



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1330-1338. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019281 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019281
蒋日进1,2,张琳琳1,2,徐开达1,2,*( ),李鹏飞1,2,肖祎1,2,樊紫薇1,2
),李鹏飞1,2,肖祎1,2,樊紫薇1,2
收稿日期:2019-09-08
接受日期:2019-11-23
出版日期:2019-12-20
发布日期:2020-01-14
通讯作者:
徐开达
基金资助:
Rijin Jiang1,2,Linlin Zhang1,2,Kaida Xu1,2,*( ),Pengfei Li1,2,Yi Xiao1,2,Ziwei Fan1,2
),Pengfei Li1,2,Yi Xiao1,2,Ziwei Fan1,2
Received:2019-09-08
Accepted:2019-11-23
Online:2019-12-20
Published:2020-01-14
Contact:
Xu Kaida
摘要:
为探明浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物的群落结构和多样性, 作者于2016年春季进行了2个航次的底拖网调查, 应用生物多样性指数、冗余分析对游泳动物功能群组成进行了研究。结果表明, 该海域166种游泳动物依据摄食习性可分为6个功能群, 平均丰度百分比最高的为浮游动物/游泳动物食性功能群, 最低的为底栖动物食性功能群; 平均生物量百分比最高的为浮游动物食性功能群, 最低的为碎屑食性功能群。相似性分析结果显示, 该海域游泳动物的功能群结构在不同月份之间差异极显著。4月和5月的功能群多样性均值分别为1.30和1.23, 功能群多样性指数与大个体种类(体质量 > 50 g)的总生物量呈极显著正相关, 功能群多样性与物种多样性呈正相关关系。冗余分析显示该海域游泳动物食性功能群受温度变化影响较大; 底栖动物食性功能群受水深变化影响较大。上述结果表明, 浙江中南部海域游泳动物群落结构相对较稳定。
蒋日进,张琳琳,徐开达,李鹏飞,肖祎,樊紫薇 (2019) 浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物功能群特征与多样性. 生物多样性, 27, 1330-1338. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019281.
Rijin Jiang,Linlin Zhang,Kaida Xu,Pengfei Li,Yi Xiao,Ziwei Fan (2019) Characteristics and diversity of nekton functional groups in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1330-1338. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019281.
| 功能群 Functional group | 丰度百分比 Abundance percentage (%) | 生物量百分比 Biomass percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4月 April | 5月 May | 4月 April | 5月 May | |
| 浮游动物食性 Zooplanktivores functional group (FG1) | 8.36 | 10.83 | 6.43 | 12.02 |
| 浮游动物/游泳动物食性 Zooplanktivores /Piscivores functional group (FG2) | 33.19 | 61.23 | 17.13 | 25.09 |
| 游泳动物食性 Piscivores functional group (FG3) | 7.11 | 7.73 | 27.55 | 30.74 |
| 底栖动物食性 Benthivores functional group (FG4) | 1.89 | 1.00 | 9.17 | 8.87 |
| 碎屑食性 Detritivores functional group (FG5) | 15.22 | 7.63 | 4.60 | 3.76 |
| 杂食性 Omnivores functional group (FG6) | 34.22 | 11.58 | 35.12 | 19.52 |
表1 浙江中南部近岸海域4月和5月游泳动物群落功能群的丰度百分比和生物量百分比
Table 1 Abundance percentage and biomass percentage of different nekton functional groups in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province during April and May
| 功能群 Functional group | 丰度百分比 Abundance percentage (%) | 生物量百分比 Biomass percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4月 April | 5月 May | 4月 April | 5月 May | |
| 浮游动物食性 Zooplanktivores functional group (FG1) | 8.36 | 10.83 | 6.43 | 12.02 |
| 浮游动物/游泳动物食性 Zooplanktivores /Piscivores functional group (FG2) | 33.19 | 61.23 | 17.13 | 25.09 |
| 游泳动物食性 Piscivores functional group (FG3) | 7.11 | 7.73 | 27.55 | 30.74 |
| 底栖动物食性 Benthivores functional group (FG4) | 1.89 | 1.00 | 9.17 | 8.87 |
| 碎屑食性 Detritivores functional group (FG5) | 15.22 | 7.63 | 4.60 | 3.76 |
| 杂食性 Omnivores functional group (FG6) | 34.22 | 11.58 | 35.12 | 19.52 |
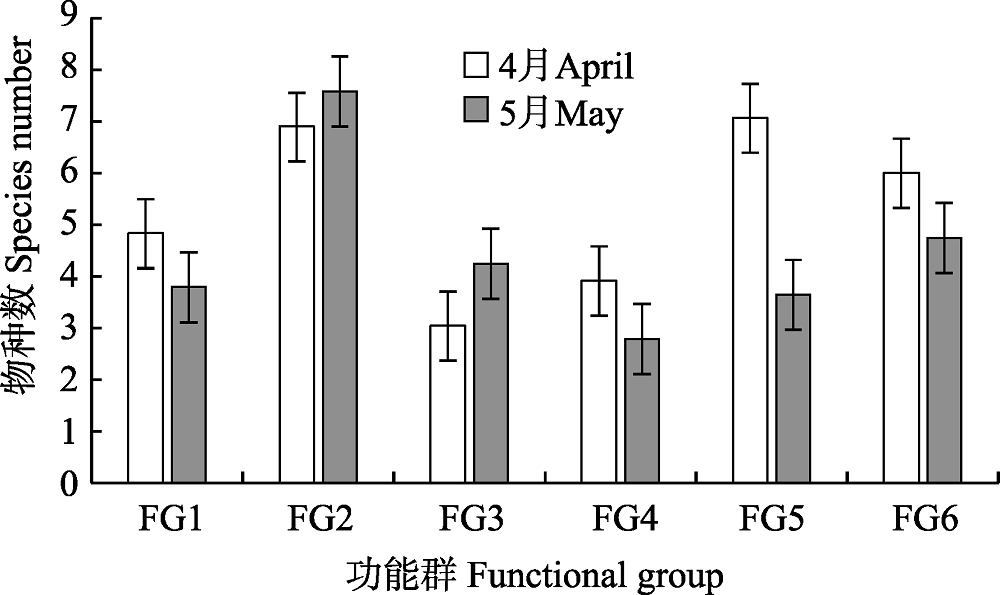
图2 4月和5月浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物群落各功能群所含物种数。功能群代号同表1。
Fig. 2 Species number of each nekton functional group in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province during April and May. Functional group codes are the same as in Table 1.
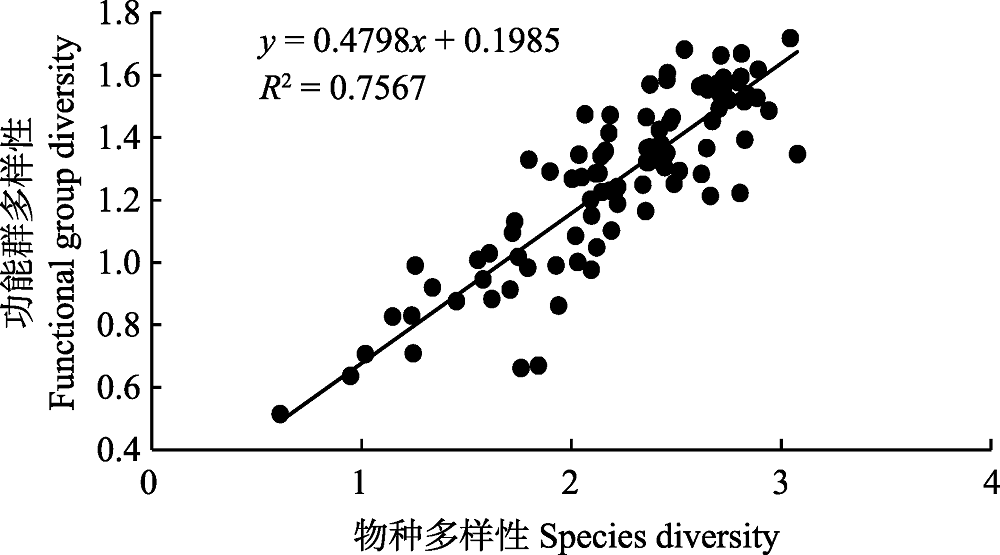
图3 浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物群落物种多样性与功能群多样性的线性关系
Fig. 3 The linear relationship between species diversity and functional diversity for the nekton community in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province
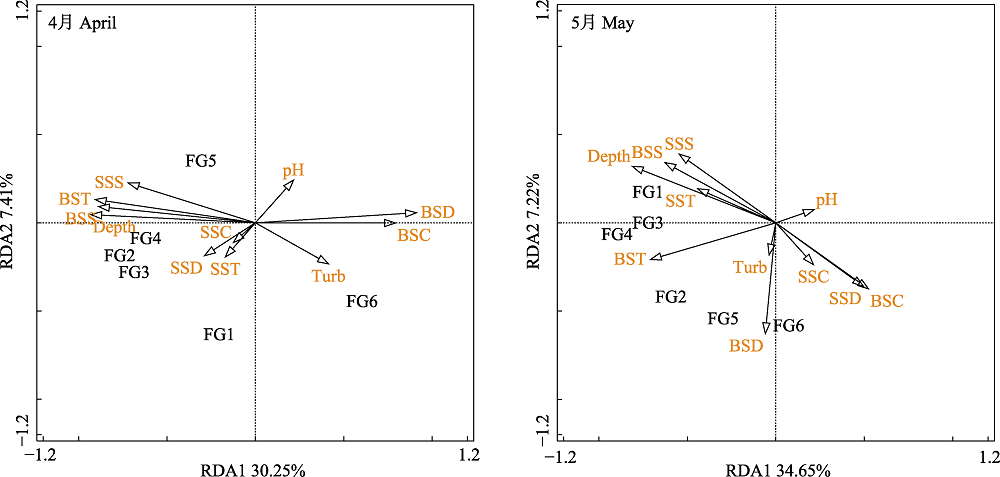
图4 4月和5月浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物功能群与环境因子的RDA排序图。SST: 表层温度; SSS: 表层盐度; SSC: 表层叶绿素; SSD: 表层溶解氧; BST: 底层温度: BSS: 底层盐度; BSC: 底层叶绿素; BSD: 底层溶解氧; pH: 酸碱度; Turb: 浑浊度; Depth: 水深。功能群代号同表1。
Fig. 4 Redundancy analysis ordination diagrams for nekton functional groups and environmental factors in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province during April and May. SST, Surface temperature; SSS, Surface salinity; SSC, Surface chlorophyll; SSD, Surface dissolved oxygen; BST, Bottom temperature; BSS, Bottom salinity; BSC, Bottom chlorophyll; BSD, Bottom dissolved oxygen; Turb, Turbidity; Depth, Depth of water. Functional group codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 环境参数 Environmental variables | 4月 April | 5月 May | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDA1 (30.25%) | RDA2 (7.41%) | RDA1 (34.65% ) | RDA2 (7.22% ) | |
| 表层温度 Surface temperature (SST) | -0.15 | -0.13 | -0.40 | 0.12 |
| 表层盐度 Surface salinity (SSS) | -0.62 | 0.16 | -0.49 | 0.24 |
| 表层叶绿素 Surface chlorophyll (SSC) | -0.11 | -0.08 | 0.19 | -0.15 |
| 表层溶解氧 Surface dissolved oxygen (SSD) | -0.25 | -0.13 | 0.45 | -0.22 |
| 底层温度 Bottom temperature (BST) | -0.78 | 0.09 | -0.64 | -0.13 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom salinity (BSS) | -0.76 | 0.06 | -0.56 | 0.21 |
| 底层叶绿素 Bottom chlorophyll (BSC) | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.47 | -0.23 |
| 底层溶解氧 Bottom dissolved oxygen (BSD) | 0.78 | 0.04 | -0.05 | -0.38 |
| pH | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| 浑浊度 Turbidity (Turb) | 0.36 | -0.16 | -0.03 | -0.11 |
| 水深 Depth of water (Depth) | -0.80 | 0.03 | -0.73 | 0.20 |
表2 4月和5月浙江中南部近岸海域游泳动物功能群与环境因子的RDA分析结果
Table 2 Results of redundancy analysis of nekton functional groups and environmental factors in the coastal waters of south-central Zhejiang Province during April and May
| 环境参数 Environmental variables | 4月 April | 5月 May | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDA1 (30.25%) | RDA2 (7.41%) | RDA1 (34.65% ) | RDA2 (7.22% ) | |
| 表层温度 Surface temperature (SST) | -0.15 | -0.13 | -0.40 | 0.12 |
| 表层盐度 Surface salinity (SSS) | -0.62 | 0.16 | -0.49 | 0.24 |
| 表层叶绿素 Surface chlorophyll (SSC) | -0.11 | -0.08 | 0.19 | -0.15 |
| 表层溶解氧 Surface dissolved oxygen (SSD) | -0.25 | -0.13 | 0.45 | -0.22 |
| 底层温度 Bottom temperature (BST) | -0.78 | 0.09 | -0.64 | -0.13 |
| 底层盐度 Bottom salinity (BSS) | -0.76 | 0.06 | -0.56 | 0.21 |
| 底层叶绿素 Bottom chlorophyll (BSC) | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.47 | -0.23 |
| 底层溶解氧 Bottom dissolved oxygen (BSD) | 0.78 | 0.04 | -0.05 | -0.38 |
| pH | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| 浑浊度 Turbidity (Turb) | 0.36 | -0.16 | -0.03 | -0.11 |
| 水深 Depth of water (Depth) | -0.80 | 0.03 | -0.73 | 0.20 |
| [1] | Arenas F, Iñigo S, Jenkins HSR ( 2006) The invasibility of marine algal assemblages: Role of functional diversity and identity. Ecology, 87, 2851-2861. |
| [2] | Bai YF, Li LH, Huang JH, Chen ZZ ( 2001) The influence of plant diversity and functional composition on ecosystem stability of four Stipa communities in the Inner Mongolia Plateau. Acta Botanica Sinica, 43, 280-287. |
| [3] | Begon M, Harper JL, Towsend CR ( 1996) Ecology: Individuals, Populations and Communities. Blackwell Scientific, Victoria (Australia). |
| [4] | Bellwood DR, Hoey A, Choat JH ( 2003) Limited functional redundancy in high diversity systems: Resilience and ecosystem function on coral reefs. Ecology Letters, 6, 281-285. |
| [5] | Cheng JS, Zhu JS ( 1997) Study on feeding characteristics and nutrient level of main economic invertebrates in the Yellow Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 19(6), 102-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程济生, 朱金声 ( 1997) 黄海主要经济无脊椎动物摄食特征及其营养层次的研究. 海洋学报, 19(6), 102-108.] | |
| [6] | Clarke KR ( 1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Australian Journal of Ecology, 18, 117-143. |
| [7] | Dai LB, Tian SQ, Peng X, Gao CX, Ye S, Du XX, Liu P ( 2018) Distribution of Larimichthys polyactis and its relationship with environmental factors in offshore water of southern Zhejiang. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29, 1352-1358. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴黎斌, 田思泉, 彭欣, 高春霞, 叶深, 杜晓雪, 刘攀 ( 2018) 浙江南部近海小黄鱼资源分布及其与环境因子的关系. 应用生态学报, 29, 1352-1358.] | |
| [8] | Deng JY, Zhao CY ( 1991) Marine Fishery Biology. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邓景耀, 赵传絪 ( 1991) 海洋渔业生物学. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Dolbeth M, Teixeira H, Marques JC, Pardal MÂ ( 2009) Feeding guild composition of a macrobenthic subtidal community along a depth gradient. Scientia Marina, 73, 225-237. |
| [10] | Floeter SR, Ferreira CEL, Dominici-Arosemena A, Zalmon IR ( 2004) Latitudinal gradients in Atlantic reef fish communities: Trophic structure and spatial use patterns. Journal of Fish Biology, 64, 1680-1699. |
| [11] | Garrison LP ( 2000) Spatial and dietary overlap in the Georges Bank ground fish community. Canadian Journal of Fishery and Aquatic Sciences, 57, 1679-1691. |
| [12] | Greenstreet SPR, Rogers S ( 2006) Indicators of the health of the North Sea fish community: Identifying reference levels for an ecosystem approach to management. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 63, 573-593. |
| [13] | Hu CY, Shui YY, Tian K, Li L, Qin HL, Zhang CC, Ji MM, Shui BN ( 2016) Functional group classification and niche identification of major fish species in the Qixing Islands Marine Reserve, Zhejiang Province. Biodiversity Science, 24, 175-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡成业, 水玉跃, 田阔, 李良, 覃胡林, 张春草, 冀萌萌, 水柏年 ( 2016) 浙江七星列岛海洋特别保护区主要鱼类功能群划分及生态位分析. 生物多样性, 24, 175-184.] | |
| [14] | Jiang RJ, Xu HX, Jin HW, Zhou YD, He ZT ( 2012) Feeding habits of blue mackerel scad Decapterus maruadsi Temminck et Schlegel in the East China Sea. Journal of Fisheries of China, 36, 216-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋日进, 徐汉祥, 金海卫, 周永东, 贺舟挺 ( 2012) 东海蓝圆鰺的摄食习性研究. 水产学报, 36, 216-227.] | |
| [15] | Jiang YZ, Cheng JH, Li SF ( 2008) Variation in fish community structure and biodiversity in the north of the East China Sea between two periods. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 15, 453-459. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜亚洲, 程家骅, 李圣法 ( 2008) 东海北部鱼类群落多样性及其结构特征的变化. 中国水产科学, 15, 453-459.] | |
| [16] | Jiang YZ, Lin N, Yuan XW, Jiao HF, Li SF ( 2014) Functional group composition and functional diversity of nekton community in the Xiangshan Bay. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 45, 108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜亚洲, 林楠, 袁兴伟, 焦海峰, 李圣法 ( 2014) 象山港游泳动物群落功能群组成与功能群多样性. 海洋与湖沼, 45, 108-114.] | |
| [17] | Jiao HF, Peng XM, You ZJ, Shi HX, Lou ZJ, Liu HD ( 2011) Species diversity of macrobenthos in the rocky intertidal zone of Yushan Island. Biodiversity Science, 19, 511-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 焦海峰, 彭小明, 尤仲杰, 施慧雄, 楼志军, 刘红丹 ( 2011) 渔山岛岩石相潮间带大型底栖动物物种多样性. 生物多样性, 19, 511-518.] | |
| [18] | Kong DL, Wu HF, Zeng H, Lü XT, Simmons M, Wang M, Sun XF, Han XG ( 2011) Plant functional group removal alters root biomass and nutrient cycling in a typical steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Plant and Soil, 346, 133-144. |
| [19] | Lanta V, Lepš J ( 2006) Effect of functional group richness and species richness in manipulated productivity-diversity studies: A glasshouse pot experiment. Acta Oecologica, 29, 85-96. |
| [20] | Lepš J, Šmolauer P ( 2003) Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, New York. |
| [21] | Li GG, Fan ZG ( 2011) Marine Ecology. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李冠国, 范振刚 ( 2011) 海洋生态学. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Lie HJ, Cho CH ( 2002) Recent advances in understanding the circulation and hydrography of the East China Sea. Fisheries Oceanography, 11, 318-328. |
| [23] | Lin LS, Yan LP, Ling JZ, Liu Y, Zhou RK ( 2005) Food habits of hairtail in the East China Sea region. Marine Fisheries, 27, 187-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林龙山, 严利平, 凌建忠, 刘勇, 周荣康 ( 2005) 东海带鱼摄食习性的研究. 海洋渔业, 27, 187-192.] | |
| [24] | Liu K, Lin HS, He XB, Huang YQ, Lin JH, Mou JF, Zhang SY, Wang JJ ( 2016) Functional feeding group of macrozoobenthos and their relationships to environmental factors in Xiamen coastal waters. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 38, 95-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘坤, 林和山, 何雪宝, 黄雅琴, 林俊辉, 牟剑锋, 张舒怡, 王建军 ( 2016) 厦门近岸海域大型底栖动物摄食功能群及其与环境因子的关系. 海洋学报, 38, 95-105.] | |
| [25] | Liu RY ( 2008) Checklist of Marine Biota of China Sea. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘瑞玉 ( 2008) 中国海洋生物名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [26] | Liu Y, Li SF, Cheng JH ( 2006) A study on seasonal changes of the fish communities in the East China Sea and the Huanghai Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 28(4), 108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘勇, 李圣法, 程家骅 ( 2006) 东海、黄海鱼类群落结构的季节变化研究. 海洋学报, 28(4), 108-114.] | |
| [27] | Long H ( 2005) The effect of temperature on fish survival. Fishery Modernization, 32(2), 20-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 龙华 ( 2005) 温度对鱼类生存的影响. 渔业现代化, 32(2), 20-22.] | |
| [28] | Lü ZB, Li F, Xu BQ, Wang B ( 2012) Fish community diversity during spring and autumn in the Yellow Sea off the coast of Shandong. Biodiversity Science, 20, 207-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吕振波, 李凡, 徐炳庆, 王波 ( 2012) 黄海山东海域春、秋季鱼类群落多样性. 生物多样性, 20, 207-214.] | |
| [29] | Ma WJ, Zhang Q, Niu JM, Kang S, Liu PT, He X, Yang Y, Zhang YN, Wu JG ( 2013) Relationship of ecosystem primary productivity to species diversity and functional group diversity: Evidence from Stipa breviflora grassland in Nei Mongol. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 37, 620-630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马文静, 张庆, 牛建明, 康萨如拉, 刘朋涛, 何欣, 杨艳, 张艳楠, 邬建国 ( 2013) 物种多样性和功能群多样性与生态系统生产力的关系——以内蒙古短花针茅草原为例. 植物生态学报, 37, 620-630.] | |
| [30] | Micheli F, Halpern BS ( 2005) Low functional redundancy in coastal marine assemblages. Ecology Letters, 8, 391-400. |
| [31] | Poff NL, Allan JD ( 1995) Functional organization of stream fish assemblages in relation to hydrological variability. Ecology, 76, 606-627. |
| [32] | Qian YQ, Ma KP ( 1994) Principle and Method of Biodiversity Studies. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 钱迎倩, 马克平 ( 1994) 生物多样性研究的原理与方法. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Shan XJ, Jin XS, Zhou ZP, Dai FQ ( 2011) Fish community diversity in the middle continental shelf of the East China Sea. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 29, 1199-1208. |
| [34] | Sheng FL, Zeng XQ, Xue Y ( 2009) Study on propagation and feeding habits of Oratosquilla oratoria in the inshore waters of Qingdao. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 39, 326-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 盛福利, 曾晓起, 薛莹 ( 2009) 青岛近海口虾蛄的繁殖及摄食习性研究. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 39, 326-332.] | |
| [35] | Sun BB, Yu CG, Liu H, Yan WC, Zhang WJ, Dai DX ( 2019) Spring and autumn shrimp and crab biodiversity in the east Nanji Islands. Biodiversity Science, 27, 787-795. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙蓓蓓, 俞存根, 刘惠, 颜文超, 张文俊, 戴冬旭 ( 2019) 南麂列岛东侧海域春秋季虾蟹类生物多样性. 生物多样性, 27, 787-795.] | |
| [36] | Tang QS, Su JL, Zhang J ( 2005) Key processes and sustainable mechanisms of ecosystem food production in the coastal ocean of China. Advance in Earth Sciences, 20, 1280-1287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐启升, 苏纪兰, 张经 ( 2005) 我国近海生态系统食物产出的关键过程及其可持续机理. 地球科学进展, 20, 1280-1287.] | |
| [37] | Thrush SF, Hewitt JE, Gibbs M, Lundquist G, Norkko A ( 2006) Functional role of large organisms in intertidal communities: Community effects and ecosystem function. Ecosystem, 9, 1029-1040. |
| [38] | Wang K, Zhang SY, Wang ZH, Zhao J, Jiang RJ ( 2014) Dietary composition and feeding strategy of Agrammus agrammus off the Ma’an Archipelago Special Marine Reserves. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 23, 251-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王凯, 章守宇, 汪振华, 赵静, 蒋日进 ( 2014) 马鞍列岛海洋特别保护区斑头六线鱼的摄食习性. 上海海洋大学学报, 23, 251-257.] | |
| [39] | Wei FW, Nie YG, Miao HX, Lu H, Hu YB ( 2014) Advancements of the researches on biodiversity loss mechanisms. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 430-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏辅文, 聂永刚, 苗海霞, 路浩, 胡义波 ( 2014) 生物多样性丧失机制研究进展. 科学通报, 59, 430-437.] | |
| [40] | Woodward G, Ebenman B, Emmerson M, Montoya JM, Olesen JM, Valido A, Warren PH ( 2005) Body size in ecological networks. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 20, 402-409. |
| [41] | Xu KD, Lu KE, Lu ZH, Dai Q ( 2018) Ecological niche analysis of dominant shrimp species in the Jiushan Islands Marine Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 26, 601-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐开达, 卢衎尔, 卢占晖, 戴乾 ( 2018) 韭山列岛自然保护区虾类优势种生态位. 生物多样性, 26, 601-610.] | |
| [42] | Xue Y, Xu BD, Gao TX, Xu H, Lin LS ( 2010) Preliminary study on the feeding habit of Lophius litulon during autumn in the North Yellow Sea. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 40, 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 薛莹, 徐宾铎, 高天翔, 徐浩, 林龙山 ( 2010) 北黄海秋季黄鮟鱇摄食习性的初步研究. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 40, 39-44.] | |
| [43] | Zhang B, Jin XS, Tang QS ( 2009) Functional groups of high trophic level communities in adjacent waters of Changjiang estuary. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20, 344-351. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张波, 金显仕, 唐启升 ( 2009) 长江口及邻近海域高营养层次生物群落功能群及其变化. 应用生态学报, 20, 344-351.] | |
| [44] | Zhang B, Tang QS, Jin XS ( 2007) Functional groups of fish assemblages and their major species at high trophic level in the East China Sea. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 14, 939-949. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张波, 唐启升, 金显仕 ( 2007) 东海高营养层次鱼类功能群及其主要种类. 中国水产科学, 14, 939-949.] | |
| [45] | Zhang HL, Song ZQ, Pan GL, Chen F, Zhou YD ( 2013) Diversity analysis of fish in the coastal area of Zhejiang during spring. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 44, 126-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张洪亮, 宋之琦, 潘国良, 陈峰, 周永东 ( 2013) 浙江南部近海春季鱼类多样性分析. 海洋与湖沼, 44, 126-134.] | |
| [46] | Zhang LL, Jiang RJ, Yin R, Xu KD, Fang F, Xu YP, Ke AY ( 2019) Spatial niche and differentiation of major nekton species in Yueqing Bay, Zhejiang, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30, 3911-3920. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张琳琳, 蒋日进, 印瑞, 徐开达, 方芳, 徐义平, 柯爱英 ( 2019) 乐清湾主要游泳动物空间生态位及其分化. 应用生态学报, 30, 3911-3920.] | |
| [47] | Zhao SL, Xu HX, Zhong JS, Chen J ( 2016) Zhejiang Marine Ichthyology. Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵盛龙, 徐汉祥, 钟俊生, 陈健 ( 2016) 浙江海洋鱼类志. 浙江科学技术出版社, 杭州.] | |
| [48] | Zhao YQ, Zeng JN, Gao AG, Chen QZ, Liao YB, Shou L ( 2009) Community pattern and diversity of macrozoobenthos in an intertidal flat, Jiaojiang Estuary. Biodiversity Science, 17, 303-309. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵永强, 曾江宁, 高爱根, 陈全震, 廖一波, 寿鹿 ( 2009) 椒江口滩涂大型底栖动物群落格局与多样性. 生物多样性, 17, 303-309.] | |
| [49] | Zhuang P, Luo G, Zhang T, Zhang LZ, Liu J, Feng GP, Hou JL ( 2010) Food comparison among juvenile Acipen sersinensis and other six economic fishes in the Yangtze estuary. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 5544-5554. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 庄平, 罗刚, 张涛, 章龙珍, 刘健, 冯广朋, 侯俊利 ( 2010) 长江口水域中华鲟幼鱼与6种主要经济鱼类的食性及食物竞争. 生态学报, 30, 5544-5554.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn