



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 1481-1489. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021085 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021085
收稿日期:2021-03-09
接受日期:2021-07-14
出版日期:2021-11-20
发布日期:2021-11-12
通讯作者:
杨娟
作者简介:E-mail: yangjuan@cugb.edu.cn基金资助:
Mengxia Wang, Xinyi Chen, Jie Zhang, Yuhang Song, Juan Yang( )
)
Received:2021-03-09
Accepted:2021-07-14
Online:2021-11-20
Published:2021-11-12
Contact:
Juan Yang
摘要:
菲律宾海邻近全球生物多样性和进化的中心, 分布着多种重要生物资源。了解本区生物多样性及受威胁物种的分布特征可对掌握其生物多样性现状, 以及未来实施有效的生物多样性保护管理策略提供重要依据。本文利用海洋生物地理信息系统(Ocean Biogeographic Information System, OBIS)数据库, 并参考世界自然保护联盟濒危物种红色名录(IUCN Redlist)的物种濒危程度评估结果, 构建了菲律宾海脊索动物生物多样性和受威胁物种数据库, 结合海洋生态因子特征对该海区脊索动物的物种多样性和不同等级受威胁物种的数量空间分布格局进行了初步分析, 并对脊索动物不同分类阶元生物多样性与生态因子的关系进行了相关性分析。结果表明, 本区海洋脊索动物门已报道11纲56目320科1,171属2,876种。其中在菲律宾海的边缘区域, 特别是菲律宾群岛、台湾岛、日本群岛、马里亚纳群岛及中央的九州-帕劳海脊附近海域, 生物多样性水平相对较高, 而中央海盆区的生物多样性较低。本海域鱼类生物多样性尤其丰富, 共计4纲45目292科1,105属2,768种, 在物种水平上占本区脊索动物物种数的96%。各分类阶元水平的多样性与初级生产力呈显著正相关, 而与水深呈显著负相关。本区脊索动物门受威胁物种共计54种, 其中极危3种、濒危5种、易危22种、近危24种, 分别约占全区脊索动物总种数的0.10%、0.17%、0.76%、0.83%。与本区生物多样性分布格局相似, 受威胁物种多分布于菲律宾海边缘区域, 在中央海脊和深水盆地区域分布较少。本研究表明, 对菲律宾海脊索动物特别是受威胁物种的保护应当以边缘区域优先; 但考虑到当前菲律宾海深海区域生物多样性数据的不足, 也应加强对中央海脊和深水盆地等区域的生物多样性普查。
王梦霞, 陈心怡, 张洁, 宋宇航, 杨娟 (2021) 菲律宾海脊索动物多样性评估: 基于OBIS数据库. 生物多样性, 29, 1481-1489. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021085.
Mengxia Wang, Xinyi Chen, Jie Zhang, Yuhang Song, Juan Yang (2021) Biodiversity of Chordata in the Philippine Sea: A case study based on OBIS. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1481-1489. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021085.
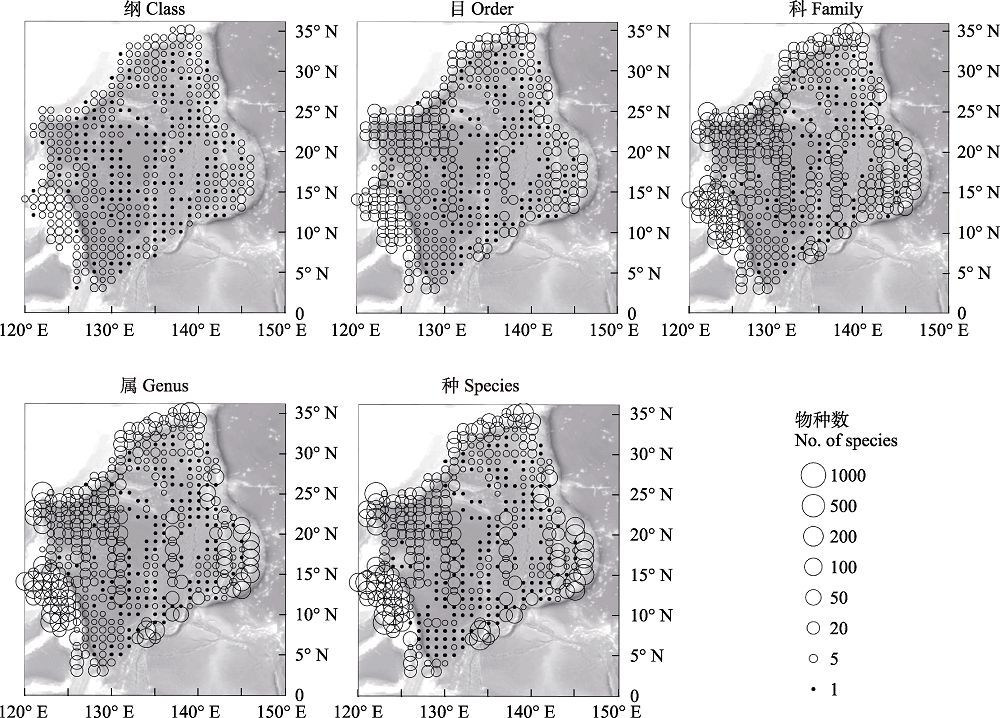
图2 菲律宾海海洋脊索动物门的纲、目、科、属、种水平的生物多样性分布
Fig. 2 Biodiversity distribution at class, order, family, genus and species levels of marine Chordata in the Philippine Sea
| 分类阶元Taxonomic levels | 水深 Water depth | 净初级生产力Net primary productivity | 海水表层温度 Sea surface temperature (SST) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 纲 Class | -0.45** | 0.25** | -0.12* |
| 目 Order | -0.53** | 0.30** | -0.12* |
| 科 Family | -0.51** | 0.25** | - |
| 属 Genus | -0.48** | 0.24** | - |
| 种 Species | -0.42** | 0.21** | - |
表1 不同分类阶元生物多样性与生态因子的相关性
Table 1 Correlation between biodiversity and ecological factors at different taxonomic levels
| 分类阶元Taxonomic levels | 水深 Water depth | 净初级生产力Net primary productivity | 海水表层温度 Sea surface temperature (SST) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 纲 Class | -0.45** | 0.25** | -0.12* |
| 目 Order | -0.53** | 0.30** | -0.12* |
| 科 Family | -0.51** | 0.25** | - |
| 属 Genus | -0.48** | 0.24** | - |
| 种 Species | -0.42** | 0.21** | - |
| [1] | Berghe EV, Stocks KI, Grassle JF (2010) Data integration:The Ocean Biogeographic Information System. In: Life in the World’s Oceans: Diversity, Distribution, and Abundance (ed. Mclntyre AD), pp. 331-353. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford. |
| [2] | Carpenter KE, Springer VG (2005) The center of the center of marine shore fish biodiversity:The Philippine Islands. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 72, 467-480. |
| [3] |
Chen YY, Sun XX, Zhu ML, Zheng S, Yuan YQ, Denis M (2017) Spatial variability of phytoplankton in the Pacific western boundary currents during summer 2014. Marine and Freshwater Research, 68, 1887-1900.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Costello MJ (2004) The Ocean Biogeographic Information System. In:Proceedings of the Xixth International Congress of Zoology (China Association for Science and Technology), p. 151. Beijing. |
| [5] | Gui J, Fan XT, Gong YF, Jiang L (2013) An overview of the international existing marine protected area of high seas and its management mechanism. Environment and Sustainable Development, 38(5), 41-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 桂静, 范晓婷, 公衍芬, 姜丽 (2013) 国际现有公海保护区及其管理机制概览. 环境与可持续发展, 38(5), 41-45.] | |
| [6] | Jiang L, Gui J, Luo TT, Wang Q (2013) A preliminary study on the problem of high seas marine proteced areas. Marine Development and Management, 30(9), 6-10. (in Chinese) |
| [ 姜丽, 桂静, 罗婷婷, 王群 (2013) 公海保护区问题初探. 海洋开发与管理, 30(9), 6-10.] | |
| [7] |
Klein E, Appeltans W, Provoost P, Saeedi H, Benson A, Bajona L, Peralta AC, Bristol RS (2019) OBIS infrastructure, Lessons Learned, and Vision for the Future. Frontiers in Marine Science, 6, 588.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Kodama T, Watanabe T, Taniuchi Y, Kuwata A, Hasegawa D (2021) Micro-size plankton abundance and assemblages in the western North Pacific Subtropical Gyre under microscopic observation. PLoS ONE, 16, e0250604. |
| [9] | Li CZ, Li NS, Lin MH (2000) Terrain features of the Philippine Sea. Marine Science, 24(6), 47-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李常珍, 李乃胜, 林美华 (2000) 菲律宾海的地势特征. 海洋科学, 24(6), 47-51] | |
| [10] |
Liao JJ, Huang H, Li WW, Wang L, An LN (2019) A new perspective on marine biological diversity of areas beyond national jurisdiction (BBNJ): Making use of area-based management tools (ABMTs), including marine protected areas (MPAs). Biodiversity Science, 27, 1153-1161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 廖建基, 黄浩, 李伟文, 王磊, 安丽娜 (2019) 国家管辖范围以外区域海洋生物多样性保护的新视域: 包括海洋保护区在内的划区管理工具. 生物多样性, 27, 1153-1161.]
DOI |
|
| [11] |
Pinheiro HT, Shepherd B, Castillo C, Abesamis RA, Copus JM, Pyle RL, Greene BD, Coleman RR, Whitton RK, Thillainath E, Bucol AA, Birt M, Catania D, Bell MV, Rocha LA (2019) Deep reef fishes in the world’s epicenter of marine biodiversity. Coral Reefs, 38, 985-995.
DOI |
| [12] |
Quimpo TJR, Cabaitan PC, Go KTB, Dumalagan EE Jr, Villanoy CL, Siringan FP (2019) Similarity in benthic habitat and fish assemblages in the upper mesophotic and shallow water reefs in the West Philippine Sea. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 99, 1507-1517.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Shao KT, Li H, Lin YC, Lai KC (2014) A review of marine biodiversity information resources. Biodiversity Science, 22, 253-263. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 邵广昭, 李瀚, 林永昌, 赖昆祺 (2014) 海洋生物多样性信息资源. 生物多样性, 22, 253-263.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Sun J, Lin M, Chen MX, Xu KD (2016) Marine biodiversity under global climate change. Biodiversity Science, 24, 737-738. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[ 孙军, 林茂, 陈孟仙, 徐奎栋 (2016) 全球气候变化下的海洋生物多样性. 生物多样性, 24, 737-738.]
DOI |
|
| [15] | Sun XX, Guo SJ, Liu MT, Li HB (2021) Research progress on phytoplankton and zooplankton ecology in Indo-Pacific convergence region. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 52, 323-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙晓霞, 郭术津, 刘梦坛, 李海波 (2021) 印太交汇区浮游植物和浮游动物生态学研究进展. 海洋与湖沼, 52, 323-331.] | |
| [16] |
Tsukamoto K (1992) Discovery of the spawning area for Japanese eel. Nature, 356, 789-791.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Tsukamoto K (2006) Oceanic biology: Spawning of eels near a seamount. Nature, 439, 929-929.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Tsukamoto K, Chow S, Otake T, Kurogi H, Mochioka N, Miller MJ, Aoyama J, Kimura S, Watanabe S, Yoshinaga T, Shinoda A, Kuroki M, Oya M, Watanabe T, Hata K, Ijiri S, Kazeto Y, Nomura K, Tanaka H (2011) Oceanic spawning ecology of freshwater eels in the western North Pacific. Nature Communications, 2, 279-316.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Tupper M, Asif F, Garces LR, Pido MD (2015) Evaluating the management effectiveness of marine protected areas at seven selected sites in the Philippines. Marine Policy, 56, 33-42.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Wang JP (2020) On practical dilemmas and international law-making of marine protected areas beyond national jurisdiction. Pacific Journal, 28(9), 52-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王金鹏 (2020) 论国家管辖范围以外区域海洋保护区的实践困境与国际立法要点. 太平洋学报, 28(9), 52-63.] | |
| [21] | Xu JZ (1994) Marine fisheries in Philippines. Modern Fisheries Information, 9(6), 13-15. (in Chinese) |
| [ 徐君卓 (1994) 菲律宾的海洋渔业. 现代渔业信息, 9(6), 13-15.] | |
| [22] | Xu W (2015) Research on the relationship between high seas marine protected areas with the current system of Law of the Sea-An analysis based on the United Nations’ Convention on the Law of the Sea. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Humanities Edition), 32(6), 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 许望 (2015) 公海保护区与现行海洋法体系的关系问题研究--基于《联合国海洋法公约》的分析. 浙江海洋学院学报(人文科学版), 32(6), 7-12.] | |
| [23] |
Yang G, Li CL, Wang YQ, Wang XC, Dai LP, Tao ZC, Ji P (2017) Spatial variation of the zooplankton community in the western tropical Pacific Ocean during the summer of 2014. Continental Shelf Research, 135, 14-22.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Zhang YQ, Grassle JF (2002) A portal for the Ocean Biogeographic Information System. Oceanologica Acta, 25, 193-197.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn