



生物多样性 ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (6): 737-745. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.140073 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.140073
所属专题: 野生动物的红外相机监测
贾晓东1,2, 刘雪华2( ), 武鹏峰3, 杨兴中1, 蔡琼5, 何祥博6, 朱云5
), 武鹏峰3, 杨兴中1, 蔡琼5, 何祥博6, 朱云5
收稿日期:2013-04-08
接受日期:2014-11-28
出版日期:2014-11-20
发布日期:2014-12-11
基金资助:
Xiaodong Jia1,2, Xuehua Liu2,*( ), Xingzhong Yang1, Pengfeng Wu3, Melissa Songer4, Qiong Cai5, Xiangbo He6, Yun Zhu5
), Xingzhong Yang1, Pengfeng Wu3, Melissa Songer4, Qiong Cai5, Xiangbo He6, Yun Zhu5
Received:2013-04-08
Accepted:2014-11-28
Online:2014-11-20
Published:2014-12-11
Contact:
Liu Xuehua
摘要:
2009年8月至2013年4月期间, 在陕西观音山自然保护区, 利用18台红外相机收集到羚牛(Budorcas taxicolor)、川西斑羚(Naemorhedus griseus)、中华鬣羚(Capricornis milneedwardsii)、毛冠鹿(Elaphodus cephalophus)、小麂(Muntiacus reevesi)、林麝(Moschus berezovskii) 6种有蹄类动物的照片数据, 通过相对丰富度指数分析了它们的活动规律及季节性差异。结果表明: (1)6种有蹄类动物在研究区域总丰富度达到了58.71%, 其中羚牛的相对丰富度是28.02%, 川西斑羚13.24%, 毛冠鹿10.08%, 中华鬣羚4.21%, 小麂2.26%, 林麝0.90%。(2)6种有蹄类动物的月相对丰富度反映了其年活动格局, 其中羚牛、川西斑羚、毛冠鹿、中华鬣羚、小麂表现出一致性, 即夏季活动最为频繁, 秋季减弱, 冬季达到活动低谷, 春季逐渐回升; 而林麝则在冬季活动最为频繁, 夏季最弱。(3)日时间段相对丰富度反映了动物全年的日活动规律, 其中川西斑羚和羚牛相似, 主要以白天活动为主; 毛冠鹿、小麂、林麝具有明显的晨昏活动习性; 中华鬣羚活动高峰出现在02:00-06:00和20:00-22:00, 以夜间活动为主。(4)分析不同季节6种有蹄类动物日活动规律, 羚牛在春季出现一定的差异, 活动高峰出现在16:00-20:00; 川西斑羚、毛冠鹿、中华鬣羚在冬季表现出一定的差异, 活动高峰相对延迟或者提前; 小麂春季表现出差异, 活动主要集中在00:00-10:00和18:00-20:00; 林麝由于数据相对较少, 在4个季节表现出不同的活动规律。(5)夜行性分析得到中华鬣羚具有较强的夜间活动能力, 夜间相对丰富度达到了65.81%。这些研究结果有助于监测有蹄类动物种群的变化, 为保护区有效保护管理提供了数据支持。
贾晓东, 刘雪华, 武鹏峰, 杨兴中, 蔡琼, 何祥博, 朱云 (2014) 利用红外相机技术分析秦岭有蹄类动物活动节律的季节性差异. 生物多样性, 22, 737-745. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.140073.
Xiaodong Jia, Xuehua Liu, Xingzhong Yang, Pengfeng Wu, Melissa Songer, Qiong Cai, Xiangbo He, Yun Zhu (2014) Seasonal activity patterns of ungulates in Qinling Mountains based on camera-trap data. Biodiversity Science, 22, 737-745. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.140073.
| 物种 Species | 有效照片数 Independents captures | 样本量 Sample size | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | ||
| 总和 Sum | 396 | 870 | 544 | 350 | 2,160 |
| 羚牛 Budorcas taxicolor | 181 | 333 | 300 | 217 | 1,031 |
| 川西斑羚 Naemorhedus griseus | 91 | 257 | 77 | 62 | 487 |
| 毛冠鹿 Elaphodus cephalophus | 62 | 176 | 115 | 18 | 371 |
| 中华鬣羚 Capricornis milneedwardsii | 27 | 53 | 43 | 32 | 155 |
| 小麂 Muntiacus reevesi | 26 | 45 | 4 | 8 | 83 |
| 林麝 Moschus berezovskii | 9 | 6 | 5 | 13 | 33 |
表1 6种有蹄类动物春夏秋冬4个季节的照片数
Table 1 The number of photos of six ungulates in four seasons at Guanyinshan
| 物种 Species | 有效照片数 Independents captures | 样本量 Sample size | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | ||
| 总和 Sum | 396 | 870 | 544 | 350 | 2,160 |
| 羚牛 Budorcas taxicolor | 181 | 333 | 300 | 217 | 1,031 |
| 川西斑羚 Naemorhedus griseus | 91 | 257 | 77 | 62 | 487 |
| 毛冠鹿 Elaphodus cephalophus | 62 | 176 | 115 | 18 | 371 |
| 中华鬣羚 Capricornis milneedwardsii | 27 | 53 | 43 | 32 | 155 |
| 小麂 Muntiacus reevesi | 26 | 45 | 4 | 8 | 83 |
| 林麝 Moschus berezovskii | 9 | 6 | 5 | 13 | 33 |
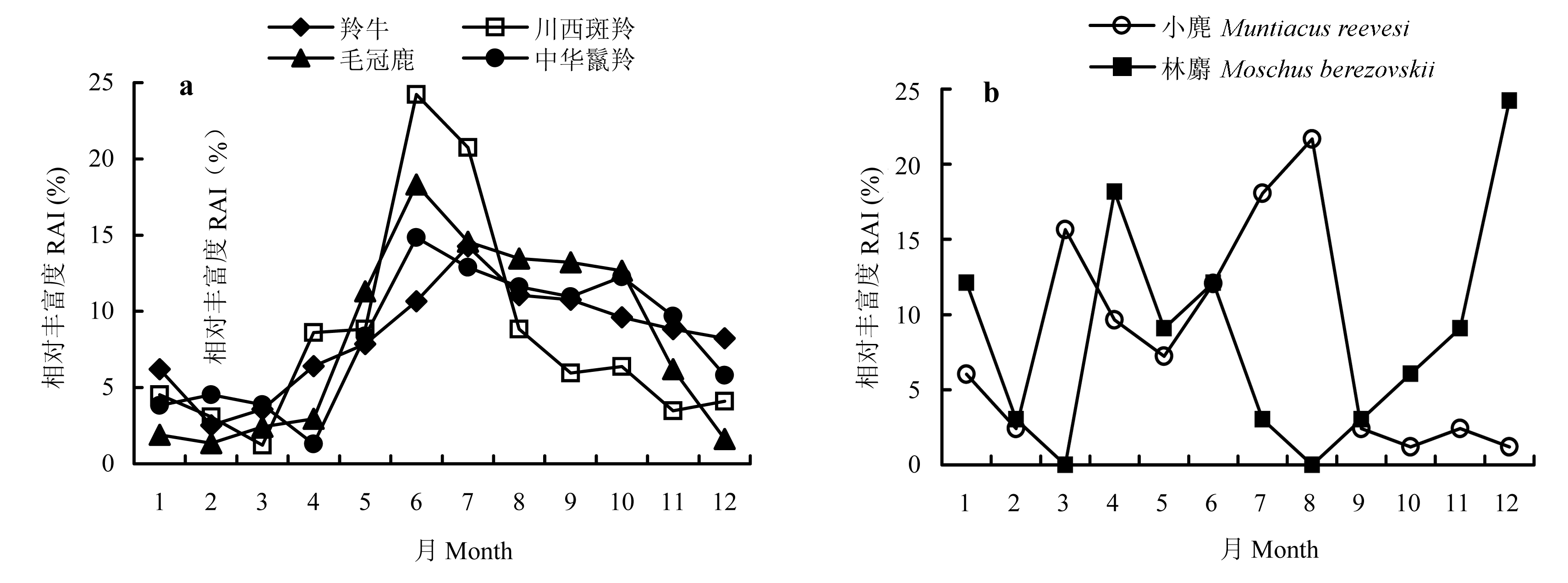
图2 观音山6种有蹄类动物的年活动格局
Fig. 2 Annual activity patterns of six ungulates at Guanyinshan. (a)Budorcas taxicolor; Naemorhedus griseus; Elaphodus cephalophus; Capricornis milneedwardsii; (b) Muntiacus reevesi and Moschus berezovskii.
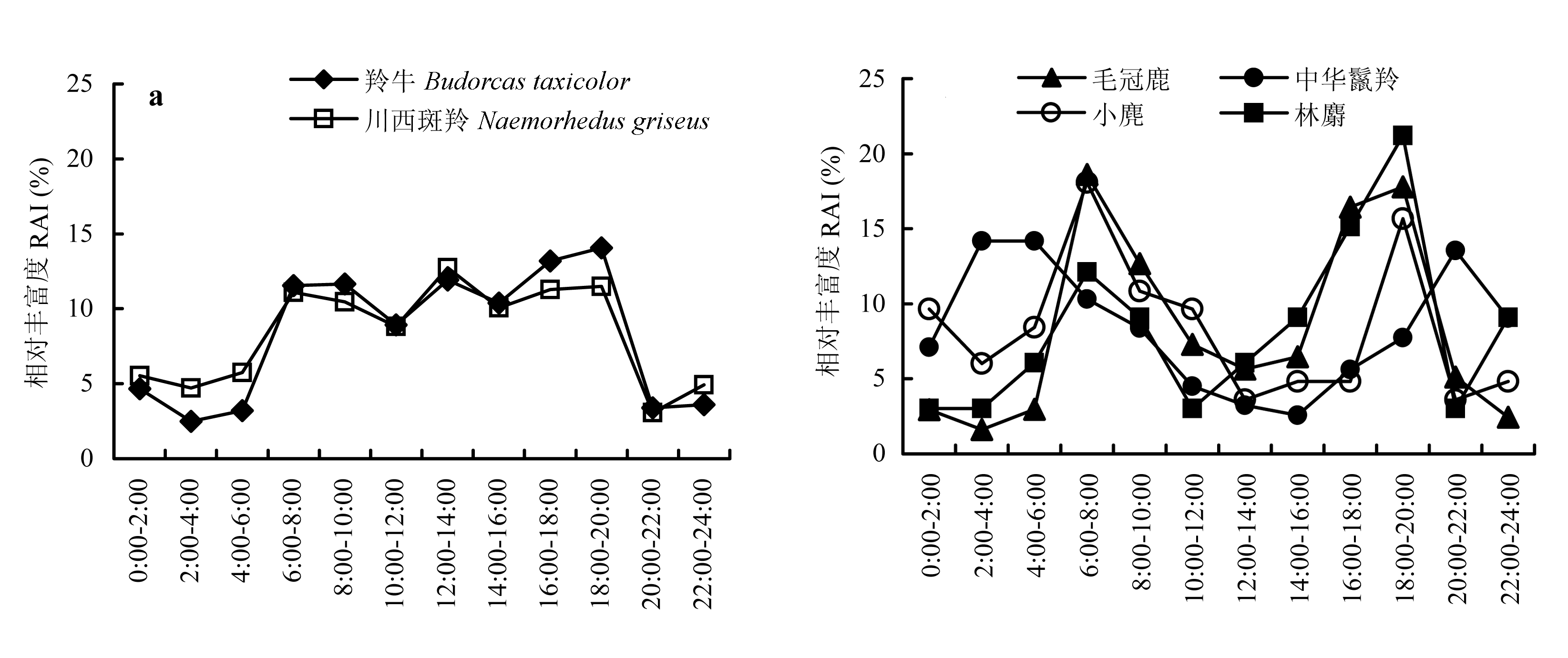
图3 观音山6种有蹄类动物的日活动规律
Fig. 3 The daily activity patterns of six ungulates at Guanyinshan. (a) Budorcas taxicolor and Naemorhedus griseus; (b) Elaphodus cephalophus; Capricornis milneedwardsii; Muntiacus reevesi; Moschus berezovskii.
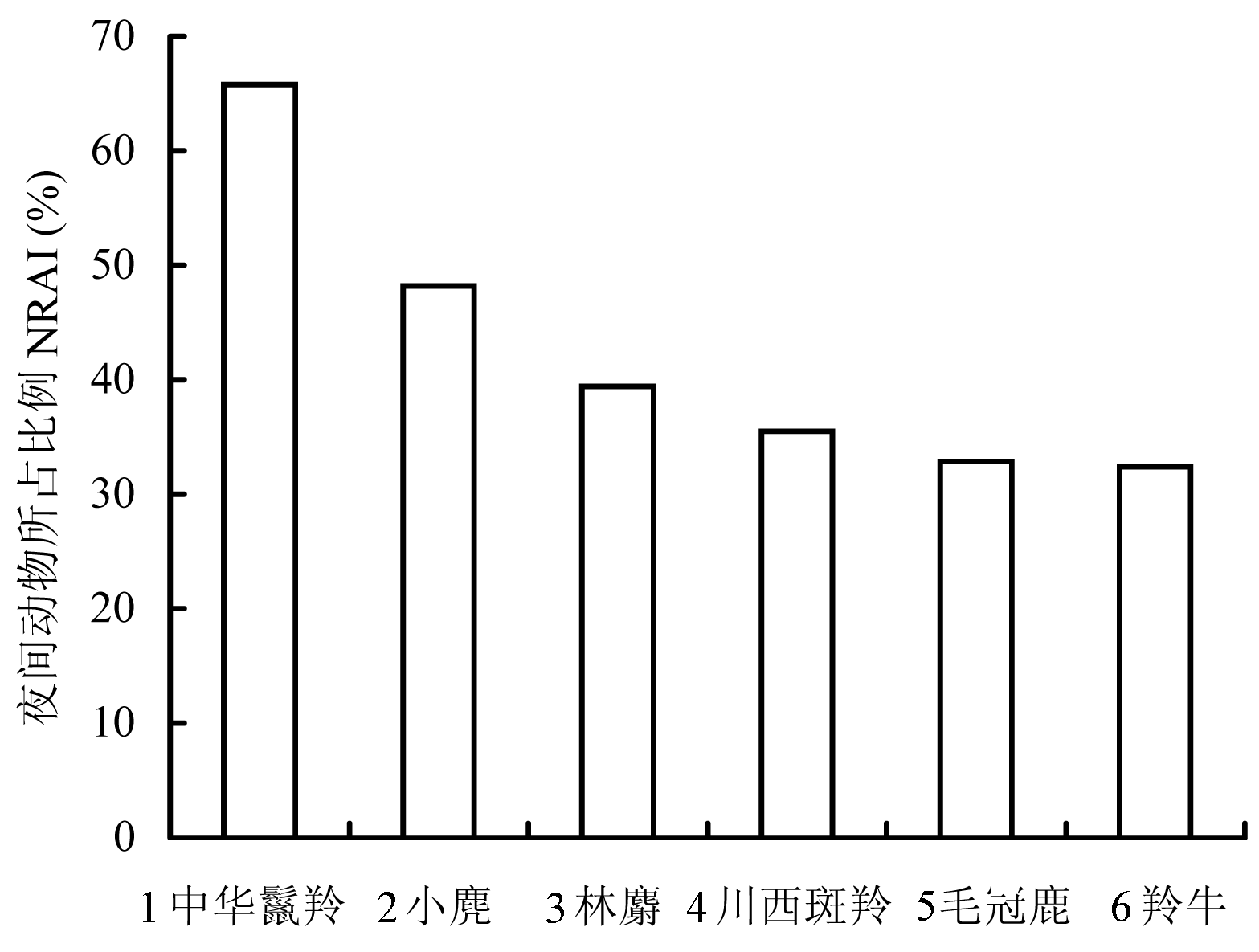
图5 观音山6种有蹄类动物的夜间相对丰富度
Fig. 5 The norcturnal RAI of six ungulates at Guanyinshan. 1. Capricornis milneedwardsii; 2. Muntiacus reevesi; 3. Moschus berezovski; 4.Naemorhedus griseus; 5.Elaphodus cephalophus; 6. Budorcas taxicolor.
| [1] | Champion FW (1927) With a Camera in Tiger Land. Chatto &Windus, London. |
| [2] | Chen W (陈伟), Hu JC (胡锦矗) (2012) Seasonal differences in microhabitat use by tufted deer (Elaphodus cephalophus) in Tangjiahe Nature Reserve.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 32, 188-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Chen W, Hu JC, Lu X (2009) Microhabitat use and separation between the serow (Capricornis sumatraensis) and the Chinese goral (Naemorhedus griseus) in winter.Mammalia, 73, 249-252. |
| [4] | Chen W, Wu QG, Hu JC, Lu X, You ZQ (2012) Seasonal habitat use of Chinese goral (Naemorhedus griseus) in a subtropical forest.Russian Journal of Ecology, 43, 256-260. |
| [5] | Gysel LW, Davis EM (1956) A simple automatic photographic unit for wildlife research.Journal of Wildlife Management, 20, 451-453. |
| [6] | Han LX (韩联宪), Liu SL (刘尚莲), Liang HM (梁惠媚), Yang XX (杨秀熙), Yang GS (杨光姒) (1999) A preliminary observation on behavior and activity circadian rhythms of Muntiacus reevesi in captivity.Journal of Southwest Forestry College(西南林学院学报), 19, 192-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Hu TH (胡天华), Li YG (李元刚) (2013) Application of infrared triggered cameras to monitoring of wild animal in Helan Mountain Nature Reserve.Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forest Science and Technology(宁夏农林科技), 54, 57-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Karanth KU (1995) Estimating tiger Panthera tigris populations from camera-trap data using capture-recapture models.Biological Conservation, 71, 333-338. |
| [9] | Kong F (孔飞), Zhu Y (朱云), Chang BH (常保华), Cai Q (蔡琼), Zhang HF (张洪峰), Li P (李鹏), Wu XM (吴晓民) (2013) Research on the habitats selection by mainland serow (Capricornis sunatraensis) in winter in Guanyin Mountain. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology(陕西林业科技),27, 56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Liu XH, Wu PF, Songer M, Cai Q, He XB, Zhu Y, Shao XM (2013) Monitoring wildlife abundance and diversity with infra-red camera traps in Guanyinshan Nature Reserve of Shaanxi Province, China.Ecological Indicators, 33, 121-128. |
| [11] | Lu XL (卢学理), Jiang ZG (蒋志刚), Tang JR (唐继荣), Wang XJ (王学杰), Xiang DQ (向定乾), Zhang JP (张建平) (2005) Auto-trigger camera traps for studying giant panda and its sympatric wildlife species.Acta Zoologica Sinica(动物学报), 51, 495-500. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Ma SL (马世来), Harris RB (1996) Use of auto-trigger camera system in wildlife survey.Zoological Research(动物学研究), 17, 360-370. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Rovero F, Marshall AR (2009) Camera trapping photographic rate as an index of density in forest ungulates.Journal of Applied Ecology, 46, 1011-1017. |
| [14] | Tape KD, Gustine DD (2014) Capturing migration phenology of terrestrial wildlife using camera traps.BioScience, 64, 117-124. |
| [15] | Wallace RB, Gomez H, Ayala G, Espinoza F (2003) Camera trapping for jaguar (Panthera onca) in the Tuichi Valley, Bolivia.Mastozoologia Neotropical, 10, 133-139. |
| [16] | Wan XR (宛新荣), Wang MJ (王梦军), Wang GH (王广和), Liu W (刘伟), Zhong WQ (钟文勤) (2002) Numerical indices for evaluating the activity patterns of rodent species.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 22, 211-217. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Wang T, Skidmore AK, Zeng Z, Beck PSA, Si Y, Song Y, Liu X, Prins HHT (2010) Migration patterns of two endangered sympatric species from a remote sensing perspective.Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 76, 1343-1352. |
| [18] | Wu H (吴华), Hu JC (胡锦矗) (2001) A comparison in spring and winter habitat selection of takin, serow and groal in Tangjiahe, Sichuan.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 21, 1627-1633. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Wu PF (武鹏峰), Liu XH (刘雪华), Cai Q (蔡琼), He XB (何祥博), Melissa S, Zhu Y (朱云), Shao XM (邵小明) (2012) The application of infrared camera in mammal research in Guanyinshan Nature Reserve, Shaanxi.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 32, 67-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Xue H (薛辉), Li YM (李永民), Wu XB (吴孝兵), Gu CM (顾长明), Chen WH (陈文豪), Wu JZ (吴建中) (2013) Application of the passive infrared sensor camera in the survey of pheasants and beasts in Guniujiang National Nature Reserve.Anhui Forestry Science and Technology(安徽林业科技), 39, 36-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Yu LG (余梁哥), Chen MJ (陈敏杰), Yang SJ (杨士剑), Li XY (李学友), Shi L (师蕾) (2013) Camera trapping survey of Nyticebus pygmaeus, Nyticebus coucang and other sympatric mammals at Dawei Mountain,Yunnan.Sichuan Journal of Zoology(四川动物), 32, 814-818. (in Chinese) |
| [22] | Zhang SS (章书声), Bao YY (鲍毅新), Wang YN (王艳妮), Fang PF (方平福), Ye B (叶彬) (2012) Activity rhythms of black muntjac (Muntiacus crinifron) revealed with infrared camera.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 32, 368-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Zheng JQ (郑建清) (2011) Time budgets and behavior of captive red goral (Nemorhaedus cranbrooki) in summer.Chinese Journal of Wildlife(野生动物), 32, 249-251. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Zheng X (郑祥), Bao YY (鲍毅新), Ge BM (葛宝明), Zheng RQ (郑荣泉) (2006) Seasonal changes in habitat use of black muntjac (Muntiacus crinifrons) in Zhejiang.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 26, 201-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Zheng LB (张履冰), Xu HF (徐宏发), Xue WJ (薛文杰), Jiang HR (姜海瑞), Meng XX (孟秀祥) (2008) Winter and spring diet composition of musk deer in Feng County, Shaanxi.Sichuan Journal of Zoology(四川动物), 27, 110-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Zeng ZG (曾治高), Song YL (宋延龄) (2001) Daily activity rhythm and time budget of golden takin in spring and summer.Acta Theriologica Sinica(兽类学报), 21, 7-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [2] | 龚翠凤, 韦伟, 罗概, 韩一敏, 吴鹏程, 何梦楠, 闵清悦, 付强, 陈鹏. 大熊猫国家公园崇州片区有蹄类动物空间分布及共存关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24260-. |
| [3] | 卢佳玉, 石小亿, 多立安, 王天明, 李治霖. 基于红外相机技术的天津城市地栖哺乳动物昼夜活动节律评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [4] | 高翔, 潘淑芳, 孙争争, 李霁筱, 高天雨, 董路, 王宁. 广东珠海凤凰山和淇澳岛小灵猫的分布与活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24045-. |
| [5] | 张明军, 王合升, 颜文博, 符运南, 王琦, 曾治高. 海南大田国家级自然保护区小灵猫的活动节律与栖息地选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23420-. |
| [6] | 任嘉隆, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 赵文智, 严祺涵, 秦畅, 方静, 辛未冬, 刘继亮. 基于陷阱法采集的河西走廊戈壁荒漠甲虫数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23375-. |
| [7] | 麦晓烔, 康佳, 李梓琛, 王天明. 东北虎豹国家公园梅花鹿活动节律及其对道路的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24178-. |
| [8] | 赵坤明, 陈圣宾, 杨锡福. 基于红外相机技术调查四川都江堰破碎化森林鸟兽多样性及优势种活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22529-. |
| [9] | 王怡涵, 赵倩倩, 刁奕欣, 顾伯健, 翁悦, 张卓锦, 陈泳滨, 王放. 基于红外相机调查上海市区小灵猫的活动节律、栖息地利用及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22294-. |
| [10] | 李飞, 黄湘元, 张兴超, 欧梓键, 陈辈乐. 基于红外相机对云南腾冲高黎贡山云猫的调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22089-. |
| [11] | 韦怡, 姜广顺. 虎豹及有蹄类猎物种群数量监测方法概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 21551-. |
| [12] | 孔玥峤, 刘炎林, 贺成武, 李天醍, 李全亮, 马存新, 王大军, 李晟. 评估荒漠猫的日活动节律: 基于红外相机与卫星颈圈数据的对比[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22081-. |
| [13] | 杨剑焕, 李敬华, 杨浩炫, 欧梓键, 郑玺, Anthony J. Giordano, 陈辈乐. 基于红外相机数据评估华南地区豹猫的种群密度和活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 21357-. |
| [14] | 邓雪琴, 刘统, 刘天时, 徐恺, 姚松, 黄小群, 肖治术. 河南内乡宝天曼国家级自然保护区豹猫及其潜在猎物之间日活动节律的季节性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22263-. |
| [15] | 胡远芳, 李斌强, 梁丹, 李兴权, 刘兰香, 杨家伟, 罗旭. 人为干扰对白腹锦鸡活动节律的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21484-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()