



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 1204-1211. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018044 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018044
收稿日期:2018-03-08
接受日期:2018-07-04
出版日期:2018-11-20
发布日期:2019-01-08
通讯作者:
董志军
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Qingqing Liu1,2, Zhijun Dong1,3,*( )
)
Received:2018-03-08
Accepted:2018-07-04
Online:2018-11-20
Published:2019-01-08
Contact:
Dong Zhijun
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
钩手水母(Gonionemus vertens)为大西洋和太平洋广布种, 是我国习见的有毒水母种类之一。本文对采自黄渤海海域4个地理群体的104个钩手水母线粒体COI基因序列进行扩增, 并结合GenBank上其他182个钩手水母同源序列进行序列变异分析。在286个基因序列中共检测出52个多态位点, 定义了14种单倍型。总群体的单倍型多样性和核苷酸多样性分别为0.743 ± 0.012和1.046% ± 0.097%, 与其他几种大型水母相比, 钩手水母总群体的遗传多样性处于较高水平。AMOVA结果显示, 60.17%的分子变异源于群组间, 13.37%的分子变异源于群体内, 26.46%的分子变异源于组内群体间, 群组间、群体内和组内群体间的遗传分化均极显著。Fst值统计检验表明, 中国厦门群体与乐亭、东营、烟台、大连群体间存在显著的遗传分化, 大连与东营、烟台群体间也存在显著的遗传分化。系统分析结果显示, 钩手水母群体间存在2个明显的单倍型谱系分支。不同的钩手水母地理群体间具有复杂的遗传模式, 钩手水母复杂的生活史、扩散能力、地理隔离和海流分布可能是影响钩手水母遗传结构的重要因素。
刘青青, 董志军 (2018) 基于线粒体COI基因分析钩手水母的群体遗传结构. 生物多样性, 26, 1204-1211. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018044.
Qingqing Liu, Zhijun Dong (2018) Population genetic structure of Gonionemus vertens based on the mitochondrial COI sequence. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1204-1211. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018044.
| 采样点 Site | 样本量 N | 单倍型 H | 单倍型组成(样本数) Haplotype composition (No. of inds.) | 单倍型多样性 Hd | 核苷酸多样性 π (%) | GenBank序列号 GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西北大西洋 Northwest Atlantic (NWA) | ||||||
| 美国新罕布什尔州大海湾 Great Bay, New Hampshire, America (GB) | 7 | 2 | Hap1(3); Hap14(4) | 0.571 ± 0.119 | 0.912 ± 0.191 | KY437905-911 |
| 美国雅茅斯巴斯河 Bass River, Yarmouth, America (BR) | 17 | 3 | Hap1(2); Hap12(12); Hap14(3) | 0.485 ± 0.126 | 1.004 ± 0.270 | KY437888-904 |
| 美国马什皮汉布林池塘 Hamblin Pond, Mashpee, America (HP) | 18 | 1 | Hap12(18) | 0 | 0 | KY437834-851 |
| 美国奥克布拉夫斯农场池塘 Farm Pond, Oak Bluffs, America (FP) | 17 | 2 | Hap1(1); Hap12(16) | 0.118 ± 0.101 | 0.164 ± 0.141 | KY437814-830 |
| 美国埃德加敦森格肯塔克池塘 Sengekontacket Pond, Edgartown, America (SG) | 3 | 2 | Hap1(2); Hap12(1) | 0.667 ± 0.314 | 0.931 ± 0.439 | KY437831-833 |
| 美国北金斯敦波特池塘 Potter Pond, North Kingston, America (PP) | 22 | 2 | Hap1(2); Hap12(20) | 0.173 ± 0.101 | 0.242 ± 0.141 | KY437912-933 |
| 美国格罗顿芒福德湾 Mumford Cove, Groton, America (MC) | 14 | 2 | Hap1(13); Hap12(1) | 0.143 ± 0.119 | 0.200 ± 0.166 | KY437934-947 |
| 美国格罗顿松岛 Pine Island, Groton, America (PI) | 24 | 2 | Hap1(23); Hap12(1) | 0.083 ± 0.075 | 0.116 ± 0.105 | KY437864-887 |
| 西北太平洋 Northwest Pacific (NWP) | ||||||
| 俄罗斯阿穆尔湾 Amur Bay, Peter the Great Gulf, Russia (AB) | 3 | 1 | Hap1(3) | 0 | 0 | KY437948-950 |
| 俄罗斯沃斯托克湾 Vostok Bay, Peter the Great Gulf, Russia (VB) | 30 | 2 | Hap1(26); Hap11(4) | 0.239 ± 0.092 | 0.048 ± 0.018 | KY437951-980 |
| 日本越喜来湾 Okirai Bay, Japan (JP) | 12 | 2 | Hap1(1); Hap2(11) | 0.167 ± 0.134 | 0.100 ± 0.080 | KY437852-863 |
| 中国厦门 Xiamen, China (XM) | 10 | 1 | Hap10(10) | 0 | 0 | KF962130-139 |
| 中国烟台 Yantai, China (YT) | 27 | 5 | Hap2(23); Hap3(1); Hap4(1); Hap8(1); Hap9(1) | 0.279 ± 0.112 | 0.148 ± 0.095 | MH020717-743 |
| 中国大连 Dalian, China (DL) | 30 | 4 | Hap1(6); Hap2(19); Hap5(4); Hap6(1) | 0.559 ± 0.086 | 0.307 ± 0.058 | MH020640-669 |
| 中国东营 Dongying, China (DY) | 18 | 1 | Hap2(18) | 0 | 0 | MH020670-687 |
| 中国乐亭 Laoting, China (LT) | 29 | 3 | Hap1(2); Hap2(25); Hap7(2) | 0.256 ± 0.102 | 0.106 ± 0.050 | MH020688-716 |
| 东北太平洋 Northeast Pacific (NEP) | ||||||
| 美国圣胡安岛 San Juan Island, America (FH) | 4 | 1 | Hap13(4) | 0 | 0 | KY437982-985 |
| 东北大西洋 Northeast Atlantic (NEA) | ||||||
| 冰岛阿夫塔内斯 Álftanes, Iceland (IC) | 1 | 1 | Hap13(1) | 0 | 0 | KY437981 |
| 总群体 Total | - | 286 | 14 | - | 0.743 ± 0.012 | 1.046 ± 0.097 |
表1 钩手水母样本信息及遗传多样性指数
Table 1 Locations, number of individuals and diversity parameters for the population of Gonionemus vertens
| 采样点 Site | 样本量 N | 单倍型 H | 单倍型组成(样本数) Haplotype composition (No. of inds.) | 单倍型多样性 Hd | 核苷酸多样性 π (%) | GenBank序列号 GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西北大西洋 Northwest Atlantic (NWA) | ||||||
| 美国新罕布什尔州大海湾 Great Bay, New Hampshire, America (GB) | 7 | 2 | Hap1(3); Hap14(4) | 0.571 ± 0.119 | 0.912 ± 0.191 | KY437905-911 |
| 美国雅茅斯巴斯河 Bass River, Yarmouth, America (BR) | 17 | 3 | Hap1(2); Hap12(12); Hap14(3) | 0.485 ± 0.126 | 1.004 ± 0.270 | KY437888-904 |
| 美国马什皮汉布林池塘 Hamblin Pond, Mashpee, America (HP) | 18 | 1 | Hap12(18) | 0 | 0 | KY437834-851 |
| 美国奥克布拉夫斯农场池塘 Farm Pond, Oak Bluffs, America (FP) | 17 | 2 | Hap1(1); Hap12(16) | 0.118 ± 0.101 | 0.164 ± 0.141 | KY437814-830 |
| 美国埃德加敦森格肯塔克池塘 Sengekontacket Pond, Edgartown, America (SG) | 3 | 2 | Hap1(2); Hap12(1) | 0.667 ± 0.314 | 0.931 ± 0.439 | KY437831-833 |
| 美国北金斯敦波特池塘 Potter Pond, North Kingston, America (PP) | 22 | 2 | Hap1(2); Hap12(20) | 0.173 ± 0.101 | 0.242 ± 0.141 | KY437912-933 |
| 美国格罗顿芒福德湾 Mumford Cove, Groton, America (MC) | 14 | 2 | Hap1(13); Hap12(1) | 0.143 ± 0.119 | 0.200 ± 0.166 | KY437934-947 |
| 美国格罗顿松岛 Pine Island, Groton, America (PI) | 24 | 2 | Hap1(23); Hap12(1) | 0.083 ± 0.075 | 0.116 ± 0.105 | KY437864-887 |
| 西北太平洋 Northwest Pacific (NWP) | ||||||
| 俄罗斯阿穆尔湾 Amur Bay, Peter the Great Gulf, Russia (AB) | 3 | 1 | Hap1(3) | 0 | 0 | KY437948-950 |
| 俄罗斯沃斯托克湾 Vostok Bay, Peter the Great Gulf, Russia (VB) | 30 | 2 | Hap1(26); Hap11(4) | 0.239 ± 0.092 | 0.048 ± 0.018 | KY437951-980 |
| 日本越喜来湾 Okirai Bay, Japan (JP) | 12 | 2 | Hap1(1); Hap2(11) | 0.167 ± 0.134 | 0.100 ± 0.080 | KY437852-863 |
| 中国厦门 Xiamen, China (XM) | 10 | 1 | Hap10(10) | 0 | 0 | KF962130-139 |
| 中国烟台 Yantai, China (YT) | 27 | 5 | Hap2(23); Hap3(1); Hap4(1); Hap8(1); Hap9(1) | 0.279 ± 0.112 | 0.148 ± 0.095 | MH020717-743 |
| 中国大连 Dalian, China (DL) | 30 | 4 | Hap1(6); Hap2(19); Hap5(4); Hap6(1) | 0.559 ± 0.086 | 0.307 ± 0.058 | MH020640-669 |
| 中国东营 Dongying, China (DY) | 18 | 1 | Hap2(18) | 0 | 0 | MH020670-687 |
| 中国乐亭 Laoting, China (LT) | 29 | 3 | Hap1(2); Hap2(25); Hap7(2) | 0.256 ± 0.102 | 0.106 ± 0.050 | MH020688-716 |
| 东北太平洋 Northeast Pacific (NEP) | ||||||
| 美国圣胡安岛 San Juan Island, America (FH) | 4 | 1 | Hap13(4) | 0 | 0 | KY437982-985 |
| 东北大西洋 Northeast Atlantic (NEA) | ||||||
| 冰岛阿夫塔内斯 Álftanes, Iceland (IC) | 1 | 1 | Hap13(1) | 0 | 0 | KY437981 |
| 总群体 Total | - | 286 | 14 | - | 0.743 ± 0.012 | 1.046 ± 0.097 |
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 d.f. | 平方和 Sum of squares | 方差比例 % of variation | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群组间 Among groups | 3 | 362.274 | 60.17 | Fsc = 0.66436 | 0.0000 |
| 组内群体间 Among populations within groups | 14 | 247.509 | 26.46 | Fst = 0.86631 | 0.0000 |
| 群体内 Within populations | 268 | 136.735 | 13.37 | Fct = 0.60168 | 0.0002 |
| 总计 Total | 285 | 746.517 | 100 |
表2 钩手水母群体分子变异的空间方差分析
Table 2 Spatial analysis of molecular variance among population of Gonionemus vertens
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 d.f. | 平方和 Sum of squares | 方差比例 % of variation | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群组间 Among groups | 3 | 362.274 | 60.17 | Fsc = 0.66436 | 0.0000 |
| 组内群体间 Among populations within groups | 14 | 247.509 | 26.46 | Fst = 0.86631 | 0.0000 |
| 群体内 Within populations | 268 | 136.735 | 13.37 | Fct = 0.60168 | 0.0002 |
| 总计 Total | 285 | 746.517 | 100 |
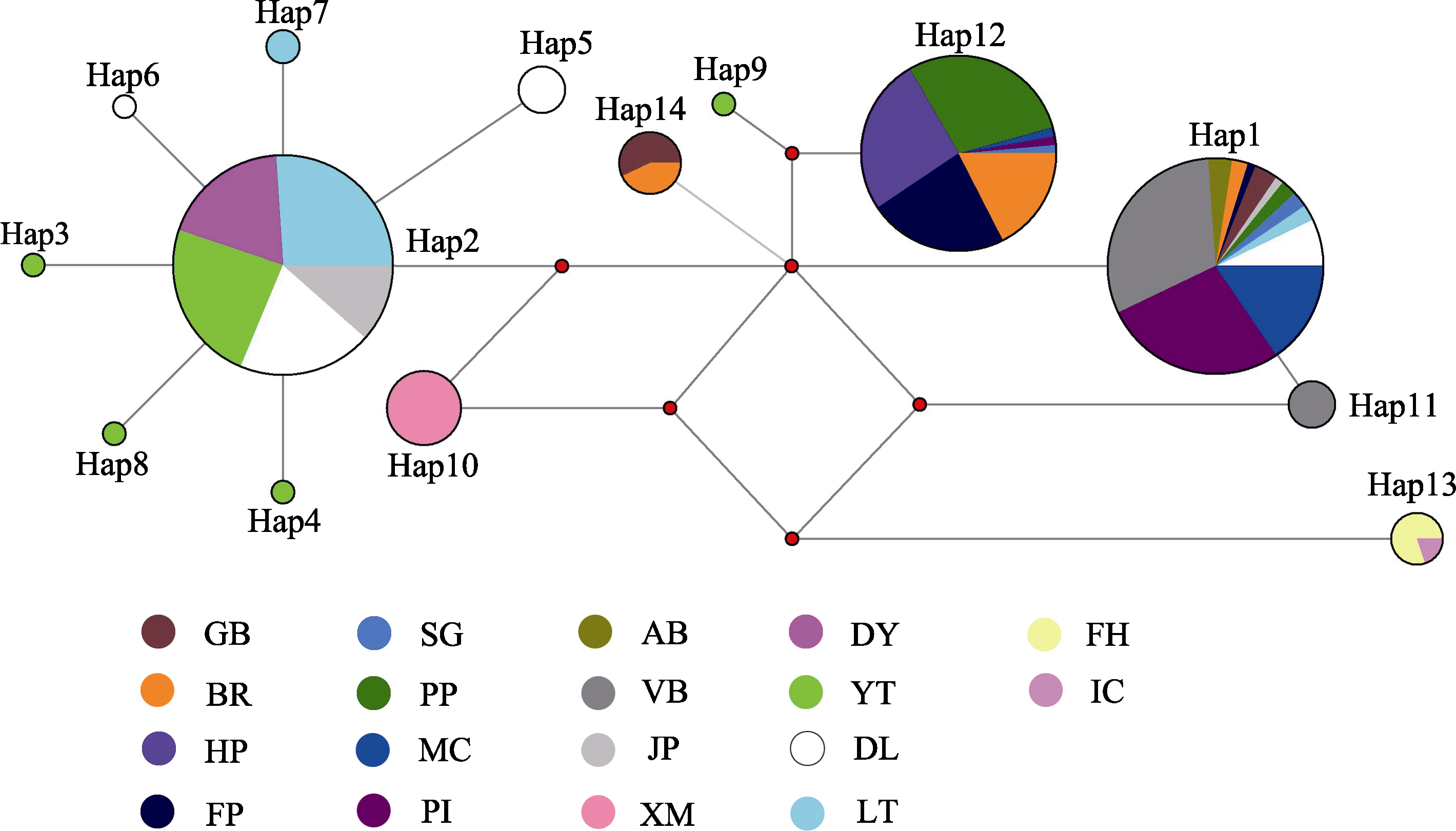
图3 基于COI基因的钩手水母单倍型的中介网络图。彩色扇形面积表示各样品群体在同一单倍型中所占的比例; 圆面积表示单倍型出现频率; 红色圆点代表中间突变节点。图中采样点简称与表1一致。
Fig. 3 Median-joining haplotype network of Gonionemus vertens based on the combined sequence of COI. The color fan area indicates the proportion of each sample population in the same haplotype; the circle area indicates the frequency of haplotype occurrence; the red dot represents the intermediate mutation node. The abbreviation of the sampling points in the figure is consistent with Table 1.
| [5] | Dawson MN, Gupta AS, England MH (2005) Coupled biophysical global ocean model and molecular genetic analyses identify multiple introductions of cryptogenic species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 11968-11973. |
| [6] | Dong ZJ, Liu ZY, Liu DY (2015) Genetic characterization of the scyphozoan jellyfish Aurelia spp. in Chinese coastal waters using mitochondrial markers. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 60, 15-23. |
| [7] | Dong ZJ, Liu ZY, Liu DY, Liu QQ, Sun TT (2016) Low genetic diversity and lack of genetic structure in the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai in Chinese coastal waters. Marine Biology Research, 12, 769-775. |
| [8] | Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Molecular Ecology Resources, 10, 564-567. |
| [9] | Govindarajan AF, Boero F, Halanych KM (2006) Phylogenetic analysis with multiple markers indicates repeated loss of the adult medusa stage in Campanulariidae (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 38, 820-834. |
| [10] | Govindarajan AF, Carman MR, Khaidarov MR, Semenchenko A, Wares JP (2017) Mitochondrial diversity in Gonionemus (Trachylina: Hydrozoa) and its implications for understanding the origins of clinging jellyfish in the Northwest Atlantic Ocean. PeerJ, 5, e3205. |
| [11] | Hall BG (2004) Comparison of the accuracies of several phylogenetic methods using protein and DNA sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 22, 792-802. |
| [12] | Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95-98. |
| [13] | Harrison JS (2004) Evolution, biogeography, and the utility of mitochondrial 16S and COI genes in phylogenetic analysis of the crab genus Austinixa (Decapoda: Pinnotheridae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 30, 743-754. |
| [14] | Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 270, 313-321. |
| [15] | Jiang HC, Liu N, Gao JQ, Su B, Li JH, He JL, Liu AY (2017) Zooplankton community structure in Sishili Bay and its relationship with environmental factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 1318-1327. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜会超, 刘宁, 高继庆, 苏博, 李佳蕙, 何健龙, 刘爱英 (2017) 烟台四十里湾浮游动物群落特征及与环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 37, 1318-1327.] | |
| [16] | Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870-1874. |
| [17] | Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics, 25, 1451-1452. |
| [18] | Li YL, Dong J, Wang B, Li YP, Yu XG, Fu J, Wang WB (2016) Genetic characterization of different populations of Rhopilema esculentum based on the mitochondrial COI sequence. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 2340-2347. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李玉龙, 董婧, 王彬, 李轶平, 于旭光, 付杰, 王文波 (2016) 基于线粒体COI基因的海蜇不同地理群体遗传特征. 应用生态学报, 27, 2340-2347.] | |
| [19] | Li YL, Kong XY, Yu ZN, Kong J, Ma S, Chen LM (2009) Genetic diversity and historical demography of Chinese shrimp Feneropenaeus chinensis in Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea based on mitochondrial DNA analysis. African Journal of Biotechnology, 8, 1193-1202. |
| [20] | Neigel JE, Avise JC (1993) Application of a random walk model to geographic distributions of animal mitochondrial DNA variation. Genetics, 135, 1209-1220. |
| [21] | Nylander JAA, Olsson U, Alström P, Sanmartín I (2008) Accounting for phylogenetic uncertainty in biogeography: A Bayesian approach to dispersal-vicariance analysis of the thrushes (Aves: Turdus). Systematic Biology, 57, 257-268. |
| [22] | Palumbi SR (1994) Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, and marine speciation. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 25, 547-572. |
| [23] | Pigulevsky SV, Michaleff PV (1969) Poisoning by the medusa Gonionemus vertens in the sea of Japan. Toxicon, 7, 145-149. |
| [24] | Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Van Der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Hohna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539-542. |
| [25] | Stabile J, Waldman JR, Parauka F, Wirgin I (1996) Stock structure and homing fidelity in Gulf of Mexico sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi) based on restriction fragment length polymorphism and sequence analyses of mitochondrial DNA. Genetics, 144, 767-775. |
| [26] | Stopar K, Ramšak A, Trontelj P, Malej A (2010) Lack of genetic structure in the jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa: Semaeostomeae) across European seas. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 57, 417-428. |
| [27] | Tian JL (1987) Preliminary exploration of Gonionemus vertens in the sea of Jiaozhou Bay. Journal of Biology, 15, 17-18. (in Chinese) |
| [田金良 (1987) 胶州湾钩手水母初探. 生物学杂志, 15, 17-18.] | |
| [28] | Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 3, 294-299. |
| [29] | Ward RD, Woodwark M, Skibinskid OF (1994) A comparison of genetic diversity levels in marine, freshwater, and anadromous fishes. Journal of Fish Biology, 44, 213-232. |
| [30] | Wright S (1943) Isolation by distance. Genetics, 28, 114. |
| [31] | Wright S (1949) The genetical structure of populations. Annals of Human Genetics, 15, 323-354. |
| [32] | Yakovlev YM, Vaskovsky VE (1993) The toxic krestovik medusa Gonionemus vertens. Russian Journal of Marine Biology, 19, 287-294. |
| [33] | Zhang DN, Zheng LM, He JR, Zhang WJ, Lin YS, Li Y (2015) DNA barcoding of hydromedusae in northern Beibu Gulf for species identification. Biodiversity Science, 23, 50-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张珰妮, 郑连明, 何劲儒, 张文静, 林元烧, 李阳 (2015) 基于线粒体COI和16S片段序列的北部湾北部水螅水母 DNA 条形码分析. 生物多样性, 23, 50-60.] | |
| [34] | Zhao M, Song W, Ma CY, Zhang FY, Jiang KJ, Song ZM, Ma LB (2015) Population genetic structure of Collichthys lucidus based on the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I sequence. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 22, 233-242. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Avise JC, Neigel JE, Arnold J (1984) Demographic influences on mitochondrial DNA lineage survivorship in animal populations. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 20, 99-105. |
| [2] | Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37-48. |
| [3] | Brown WM, George M, Wilson AC (1979) Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 76, 1967-1971. |
| [4] | Cheng FP, Wang MX, Wang YT, Zhang F, Li CL, Sun S (2012) DNA barcoding of common medusozoa in northern China based on mtCOI sequence. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 43, 451-459. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | [赵明, 宋炜, 马春艳, 张凤英, 蒋科技, 宋志明, 马凌波 (2015) 基于线粒体COI基因序列的棘头梅童鱼7个野生群体遗传结构分析. 中国水产科学, 22, 233-242.] |
| [4] | [程方平, 王敏晓, 王彦涛, 张芳, 李超伦, 孙松 (2012) 中国北方习见水母类的DNA条形码分析. 海洋与湖沼, 43, 451-459.] |
| [1] | 罗小燕, 李强, 黄晓磊. 戴云山国家级自然保护区访花昆虫DNA条形码数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23236-. |
| [2] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [3] | 吴帆, 刘深云, 江虎强, 王茜, 陈开威, 李红亮. 中华蜜蜂和意大利蜜蜂秋冬期传粉植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22528-. |
| [4] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [5] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [6] | 俞正森, 宋娜, 本村浩之, 高天翔. 中国银口天竺鲷属鱼类的分类厘定[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 971-979. |
| [7] | 胡芮, 王儒晓, 杜诗雨, 李萌, 邢雨辉, 潘达, 徐海根, 孙红英. 扬州宝应湖底栖大型无脊椎动物的生物多样性及其变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1558-1569. |
| [8] | 翁茁先, 黄佳琼, 张仕豪, 余锴纯, 钟福生, 黄勋和, 张彬. 利用线粒体COI基因揭示中国乌骨鸡遗传多样性和群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 667-676. |
| [9] | 邵昕宁, 宋大昭, 黄巧雯, 李晟, 姚蒙. |
| [10] | 刘山林. DNA条形码参考数据集构建和序列分析相关的新兴技术[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(5): 526-533. |
| [11] | 侯勤曦, 慈秀芹, 刘志芳, 徐武美, 李捷. 基于DNA条形码评估西双版纳国家级自然保护区对樟科植物进化历史的保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 217-228. |
| [12] | 武星彤, 陈璐, 王敏求, 张原, 林雪莹, 李鑫玉, 周宏, 文亚峰. 丹霞梧桐群体遗传结构及其遗传分化[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1168-1179. |
| [13] | 郝金凤, 张晓红, 王昱淞, 刘金林, 智永超, 李新江. 白洋淀湿地蝗虫多样性调查及DNA条形码应用研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(4): 409-417. |
| [14] | 慈秀芹, 李捷. 系统发育多样性在植物区系研究与 生物多样性保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(2): 175-181. |
| [15] | 魏亚男, 王晓梅, 姚鹏程, 陈小勇, 李宏庆. 比较不同DNA条形码对中国海岸带耐盐植物的识别率[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(10): 1095-1104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn