



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 65-71. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020050 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020050
魏鑫磊, 李姝, 窦文俊, 亓宝, 王琦*( )(
)( ), 李玉(
), 李玉( )
)
收稿日期:2020-02-20
接受日期:2020-05-11
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2020-07-15
通讯作者:
王琦
基金资助:
Xinlei Wei, Shu Li, Wenjun Dou, Bao Qi, Qi Wang*( )(
)( ), Yu Li(
), Yu Li( )
)
Received:2020-02-20
Accepted:2020-05-11
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2020-07-15
Contact:
Qi Wang
摘要:
黏菌是森林生态系统中不可或缺的生物资源, 在生态系统中发挥重要的作用。为了探讨黏菌在西北地区森林中的物种多样性及影响物种组成和多样性的因素, 本文对甘肃省祁连山国家级自然保护区进行为期2年的多点调查采样, 获得黏菌标本826份, 经形态学鉴定属于4目5科22属71种, 其中甘肃省新记录种30种。发现鹅绒菌(Ceratiomyxa fruticulosa)等9个物种是祁连山保护区广泛分布的物种, 针叶林中的黏菌总物种数(58种)和特有物种数(38种)均高于阔叶林(33种; 13种), 海拔高度对黏菌多样性无明显影响。主成分分析结果表明, 腐木型基质上的黏菌物种多样性最丰富, 木本基物与草本基物上的黏菌物种组成具有明显差异。研究结果表明, 甘肃省祁连山自然保护区的山地森林带的植被类型与基物类型是影响黏菌物种组成和多样性的重要因素。
魏鑫磊, 李姝, 窦文俊, 亓宝, 王琦, 李玉 (2021) 甘肃省祁连山国家级自然保护区的黏菌物种多样性. 生物多样性, 29, 65-71. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020050.
Xinlei Wei, Shu Li, Wenjun Dou, Bao Qi, Qi Wang, Yu Li (2021) Species diversity of myxomycetes in Qilian Mountain National Nature Reserve, Gansu Province. Biodiversity Science, 29, 65-71. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020050.
| 序号 No. | 保护站 Station | 采集点 Collection site | 经纬度 Locality | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 大黄山站 Dahuangshan Station | 焉支山 Yanzhi Mountain | 101°14° E, 38°26°N | 2,846 |
| 2 | 古城站 Gucheng Station | 科拉村 Kela Village | 102°36° E, 36°56°N | 3,032 |
| 朱岔峡 Zhucha Gorge | 102°33° E, 36°56° N | 2,604 | ||
| 3 | 哈溪站 Haxi Station | 哈溪 Haxi | 102°33° E, 37°23° N | 2,568 |
| 4 | 康乐站 Kangle Station | 康乐 Kangle | 99°47° E, 30°44° N | 3,087 |
| 5 | 祁连站 Qilian Station | 冰沟河 Binggou River | 102°17° E, 37°40° N | 2,816 |
| 6 | 上房寺站 Shangfangsi Station | 上房寺 Shangfangsi | 102°37° E, 37°38° N | 3,087 |
| 7 | 十八里堡站 Shibalipu Station | 尚家沟 Shangjiagou | 103°00° E, 37°20° N | 2,705 |
| 8 | 寺大隆站 Sidalong Station | 向阳台 Xiangyangtai | 99°54° E, 38°26° N | 2,716 |
| 9 | 乌鞘岭站 Wushaoling Station | 乌鞘岭 Wushaoling | 102°59° E, 37°16° N | 2,824 |
| 朵什乡 Duoshi Township | 102°59° E, 37°16° N | 2,816 | ||
| 10 | 西水站 Xishui Station | 大野口 Dayekou | 100°17° E, 38°33° N | 2,482 |
| 西水 Xishui | 100°17° E, 38°32° N | 2,814 | ||
| 11 | 夏玛站 Xiama Station | 夏玛 Xiama | 103°09° E, 37°18° N | 2,604 |
| 12 | 大河口站 Dahekou Station | 大河口 Dahekou | 100°45° E, 38°17° N | 2,905 |
| 小河滩 Xiaohetan | 103°09° E, 37°18° N | 2,702 |
表1 祁连山自然保护区黏菌标本采集地点信息
Table 1 Information of the collecting sites of myxomycetes specimens in the Qilian Mountain Nature Reseve
| 序号 No. | 保护站 Station | 采集点 Collection site | 经纬度 Locality | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 大黄山站 Dahuangshan Station | 焉支山 Yanzhi Mountain | 101°14° E, 38°26°N | 2,846 |
| 2 | 古城站 Gucheng Station | 科拉村 Kela Village | 102°36° E, 36°56°N | 3,032 |
| 朱岔峡 Zhucha Gorge | 102°33° E, 36°56° N | 2,604 | ||
| 3 | 哈溪站 Haxi Station | 哈溪 Haxi | 102°33° E, 37°23° N | 2,568 |
| 4 | 康乐站 Kangle Station | 康乐 Kangle | 99°47° E, 30°44° N | 3,087 |
| 5 | 祁连站 Qilian Station | 冰沟河 Binggou River | 102°17° E, 37°40° N | 2,816 |
| 6 | 上房寺站 Shangfangsi Station | 上房寺 Shangfangsi | 102°37° E, 37°38° N | 3,087 |
| 7 | 十八里堡站 Shibalipu Station | 尚家沟 Shangjiagou | 103°00° E, 37°20° N | 2,705 |
| 8 | 寺大隆站 Sidalong Station | 向阳台 Xiangyangtai | 99°54° E, 38°26° N | 2,716 |
| 9 | 乌鞘岭站 Wushaoling Station | 乌鞘岭 Wushaoling | 102°59° E, 37°16° N | 2,824 |
| 朵什乡 Duoshi Township | 102°59° E, 37°16° N | 2,816 | ||
| 10 | 西水站 Xishui Station | 大野口 Dayekou | 100°17° E, 38°33° N | 2,482 |
| 西水 Xishui | 100°17° E, 38°32° N | 2,814 | ||
| 11 | 夏玛站 Xiama Station | 夏玛 Xiama | 103°09° E, 37°18° N | 2,604 |
| 12 | 大河口站 Dahekou Station | 大河口 Dahekou | 100°45° E, 38°17° N | 2,905 |
| 小河滩 Xiaohetan | 103°09° E, 37°18° N | 2,702 |
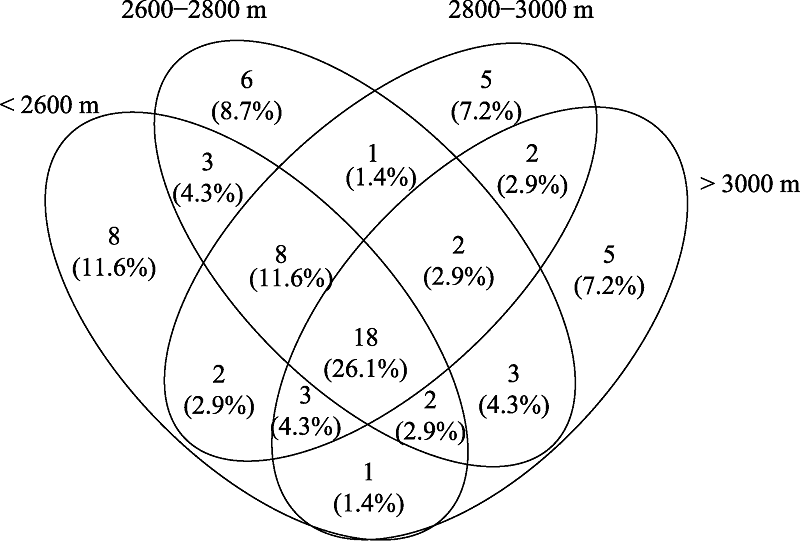
图1 祁连山自然保护区4个海拔区间内黏菌物种组成对比的维恩图
Fig. 1 Venn diagram of myxomycetes species composition comparison at four elevations of the Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve
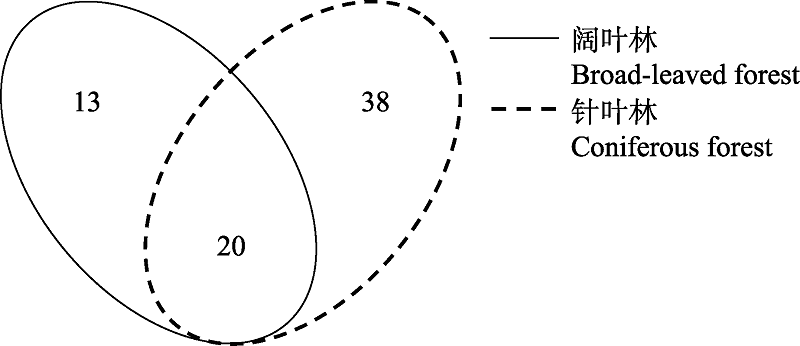
图2 祁连山自然保护区阔叶林与针叶林内黏菌物种组成对比的维恩图
Fig. 2 Venn diagram of myxomycetes species composition comparison in broad-leaved and coniferous forests of Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve
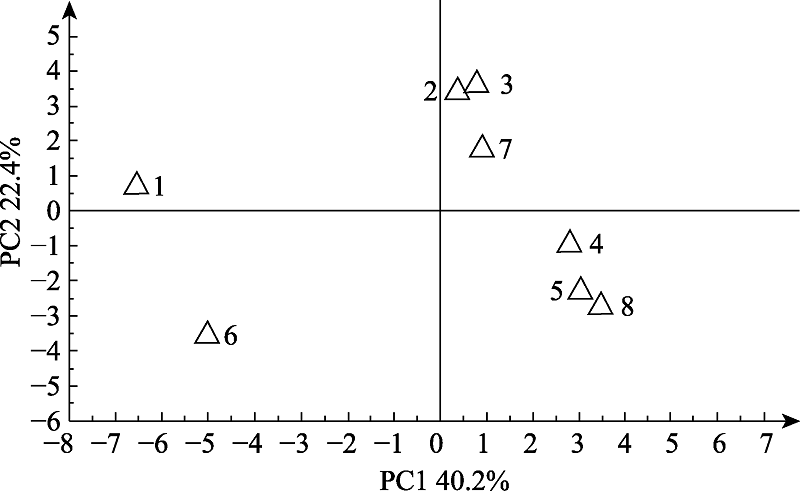
图5 祁连山自然保护区8种基物类型与黏菌间的PCA得分图(PC1与PC2处在95%置信区间的椭圆内)。1: 腐木, 2: 枯枝, 3: 树皮, 4: 枯叶, 5: 枯草, 6: 苔藓, 7: 松塔, 8: 马勃
Fig. 5 PCA score diagram of eight substrate types and myxomycetes in the Qilian Mountain Nature Reseve (PC1 vs PC2 with 95% confidence interval error ellipse). 1, Dead wood; 2, Dead branch; 3, Bark; 4, Dead leaves; 5 Dry grass; 6, Moss; 7, Pine tower; 8, Puff ball.

图6 祁连山自然保护区8种基物类型与黏菌发生间的PCA载荷图(PC1与PC2处在95%置信区间的椭圆内)
Fig. 6 PCA load diagram of eight substrate types and myxomycetes in Qilian Mountain Nature Reseve. PC1 vs PC2 with 95% confidence interval error ellipse.
| [1] | Abdel-Raheem AM (2002) Myxomycetes from Upper Egypt. Microbiological Research, 157, 47-67. |
| [2] | Chen MX, Zhao XJ, Zhao PQ (2018) A study on the distribution characteristics and protection system of biodiversity in Qilian Mountains (north slope). Environment and Development, 30, 200-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈明霞, 赵晓冏, 赵培强 (2018) 祁连山北坡生物多样性分布特征与保护体系研究. 环境与发展, 30, 200-202.] | |
| [3] | Chen P, Xu MQ, Chen SL (2006) Notes on myxomycetes from Gansu Province. Journal of Gansu Sciences, 18(3), 35-38. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈萍, 徐美琴, 陈双林 (2006) 甘肃粘菌考录. 甘肃科学学报, 18(3), 35-38.] | |
| [4] | Chen SL, Dai Q, Chen P, Li Y (2009) Myxomycetes from the mid-upper reaches of Bailong River, Gansu Province, China. Mycosystema, 28, 86-91. |
| [5] | Dai Q, Yan SZ, Yao HQ, Chen SL (2013) Myxomycete diversity in hilly forests of East China. Biodiversity Science, 21, 507-513. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴群, 闫淑珍, 姚慧琴, 陈双林 (2013) 华东丘陵林地黏菌的物种多样性. 生物多样性, 21, 507-513.] | |
| [6] | Deng SQ (1963) Fungi of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邓叔群 (1963) 中国的真菌. 科学出版社. 北京. ] | |
| [7] | Eliasson UH (2004) A critical review of myxomycete records from the Hawaiian Islands. Systematics and Geography of Plants, 74, 81-86. |
| [8] | Hosokawa A, Reid CR, Latty T (2019) Slimes in the city: The diversity of myxomycetes from inner-city and semi-urban parks in Sydney, Australia. Fungal Ecology, 39, 37-44. |
| [9] | Jin F, Zhang ZM, Yu XX, Rao LY, Niu JZ, Lu SW, Xie YY (2005) Service function and value evaluation of forest ecosystem in Qilian Mountain, Gansu Province. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, (3), 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 靳芳, 张振明, 余新晓, 饶良懿, 牛健植, 鲁绍伟, 谢媛媛 (2005) 甘肃祁连山森林生态系统服务功能及价值评估. 中国水土保持科学, (3), 53-57.] | |
| [10] | Li Y, Li HZ (1989) Myxomycetes from China I. A checklist of myxomycetes from China. Mycotaxon, 35, 429-436. |
| [11] | Li Y, Li HZ, Wang Q, Chen SL (2008a) Flora Myxomycetes Sinicorum I. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李玉, 李惠中, 王琦, 陈双林 (2008a) 中国真菌志黏菌卷一. 科学出版社. 北京. ] | |
| [12] | Li Y, Li HZ, Wang Q, Chen SL (2008b) Flora Myxomycetes. Sinicorum II. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李玉, 李惠中, 王琦, 陈双林 (2008b) 中国真菌志, 黏菌卷(二). 科学出版社. 北京. ] | |
| [13] | Stephenson SL, Stempen H (1996) Myxomycetes: A handbook of slime molds. Quarterly Review of Biology, 45, 601-602. |
| [14] | Takahashi K, Hada Y (2012) Seasonal occurrence and distribution of myxomycetes on different types of leaf litter in a warm temperate forest of western Japan. Mycoscience, 53, 245-255. |
| [15] | Wang W, Li S, Yuan CF, Wei XL, Zhu XY, Qi B, Wang Q, Li Y (2018) Study on the diversity of myxomycetes in Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. In: Reports Presented at 2018 Annual Meeting of Mycological Society of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王琬, 李姝, 原超峰, 魏鑫磊, 朱相杨, 亓宝, 王琦, 李玉 (2018) 青藏高原东部森林黏菌多样性研究. 见: 中国菌物学会2018年学术年会论文汇编. 科学出版社, 北京. ] | |
| [16] | Wei SW, Li S, Qi B, Li Z, Hu YP, Wang Q, Li Y (2019) Macromycetes and myxomycetes diversity of Minqin County, Gansu Province. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(9), 140-144. (in Chinese) |
| [ 魏书威, 李姝, 亓宝, 李壮, 胡亚萍, 王琦, 李玉 (2019) 甘肃省民勤县大型真菌及黏菌多样性调查. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(9), 140-144.] | |
| [17] | Xi YL, Wang ZJ, Yu HP, Wei SL (2011) Preliminary report on macromycetes resources in Qilian Mountain National Nature Reserve. China Edible Fungi, 30, 7-13. (in Chinese) |
| [ 席亚丽, 王治江, 于海萍, 魏生龙 (2011) 祁连山国家自然保护区大型真菌资源研究初报. 中国食用菌, 30, 7-13.] | |
| [18] | Yan SZ, Liu QS, Li Y, Chen SL (2012) Known species of myxomycetes from tropical China. Journal of Fungal Research, 10, 157-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 闫淑珍, 刘歧莎, 李玉, 陈双林 (2012) 中国热带黏菌的已知种类. 菌物研究, 10, 157-172.] | |
| [19] | Zhao FY, Li Y, Tom Hsiang, Liu SY (2019) Species diversity of myxomycetes in two forests of the Lesser Khinggan Mountains, China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 896-902. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵凤云, 李玉, Hsiang Tom, 刘淑艳 (2019) 小兴安岭两种林地的黏菌物种多样性. 生物多样性, 27, 896-902.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 周璇, 张生芳, 刘宁, 鲁玉杰, 郑斯竹, 杨晓军, 路园园, 刘梅柯, 白明. 储藏物甲虫系统地位厘清及拉英汉名录更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24238-. |
| [3] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [4] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 陈丁松, 刘子恺, 贺子洋, 陈伟东. 缓步动物多样性、分布特征和生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24406-. |
| [7] | 张颂琪, 陆义, 陈炳耀, 杨光, 王彦平, 陈传武. 全球鲸豚类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24442-. |
| [8] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [9] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [10] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [11] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [12] | 何欣怡, 潘玉梅, 祝燕, 陈佳仪, 张思榕, 张乃莉. 暖温带森林外生菌根树种优势和植物多样性对土壤氮素周转的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24173-. |
| [13] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [14] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [15] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()