



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 53-64. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020137 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020137
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康; 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
李世雄1,2,3, 王彦龙1,2,3, 王玉琴1, 尹亚丽1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-04-03
接受日期:2020-08-11
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2020-09-30
通讯作者:
尹亚丽
基金资助:
Shixiong Li1,2,3, Yanlong Wang1,2,3, Yuqin Wang1, Yali Yin1,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-04-03
Accepted:2020-08-11
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2020-09-30
Contact:
Yali Yin
摘要:
为明确高寒草甸土壤细菌物种组成及功能结构对草地环境恶化的响应规律, 本文采用高通量基因测序技术对高寒草甸未退化、轻度退化、中度退化、重度退化和极重度退化草地土壤细菌的组成、格局和功能进行了研究。结果表明: 高寒草甸土壤优势细菌为酸杆菌门、放线菌门、浮霉菌门、变形菌门和疣微菌门, 在土壤细菌中占比分别为16%‒18%、9%‒12%、12%‒14%、23%‒29%和11%‒12%。退化草地中土壤细菌物种组成明显改变, 变形菌门细菌丰度降低, 酸杆菌门和浮霉菌门丰度增加, 不同草地科水平细菌丰度差异因土层而异。草地退化对细菌Chao1指数无影响, 轻度退化提高了细菌Simpson指数, 重度退化草地土壤细菌Shannon-Wiener指数最高。Faprotax细菌功能分组以化能异养、硝化作用、亚硝酸盐氧化及硫代谢作用为主, 草地退化改变了微生物介导的碳循环、氮循环、硫循环、铁循环和锰循环。重度及极重度退化提高了细菌氨氧化功能作用, 降低了硫化物、亚硝酸盐氧化及尿素水解作用; 草地退化过程中细菌化能异养、芳香族化合物降解及反硝化作用功能等均呈先降低后升高的变化趋势, 中度退化阶段是微生物群落生态功能结构转变的拐点。高寒草甸退化改变了土壤细菌的群落及功能结构, 土壤含水量、pH、总有机碳、全氮、全钾和有效氮磷比是土壤细菌群落及功能结构变化的主要驱动因子。
李世雄, 王彦龙, 王玉琴, 尹亚丽 (2021) 土壤细菌群落特征对高寒草甸退化的响应. 生物多样性, 29, 53-64. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020137.
Shixiong Li, Yanlong Wang, Yuqin Wang, Yali Yin (2021) Response of soil bacterial community characteristics to alpine meadow degradation. Biodiversity Science, 29, 53-64. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020137.
| 土层深度 Soil depth | 退化程度 Degradation degree | 多样性指数 Diversity index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson index | ||
| 0‒10 cm | 未退化 Non-degradation | 8,828.18 ± 363.61a | 10.31 ± 0.15c | 0.997 ± 0.001bc |
| 轻度退化 Light-degradation | 9,015.26 ± 2,567.38a | 10.54 ± 0.13ab | 0.998 ± 0.000a | |
| 中度退化 Moderate-degradation | 9,904.47 ± 490.73a | 10.32 ± 0.05bc | 0.997 ± 0.000abc | |
| 重度退化 Severe-degradation | 11,054.59 ± 1,330.52a | 10.63 ± 0.07a | 0.997 ± 0.000ab | |
| 极重度退化 Extreme-degradation | 9,517.00 ± 1,023.90a | 10.52 ± 0.18abc | 0.996 ± 0.001c | |
| 10‒20 cm | 未退化 Non-degradation | 7,686.14 ± 636.88a | 9.95 ± 0.19cd | 0.996 ± 0.000c |
| 轻度退化 Light-degradation | 8,022.41 ± 1,254.05a | 10.19 ± 0.15bc | 0.997 ± 0.000b | |
| 中度退化 Moderate-degradation | 7,251.09 ± 706.01a | 9.91 ± 0.05d | 0.996 ± 0.000c | |
| 重度退化 Severe-degradation | 8,891.85 ± 1,224.30a | 10.48 ± 0.11a | 0.998 ± 0.000a | |
| 极重度退化 Extreme-degradation | 8,756.00 ± 1,594.71a | 10.29 ± 0.22ab | 0.997 ± 0.000b | |
表1 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤细菌α-多样性
Table 1 Soil bacterial α-diversity in different degraded alpine meadows
| 土层深度 Soil depth | 退化程度 Degradation degree | 多样性指数 Diversity index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson index | ||
| 0‒10 cm | 未退化 Non-degradation | 8,828.18 ± 363.61a | 10.31 ± 0.15c | 0.997 ± 0.001bc |
| 轻度退化 Light-degradation | 9,015.26 ± 2,567.38a | 10.54 ± 0.13ab | 0.998 ± 0.000a | |
| 中度退化 Moderate-degradation | 9,904.47 ± 490.73a | 10.32 ± 0.05bc | 0.997 ± 0.000abc | |
| 重度退化 Severe-degradation | 11,054.59 ± 1,330.52a | 10.63 ± 0.07a | 0.997 ± 0.000ab | |
| 极重度退化 Extreme-degradation | 9,517.00 ± 1,023.90a | 10.52 ± 0.18abc | 0.996 ± 0.001c | |
| 10‒20 cm | 未退化 Non-degradation | 7,686.14 ± 636.88a | 9.95 ± 0.19cd | 0.996 ± 0.000c |
| 轻度退化 Light-degradation | 8,022.41 ± 1,254.05a | 10.19 ± 0.15bc | 0.997 ± 0.000b | |
| 中度退化 Moderate-degradation | 7,251.09 ± 706.01a | 9.91 ± 0.05d | 0.996 ± 0.000c | |
| 重度退化 Severe-degradation | 8,891.85 ± 1,224.30a | 10.48 ± 0.11a | 0.998 ± 0.000a | |
| 极重度退化 Extreme-degradation | 8,756.00 ± 1,594.71a | 10.29 ± 0.22ab | 0.997 ± 0.000b | |
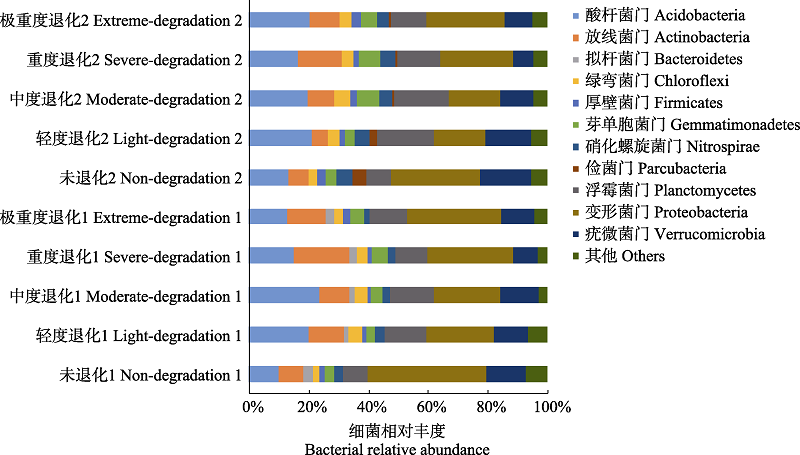
图1 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤细菌门水平的相对丰度。图中1和2分别代表0‒10 cm和10‒20 cm土层。
Fig. 1 Soil bacterial relative abundance at the phylum level in different degraded alpine meadows. Numbers 1 and 2 in the figure represent 0‒10 cm and 10‒20 cm soil layer, respectively.
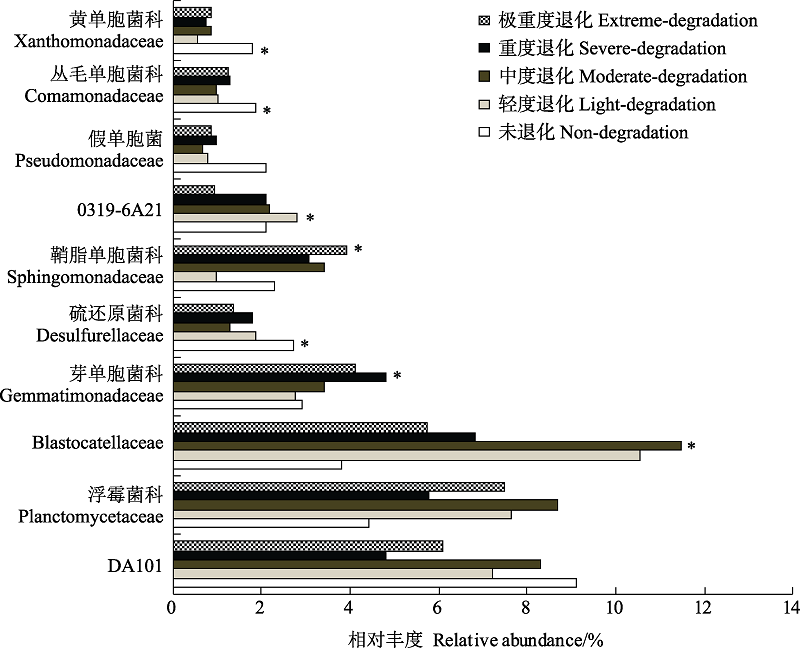
图2 不同退化程度高寒草甸0-10 cm土壤科水平细菌丰度差异。* P < 0.05。
Fig. 2 The soil bacterial abundance in family level at soil depth of 0‒10 cm in different degraded alpine meadows. *P < 0.05.
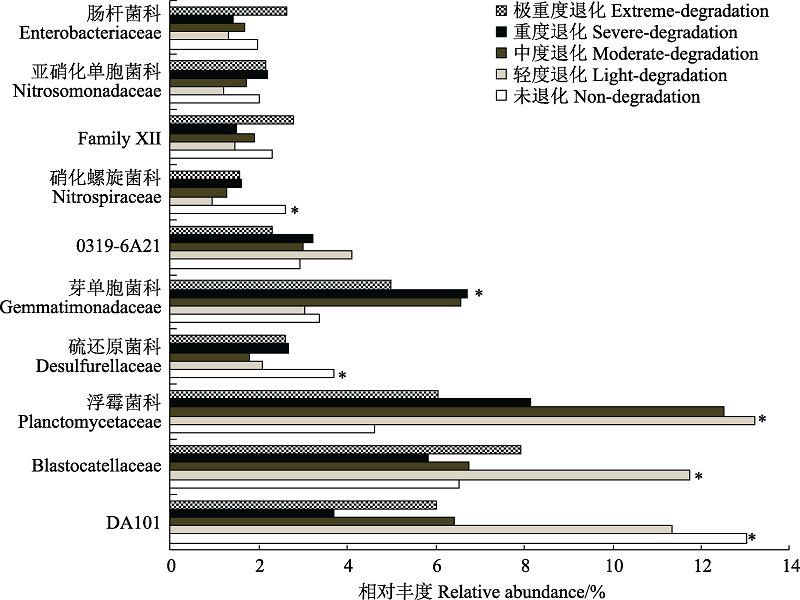
图3 不同退化程度高寒草甸10‒20 cm土壤科水平细菌丰度差异。* P < 0.05。
Fig. 3 The soil bacterial abundance in family level at soil depth of 10‒20 cm in different degraded alpine meadows. *P < 0.05.
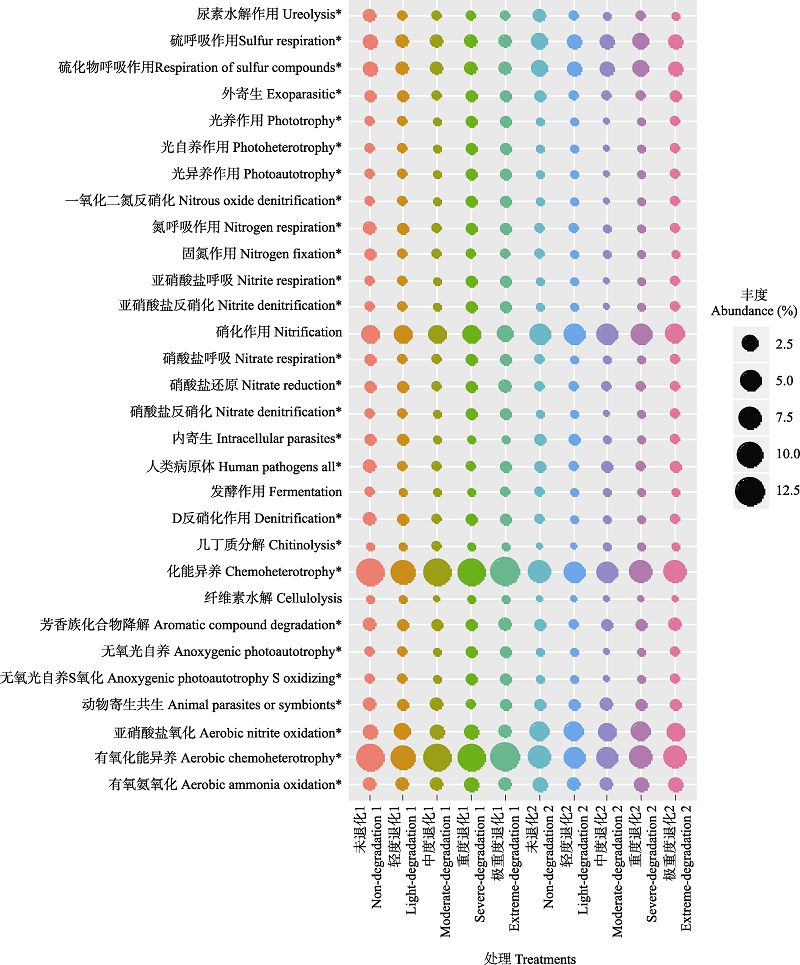
图4 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤细菌生态功能多样性。图中1和2分别代表0‒10 cm和10‒20 cm土层。*P < 0.05。
Fig. 4 Ecological functiona diversity of soil bacterial community in different degraded alpine meadows. Numbers 1 and 2 in the figure represent 0‒10 cm and 10‒20 cm soil layer, respectively. *P < 0.05.
| 指标 Item | 细菌群落结构 Bacterial community composition | Faprotax生态功能结构 Faprotax ecological functional structure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | |
| 植物Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | -0.01 | 0.52 | 0.07 | 0.23 |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.39 |
| 植被盖度 Coverage | 0.02 | 0.38 | 0.08 | 0.23 |
| 地上生物量 Above-ground biomass | 0.04 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| 地下生物量 Below-ground biomass | -0.04 | 0.62 | ‒0.08 | 0.09 |
| 土壤含水量 SWC | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.02 |
| 土壤酸碱度 pH | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.04 |
| 总有机碳 TOC | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.02 |
| 全氮 TN | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.03 |
| 铵态氮 NH4+-N | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.008 |
| 硝态氮 NO3--N | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.06 |
| 全磷 TP | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| 速效磷 AP | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.20 |
| 全钾 TK | 0.22 | 0.006 | 0.21 | 0.02 |
| 速效钾 AK | 0.07 | 0.19 | ﹣0.04 | 0.61 |
| 土壤有效氮磷比AN/AP | 0.15 | 0.048 | 0.20 | 0.03 |
| 土壤碳氮比 C/N | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.22 |
表2 植被特征、土壤性质与土壤细菌群落结构的Mantel test分析
Table 2 Mantel test analysis of plant community characters, soil properties and soil bacterial community composition in an alpine meadow
| 指标 Item | 细菌群落结构 Bacterial community composition | Faprotax生态功能结构 Faprotax ecological functional structure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | |
| 植物Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | -0.01 | 0.52 | 0.07 | 0.23 |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.39 |
| 植被盖度 Coverage | 0.02 | 0.38 | 0.08 | 0.23 |
| 地上生物量 Above-ground biomass | 0.04 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| 地下生物量 Below-ground biomass | -0.04 | 0.62 | ‒0.08 | 0.09 |
| 土壤含水量 SWC | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.02 |
| 土壤酸碱度 pH | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.04 |
| 总有机碳 TOC | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.02 |
| 全氮 TN | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.03 |
| 铵态氮 NH4+-N | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.008 |
| 硝态氮 NO3--N | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.06 |
| 全磷 TP | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| 速效磷 AP | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.20 |
| 全钾 TK | 0.22 | 0.006 | 0.21 | 0.02 |
| 速效钾 AK | 0.07 | 0.19 | ﹣0.04 | 0.61 |
| 土壤有效氮磷比AN/AP | 0.15 | 0.048 | 0.20 | 0.03 |
| 土壤碳氮比 C/N | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.22 |
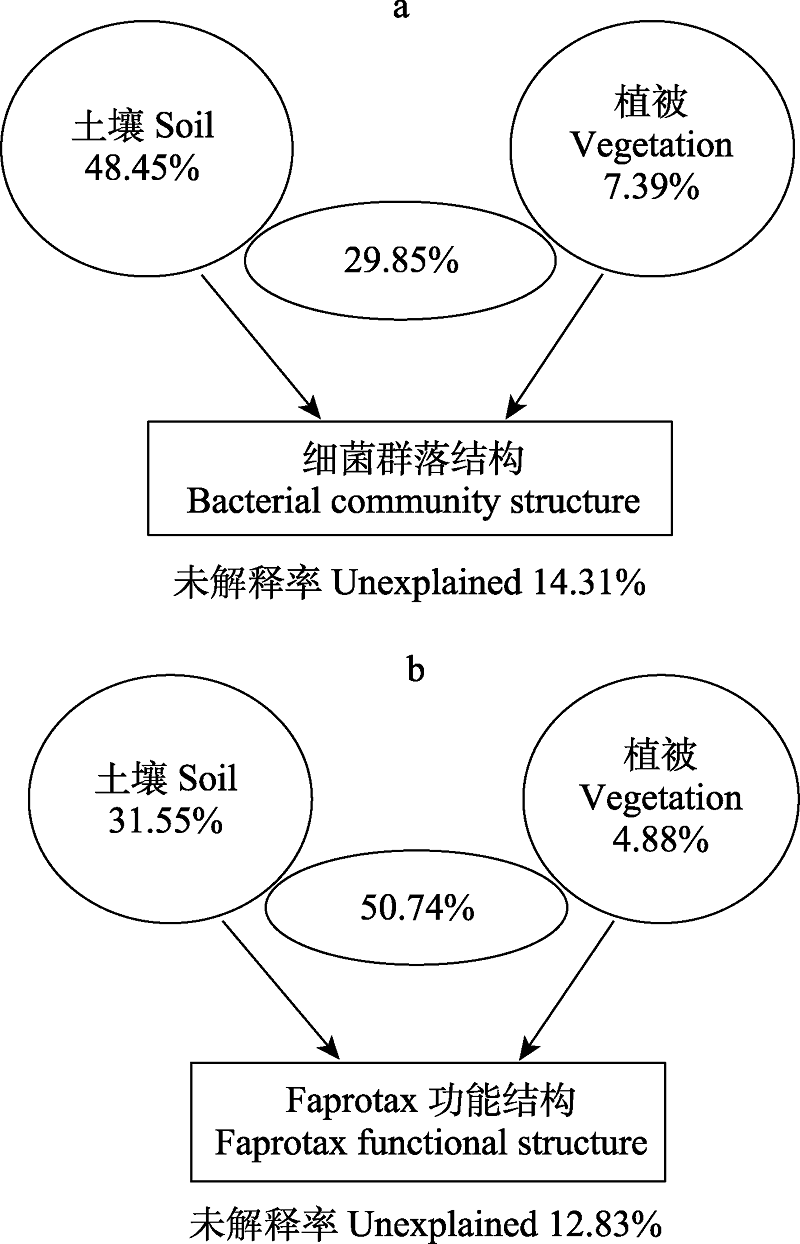
图6 高寒草甸土壤和植被环境因子与土壤细菌群落的冗余分析。圆圈表示环境因子, 圆中的数字表示解释率, 中心椭圆的数字表示两个环境因子的共同解释率。
Fig. 6 Redundancy analysis of soil and vegetation environmental factors to soil bacterial community in an alpine meadow. The circles show the variation explained by each factor alone. The number in the ellipse represents interactions of the two factors.
| [1] | Bao M, He HX, Ma XL, Wang ZH, Qiu WH (2018) Effects of chemical nitrogen fertilizer and green manure on diversity and functions of soil bacteria in wheat field. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 55, 734-743. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 包明, 何红霞, 马小龙, 王朝辉, 邱炜红 (2018) 化学氮肥与绿肥对麦田土壤细菌多样性和功能的影响. 土壤学报, 55, 734-743.] | |
| [2] |
Cao H, Li YG, Zhou CR, Ning LF, Yang HQ (2016) Effect of carbonized apple branches on bacterial and fungal diversities in apple root-zone soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 49, 3413-3424. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 曹辉, 李燕歌, 周春然, 宁留芳, 杨洪强 (2016) 炭化苹果枝对苹果根区土壤细菌和真菌多样性的影响. 中国农业科学, 49, 3413-3424.] | |
| [3] | Che RX, Wang YF, Li KX, Xu ZH, Hu JM, Wang F, Rui YC, Li LF, Pang Z, Cui XY (2019) Degraded patch formation significantly changed microbial community composition in alpine meadow soils. Soil and Tillage Research, 195, 104426. |
| [4] |
Chen YL, Deng Y, Ding JZ, Hu HW, Xu TL, Li F, Yang GB, Yang YH (2017) Distinct microbial communities in the active and permafrost layers on the Tibetan Plateau. Molecular Ecology, 26, 6608-6620.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Chu HY (2013) Microbial communities in high latitudes and high altitudes ecosystems. Microbiology China, 40, 123-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 褚海燕 (2013) 高寒生态系统微生物群落研究进展. 微生物学通报, 40, 123-136.] | |
| [6] | Cui YX, Bing HJ, Fang LC, Wu YH, Yu JL, Shen GT, Jiang M, Wang X, Zhang XC (2019) Diversity patterns of the rhizosphere and bulk soil microbial communities along an altitudinal gradient in an alpine ecosystem of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma, 338, 118-127. |
| [7] | Dai YT, Yan ZJ, Xie JH, Wu HX, Xu LB, Hou XY, Gao L, Cui YW (2017) Soil bacteria diversity in rhizosphere under two types of vegetation restoration based on high throughput sequencing. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 54, 735-748. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴雅婷, 闫志坚, 解继红, 吴洪新, 徐林波, 侯向阳, 高丽, 崔艳伟 (2017) 基于高通量测序的两种植被恢复类型根际土壤细菌多样性研究. 土壤学报, 54, 735-748.] | |
| [8] | Escalas A, Hale L, Voordeckers JW, Yang YF, Firestone MK, Alvarez-Cohen L, Zhou JZ (2019) Microbial functional diversity: From concepts to applications. Ecology and Evolution, 9, 12000-12016. |
| [9] | He D, Xiang XJ, He JS, Wang C, Cao GM, Adams J, Chu HY (2016) Composition of the soil fungal community is more sensitive to phosphorus than nitrogen addition in the alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 52, 1059-1072. |
| [10] | Hu YJ, Veresoglou SD, Tedersoo L, Xu TL, Ge TD, Liu L, Chen YL, Hao ZP, Su YR, Rillig MC, Chen BD (2019) Contrasting latitudinal diversity and co-occurrence patterns of soil fungi and plants in forest ecosystems. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 131, 100-110. |
| [11] | Li F, Liu ZH, Jia TH, Li SS, Bai YF, Guo CC, Wang WW, Kong M, Zhang T, Iqbal A, Zhou HK, Jia Y, Shang ZH (2018) Functional diversity of soil microbial community carbon metabolism with the degradation and restoration of alpine wetlands and meadows. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 6006-6015. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李飞, 刘振恒, 贾甜华, 李珊珊, 白彦福, 郭灿灿, 王惟惟, 孔猛, 张涛, Iqbal A, 周华坤, 贾宇, 尚占环 (2018) 高寒湿地和草甸退化及恢复对土壤微生物碳代谢功能多样性的影响. 生态学报, 38, 6006-6015.] | |
| [12] |
Li M, Zhang XZ, He YT, Niu B, Wu JS (2020) Assessment of the vulnerability of alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. PeerJ, 8, e8513.
URL PMID |
| [13] | Li YM, Wang SP, Jiang LL, Zhang LR, Cui SJ, Meng FD, Wang Q, Li XE, Zhou Y (2016) Changes of soil microbial community under different degraded gradients of alpine meadow. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 222, 213-222. |
| [14] | Liu AR, Yang T, Xu W, Shangguan ZJ, Wang JZ, Liu HY, Shi Y, Chu HY, He JS (2018) Status, issues and prospects of belowground biodiversity on the Tibetan alpine grassland. Biodiversity Science, 26, 972-987. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘安榕, 杨腾, 徐炜, 上官子健, 王金洲, 刘慧颖, 时玉, 褚海燕, 贺金生 (2018) 青藏高原高寒草地地下生物多样性: 进展、问题与展望. 生物多样性, 26, 972-987.] | |
| [15] | Liu Y, Chen JS, Liu Q, Chen LW (2006) Advances in studies of soil nitrification and denitrification and controlling factors. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 27(2), 36-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘义, 陈劲松, 刘庆, 陈林武 (2006) 土壤硝化和反硝化作用及影响因素研究进展. 四川林业科技, 27(2), 36-41.] | |
| [16] | Liu YH, Yang YW, Zhang Y (2018) Redundancy analysis of the relationship between plant functional groups and soil factors in the degraded alpine meadow. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 34, 1112-1121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘育红, 杨元武, 张英 (2018) 退化高寒草甸植物功能群与土壤因子关系的冗余分析. 生态与农村环境学报, 34, 1112-1121.] | |
| [17] | Long RJ (2007) Functions of ecosystem in the Tibetan grassland. Science & Technology Review, 25(9), 26-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 龙瑞军 (2007) 青藏高原草地生态系统之服务功能. 科技导报, 25(9), 26-28.] | |
| [18] | Luo ZM, Liu JX, Jia T, Chai BF, Wu TH (2020) Soil bacterial community response and nitrogen cycling variations associated with subalpine meadow degradation on the Loess Plateau, China. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 86, e00180-20. |
| [19] |
Ma XY, Zhang QT, Zheng MM, Gao Y, Yuan T, Hale L, van Nostrand JD, Zhou JZ, Wan SQ, Yang YF (2019) Microbial functional traits are sensitive indicators of mild disturbance by lamb grazing. The ISME Journal, 13, 1370-1373.
URL PMID |
| [20] | Ma YS, Lang BN, Li QY, Shi JJ, Dong QM (2002) Study on rehabilitating and rebuilding technologies for degenerated alpine meadow in the Changjiang and Yellow River source region. Pratacultural Science, 19(9), 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马玉寿, 郎百宁, 李青云, 施建军, 董全民 (2002) 江河源区高寒草甸退化草地恢复与重建技术研究. 草业科学, 19(9), 1-5.] | |
| [21] | Mganga KZ, Razavi BS, Kuzyakov Y (2016) Land use affects soil biochemical properties in Mt. Kilimanjaro region. Catena, 141, 22-29. |
| [22] |
Nixon SL, Daly RA, Borton MA, Solden LM, Welch SA, Cole DR, Mouser PJ, Wilkins MJ, Wrighton KC (2019) Genome-resolved metagenomics extends the environmental distribution of the verrucomicrobia phylum to the deep terrestrial subsurface. mSphere, 4, e00613-19.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 41, D590-D596.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Robertson K, Klemedtsson L (1996) Assessment of denitrification in organogenic forest soil by regulating factors. Plant and Soil, 178, 49-57. |
| [25] | Sørensen LI, Mikola J, Kytöviita MM, Olofsson J (2009) Trampling and spatial heterogeneity explain decomposer abundances in a sub-arctic grassland subjected to simulated reindeer grazing. Ecosystems, 12, 830-842. |
| [26] | Wang F, Ren LL, An TT, Liu LZ (2020) Effect of long-term fertilization and seasonal variation on abundance and population diversity of soil ammonia oxidizing bacteria. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 39, 86-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王丰, 任灵玲, 安婷婷, 刘灵芝 (2020) 长期施肥对土壤中氨氧化细菌丰度和种群多样性的影响. 华中农业大学学报, 39, 86-94.] | |
| [27] |
Wang LW, Li F, Zhan Y, Zhu LZ (2016) Shifts in microbial community structure during in situ surfactant-enhanced bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon- contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 14451-14461.
URL PMID |
| [28] | Wang N, Gao J, Wei J, Liu Y, Zhuang XL, Zhuang GQ (2019) Effects of wetland reclamation on soil microbial community structure in the Sanjiang plain. Environmental Science, 40, 2375-2381. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王娜, 高婕, 魏静, 刘颖, 庄绪亮, 庄国强 (2019) 三江平原湿地开垦对土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 环境科学, 40, 2375-2381.] | |
| [29] | Wang XP, Yang X, Yang N, Xin XJ, Qu YB, Zhao NX, Gao YB (2019) Effects of litter diversity and composition on litter decomposition characteristics and soil microbial community. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 6264-6272. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王小平, 杨雪, 杨楠, 辛晓静, 曲耀冰, 赵念席, 高玉葆 (2019) 凋落物多样性及组成对凋落物分解和土壤微生物群落的影响. 生态学报, 39, 6264-6272.] | |
| [30] | Wang YB, Wang GX, Shen YP, Wang YL (2005) Degradation of the eco-environmental system in alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 27, 633-640. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王一博, 王根绪, 沈永平, 王彦莉 (2005) 青藏高原高寒区草地生态环境系统退化研究. 冰川冻土, 27, 633-640.] | |
| [31] | Wang YQ, Yin YL, Li SX (2019) Physicochemical properties and enzymatic activities of alpine meadow at different degradation degrees. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28, 1108-1116. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王玉琴, 尹亚丽, 李世雄 (2019) 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤理化性质及酶活性分析. 生态环境学报, 28, 1108-1116.] | |
| [32] | Xiu SY (1993) Microbial geochemistry of sulfur and its implication to geololgy. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 15, 101-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 修世荫 (1993) 硫元素微生物地球化学研究及其地质意义. 化工地质, 15, 101-106.] | |
| [33] | Yang H, Zhang GZ, Yang XN, Wu FP, Zhao W, Zhang HW, Zhang X (2017) Microbial community structure and diversity in cellar water by 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing. Environmental Science, 38, 1704-1716. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨浩, 张国珍, 杨晓妮, 武福平, 赵炜, 张洪伟, 张翔 (2017) 16S rRNA高通量测序研究集雨窖水中微生物群落结构及多样性. 环境科学, 38, 1704-1716.] | |
| [34] | Yang YD, Wang ZM, Hu YG, Zeng ZH (2017) Irrigation frequency alters the abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in a northern Chinese upland soil. European Journal of Soil Biology, 83, 34-42. |
| [35] | Yang YD, Zhang MC, Hu JW, Zhang K, Hu YG, Zeng ZH (2017) Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizing bacteria and Archaea in a North China agricultural soil. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 3636-3646. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨亚东, 张明才, 胡君蔚, 张凯, 胡跃高, 曾昭海 (2017) 施氮肥对华北平原土壤氨氧化细菌和古菌数量及群落结构的影响. 生态学报, 37, 3636-3646.] | |
| [36] |
Yang YF, Wu LW, Lin QY, Yuan MT, Xu DP, Yu H, Hu YG, Duan JC, Li XZ, He ZL, Xue K, van Nostrand J, Wang SP, Zhou JZ (2013) Responses of the functional structure of soil microbial community to livestock grazing in the Tibetan alpine grassland. Global Change Biology, 19, 637-648.
URL PMID |
| [37] | Yang YS, Li HQ, Zhang L, Zhu JB, He HD, Wei YX, Li YN (2016) Characteristics of soil water percolation and dissolved organic carbon leaching and their response to long-term fencing in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75, 1471. |
| [38] | Yang YW, Li XL, Zhou XH, Qi YJ, Shi YY, Li CY, Zhou HK (2016) Study on relationship between plant community degradation and soil environment in an alpine meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 24, 1211-1217. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨元武, 李希来, 周旭辉, 祁银姐, 师月英, 李成一, 周华坤 (2016) 高寒草甸植物群落退化与土壤环境特征的关系研究. 草地学报, 24, 1211-1217.] | |
| [39] |
Yin YL, Wang YQ, Bao GS, Wang HS, Li SX, Song ML, Shao BL, Wen YC (2017) Characteristics of soil microbes and enzyme activities in different degraded alpine meadows. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 3881-3890. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
| [ 尹亚丽, 王玉琴, 鲍根生, 王宏生, 李世雄, 宋梅玲, 邵宝莲, 温玉存 (2017) 退化高寒草甸土壤微生物及酶活性特征. 应用生态学报, 28, 3881-3890.] | |
| [40] | Yin YL, Wang YQ, Li SX, Liu Y, Zhao W, Ma YS, Bao GS (2021) Soil microbial character response to plant community variation after grazing prohibition for 10 years in a Qinghai-Tibetan alpine meadow. Plant Soil, 458, 175-189. |
| [41] | Zhang Y, Cao CY, Peng M, Xu XJ, Zhang P, Yu QJ, Sun T (2014) Diversity of nitrogen-fixing, ammonia-oxidizing, and denitrifying bacteria in biological soil crusts of a revegetation area in Horqin Sandy Land, Northeast China. Ecological Engineering, 71, 71-79. |
| [42] | Zhang ZH, Zhou HK, Zhao XQ, Yao BQ, Ma Z, Dong QM, Zhang ZH, Wang WY, Yang YW (2018) Relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 26, 111-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张中华, 周华坤, 赵新全, 姚步青, 马真, 董全民, 张振华, 王文颖, 杨元武 (2018) 青藏高原高寒草地生物多样性与生态系统功能的关系. 生物多样性, 26, 111-129.] | |
| [43] | Zhao XQ, Zhou HK (2005) Eco-environmental degradation vegetation regeneration and sustainable development in the headwaters of three rivers on Tibetan Plateau. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 20, 471-476. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵新全, 周华坤 (2005) 三江源区生态环境退化、恢复治理及其可持续发展. 中国科学院院刊, 20, 471-476.] | |
| [44] | Zhou H, Zhang DG, Jiang ZH, Sun P, Xiao HL, Wu YX, Chen JG (2019) Changes in the soil microbial communities of alpine steppe at Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau under different degradation levels. Science of the Total Environment, 651, 2281-2291. |
| [45] | Zhu JS, Zhang H, Ma LJ, Liao DX, Yang XY, Wang LC, Wang DY (2018). Diversity of the microbial community in rice paddy soil with biogas slurry irrigation analyzed by illumine sequencing technology. Environmental Science, 39, 2400-2411. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱金山, 张慧, 马连杰, 廖敦秀, 杨星勇, 王龙昌, 王定勇 (2018) 不同沼灌年限稻田土壤微生物群落分析. 环境科学, 39, 2400-2411.] |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [3] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [4] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [5] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [6] | 林迪, 陈双林, 杜榷, 宋文龙, 饶固, 闫淑珍. 大别山黏菌的物种多样性调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [7] | 姚嘉, 张聪伶, 李时轩, 林阳, 王震, 张煜涵, 周伟龙, 潘心禾, 朱珊, 吴逸卿, 王丹, 刘金亮, 谭珊珊, 沈国春, 于明坚. 百山祖连续海拔样带植物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [8] | 陈哲涵, 尹进, 叶吉, 刘冬伟, 毛子昆, 房帅, 蔺菲, 王绪高. 增温对东北温带次生林草本群落季节动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [9] | 刘金花, 李风, 田桃, 肖海峰. 土壤细菌和线虫对热带雨林优势植物凋落物特性和多样性的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23276-. |
| [10] | 王晓凤, 米湘成, 王希华, 江明喜, 杨涛, 张健, 沈泽昊. 中国中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23296-. |
| [11] | 杨涛, 沈泽昊, 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘倩, 钱恒君, 解宇阳, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 张玉坤, 侯波, 李建斌, 欧晓昆. 滇中高原亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| [12] | 崔家鹤, 李智勇, 王宇池, 孙蔷, 莎娜, 李紫晶, 武艳涛, 史亚博, 韩瀛, 李明乐, 王立新, 赵利清, 梁存柱. 垫状驼绒藜群落特征及地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23172-. |
| [13] | 王健铭, 雷训, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23144-. |
| [14] | 李正飞, 蒋小明, 王军, 孟星亮, 张君倩, 谢志才. 雅鲁藏布江中下游底栖动物物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21431-. |
| [15] | 赵琦, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 金清, 李佳丽, 邱江平. 海南岛蚯蚓物种组成及其系统发育分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22224-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()