



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 749-759. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018055 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018055
王世彤1,2, 吴浩1,2, 刘梦婷1,2, 张佳鑫1,2, 刘检明1,2, 孟红杰1, 徐耀粘1, 乔秀娟1, 魏新增1,*( ), 卢志军1, 江明喜1
), 卢志军1, 江明喜1
收稿日期:2018-02-11
接受日期:2018-04-02
出版日期:2018-07-20
发布日期:2018-09-11
通讯作者:
魏新增
基金资助:
Wang Shitong1,2, Wu Hao1,2, Liu Mengting1,2, Zhang Jiaxin1,2, Liu Jianming1,2, Meng Hongjie1, Xu Yaozhan1, Qiao Xiujuan1, Wei Xinzeng1,*( ), Lu Zhijun1, Jiang Mingxi1
), Lu Zhijun1, Jiang Mingxi1
Received:2018-02-11
Accepted:2018-04-02
Online:2018-07-20
Published:2018-09-11
Contact:
Wei Xinzeng
摘要:
本文以极小种群野生植物黄梅秤锤树(Sinojackia huangmeiensis)当前唯一的野生种群为依托建立了1 ha的固定样地, 研究了黄梅秤锤树野生植物群落的物种组成、优势种的径级结构、黄梅秤锤树的空间分布格局、种内与种间空间关联性和种群更新特征。样地内共记录到胸径 ≥ 1.0 cm的木本植物31种, 隶属于21科28属。群落更新良好, 样地中所有1,225株个体中小径木占比为67.18%。群落优势种为麻栎(Quercus acutissima)、枸骨(Ilex cornuta)、朴树(Celtis sinensis)和黄梅秤锤树。麻栎的径级结构呈单峰型, 为衰退型种群; 枸骨、朴树和黄梅秤锤树的径级结构呈倒“J”型或偏倒“J”型, 表明更新良好。黄梅秤锤树的空间分布格局在小尺度上呈聚集分布, 在大尺度上呈随机或均匀分布, 并且与其他3个优势种(麻栎、枸骨、朴树)在空间上主要呈负关联性。黄梅秤锤树的成树和幼苗、幼树和幼苗都是在小尺度上呈负关联性, 在大尺度上关联性不显著, 而成树和幼树在整体上关联性不显著。黄梅秤锤树的萌蘖现象非常明显, 萌蘖数与母株胸径具有极显著的正相关性(R2 = 0.330, P < 0.001), 萌蘖率与相对幼苗密度具有极显著的负相关性(R2 = 0.438, P < 0.001)。总体来说, 高比例的小径木和普遍的种间负关联均表明该群落处于演替的早中期, 物种组成和群落结构还未达到稳定阶段。作为长江中下游冲积平原区具有代表性的残存风水林, 该野生植物群落在生物多样性维持和珍稀植物保护方面具有重要的作用, 应加强保护和管理。
王世彤, 吴浩, 刘梦婷, 张佳鑫, 刘检明, 孟红杰, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 卢志军, 江明喜 (2018) 极小种群野生植物黄梅秤锤树群落结构与动态. 生物多样性, 26, 749-759. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018055.
Wang Shitong, Wu Hao, Liu Mengting, Zhang Jiaxin, Liu Jianming, Meng Hongjie, Xu Yaozhan, Qiao Xiujuan, Wei Xinzeng, Lu Zhijun, Jiang Mingxi (2018) Community structure and dynamics of a remnant forest dominated by a plant species with extremely small population (Sinojackia huangmeiensis) in central China. Biodiversity Science, 26, 749-759. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018055.
| 物种 Species | 多度 Abundance | 胸径 DBH (mean ± SE) (cm) | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2/ha) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 麻栎 Quercus acutissima | 212 | 24.18 ± 0.75 | 11.99 | 27.40 |
| 枸骨 Ilex cornuta | 282 | 5.25 ± 0.26 | 4.02 | 17.16 |
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | 125 | 6.01 ± 0.61 | 0.97 | 7.01 |
| 黄梅秤锤树 Sinojackia huangmeiensis | 159 | 2.72 ± 0.19 | 0.26 | 6.45 |
| 枫香 Liquidambar formosana | 55 | 16.00 ± 1.20 | 1.46 | 6.26 |
| 槲栎 Quercus aliena | 40 | 15.82 ± 1.67 | 1.15 | 4.84 |
| 野桐 Mallotus tenuifolius | 77 | 2.75 ± 0.14 | 0.07 | 4.32 |
| 黄连木 Pistacia chinensis | 27 | 9.74 ± 1.46 | 0.32 | 3.21 |
| 大青 Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum | 40 | 1.97 ± 0.12 | 0.02 | 3.10 |
| 樟树 Cinnamomum camphora | 24 | 7.89 ± 1.83 | 0.44 | 3.05 |
| 山胡椒 Lindera glauca | 20 | 3.29 ± 0.23 | 0.03 | 2.18 |
| 乌桕 Sapium sebiferum | 30 | 8.91 ± 1.02 | 0.26 | 1.88 |
| 白檀 Symplocos paniculata | 20 | 2.37 ± 0.18 | 0.01 | 1.62 |
| 华山矾 Symplocos chinensis | 16 | 2.96 ± 0.52 | 0.02 | 1.52 |
| 柿树 Diospyros kaki | 12 | 11.69 ± 2.25 | 0.18 | 1.27 |
| 榆树 Ulmus pumila | 15 | 3.46 ± 0.44 | 0.02 | 1.23 |
| 牡荆 Vitex negundo var. cannabifolia | 12 | 2.07 ± 0.23 | 0.01 | 1.13 |
| 其他 Others | 59 | - | 0.42 | 6.36 |
| 总计 Total | 1,225 | - | 21.64 | 100 |
表1 1 ha 样地内重要值 ≥ 1%的物种的数量特征
Table 1 Quantitative characteristics of species with importance value ≥ 1% in the 1-ha plot
| 物种 Species | 多度 Abundance | 胸径 DBH (mean ± SE) (cm) | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2/ha) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 麻栎 Quercus acutissima | 212 | 24.18 ± 0.75 | 11.99 | 27.40 |
| 枸骨 Ilex cornuta | 282 | 5.25 ± 0.26 | 4.02 | 17.16 |
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | 125 | 6.01 ± 0.61 | 0.97 | 7.01 |
| 黄梅秤锤树 Sinojackia huangmeiensis | 159 | 2.72 ± 0.19 | 0.26 | 6.45 |
| 枫香 Liquidambar formosana | 55 | 16.00 ± 1.20 | 1.46 | 6.26 |
| 槲栎 Quercus aliena | 40 | 15.82 ± 1.67 | 1.15 | 4.84 |
| 野桐 Mallotus tenuifolius | 77 | 2.75 ± 0.14 | 0.07 | 4.32 |
| 黄连木 Pistacia chinensis | 27 | 9.74 ± 1.46 | 0.32 | 3.21 |
| 大青 Clerodendrum cyrtophyllum | 40 | 1.97 ± 0.12 | 0.02 | 3.10 |
| 樟树 Cinnamomum camphora | 24 | 7.89 ± 1.83 | 0.44 | 3.05 |
| 山胡椒 Lindera glauca | 20 | 3.29 ± 0.23 | 0.03 | 2.18 |
| 乌桕 Sapium sebiferum | 30 | 8.91 ± 1.02 | 0.26 | 1.88 |
| 白檀 Symplocos paniculata | 20 | 2.37 ± 0.18 | 0.01 | 1.62 |
| 华山矾 Symplocos chinensis | 16 | 2.96 ± 0.52 | 0.02 | 1.52 |
| 柿树 Diospyros kaki | 12 | 11.69 ± 2.25 | 0.18 | 1.27 |
| 榆树 Ulmus pumila | 15 | 3.46 ± 0.44 | 0.02 | 1.23 |
| 牡荆 Vitex negundo var. cannabifolia | 12 | 2.07 ± 0.23 | 0.01 | 1.13 |
| 其他 Others | 59 | - | 0.42 | 6.36 |
| 总计 Total | 1,225 | - | 21.64 | 100 |
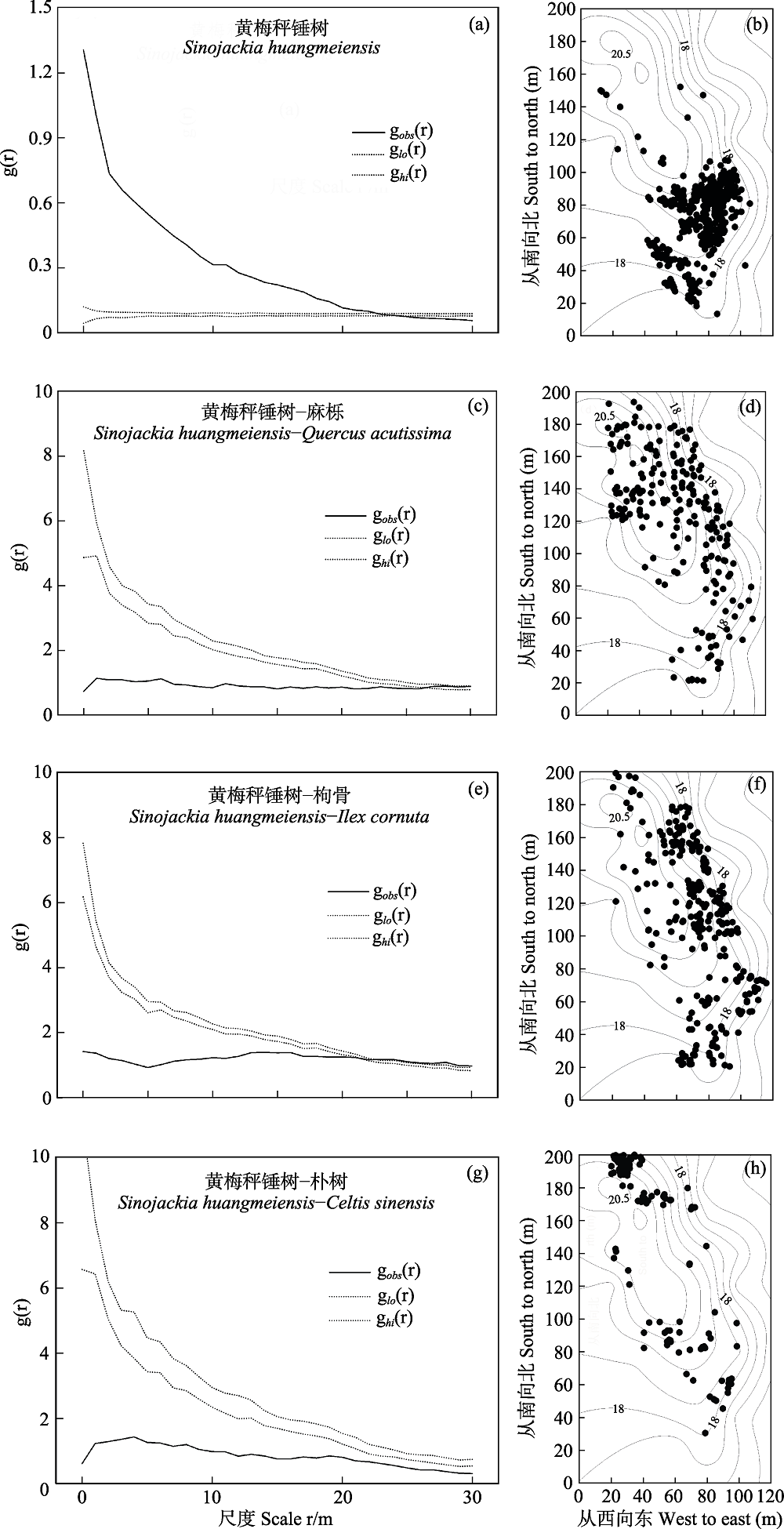
图3 黄秤锤树点格局分析(a)及其与其他3个优势种的关联分析(c, e和g)。图b, d, f和h分别为黄梅秤锤树、麻栎、枸骨和朴树的空间分布图。图中黑色实线代表g (r)在尺度r上的实际观测值, 细虚线代表模拟99次形成的置信区间。点格局分析中,黑色实线高于(低于)置信区间上限(下限)表示聚集分布(均匀分布), 黑色实线位于置信区间之内, 则表示随机分布。关联分析中, 黑色实线高于(低于)置信区间上限(下限)表示正关联(负关联), 黑色实线位于置信区间之内, 则表示无关联。
Fig. 3 Point pattern analysis of Sinojackia huangmeiensis (a), correlation analyses between S. huangmeiensis and the other three dominant species (Quercus acutissima, Ilex cornuta, and Celtis sinensis) (c, e, and g), and point diagram of individual distribution of the four dominant species (b, d, f, and h). In the left panels, black solid lines indicate the values of the g(r) function; thin dashed lines indicate the confidence envelope of the null model. In point pattern analysis (a), values of the g(r) function above (below) the upper (lower) envelope indicate aggregated (regular), within envelope indicate random. In correlation analysis (c, e, g), values of the g(r) function above (below) the upper (lower) envelope indicate positive (negative) association, within envelope indicate no association.
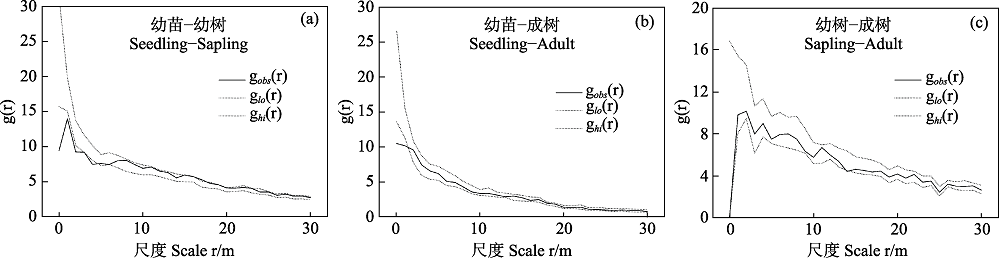
图4 黄梅秤锤树幼苗(DBH < 1 cm)、幼树(1 cm ≤ DBH < 2.5 cm)和成年个体(DBH ≥ 2.5 cm)之间的关联分析。图中黑色实线代表g(r)在尺度r上的实际观测值, 细虚线代表模拟99次形成的置信区间。黑色实线高于(低于)置信区间上限(下限)表示正关联(负关联)。黑色实线位于置信区间之内, 则表示无关联。
Fig. 4 Correlation analyses between seedling (DBH < 1 cm), sapling (1 cm ≤ DBH < 2.5 cm) and adult (DBH ≥ 2.5 cm) of Sinojackia huangmeiensis. Black solid lines indicate the values of the g(r) function; thin dashed lines indicate the confidence envelope of the null model. Values of the g(r) function above (below) the upper (lower) envelope indicate positive (negative) association, within envelope indicate no association.
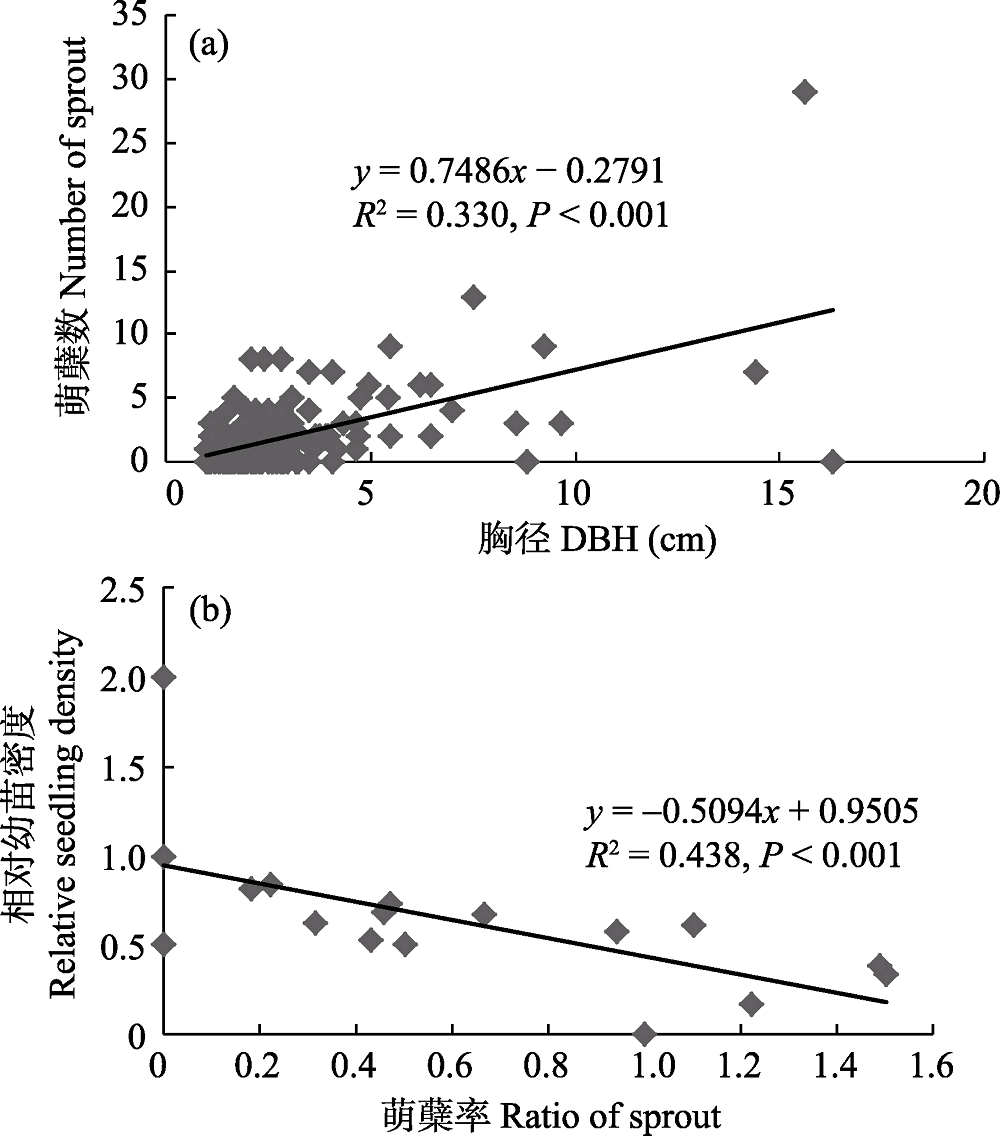
图5 黄梅秤锤树萌蘖数与母株胸径的关系(a)和萌蘖率与相对幼苗密度的关系(b)
Fig. 5 Relationships between number of sprout and DBH (a), and relative seedling density and ratio of sprout (b). DBH, diameter at breast height.
| [1] | Aerts R, Overtveld KV, Haile M, Hermy M, Deckers J, Muys B (2006) Species composition and diversity of small Afromontane forest fragments in northern Ethiopia. Plant Ecology, 187, 127-142. |
| [2] | Bellingham PJ, Sparrow AD (2009) Multi stemmed trees in montane rain forests: Their frequency and demography in relation to elevation, soil nutrients and disturbance. Journal of Ecology, 97, 472-483. |
| [3] | Chen M, Cao M, Lin LX (2007) Research advances in regeneration of woody plants by sprouting. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 26, 1114-1118. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈沐, 曹敏, 林露湘 (2007) 木本植物萌生更新研究进展. 生态学杂志, 26, 1114-1118.] | |
| [4] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. |
| [5] | Da LJ, Yang YC, Song YC (2004) Population structure and regeneration types of dominant species in an evergreen broadleaved forest in Tiantong National Forest Park, Zhejiang, China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 28, 376-384. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [达良俊, 杨永川, 宋永昌 (2004) 浙江天童国家森林公园常绿阔叶林主要组成种的种群结构及更新类型. 植物生态学报, 28, 376-384.] | |
| [6] | Dale MRT (1999)Spatial Pattern Analysis in Plant Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [7] | Editorial Committee of Flora of China(2004) Flora of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国植物志编辑委员会(2004) 中国植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Fu SX (2003) Flora Hubeiensis. Hubei Science & Technology Press, Wuhan. (in Chinese) |
| [傅书遐 (2003) 湖北植物志. 湖北科学技术出版社, 武汉.] | |
| [9] | Gao FY, Zhao CZ, Zhuo Ma LC (2014) Spatial distribution and spatial association of Stellera chamaejasme population in the different altitude in degraded alpine grassland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 605-612. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高福元, 赵成章, 卓马兰草 (2014) 高寒退化草地不同海拔梯度狼毒种群分布格局及空间关联性. 生态学报, 34, 605-612.] | |
| [10] | Guo J, Yu LH, Fang X, Xiang WH, Deng XW, Lu X (2015) Litter production and turnover in four types of subtropical forests in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 4668-4677. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭婧, 喻林华, 方晰, 项文化, 邓湘雯, 路翔 (2015) 中亚热带4种森林凋落物量、组成、动态及其周转期. 生态学报, 35, 4668-4677.] | |
| [11] | Guo YL, Wang B, Xiang WS, Ding T, Lu SH, Wen SJ, Huang FZ, Li DX, Li XK (2015) Sprouting characteristics of tree species in 15-hm2 plot of northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 955-961. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 文淑均, 黄甫昭, 李冬兴, 李先琨 (2015) 弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林15 hm2 样地木本植物萌生特征. 生态学杂志, 34, 955-961.] | |
| [12] | Guo YX, Kang B, Li G, Wang DX, Yang GH, Wang DW (2011) Species composition and point pattern analysis of standing trees in secondary Betula albo-sinensis forest in Xiaolongshan of west Qinling Mountains. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22, 2574-2580. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭垚鑫, 康冰, 李刚, 王得祥, 杨改河, 王大伟 (2011) 小陇山红桦次生林物种组成与立木的点格局分析. 应用生态学报, 22, 2574-2580.] | |
| [13] | Han YZ, Wang ZQ (2002) Spatial heterogeneity and forest regeneration. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 13, 615-619. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [韩有志, 王政权 (2002) 森林更新与空间异质性. 应用生态学报, 13, 615-619.] | |
| [14] | He D, Wei XZ, Li LF, Jiang MX, Yang JY, Yu J (2009) Population structure and dynamics of Cercidiphyllum japonicum in riparian zones of the Shennongjia Mountainous Region, Central China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 33, 469-481. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何东, 魏新增, 李连发, 江明喜, 杨敬元, 喻杰 (2009) 神农架山地河岸带连香树的种群结构与动态. 植物生态学报, 33, 469-481.] | |
| [15] | He JS, Chen WL, Liu F (1998) Study on the sprouting process of Fagus engleriana in Shennongjia Mountains. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 22, 385-391. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贺金生, 陈伟烈, 刘峰 (1998) 神农架地区米心水青冈萌枝过程的研究. 植物生态学报, 22, 385-391.] | |
| [16] | He JS, Liu F, Chen WL, Chen LZ (1999) History of disturbance and regeneration strategies of Fagus engleriana and Quercus aliena var. acuteserrata forests in Shennongjia, Hubei Province. Acta Botanica Sinica, 41, 887-892. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贺金生, 刘峰, 陈伟烈, 陈灵芝 (1999) 神农架地区米心水青冈林和锐齿槲栎林群落干扰历史及更新策略. 植物学报, 41, 887-892.] | |
| [17] | John R, Dalling JW, Harms KE, Yavitt JB, Stallard RF, Mirabello M, Hubbell SP, Valencia R, Navarrete H, Foster RB (2007) Soil nutrients influence spatial distributions of tropical tree species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, USA, 104, 864-869. |
| [18] | Liang S, Xu H, Lin JY, Li YD, Lin MX (2014) Spatial distribution pattern of the dominant species Gironniera subaequalis in tropical montane rainforest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 1273-1282. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梁爽, 许涵, 林家怡, 李意德, 林明献 (2014) 尖峰岭热带山地雨林优势树种白颜树空间分布格局. 植物生态学报, 38, 1273-1282.] | |
| [19] | Liu HB, Wang QG, Lu JM, Xu YZ, Lu ZJ, Qiao XJ, Bao DC, Guo YL, Meng HJ, Jiang MX (2014) Root-sprouting ability in an evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 3491-3498. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘海波, 王庆刚, 路俊盟, 徐耀粘, 卢志军, 乔秀娟, 鲍大川, 郭屹立, 孟红杰, 江明喜 (2014) 八大公山常绿落叶阔叶混交林根萌能力. 科学通报, 59, 3491-3498.] | |
| [20] | Liu MX (2017) Spatial distribution and spatial association of Potentilla fruticosa populations on different slope aspects in subalpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 1817-1823. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘旻霞 (2017) 亚高寒草甸不同坡向金露梅种群的空间分布格局及空间关联. 应用生态学报, 28, 1817-1823.] | |
| [21] | Liu YH, Liu JF, He ZS, Hong W, Feng XP, Ya ZC (2017) Pinus taiwanensis community composition and structure based on fixed sample Daiyun Mountain. Guihaia, 37, 881-890. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘艳会, 刘金福, 何中声, 洪伟, 冯雪萍, 崖佐朝 (2017) 基于戴云山固定样地黄山松群落物种组成与结构研究. 广西植物, 37, 881-890.] | |
| [22] | Nong Y, Zheng L, Jia HY, Lu LH, Huang DW, Huang BH, Lei LQ (2015) Community characteristics and spatial distribution of dominant tree species in a secondary forest of Daqing Mountains, southwestern Guangxi, China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 321-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [农友, 郑路, 贾宏炎, 卢立华, 黄德卫, 黄柏华, 雷丽群 (2015) 广西大青山次生林的群落特征及主要乔木种群的空间分布格局. 生物多样性, 23, 321-331.] | |
| [23] | Omelko A, Ukhvatkina O, Zhmerenetsky A, Sibirina L, Petrenko T, Bobrovsky M (2018) From young to adult trees: How spatial patterns of plants with different life strategies change during age development in an old-growth Korean pine-broadleaved forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 411, 46-66. |
| [24] | Ravento’s J, Wiegand T, Luis MD (2010) Evidence for the spatial segregation hypothesis: A test with nine-year survivorship data in a Mediterranean shrubland. Ecology, 91, 2110-2120. |
| [25] | Ripley BD (1977) Modeling spatial patterns. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 39, 172-212. |
| [26] | Ruan YM, Zhang JJ, Yao XH, Ye QG (2012) Genetic diversity and fine-scale spatial genetic structure of different lifehistory stages in a small, isolated population of Sinojackia huangmeiensis (Styracaceae). Biodiversity Science, 20, 460-469. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [阮咏梅, 张金菊, 姚小洪, 叶其刚 (2012) 黄梅秤锤树孤立居群的遗传多样性及其小尺度空间遗传结构. 生物多样性, 20, 460-469.] | |
| [27] | Seidler TG, Plotkin JB (2006) Seed dispersal and spatial pattern in tropical trees. PLoS Biology, 4, 2132-2137. |
| [28] | Song YC, Yan ER, Song K (2015) Synthetic comparison of eight dynamics plots in evergreen broadleaf forests, China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 139-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋永昌, 阎恩荣, 宋坤 (2015) 中国常绿阔叶林8大动态监测样地植被的综合比较. 生物多样性, 23, 139-148.] | |
| [29] | Tang CQ, Yang YC, Ohsawa M, Momohara A, Mu JZ, Robertson K (2013) Survival of a tertiary relict species, Liriodendron chinese (Magnoliaceae), in southern China, with special reference to village fengshui forests. American Journal of Botany, 100, 2112-2119. |
| [30] | Tian YQ, Li X, Hu LL, Huang HD, Jiang MX (2002) The characteristics of tree layer structure of the rare plant community in Houhe Nature Reserve. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 20, 443-448. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [田玉强, 李新, 胡理乐, 黄汉东, 江明喜 (2002) 后河自然保护区珍稀濒危植物群落乔木层结构特征. 武汉植物学研究, 20, 443-448.] | |
| [31] | Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature, 441, 629-632. |
| [32] | Wang L, Sun QW, Hao ZY, Tian SN, Zhang SS, Chen YK, Zhang XP (2010) Point pattern analysis of different age-class Taxus chinensis var. mairei individuals in mountainous area of southern Anhui Province. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21, 272-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王磊, 孙启武, 郝朝运, 田胜尼, 张姗姗, 陈一锟, 张小平 (2010) 皖南山区南方红豆杉种群不同龄级立木的点格局分析. 应用生态学报, 21, 272-278.] | |
| [33] | Wei X, Wu H, Meng H, Pang C, Jiang M (2015) Regeneration dynamics of Euptelea pleiospermum along latitudinal and altitudinal gradients: Trade-offs between seedling and sprout. Forest Ecology and Management, 353, 232-239. |
| [34] | Wiegand T, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N (2007) Species association in a heterogeneous Sri Lankan dipterocarp forest. The American Naturalist, 170, E77-E95. |
| [35] | Wright JS (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forest: A review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia, 130, 1-14. |
| [36] | Wu CP, Yuan WG, Sheng WX, Huang YJ, Chen QB, Shen AH, Zhu JR, Jiang B (2018) Spatial distribution patterns and association of tree species in typical natural secondary forest communities in Zhejiang Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 537-549. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴初平, 袁位高, 盛卫星, 黄玉洁, 陈庆标, 沈爱华, 朱锦茹, 江波 (2018) 浙江省典型天然次生林主要树种空间分布格局及其关联性. 生态学报, 38, 537-549.] | |
| [37] | Xie CQ, Tian MX, Zhao ZR, Zheng WL, Wang GY (2015) Spatial point pattern analysis of Abies georgei var. smithii in forest of Sygera Mountains in southeast Tibet, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26, 1617-1624. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [解传奇, 田民霞, 赵忠瑞, 郑维列, 王国严 (2015) 西藏色季拉山急尖长苞冷杉种群点格局分析. 应用生态学报, 26, 1617-1624.] | |
| [38] | Xu LN, Jin GZ (2012) Species composition and community structure of a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) forest plot in Liangshui Nature Reserve, Northeast China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 470-481. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐丽娜, 金光泽 (2012) 小兴安岭凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地: 物种组成与群落结构. 生物多样性, 20, 470-481.] | |
| [39] | Yang YC, Yuan XZ, Li BZ, Sun R, Wang Q (2007) Characteristics and significance of the remnant evergreen broad-leaved forest in the urban area of Chongqing, China. Biodiversity Science, 15, 247-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨永川, 袁兴中, 李百战, 孙荣, 王强 (2007) 重庆都市区残存常绿阔叶林的群落特征及其意义. 生物多样性, 15, 247-256.] | |
| [40] | Yao XH, Ye QG, Ge JW, Kang M, Huang HW (2007) A new species of Sinojackia (Styracaceae) from Hubei, Central China. Novon, 17, 138-140. |
| [41] | Zhang JJ, Ye QG, Gao PX, Yao XH (2012) Genetic footprints of habitat fragmentation in the extant populations of Sinojackia (Styracaceae): Implications for conservation. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 170, 232-242. |
| [42] | Zhang JJ, Ye QG, Yao XH, Zhang SJ, Huang HW (2008) Preliminary studies on the floral biology, breeding system and reproductive success of Sinojackia huangmeiensis, an endangered plant in a fragmented habitat in Hubei Province, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 32, 743-750. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张金菊, 叶其刚, 姚小洪, 张胜菊, 黄宏文 (2008) 片断化生境中濒危植物黄梅秤锤树的开花生物学、繁育系统与生殖成功的因素. 植物生态学报, 32, 743-750.] | |
| [43] | Zhang YT, Li JM, Chang SL, Li X, Lu JJ (2011) Spatial distribution pattern of Picea schrenkiana var. tianshanica population and its relationships with topographic factors in middle part of Tianshan Mountain. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22, 2799-2806. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张毓涛, 李吉玫, 常顺利, 李翔, 芦建江 (2011) 天山中部天山云杉种群空间分布格局及其与地形因子的关系. 应用生态学报, 22, 2799-2806.] | |
| [44] | Zhang Z, Liu P, Ding Y, Liu LM (2010) Distribution patterns of Picea schrenkiana var. tianshanica populations at different developmental stages in the western Tianshan Mountain, northwestern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 32(3), 75-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张震, 刘萍, 丁易, 刘黎明 (2010) 天山云杉林不同发育阶段种群分布格局研究. 北京林业大学学报, 32(3), 75-79.] | |
| [45] | Zhao J, Tong Y, Ge T, Ge J (2016) Genetic diversity estimation and core collection construction of Sinojackia huangmeiensis based on novel microsatellite markers. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 64, 74-80. |
| [46] | Zhou SX, Jiang MX, Bao DC, Tao M, Huang HD (2011) Population structure and regenerative characteristics of major tree species of rare plant community in Houhe Nature Reserve. Guihaia, 31, 209-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周赛霞, 江明喜, 鲍大川, 陶敏, 黄汉东 (2011) 后河自然保护区珍稀植物群落结构及更新特性. 广西植物, 31, 209-216.] | |
| [47] | Zhu Y (2009) The Prevalence of Density Dependence in Gutianshan Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaved Forest, China. PhD dissertation, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祝燕 (2009) 古田山亚热带常绿阔叶林密度制约普遍性研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院植物研究所, 北京.] | |
| [48] | Zhu Y, Bai F, Liu HF, Li WC, Li L, Li GQ, Wang SZ, Sang WG (2011) Population distribution patterns and interspecific spatial associations in warm temperate secondary forests, Beijing. Biodiversity Science, 19, 252-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祝燕, 白帆, 刘海丰, 李文超, 李亮, 李广起, 王顺忠, 桑卫国 (2011) 北京暖温带次生林种群分布格局与种间空间关联性. 生物多样性, 19, 252-259.] |
| [1] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [2] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [3] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [4] | 林迪, 陈双林, 杜榷, 宋文龙, 饶固, 闫淑珍. 大别山黏菌的物种多样性调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [5] | 姚嘉, 张聪伶, 李时轩, 林阳, 王震, 张煜涵, 周伟龙, 潘心禾, 朱珊, 吴逸卿, 王丹, 刘金亮, 谭珊珊, 沈国春, 于明坚. 百山祖连续海拔样带植物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [6] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [7] | 王明慧, 陈昭铨, 李帅锋, 黄小波, 郎学东, 胡子涵, 尚瑞广, 刘万德. 云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林不同种子扩散方式的优势种空间点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [8] | 陈哲涵, 尹进, 叶吉, 刘冬伟, 毛子昆, 房帅, 蔺菲, 王绪高. 增温对东北温带次生林草本群落季节动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [9] | 杨涛, 沈泽昊, 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘倩, 钱恒君, 解宇阳, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 张玉坤, 侯波, 李建斌, 欧晓昆. 滇中高原亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| [10] | 王晓凤, 米湘成, 王希华, 江明喜, 杨涛, 张健, 沈泽昊. 中国中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23296-. |
| [11] | 刘文聪, 田希, 杨涛, 饶杰生, 王晓凤, 钱恒君, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林优势树种的种群结构与更新特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23251-. |
| [12] | 李正飞, 蒋小明, 王军, 孟星亮, 张君倩, 谢志才. 雅鲁藏布江中下游底栖动物物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21431-. |
| [13] | 孙哲明, 刘亚恒, 彭秋桐, 徐芷妍, 杨予静, 欧文慧, 李中强. 湖北省极小种群野生植物在原生群落中的竞争地位及保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21517-. |
| [14] | 鲁梦珍, 曾馥平, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 苏樑, 刘坤平, 谭卫宁, 杜虎. 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林死亡个体空间分布格局及生境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21340-. |
| [15] | 赵琦, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 金清, 李佳丽, 邱江平. 海南岛蚯蚓物种组成及其系统发育分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22224-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn