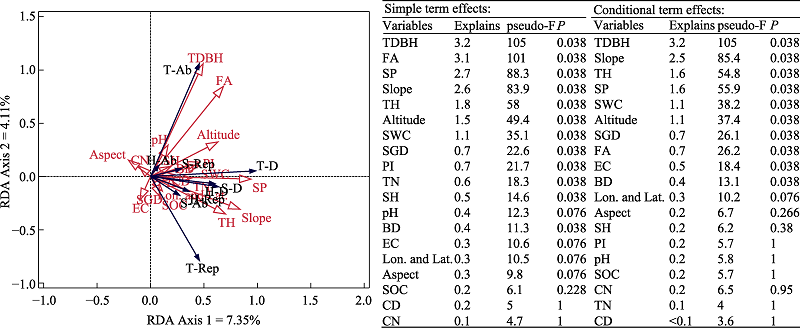
图4 地理地形、保护强度、土壤因子、群落结构与beta多样性复杂关系的冗余分析(RDA)排序分析(左)和最显著解释因子筛选(右)。T-D: 乔木层beta多样性; T-Ab: 乔木层物种多度差异组分; T-Rep: 乔木层物种周转组分; S-D: 灌木层beta多样性; S-Ab: 灌木层物种多度差异组分; S-Rep: 灌木层物种周转组分; H-D: 草本层beta多样性; H-Ab: 草本层物种多度差异组分; H-Rep: 草本层物种周转组分; Lon. and Lat.: 经纬度; Altitude: 海拔; Slope: 坡度; SP: 坡位; Aspect: 坡向; PI: 保护强度; CD: 郁闭度; FA: 林龄; TDBH: 乔木胸径; TH: 乔木树高; SH: 灌木树高; SGD: 灌木地径; SOC: 土壤有机碳; TN: 全氮; CN: 碳氮比; EC: 电导率; BD: 土壤容重; SWC: 土壤含水量。
Fig. 4 Redundancy analysis (RDA) ordination between geography and terrain, protection intensity, soil matrix, and community characteristics and beta diversity indices (left) and the most significant explaining factors (right). Btotal, Beta diversity; AbDiff, component of abundance differences; Repl, component of species turnover; T-D, Arbor Btotal; T-Ab, Arbor AbDiff; T-Rep, Arbor Repl; S-D, Shrub Btotal; S-Ab, Shrub AbDiff; S-Rep, Shrub Repl; H-D, Herb Btotal; H-Ab, Herb AbDiff; H-Rep, Herb Repl; Lon. And Lat., Longitude and Latitude; SP, Slope position; PI, Protection intensity; CD, Crown density; FA, Forest age; TDBH, Tree diameter; TH, Tree height; SH, Shrub height; SGD, Shrub ground diameter; SOC, Soil organic carbon; TN, Total nitrogen; CN, C : N; EC, Electroconductibility; BD, Soil bulk density; SWC, Soil water content.
| [1] | Bao SD (2000) Soil Agro-chemistry Analysis, 3rd edn. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 鲍士旦 (2000) 土壤农化分析(第3版). 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [2] |
Carvalho JC, Cardoso P, Gomes P (2012) Determining the relative roles of species replacement and species richness differences in generating beta-diversity patterns. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 760-771.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chen C, Wang Y, Wang JM, Yang H, Wang YC, Xu C, Li JW, Chu JM (2020) Species diversity of plant communities and its main influencing factors in Horqin Sandy Land, Inner Mongolia of northern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 42(5), 106-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈晨, 王寅, 王健铭, 杨欢, 王雨辰, 徐超, 李景文, 褚建民 (2020) 科尔沁沙地植物群落物种多样性及其主要影响因素. 北京林业大学学报, 42(5), 106-114.] | |
| [4] |
Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.]
DOI |
|
| [5] | Chen XB, Zhu DQ, Zhao CC, Zhang LL, Chen LX, Duan WB (2019) Community composition and diversity of fungi in soils under different types of Pinus koraiensis forests. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 56, 1221-1234. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈秀波, 朱德全, 赵晨晨, 张路路, 陈立新, 段文标 (2019) 不同林型红松林土壤真菌群落组成和多样性. 土壤学报, 56, 1221-1234.] | |
| [6] |
Condit R, Pitman N, Leigh EG Jr, Chave J, Terborgh J, Foster RB, Núñez P, Aguilar S, Valencia R, Villa G, Muller-Landau HC, Losos E, Hubbell SP (2002) Beta-diversity in tropical forest trees. Science, 295, 666-669.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Dray S, Blanchet FG, Legendre P, Madi N, Wagner H (2017) adespatial: Multivariate Multiscale Spatital Analysis. R package version 0.2-0. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/adespatital/ . (accessed on 2018-05-23) |
| [8] |
Fernandez-Going BM, Harrison SP, Anacker BL, Safford HD (2013) Climate interacts with soil to produce beta diversity in Californian plant communities. Ecology, 94, 2007-2018.
PMID |
| [9] |
Gutiérrez-Cánovas C, Millán A, Velasco J, Vaughan IP, Ormerod SJ (2013) Contrasting effects of natural and anthropogenic stressors on beta diversity in river organisms. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 796-805.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Hájek M, Hájková P, Kočí M, Jiroušek M, Mikulášková E, Kintrová K (2012) Do we need soil moisture measurements in the vegetation-environment studies in wetlands? Journal of Vegetation Science, 24, 127-137.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Harrison S, Ross SJ, Lawton JH (1992) Beta diversity on geographic gradients in Britain. Journal of Animal Ecology, 61, 151-158.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [13] | Kong LW, Chen XW, Lu SW, Li SN, Chen B, Gao C, Shi Y, Yang XY (2014) Relationships among growth of Larix principis-rupprechtii, herbaceous plants diversity and landform. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(5), 60-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孔令伟, 陈祥伟, 鲁绍伟, 李少宁, 陈波, 高琛, 石媛, 杨小燕 (2014) 华北落叶松林木生长、草本植物多样性及地形因子之间的关系. 水土保持通报, 34(5), 60-66.] | |
| [14] |
Kraft NJB, Valencia R, Ackerly DD (2008) Functional traits and niche-based tree community assembly in an Amazonian forest. Science, 322, 580-582.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Legendre P (2014) Interpreting the replacement and richness difference components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 1324-1334.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Lennon JJ, Koleff P, GreenwooD JJD, Gaston KJ (2001) The geographical structure of British bird distributions: Diversity, spatial turnover and scale. Journal of Animal Ecology, 70, 966-979.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Leprieur F, Tedesco PA, Hugueny B, Beauchard O, Dürr HH, Brosse S, Oberdorff T (2011) Partitioning global patterns of freshwater fish beta diversity reveals contrasting signatures of past climate changes. Ecology Letters, 14, 325-334.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Li XH, Liu YH, Liu Y, Xu Y, Yang Y, Shen ZH (2016) Impacts of geographical distances and environmental differences on the beta diversity of plant communities in the dry-hot valley of the Yuanjiang River. Biodiversity Science, 24, 399-406. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李新辉, 刘延虹, 刘晔, 许玥, 杨阳, 沈泽昊 (2016) 地理距离及环境差异对云南元江干热河谷植物群落beta多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 24, 399-406.]
DOI |
|
| [19] | Liu HW, Chen LX, Ma HJ, Qiao L, Zhang J (2010) Seasonal dynamics of soil phosphorus for main forest types in Liangshui Nature Reserve and its availability. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 38(4), 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘宏伟, 陈立新, 马海娟, 乔璐, 张杰 (2010) 凉水自然保护区主要森林类型土壤磷季节动态及有效性. 东北林业大学学报, 38(4), 62-65.] | |
| [20] | Liu SC, Duan WB, Feng J, Han SZ (2011) Effects of forest gap on tree species regeneration and diversity of mixed broadleaved Korean pine forest in Xiaoxing’an Mountains. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22, 1381-1388. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘少冲, 段文标, 冯静, 韩生忠 (2011) 林隙对小兴安岭阔叶红松林树种更新及物种多样性的影响. 应用生态学报, 22, 1381-1388.] | |
| [21] | Lu ZS, Guo JP, Hu SC (1993) Use the growth cone-like wood method to determine the number of stands at maturity. East China Forest Management, 7(2), 29-33. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陆兆苏, 郭晋平, 胡世才 (1993) 用生长锥样木法确定林分数量成熟龄. 华东森林经理, 7(2), 29-33.] | |
| [22] |
Podani J, Schmera D (2011) A new conceptual and methodological framework for exploring and explaining pattern in presence-absence data. Oikos, 120, 1625-1638.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Si XF, Zhao YH, Chen CW, Ren P, Zeng D, Wu LB, Ding P (2017) Beta-diversity partitioning: Methods, applications and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 25, 464-480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 斯幸峰, 赵郁豪, 陈传武, 任鹏, 曾頔, 吴玲兵, 丁平 (2017) Beta多样性分解: 方法、应用与展望. 生物多样性, 25, 464-480.]
DOI |
|
| [24] |
Socolar JB, Gilroy JJ, Kunin WE, Edwards DP (2016) How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 31, 67-80.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Soininen J, Heino J, Wang JJ (2018) A meta-analysis of nestedness and turnover components of beta diversity across organisms and ecosystems. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 96-109.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Tan SS, Ye ZL, Yuan LB, Zhou RF, Hu G, Jin XF, Yu MJ (2013) Beta diversity of plant communities in Baishanzu Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 6944-6956. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 谭珊珊, 叶珍林, 袁留斌, 周荣飞, 胡广, 金孝锋, 于明坚 (2013) 百山祖自然保护区植物群落beta多样性. 生态学报, 33, 6944-6956.] | |
| [27] |
Tang ZY, Fang JY, Zhang L (2004) Patterns of woody plant species diversity along environmental gradients on Mt. Taibai, Qinling Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 12, 115-122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 唐志尧, 方精云, 张玲 (2004) 秦岭太白山木本植物物种多样性的梯度格局及环境解释. 生物多样性, 12, 115-122.]
DOI |
|
| [28] |
Tisseuil C, Leprieur F, Grenouillet G, Vrac M, Lek S (2012) Projected impacts of climate change on spatio-temporal patterns of freshwater fish beta diversity: A deconstructing approach. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1213-1222.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Tuomisto H, Ruokolainen K, Yli-Halla M (2003) Dispersal, environment, and floristic variation of western Amazonian forests. Science, 299, 241-244.
PMID |
| [30] | Wang SX, Xia TT, Wang XA (2021) Understory β diversity differences and influential factors between Pinus tabuliformis plantation and natural Quercus wutaishanica forest on the Loess Plateau. Guilhaia, 41, 362-371. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王世雄, 夏婷婷, 王孝安 (2021) 黄土高原油松和辽东栎林下植物β多样性差异及影响因素. 广西植物, 41, 362-371.] | |
| [31] | Wang WJ, Du HJ, Xiao L, Zhang JY, Zhong ZL, Zhou W, Zhang B, Wang HY (2019) Differences in plant composition and forest structure among of 3 forest types in Liangshui National Nature Reserve. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 55, 166-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王文杰, 杜红居, 肖路, 张建宇, 仲召亮, 周伟, 张波, 王洪元 (2019) 凉水自然保护区3种森林类型的植物组成和林分结构特征. 林业科学, 55, 166-176.] | |
| [32] |
Wang WJ, Sun JX, Zhong ZL, Xiao L, Wang YY, Wang HM (2021) Relating macrofungal diversity and forest characteristics in boreal forests in China: Conservation effects, inter-forest-type variations, and association decoupling. Ecology and Evolution, 11, 13268-13282.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Wang XG, Wiegand T, Anderson-Teixeira KJ, Bourg NA, Myers JA (2018) Ecological drivers of spatial community dissimilarity, species replacement and species nestedness across temperate forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 581-592.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Whittaker RH (1972) Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon, 21, 213-251.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Williams PH (1996) Mapping variations in the strength and breadth of biogeographic transition zones using species turnover. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 263, 579-588. |
| [36] | Yao XY, Hu YS, Liu YH (2014) Functional diversity of typical broad-leaved Korean pine forest communities in Changbai Mountains and its relationship with topographical factors. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 42(10), 95-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 么旭阳, 胡耀升, 刘艳红 (2014) 长白山阔叶红松林典型森林群落功能多样性及其与地形因子的关系. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 42(10), 95-102.] | |
| [37] |
Yao ZL, Wen HD, Deng Y, Cao M, Lin LX (2020) Driving forces underlying the beta diversity of tree species in subtropical mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forests in Ailao Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 28, 445- 454. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 姚志良, 温韩东, 邓云, 曹敏, 林露湘 (2020) 哀牢山亚热带中山湿性常绿阔叶林树种beta多样性格局形成的驱动力. 生物多样性, 28, 445-454.]
DOI |
|
| [38] | Zhang JY, Wang WJ, Du HJ, Zhong ZL, Xiao L, Zhou W, Zhang B, Wang HY (2018) Differences in community characteristics, species diversity, and their coupling associations among three forest types in the Huzhong area, Daxinganling Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 4684-4693. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张建宇, 王文杰, 杜红居, 仲召亮, 肖路, 周伟, 张波, 王洪元 (2018) 大兴安岭呼中地区3种林分的群落特征、物种多样性差异及其耦合关系. 生态学报, 38, 4684-4693.] | |
| [39] | Zhang XT, Zhang JY, Li SW, Zhong ZL, Hu XG, Wang WJ (2021) Characteristics of plant diversity and community structure in Shuanghe Nature Reserve in Daxing’anling area of northeastern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 43(7), 79-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张喜亭, 张建宇, 李斯雯, 仲召亮, 胡晓光, 王文杰 (2021) 大兴安岭双河保护区植物多样性和群落结构特征分析. 北京林业大学学报, 43(7), 79-87.] | |
| [40] |
Zhen Z, Guo ZY, Zhao YH, Li FR, Wei QB (2016) Spatial distribution of soil total nitrogen in Liangshui National Nature Reserve based on local model. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 549-558. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PMID |
|
[ 甄贞, 郭志英, 赵颖慧, 李凤日, 魏庆彬 (2016) 基于局域模型的凉水国家自然保护区土壤全氮空间分布. 应用生态学报, 27, 549-558.]
PMID |
|
| [41] |
Zhu B, Chen AP, Liu ZL, Fang JY (2004) Plant community composition and tree species diversity on eastern and western Nanling Mountains, China. Biodiversity Science, 12, 53-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 朱彪, 陈安平, 刘增力, 方精云 (2004) 南岭东西段植物群落物种组成及其树种多样性垂直格局的比较. 生物多样性, 12, 53-62.]
DOI |
|
| [42] | Zhu LJ, Jin GZ, Du WX, Wang XC (2016) Characteristics of canopy disturbance for a typical broadleaf-Korean pine mixed forest in Xiaoxing’an Mountains, Liangshui, northeastern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 38(6), 17-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱良军, 金光泽, 杜文先, 王晓春 (2016) 小兴安岭凉水典型阔叶红松林林冠干扰特征分析. 北京林业大学学报, 38(6), 17-27.] |
| [1] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [2] | 王健铭, 雷训, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23144-. |
| [3] | 李艳辉, 兰天元, 王月, 于洋, 赵常明, 李利华, 徐文婷, 申国珍. 神农架植物物种空间周转的驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21377-. |
| [4] | 曲梦君, 努尔依拉·阿巴拜克, 邹旭阁, 赵航, 朱威霖, 王健铭, 李景文. 地理距离和环境因子对阿拉善戈壁植物群落β多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22029-. |
| [5] | 贺佳云, 张东, 储玲, 严云志. 人为干扰对溪流鱼类功能多样性及其纵向梯度格局的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 927-937. |
| [6] | 邹怡. 样本量不一致时的β多样性计算[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 790-797. |
| [7] | 姚志良,温韩东,邓云,曹敏,林露湘. 哀牢山亚热带中山湿性常绿阔叶林树种beta多样性格局形成的驱动力[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 445-454. |
| [8] | 李明家, 吴凯媛, 孟凡凡, 沈吉, 刘勇勤, 肖能文, 王建军. 西藏横断山区溪流细菌beta多样性组分对气候和水体环境的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1570-1580. |
| [9] | 蒙洋, 邱月, 张亮, 王翠玲, 臧振华, 张学耀, 申国珍, 闫彩凤, 陈全胜. 地理距离、海拔和气候差异对独龙江流域维管植物群落物种空间相异性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(12): 1313-1320. |
| [10] | 赵鸣飞, 王国义, 邢开雄, 王宇航, 薛峰, 康慕谊, 罗开. 秦岭西部森林群落相似性递减格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(1): 3-10. |
| [11] | 李新辉, 刘延虹, 刘晔, 许玥, 杨阳, 沈泽昊. 地理距离及环境差异对云南元江干热河谷植物群落beta多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 399-406. |
| [12] | 陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚. Beta多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(4): 323-335. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn