



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 135-143. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019233 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019233
所属专题: 有机农业
池秀莲1, 郭婷2, 王庆刚2, 景志贤1, 张小波1, 李晓琳1, 孙楷1, 王铁霖1, 杨光1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-07-23
接受日期:2019-10-23
出版日期:2020-02-20
发布日期:2020-03-27
通讯作者:
杨光
基金资助:
Xiulian Chi1, Ting Guo2, Qinggang Wang2, Zhixian Jing1, Xiaobo Zhang1, Xiaolin Li1, Kai Sun1, Tielin Wang1, Guang Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2019-07-23
Accepted:2019-10-23
Online:2020-02-20
Published:2020-03-27
Contact:
Guang Yang
摘要:
药用植物野生资源的保护正受到学界乃至全社会的广泛关注。本研究通过收集华中地区(包括湖南、湖北和河南三省)的49个国家级自然保护区的科学考察报告、多样性研究报告以及其他相关文献资料, 结合第四次全国中药资源普查数据, 建立了华中地区国家级自然保护区内药用维管植物数据库, 并评估了这些保护区对华中地区药用维管植物的保护成效。研究发现: 华中地区国家级自然保护区内分布有6,071种药用维管植物, 就地保护比例为81.93%; 其中特有、受威胁和常用药用植物物种数分别为1,479种、224种和448种, 三者受保护比例分别为87.98%、78.87%和91.80%。有32.16%的药用维管植物(2,383种, 特有、受威胁和常用药用植物物种数分别为644种、119种和69种)仅分布于1-5个自然保护区中。森林生态系统类型的自然保护区对不同类群药用植物的保护效果均最好。神农架、金童山、莽山、星斗山及湖南舜皇山5个保护区是所有、特有以及受威胁药用植物物种多样性的热点地区, 是华中地区药用植物保护的重要区域。总体上, 华中地区现有国家级自然保护区较好地覆盖了该地区的药用维管植物, 但药用维管植物的就地保护仍不容懈怠。建议加强对该区域保护空缺物种的野外动态监测和保护。
池秀莲, 郭婷, 王庆刚, 景志贤, 张小波, 李晓琳, 孙楷, 王铁霖, 杨光 (2020) 华中地区国家级自然保护区对药用维管植物的就地保护现状. 生物多样性, 28, 135-143. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019233.
Xiulian Chi, Ting Guo, Qinggang Wang, Zhixian Jing, Xiaobo Zhang, Xiaolin Li, Kai Sun, Tielin Wang, Guang Yang (2020) Evaluation of in situ conservation effectiveness on medicinal vascular plants in national nature reserves in central China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 135-143. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019233.
| 植物类群 Groups | 蕨类植物 Fern | 裸子植物 Gymnosperm | 被子植物 Angiosperm | 合计 Total | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科数 Family | 属数 Genus | 物种数 Species | 科数 Family | 属数 Genus | 物种数 Species | 科数 Family | 属数 Genus | 物种数 Species | 科数 Family | 属数 Genus | 物种数 Species | |
| 所有药用植物 All medicinal plants | 43/44 | 102/108 | 394/449 | 10/10 | 30/32 | 69/85 | 192/201 | 1,375/1,580 | 5,608/6,876 | 245/255 | 1,507/1,720 | 6,071/7,410 |
| 特有药用植物 Endemic medicinal plants | 10/11 | 17/18 | 24/28 | 7/7 | 13/13 | 24/26 | 123/126 | 482/525 | 1,431/1,627 | 140/144 | 512/556 | 1,479/1,681 |
| 常用药用植物 Frequently used medicinal plants | 9/9 | 9/9 | 12/12 | 5/5 | 6/6 | 7/8 | 103/108 | 289/312 | 429/468 | 117/122 | 304/327 | 448/488 |
| 受威胁药用植物 Threatened medicinal plants | 4/6 | 6/8 | 8/10 | 8/8 | 17/18 | 24/27 | 64/73 | 116/145 | 192/247 | 76/87 | 139/171 | 224/284 |
表1 华中地区不同类群药用维管植物数量。“/”前、后数字分别表示国家级自然保护区范围内及整个华中地区范围内的药用维管植物数量。
Table 1 Numbers of medicinal vascular plant species in different groups in central China. The numbers before and after the slash represent numbers of medicinal vascular plant species within 49 national nature reserves and across whole region in central China, respectively.
| 植物类群 Groups | 蕨类植物 Fern | 裸子植物 Gymnosperm | 被子植物 Angiosperm | 合计 Total | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科数 Family | 属数 Genus | 物种数 Species | 科数 Family | 属数 Genus | 物种数 Species | 科数 Family | 属数 Genus | 物种数 Species | 科数 Family | 属数 Genus | 物种数 Species | |
| 所有药用植物 All medicinal plants | 43/44 | 102/108 | 394/449 | 10/10 | 30/32 | 69/85 | 192/201 | 1,375/1,580 | 5,608/6,876 | 245/255 | 1,507/1,720 | 6,071/7,410 |
| 特有药用植物 Endemic medicinal plants | 10/11 | 17/18 | 24/28 | 7/7 | 13/13 | 24/26 | 123/126 | 482/525 | 1,431/1,627 | 140/144 | 512/556 | 1,479/1,681 |
| 常用药用植物 Frequently used medicinal plants | 9/9 | 9/9 | 12/12 | 5/5 | 6/6 | 7/8 | 103/108 | 289/312 | 429/468 | 117/122 | 304/327 | 448/488 |
| 受威胁药用植物 Threatened medicinal plants | 4/6 | 6/8 | 8/10 | 8/8 | 17/18 | 24/27 | 64/73 | 116/145 | 192/247 | 76/87 | 139/171 | 224/284 |
| 所有药用植物 All medicinal plants | 特有药用植物 Endemic medicinal plants | 受威胁药用植物 Threatened medicinal plants | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保护区简称 Abbreviated name | 累计物种数 Accumulative no. of species | 累计贡献率 Accumulative contribution rate (%) | 保护区简称 Abbreviated name | 累计物种数 Accumulative no. of species | 累计贡献率 Accumulative contribution rate (%) | 保护区简称 Abbreviated name | 累计物种数 Accumulative no. of species | 累计贡献率 Accumulative contribution rate (%) |
| 神农架 Shennongjia | 3,294 | 58.49 | 神农架 Shennongjia | 857 | 57.94 | 神农架 Shennongjia | 103 | 45.98 |
| 宝天曼 Baotianman | 3,874 | 68.79 | 湖南舜皇山 Shunhuangshan, Hunan | 984 | 66.53 | 鸡公山 Jigongshan | 127 | 56.70 |
| 金童山 Jintongshan | 4,302 | 76.38 | 宝天曼 Baotianman | 1,071 | 72.41 | 湖南舜皇山 Shunhuangshan, Hunan | 146 | 65.18 |
| 高望界 Gaowangjie | 4,531 | 80.45 | 莽山 Mangshan | 1,140 | 77.08 | 星斗山 Xingdoushan | 157 | 70.09 |
| 太行山猕猴 Taihangshan- mihou | 4,719 | 83.79 | 星斗山 Xingdoushan | 1,184 | 80.05 | 五峰后河 Wufenghouhe | 164 | 73.21 |
| 莽山 Mangshan | 4,889 | 86.81 | 金童山 Jintongshan | 1,215 | 82.15 | 莽山 Mangshan | 170 | 75.89 |
| 星斗山 Xingdoushan | 5,014 | 89.03 | 五峰后河 Wufenghouhe | 1,244 | 84.11 | 八大公山 Badagongshan | 176 | 78.57 |
| 湖南舜皇山 Hunan Shunhuangshan | 5,127 | 91.03 | 河南大别山 Henan Dabieshan | 1,272 | 86.00 | 堵河源 Duheyuan | 182 | 81.25 |
| 高望界 Gaowangjie | 1,295 | 87.56 | 小秦岭 Xiaoqinling | 187 | 83.48 | |||
| 十八里长峡 Shibalichangxia | 1,314 | 88.84 | 金童山 Jintongshan | 192 | 85.71 | |||
| 九嶷山 Jiuyishan | 1,331 | 89.99 | 炎陵桃源洞 Yanlingtaoyuandong | 196 | 87.50 | |||
| 七姊妹山 Qizimeishan | 1,348 | 91.14 | 十八里长峡 Shibalichangxia | 200 | 89.29 | |||
| 九宫山 Jiugongshan | 203 | 90.63 | ||||||
表2 华中地区对药用维管植物累计保护贡献率达90%的国家级自然保护区情况
Table 2 The national nature reserves with accumulative contribution rate more than 90% in conservation of medicinal vascular plants
| 所有药用植物 All medicinal plants | 特有药用植物 Endemic medicinal plants | 受威胁药用植物 Threatened medicinal plants | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 保护区简称 Abbreviated name | 累计物种数 Accumulative no. of species | 累计贡献率 Accumulative contribution rate (%) | 保护区简称 Abbreviated name | 累计物种数 Accumulative no. of species | 累计贡献率 Accumulative contribution rate (%) | 保护区简称 Abbreviated name | 累计物种数 Accumulative no. of species | 累计贡献率 Accumulative contribution rate (%) |
| 神农架 Shennongjia | 3,294 | 58.49 | 神农架 Shennongjia | 857 | 57.94 | 神农架 Shennongjia | 103 | 45.98 |
| 宝天曼 Baotianman | 3,874 | 68.79 | 湖南舜皇山 Shunhuangshan, Hunan | 984 | 66.53 | 鸡公山 Jigongshan | 127 | 56.70 |
| 金童山 Jintongshan | 4,302 | 76.38 | 宝天曼 Baotianman | 1,071 | 72.41 | 湖南舜皇山 Shunhuangshan, Hunan | 146 | 65.18 |
| 高望界 Gaowangjie | 4,531 | 80.45 | 莽山 Mangshan | 1,140 | 77.08 | 星斗山 Xingdoushan | 157 | 70.09 |
| 太行山猕猴 Taihangshan- mihou | 4,719 | 83.79 | 星斗山 Xingdoushan | 1,184 | 80.05 | 五峰后河 Wufenghouhe | 164 | 73.21 |
| 莽山 Mangshan | 4,889 | 86.81 | 金童山 Jintongshan | 1,215 | 82.15 | 莽山 Mangshan | 170 | 75.89 |
| 星斗山 Xingdoushan | 5,014 | 89.03 | 五峰后河 Wufenghouhe | 1,244 | 84.11 | 八大公山 Badagongshan | 176 | 78.57 |
| 湖南舜皇山 Hunan Shunhuangshan | 5,127 | 91.03 | 河南大别山 Henan Dabieshan | 1,272 | 86.00 | 堵河源 Duheyuan | 182 | 81.25 |
| 高望界 Gaowangjie | 1,295 | 87.56 | 小秦岭 Xiaoqinling | 187 | 83.48 | |||
| 十八里长峡 Shibalichangxia | 1,314 | 88.84 | 金童山 Jintongshan | 192 | 85.71 | |||
| 九嶷山 Jiuyishan | 1,331 | 89.99 | 炎陵桃源洞 Yanlingtaoyuandong | 196 | 87.50 | |||
| 七姊妹山 Qizimeishan | 1,348 | 91.14 | 十八里长峡 Shibalichangxia | 200 | 89.29 | |||
| 九宫山 Jiugongshan | 203 | 90.63 | ||||||
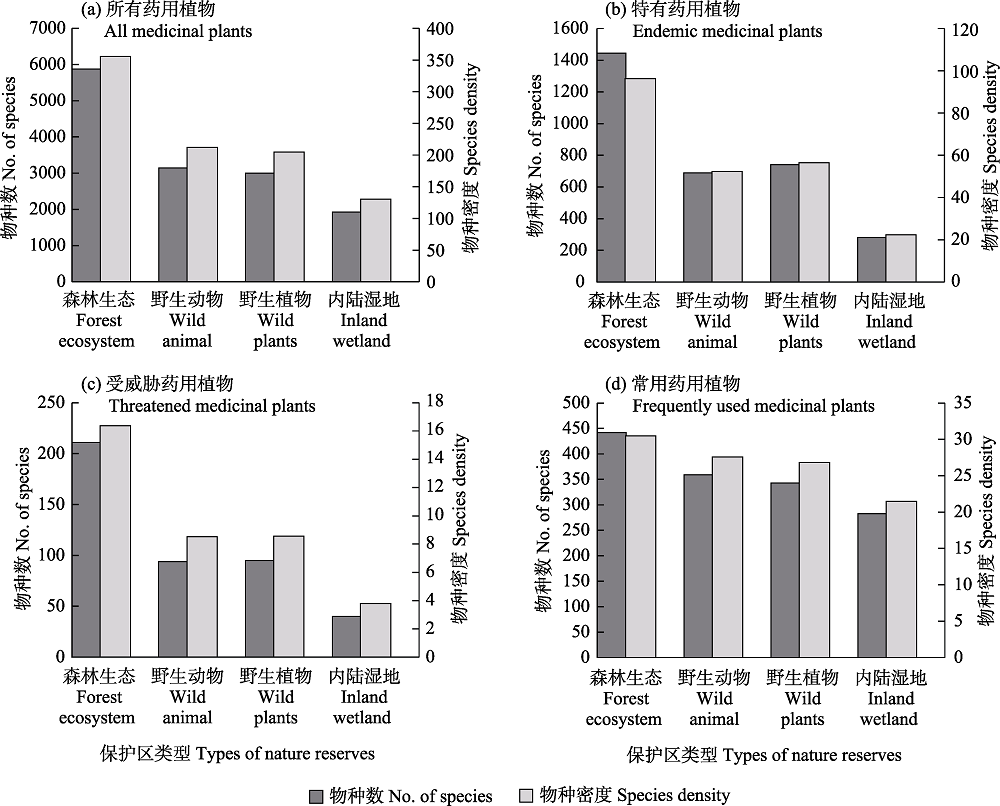
图2 华中地区不同类型国家级自然保护区对不同类群药用维管植物的保护差异
Fig. 2 Differences in number of medicinal vascular plants distributed within different types of national nature reserves in central China
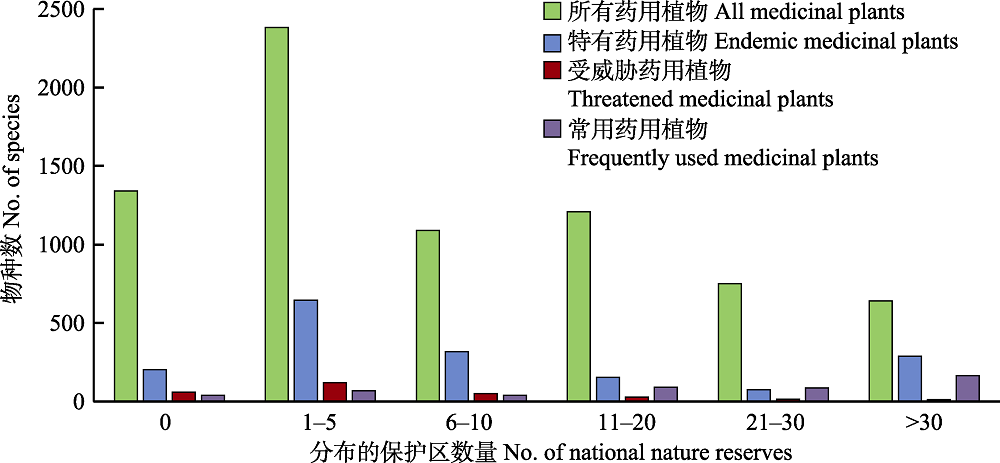
图3 华中地区不同类群药用维管植物分布的国家级自然保护区数量频率分布
Fig. 3 Frequency distribution of numbers of different groups of medicinal vascular plants covered by national nature reserves in central China
| [1] |
Chi XL, Wang QG, Wang TL, Li XL, Guo T, Sun K, Li Y, Cheng M, Yang G (2020) Assessing in-situ conservation status of threatened medicinal vascular plants in central China. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 45, 52-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL PMID |
| [ 池秀莲, 王庆刚, 王铁霖, 李晓琳, 郭婷, 孙楷, 李颖, 程蒙, 杨光 (2020) 华中地区受威胁药用维管植物的就地保护现状分析. 中国中药杂志, 45, 52-58.] | |
| [2] | Chi XL, Zhang ZJ, Xu XT, Zhang XB, Zhao ZP, Liu YN, Wang QG, Wang H, Li Y, Yang G, Guo LP, Tang ZY, Huang LQ (2017) Threatened medicinal plants in China: Distributions and conservation priorities. Biological Conservation, 210, 89-95. |
| [3] | China National Chinese Medicinal Material Corporation(1994) China Traditional Chinese Medicine Resources Records. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 中国药材公司(1994) 中国中药资源志要. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [4] | Chinese Material Medica Editorial Committee of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine(1999) Chinese Material Medica. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家中医药管理局中华本草编委会(1999) 中华本草. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [5] | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2015) Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2015 edition, Part I). China Medical Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家药典委员会(2015) 中华人民共和国药典(一部). 中国医药科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] |
Dobson AP, Rodriguez JP, Roberts WM, Wilcove DS (1997) Geographic distribution of endangered species in the United States. Science, 275, 550-553.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Editorial Committee of Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae(1959-2004) Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会(1959-2004) 中国植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Fang JY, Wang ZH, Tang ZY (2009) Atlas of Woody Plants in China. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 方精云, 王志恒, 唐志尧 (2009) 中国木本植物分布图集. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Huang LQ, Ma XJ (2017) Endemic Species of Chinese Medicinal Plants. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 黄璐琦, 马小军 (2017) 中国药用植物特有种. 人民卫生出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Huang LQ, Xiao PG, Wang YY (2012) Chinese Rare and Endangered Medicinal Plants Resources Survey. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 黄璐琦, 肖培根, 王永炎 (2012) 中国珍稀濒危药用植物资源调查. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [11] | Jia MR, Li XW (2005) China Ethnic Medicine Resources Records. China Medical Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 贾敏如, 李星炜 (2005) 中国民族药志要. 中国医药科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [12] |
Kong JM, Goh NK, Chia LS, Chia TF (2003) Recent advances in traditional plant drugs and orchids. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 24, 7-21.
URL PMID |
| [13] | Li JH (2002) Development and application prospects of natural drug. Herald of Medicine, 21, 472-475. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李继珩 (2002) 天然药物开发应用前景. 医药导报, 21, 472-475.] | |
| [14] | Qian H (1998) Large-scale biogeographic patterns of vascular plant richness in North America: An analysis at the generic level. Journal of Biogeography, 25, 829-836. |
| [15] | Qin WH, Jiang MK, Xu WG, He ZH (2012) Assessment of in situ conservation of 1,334 native orchids in China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 177-183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 秦卫华, 蒋明康, 徐网谷, 贺昭和 (2012) 中国1,334种兰科植物就地保护状况评价. 生物多样性, 20, 177-183.] | |
| [16] | Sun F (2007) Characteristics of wild medicinal plant resource in Hubei Province. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 18, 3147-3148. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙芳 (2007) 湖北省野生药用植物资源特点. 时珍国医国药, 18, 3147-3148.] | |
| [17] | Wang LS, Jia Y, Zhang XC, Qin HN (2015) Overview of higher plant diversity in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 217-224. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王利松, 贾渝, 张宪春, 覃海宁 (2015) 中国高等植物多样性. 生物多样性, 23, 217-224.] | |
| [18] | Wang ZH, Chen AP, Piao SL, Fang JY (2004) Pattern of species richness along an altitudinal gradient on Gaoligong Mountains, Southwest China. Biodiversity Science, 12, 82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王志恒, 陈安平, 朴世龙, 方精云 (2004) 高黎贡山种子植物物种丰富度沿海拔梯度的变化. 生物多样性, 12, 82-88.] | |
| [19] | Xie ZW, Yu YQ (1996) National Chinese Herbal Medicine List. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 谢宗万, 余友芩 (1996) 全国中草药名鉴. 人民卫生出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Yuan H, Zhang YB, Qin HN, Liu Y, Yu M (2009) The in situ conservation of state key protected wild plants in national nature reserves in China. Biodiversity Science, 17, 280-287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 苑虎, 张殷波, 覃海宁, 刘燕, 喻梅 (2009) 中国国家重点保护野生植物的就地保护现状. 生物多样性, 17, 280-287.] | |
| [21] | Zhang HN, Qin WH, Li ZL, Xu WG, Xia X, Jiang MK (2016) Evaluation of in-situ conservation of higher plants in China. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 32, 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张昊楠, 秦卫华, 李中林, 徐网谷, 夏欣, 蒋明康 (2016) 中国高等植物就地保护状况评价. 生态与农村环境学报, 32, 1-6.] | |
| [22] | Zhang WJ, Chen JK (2003) Advances in study of the distribution area of species. Biodiversity Science, 11, 364-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张文驹, 陈家宽 (2003) 物种分布区研究进展. 生物多样性, 11, 364-369.] | |
| [23] | Zhang Y, Wang QG, Tian Y, Xu J, Que L, Yang G, Chi XL (2018) Conservation effectiveness of national nature reserves on medicinal vascular plants in North China. Biotic Resources, 40, 193-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张毓, 王庆刚, 田瑜, 徐靖, 阙灵, 杨光, 池秀莲 (2018) 华北地区国家级自然保护区对药用维管植物的保护状况. 生物资源, 40, 193-202.] | |
| [24] | Zhang YB, Zhang XL, Yuan H (2014) Assessing the in situ conservation status of key protected wild plants in Shanxi Province. Biodiversity Science, 22, 167-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张殷波, 张晓龙, 苑虎 (2014) 山西省重点保护野生植物就地保护现状. 生物多样性, 22, 167-173.] | |
| [25] | Zhang ZJ, He JS, Li JS, Tang ZY (2015) Distribution and conservation of threatened plants in China. Biological Conservation, 192, 454-460. |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 王艳丽, 张英, 戚春林, 张昌达, 史佑海, 杜彦君, 丁琼. 海南热带雨林国家公园生物多样性热点与保护空缺区域识别: 基于大型真菌与植物视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [3] | 李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦. 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [4] | 王启蕃, 刘小慧, 朱紫薇, 刘磊, 王鑫雪, 汲旭阳, 周绍春, 张子栋, 董红雨, 张明海. 黑龙江北极村国家级自然保护区鸟类与兽类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [5] | 所翟, 俞渃茜, 李媛辉, 徐基良. 基于实证分析中国自然保护区地方立法问题检视和优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [6] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [7] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [8] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [9] | 毛锐锐, 沈拓, 李慧, 田琳楚, 谭海蓉, 卢李荣, 吴小刚, 范宗骥, 伍国仪, 李杰, 吴勇, 朱弼成, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区无尾两栖类动物鸣声特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [10] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [11] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [12] | 陈本平, 陈建武, 凌征文, 杨旭, 陈鑫, 李生强, 杨彪. 四川老君山国家级自然保护区林下鸟兽多样性及动态变化数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22566-. |
| [13] | 姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健. 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22685-. |
| [14] | 赵梦乔, 陈友, 徐正会, 王戌勃, 赵忠良, 徐文川, 何宗辉, 王文华. 云南哀牢山国家级自然保护区东坡垂直带蚂蚁物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23168-. |
| [15] | 胡远芳, 李斌强, 梁丹, 李兴权, 刘兰香, 杨家伟, 罗旭. 人为干扰对白腹锦鸡活动节律的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21484-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn