



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 543-556. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018214 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018214
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全; 物种形成与系统进化
邵昕宁1,2,宋大昭3,黄巧雯3,李晟1,2,姚蒙1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-08-03
接受日期:2019-01-25
出版日期:2019-05-20
发布日期:2019-05-20
通讯作者:
姚蒙
Shao Xinning1,2,Song Dazhao3,Huang Qiaowen3,Li Sheng1,2,Yao Meng1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-08-03
Accepted:2019-01-25
Online:2019-05-20
Published:2019-05-20
Contact:
Yao Meng
摘要:
在陆地生态系统中, 大型食肉动物对于稳定食物网结构和生态系统功能有重要作用。在世界范围内, 由于栖息地丧失和破碎化、猎杀、人类活动干扰以及病原体的传播, 大型食肉动物生存正面临严重威胁, 多种食肉动物地理分布范围及种群数量大幅度缩减。如何有效保护大型食肉动物物种多样性及种群已经成为世界关注的焦点问题和保护生物学的重要研究方向。川西高原地处我国西南山地与青藏高原东缘交界地带, 属于世界生物多样性热点地区, 是世界大型食肉动物物种最丰富的地区之一, 而日益增强的人类活动可能会加剧对当地动植物资源的破坏, 进而威胁野生食肉动物的生存。获得准确的物种多样性信息及食肉动物食性数据有助于深入了解该地区生态系统结构及食物网关系, 对研究物种共存机制及生物多样性保护有重要意义。本研究通过从四川甘孜藏族自治州新龙县和石渠县野外采集的食肉动物粪便样品中提取DNA, 利用DNA条形码进行物种鉴定, 快速获得该地区食肉动物物种构成信息。38份粪便样品经鉴定来自于7种食肉动物, 分别为5种大型食肉动物(狼Canis lupus、棕熊Ursus arctos、豹Panthera pardus、雪豹P. unica、狗Canis lupus familiaris)和2种中小型食肉动物(豹猫Prionailurus bengalensis、赤狐Vulpes vulpes)。进一步利用高通量测序和宏条形码技术对7种食肉动物粪便中的食物DNA进行精准食性分析, 得到包含19种哺乳类、8种鸟类和1种鱼类共计28个不同的食物分子可操作分类单元(molecular operational taxonomic unit, MOTU)。结果显示, 狼、狗、棕熊最主要的食物来源为偶蹄目动物, 其中取食频率最高的物种为家牦牛(Bos grunniens); 而豹猫和赤狐食物中小型哺乳动物如啮齿目和兔形目占重要比例, 其中高原松田鼠(Neodon irene)和高原鼠兔(Ochotona curzoniae)被取食频率最高。豹和雪豹的食物分别为偶蹄目的中华斑羚(Naemorhedus griseus)和岩羊(Pseudois nayaur)。本研究显示了粪便DNA及宏条形码技术在食肉动物多样性快速调查及高通量精确食性分析中的应用前景, 并为此类研究提供了技术路线的有力借鉴。
邵昕宁, 宋大昭, 黄巧雯, 李晟, 姚蒙 (2019) 基于粪便DNA及宏条形码技术的食肉动物快速调查及食性分析. 生物多样性, 27, 543-556.
DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018214.
Shao Xinning, Song Dazhao, Huang Qiaowen, Li Sheng, Yao Meng (2019) Fast surveys and molecular diet analysis of carnivores based on fecal DNA and metabarcoding. Biodiversity Science, 27, 543-556. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018214.
| 物种 Species | 样品数 No. of sample | 物种预判 样品数 No. of morphologically identified sample | 预判正确 样品数 No. of correctly identified sample | 预判正确率 Accuracy of morphological identification (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 狼 Canis lupus | 8 | 4 | 1 | 25.0 | |
| 狗 Canis lupus familiaris | 6 | 6 | 1 | 16.7 | |
| 豹猫 Prionailurus bengalensis | 6 | 4 | 4 | 100 | |
| 赤狐 Vulpes vulpes | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 棕熊 Ursus arctos | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 豹 Panthera pardus | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | |
| 雪豹 Panthera uncia | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | |
| 合计 Total | 28 | 22 | 8 | 36.4 | |
表1 物种分子鉴定结果及形态物种预判正确率
Table 1 Summary of species identification by DNA barcoding and fecal morphology
| 物种 Species | 样品数 No. of sample | 物种预判 样品数 No. of morphologically identified sample | 预判正确 样品数 No. of correctly identified sample | 预判正确率 Accuracy of morphological identification (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 狼 Canis lupus | 8 | 4 | 1 | 25.0 | |
| 狗 Canis lupus familiaris | 6 | 6 | 1 | 16.7 | |
| 豹猫 Prionailurus bengalensis | 6 | 4 | 4 | 100 | |
| 赤狐 Vulpes vulpes | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 棕熊 Ursus arctos | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 豹 Panthera pardus | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | |
| 雪豹 Panthera uncia | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | |
| 合计 Total | 28 | 22 | 8 | 36.4 | |
| 分类等级 Taxonomic level | 种 Species | 属 Genus | 科 Family | 目 Order | 总计Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOTU数目 MOTU no. | 17 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 28 |
| 比例 Percentage (%) | 60.7 | 28.6 | 7.1 | 3.6 |
表2 食物分子可操作分类单元(MOTU)中不同分类级别的数目及比例
Table 2 Number of prey MOTUs assigned to various taxonomic levels
| 分类等级 Taxonomic level | 种 Species | 属 Genus | 科 Family | 目 Order | 总计Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOTU数目 MOTU no. | 17 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 28 |
| 比例 Percentage (%) | 60.7 | 28.6 | 7.1 | 3.6 |
| 食物 MOTU Food MOTU | 在不同食肉动物样品中的出现频次 Occurrence frequency in different carnivore samples | GenBank 最佳匹配物种 Best match species in GenBank | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拉丁学名 Scientific name | MOTU 名称 MOTU name | 狼 Wolf | 狗 Dog | 豹猫 Leopard cat | 棕熊 Brown bear | 赤狐 Red fox | 豹 Leopard | 雪豹 Snow leopard | 中文名 Chinese name | 拉丁名 Scientific name | 最高一致度 Best identity (%) | 序列号 Accession no. | ||||||||||||||
| N = 8 | N = 6 | N = 6 | N = 3 | N = 3 | N = 1 | N = 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 偶蹄目 Artiodactyla | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bos grunniens | 家牦牛 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 家牦牛 | Bos grunniens | 100 | KX232527.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Elaphodus cephalophus | 毛冠鹿 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 毛冠鹿 | Elaphodus cephalophus | 99 | DQ873526.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Sus scrofa | 野猪 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 野猪 | Sus scrofa | 100 | KX886757.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Pseudois nayaur | 岩羊 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 岩羊 | Pseudois nayaur | 100 | KP998469.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Moschus | 麝属 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 马麝/林麝 | Moschus chrysogaster/ Moschus berezovskii | 100 | KP684123.1/ AY184425.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Przewalskium albirostris | 白唇鹿 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 白唇鹿 | Przewalskium albirostris | 100 | JN632690.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Naemorhedus griseus | 中华斑羚 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 中华斑羚 | Naemorhedus griseus | 100 | JN632664.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 奇蹄目 Perissodactyla | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equus caballus | 马 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 马 | Equus caballus | 100 | KU575247.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 兔形目 Lagomorpha | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ochotona curzoniae | 高原鼠兔 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 高原鼠兔 | Ochotona curzoniae | 100 | KM225732.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Lepus oiostolus | 高原兔 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 高原兔 | Lepus oiostolus | 99 | AY745187.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 啮齿目 Rodentia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neodon irene | 高原松田鼠 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 高原松田鼠 | Neodon irene | 100 | HQ416908.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Apodemus | 姬鼠属 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 大耳姬鼠| 高山姬鼠 | Apodemus latronum| Apodemus chevrier | 100| 99 | HQ333256.1| HQ896683.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Marmota himalayana | 喜马拉雅 旱獭 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 喜马拉雅 旱獭 | Marmota himalayana | 100 | JX069958.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Niviventer excelsior | 川西白腹鼠 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 川西白腹鼠 | Niviventer excelsior | 99 | JQ927552.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Trogopterus xanthipes | 复齿鼯鼠 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 复齿鼯鼠 | Trogopterus xanthipes | 97 | AY227546.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Petaurista | 鼯鼠属 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 红背鼯鼠/ 霜背大鼯鼠| 红白鼯鼠 | Petaurista petaurista/ Petaurista philippensis| Petaurista alborufus | 98| 97 | KP973556.1/ KP973555.1| AY227541.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Eozapus setchuanus | 林跳鼠 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 林跳鼠 | Eozapus setchuanus | 98 | KJ648495.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 食物MOTU Food MOTU | 在不同食肉动物样品中的出现频次 Occurrence frequency in different carnivore samples | GenBank最佳匹配物种 Best match species in GenBank | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拉丁学名 Scientific name | MOTU 名称 MOTU name | 狼 Wolf | 狗 Dog | 豹猫 Leopard cat | 棕熊 Brown bear | 赤狐 Red fox | 豹 Leopard | 雪豹 Snow leopard | 中文名 Chinese name | 拉丁名 Scientific name | 最高一致度 Best identity (%) | 序列号 Accession no. | ||||||||||||||
| N = 8 | N = 6 | N = 6 | N = 3 | N = 3 | N = 1 | N = 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 食肉目 Carnivora | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arctonyx albogularis | 猪獾 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 猪獾 | Arctonyx albogularis | 100 | HM106329.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 鼩形目 Soricomorpha | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sorex | 鼩鼱属 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 纹背鼩鼱/ 小纹背鼩鼱| 长爪鼩鼱/ 普通鼩鼱 | Sorex cylindricauda/ Sorex bedfordiae| Sorex unguiculatus/ Sorex araneus | 99| 98 | KF696672.1/ GU981054.1| KX754508.1/ KT210896.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyprinidae | 鲤科 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 汪氏近红鲌/ 厚颌鲂 | Ancherythroculter wangi/ Megalobrama pellegrini | 100 | MG783573.1/ JX242529.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 鸡形目 Galliformes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crossoptilon crossoptilon | 白马鸡 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 白马鸡 | Crossoptilon crossoptilon | 100 | KP259808.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Gallus gallus | 家鸡 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 原鸡 | Gallus gallus | 100 | KX987152.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Perdix | 山鹑属 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 斑翅山鹑/ 高原山鹑/ 灰山鹑 | Perdix dauurica/ Perdix hodgsoniae/ Perdix perdix | 100 | KY411596.1/ KF027440.1/ KF781322.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 雁形目 Anseriformes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anas | 鸭属 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 绿头鸭/ 琵嘴鸭/ 绿翅鸭/ 斑嘴鸭/ 针尾鸭 | Anas platyrhynchos/ Anas clypeata/ Anas crecca/ Anas poecilorhyncha/ Anas acuta | 100 | KX592536.1/ KT345702.1/ KC771255.1/ KC466567.1/ KF312717.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 雀形目 Passeriformes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylloscopus 1 | 柳莺属1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 暗绿柳莺| 淡眉柳莺 | Phylloscopus trochiloides| Phylloscopus humei | 99| 98 | KP267717.1| KP267716.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Phylloscopus 2 | 柳莺属2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 褐柳莺/ 黄腰柳莺/ 乌嘴柳莺 | Phylloscopus fuscatus/ Phylloscopus proregulus/ Phylloscopus maculipennis | 100 | JF505332.1/ AY635103.1 /AY635100.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Muscicapidae 1 | 鸫科 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 鹊鸲/ 北红尾鸲 | Copsychus saularis/ Phoenicurus auroreus | 99 | KU058637.1/ KF997864.1/ KF997863.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Passeriformes | 雀形目 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 家燕/ 红喉歌鸲 | Hirundo rustica/ Luscinia calliope | 96 | KX398931.1/ HQ690246.1 | ||||||||||||||
表3 7种食肉动物食物分子可操作分类单元(MOTU)分子鉴定结果。最佳匹配物种结果中斜线(/)用于分隔序列一致度相同的物种, 竖线(|)用于分隔一致度相差 ≥ 1%的物种。
Table 3 Summary of prey MOTUs of seven carnivores identified by molecular dietary analysis. Species with the identical sequence identity are separated by “/”, and species with ≥ 1% difference in sequence identity are separated by “|”.
| 食物 MOTU Food MOTU | 在不同食肉动物样品中的出现频次 Occurrence frequency in different carnivore samples | GenBank 最佳匹配物种 Best match species in GenBank | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拉丁学名 Scientific name | MOTU 名称 MOTU name | 狼 Wolf | 狗 Dog | 豹猫 Leopard cat | 棕熊 Brown bear | 赤狐 Red fox | 豹 Leopard | 雪豹 Snow leopard | 中文名 Chinese name | 拉丁名 Scientific name | 最高一致度 Best identity (%) | 序列号 Accession no. | ||||||||||||||
| N = 8 | N = 6 | N = 6 | N = 3 | N = 3 | N = 1 | N = 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 偶蹄目 Artiodactyla | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bos grunniens | 家牦牛 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 家牦牛 | Bos grunniens | 100 | KX232527.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Elaphodus cephalophus | 毛冠鹿 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 毛冠鹿 | Elaphodus cephalophus | 99 | DQ873526.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Sus scrofa | 野猪 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 野猪 | Sus scrofa | 100 | KX886757.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Pseudois nayaur | 岩羊 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 岩羊 | Pseudois nayaur | 100 | KP998469.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Moschus | 麝属 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 马麝/林麝 | Moschus chrysogaster/ Moschus berezovskii | 100 | KP684123.1/ AY184425.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Przewalskium albirostris | 白唇鹿 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 白唇鹿 | Przewalskium albirostris | 100 | JN632690.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Naemorhedus griseus | 中华斑羚 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 中华斑羚 | Naemorhedus griseus | 100 | JN632664.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 奇蹄目 Perissodactyla | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equus caballus | 马 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 马 | Equus caballus | 100 | KU575247.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 兔形目 Lagomorpha | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ochotona curzoniae | 高原鼠兔 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 高原鼠兔 | Ochotona curzoniae | 100 | KM225732.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Lepus oiostolus | 高原兔 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 高原兔 | Lepus oiostolus | 99 | AY745187.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 啮齿目 Rodentia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Neodon irene | 高原松田鼠 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 高原松田鼠 | Neodon irene | 100 | HQ416908.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Apodemus | 姬鼠属 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 大耳姬鼠| 高山姬鼠 | Apodemus latronum| Apodemus chevrier | 100| 99 | HQ333256.1| HQ896683.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Marmota himalayana | 喜马拉雅 旱獭 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 喜马拉雅 旱獭 | Marmota himalayana | 100 | JX069958.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Niviventer excelsior | 川西白腹鼠 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 川西白腹鼠 | Niviventer excelsior | 99 | JQ927552.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Trogopterus xanthipes | 复齿鼯鼠 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 复齿鼯鼠 | Trogopterus xanthipes | 97 | AY227546.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Petaurista | 鼯鼠属 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 红背鼯鼠/ 霜背大鼯鼠| 红白鼯鼠 | Petaurista petaurista/ Petaurista philippensis| Petaurista alborufus | 98| 97 | KP973556.1/ KP973555.1| AY227541.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Eozapus setchuanus | 林跳鼠 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 林跳鼠 | Eozapus setchuanus | 98 | KJ648495.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 食物MOTU Food MOTU | 在不同食肉动物样品中的出现频次 Occurrence frequency in different carnivore samples | GenBank最佳匹配物种 Best match species in GenBank | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拉丁学名 Scientific name | MOTU 名称 MOTU name | 狼 Wolf | 狗 Dog | 豹猫 Leopard cat | 棕熊 Brown bear | 赤狐 Red fox | 豹 Leopard | 雪豹 Snow leopard | 中文名 Chinese name | 拉丁名 Scientific name | 最高一致度 Best identity (%) | 序列号 Accession no. | ||||||||||||||
| N = 8 | N = 6 | N = 6 | N = 3 | N = 3 | N = 1 | N = 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 食肉目 Carnivora | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arctonyx albogularis | 猪獾 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 猪獾 | Arctonyx albogularis | 100 | HM106329.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 鼩形目 Soricomorpha | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sorex | 鼩鼱属 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 纹背鼩鼱/ 小纹背鼩鼱| 长爪鼩鼱/ 普通鼩鼱 | Sorex cylindricauda/ Sorex bedfordiae| Sorex unguiculatus/ Sorex araneus | 99| 98 | KF696672.1/ GU981054.1| KX754508.1/ KT210896.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyprinidae | 鲤科 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 汪氏近红鲌/ 厚颌鲂 | Ancherythroculter wangi/ Megalobrama pellegrini | 100 | MG783573.1/ JX242529.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 鸡形目 Galliformes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crossoptilon crossoptilon | 白马鸡 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 白马鸡 | Crossoptilon crossoptilon | 100 | KP259808.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Gallus gallus | 家鸡 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 原鸡 | Gallus gallus | 100 | KX987152.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Perdix | 山鹑属 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 斑翅山鹑/ 高原山鹑/ 灰山鹑 | Perdix dauurica/ Perdix hodgsoniae/ Perdix perdix | 100 | KY411596.1/ KF027440.1/ KF781322.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 雁形目 Anseriformes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anas | 鸭属 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 绿头鸭/ 琵嘴鸭/ 绿翅鸭/ 斑嘴鸭/ 针尾鸭 | Anas platyrhynchos/ Anas clypeata/ Anas crecca/ Anas poecilorhyncha/ Anas acuta | 100 | KX592536.1/ KT345702.1/ KC771255.1/ KC466567.1/ KF312717.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 雀形目 Passeriformes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylloscopus 1 | 柳莺属1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 暗绿柳莺| 淡眉柳莺 | Phylloscopus trochiloides| Phylloscopus humei | 99| 98 | KP267717.1| KP267716.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Phylloscopus 2 | 柳莺属2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 褐柳莺/ 黄腰柳莺/ 乌嘴柳莺 | Phylloscopus fuscatus/ Phylloscopus proregulus/ Phylloscopus maculipennis | 100 | JF505332.1/ AY635103.1 /AY635100.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Muscicapidae 1 | 鸫科 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 鹊鸲/ 北红尾鸲 | Copsychus saularis/ Phoenicurus auroreus | 99 | KU058637.1/ KF997864.1/ KF997863.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Passeriformes | 雀形目 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 家燕/ 红喉歌鸲 | Hirundo rustica/ Luscinia calliope | 96 | KX398931.1/ HQ690246.1 | ||||||||||||||
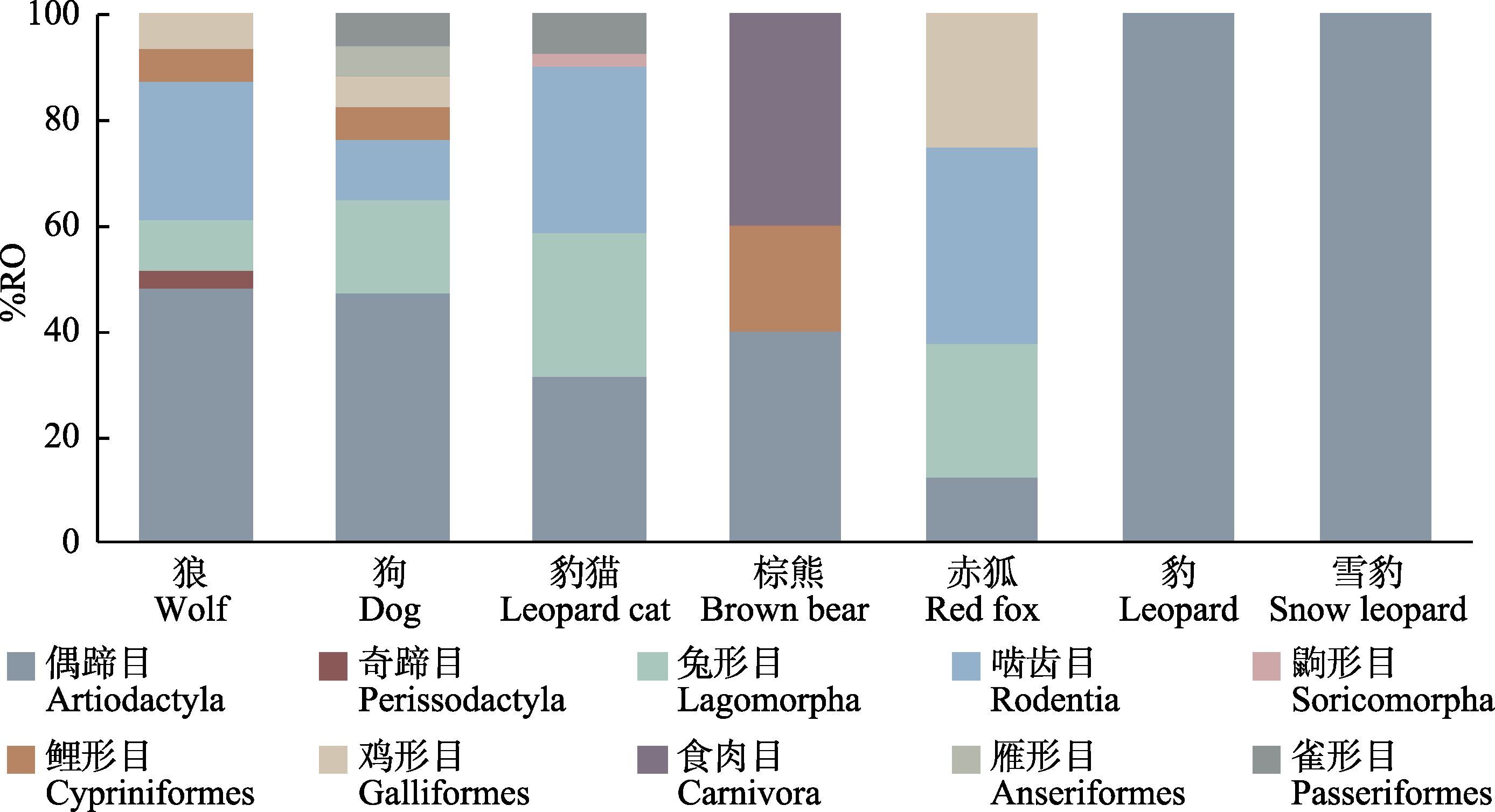
图2 目水平上不同食肉动物食物组成。%RO为不同食物分子可操作分类单元(MOTU)出现的相对频率。
Fig. 2 Dietary compositions by prey order identified in the diets of different carnivores. %RO indicates the relative frequency of occurrence of different food MOTUs.
| [1] | Austin SC, Tewes ME, Grassman LI, Silvy NJ ( 2007) Ecology and conservation of the leopard cat Prionailurus bengalensis and clouded leopard Neofelis nebulosa in Khao Yai National Park, Thailand. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 53, 1-14. |
| [2] |
Baker PJ, Boitani L, Harris S, Saunders G, White PCL ( 2008) Terrestrial carnivores and human food production: Impact and management. Mammal Review, 38, 123-166.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Bellemain E, Swenson JE, Tallmon D, Brunberg S, Taberlet P ( 2010) Estimating population size of elusive animals with DNA from hunter-collected feces: Four methods for brown bears. Conservation Biology, 19, 150-161. |
| [4] |
Cardinale BJ, Duffy JE, Gonzalez A, Hooper DU, Perrings C, Venail P, Narwani A, Mace GM, Tilman D, Wardle DA, Kinzig AP, Daily GC, Loreau M, Grace JB, Larigauderie A, Srivastava DS, Naeem S ( 2012) Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature, 486, 59-67.
DOI |
| [5] | Chen SL, Pang XH, Luo K, Yao H, Han JP, Song JY ( 2013) DNA barcoding of biological resources. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 25, 458-466. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈士林, 庞晓慧, 罗焜, 姚辉, 韩建萍, 宋经元 ( 2013) 生物资源的DNA条形码技术. 生命科学, 25, 458-466.] | |
| [6] | Cheng XT, Wang AM, Gu ZF, Wang Y, Zhan X, Shi YH ( 2011) Current progress of DNA barcoding. Genomics and Applied Biology, 30, 748-758. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程希婷, 王爱民, 顾志峰, 王嫣, 战欣, 石耀华 ( 2011) DNA条形码研究进展. 基因组学与应用生物学, 30, 748-758.] | |
| [7] |
Coissac E ( 2012) OligoTag: A program for designing sets of tags for next-generation sequencing of multiplexed samples. Methods in Molecular Biology, 888, 13-31.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Cole DN, Landres PB ( 1996) Threats to ecosystems: Impacts and research needs. Ecological Applications, 6, 168-184.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Creer S, Fonseca VG, Porazinska DL, Giblin-Davis RM, Sung W, Power DM, Packer M, Carvalho GR, Blaxter ML, Lambshead PJ, Thomas WK ( 2010) Ultrasequencing of the meiofaunal biosphere: Practice, pitfalls and promises. Molecular Ecology, 19, 4-20.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Gómez-Ortiz Y, Monroy-Vilchis O, Mendoza-Martínez GD ( 2015) Feeding interactions in an assemblage of terrestrial carnivores in central Mexico. Zoological Studies, 54, 16.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Glen AS, Fay AR, Dickman CR ( 2006) Diets of sympatric red foxes Vulpes vulpes and wild dogs Canis lupus in the Northern Rivers Region, New South Wales. Australian Mammalogy, 28, 101-104.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Glen AS, Dickman CR ( 2008) Niche overlap between marsupial and eutherian carnivores: Does competition threaten the endangered spotted-tailed quoll? Journal of Applied Ecology, 45, 700-707.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, Dewaard JR ( 2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 270, 313-321.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ, Byrnes JE, Hungate BA, Matulich KL, Gonzalez A, Duffy JE, Gamfeldt L, O’Connor MI ( 2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature, 486, 105-108.
DOI |
| [15] |
Hooper DU, Chapin FS Ⅲ, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S ( 2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Kasper CB, Peters FB, Christoff AU, de Freitas TRO ( 2016) Trophic relationships of sympatric small carnivores in fragmented landscapes of southern Brazil: Niche overlap and potential for competition. Mammalia, 80, 143-152. |
| [17] |
Kelly RP, Port JA, Yamahara KM, Crowder LB ( 2014) Using environmental DNA to census marine fishes in a large mesocosm. PLoS ONE, 9, e86175.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Kircher M, Kelso J ( 2010) High-throughput DNA sequencing concepts and limitations. Bioessays, 32, 524-536.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Kress WJ, Garcia-Robledo C, Uriarte M, Erickson DL ( 2015) DNA barcodes for ecology, evolution, and conservation. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 30, 25-35.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Lee O, Lee S, Nam DH, Lee HY ( 2014) Food habits of the leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis euptilurus) in Korea. Mammal Study, 39, 43-46.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Liu B, Jiang ZG ( 2003) Diet composition of wolves Canis lupus in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Acta Theriologica, 48, 255-263.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Lonsinger RC, Gese EM, Waits LP ( 2015) Evaluating the reliability of field identification and morphometric classifications for carnivore scats confirmed with genetic analysis. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 39, 593-602.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Ma L ( 2013) Research progress in DNA minibarcoding and metabarcoding. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 3(6), 58-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马兰 ( 2013) DNA微型条形码和复合条形码研究进展. 农业灾害研究, 3(6), 58-60.] | |
| [24] |
Marfuard P ( 1998) Food habits of Arctic wolves in Greenland. Journal of Mammalogy, 79, 236-244.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Mitchell BD, Banks PB ( 2005) Do wild dogs exclude foxes? Evidence for competition from dietary and spatial overlaps. Austral Ecology, 30, 581-591.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Monterroso P, Castro D, Silva TL, Ferreras P, Godinho R, Alves PC ( 2013) Factors affecting the (in)accuracy of mammalian mesocarnivore scat identification in South- western Europe. Journal of Zoology, 289, 243-250.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Montoya JM, Rodríguez MA, Hawkins BA ( 2003) Food web complexity and higher-level ecosystem services. Ecology Letters, 6, 587-593.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Murray DC, Haile J, Dortch J, White NE, Haouchar D, Bellgard MI, Allcock RJ, Prideaux GJ, Bunce M ( 2013) Scrapheap challenge: A novel bulk-bone metabarcoding method to investigate ancient DNA in faunal assemblages. Scientific Reports, 3, 3371.
DOI |
| [29] |
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GAB, Kent J ( 2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403, 853-858.
DOI |
| [30] |
Pelton MR, Gittleman JL, Funk SM, Macdonald DW, Wayne RK ( 2003) Carnivore conservation. Journal of Wildlife Management, 67, 229-230.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Pompanon F, Deagle BE, Symondson WO, Brown DS, Jarman SN, Taberlet P ( 2012) Who is eating what: Diet assessment using next generation sequencing. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1931-1950.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Porazinska DL, Giblin-Davis RM, Esquivel A, Powers TO, Sung W, Thomas WK ( 2010) Ecometagenetics confirm high tropical rainforest nematode diversity. Molecular Ecology, 19, 5521-5530.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Rajaratnam R, Sunquist M, Rajaratnam L, Ambu L ( 2007) Diet and habitat selection of the leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis borneoensis) in an agricultural landscape in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 23, 209-217.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Riaz T, Shehzad W, Viari A, Pompanon F, Taberlet P, Coissac E ( 2011) ecoPrimers: Inference of new DNA barcode markers from whole genome sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 39, e145.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Ripple WJ, Estes JA, Beschta RL, Wilmers CC, Ritchie EG, Hebblewhite M, Berger J, Elmhagen B, Letnic M, Nelson MP, Schmitz OJ, Smith DW, Wallach AD, Wirsing AJ ( 2014) Status and ecological effects of the world’s largest carnivores. Science, 343, 1241484.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Seidensticker J ( 1976) On the ecological separation between tigers and leopards. Biotropica, 8, 225-234.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Shehzad W, Riaz T, Nawaz MA, Miquel C, Poillot C, Shah SA, Pompanon F, Coissac E, Taberlet P ( 2012 a) Carnivore diet analysis based on next-generation sequencing: Application to the leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) in Pakistan. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1951-1965.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Shehzad W, Mccarthy TM, Pompanon F, Purevjav L, Coissac E, Riaz T, Taberlet P ( 2012 b) Prey preference of snow leopard (Panthera uncia) in South Gobi, Mongolia. PLoS ONE, 7, e32104. |
| [39] |
Shehzad W, Nawaz MA, Pompanon F, Coissac E, Riaz T, Shan SA, Taberlet P ( 2015) Forest without prey: Livestock sustain a leopard Panthera pardus population in Pakistan. Oryx, 49, 248-253.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Shi ZY, Yang CQ, Hao MD, Wang XY, Ward RD, Zhang AB ( 2017) FuzzyID2: A software package for large dataset species identification via barcoding and metabarcoding using Hidden Markov Models and fuzzy set methods. Molecular Ecology Resource, 18, 666-675. |
| [41] | Smith AT, Xie Y ( 2009) A Guide to the Mammals of China. Hunan Education Publishing House, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [ Smith AT, 解焱( 2009) 中国兽类野外手册.湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [42] |
Symondson WO ( 2002) Molecular identification of prey in predator diets. Molecular Ecology, 11, 627-641.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Taberlet P, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Brochmann C, Willerslev E ( 2012) Towards next-generation biodiversity assessment using DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology, 21, 2045-2050.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Valentini A, Pompanon F, Taberlet P ( 2009) DNA barcoding for ecologists. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 24, 110-117.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Vallet D, Petit EJ, Gatti S, Levréro F, Ménard N ( 2007) A new 2CTAB/PCI method improves DNA amplification success from faeces of Mediterranean (Barbary macaques) and tropical (lowland gorillas) primates. Conservation Genetics, 9, 677-680. |
| [46] |
Vestheim H, Jarman SN ( 2008) Blocking primers to enhance PCR amplification of rare sequences in mixed samples—A case study on prey DNA in Antarctic krill stomachs. Frontiers in Zoology, 5, 12.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Voolstra CR, Hajibabaei M, Shokralla S, Zhou X, Singer GAC, Baird DJ ( 2011) Environmental barcoding: A next- generation sequencing approach for biomonitoring applications using river benthos. PLoS ONE, 6, e17497.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Wang J, Laguardia A, Damerell PJ, Riordan P, Shi K ( 2014) Dietary overlap of snow leopard and other carnivores in the Pamirs of Northwestern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 3162-3168. |
| [49] |
Wang SW, Macdonald DW ( 2009) Feeding habits and niche partitioning in a predator guild composed of tigers, leopards and dholes in a temperate ecosystem in central Bhutan. Journal of Zoology, 277, 275-283.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Wang XQ, Wang GH, Qiao F, Gao QK, Heong KL, Zhu ZR, Cheng JA ( 2015) Progress on high-throughput sequencing and its applications in food web analysis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 2530-2539. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王雪芹, 王光华, 乔飞, 高其康, Heong KL, 祝增荣, 程家安 ( 2015) 高通量测序及其在食物网解析中的应用进展. 生态学报, 37, 2530-2539.] | |
| [51] |
Xiong MY, Wang DJ, Bu HL, Shao XN, Zhang D, Li S, Wang RJ, Yao M ( 2017) Molecular dietary analysis of two sympatric felids in the Mountains of Southwest China biodiversity hotspot and conservation implications. Scientific Reports, 7, 41909.
DOI |
| [52] |
Xiong MY, Shao XN, Long Y, Bu HL, Zhang D, Wang DJ, Li S, Wang RJ, Yao M ( 2016) Molecular analysis of vertebrates and plants in scats of leopard cats (Prionailurus bengalensis) in southwest China. Journal of Mammalogy, 97, 1054-1064.
DOI URL |
| [53] | Yan WB, Zhang HH, Yang HJ, Dou HS, Shen XQ ( 2016) Seasonal diet of wolves in the Dalaihu Nature Reserve, Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 41, 46-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 颜文博, 张洪海, 杨红军, 窦华山, 沈秀清 ( 2006) 内蒙古达赉湖自然保护区狼食性的季节性变化. 动物学杂志, 41, 46-51.] | |
| [54] | Yin HB, Yu GJ, Wang GL, Zhou YB, Wu MM ( 2008) Study methods of diets of carnivorous animals. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Sciences Edition), 32(1), 90-94. (in Chinese) |
| [ 尹华宝, 余冠军, 王贵林, 周友兵, 武梅梅 ( 2008) 食肉目动物食性研究方法. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 32(1), 90-94.] | |
| [55] |
Yoccoz NG, Bråthen KA, Gielly L, Haile J, Edwards ME, Goslar T, Von SH, Brysting AK, Coissac E, Pompanon F ( 2012) DNA from soil mirrors plant taxonomic and growth form diversity. Molecular Ecology, 21, 3647-3655.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Zhang AB, Hao MD, Yang CQ, Shi ZY ( 2017) BarcodingR: An integrated R package for species identification using DNA barcodes. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 627-634.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Zhang HH, Wang ZL, Ma WX, Sun YY ( 2000) Food habits of wolf (Canis lupus) in Xing’anling Mountains. Journal of Qufu Normal University, 26(1), 80-82. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张洪海, 王振龙, 马文祥, 孙玉英 ( 2000) 大、小兴安岭地区狼的食性. 曲阜师范大学学报, 26(1), 80-82.] | |
| [58] | Zhang S, Bao QQ, Tang PZ, Zhang SL, Yang YX, Li GL, Bao WD ( 2013) Description on foot tracts and fecal morphology of several carnivore species. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 32, 857-861. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张帅, 鲍清泉, 汤鹏展, 张书理, 杨永昕, 李桂林, 鲍伟东 ( 2013) 几种食肉目动物的足迹与粪便形态描述. 四川动物, 32, 857-861.] | |
| [59] | Zhou YW, Yang YH ( 2009) Review of non-DNA methods for identification of animal species. Journal of Tonghua Teachers College, 30(10), 58-61. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周用武, 杨玉华 ( 2009) 动物物种鉴定的非DNA方法评述. 通化师范学院学报, 30(10), 58-61.] | |
| [60] |
Zhou X, Li YY, Liu SL, Yang Q, Su X, Zhou LL, Tang M, Fu RB, Li JG, Huang QF ( 2013) Ultra-deep sequencing enables high-fidelity recovery of biodiversity for bulk arthropod samples without PCR amplification. GigaScience, 2, 4.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈丁松, 刘子恺, 贺子洋, 陈伟东. 缓步动物多样性、分布特征和生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24406-. |
| [2] | 赵榕江, 吴纪华, 何维明, 赵彩云, 周波, 李博, 杨强. 土壤生物多样性与外来植物入侵: 进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24243-. |
| [3] | 牛永杰, 马全会, 朱玉, 刘海荣, 吕佳乐, 邹元春, 姜明. 氮沉降对草地昆虫多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23130-. |
| [4] | 罗小燕, 李强, 黄晓磊. 戴云山国家级自然保护区访花昆虫DNA条形码数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23236-. |
| [5] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [6] | 吴帆, 刘深云, 江虎强, 王茜, 陈开威, 李红亮. 中华蜜蜂和意大利蜜蜂秋冬期传粉植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22528-. |
| [7] | 刘童祎, 姜立云, 乔格侠. 中国半翅目等29目昆虫新分类单元2021年年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22300-. |
| [8] | 郭淳鹏, 钟茂君, 汪晓意, 杨胜男, 唐科, 贾乐乐, 张春兰, 胡军华. 福建省两栖、爬行动物更新名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22090-. |
| [9] | 姚海凤, 张赛超, 上官华媛, 李志鹏, 孙新. 城市化对土壤动物群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22547-. |
| [10] | 姚保民, 曾青, 张丽梅. 土壤原生生物多样性及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22353-. |
| [11] | 胡惠玲, 姚致远, 高世斌, 朱波. 紫色土线虫对长期不同施肥措施的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22189-. |
| [12] | 李晟, 王大军, 陈祥辉, 卜红亮, 刘小庚, 靳彤. 四川老河沟保护地2011-2015年野生动物红外相机监测数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1170-1174. |
| [13] | 俞正森, 宋娜, 本村浩之, 高天翔. 中国银口天竺鲷属鱼类的分类厘定[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 971-979. |
| [14] | 田佳, 朱淑怡, 张晓峰, 何礼文, 古晓东, 官天培, 李晟. 大熊猫国家公园的地栖大中型鸟兽多样性现状: 基于红外相机数据的分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1490-1504. |
| [15] | 胡芮, 王儒晓, 杜诗雨, 李萌, 邢雨辉, 潘达, 徐海根, 孙红英. 扬州宝应湖底栖大型无脊椎动物的生物多样性及其变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1558-1569. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn