



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1164-1176. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016085 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016085
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
收稿日期:2016-03-27
接受日期:2016-09-02
出版日期:2016-10-20
发布日期:2016-11-10
通讯作者:
刘波
基金资助:
Cibin Ge, Rong Zheng, Bo Liu*( ), Guohong Liu, Jianmei Che, Jianyang Tang
), Guohong Liu, Jianmei Che, Jianyang Tang
Received:2016-03-27
Accepted:2016-09-02
Online:2016-10-20
Published:2016-11-10
Contact:
Liu Bo
摘要:
为了解武夷山自然保护区土壤中可培养芽胞杆菌的分布状况, 2012年6月从该保护区的黄岗山顶部、中部、底部和桐木关、挂墩、大竹岚等6个地点采集土样75份。用80℃水浴加热、稀释平板法进行芽胞杆菌的分离, 并根据16S rRNA基因序列分析对菌株进行初步鉴定。从土样中分离出芽胞杆菌418株, 鉴定为8个属42个种, 其中Bacillus属的种数最多, 有20种, Paenibacillus属和Lysinibacillus属分别有8种和7种。不同地点分离到的芽胞杆菌在种类、数量上存在差异: 从大竹岚土壤中分离到的芽胞杆菌种类最多, 从黄岗山中部和底部分离到的种类数则较少; 挂墩、大竹岚土壤中芽胞杆菌的数量较大, 达3.6×106 cfu/g以上, 而黄岗山顶部和中部土壤中的数量则少于4.9×105 cfu/g。Bacillus cereus、B. mycoides、B. thuringiensis和Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus等4个种在6个地点的土样中均有分离到, 其中B. thuringiensis、L. xylanilyticus是该保护区土壤中的优势种。桐木关土壤中芽胞杆菌的种类多样性和均匀度指数都比其他5个地点的高, 而挂墩土壤中芽胞杆菌的Shannon-Wiener多样性、均匀度和优势度指数都最低。B. mycoides和B. thuringiensis的数量与海拔显著相关, 相关系数分别为0.852和-0.834, B. cereus、B. mycoides、B. thuringiensis的分离频度与海拔的相关性极显著, 相关系数分别为0.960、0.952和-0.931。研究结果表明, 武夷山自然保护区土壤中可培养芽胞杆菌的种类丰富、数量较大, 具有较高的多样性。
葛慈斌, 郑榕, 刘波, 刘国红, 车建美, 唐建阳 (2016) 武夷山自然保护区土壤可培养芽胞杆菌 的物种多样性及分布. 生物多样性, 24, 1164-1176. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016085.
Cibin Ge, Rong Zheng, Bo Liu, Guohong Liu, Jianmei Che, Jianyang Tang (2016) Diversity and distribution of cultivable Bacillus-like species in soils collected from Wuyishan Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1164-1176. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016085.
| 采集地点 Location | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 土壤样品数 No. of samples | 生境类型 Habitat | 土壤类型 Agrotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄岗山顶部 Peak of the Huanggang Mountain (PHM) | 2,158 | 15 | 草甸、岩石 Meadow, rock | 山地草甸土 Mountain meadow soil |
| 黄岗山中部 Middle of the Huanggang Mountain (MHM) | 1,700 | 13 | 树林、草丛、路边等 Forest, grass, roadside | 黄壤 Yellow soil |
| 黄岗山底部 Base of the Huanggang Mountain (BHM) | 1,100 | 7 | 树林、草丛、路边等 Forest, grass, roadside | 红黄壤、黄壤 Red and yellow soil, yellow soil |
| 桐木关 Tongmuguan (TMG) | 890 | 12 | 树林、草丛、路边等 Forest, grass, roadside | 红黄壤 Red and yellow soil |
| 挂墩 Guadun (GD) | 1,200 | 14 | 树林、草丛、路边等 Forest, grass, roadside | 红黄壤、黄壤 Red and yellow soil, yellow soil |
| 大竹岚 Dazhulan (DZL) | 1,000 | 14 | 树林、草丛 Forest, grass | 红黄壤、黄壤 Red and yellow soil, yellow soil |
表1 采自武夷山自然保护区的土壤样品信息
Table 1 Information of the soil samples collected from Wuyishan Nature Reserve
| 采集地点 Location | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 土壤样品数 No. of samples | 生境类型 Habitat | 土壤类型 Agrotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄岗山顶部 Peak of the Huanggang Mountain (PHM) | 2,158 | 15 | 草甸、岩石 Meadow, rock | 山地草甸土 Mountain meadow soil |
| 黄岗山中部 Middle of the Huanggang Mountain (MHM) | 1,700 | 13 | 树林、草丛、路边等 Forest, grass, roadside | 黄壤 Yellow soil |
| 黄岗山底部 Base of the Huanggang Mountain (BHM) | 1,100 | 7 | 树林、草丛、路边等 Forest, grass, roadside | 红黄壤、黄壤 Red and yellow soil, yellow soil |
| 桐木关 Tongmuguan (TMG) | 890 | 12 | 树林、草丛、路边等 Forest, grass, roadside | 红黄壤 Red and yellow soil |
| 挂墩 Guadun (GD) | 1,200 | 14 | 树林、草丛、路边等 Forest, grass, roadside | 红黄壤、黄壤 Red and yellow soil, yellow soil |
| 大竹岚 Dazhulan (DZL) | 1,000 | 14 | 树林、草丛 Forest, grass | 红黄壤、黄壤 Red and yellow soil, yellow soil |
| 类群 Group | 代表菌株 Strains | 登录号 GenBank accession no. | 最相近菌种 Closest match | 相似性 Sequence identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 芽胞杆菌属 Bacillus | FJAT-16209 | KF278157 | 阿氏芽胞杆菌 Bacillus aryabhattai | 100.0 |
| FJAT-16883 | KF278197 | 巴达维亚芽胞杆菌 B. bataviensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16354 | KF278179 | 科研中心芽胞杆菌 B. cecembensis | 95.95 | |
| FJAT-16889 | KF278199 | 蜡样芽胞杆菌 B. cereus | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16469 | KF278181 | 根内芽胞杆菌 B. endoradicis | 99.12 | |
| FJAT-16705 | KF278193 | 盐敏芽胞杆菌 B. halmapalus | 98.52 | |
| FJAT-16532 | KF278187 | 印空研芽胞杆菌 B. isronensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16048 | KF278123 | 万里浦芽胞杆菌 B. manliponensis | 98.46 | |
| FJAT-16291 | KF278168 | 地衣芽胞杆菌 B. licheniformis | 99.85 | |
| FJAT-16872 | KF278195 | 黄海芽胞杆菌 B. marisflavi | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16134 | KF278130 | 甲基营养型芽胞杆菌 B. methylotrophicus | 99.86 | |
| FJAT-16162 | KF278147 | 壁芽胞杆菌 B. muralis | 99.85 | |
| FJAT-16884 | KF278198 | 蕈状芽胞杆菌 B. mycoides | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16339 | KF278175 | 休闲地芽胞杆菌 B. novalis | 99.83 | |
| FJAT-16201 | KF278155 | 假蕈状芽胞杆菌 B. pseudomycoides | 99.85 | |
| FJAT-16578 | KF278189 | 沙福芽胞杆菌 B. safensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-17017 | KF278204 | 简单芽胞杆菌 B. simplex | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-17042 | KF278206 | 特基拉芽胞杆菌 B. tequilensis | 99.89 | |
| FJAT-16178 | KF278153 | 苏云金芽胞杆菌 B. thuringiensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16301 | KF278171 | 韦氏芽胞杆菌 B. weihenstephanensis | 100.0 | |
| 短芽胞杆菌属 Brevibacillus | FJAT-16350 | KF278177 | 土壤短芽胞杆菌 Brevibacillus agri | 99.38 |
| 虚构芽胞杆菌属 Fictibacillus | FJAT-17014 | KF278203 | 南海虚构芽胞杆菌 Fictibacillus nanhaiensis | 100.0 |
| 赖氨酸芽胞杆菌属 Lysinibacillus | FJAT-16156 | KF278145 | 纺锤形赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 Lysinibacillus fusiformis | 100.0 |
| FJAT-16167 | KF278149 | 延长赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. macroides | 99.57 | |
| FJAT-16506 | KF278185 | 芒果土赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. mangiferahumi | 99.98 | |
| FJAT-16266 | KF278163 | 马赛赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. massiliensis | 97.51 | |
| FJAT-16248 | KF278158 | 低硼赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. parviboronicapiens | 99.22 | |
| FJAT-16141 | KF278135 | 球形赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. sphaericus | 99.14 | |
| FJAT-16140 | KF278134 | 解木糖赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. xylanilyticus | 100.0 | |
| 类芽胞杆菌属 Paenibacillus | FJAT-16151 | KF278140 | 蜂房类芽胞杆菌 Paenibacillus alvei | 98.82 |
| FJAT-16703 | KF278192 | 蜜蜂类芽胞杆菌 P. apiarius | 98.88 | |
| FJAT-16893 | KF278200 | 栗树类芽胞杆菌 P. castaneae | 98.05 | |
| FJAT-16129 | KF278128 | 埃及类芽胞杆菌 P. elgii | 99.40 | |
| FJAT-16135 | KF278131 | 灿烂类芽胞杆菌 P. lautus | 99.13 | |
| FJAT-16879 | KF278196 | 松树类芽胞杆菌 P. pini | 99.98 | |
| FJAT-16903 | KF278201 | 台中类芽胞杆菌 P. taichungensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16927 | KF278202 | 土地类芽胞杆菌 P. terrigena | 97.61 | |
| 嗜冷芽胞杆菌属 Psychrobacillus | FJAT-16132 | KF278129 | 奇特嗜冷芽胞杆菌 Psychrobacillus insolitus | 98.70 |
| FJAT-16497 | KF278183 | 忍冷嗜冷芽胞杆菌 P. psychrodurans | 99.82 | |
| 鲁氏芽胞杆菌属 Rummeliibacillus | FJAT-16098 | KF278125 | 厚细胞鲁氏芽胞杆菌 Rummeliibacillus pycnus | 98.39 |
| 绿芽胞杆菌属 Viridibacillus | FJAT-17036 | KF278205 | 沙地绿芽胞杆菌 Viridibacillus arenosi | 100.0 |
| FJAT-16340 | KF278176 | 田地绿芽胞杆菌 V. arvi | 100.0 |
表2 从武夷山自然保护区分离得到的芽胞杆菌的种类概况
Table 2 Bacillus-like species isolated from Wuyishan Nature Reserve
| 类群 Group | 代表菌株 Strains | 登录号 GenBank accession no. | 最相近菌种 Closest match | 相似性 Sequence identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 芽胞杆菌属 Bacillus | FJAT-16209 | KF278157 | 阿氏芽胞杆菌 Bacillus aryabhattai | 100.0 |
| FJAT-16883 | KF278197 | 巴达维亚芽胞杆菌 B. bataviensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16354 | KF278179 | 科研中心芽胞杆菌 B. cecembensis | 95.95 | |
| FJAT-16889 | KF278199 | 蜡样芽胞杆菌 B. cereus | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16469 | KF278181 | 根内芽胞杆菌 B. endoradicis | 99.12 | |
| FJAT-16705 | KF278193 | 盐敏芽胞杆菌 B. halmapalus | 98.52 | |
| FJAT-16532 | KF278187 | 印空研芽胞杆菌 B. isronensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16048 | KF278123 | 万里浦芽胞杆菌 B. manliponensis | 98.46 | |
| FJAT-16291 | KF278168 | 地衣芽胞杆菌 B. licheniformis | 99.85 | |
| FJAT-16872 | KF278195 | 黄海芽胞杆菌 B. marisflavi | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16134 | KF278130 | 甲基营养型芽胞杆菌 B. methylotrophicus | 99.86 | |
| FJAT-16162 | KF278147 | 壁芽胞杆菌 B. muralis | 99.85 | |
| FJAT-16884 | KF278198 | 蕈状芽胞杆菌 B. mycoides | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16339 | KF278175 | 休闲地芽胞杆菌 B. novalis | 99.83 | |
| FJAT-16201 | KF278155 | 假蕈状芽胞杆菌 B. pseudomycoides | 99.85 | |
| FJAT-16578 | KF278189 | 沙福芽胞杆菌 B. safensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-17017 | KF278204 | 简单芽胞杆菌 B. simplex | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-17042 | KF278206 | 特基拉芽胞杆菌 B. tequilensis | 99.89 | |
| FJAT-16178 | KF278153 | 苏云金芽胞杆菌 B. thuringiensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16301 | KF278171 | 韦氏芽胞杆菌 B. weihenstephanensis | 100.0 | |
| 短芽胞杆菌属 Brevibacillus | FJAT-16350 | KF278177 | 土壤短芽胞杆菌 Brevibacillus agri | 99.38 |
| 虚构芽胞杆菌属 Fictibacillus | FJAT-17014 | KF278203 | 南海虚构芽胞杆菌 Fictibacillus nanhaiensis | 100.0 |
| 赖氨酸芽胞杆菌属 Lysinibacillus | FJAT-16156 | KF278145 | 纺锤形赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 Lysinibacillus fusiformis | 100.0 |
| FJAT-16167 | KF278149 | 延长赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. macroides | 99.57 | |
| FJAT-16506 | KF278185 | 芒果土赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. mangiferahumi | 99.98 | |
| FJAT-16266 | KF278163 | 马赛赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. massiliensis | 97.51 | |
| FJAT-16248 | KF278158 | 低硼赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. parviboronicapiens | 99.22 | |
| FJAT-16141 | KF278135 | 球形赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. sphaericus | 99.14 | |
| FJAT-16140 | KF278134 | 解木糖赖氨酸芽胞杆菌 L. xylanilyticus | 100.0 | |
| 类芽胞杆菌属 Paenibacillus | FJAT-16151 | KF278140 | 蜂房类芽胞杆菌 Paenibacillus alvei | 98.82 |
| FJAT-16703 | KF278192 | 蜜蜂类芽胞杆菌 P. apiarius | 98.88 | |
| FJAT-16893 | KF278200 | 栗树类芽胞杆菌 P. castaneae | 98.05 | |
| FJAT-16129 | KF278128 | 埃及类芽胞杆菌 P. elgii | 99.40 | |
| FJAT-16135 | KF278131 | 灿烂类芽胞杆菌 P. lautus | 99.13 | |
| FJAT-16879 | KF278196 | 松树类芽胞杆菌 P. pini | 99.98 | |
| FJAT-16903 | KF278201 | 台中类芽胞杆菌 P. taichungensis | 100.0 | |
| FJAT-16927 | KF278202 | 土地类芽胞杆菌 P. terrigena | 97.61 | |
| 嗜冷芽胞杆菌属 Psychrobacillus | FJAT-16132 | KF278129 | 奇特嗜冷芽胞杆菌 Psychrobacillus insolitus | 98.70 |
| FJAT-16497 | KF278183 | 忍冷嗜冷芽胞杆菌 P. psychrodurans | 99.82 | |
| 鲁氏芽胞杆菌属 Rummeliibacillus | FJAT-16098 | KF278125 | 厚细胞鲁氏芽胞杆菌 Rummeliibacillus pycnus | 98.39 |
| 绿芽胞杆菌属 Viridibacillus | FJAT-17036 | KF278205 | 沙地绿芽胞杆菌 Viridibacillus arenosi | 100.0 |
| FJAT-16340 | KF278176 | 田地绿芽胞杆菌 V. arvi | 100.0 |
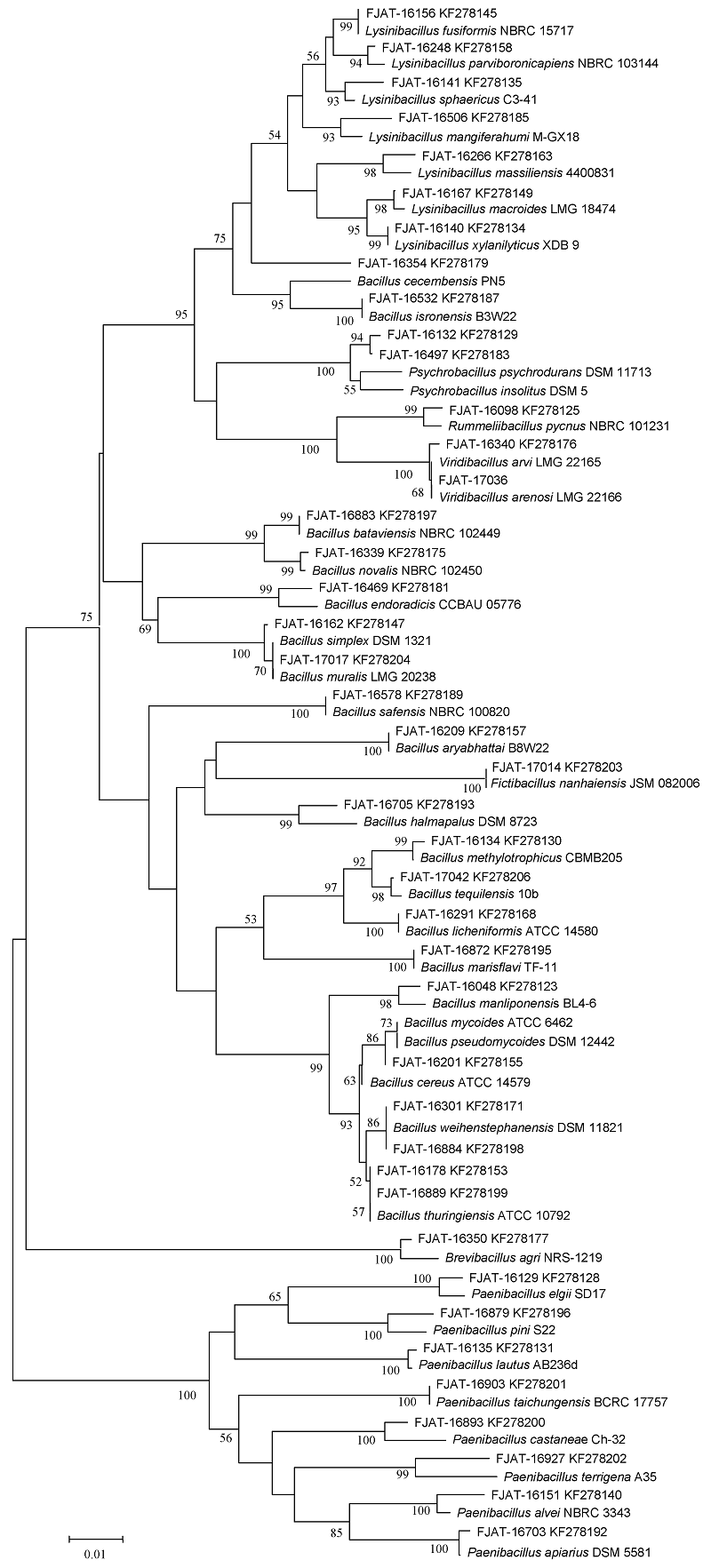
图1 基于16S rRNA基因序列的武夷山自然保护区芽胞杆菌系统发育树。数字表示各节点的自展支持率数值(>50%)。
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree of Bacillus-like strains isolated from Wuyishan Nature Reserve based on 16S rRNA gene sequences using neighbor-joining method. Bootstrap values above 50% are shown at the branching points.
| 芽胞杆菌种类 Bacillus-like species | 黄岗山顶部 Peak of the Huanggang Mountain | 黄岗山中部 Middle of the Huanggang Mountain | 黄岗山底部 Base of the Huanggang Mountain | 桐木关 Tongmuguan | 挂墩 Guadun | 大竹岚 Dazhulan | 总体 Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequ-ency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | |||||||
| Bacillus aryabhattai | 0 | 0 | 7.69 | 0.02 | 14.29 | 0.10 | 8.33 | 2.42 | 14.29 | 0.05 | 14.29 | 0.62 | 9.33 | 3.20 | ||||||
| B. bataviensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.43 | 1.33 | 0.43 | ||||||
| B. cecembensis | 6.67 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| B. cereus | 66.67 | 0.26 | 53.85 | 1.27 | 28.57 | 0.72 | 16.67 | 0.29 | 42.86 | 0.64 | 21.43 | 0.40 | 40 | 3.58 | ||||||
| B. endoradicis | 13.33 | 0.02 | 7.69 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.03 | ||||||
| B. halmapalus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| B. isronensis | 6.67 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| B. manliponensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 2.67 | 0.07 | ||||||
| B. licheniformis | 6.67 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.03 | ||||||
| B. marisflavi | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.11 | 1.33 | 0.11 | ||||||
| B. methylotrophicus | 6.67 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.67 | 0.02 | ||||||
| B. muralis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25.00 | 0.67 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.77 | 6.67 | 1.43 | ||||||
| B. mycoides | 100.0 | 3.26 | 69.20 | 1.42 | 28.57 | 0.95 | 16.67 | 0.47 | 7.14 | 0.04 | 14.29 | 1.24 | 41.33 | 7.37 | ||||||
| B. novalis | 6.67 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.07 | ||||||
| B. pseudomycoides | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.57 | 0.21 | 8.33 | 0.42 | 42.86 | 2.44 | 14.29 | 0.09 | 14.67 | 3.16 | ||||||
| B. safensis | 0 | 0 | 7.69 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.36 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.36 | ||||||
| B. simplex | 26.67 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.05 | 6.67 | 0.23 | ||||||
| B. tequilensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 16.19 | 1.33 | 16.19 | ||||||
| B. thuringiensis | 20 | 0.18 | 30.77 | 0.63 | 100.0 | 6.73 | 83.33 | 11.00 | 71.43 | 3.24 | 85.71 | 13.47 | 61.33 | 35.25 | ||||||
| B. weihenstephanensis | 0 | 0 | 7.69 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.02 | ||||||
| Brevibacillus agri | 6.67 | 0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.19 | ||||||
| Fictibacillus nanhaiensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 0.10 | ||||||
| Lysinibacillus fusiformis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.57 | 0.31 | 8.33 | 0.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.89 | ||||||
| L. macroides | 6.67 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.67 | 0.10 | ||||||
| L. mangiferahumi | 13.33 | 0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.19 | ||||||
| L. massiliensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.14 | ||||||
| L. parviboronicapiens | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.57 | 1.29 | 16.67 | 0.65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.33 | 1.93 | ||||||
| L. sphaericus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.13 | 7.14 | 0.04 | 21.43 | 0.87 | 6.67 | 1.03 | ||||||
| L. xylanilyticus | 60 | 0.27 | 30.77 | 0.11 | 57.14 | 0.74 | 58.33 | 3.68 | 78.57 | 3.22 | 21.43 | 1.08 | 50.67 | 9.10 | ||||||
| Paenibacillus alvei | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 28.57 | 0 | 0 | 2.67 | 28.60 | ||||||
| P. apiarius | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.31 | ||||||
| P. castaneae | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.04 | 1.33 | 0.04 | ||||||
| P. elgii | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| P. lautus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.05 | ||||||
| P. pini | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.57 | 1.33 | 0.57 | ||||||
| P. taichungensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.48 | 2.67 | 0.54 | ||||||
| P. terrigena | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.01 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Psychrobacillus insolitus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.31 | ||||||
| Psychrobacillus psychrodurans | 13.33 | 0.11 | 7.69 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.12 | ||||||
| Rummeliibacillus pycnus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 64.29 | 0.64 | 0 | 0 | 12.00 | 0.64 | ||||||
| Viridibacillus arenosi | 26.67 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 1.33 | 14.29 | 0.11 | 14.29 | 0.31 | 12.00 | 1.86 | ||||||
| V. arvi | 20 | 0.01 | 7.69 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.33 | 0.02 | ||||||
| 总计 Total | - | 4.866 | - | 3.485 | - | 11.222 | - | 22.137 | - | 39.761 | - | 36.795 | - | - | ||||||
表3 武夷山自然保护区各地区芽胞杆菌的分离频度(%)和平均数量(×105 cfu/g)
Table 3 The frequency (%) and average quantification (×105 cfu/g) of Bacillus-like species isolated from different sites in Wuyishan Nature Reserve
| 芽胞杆菌种类 Bacillus-like species | 黄岗山顶部 Peak of the Huanggang Mountain | 黄岗山中部 Middle of the Huanggang Mountain | 黄岗山底部 Base of the Huanggang Mountain | 桐木关 Tongmuguan | 挂墩 Guadun | 大竹岚 Dazhulan | 总体 Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequ-ency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | 频度 Frequency | 数量 Quantification | |||||||
| Bacillus aryabhattai | 0 | 0 | 7.69 | 0.02 | 14.29 | 0.10 | 8.33 | 2.42 | 14.29 | 0.05 | 14.29 | 0.62 | 9.33 | 3.20 | ||||||
| B. bataviensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.43 | 1.33 | 0.43 | ||||||
| B. cecembensis | 6.67 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| B. cereus | 66.67 | 0.26 | 53.85 | 1.27 | 28.57 | 0.72 | 16.67 | 0.29 | 42.86 | 0.64 | 21.43 | 0.40 | 40 | 3.58 | ||||||
| B. endoradicis | 13.33 | 0.02 | 7.69 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.03 | ||||||
| B. halmapalus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| B. isronensis | 6.67 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| B. manliponensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 2.67 | 0.07 | ||||||
| B. licheniformis | 6.67 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.03 | ||||||
| B. marisflavi | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.11 | 1.33 | 0.11 | ||||||
| B. methylotrophicus | 6.67 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.67 | 0.02 | ||||||
| B. muralis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25.00 | 0.67 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.77 | 6.67 | 1.43 | ||||||
| B. mycoides | 100.0 | 3.26 | 69.20 | 1.42 | 28.57 | 0.95 | 16.67 | 0.47 | 7.14 | 0.04 | 14.29 | 1.24 | 41.33 | 7.37 | ||||||
| B. novalis | 6.67 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.07 | ||||||
| B. pseudomycoides | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.57 | 0.21 | 8.33 | 0.42 | 42.86 | 2.44 | 14.29 | 0.09 | 14.67 | 3.16 | ||||||
| B. safensis | 0 | 0 | 7.69 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.36 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.36 | ||||||
| B. simplex | 26.67 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.05 | 6.67 | 0.23 | ||||||
| B. tequilensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 16.19 | 1.33 | 16.19 | ||||||
| B. thuringiensis | 20 | 0.18 | 30.77 | 0.63 | 100.0 | 6.73 | 83.33 | 11.00 | 71.43 | 3.24 | 85.71 | 13.47 | 61.33 | 35.25 | ||||||
| B. weihenstephanensis | 0 | 0 | 7.69 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.02 | ||||||
| Brevibacillus agri | 6.67 | 0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.19 | ||||||
| Fictibacillus nanhaiensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 0.10 | ||||||
| Lysinibacillus fusiformis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.57 | 0.31 | 8.33 | 0.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.89 | ||||||
| L. macroides | 6.67 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.67 | 0.10 | ||||||
| L. mangiferahumi | 13.33 | 0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.19 | ||||||
| L. massiliensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.14 | ||||||
| L. parviboronicapiens | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.57 | 1.29 | 16.67 | 0.65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.33 | 1.93 | ||||||
| L. sphaericus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.13 | 7.14 | 0.04 | 21.43 | 0.87 | 6.67 | 1.03 | ||||||
| L. xylanilyticus | 60 | 0.27 | 30.77 | 0.11 | 57.14 | 0.74 | 58.33 | 3.68 | 78.57 | 3.22 | 21.43 | 1.08 | 50.67 | 9.10 | ||||||
| Paenibacillus alvei | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.29 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 28.57 | 0 | 0 | 2.67 | 28.60 | ||||||
| P. apiarius | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.31 | ||||||
| P. castaneae | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.04 | 1.33 | 0.04 | ||||||
| P. elgii | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| P. lautus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.05 | ||||||
| P. pini | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.57 | 1.33 | 0.57 | ||||||
| P. taichungensis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.48 | 2.67 | 0.54 | ||||||
| P. terrigena | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 0.01 | 1.33 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Psychrobacillus insolitus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.33 | 0.31 | ||||||
| Psychrobacillus psychrodurans | 13.33 | 0.11 | 7.69 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.00 | 0.12 | ||||||
| Rummeliibacillus pycnus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 64.29 | 0.64 | 0 | 0 | 12.00 | 0.64 | ||||||
| Viridibacillus arenosi | 26.67 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.33 | 1.33 | 14.29 | 0.11 | 14.29 | 0.31 | 12.00 | 1.86 | ||||||
| V. arvi | 20 | 0.01 | 7.69 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.33 | 0.02 | ||||||
| 总计 Total | - | 4.866 | - | 3.485 | - | 11.222 | - | 22.137 | - | 39.761 | - | 36.795 | - | - | ||||||
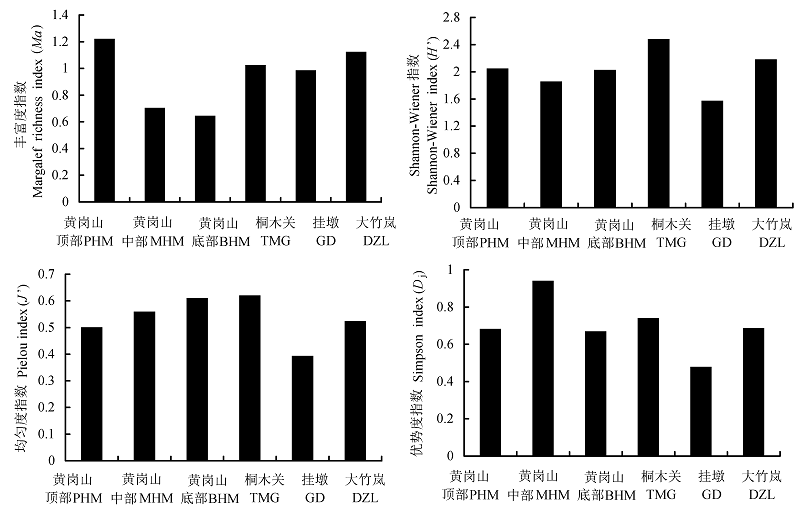
图2 武夷山保护区不同采样地点土壤芽胞杆菌的多样性指数。PHM、MHM、BHM、TMG、GD、DZL的含义见表1。
Fig. 2 Diversity indices of Bacillus-like species isolated from different sampling sites in Wuyishan Nature Reserve. See Table 1 for PHM, MHM, BHM, TMG, GD, DZL.
| 芽胞杆菌种类 Bacillus-like species | 数量与海拔的相关性 Correlation between quantification and altitude | 分离频度与海拔的相关性 Correlation between frequency and altitude | 数量与分离频度的相关性 Correlation between quantification and frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus cereus | 0.136 | 0.960** | 0.220 |
| Bacillus mycoides | 0.852* | 0.952** | 0.906* |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | -0.834* | -0.931** | 0.792 |
| Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus | -0.635 | 0.034 | -0.273 |
表4 武夷山自然保护区芽胞杆菌数量、分离频度、海拔间的相关性
Table 4 The correlations among frequency, quantification of four Bacillus-like species distribution and altitude in Wuyishan Nature Reserve
| 芽胞杆菌种类 Bacillus-like species | 数量与海拔的相关性 Correlation between quantification and altitude | 分离频度与海拔的相关性 Correlation between frequency and altitude | 数量与分离频度的相关性 Correlation between quantification and frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus cereus | 0.136 | 0.960** | 0.220 |
| Bacillus mycoides | 0.852* | 0.952** | 0.906* |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | -0.834* | -0.931** | 0.792 |
| Lysinibacillus xylanilyticus | -0.635 | 0.034 | -0.273 |
| 1 | Chen S, Hu W, Xiao Y, Deng Y, Jia J, Hu M (2012) Degradation of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by aBacillus sp. PLoS ONE, 7, e50456. |
| 2 | Eduardo EC, José RA, José ÁVQ, María MSR, Juan AED, Humberto GR, César MCA (2015) Classification and ordination of main plant communities along an altitudinal gradient in the arid and temperate climates of northeastern Mexico. The Science of Nature, 102, 58-68. |
| 3 | Fang YH (2005) Species composition and diversity of evergreen broad-leaved forest of Castanopsis carlesii and C. eyrei in Wuyishan National Nature Reserve, Fujian, China. Biodiversity Science, 13, 148-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [方燕鸿 (2005) 武夷山米槠、甜槠常绿阔叶林的物种组成及多样性分析. 生物多样性, 13, 148-155.] | |
| 4 | Fierer N, Mccain CM, Meir P, Zimmermann M, Rapp JM, Silman MR, Knight R (2011) Microbes do not follow the elevational diversity patterns of plants and animals. Ecology, 92, 797-804. |
| 5 | Gartner A, Blumel M, Wiese J, Imhoff JF (2011) Isolation and characterisation of bacteria from the Eastern Mediterranean deep sea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 100, 421-435. |
| 6 | Ge CB, Liu B, Che JM, Chen MC, Liu GH, Wei JC (2015) Diversity of Bacillus species inhabiting on the surface and endophyte of lichens collected from Wuyi Mountain. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 55, 551-563. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [葛慈斌, 刘波, 车建美, 陈梅春, 刘国红, 魏江春 (2015) 武夷山地衣表生和内生芽胞杆菌种群的多样性. 微生物学报, 55, 551-563.] | |
| 7 | Guo XH, Zhao ZD, Xiong HR (2010) Review on the intestinal microecology of Bacilli-derived probiotics. Chinese Journal of Microecology, 22, 1136-1139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭小华, 赵志丹, 熊海容 (2010) 益生芽胞杆菌肠道微生态学研究进展. 中国微生态学杂志, 22, 1136-1139.] | |
| 8 | Hayat R, Rizwan AS, Muhammad IH, Ahmed I (2013) Characterization and identification of compost bacteria based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Annals of Microbiology, 63, 905-912. |
| 9 | Hu LL, Yan BQ, Jiang MX, Zhu JJ (2007) The diversity of plant communities with endangered plant, Berchemiella wilsonii vat. pubipetiolata. Acta Botanica Boreali- Occidentalia Sinica, 27, 594-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡理乐, 闫伯前, 江明喜, 朱教君 (2007) 毛柄小勾儿茶伴生群落种类组成及多样性研究. 西北植物学报, 27, 594-600.] | |
| 10 | José AS, Rosa M (2016) Abundance and diversity of bacterial, archaeal, and fungal communities along an altitudinal gradient in alpine forest soils: what are the driving factors? Microbial Ecology, 72, 207-220. |
| 11 | Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 64, 346-351. |
| 12 | Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing Eztaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 62, 716-721. |
| 13 | Kim YH, Kim IS, Moon EY, Park JS, Kim SJ, Lim JH, Park BT, Lee EJ (2011) High abundance and role of antifungal bacteria in compost-treated soils in a wildfire area. Microbial Ecology, 62, 725-737. |
| 14 | Köberl M, Müller H, Ramadan EM, Berg G (2011) Desert farming benefits from microbial potential in arid soils and promotes diversity and plant health. PLoS ONE, 6, 244-252. |
| 15 | Lee CS, Jung YT, Park S, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2010) Lysibibacillus xylanilyticus sp. nov., a xalan-degrading bacterium isolated from forest humus. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 60, 281-286. |
| 16 | Li XM, Che KJ, Yang YH, Wang H, Ma WW, Wang H, Huang R (2014) Variation pattern of soil nutrients in forests at dif- ferent altitudes at upstream of Bailongjiang River. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 49(6), 131-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李兴民, 车克钧, 杨永红, 王辉, 马维维, 王惠, 黄蓉 (2014) 白龙江上游不同海拔森林土壤养分变化规律研究. 甘肃农业大学学报, 49(6), 131-137.] | |
| 17 | Li ZJ, Chen LZ, Lin QX, Lin JL, Liu DL, Liu CD, He JY, Chen BH, Huang ZH, Lin WQ, Shi DM (2002) Study on the species diversity of higher plants in Buxus sinica var. parvifolia dwarf community in Wuyishan Mountains. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 41, 574-578. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李振基, 陈鹭真, 林清贤, 林建丽, 刘德龙, 刘初钿, 何健源, 陈炳华, 黄泽豪, 林文群, 石冬梅 (2002) 武夷山自然保护区生物多样性研究. I. 小叶黄杨矮曲林物种多样性. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 41, 574-578.] | |
| 18 | Liu M, Cui Y, Huang HQ, Sun QG, Zhu J, Zou XX, Bao SX (2014) Isolation and diversity of Bacillus-like species from Dongzhai Harbor mangrove soil. Journal of Microbiology, 34(5), 21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘敏, 崔莹, 黄惠琴, 孙前光, 朱军, 邹潇潇, 鲍时翔 (2014) 东寨港红树林土壤芽胞杆菌分离及其多样性分析. 微生物学杂志, 34(5), 21-26.] | |
| 19 | Lu H, Cong J, Liu X, Wang XL, Tang J, Li DQ, Zhang YG (2015) Plant diversity patterns along altitudinal gradients in alpine meadows in the Three River Headwater region, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 24(7), 197-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢慧, 丛静, 刘晓, 王秀磊, 唐军, 李迪强, 张于光 (2015) 三江源区高寒草甸植物多样性的海拔分布格局. 草业学报, 24(7), 197-204.] | |
| 20 | Lugo MA, Ferrero M, Menoyo E, Estévez MC, Siñeriz F, Anton A (2008) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizospheric bacteria diversity along an altitudinal gradient in South American Puna grassland. Microbial Ecology, 55, 705-713. |
| 21 | Sanahuja G, Banakar R, Twyman RM, Capell T, Christou P (2011) Bacillus thuringiensis: a century of research, devel- opment and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 9, 283-300. |
| 22 | Schnepf E, Crickmore N, van Rie J, Lereclus D, Baum J, Feitelson J, Zeigler DR, Dean DH (1998) Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal protein. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 62, 775-806. |
| 23 | Singh D, Lee CL, Kim WS, Kerfahi D, Chun JH, Adams JM (2014) Strong elevational trends in soil bacterial community composition on Mt. Halla, South Korea. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 68, 140-149. |
| 24 | Song J, Du LX, Wang RY, Wei LM, Cao WP, Song J, Wang JY, Feng SL (2011) Research on the distribution and diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis from Damaoshan Mountains. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27, 166-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋健, 杜立新, 王容燕, 魏利民, 曹伟平, 宋健, 王金耀, 冯书亮 (2011) 大茂山地区苏云金芽胞杆菌分布与多样性研究. 中国农学通报, 27(1), 166-169.] | |
| 25 | Song ZQ, Wang L, Liu XH, Lv G, Yang Q, Liang F (2013) Genetic diversity of Bacillus in agricultural soils in Henan Province. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 42(9), 73-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋兆齐, 王莉, 刘秀花, 吕刚, 杨清, 梁峰 (2013) 河南省农田土壤芽胞杆菌的遗传多样性分析. 河南农业科学, 42(9), 73-78.] | |
| 26 | Sophie T, Hu XM, Jacques M (2011) Characterization of Bacilli isolated from the confined environments of the Antarctic Concordia Station and the International Space Station. Astrobiology, 11, 323-334. |
| 27 | Sun HG, Huang HL, Zheng J, Jin X (2012) Optimization of fermentation conditions for high production of antimicrobial substance by Bacillus mycoides SH-1. Journal of Xuzhou Institute of Technology (Natural Sciences), 27(2), 45-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙会刚, 黄海亮, 郑进, 金鑫 (2012) 蕈状芽胞杆菌SH-1抗菌活性物质发酵条件优化. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版), 27(2), 45-49.] | |
| 28 | Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725-2729. |
| 29 | Tang QY (2010) Data Processing System. Beijing: Science Press. |
| [唐启义 (2010) DPS数据处理系统. 北京; 科学出版社.] | |
| 30 | Tang ZY, Gong GS, Liu P, Shao BL, Zhang SR (2009) A preliminary study of soil Bacillus in the suburbs of Chengdu. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University (Natural Science), 27, 188-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [唐志燕, 龚国淑, 刘萍, 邵宝林, 张世熔 (2009)成都市郊区土壤芽胞杆菌的初步研究. 西南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 27, 188-192.] | |
| 31 | Timmell TE (1967) Recent progress in the chemistry of wood hemicelluloses. Wood Sciences Technology, 1, 45-70. |
| 32 | Trick I, Salcher O, Lingens F (1984) Characterization of filament forming Bacillus strains isolated from bulking sludge. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19, 120-124. |
| 33 | Vasudevan G, Siddarthan V, Ramatchandirane PS (2015) Predominance of Bacillus sp. in soil samples of the southern regions of Western Ghats, India. Annals of Microbiology, 65, 431-441. |
| 34 | Wang GX, Fu WF, Cui J, Yuan M, Yao L (2006) Effects of active components from Bacillus mycoides metabolite on immune functions of mice. Chinese Veterinary Science, 36, 983-987. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王高学, 付维法, 崔婧, 袁明, 姚璐 (2006) 蕈状芽胞杆菌代谢产物活性成分对小鼠免疫功能的影响. 中国兽医科学, 36, 983-987.] | |
| 35 | Wang JS (2007) The species diversity of subfamily Nymphulinae (Lepidoptera: Nymphulinae) communities in the Wuyishan Nature Reserve in Fujian, China. Entomological Journal of East China, 16(1), 59-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪家社 (2007) 武夷山自然保护区水螟亚科昆虫物种多样性研究. 华东昆虫学报, 16(1), 59-63.] | |
| 36 | Wang JS (2006) The species diversity of subfamily Pyralinae (Lepidoptera: Pyralinae) communities in Wuyishan Nature Reserve. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences), 30(3), 98-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪家社 (2006) 武夷山自然保护区螟蛾亚科昆虫的物种多样性. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 30(3), 98-100.] | |
| 37 | Wang JT, Cao P, Hu HW, Li J, Han LL, Zhang LM, Zheng YM, He JZ (2015) Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial and archaeal communities along Mt. Shegyla on the Tibetan Plateau. Microbial Ecology, 69, 135-145. |
| 38 | Wang K, Yan PS, Ding QL, Wu QX, Wang ZB, Peng J (2013) Diversity of culturable root-associated/endophytic bacteria and their chitinolytic and aflatoxin inhibition activity of peanut plant in China. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 29, 1-10. |
| 39 | Wang LG, Xu C (2010) Preliminary discussion on the plant of Magnoliaceae in Wuyishan Nature Reserve. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology(福建林业科技), 37(2), 90-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王良桂, 徐晨 (2010) 福建武夷山国家级自然保护区木兰科植物资源初探. 福建林业科技, 37(2), 90-93.] | |
| 40 | Wang SJ, Ruan HH, Wang JS, Xu ZK, Wu YY (2010) Dynamic change of soil fauna community structure in the course of litter decomposition on the Wuyi Mountains. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 30(6), 43-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王邵军, 阮宏华, 汪家社, 徐自坤, 吴焰玉 (2010) 武夷山土壤动物群落结构在凋落物分解过程中的变化. 西南林学院学报, 30(6), 43-47.] | |
| 41 | Wang ZX, Liu B, Lin YZ, Liu GH (2012) Collection, identification and phylogenetic diversity of Bacillus species in soil samples from Xinjiang. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 27, 187-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王子旋, 刘波, 林营志, 刘国红 (2012) 新疆土壤芽胞杆菌采集鉴定及其分布多样性. 福建农业学报, 27, 187-195.] | |
| 42 | Wei X, Zheng XF, Zhang SX (2014) Forest soil physicochemical properties along different altitudinal gradients at Huoditang in the Qinling Mountains. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 29(3), 9-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏新, 郑小锋, 张硕新 (2014) 秦岭火地塘不同海拔梯度森林土壤理化性质研究. 西北林学院学报, 29(3), 9-14. | |
| 43 | Wu ZY, Lin WX, Chen ZF, Fang CX, Zhang ZX, Wu LK, Zhou MM, Shen LH (2013) Characteristics of soil microbial community under different vegetation types in Wuyishan National Nature Reserve, East China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 2301-2309. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴则焰, 林文雄, 陈志芳, 方长旬, 张志兴, 吴林坤, 周明明, 沈荔花 (2013) 武夷山国家自然保护区不同植被类型土壤微生物群落特征. 应用生态学报, 24, 2301-2309.] | |
| 44 | Wu ZY, Lin WX, Chen ZF, Liu JF, Fang CX, Zhang ZX, Wu LK, Chen T (2014) Phospholopid fatty acid analysis of soil microbes at different elevation of Wuyi Mountains. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 50(7), 105-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴则焰, 林文雄, 陈志芳, 刘金福, 方长旬, 张志兴, 吴林坤, 陈婷 (2014) 武夷山不同海拔植被带土壤微生物PLFA分析. 林业科学, 50(7), 105-112.] | |
| 45 | Xu SX, Shi HF, Zeng YP, Zhang FY, Wang ZH (1998) Biologic characteristics of Bacillus mycoides and application of radiation protection. Chinese Journal of Microecology, 10, 155-156, 163. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐书显, 时华富, 曾亚平, 张风云, 王忠海 (1998) 蕈状芽胞杆菌的特性及在辐射防护中的应用. 中国微生态学杂志, 10, 155-156, 163.] | |
| 46 | Yazdani M, Naderi-Manesh H, Khajeh K, Soudi MR, Asghari SM, Sharifzadeh M (2009) Isolation and characterization of a novel gamma-radiation-resistant bacterium from hot spring in Iran. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 49, 119-127. |
| 47 | Yu ZN, Wang JP, He J (2013) Advance in genome research of Bacillus thuringiensis. Journal of Microbiology, 33(2), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [喻子牛, 王阶平, 何进 (2013) 苏云金芽胞杆菌基因组研究. 微生物学杂志, 33(2), 1-6.] | |
| 48 | Zhang FT, Huang HQ, Cui Y, Sun QG, Zhu J, Liu M, Bao SX (2014) Isolation and diversity of Bacillus species from Jiaxi tropical rain forest soil. Journal of Microbiology, 34(4), 42-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张福特, 黄惠琴, 崔莹, 孙前光, 朱军, 刘敏, 鲍时翔 (2014) 佳西热带雨林土壤芽胞杆菌分离与多样性分析. 微生物学杂志, 34(4), 42-46.] | |
| 49 | Zhang W, Wei HL, Gao HW, Hu YG (2005) Advances of studies on soil microbial diversity and environmental impact factors. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 24(1), 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张薇, 魏海雷, 高洪文, 胡跃高 (2005) 土壤微生物多样性及其环境影响因子研究进展. 生态学杂志, 24(1), 48-52.] | |
| 50 | Zhang WF, Quan JX, Xie L, Wang Q, Yi YT, Feng MM, Zhu L, Wang RP, Fang XJ (2009) Collection of Bacillus and identification of Bacillus thuringensis isolates from tropical rain forest reserves of Hainan Island. Genomics and Applied Biology, 28, 265-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张文飞, 全嘉新, 谢柳, 王茜, 易艳桃, 丰玫玫, 朱麟, 王锐萍, 方宣钧 (2009) 海南岛热带雨林区芽胞杆菌收集及Bt菌鉴定. 基因组学与应用生物学, 28, 265-274.] | |
| 51 | Zhang Y, Cong J, Lu H, Li G, Qu Y, Su X, Zhou J, Li D (2014) Community structure and elevational diversity patterns of soil Acidobacteria. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 26, 1717-1724. |
| 52 | Zhang Y, Guo LD, Liu RJ (2003) Diversity and ecology of arbuscular mycorrhizal. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 27, 537-544. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张英, 郭良栋, 刘润进 (2003) 都江堰地区丛枝菌根真菌多样性与生态研究. 植物生态学报, 27, 537-544.] | |
| 53 | Zhang YG, Su XJ, Cong J, Chen Z, Lu H, Liu MC, Li DQ (2014) Variation of soil microbial community along elevation in the Shennongjia Mountain. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 50(9), 161-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张于光, 宿秀江, 丛静, 陈展, 卢慧, 刘敏超, 李迪强 (2014) 神农架土壤微生物群落的海拔梯度变化. 林业科学, 50(9), 161-166.] | |
| 54 | Zhou QP, Huang HQ, Cui Y, Liu M, Sun QG, Bao SX (2015) Diversity analysis of culturable Bacillus-like species from Jianfengling tropical rain forest soil. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 42(2), 59-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周秋平, 黄惠琴, 崔莹, 刘敏, 孙前光, 鲍时翔 (2015) 尖峰岭热带雨林土壤中可培养芽胞杆菌多样性分析. 广东农业科学, 42(2), 59-63.] | |
| 55 | Zhou WC, Lin J, Xiao Q (2011) Study on species diversity of land seashell in Wuyi Mountain Nature Reserve. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 38(3), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周卫川, 林晶, 肖琼 (2011) 武夷山自然保护区陆生贝类物种多样性研究. 福建林业科技, 38(3), 1-7.] | |
| 56 | Zhuang TC, Lin P, Chen RH (1997) Amount and group of soil heterotrophic microorganisms in different forest types of Wuyi Mountains. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 36, 293-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [庄铁成, 林鹏, 陈仁华 (1997) 武夷山不同森林类型土壤异养微生物数量与类群组成. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 36, 293-298.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn