



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 779-786. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019405 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019405
张峰, 郑佳华, 赵萌莉*( ), 陈大岭, 杨阳, 乔荠瑢, 赵天启
), 陈大岭, 杨阳, 乔荠瑢, 赵天启
收稿日期:2019-12-23
接受日期:2020-07-02
出版日期:2020-07-20
发布日期:2020-09-29
通讯作者:
赵萌莉
作者简介:* E-mail: nmgmlzh@126.com基金资助:
Feng Zhang, Jiahua Zheng, Mengli Zhao*( ), Daling Chen, Yang Yang, Jirong Qiao, Tianqi Zhao
), Daling Chen, Yang Yang, Jirong Qiao, Tianqi Zhao
Received:2019-12-23
Accepted:2020-07-02
Online:2020-07-20
Published:2020-09-29
Contact:
Mengli Zhao
摘要:
在草地刈割过程中, 群落地上生物量的时间稳定性与物种多样性及物种异步性关系密切。本文基于2014-2018年的野外刈割实验, 研究了围封(对照, 无刈割)、轻度(留茬8 cm)、中度(留茬5 cm)和重度(留茬2 cm)等不同刈割强度对内蒙古大针茅(Stipa grandis)典型草原地上生物量时间稳定性的影响。结果表明: (1)与围封相比, 刈割对群落时间稳定性无显著影响, 但对种群平均时间稳定性影响显著, 重度刈割处理的种群平均时间稳定性显著降低; 且种群平均时间稳定性与群落时间稳定性无显著相关关系, 表明这二者独立波动。(2)与围封相比, 重度刈割处理的物种丰富度显著降低, 但它与群落时间稳定性无显著相关关系, 表明物种丰富度不是群落地上生物量时间稳定性的主导因素; 此外, 重度刈割处理的群落抵抗力显著降低, 但也与群落时间稳定性无显著相关关系。(3)异步性与群落稳定性存在极显著正相关关系, 但刈割对异步性无显著影响, 故未造成群落稳定性显著变化。因此, 异步性可能是影响群落时间稳定性的主导效应之一, 在草地管理与利用过程中, 可从物种异步性角度来对草地稳定性进行评价。
张峰, 郑佳华, 赵萌莉, 陈大岭, 杨阳, 乔荠瑢, 赵天启 (2020) 刈割强度对大针茅草原地上生物量时间稳定性的影响. 生物多样性, 28, 779-786. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019405.
Feng Zhang, Jiahua Zheng, Mengli Zhao, Daling Chen, Yang Yang, Jirong Qiao, Tianqi Zhao (2020) Effects of mowing intensity on temporal stability of aboveground biomass in the Stipa grandis steppe. Biodiversity Science, 28, 779-786. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019405.
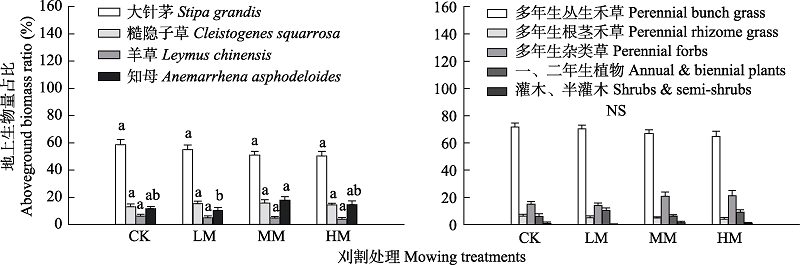
图1 不同刈割强度下优势物种(A)及功能群(B)地上生物量的比例。CK: 对照, 围封不刈割; LM: 轻度刈割; MM: 中度刈割; HM: 重度刈割。不同字母表示差异显著; NS: 不显著。
Fig. 1 Aboveground biomass ratio of dominant species (A) and functional groups (B) to total aboveground biomass under different mowing intensity. CK, Control, enclosure and not mowing; LM, Light mowing; MM, Moderate mowing; HM, Heavy mowing. Different letters indicate significant difference; NS, Not significant.
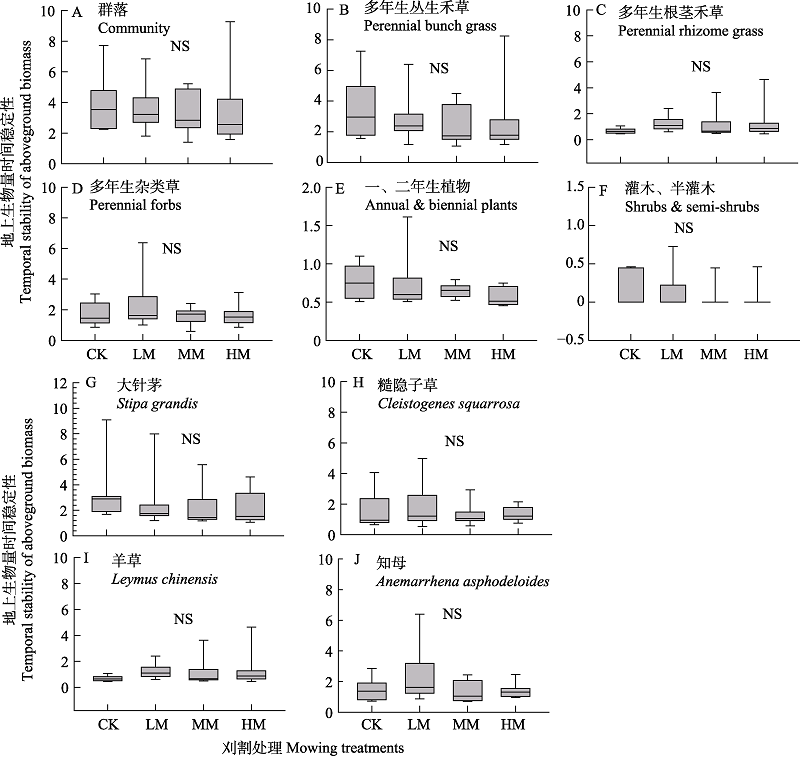
图2 不同刈割强度下群落(A)、功能群(B-F)及优势物种(G-J)地上生物量的时间稳定性(n = 9)。CK: 对照, 围封不刈割; LM: 轻度刈割; MM: 中度刈割; HM: 重度刈割; NS: 不显著。
Fig. 2 Temporal stability of community (A), functional groups (B-F), and dominant species (G-J) aboveground biomass under different mowing intensity (n = 9). CK, Control, enclosure and not mowing; LM, Light mowing; MM, Moderate mowing; HM, Heavy mowing; NS, Not significant.
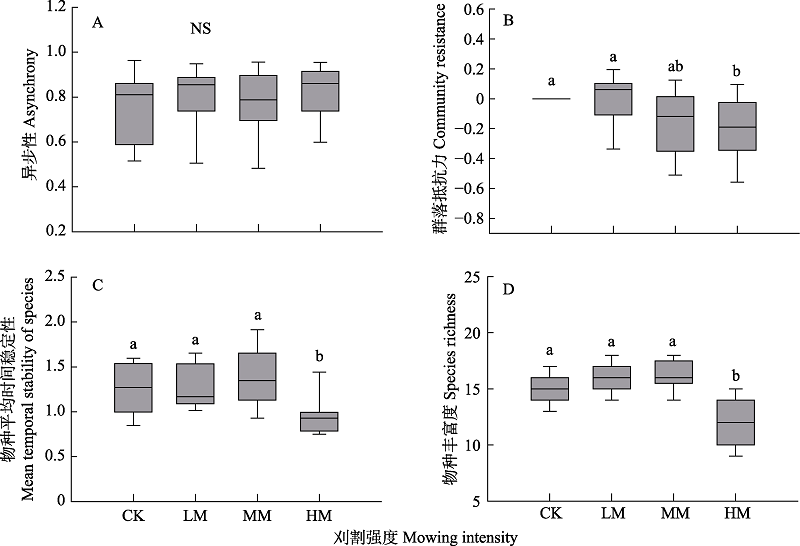
图3 不同刈割强度下异步性(A)、群落抵抗力(B)、物种平均时间稳定性(C)和物种丰富度(D)。CK: 对照, 围封不刈割; LM: 轻度刈割; MM: 中度刈割; HM: 重度刈割。不同字母表示差异显著(n = 9); NS: 不显著。
Fig. 3 Asynchrony (A), community resistance (B), mean temporal stability of species (C), and species richness (D) under different mowing intensity. CK, Control, enclosure and not mowing; LM, Light mowing; MM, Moderate mowing; HM, Heavy mowing. Different letters indicate significant difference (n = 9); NS: Not significant.
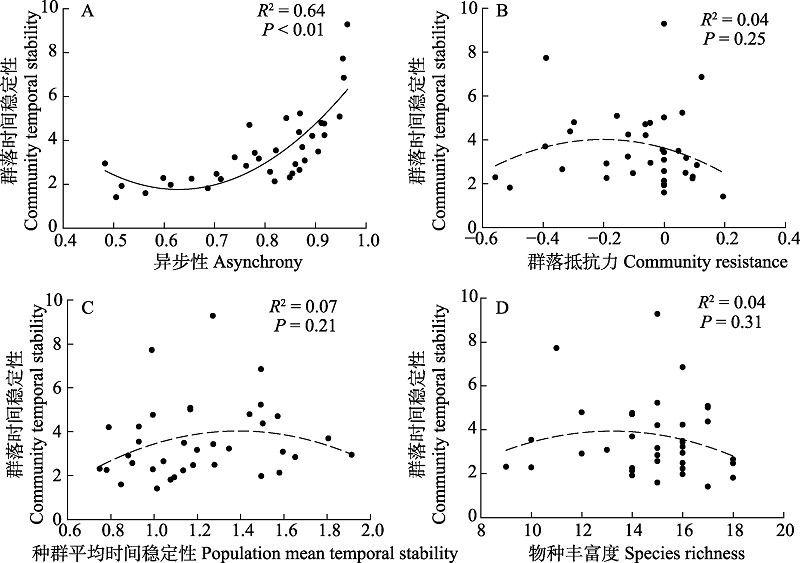
图4 异步性(A)、群落抵抗力(B)、种群平均时间稳定性(C)及物种丰富度(D)与群落时间稳定性间的关系(n = 36)
Fig. 4 Relationships of community temporal stability with asynchrony (A), community resistance (B), species mean temporal stability (C), and species richness (D) (n = 36)
| [1] | Adler PB, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Hillebrand H, Hautier Y, Hector A, Harpole WS, O’Halloran LR, Grace JB, Anderson TM, Bakker JD (2011) Productivity is a poor predictor of plant species richness. Science, 333, 1750-1753. |
| [2] | Baert JM, De Laender F, Sabbe K, Janssen CR (2016) Biodiversity increases functional and compositional resistance, but decreases resilience in phytoplankton communities. Ecology, 97, 3433-3440. |
| [3] | Bai YF, Chen ZZ (2000) Effects of long-term variability of plant species and functional groups on stability of a Leymus chinensis community in the Xilin River basin, Inner Mongolia. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24, 641-647. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 白永飞, 陈佐忠 (2000) 锡林河流域羊草草原植物种群和功能群的长期变异性及其对群落稳定性的影响. 植物生态学报, 24, 641-647.] | |
| [4] | Bakker ES, Olff H (2003) Impact of different-sized herbivores on recruitment opportunities for subordinate herbs in grasslands. Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 465-474. |
| [5] | Cardinale BJ, Srivastava DS, Duffy JE, Wright JP, Downing AL, Sankaran M, Jouseau C (2006) Effects of biodiversity on the functioning of trophic groups and ecosystems. Nature, 443, 989-992. |
| [6] | Cardinale BJ, Gross K, Fritschie K, Flombaum P, Fox JW, Rixen C, Ruijven JV, Reich PB, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Brian J, Wilsey BJ (2013) Biodiversity simultaneously enhances the production and stability of community biomass, but the effects are independent. Ecology, 94, 1697-1707. |
| [7] | Collins SL, Knapp AK, Briggs JM, Blair JM, Steinauer EM (1998) Modulation of diversity by grazing and mowing in native tall grass prairie. Nature, 280, 745-747. |
| [8] | Dong SK, Tang L, Zhang XF, Liu SL, Liu QR, Su XK, Zhang Y, Wu XY, Zhao ZZ, Li Y, Sha W (2017) Relationship between plant species diversity and functional diversity in alpine grasslands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 1472-1483. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 董世魁, 汤琳, 张相锋, 刘世梁, 刘全儒, 苏旭坤, 张勇, 武晓宇, 赵珍珍, 李钰, 沙威 (2017) 高寒草地植物物种多样性与功能多样性的关系. 生态学报, 37, 1472-1483.] | |
| [9] | Goodman D (1975) The theory of diversity-stability relationships in ecology. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 50, 237-266. |
| [10] |
Grace JB, Anderson TM, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Adler PB, Harpole WS, Hautier Y, Hillebrand H, Lind EM, Pärtel M, Bakker JD (2016) Integrative modelling reveals mechanisms linking productivity and plant species richness. Nature, 529, 390-393.
URL PMID |
| [11] |
Grace JB, Anderson TM, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Adler PB, Harpole WS, Hautier Y, Hillebrand H, Lind EM, Pärtel M, Bakker JD (2007) Does species diversity limit productivity in natural grassland communities. Ecology Letters, 10, 680-689.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] | Grime JP (1998) Benefits of plant diversity to ecosystems: Immediate, filter and founder effects. Journal of Ecology, 86, 902-910. |
| [13] | Grman E, Lau JA, Schoolmaster DR, Gross KL (2010) Mechanisms contributing to stability in ecosystem function depend on the environmental context. Ecology Letters, 13, 1400-1410. |
| [14] | Gross K, Cardinale BJ, Fox JW, Gonzalez A, Loreau M, Wayne Polley H, Reich PB, van Ruijven J (2014) Species richness and the temporal stability of biomass production: A new analysis of recent biodiversity experiments. The American Naturalist, 183, 1-12. |
| [15] | Guo CL (2017) Clipping and Fertilizing Disturbances on the Temporal Stability and Its Maintenance Mechanisms in Alpine Meadow. PhD dissertation, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭成龙 (2017) 刈割和施肥扰动下青藏高原高寒草甸群落的时间稳定性及其维持机制. 博士学位论文, 陕西师范大学, 西安.] | |
| [16] | Hautier Y, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Adler PB, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Lind EM, MacDougall AS, Stevens CJ, Bakker JD, Buckley YM (2014) Eutrophication weakens stabilizing effects of diversity in natural grasslands. Nature, 508, 521-525. |
| [17] |
Hector A, Hautier Y, Saner P, Wacker L, Bagchi R, Joshi J, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Spehn EM, Bazeley-White E, Weilenmann M, Caldeira MC (2010) General stabilizing effects of plant diversity on grassland productivity through population asynchrony and overyielding. Ecology, 91, 2213-2220.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Hooper DU, Chapin FS, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setälä H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA, Schmid B (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35. |
| [19] |
Isbell FI, Polley HW, Wilsey BJ (2009) Biodiversity, productivity and the temporal stability of productivity: Patterns and processes. Ecology Letters, 12, 443-451.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
Isbell F, Calcagno V, Hector A, Connolly J, Harpole WS, Reich PB, Scherer-Lorenzen MB, Schmid D, Tilman JV, Ruijven A, Weigelt BJ, Wilsey ES, Zavaleta , Weigelt A (2011) High plant diversity is needed to maintain ecosystem services. Nature, 477, 199.
URL PMID |
| [21] | Isbell F, Reich PB, Tilman D, Hobbie SE, Polasky S, Binder S (2013a) Nutrient enrichment, biodiversity loss, and consequent declines in ecosystem productivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 110, 11911-11916. |
| [22] |
Isbell F, Tilman D, Polasky S, Binder S, Hawthorne P (2013b) Low biodiversity state persists two decades after cessation of nutrient enrichment. Ecology Letters, 16, 454-460.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Jiang L, Pu ZC (2009) Different effects of species diversity on temporal stability in single-trophic and multitrophic communities. The American Naturalist, 174, 651-659.
URL PMID |
| [24] |
Jiang L, Joshi H, Patel SN (2009) Predation alters relationships between biodiversity and temporal stability. The American Naturalist, 173, 389-399.
URL PMID |
| [25] | King AW, Pimm SL (1983) Complexity, diversity, and stability: A reconciliation of theoretical and empirical results. The American Naturalist, 122, 229-239. |
| [26] | Longo G, Seidler TG, Garibaldi LA, Tognetti PM, Chaneton EJ (2013) Functional group dominance and identity effects influence the magnitude of grassland invasion. Journal of Ecology, 101, 1114-1124. |
| [27] |
Loreau M, de Mazancourt C (2013) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability: A synthesis of underlying mechanisms. Ecology Letters, 16, 106-115.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] | Mariotte P, Vandenberghe C, Kardol P, Hagedorn F, Buttler A (2013) Subordinate plant species enhance community resistance against drought in semi-natural grasslands. Journal of Ecology, 101, 763-773. |
| [29] |
Pan Q, Tian D, Naeem S, Auerswald K, Elser JJ, Bai Y, Huang J, Wang Q, Wang H, Wu J, Han X (2016) Effects of functional diversity loss on ecosystem functions are influenced by compensation. Ecology, 97, 2293-2302.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] | Pan SY, Kong BB, Yao TH, Wei XH, Li YN, Zhu ZH (2015) Effects of clipping and fertilizing on the relationship between functional diversity and aboveground net primary productivity in an alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 867-877. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 潘石玉, 孔彬彬, 姚天华, 卫欣华, 李英年, 朱志红 (2015) 刈割和施肥对高寒草甸功能多样性与地上净初级生产力关系的影响. 植物生态学报, 39, 867-877.] | |
| [31] | Pimm SL (1984) The complexity and stability of ecosystems. Nature, 307, 321-326. |
| [32] |
Ren H, Schönbach P, Wan H, Gierus M, Taube F (2012) Effects of grazing intensity and environmental factors on species composition and diversity in typical steppe of Inner Mongolia, China. PLoS ONE, 7, e52180.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] | Saccone P, Pyykkonen T, Eskelinen A, Virtanen R (2014) Environmental perturbation, grazing pressure and soil wetness jointly drive mountain tundra toward divergent alternative states. Journal of Ecology, 102, 1661-1672. |
| [34] | Sandau N, Fabian Y, Bruggisser OT, Rohr RP, Naisbit RE, Kehrli P, Aebi A, Bersier LF (2016) The relative contribution of species richness and species composition to ecosystem functioning. Oikos, 126, 782-791. |
| [35] | Shi Z, Sherry R, Xu X, Hararuk O, Souza L, Jiang LF, Xia JY, Liang JY, Luo YQ (2015) Evidence for long-term shift in plant community composition under decadal experimental warming. Journal of Ecology, 103, 1131-1140. |
| [36] | Smith MD, Knapp AK (2003) Dominant species maintain ecosystem function with non-random species loss. Ecology Letters, 6, 509-517. |
| [37] | Tilman D (1999) The ecological consequences of changes in biodiversity: A search for general principles. Ecology, 80, 1455-1474. |
| [38] | Waide RB, Willig MR, Steiner CF, Mittelbach G, Gough L, Dodson SI, Juday GP, Parmenter R (1999) The relationship between productivity and species richness. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 30, 257-300. |
| [39] | Wang HD, Zhang LL, Zhu ZH (2013) Effects of clipping and fertilizing on the relationships between species diversity and ecosystem functioning and mechanisms of community stability in alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 37, 279-295. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王海东, 张璐璐, 朱志红 (2013) 刈割、施肥对高寒草甸物种多样性与生态系统功能关系的影响及群落稳定性机制. 植物生态学报, 37, 279-295.] | |
| [40] | Wilsey BJ, Martin LM (2015) Top-down control of rare species abundances by native ungulates in a grassland restoration. Restoration Ecology, 23, 465-472. |
| [41] |
Winfree R, Fox JW, Williams NM, Reilly JR, Cariveau DP (2015) Abundance of common species, not species richness, drives delivery of a real-world ecosystem service. Ecology Letters, 18, 626-635.
URL PMID |
| [42] | Xu Z, Ren H, Li MH, van Ruijven J, Han X, Wan S, Li H, Yu Q, Jiang Y, Jiang L (2015) Environmental changes drive the temporal stability of semi-arid natural grasslands through altering species asynchrony. Journal of Ecology, 103, 1308-1316. |
| [43] |
Yang H, Jiang L, Li L, Li A, Wu M, Wan S (2012) Diversity-dependent stability under mowing and nutrient addition: Evidence from a 7-year grassland experiment. Ecology Letters, 15, 619-626.
DOI URL PMID |
| [44] | Yao TH, Zhu ZH, Li YN, Pan SY, Kong BB, Wei XH, Du JL (2016) Effects of functional diversity and functional redundancy on the community stability of an alpine meadow. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 1547-1558. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姚天华, 朱志红, 李英年, 潘石玉, 孔彬彬, 卫欣华, 杜家丽 (2016) 功能多样性和功能冗余对高寒草甸群落稳定性的影响. 生态学报, 36, 1547-1558.] |
| [1] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [2] | 何林君, 杨文静, 石宇豪, 阿说克者莫, 范钰, 王国严, 李景吉, 石松林, 易桂花, 彭培好. 火烧干扰下植物群落系统发育和功能多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [3] | 龙诗怡, 张博博, 夏宇辰, 费杨帆, 孟亚妮, 吕冰薇, 宋月青, 郑普, 郭陶然, 张健, 黎绍鹏. 本地群落多样性和时间稳定性对加拿大一枝黄花生物量的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24263-. |
| [4] | 吴春玲, 罗竹慧, 李意德, 许涵, 陈德祥, 丁琼. 热带山地雨林木本豆科和樟科植物叶内生细菌群落: 物种与功能群多样性及驱动因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23146-. |
| [5] | 林魏巍, 田呈明, 熊典广, 刘伟航, 热依汗古丽·斯地克, 梁英梅. 新疆杨树人工林中蜘蛛群落多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22493-. |
| [6] | 高瑞贺, 范世明, 董江海, 李蓉姣, 张志伟. 关帝山不同海拔昆虫功能群特征及分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23152-. |
| [7] | 王安伦, 何萍, 龙心远. 长江干流鱼类功能群空间分异[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23095-. |
| [8] | 雍青措姆, 习新强, 牛克昌. 高寒草甸植物物种丧失对草原毛虫的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22069-. |
| [9] | 张宇, 王露雨, 向昌林, 段美春, 张志升. 不同放牧强度对赛罕乌拉草原蜘蛛多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 467-476. |
| [10] | 蒋日进,张琳琳,徐开达,李鹏飞,肖祎,樊紫薇. 浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物功能群特征与多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(12): 1330-1338. |
| [11] | 张东, 宛凤英, 储玲, 严云志. 青弋江鱼类分类群和功能群的α和β多样性纵向梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(1): 1-13. |
| [12] | 颜露露, 蔡立哲, 陈昕韡, 李国强, 李文君, 曾佳丽, 饶义勇. 广州南沙十四涌潮间带大型底栖动物的功能群[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(7): 802-810. |
| [13] | 胡成业, 水玉跃, 田阔, 李良, 覃胡林, 张春草, 冀萌萌, 水柏年. 浙江七星列岛海洋特别保护区主要鱼类功能群划分及生态位分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 175-184. |
| [14] | 齐月, 李俊生, 闫冰, 邓贞贞, 付刚. 化学除草剂对农田生态系统野生植物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 228-236. |
| [15] | 张宇阳, 沙志鹏, 关法春, 王军峰. 玉米田养鹅措施对杂草群落生态特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(4): 492-501. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()