



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 856-863. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016348 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016348
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
刘国红1, 刘波1,*( ), 车建美1, 陈倩倩1, 林乃铨2, 崔卫东3
), 车建美1, 陈倩倩1, 林乃铨2, 崔卫东3
收稿日期:2017-03-08
接受日期:2017-06-06
出版日期:2017-08-20
发布日期:2017-08-31
通讯作者:
刘波
作者简介:# 共同第一作者 Co-first authors
基金资助:
Guohong Liu1, Bo Liu1,*( ), Jianmei Che1, Qianqian Chen1, Naiquan Lin2, Weidong Cui3
), Jianmei Che1, Qianqian Chen1, Naiquan Lin2, Weidong Cui3
Received:2017-03-08
Accepted:2017-06-06
Online:2017-08-20
Published:2017-08-31
Contact:
Liu Bo
摘要:
了解马铃薯根际土壤中芽胞杆菌种类多样性, 可为挖掘芽胞杆菌新资源提供基础。从新疆伊犁州9个地点采集了30份马铃薯根际土壤样品, 采用可培养法从中分离芽胞杆菌, 通过16S rRNA基因同源性鉴定了分离菌株的分类地位。共获得芽胞杆菌349株, 基于菌落形态特征和16S rRNA基因序列确定了66个代表菌株, 其中14株与近缘种模式菌株的16S rRNA基因序列相似性介于93.0-98.5%之间, 为潜在芽胞杆菌新种。349株芽胞杆菌属于9属66种, 分别为芽胞杆菌属(Bacillus)的41个种(41/66, 62.1%), 为最优势属; 类芽胞杆菌属(Paenibacillus)有9种(9/66, 13.6%), 赖氨酸芽胞杆菌属(Lysinibacillus)共6种(6/66, 9.1%), 嗜冷芽胞杆菌属(Pscychrobacillus)共4种(4/66, 6.1%), 虚构芽胞杆菌属(Fictibacillus)有2种(2/66, 3.0%), 短芽胞杆菌属(Brevibacillus)、大洋芽胞杆菌属(Oceanobacillus)、鲁梅尔芽胞杆菌属(Rummelibacillus)和解硫胺素芽胞杆菌属(Aneurinibacillus)皆为1种。新疆9个地点马铃薯根际土壤中芽胞杆菌含量为2.20-8.86 × 104 cfu/g, 其中特克斯蒙古乡马铃薯根际土壤中芽胞杆菌的菌落含量和种类最多, 分别为8.86 × 104 cfu/g和37种; 尼勒克县马场马铃薯根际土壤中的芽胞杆菌含量最少, 特克斯去昭苏路上和阜康西沟村的芽胞杆菌种类最少, 仅9种。但每个地点的优势种均相同, 均为简单芽胞杆菌(Bacillus simplex)和阿氏芽胞杆菌(B. aryabhattai)。芽胞杆菌种类可划分为高频度分布型(简单芽胞杆菌等4种)、中频度分布型(植物内生芽胞杆菌等12种)和低频度分布型(其余51种芽胞杆菌, 如蕈状芽胞杆菌)。新疆9个地点芽胞杆菌种类分布可分为高含量高丰度型(特克斯蒙古乡和农技推广园)和低含量低丰度型(如尼勒克县马场等地)。相关性分析发现, 马铃薯根际芽胞杆菌种类分布与海拔高度无显著相关性。新疆马铃薯根际土壤蕴含种类丰富的芽胞杆菌资源, 可为芽胞杆菌功能菌株开发提供丰富的菌种来源。
刘国红, 刘波, 车建美, 陈倩倩, 林乃铨, 崔卫东 (2017) 新疆伊犁马铃薯根际芽胞杆菌纯培养多样性. 生物多样性, 25, 856-863. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016348.
Guohong Liu, Bo Liu, Jianmei Che, Qianqian Chen, Naiquan Lin, Weidong Cui (2017) Diversity of Bacillus-like species isolated from potato rhizosphere soils in Yili, Xinjiang. Biodiversity Science, 25, 856-863. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016348.
| 编号 No. | 采集地点 Collection site | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 经纬度 Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 尼勒克县尼勒克镇公社种子队 Seed Team of Nilka Township, Nilka County | 1,138 | 43°46°28? N, 82°35°01? E |
| S2 | 阜康市上户沟乡西沟村 Xigou Village, Shanghugou Township, Fukang City | 1,261 | 44°00°17? N, 88°33°46? E |
| S3 | 尼勒克县马场 Machang, Nilka County | 1,139 | 43°45°58? N, 82°34°43? E |
| S4 | 尼勒克县沙勒漫乡 Shaleman Township, Nilka County | 1,110 | 43°47°08? N, 82°32°15? E |
| S5 | 昭苏县农业局试验场 Testing Ground of Agricultural Bureau, Zhaosu County | 1,856 | 44°09'46? N, 81°09°14? E |
| S6 | 特克斯蒙古乡(施药) Mongolia Township, Tekes County (pesticide applied) | 1,171 | 43°13°25? N, 81°54°27? E |
| S7 | 特克斯蒙古乡 Mongolia Township, Tekes County | 1,181 | 43°13°17? N, 81°52°33? E |
| S8 | 特克斯去昭苏路上 On the way from Tekes to Zhaosu County | 1,808 | - |
| S9 | 特克斯县农业技术推广园 Agro Technical Extension Garden, Tekes County | 1,181 | 43°13°17? N, 81°52°33? E |
表1 新疆马铃薯根际土壤样本采集信息
Table 1 Information of potato rhizosphere soil samples from Xinjiang
| 编号 No. | 采集地点 Collection site | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 经纬度 Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 尼勒克县尼勒克镇公社种子队 Seed Team of Nilka Township, Nilka County | 1,138 | 43°46°28? N, 82°35°01? E |
| S2 | 阜康市上户沟乡西沟村 Xigou Village, Shanghugou Township, Fukang City | 1,261 | 44°00°17? N, 88°33°46? E |
| S3 | 尼勒克县马场 Machang, Nilka County | 1,139 | 43°45°58? N, 82°34°43? E |
| S4 | 尼勒克县沙勒漫乡 Shaleman Township, Nilka County | 1,110 | 43°47°08? N, 82°32°15? E |
| S5 | 昭苏县农业局试验场 Testing Ground of Agricultural Bureau, Zhaosu County | 1,856 | 44°09'46? N, 81°09°14? E |
| S6 | 特克斯蒙古乡(施药) Mongolia Township, Tekes County (pesticide applied) | 1,171 | 43°13°25? N, 81°54°27? E |
| S7 | 特克斯蒙古乡 Mongolia Township, Tekes County | 1,181 | 43°13°17? N, 81°52°33? E |
| S8 | 特克斯去昭苏路上 On the way from Tekes to Zhaosu County | 1,808 | - |
| S9 | 特克斯县农业技术推广园 Agro Technical Extension Garden, Tekes County | 1,181 | 43°13°17? N, 81°52°33? E |
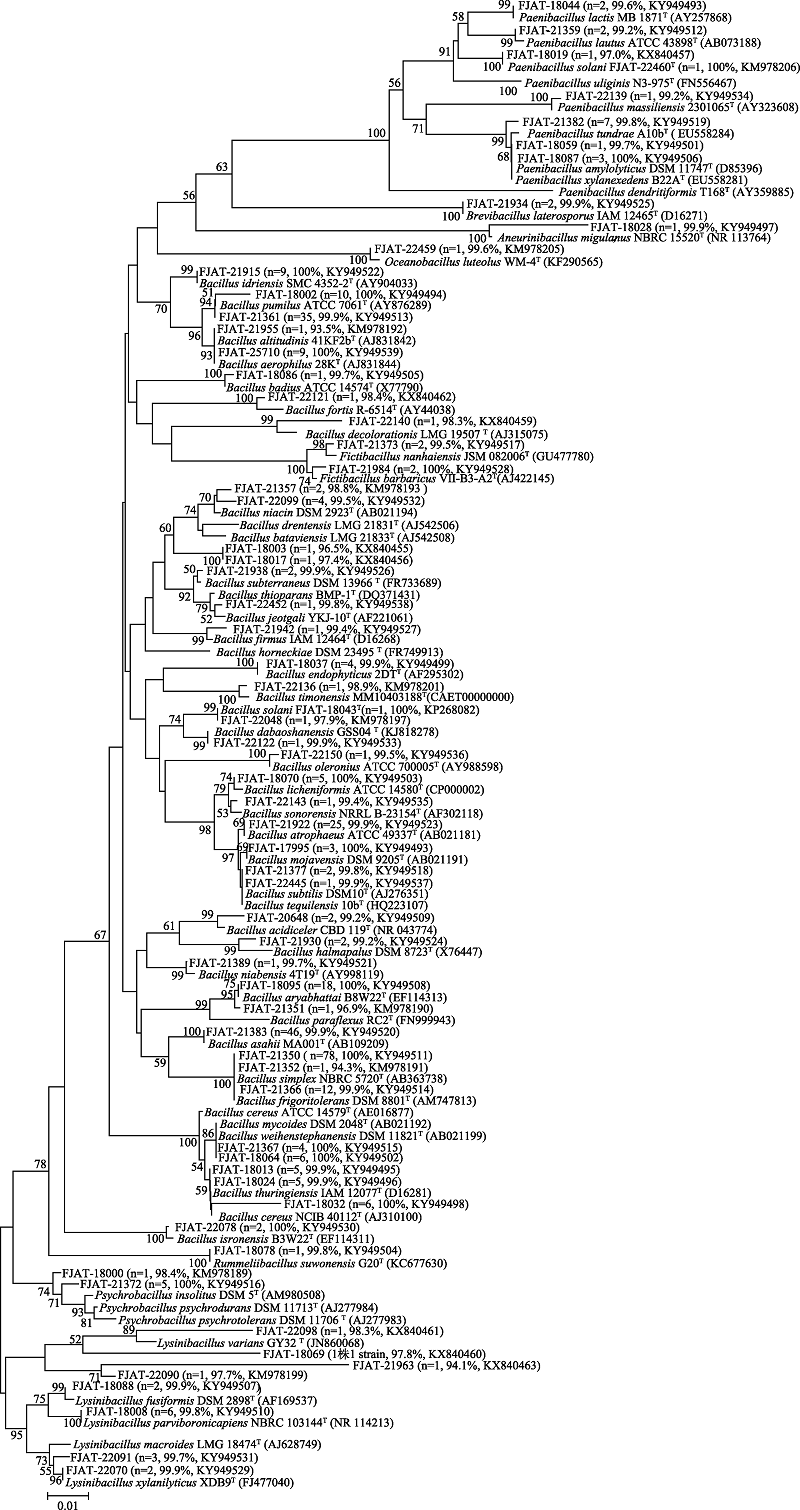
图1 基于16S rRNA基因的芽胞杆菌系统发育分析。n代表分离菌株数量, 百分比值为分离菌株与近缘模式菌的16S rRNA基因相似性。
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic analysis of Bacillus species based on 16S rRNA gene sequence. n represents number of isolates, and percent values represent the 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities between isolates and related type species.
| 样本编号 Sample no. | 芽胞杆菌含量 Bacillus colonies content (×104 cfu/g) | 种类数 Species number |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 3.25 | 19 |
| S2 | 5.00 | 9 |
| S3 | 2.20 | 11 |
| S4 | 6.60 | 15 |
| S5 | 3.97 | 15 |
| S6 | 7.70 | 15 |
| S7 | 8.86 | 37 |
| S8 | 4.30 | 9 |
| S9 | 3.76 | 31 |
表2 新疆马铃薯根际土壤中芽胞杆菌含量分布(样品编号同表1)
Table 2 The content of Bacillus species in the potato rhizoshpere soil from Xinjiang. Soil sample number see Table 1.
| 样本编号 Sample no. | 芽胞杆菌含量 Bacillus colonies content (×104 cfu/g) | 种类数 Species number |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 3.25 | 19 |
| S2 | 5.00 | 9 |
| S3 | 2.20 | 11 |
| S4 | 6.60 | 15 |
| S5 | 3.97 | 15 |
| S6 | 7.70 | 15 |
| S7 | 8.86 | 37 |
| S8 | 4.30 | 9 |
| S9 | 3.76 | 31 |
| [1] | Ambardar S, Vakhlu J (2013) Plant growth promoting bacteria from Crocus sativus rhizosphere. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 29, 2271-2279. |
| [2] | Asari S, Matzén S, Petersen MA, Bejai S, Meijer J (2016) Multiple effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens volatile compounds: plant growth promotion and growth inhibition of phytopathogens. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 92, pii: fiw070. |
| [3] | Cheng HR, Jiang N (2006) Extremely rapid extraction of DNA from bacteria and yeasts. Biotechnology Letters, 28, 55-59. |
| [4] | Calvo P, Ormeño-Orrillo E, Martínez-Romero E, Zúñiga D (2010) Characterization of Bacillus isolates of potato rhizosphere from andean soils of Peru and their potential PGPR characteristics. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 41, 899-906. |
| [5] | Erturk Y, Ercisli S, Haznedar A, Cakmakci R (2010) Effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on rooting and root growth of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) stem cuttings. Biological Research, 43, 91-98. |
| [6] | Fan ZY, Miao CP, Qiao XG, Zheng YK, Chen HH, Chen YW, Xu LH, Zhao LX, Guan HL (2016) Diversity, distribution, and antagonistic activities of rhizobacteria of Panax notoginseng. Journal of Ginseng Research, 40, 97-104. |
| [7] | Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39, 783-789. |
| [8] | Hanif MK, Hameed S, Imran A, Naqqash T, Shahid M, Van Elsas JD (2015) Isolation and characterization of a β-propeller gene containing phosphobacterium Bacillus subtilis strain KPS-11 for growth promotion of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 583. |
| [9] | Huang XF, Zhou D, Guo J, Manter DK, Reardon KF, Vivanco JM (2015) Bacillus spp. from rainforest soil promote plant growth under limited nitrogen conditions. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 118, 672-684. |
| [10] | Ge CB, Liu B, Che JM, Chen MC, Liu GH, Wei JC (2015) Diversity of Bacillus species inhabiting on the surface and endophyte of lichens collected from Wuyi Mountain. Acta Microbiologica Sinica , 55, 551-563. (in Chinese) |
| [葛慈斌, 刘波, 车建美, 陈梅春, 刘国红, 魏江春 (2015) 武夷山地衣表生和内生芽胞杆菌种群的多样性. 微生物学报, 55, 551-563.] | |
| [11] | Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In Mammalian Protein Metabolism, Vol. 3 (ed. Munro HN), pp. 21-132. Academic Press, New York. |
| [12] | Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 62, 716-721. |
| [13] | Lee S, Ka JO, Song HG (2012) Growth promotion of Xanthium italicum by application of rhizobacterial isolates of Bacillus aryabhattai in microcosm soil. Journal of Microbiology, 50, 45-49. |
| [14] | Li LB, Liu M, Yang SZ, Liu L, Miao K, Yang K, Han JG (2008) Cultivable microbial diversity at the rhizosphere of Phyllostachys pubescens. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 48, 772-779. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李潞滨, 刘敏, 杨淑贞, 刘亮, 缪崑, 杨凯, 韩继刚 (2008) 毛竹根际可培养微生物种群多样性分析. 微生物学报, 48, 772-779.] | |
| [15] | Lin FM, Ji WX, Li HL (2011) Phylogenetic diversity of culturable bacteria in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere of tabacco. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 50, 1058-1062. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [林凤敏, 姬文秀, 李虎林 (2011) 烟草根际与非根际细菌的系统发育多样性研究. 湖北农业科学, 50, 1058-1062.] | |
| [16] | Liu B, Liu GH, Cetin S, Schumann P, Pan ZZ, Chen QQ (2016a) Bacillus gobiensis sp. nov., isolated from a soil sample. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66, 379-384. |
| [17] | Liu B, Liu GH, Sengonca C, Schumann P, Ge CB, Wang JP, Cui WD, Lin NQ (2015) Bacillus solani sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil of potato field in Xinjiang of China. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 65, 4066-4071. |
| [18] | Liu B, Liu GH, Sengonca C, Schumann P, Lan JL, Chen DJ, Cui WD, Lin NQ (2016b) Paenibacillus solani sp. nov., isolated from potato rhizosphere soil in Xinjiang, China. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66, 4486-4491. |
| [19] | Liu GH, Zhu YJ, Liu B, Che JM, Tang JY, Pan ZZ, Chen ZH (2014) Diversity of culturable Bacillus species from maize (Zea mays) rhizosphere soil. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 22, 1367-1379. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘国红, 朱育菁, 刘波, 车建美, 唐建阳, 潘志针, 陈泽辉 (2014) 玉米根际土壤芽胞杆菌的多样性. 农业生物技术学报, 22, 1367-1379.] | |
| [20] | Liu Y, Chen L, Zhang N, Li Z, Zhang G, Xu Y, Shen Q, Zhang R (2016) Plant-microbe communication enhances auxin biosynthesis by a root-associated bacterium, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 29, 324-330. |
| [21] | Ma NN (2013) Study on soil microbial of properties in protected tomato root cirumference. PhD dissertation, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马宁宁 (2013) 设施番茄根围土壤的微生物特性研究. 博士学位论文, 沈阳农业大学, 沈阳.] | |
| [22] | Pisa G, Magnani GS, Weber H, Souza EM, Faoro H, Monteiro RA, Daros E, Baura V, Bespalhok JP, Pedrosa FO, Cruz LM (2011) Diversity of 16S rRNA genes from bacteria of sugarcane rhizosphere soil. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 44, 1215-1221. |
| [23] | Qin Y, Ma K, Liu P (2015) Effect of potato continuous cropping on genetic diversity of soil microorganisms. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 23, 589-596. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [秦越, 马琨, 刘萍 (2015) 马铃薯连作栽培对土壤微生物多样性的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 23, 589-596.] | |
| [24] | Rahman MM, Ali ME, Khan AA, Akanda AM, Uddin MK, Hashim U, Hamid SBA (2012) Isolation, characterization, and identification of biological control agent for potato soft rot in Bangladesh. Scientific World Journal, 2012, 723293. |
| [25] | Saber WI, Ghoneem KM, Al-Askar AA, Rashad YM, Ali AA, Rashad EM (2015) Chitinase production by Bacillus subtilis ATCC 11774 and its effect on biocontrol of rhizoctonia diseases of potato. Acta Biologica Hungarica, 66, 436-448. |
| [26] | Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4, 406-425. |
| [27] | Sikorski J, Brambilla E, Kroppenstedt RM, Tindall BJ (2008) The temperature-adaptive fatty acid content in Bacillus simplex strains from ‘Evolution Canyon’, Israel. Microbiology, 154, 2416-2426. |
| [28] | Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA 6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725-2729. |
| [29] | Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876-4882. |
| [30] | Velivelli SL, Kromann P, Lojan P, Rojas M, Franco J, Suarez JP, Prestwich BD (2015) Identification of mVOCs from Andean rhizobacteria and field evaluation of bacterial and mycorrhizal inoculants on growth of potato in its center of origin. Microbial Ecology, 69, 652-667. |
| [31] | Verma P, Yadav AN, Khannam KS, Kumar S, Saxena AK, Suman A (2016) Molecular diversity and multifarious plant growth promoting attributes of Bacilli associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) rhizosphere from six diverse agro- ecological zones of India. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 56, 44-58. |
| [32] | Wang N, Lu SS, Ma K, Liu P (2016) The genetic diversity of rhizosphere soil bacteria under different intercropping patterns for potato in southern mountainous area of Ningxia. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 30(12), 193-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王娜, 陆姗姗, 马琨, 刘萍 (2016) 宁夏南部山区马铃薯不同间作模式对根际土壤细菌多样性的影响. 干旱区资源与环境, 30(12), 193-198.] | |
| [33] | Weinert N, Meincke R, Gottwald C, Heuer H, Schloter M, Berg G, Smalla K (2010) Bacterial diversity on the surface of potato tubers in soil and the influence of the plant genotype. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 74, 114-123. |
| [34] | Xu HQ, Wang XL, Ma GS (2015) Nutrition feasibility analysis of development of potato as a staple food. Food and Nutrition in China, 21(7), 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐海泉, 王秀丽, 马冠生 (2015) 马铃薯及其主食产品开发的营养可行性分析. 中国生物与营养, 21(7), 10-13.] | |
| [35] | Yan YW, Zhang H, Liu L, Xian HQ, Cui DJ (2011) Isolation and identification of dominant microorganisms in rhizosphere of continuous cropping with peanut. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 51, 835-842. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [颜艳伟, 张红, 刘露, 咸洪泉, 崔德杰 (2011) 连作花生田根际土壤优势微生物的分离和鉴定. 微生物学报, 51, 835-842.] | |
| [36] | Zhang X, Li B, Wang Y, Guo Q, Lu X, Li S, Ma P (2013) Lipopeptides, a novel protein, and volatile compounds contribute to the antifungal activity of the biocontrol agent Bacillus atrophaeus CAB-1. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 9525-9534. |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn