



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 107-116. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019297 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019297
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
• 研究报告:植物多样性 • 下一篇
刘旻霞*( ), 李全弟, 蒋晓轩, 夏素娟, 南笑宁, 张娅娅, 李博文
), 李全弟, 蒋晓轩, 夏素娟, 南笑宁, 张娅娅, 李博文
收稿日期:2019-09-23
接受日期:2019-11-29
出版日期:2020-02-20
发布日期:2020-04-02
通讯作者:
刘旻霞
基金资助:
Minxia Liu*( ), Quandi Li, Xiaoxuan Jiang, Sujuan Xia, Xiaoning Nan, Yaya Zhang, Bowen Li
), Quandi Li, Xiaoxuan Jiang, Sujuan Xia, Xiaoning Nan, Yaya Zhang, Bowen Li
Received:2019-09-23
Accepted:2019-11-29
Online:2020-02-20
Published:2020-04-02
Contact:
Minxia Liu
摘要:
稀有种不仅影响群落的物种多度分布格局, 同时也是α多样性的重要贡献者。本研究主要通过加性分配和Fortran软件的RAD程序包拟合的方法, 研究了甘南亚高寒草甸不同坡向物种多样性及多度分布格局的变化, 分析了物种多度分布格局及其α多样性的变化特征, 确定了稀有种在物种多度分布格局中的相对贡献。结果表明: (1)在南坡到北坡的变化中, 环境因子差异比较明显, 其中, 土壤全磷、有机碳、速效磷、碳氮比及含水量呈递增趋势; 土壤氮磷比和pH值呈递减趋势; 土壤全氮在西坡显著低于其他坡向, 而速效氮在所有坡向上差异不显著。(2)稀有种对群落物种多样性的影响在南-北坡向梯度上依次增大, 去除稀有种的影响在各坡向均高于去除非稀有种, 可见, 稀有种在甘南亚高寒草甸物种多样性中的相对贡献高于非稀有种。(3)各坡向的稀有种资源获取模式以随机分配占领模式(random fraction模型)为主, 而非稀有种则以生态位优先占领模式(geometric series模型)为主。由于稀有种有较大的扩散率, 在物种多样性较高的生态系统中, 物种之间的生态位重叠会更加明显, 从而抑制物种多样性的增加, 因此能达到维持原有物种多样性的目的。
刘旻霞, 李全弟, 蒋晓轩, 夏素娟, 南笑宁, 张娅娅, 李博文 (2020) 甘南亚高寒草甸稀有种对物种多样性和物种多度分布格局的贡献. 生物多样性, 28, 107-116. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019297.
Minxia Liu, Quandi Li, Xiaoxuan Jiang, Sujuan Xia, Xiaoning Nan, Yaya Zhang, Bowen Li (2020) Contribution of rare species to species diversity and species abundance distribution pattern in the Gannan subalpine meadow. Biodiversity Science, 28, 107-116. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019297.
| 坡向 Aspect | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 坡度 Slope (°) | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南坡 South (S) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 28.5 ± 1.7a | 3,001 |
| 西南坡 Southwest (SW) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 29.0 ± 2.1a | 3,009 |
| 西坡 West (W) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 29.5 ± 2.1b | 3,006 |
| 西北坡 Northwest (NW) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 22 ± 2.9c | 3,001 |
| 北坡 North (N) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 27.5 ± 3.3c | 3,000 |
表1 实验样地概况
Table 1 Overview of the experimental sample area
| 坡向 Aspect | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 坡度 Slope (°) | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南坡 South (S) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 28.5 ± 1.7a | 3,001 |
| 西南坡 Southwest (SW) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 29.0 ± 2.1a | 3,009 |
| 西坡 West (W) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 29.5 ± 2.1b | 3,006 |
| 西北坡 Northwest (NW) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 22 ± 2.9c | 3,001 |
| 北坡 North (N) | 34°58° N | 102°51° E | 27.5 ± 3.3c | 3,000 |
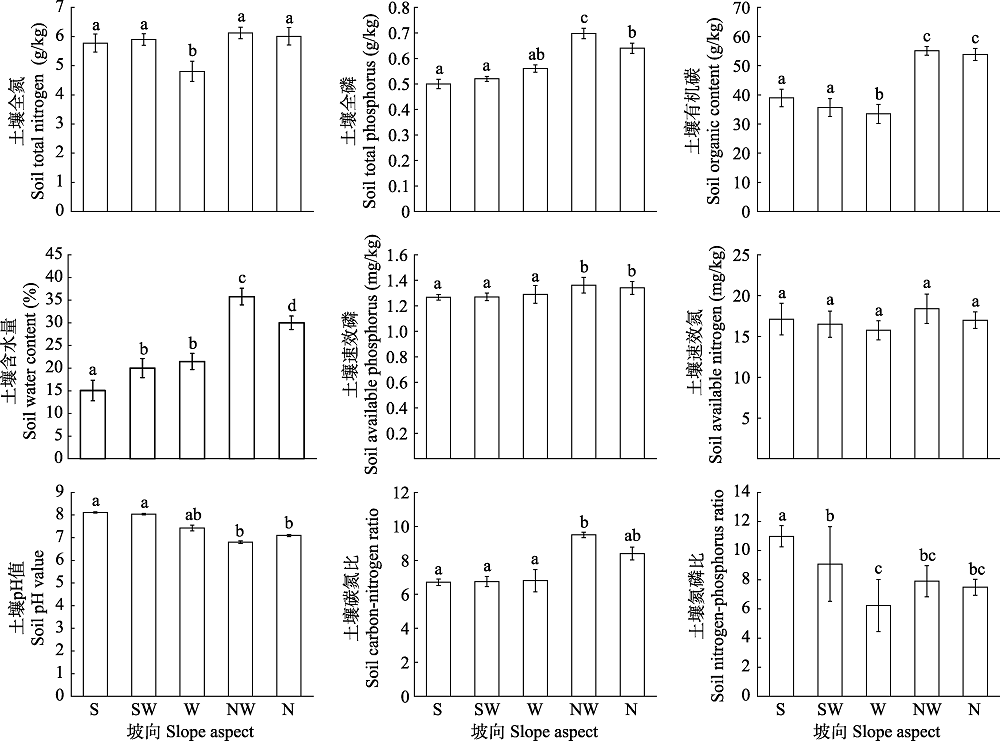
图1 甘南亚高寒草甸不同坡向土壤环境因子的变化(平均值 ± 标准差)。S: 南坡; SW: 西南坡; W: 西坡; NW: 西北坡; N: 北坡。不同小写字母代表有显著性差异。
Fig. 1 Soil environmental factors at different slope aspects in the Gannan subalpine meadow (mean ± SD). S, South; SW, Southwest; W, West; NW, Northwest; N, North. Different lowercase letters represent significant differences.
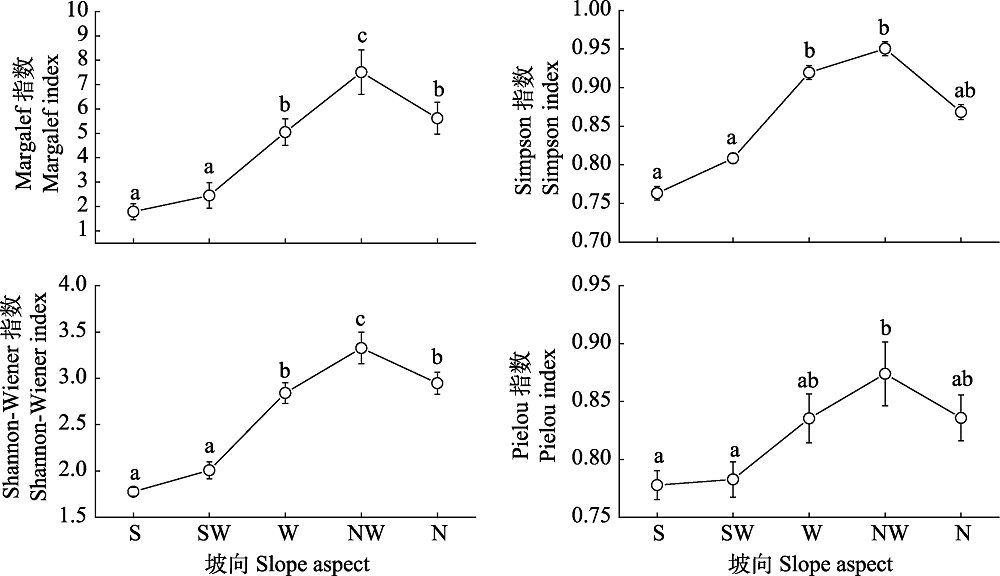
图2 甘南亚高寒草甸不同坡向物种多样性指数的变化(平均值 ± 标准差)。S: 南坡; SW: 西南坡; W: 西坡; NW: 西北坡; N: 北坡。不同小写字母代表有显著性差异。
Fig. 2 Species diversity indices at different slope aspects in the Gannan subalpine meadow (mean ± SD). S, South; SW, Southwest; W, West; NW, Northwest; N, North. Different lowercase letters represent significant differences.
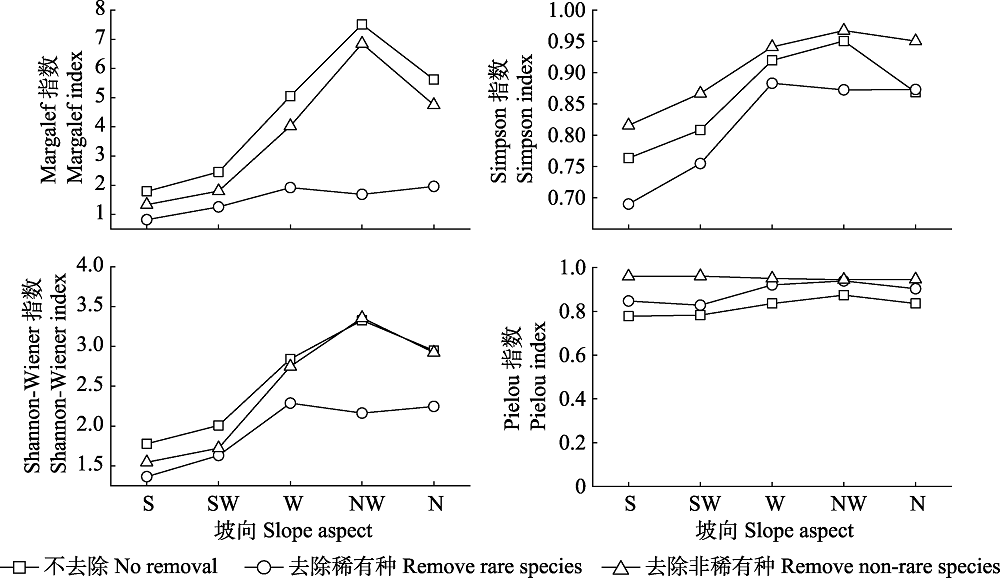
图3 甘南亚高寒草甸不同坡向稀有种和非稀有种对物种多样性的影响(平均值 ± 标准差)。S: 南坡; SW: 西南坡; W: 西坡; NW: 西北坡; N: 北坡。
Fig. 3 Effects of rare species and non-rare species on species diversity at different slope aspects in the Gannan subalpine meadow (mean ± SD). S, South; SW, Southwest; W, West; NW, Northwest; N, North.
| 坡向 Aspect | 拟合结果 Test result | 非稀有种 Non-rare species | 稀有种 Rare species | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| geo. | lser. | bro. | over. | rane. | geo. | lser. | bro. | over. | rane. | |||
| 南坡 South | R | 12.76 | 1.82 | 3.15 | - | 12.76 | 8.16 | 2.05 | 12.25 | - | 4.09 | |
| Oc | 0.80 | 0.80 | 1.15 | - | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 2.48 | - | 1.00 | ||
| CL | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.80 | - | 0.02 | 0.65 | 0.03 | 0.80 | - | 0.98 | ||
| 西南坡 Southwest | R | 54.85 | 10.89 | 5.85 | 6.07 | 91.27 | 44.10 | 220.37 | 26.85 | 28.96 | 41.14 | |
| Oc | 4.66 | 0.12 | 5.62 | 2.81 | 6.22 | 11.64 | 6.64 | 7.67 | 11.51 | 11.64 | ||
| CL | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.875 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| 西坡 West | R | 18.14 | 389.42 | 53.30 | 43.98 | 20.34 | 13.31 | 380.92 | 421.50 | 747.82 | 248.02 | |
| Oc | 1.74 | 38.34 | 16.05 | 20.39 | 1.74 | 14.28 | 161.91 | 106.40 | 359.64 | 550.49 | ||
| CL | 1.00 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.085 | ||
| 西北坡 Northwest | R | 42.42 | 156.01 | 32.16 | 36.91 | 45.74 | 154.73 | 154.72 | 106.31 | 235.95 | 22.59 | |
| Oc | 4.30 | 17.57 | 15.14 | 14.29 | 4.39 | 60.32 | 34.02 | 34.03 | 106.63 | 4.00 | ||
| CL | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.21 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 1.00 | ||
| 北坡 North | R | 39.88 | 303.2 | 72.83 | 75.73 | 49.43 | 27.50 | 161.06 | 161.62 | 246.23 | 6.33 | |
| Oc | 11.37 | 37.36 | 23.43 | 17.12 | 11.37 | 8.47 | 60.69 | 60.69 | 19.75 | 4.23 | ||
| CL | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.83 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.98 | ||
表2 甘南亚高寒草甸不同坡向稀有种和非稀有种的模型拟合
Table 2 Model fitting of rare species and non-rare species at different slope aspect in the Gannan subalpine meadow
| 坡向 Aspect | 拟合结果 Test result | 非稀有种 Non-rare species | 稀有种 Rare species | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| geo. | lser. | bro. | over. | rane. | geo. | lser. | bro. | over. | rane. | |||
| 南坡 South | R | 12.76 | 1.82 | 3.15 | - | 12.76 | 8.16 | 2.05 | 12.25 | - | 4.09 | |
| Oc | 0.80 | 0.80 | 1.15 | - | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 2.48 | - | 1.00 | ||
| CL | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.80 | - | 0.02 | 0.65 | 0.03 | 0.80 | - | 0.98 | ||
| 西南坡 Southwest | R | 54.85 | 10.89 | 5.85 | 6.07 | 91.27 | 44.10 | 220.37 | 26.85 | 28.96 | 41.14 | |
| Oc | 4.66 | 0.12 | 5.62 | 2.81 | 6.22 | 11.64 | 6.64 | 7.67 | 11.51 | 11.64 | ||
| CL | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.875 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| 西坡 West | R | 18.14 | 389.42 | 53.30 | 43.98 | 20.34 | 13.31 | 380.92 | 421.50 | 747.82 | 248.02 | |
| Oc | 1.74 | 38.34 | 16.05 | 20.39 | 1.74 | 14.28 | 161.91 | 106.40 | 359.64 | 550.49 | ||
| CL | 1.00 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.085 | ||
| 西北坡 Northwest | R | 42.42 | 156.01 | 32.16 | 36.91 | 45.74 | 154.73 | 154.72 | 106.31 | 235.95 | 22.59 | |
| Oc | 4.30 | 17.57 | 15.14 | 14.29 | 4.39 | 60.32 | 34.02 | 34.03 | 106.63 | 4.00 | ||
| CL | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.21 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 1.00 | ||
| 北坡 North | R | 39.88 | 303.2 | 72.83 | 75.73 | 49.43 | 27.50 | 161.06 | 161.62 | 246.23 | 6.33 | |
| Oc | 11.37 | 37.36 | 23.43 | 17.12 | 11.37 | 8.47 | 60.69 | 60.69 | 19.75 | 4.23 | ||
| CL | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.83 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.98 | ||
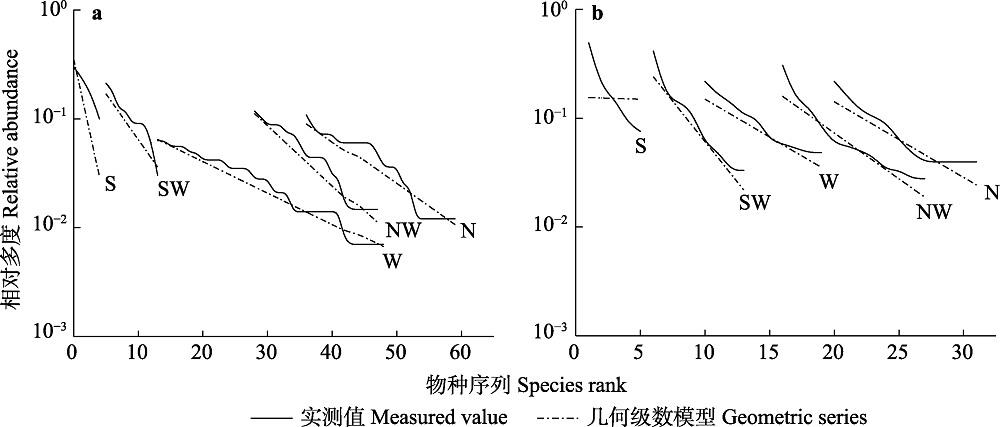
图4 甘南亚高寒草甸不同坡向基于几何级数模型分别对稀有种(a)和非稀有种(b)的拟合。S: 南坡; SW: 西南坡; W: 西坡; NW: 西北坡; N: 北坡。
Fig. 4 Comparison of rare species (a) and non-rare species (b) based on geometric series fitting values at different slope aspects in the Gannan subalpine meadow. S, South; SW, Southwest; W, West; NW, Northwest; N, North.
| [1] | Aizhexiecuo (2013) Effects of Niche Partitioning, Dispersal and Spatial Structure of Meta Community on Community Repeatability. PhD dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 艾者协措 (2013) 生态位分化、扩散和集合群落空间构型对于群落可重复性、物种稀有性和物种配置的影响. 博士学位论文, 兰州大学, 兰州.] | |
| [2] | Bao SD (2000) Analysis of Soil Agrochemistry. Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 鲍士旦 (2000) 土壤农化分析. 农业出版社, 北京. ] | |
| [3] | Benayas R, José M, Scheiner SM (2002) Plant diversity, biogeography and environment in Iberia: Patterns and possible causal factors. Journal of Vegetation Science, 13, 245-258. |
| [4] | Bi HT, Yang HZ, Fan LJ, Wang BY, Gao XM (2015) Analysis of species diversity of forest plant community in Funiu Mountains. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 49(1), 88-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 毕会涛, 杨红震, 凡琳洁, 王炳焱, 高贤明 (2015) 河南省伏牛山区植物群落物种多样性分析. 河南农业大学学报 49(1), 88-94.] | |
| [5] | Chesson P (2000) Mechanisms of maintenance of the species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology & Systematics, 31, 343-366. |
| [6] |
Christopher MC, Tilman D (2008) Loss of plant species after chronic low-level nitrogen deposition to prairie grasslands. Nature, 451, 712-715.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Fang JY, Shen ZH, Cui HT (2004) Ecological characteristics of mountains and research issues of mountain ecology. Biodiversity Science, 12, 10-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 方精云, 沈泽昊, 崔海亭 (2004) 试论山地的生态特征及山地生态学的研究内容. 生物多样性, 12, 10-19.] | |
| [8] |
Freestone AL, Inouye BD (2006) Dispersal limitation and environmental heterogeneity shape scale-dependent diversity patterns in plant communities. Ecology, 87, 2425-2432.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Gong X, Brueck K, Giese KM (2008) Slope aspect has effects on productivity and species composition of hilly grassland in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Arid Environments, 72, 483-493. |
| [10] |
Harpole WS, Tilman D (2006) Non-nuetral pattern of species abundance in grassland communities. Ecology Letters, 9, 15-23.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | He HY (2015) The Changes of Plant Species Abundance Distribution Patterns of Community with Slope Aspects and Sampling Area in Subalpine Meadow. PhD dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何红艳 (2015) 亚高寒草甸植物群落物种多度分布模式随坡向和取样面积的变化. 博士学位论文, 兰州大学, 兰州.] | |
| [12] |
Jetz W (2002) Geographic range rize and determinants of avian species richness. Science, 297, 1548-1551.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Kraft NJ, Comita LS, Chase JM, Sanders N, Swenson NG, Crist TO, Stegen JC, Vellend M, Boyle B, Anderson MJV (2011) Disentangling the drivers of β diversity along latitudinal and elevational gradients. Science, 333, 1755-1758.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
Lennon JJ, Koleff P, Greenwood JJ, Gaston KJ (2004) Contribution of rarity and commonness to patterns of species richness. Ecology Letters, 7, 81-89.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] | Li WH, Zheng SX, Bai YF (2014) Effects of grazing intensity and topography on species abundance distribution in a typical steppe of Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 178-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李文怀, 郑淑霞, 白永飞 (2014) 放牧强度和地形对内蒙古典型草原物种多度分布的影响. 植物生态学报, 38, 178-187.] | |
| [16] | Li XE (2011) Plant Functional Traits and Community Construction Mechanism on the Sunny-shady Slope Gradient of Subalpine Meadow. PhD dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李新娥 (2011) 亚高寒草甸阳坡‒阴坡梯度上植物功能性状及群落构建机制研究. 博士学位论文, 兰州大学, 兰州.] | |
| [17] | Li ZQ, Ouyang ZY, Zeng HQ (2010) Assessment methods for territorial biodiversity hotspot based on species richness at broad scale. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 1586-1593. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李智琦, 欧阳志云, 曾慧卿 (2010) 基于物种的大尺度生物多样性热点研究方法. 生态学报, 30, 1586-1593.] | |
| [18] | Liu MX (2013) Plant Community Composition and Nitrogen-Phosphorus Stoichiometry Along a Slope Aspect Gradients in an Alpine Meadow. PhD dissertation, Lanzhou University. Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘旻霞 (2013) 高寒草甸坡向梯度上植物群落组成及其氮磷化学计量学特征的研究. 博士学位论文, 兰州大学, 兰州.] | |
| [19] | Liu MX (2017) Response of plant element content and soil factors to the slope gradient of alpine meadows in Gannan. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 8275-8284. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘旻霞 (2017) 甘南高寒草甸植物元素含量与土壤因子对坡向梯度的响应. 生态学报, 37, 8275-8284.] | |
| [20] | Liu MX, Che YD, Li LR, Jiao J, Xiao W (2017a) Redundancy analysis of leaf traits and environmental factors of alpine meadow in southern Gansu Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 2473-2480. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘旻霞, 车应弟, 李俐蓉, 焦娇, 肖卫 (2017a) 甘南高寒草甸微地形上植物叶片特征与环境因子的冗余分析. 生态学杂志, 36, 2473-2480.] | |
| [21] | Liu MX, Wang G, Sheng HM (2013) Environmental factors characteristic of sunny and shady slope gradients in relation to above-ground biomass and species in an alpine meadow. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Science), 49(1), 76-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘旻霞, 王刚, 盛红梅 (2013) 高寒草甸阳坡-阴坡梯度上环境因子特征及其与地上生物量和物种丰富度的关系. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 49( 1), 76‒81.] | |
| [22] | Liu MX, Zhao RD, Zhang C, Li R, Shao P (2017b) Responses of physiological parameters in plants on sub-alpine meadow to slope aspect. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 2863-2869. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘旻霞, 赵瑞东, 张灿, 李瑞, 邵鹏 (2017b) 亚高寒草甸植物叶片生理指标对坡向的响应. 应用生态学报, 28, 2863-2869.] | |
| [23] | Liu Z, Li Q, Chen DD, Zhai WT, Zhao L, Xu XS, Zhao XQ (2015) Patterns of plant species diversity along an altitudinal gradient and its effect on above-ground biomass in alpine meadows in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 23, 451-462. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘哲, 李奇, 陈懂懂, 翟文婷, 赵亮, 徐世晓, 赵新全 (2015) 青藏高原高寒草甸物种多样性的海拔梯度分布格局及对地上生物量的影响. 生物多样性, 23, 451-462.] | |
| [24] | Lu ZH (2018) Research on α diversity index algorithm based on Matlab2014. Agriculture and Technology, 38(17), 7‒9, 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 卢志宏 (2018) 基于Matlab2014编写α多样性指数算法研究. 农业与技术, 38(17), 7‒9, 33.] | |
| [25] |
Magurran AE, Henderson PA (2003) Explaining the excess of rare species in natural species abundance distributions Nature, 422, 50‒52.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Mazaris AD, Tsianou MA, Sigkounas A, Dimopoulos P, Pantis JD, Sgardelis SP, Kallimanis AS (2013) Accounting for the capacity of common and rare species to contribute to diversity spatial patterns: Is it a sampling issue or a biological effect? Ecological Indicators, 32, 9-13. |
| [27] | Ma KM (2003) Advances of the study on species abundance pattern. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 27, 412-426. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马克明 (2003) 物种多度格局研究进展. 植物生态学报, 27, 412-426.] | |
| [28] |
Mouillot D, Leprêtre A, Andrei-Ruiz M-C, Viale D (2000) The fractal model: A new model to describe the species accumulation process and relative abundance distribution (rad). Oikos, 90, 333-342.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Nie YY, Li XE, Wang G (2010) Variation mode of a diversity and β diversity of plant community of different habitat gradients from south-facing slope to north-facing slope and its relation with different environmental factors. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Science), 46(3), 73-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 聂莹莹, 李新娥, 王刚 (2010) 阳坡-阴坡生境梯度上植物群落α多样性与β多样性的变化模式及与环境因子的关系. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版) 46(3), 73-79.] | |
| [30] | Rao MD, Fen G, Zhang JL, Mi XC, Chen JH (2013) Effects of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation on species and phylogenetic beta diversity in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58, 1204-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 饶米德, 冯刚, 张金龙, 米湘成, 陈建华 (2013) 生境过滤和扩散限制作用对古田山森林物种和系统发育β多样性的影响. 科学通报, 58, 1204-1212.] | |
| [31] | Reilly MJ, Wimberly MC, Newell CL (2006) Wildfire effects on plant species richness at multiple spatial scales in forest communities of the Southern Appalachians. Journal of Ecology, 94, 118-130. |
| [32] | Sun XM, Xiao ML, Shi RL, Han F, Wang G (2014) Effects of nutrient additions on species abundance distribution in an alpine meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Journal of Lanzhou University, 50, 853-859. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙小妹, 肖美玲, 师瑞玲, 韩非, 王刚 (2014) 营养元素添加对青藏高原亚高寒草甸物种多度分布格局的影响. 兰州大学学报, 50, 853-859.] | |
| [33] | Tetetla-Rangel E, Dupuy JM, Luis J (2017) Patterns and correlates of plant diversity differ between common and rare species in a Neotropical dry forest. Biodiversity and Conservation, 27, 1705-1721. |
| [34] | Tsang TPN, Bonebrake TC (2016) Contrasting roles of environmental and spatial processes for common and rare urban butterfly species compositions. Landscape Ecology, 32, 47-57. |
| [35] | Urich W, Ollik M (2004) Frequent and occasional species and the shape of relative abundance distributions. Diversity & Distribution, 10, 263-269. |
| [36] | Wang SX, Wang XA, Li GQ, Guo H, Zhu ZH (2010) Species diversity and environmental interpretation in the process of community succession in the Ziwu Mountain of Shaanxi Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 1638-1647. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王世雄, 王孝安, 李国庆, 郭华, 朱志红 (2010) 陕西子午岭植物群落演替过程中物种多样性变化与环境解释. 生态学报, 30, 1638-1647.] | |
| [37] | Wang SX, Wang XA, Guo H, Zhang GQ, Wang S, He YJ (2018) Relative contributions of rare and common species to the multiple-scale patterns of species diversity in communities on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 8060-8069. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王世雄, 王孝安, 郭华, 张广奇, 王姝, 何跃军 (2018) 稀有种和常见种对黄土高原辽东栎群落物种多样性贡献的多尺度分析. 生态学报, 38, 8060-8069.] | |
| [38] | Wang SX, Zhao L, Li N, Guo H, Wang XA, Duan RY (2016) The relative contributions of rare and common species to the patterns of species richness in plant communities. Biodiversity Science, 24, 658-664. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王世雄, 赵亮, 李娜, 郭华, 王孝安, 段仁燕 (2016) 稀有种和常见种对植物群落物种丰富度格局的相对贡献. 生物多样性, 24, 658-664.] | |
| [39] | Whittaker RJ, Willis KJ, Field R (2001) Scale and species richness: Towards a general, hierarchical theory of species diversity. Journal of Biogeography, 4, 453-470. |
| [40] | Xiao ML (2014) Species‒Abundance Distribution of Zoker Mound Plant Community Along Restoration Progress and Its Relationship with Mound Area. PhD dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 肖美玲 (2014) 鼢鼠土丘植物群落恢复演替过程中的物种‒多度分布及其与鼠丘面积的关系. 博士学位论文, 兰州大学, 兰州.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()