



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 195-200. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08349 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.08349
赵欣1, 林超文2, 徐明桥3, 黄晶晶2, 陈一兵2, 李传仁3, 蔡青年1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2008-12-24
接受日期:2009-03-17
出版日期:2009-03-20
发布日期:2009-03-20
通讯作者:
蔡青年
作者简介:* E-mail: caiqn@cau.edu.cn基金资助:
Xin Zhao1, Chaowen Lin2, Mingqiao Xu3, Jingjing Huang2, Yibing Chen2, Chuanren Li3, Qingnian Cai1,*( )
)
Received:2008-12-24
Accepted:2009-03-17
Online:2009-03-20
Published:2009-03-20
Contact:
Qingnian Cai
摘要:
地膜水稻作为一种新的水稻种植方式, 在我国丘陵和山区水稻生产中具有明显的增产效果。地膜稻田中杂草作为重要的有害生物, 有关其群落组成及多样性的报道不多。为了明确地膜稻田杂草的种类、发生密度、优势种及群落多样性, 我们设计了地膜和常规种植两类不同种植模式稻田, 在田间杂草营养生长盛期, 抽样调查了两类稻田中杂草密度、发生程度及生物多样性指数等。结果表明: 地膜稻田和常规稻田杂草种类分别有8科12属12种和10科14属14种。其中常规稻田的马齿苋(Portulaca oleracea)、鸭舌草(Monochoria vaginalis)、拟金茅(Eulaliopsis binata) 和四叶萍(Marsilea quadrifolia) 等在地膜稻田不发生或仅偶有发生, 覆膜稻田中杂草总密度显著降低。异型莎草(Cyperus difformis)和酢浆草(Oxalis corniculata)在两种种植模式田均为优势种, 其相对密度分别为10.29-49.26%和11.91-45.59%, 且地膜稻田的密度均显著低于常规稻田; 而马唐(Digitaria sanguinalis)和水莎草(Juncellus serotinus)仅为地膜稻田的优势种, 其相对密度分别为18.01-30.46%和17.22-23.97%。除个别调查时间外, 两种种植模式稻田杂草群落的Shannon多样性指数和Margalef丰富度指数无显著差异; 而在整个调查期间, 地膜稻田的Pielou均匀度指数均显著高于常规稻田。由此可见, 地膜水稻种植模式不仅对稻田常见杂草和优势种杂草有一定的控制作用, 而且也使整个杂草群落处于一个稳定水平, 避免了一些杂草的暴发, 这对水稻生产过程中的草害控制具有重要的意义。
赵欣, 林超文, 徐明桥, 黄晶晶, 陈一兵, 李传仁, 蔡青年 (2009) 水稻覆膜处理对稻田杂草多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 17, 195-200. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08349.
Xin Zhao, Chaowen Lin, Mingqiao Xu, Jingjing Huang, Yibing Chen, Chuanren Li, Qingnian Cai (2009) Effect of film-mulched treatment on weed diversity in rice field. Biodiversity Science, 17, 195-200. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.08349.
| 调查次数 Sampling times 杂草种类 Weed species | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规 Conventional | ||||
| 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 30.46±2.34 | - | 20.52±4.30a | 2.73±1.17b | 18.01±3.58 | - | 9.49±3.29a | 0.05±0.03b | |||
| 千金子 Leptochloa chinensis | 3.14±1.21a | 0.27±0.19b | 2.11±0.52a | 0.35±0.31b | 2.20±1.91a | 0.97±1.08a | 0.71±0.42a | 0.30±0.08a | |||
| 稗草 Echinochloa crusgalli | 7.48±3.25a | 7.60±3.72a | 0.99±1.02b | 2.05±1.13b | 0.87±1.41a | 1.73±0.80a | 1.46±1.15a | 1.66±0.56a | |||
| 拟金茅 Eulaliopsis binata | - | - | - | 0.41±0.38 | - | 0.66±0.36 | 4.18±1.59a | 1.03±0.26b | |||
| 水莎草 Juncellus serotinus | 17.22±3.76a | 2.63±0.88b | 5.96±1.60a | 0.99±0.09b | 17.92±7.51a | 0.98±0.84b | 23.97±7.63a | 0.85±0.41b | |||
| 异型莎草 Cyperus difformis | 27.10±6.43b | 49.26±9.88a | 17.26±5.35b | 10.29±5.79b | 18.01±5.93a | 21.13±4.43a | 16.07±4.34a | 3.60±0.60b | |||
| 猪殃殃 Galium aparine | 0.34±0.33b | 2.22±0.75a | 3.31±2.51b | 16.23±3.57a | 9.07±3.01b | 18.01±2.80a | 20.27±3.69a | 2.10±1.01b | |||
| 陌上菜 Lindernia procumbens | - | 8.12±4.02 | 0.11±0.27 | - | 2.43±2.08a | 0.86±0.69a | 1.39±0.78b | 21.07±6.01a | |||
| 节节菜 Rotala indica | 8.43±1.84a | 1.51±0.64b | 1.08±0.62b | 2.32±1.09a | 4.50±1.22b | 19.40±2.79a | 3.41±1.04a | 2.21±0.58b | |||
| 丁香蓼 Ludwigia prostrata | 4.25±1.43b | 16.10±3.55a | 7.09±3.24a | 9.05±1.61a | 5.37±2.47a | 7.31±1.67a | 6.34±1.00a | 5.01±1.67a | |||
| 酢浆草 Oxalis corniculata | - | 12.07±0.42 | 40.07±6.57a | 45.59±6.42a | 21.36±2.75a | 20.14±4.06 | 11.91±2.51a | 1.53±0.67b | |||
| 马齿苋 Portulaca oleracea | - | - | - | 6.28±1.90 | - | 5.74±1.80 | 0.20±0.49b | 7.88±1.64a | |||
| 鸭舌草 Monochoria vaginalis | - | - | - | 4.01±208 | - | 2.62±1.06 | - | 0.67±0.27 | |||
| 四叶萍 Marsilea quadrifolia | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 51.12±7.91 | |||
表1 地膜稻田和常规栽培稻田杂草相对密度(平均值±标准差) (%)
Table 1 Relative density (mean±SE) of weeds in film-mulched and conventional rice fields(%)
| 调查次数 Sampling times 杂草种类 Weed species | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规 Conventional | ||||
| 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 30.46±2.34 | - | 20.52±4.30a | 2.73±1.17b | 18.01±3.58 | - | 9.49±3.29a | 0.05±0.03b | |||
| 千金子 Leptochloa chinensis | 3.14±1.21a | 0.27±0.19b | 2.11±0.52a | 0.35±0.31b | 2.20±1.91a | 0.97±1.08a | 0.71±0.42a | 0.30±0.08a | |||
| 稗草 Echinochloa crusgalli | 7.48±3.25a | 7.60±3.72a | 0.99±1.02b | 2.05±1.13b | 0.87±1.41a | 1.73±0.80a | 1.46±1.15a | 1.66±0.56a | |||
| 拟金茅 Eulaliopsis binata | - | - | - | 0.41±0.38 | - | 0.66±0.36 | 4.18±1.59a | 1.03±0.26b | |||
| 水莎草 Juncellus serotinus | 17.22±3.76a | 2.63±0.88b | 5.96±1.60a | 0.99±0.09b | 17.92±7.51a | 0.98±0.84b | 23.97±7.63a | 0.85±0.41b | |||
| 异型莎草 Cyperus difformis | 27.10±6.43b | 49.26±9.88a | 17.26±5.35b | 10.29±5.79b | 18.01±5.93a | 21.13±4.43a | 16.07±4.34a | 3.60±0.60b | |||
| 猪殃殃 Galium aparine | 0.34±0.33b | 2.22±0.75a | 3.31±2.51b | 16.23±3.57a | 9.07±3.01b | 18.01±2.80a | 20.27±3.69a | 2.10±1.01b | |||
| 陌上菜 Lindernia procumbens | - | 8.12±4.02 | 0.11±0.27 | - | 2.43±2.08a | 0.86±0.69a | 1.39±0.78b | 21.07±6.01a | |||
| 节节菜 Rotala indica | 8.43±1.84a | 1.51±0.64b | 1.08±0.62b | 2.32±1.09a | 4.50±1.22b | 19.40±2.79a | 3.41±1.04a | 2.21±0.58b | |||
| 丁香蓼 Ludwigia prostrata | 4.25±1.43b | 16.10±3.55a | 7.09±3.24a | 9.05±1.61a | 5.37±2.47a | 7.31±1.67a | 6.34±1.00a | 5.01±1.67a | |||
| 酢浆草 Oxalis corniculata | - | 12.07±0.42 | 40.07±6.57a | 45.59±6.42a | 21.36±2.75a | 20.14±4.06 | 11.91±2.51a | 1.53±0.67b | |||
| 马齿苋 Portulaca oleracea | - | - | - | 6.28±1.90 | - | 5.74±1.80 | 0.20±0.49b | 7.88±1.64a | |||
| 鸭舌草 Monochoria vaginalis | - | - | - | 4.01±208 | - | 2.62±1.06 | - | 0.67±0.27 | |||
| 四叶萍 Marsilea quadrifolia | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 51.12±7.91 | |||
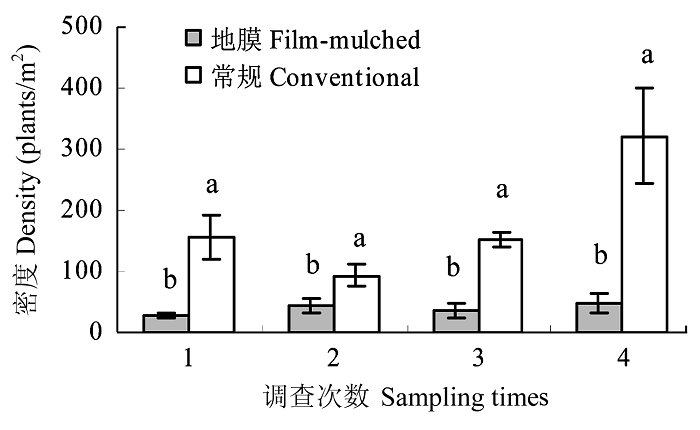
图1 地膜稻田和常规栽培稻田杂草群落总密度。图中不同小写字母表示差异显著( P < 0.05)。
Fig.1 Total density of weed community in film-mulched and conventional rice fields. Different letters indicate a significant difference at 0.05 level.
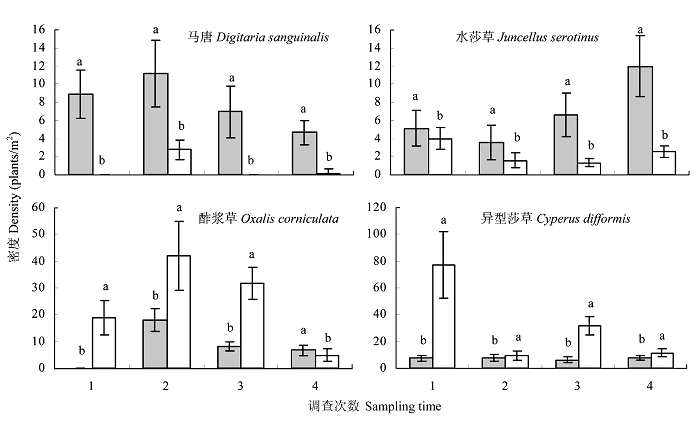
图2 地膜稻田和常规栽培稻田杂草优势种密度的比较。(■)地膜覆盖, (□)常规; 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 2 Density comparison of dominant weed species between film-mulched and conventional rice fields. Different letters indicate a significant difference at 0.05 level. (■) Film-mulched; (□) Conventional.
| 调查次数 Sampling times | Shannon-Wiener 指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H) | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (E) | Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (M) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规 Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规 Conventional | |||
| 1 | 2.30 ± 1.17 a | 1.95 ± 0.41 a | 0.87 ± 0.01 a | 0.65 ± 0.11 b | 1.17 ± 0.20 a | 1.15 ± 0.19 a | ||
| 2 | 2.27 ± 0.17 a | 2.45 ± 0.45 a | 0.78 ± 0.03 a | 0.72 ± 0.02 b | 1.32 ± 0.16 b | 1.54 ± 0.19 a | ||
| 3 | 2.71 ± 0.15 a | 2.79 ± 0.08 a | 0.86 ± 0.03 a | 0.79 ± 0.02 b | 1.68 ± 0.21 a | 1.71 ± 0.10 a | ||
| 4 | 2.74 ± 0.23 a | 2.23 ± 0.18 b | 0.82 ± 0.07 a | 0.58 ± 0.05 b | 1.85 ± 0.12 a | 1.81 ± 0.17 a | ||
表2 地膜稻田和常规栽培稻田杂草群落多样性指数(平均值±标准差)
Table 2 Biodiversity indices (mean±SE) of weed communities in film-mulched and conventional rice fields
| 调查次数 Sampling times | Shannon-Wiener 指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H) | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (E) | Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef richness index (M) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规 Conventional | 地膜 Film-mulched | 常规 Conventional | |||
| 1 | 2.30 ± 1.17 a | 1.95 ± 0.41 a | 0.87 ± 0.01 a | 0.65 ± 0.11 b | 1.17 ± 0.20 a | 1.15 ± 0.19 a | ||
| 2 | 2.27 ± 0.17 a | 2.45 ± 0.45 a | 0.78 ± 0.03 a | 0.72 ± 0.02 b | 1.32 ± 0.16 b | 1.54 ± 0.19 a | ||
| 3 | 2.71 ± 0.15 a | 2.79 ± 0.08 a | 0.86 ± 0.03 a | 0.79 ± 0.02 b | 1.68 ± 0.21 a | 1.71 ± 0.10 a | ||
| 4 | 2.74 ± 0.23 a | 2.23 ± 0.18 b | 0.82 ± 0.07 a | 0.58 ± 0.05 b | 1.85 ± 0.12 a | 1.81 ± 0.17 a | ||
| [1] | Barberi P, Silvestri N, Bonari E (1997) Weed communities of winter wheat as influenced by input level and rotation. Weed Research, 37, 301-313. |
| [2] | Cai Y (蔡艳), Tao WH (陶武辉), Zhang Y (张毅), Zhang XZ (张锡洲) (2008) Effect of planting density on the production and N utilization of rice under large-triangle intensification system. Chinese Journal of Eco- Agriculture (中国生态农业学报), 16, 1603-1605. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | Derksen DA, Thomas AG, Lafond GP, Loeppky HA, Swanton CJ (1995) Impact of post-emergence herbicides on weed community diversity within conservation-tillage systems. Weed Research, 35, 311-320. |
| [4] | Day K (1996) Agriculture’s links to biodiversity. Agricultural Outlook, 263, 32-37. |
| [5] | Gu YF (谷艳芳), Hu N (胡楠), Ding SY (丁圣彦), Zhang LX (张丽霞), Li JJ (李俊娇) (2007) Effects of cropping systems on community structure and biodiversity of weeds in wheat fields in Kaifeng and Fengqiu districts. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science) (河南大学学报(自然科学版)), 37, 391-394. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Huang YD (黄义德), Zhang ZL (张自立), Wei FZ (魏凤珍), Li JC (李金才) (1999) Eco-physiological effect of dry-cultivated and plastic film-mulched rice planting. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 10, 305-308. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Liu FM (刘方明), Liang WJ (梁文举), Wen DZ (闻大中) (2005) Effects of tillage method and herbicide on corn field weed community. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 16, 1879-1882. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Lu XH (路兴花), Wu LH (吴良欢), Liu M (刘铭), Yang LF (杨联丰) (2002) Effect of film mulched cultivation on growth and some physiological characteristics of rice. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric.& Life Sci.) (浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版)), 28, 609-614. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Liang YC (梁永超), Hu F (胡锋), Yang MC (杨茂成), Zhu XL (朱遐亮), Wang GP (王广平), Wang YL (王永乐) (1999) Mechanisms of high yield and irrigation water use efficiency of rice in plastic film mulched dryland. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 32(1), 26-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Ma KP (马克平) (1994) The measurement of community diversity. In: Principles and Methodologies of Biodiversity Studies (生物多样性研究的原理与方法) (eds Qian YQ (钱迎倩), Ma KP (马克平)), pp. 141-165. Chinese Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [11] | Nyarko KA, Ampongnyarko K, Dedatta SK (1993) Effects of nitrogen application on growth, nitrogen use efficiency and weed interaction. Weed Research, 33, 269-276. |
| [12] | Qiang S (强胜), Shen JM (沈俊明), Zhang CQ (张成群), Shao GY (邵耕耘), Hu JL (胡金良), Wang FL (王凤良) (2003) The influence of cropping systems on weed communities in the cotton fields of Jiangsu Province. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 27, 278-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Ren WT (任文涛), Xin MJ (辛明金), Lin J (林静), Bao CJ (包春江), Song YQ (宋玉秋), Wang RL (王瑞丽) (2003) Experimental study on effect of paper-mulching rice planting technology on saving water and controlling weeds. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (农业工程学报), 19(6), 60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Stevenson FC, Legere A, Simard RR, Angers DA, Pageau D, Lafond J (1997) Weed species diversity in spring barley varies with crop rotation and tillage, but not with nutrient source. Weed Science, 45, 798-806. |
| [15] | Tang QY (唐启义), Feng MG (冯明光) (1997) Practical Statistics and DPS Data Processing System (实用统计分析及其计算机处理平台). China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [16] | Wang KJ (王开金), Qiang S (强胜) (2005) Quantitative analysis of distribution of weed communities in wheat fields in the south of Jiangsu Province. Journal of Biomathematics (生物数学学报), 20, 107-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Wu LH (吴良欢), Zhu ZR (祝增荣), Liang YC (梁永超), Shi WY (石伟勇), Zhang LM (张立民) (1999) The development of the rice film mulching cultivation. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University (浙江农业大学学报), 25, 41-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Wang LP (王连平), Wang HR (王汉荣), Ru SJ (茹水江), Fang L (方丽), Zhang MZ (张明忠), Jin LX (金立新), Chen CH (陈春华) (2006) Study on weed in asparagus farmland and effects of film-covering for weeding. Acta Agriculture Jiangxi (江西农业学报), 18(4), 126-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Wei SH (魏守辉), Qiang S (强胜), Ma B (马波), Wei JG (韦继光), Chen JW (陈建卫), Wu JQ (吴建强), Xie TZ (谢桐洲), Shen XK (沈晓昆) (2005) Control effects of rice-duck farming and other weed management strategies on weed communities in paddy fields. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 16, 1067-1071. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Xu XJ (徐秀娟), Zhao ZQ (赵志强), Lu J (卢钰), Li SX (李尚霞), Liu QF (刘庆芳) (2007) Techniques for controlling weeds in organic peanut field. Weed Science (杂草科学), (1), 34-36. (in Chinese) |
| [21] | Zhang RX (张润祥), Liang RX (梁荣先), Yang ZP (杨正芃) (1995) Studies on the population dynamics and control of the main pests in maize field mulched by plastic film. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences (山西农业科学), 23(3), 51-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Zhou XG (周小刚), Zhang H (张辉) (2006) The Coloured Atlas of Common Field Weeds in Sichuan (四川农田常见杂草原色图谱). Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 顾燚芸, 薛嘉祈, 高金会, 谢心仪, 韦铭, 雷进宇, 闻丞. 一种基于公众科学数据的区域性鸟类多样性评价方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24080-. |
| [3] | 徐伟强, 苏强. 分形模型与一般性物种多度分布关系的检验解析:以贝类和昆虫群落为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| [4] | 陈蕾, 许志勇, 苏菩坤, 赖小甜, 赵兆. 依频声学多样性指数用于人类活动区域的适用能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24286-. |
| [5] | 卜向丽, 王静, 吴佳忆, 孙太福, 向荣伟, 鲁庆斌, 郝映红, 崔绍朋, 盛岩, 孟秀祥. 太行山东北部哺乳动物区系及多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 331-339. |
| [6] | 尚素琴, 吴兴波, 王召龙, 彭鹤年, 周惠丽, 张红勇, 白映禄. 兴隆山国家级自然保护区不同生境的蝴蝶群落结构与种-多度分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 983-992. |
| [7] | 李共国, 李平, 徐杭英, 于海燕, 俞建. 浙江水源地河流浮游动物多样性与环境因子的通径分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 166-175. |
| [8] | 张全建, 杨彪, 付强, 王磊, 龚旭, 张远彬. 邛崃山系水鹿的冬季食性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1192-1201. |
| [9] | 王国萍, 薛达元, 闻苡, 成功, 闵庆文. 土族生物资源利用相关的传统知识多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(7): 735-742. |
| [10] | 马燕婕, 何浩鹏, 沈文静, 刘标, 薛堃. 转基因玉米对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 419-432. |
| [11] | 叶又茵, 项鹏, 王雨, 林茂. 福建6个港湾浮游植物多样性及其与水系的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(3): 285-293. |
| [12] | 蔡文倩, 刘静, 周娟, 夏阳, 刘录三. 基于生物量的大型底栖动物功能摄食群结构 及生态质量评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(9): 1045-1055. |
| [13] | 周伟, 李明会, 李有兰. 滇西南四个自然保护区鱼类多样性及评价指标探究[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(3): 313-320. |
| [14] | 黄备, 魏娜, 孟伟杰, 张明霞. 基于压力-状态-响应模型的辽宁省长海海域海洋生物多样性评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1): 48-54. |
| [15] | 刘哲, 李奇, 陈懂懂, 翟文婷, 赵亮, 徐世晓, 赵新全. 青藏高原高寒草甸物种多样性的海拔梯度分布格局及对地上生物量的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(4): 451-462. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn