



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1095-1104. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017164 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017164
所属专题: 物种形成与系统进化
魏亚男1, 王晓梅1, 姚鹏程1, 陈小勇2, 李宏庆1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-06-02
接受日期:2017-08-30
出版日期:2017-10-20
发布日期:2018-05-05
通讯作者:
李宏庆
基金资助:
Ya’nan Wei1, Xiaomei Wang1, Pengcheng Yao1, Xiaoyong Chen2, Hongqing Li1,*( )
)
Received:2017-06-02
Accepted:2017-08-30
Online:2017-10-20
Published:2018-05-05
Contact:
Li Hongqing
摘要:
海岸带耐盐植物是一个生态和经济价值独特的庞杂类群, 人们对其DNA条形码特性的了解甚少。本文对我国从辽宁到海南10个沿海省(市)大陆及岛屿海岸带耐盐植物广泛采样, 从采集获得的样品中筛选出53科97属116个物种共562个样品进行DNA条形码研究。对3个叶绿体片段(matK、rbcL、trnH-psbA)和1个核基因片段(ITS)进行了扩增和测序, 统计各个片段的引物通用性和序列获得率, 并检验了物种识别率。从序列获得率来看, matK和trnH-psbA片段表现最好, ITS较差, ITS和matK的引物通用性比其他2个片段差。序列相似性分析表明, 单个片段ITS物种识别率最高(73.36%), 其次为matK (64.03%)和trnH-psbA (61.21%), rbcL的物种识别率最低, 仅为46.41%。系统发育树分析显示matK的物种识别率最高(82.3%), 依据trnH-psbA片段难以获得可靠的系统发育树。多维度非度量分析(non-metric multidimensional scaling, NMDS)表明在进行海岸带区域性植物的DNA条形码研究时, 叶绿体片段和核基因片段均应该考虑。综合上述研究结果, 推荐联合片段ITS + matK作为中国海岸带耐盐植物DNA条形码。本文为海岸带耐盐植物研究提供了总计1,939条DNA条形码基础数据, 为构建耐盐植物DNA条形码数据库奠定了基础。
魏亚男, 王晓梅, 姚鹏程, 陈小勇, 李宏庆 (2017) 比较不同DNA条形码对中国海岸带耐盐植物的识别率. 生物多样性, 25, 1095-1104. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017164.
Ya’nan Wei, Xiaomei Wang, Pengcheng Yao, Xiaoyong Chen, Hongqing Li (2017) Comparison of species resolution rates of DNA barcoding for Chinese coastal halo-tolerant plants. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1095-1104. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017164.
| 片段名称 Locus | 获得序列数 Species resolution rate | 序列获得率 Sequence availability | 测序成功物 种数 Species successfully sequenced | 片段长度 Fragment length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | 481 | 85.59% | 106 | 304-632 |
| matK | 502 | 89.32% | 116 | 611-721 |
| rbcL | 465 | 83.04% | 109 | 371-650 |
| trnH-psbA | 491 | 87.36% | 116 | 142-907 |
表1 序列获得率及片段长度
Table 1 Summary of the sequencing success rate and length of candidate barcoding fragments
| 片段名称 Locus | 获得序列数 Species resolution rate | 序列获得率 Sequence availability | 测序成功物 种数 Species successfully sequenced | 片段长度 Fragment length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | 481 | 85.59% | 106 | 304-632 |
| matK | 502 | 89.32% | 116 | 611-721 |
| rbcL | 465 | 83.04% | 109 | 371-650 |
| trnH-psbA | 491 | 87.36% | 116 | 142-907 |
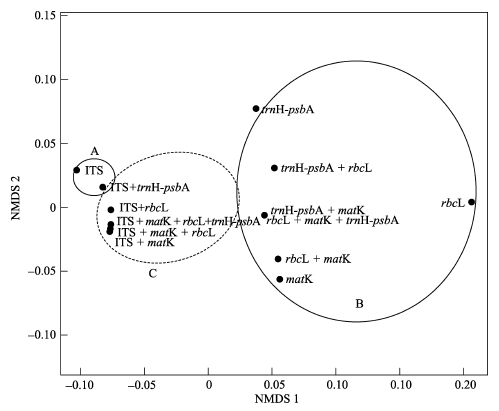
图4 候选DNA条形码片段的NMDS分析(Stress值: 0.011)
Fig. 4 Multivariate analysis of non-metric multidimensional scaling for the four barcode markers NMDS. Stress value: 0.011.
| [1] | Adoukonou-Sagbadja H, Wagner C, Ordon F, Friedt W (2010) Reproductive system and molecular phylogenetic relationships of fonio millets (Digitaria spp., Poaceae) with some polyploid wild relatives. Tropical Plant Biology, 3, 240-251. |
| [2] | Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology, 215, 403-410. |
| [3] | Alves TLS, Chauveau O, Eggers L, de Souza-Chies TT (2014) Species discrimination in Sisyrinchium (Iridaceae): assessment of DNA barcodes in a taxonomically challenging genus. Molecular Ecology Resources, 14, 324-335. |
| [4] | Bafeel SO, Arif IA, Al-Homaidan AA, Khan HA (2012) Assessment of DNA barcoding for the identification of Chenopodium murale L. (Chenopodiaceae). International Journal of Biology, 4, 66-74. |
| [5] | Barthet MM, Hilu KW (2007) Expression of matK: functional and evolutionary implications. American Journal of Botany, 94, 1402-1412. |
| [6] | Baumel A, Ainouche ML, Levasseur J (2001) Molecular investigations in populations of Spartina anglica C. E. Hubbard (Poaceae) invading coastal Brittany (France). Molecular Ecology, 10, 1689-1701. |
| [7] | Bera B, Das S, Mukherjee K (1993) Morphological studies on three cytotypes of Chenopodium album L. of Lower Gangetic Plains, West Bengal, India. Phytomorphology, 43(1-2), 93-103. |
| [8] | Braukmann TWA, Kuzmina ML, Sills J, Zakharov EV, Hebert PDN (2017) Testing the efficacy of DNA barcodes for identifying the vascular plants of Canada. PLoS ONE, 12, e0169515. |
| [9] | Burgess KS, Fazekas AJ, Kesanakurti PR, Graham SW, Husband BC, Newmaster SG, Percy DM, Hajibabaei M (2011) Discriminating plant species in a local temperate flora using the rbcL+matK DNA barcode. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2, 333-340. |
| [10] | Burland TG (2000) DNASTAR’s lasergene sequence analysis software.In: Methods in Molecular Biology (ed. Walker JM), pp. 71-91.Humana Press, New Jersey. |
| [11] | CBOL Plant Working Group (2009) A DNA barcode for land plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 12794-12797. |
| [12] | Chase MW, Cowan RS, Hollingsworth PM, van den Berg C, Madriñán S, Petersen G, Seberg O, Jørgsensen T, Cameron KM, Carine M, Pedersen N, Hedderson TAJ, Conrad F, Salazar GA, Richardson JE, Hollingsworth ML, Barraclough TG, Kelly L, Wilkinson M (2007) A proposal for a standardised protocol to barcode all land plants. Taxon, 56, 295-299. |
| [13] | Chase MW, Salamin N, Wilkinson M, Dunwell JM, Kesanakurthi RP, Haidar N, Savolainen V (2005) Land plants and DNA barcodes: short-term and long-term goals. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society: Biological Sciences, 360, 1889-1895. |
| [14] | Chen XL, An SQ, Li GQ, Cheng XL, Zhang JL, Shen BQ (1999) The economic salt-tolerant plant resources on the coastal zone of China. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 23(4), 81-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈兴龙, 安树青, 李国旗, 程晓莉, 张纪林, 沈邦勤 (1999) 中国海岸带耐盐经济植物资源. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 23(4), 81-84.] | |
| [15] | China Plant BOL Group (2011) Comparative analysis of a large dataset indicates that internal transcribed spacer (ITS) should be incorporated into the core barcode for seed plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 19641-19646. |
| [16] | Chu GL, Sergei LM, Steven EC (2003) Chenopodiaceae. In: Flora of China (eds Wu ZY, Raven PH), pp. 351-414. Science Press, Beijing & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [17] | Costion C, Ford A, Cross H, Crayn D, Harrington M, Lowe A (2011) Plant DNA barcodes can accurately estimate species richness in poorly known floras. PLoS ONE, e26841. |
| [18] | Cuénoud P, Savolainen V, Chatrou LW, Powell M, Grayer RJ, Chase MW (2002) Molecular phylogenetics of Caryophyllales based on nuclear 18S rDNA and plastid rbcL, atpB, and matK DNA sequences. American Journal of Botany, 89, 132-144. |
| [19] | De Vere N, Rich TC, Ford CR, Trinder SA, Long C, Moore CW, Satterthwaite D, Davies H, Allainguillaume J, Ronca S, Tatarinova T, Garbett H, Walker K, Wilkinson MJ (2012) DNA barcoding the native flowering plants and conifers of Wales. PLoS ONE, 7, e37945. |
| [20] | De Vere N, Rich TC, Trinder SA, Long C (2015) DNA barcoding for plants. In: Methods in Molecular Biology (ed. Walker JM), pp. 101-118.Humana Press,New Jersey. |
| [21] | Dong W, Liu J, Yu J, Wang L, Zhou S (2012) Highly variable chloroplast markers for evaluating plant phylogeny at low taxonomic levels and for DNA barcoding. PLoS ONE, 7, e35071. |
| [22] | Ebihara A, Nitta JH, Ito M (2010) Molecular species identification with rich floristic sampling: DNA barcoding the pteridophyte flora of Japan. PLoS ONE, 5, e15136. |
| [23] | Gedan KB, Altieri AH, Bertness MD (2011) Uncertain future of New England salt marshes. Marine Ecology Progress, 434, 229-237. |
| [24] | Gonzalez MA, Baraloto C, Engel J, Mori SA, Pétronelli P, Riéra B, Roger A, Thébaud C, Chave J (2009) Identification of Amazonian trees with DNA barcodes. PLoS ONE, 4, e7483. |
| [25] | Hamilton MB, Braverman JM, Soria-Hernanz DF (2003) Patterns and relative rates of nucleotide and insertion/deletion evolution at six chloroplast intergenic regions in new world species of the Lecythidaceae. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 20, 1710-1721. |
| [26] | Hebert PD, Cywinska A, Ball SL (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 270, 313-321. |
| [27] | Hollingsworth PM (2011) Refining the DNA barcode for land plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 19451-19452. |
| [28] | Hollingsworth PM, Graham SW, Little DP (2011) Choosing and using a plant DNA barcode. PLoS ONE, 6, e19254. |
| [29] | Ito Y, Ohi-Toma T, Murata J, Tanaka N (2010) Hybridization and polyploidy of an aquatic plant, Ruppia (Ruppiaceae), inferred from plastid and nuclear DNA phylogenies. American Journal of Botany, 97, 1156-1167. |
| [30] | Khalaf MA, Kochzius M (2002) Changes in trophic community structure of shore fishes at an industrial site in the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 239, 287-299. |
| [31] | Kress WJ, Erickson DL, Jones FA, Swenson NG, Perez R, Sanjur O, Bermingham E (2009) Plant DNA barcodes and a community phylogeny of a tropical forest dynamics plot in Panama. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 18621-18626. |
| [32] | Kress WJ, Garcia-Robiedo C, Uriarte M, Erickson DL (2015) DNA barcodes for ecology, evolution, and conservation. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 30, 25-35. |
| [33] | Kress WJ, Wurdack KJ, Zimmer EA, Weigt LA, Janzen DH (2005) Use of DNA barcodes to identify flowering plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 8369-8374. |
| [34] | Kruskal JB (1964) Nonmetric multidimensional scaling: a numerical method. Psychometrika, 29, 115-129. |
| [35] | Li DZ, Zeng CX (2015) Prospects for plant DNA barcoding. Biodiversity Science, 23, 297-298. (in Chinese) |
| [李德铢, 曾春霞 (2015) 植物DNA条形码研究展望. 生物多样性, 23, 297-298.] | |
| [36] | Li HQ, Chen JY, Wang S, Xiong SZ (2012) Evaluation of six candidate DNA barcoding loci in Ficus (Moraceae) of China. Molecular Ecology Resources, 12, 783-790. |
| [37] | Lin P (2006) Marine Higher Plant Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [林鹏 (2006) 海洋高等植物生态. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [38] | Liu J, Yan HF, Ge XJ (2016) The use of DNA barcoding on recently diverged species in the genus Gentiana (Gentianaceae) in China. PLoS ONE, 11, e0153008. |
| [39] | Liu J, Yan HF, Newmaster SG, Pei N, Ragupathy S, Ge XJ (2015) The use of DNA barcoding as a tool for the conservation biogeography of subtropical forests in China. Diversity and Distributions, 21, 188-199. |
| [40] | Lucas C, Thangaradjou T, Papenbrock J (2012) Development of a DNA barcoding system for seagrasses: successful but not simple. PLoS ONE, 7, e29987. |
| [41] | Molnar JL, Gamboa RL, Revenga C, Spalding MD (2008) Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 6, 485-492. |
| [42] | Munir U, Perveen A, Qamarunnisa S (2015) The utility of rbcL and matK regions for DNA barcoding analysis of the genus Suaeda (Amaranthaceae) species. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 47, 2329-2334. |
| [43] | Newmaster SG, Fazekas AJ, Ragupathy S (2006) DNA barcoding in land plants: evaluation of rbcL in a multigene tiered approach. Canadian Journal of Botany, 84, 335-341. |
| [44] | Newmaster SG, Fazekas AJ, Steeves RAD, Janovec J (2008) Testing candidate plant barcode regions in the Myristicaceae. Molecular Ecology Resources, 8, 480-490. |
| [45] | Olmstead RG, Palmer JD (1994) Chloroplast DNA systematics: a review of methods and data analysis. American Journal of Botany, 81, 1205-1224. |
| [46] | Pang XH, Liu C, Shi LC, Liu R, Liang D, Li H, Cherny SS, Chen SL (2012) Utility of the trnH-psbA intergenic spacer region and its combinations as plant DNA barcodes: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 7, e48833. |
| [47] | Parmentier I, Duminil J, Kuzmina M, Philippe M, Thomas DW, Kenfack D, Chuyong GB, Cruaud C, Hardy OJ (2013) How effective are DNA barcodes in the identification of African rainforest trees? PLoS ONE, 8, e54921. |
| [48] | Pei N, Chen B, Kress WJ (2017) Advances of community-level plant DNA barcoding in China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 225. |
| [49] | R Core Team (2012) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [50] | Rana TS, Narzary D, Ohri D (2012) Molecular differentiation of Chenopodium album complex and some related species using ISSR profiles and ITS sequences. Gene, 495, 29-35. |
| [51] | Sandilyan S, Kathiresan K (2012) Mangrove conservation: a global perspective. Biodiversity and Conservation, 21, 3523-3542. |
| [52] | Schwarzbach AE, Ricklefs RE (2000) Systematic affinities of Rhizophoraceae and Anisophylleaceae, and intergeneric relationships within Rhizophoraceae, based on chloroplast DNA, nuclear ribosomal DNA, and morphology. American Journal of Botany, 87, 547-564. |
| [53] | Seebens H, Gastner MT, Blasius B (2013) The risk of marine bioinvasion caused by global shipping. Ecology Letters, 16, 782-790. |
| [54] | Short F, Carruthers T, Dennison W, Waycott M (2007) Global seagrass distribution and diversity: a bioregional model. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 350, 3-20. |
| [55] | Steane DA (2005) Complete nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast genome from the Tasmanian blue gum, Eucalyptus globulus (Myrtaceae). DNA Research, 12, 215-220. |
| [56] | Sugita M, Shinozaki K, Sugiura M (1985) Tobacco chloroplast tRNALys (UUU) gene contains a 2.5-kilobase-pair intron: an open reading frame and a conserved boundary sequence in the intron. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 82, 3557-3561. |
| [57] | Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2731-2739. |
| [58] | Tatusova TA, Madden TL (1999) BLAST 2 Sequences, a new tool for comparing protein and nucleotide sequences. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 174, 247-250. |
| [59] | Triest L, Sierens T (2010) Chloroplast sequences reveal a diversity gradient in the Mediterranean Ruppia cirrhosa species complex. Aquatic Botany, 93, 68-74. |
| [60] | Trivedi S, Aloufi AA, Ansari AA, Ghosh SK (2016) Role of DNA barcoding in marine biodiversity assessment and conservation: an update. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 23, 161-171. |
| [61] | Vega AS, Rua GH, Fabbri LT, Rúgolo de Agrasar ZE (2009) A morphology-based cladistica analysis of Digitaria (Poaceae, Panicoideae, Paniceae). Systematic Botany, 34, 312-323. |
| [62] | Wang WQ(2013) Salt-tolerant Plant Resources of Coastal Areas of South China. Xiamen University Press,Xiamen. (in Chinese) |
| [王文卿 (2013)南方滨海耐盐植物资源.厦门大学出版社, 厦门.] | |
| [63] | Waycott M, Duarte CM, Carruthers TJB, Orthd RJ, Dennison WC, Olyarnik S, Calladine A, Fourqurean JW, Heck KL, Hughes AR, Kendrick GA, Kenworthy WJ, Short FT, Williams SL (2009) Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 106, 12377-12381. |
| [64] | White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ eds. PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications.San Diego:Academic Press. 315-322. |
| [65] | Yamashiro T, Fukuda T, Yokoyama J, Maki M (2004) Molecular phylogeny of Vincetoxicum (Apocynaceae-Asclepiadoideae) based on the nucleotide sequences of cpDNA and nrDNA. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 31, 689-700. |
| [66] | Yan HF, Liu YJ, Xie XF, Zhang CY, Hu CM, Hao G, Ge XJ (2015) DNA barcoding evaluation and its taxonomic implications in the species-rich genus Primula L. in China. PLoS ONE, 10, e0122903. |
| [67] | Yang JB, Wang YP, Moeller M, Gao LM, Wu D (2012) Applying plant DNA barcodes to identify species of Parnassia (Parnassiaceae). Molecular Ecology Resources, 12, 267-275. |
| [68] | Yu J, Xue JH, Zhou SL (2011) New universal matK primers for DNA barcoding angiosperms. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 49, 176-181. |
| [69] | Zhao KF, Li FZ (1999) Halophytes in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [赵可夫, 李法曾 (1999) 中国盐生植物: 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 陈静, 张丙昌, 刘燕晋, 武杰, 赵康, 明姣. 荒漠生物结皮细鞘丝藻类(Leptolyngbya-like)蓝藻多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24186-. |
| [2] | 罗小燕, 李强, 黄晓磊. 戴云山国家级自然保护区访花昆虫DNA条形码数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23236-. |
| [3] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [4] | 吴帆, 刘深云, 江虎强, 王茜, 陈开威, 李红亮. 中华蜜蜂和意大利蜜蜂秋冬期传粉植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22528-. |
| [5] | 俞正森, 宋娜, 本村浩之, 高天翔. 中国银口天竺鲷属鱼类的分类厘定[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 971-979. |
| [6] | 胡芮, 王儒晓, 杜诗雨, 李萌, 邢雨辉, 潘达, 徐海根, 孙红英. 扬州宝应湖底栖大型无脊椎动物的生物多样性及其变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1558-1569. |
| [7] | 丁陆彬, 马楠, 王国萍, 何思源, 闵庆文. 生物多样性相关传统知识研究热点与前沿的可视化分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(7): 716-727. |
| [8] | 邵昕宁, 宋大昭, 黄巧雯, 李晟, 姚蒙. |
| [9] | 刘山林. DNA条形码参考数据集构建和序列分析相关的新兴技术[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(5): 526-533. |
| [10] | 吉乃提汗·马木提, 成小军, 谭敦炎. 荒漠短命植物异喙菊的小花异形性及繁殖特性[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(5): 498-509. |
| [11] | 侯勤曦, 慈秀芹, 刘志芳, 徐武美, 李捷. 基于DNA条形码评估西双版纳国家级自然保护区对樟科植物进化历史的保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(3): 217-228. |
| [12] | 刘青青, 董志军. 基于线粒体COI基因分析钩手水母的群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1204-1211. |
| [13] | 郝金凤, 张晓红, 王昱淞, 刘金林, 智永超, 李新江. 白洋淀湿地蝗虫多样性调查及DNA条形码应用研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(4): 409-417. |
| [14] | 慈秀芹, 李捷. 系统发育多样性在植物区系研究与 生物多样性保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(2): 175-181. |
| [15] | 张静, 李渊, 宋娜, 林龙山, 高天翔. 我国沿海棱鳀属鱼类的物种鉴定与系统发育[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(8): 888-895. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn