



生物多样性 ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (4): 470-481. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.12233
收稿日期:2011-12-16
接受日期:2012-04-25
出版日期:2012-07-20
发布日期:2012-09-12
通讯作者:
金光泽
作者简介:*E-mail: taxus@126.com基金资助:Received:2011-12-16
Accepted:2012-04-25
Online:2012-07-20
Published:2012-09-12
Contact:
Guangze Jin
摘要:
阔叶红松(Pinus koraiensis)林是我国东北东部山区的地带性顶极植被, 按其群落特征和物种组成可分为南部红松林、典型红松林和北部红松林。依照BCI(Barro Colorado Island)50 ha样地的技术规范, 作者于2005年在典型红松林分布的黑龙江凉水国家级自然保护区建立了一块9 ha的固定监测样地, 并于2010年对样地内胸径 ≥ 1 cm的木本植物进行了全面调查。结果表明, 样地内的木本植物共有48种, 独立个体数为21,355株(包括分枝数为34,021棵), 隶属于20科34属。绝大部分种类属于长白山区系小兴安岭亚系, 同时混生有一些亚热带成分。样地内所有个体的径级分布呈倒“J”型, 群落自我更新良好。林冠层、亚冠层和中间层的径级分布均呈倒“J”型, 林下层呈“L”型。主要树种大青杨(Populus ussuriensis)、红松、枫桦(Betula costata)、水曲柳(Fraxinus mandshurica)、红皮云杉(Picea koraiensis)等的径级结构可分为近似于“正态”型、倒“J”型和“L”型3种类型。主要树种在样地的空间分布大多呈聚集分布, 但大部分物种随着径级的增加聚集程度变小。树种分布与地形紧密关联, 不同物种在不同径级表现出对生境有不同的偏好; 红松和紫椴(Tilia amurensis)各径级的分布均与地形显著相关(P < 0.05), 而冷杉(Abies nephrolepis)、花楷槭(Acer ukurunduense)、裂叶榆(Ulmus laciniata)、色木槭(Acer mono)的径级I(DBH < 10 cm)、II(10 cm≤ DBH < 30 cm)和枫桦、青楷槭(Acer tegmentosum)的径级I的分布与地形显著相关(P < 0.05), 且随着径级的增加, 地形因子对其分布的影响显著减小。
徐丽娜, 金光泽 (2012) 小兴安岭凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地:物种组成与群落结构. 生物多样性, 20, 470-481. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.12233.
Lina Xu, Guangze Jin (2012) Species composition and community structure of a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) forest plot in Liangshui Nature Reserve, Northeast China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 470-481. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.12233.
| 树种 Species | 多度 Abundance | 平均胸径 Mean DBH (cm) | 最大胸径 Max. DBH (cm) | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2/ha) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 毛榛子 Corylus mandshurica | 4,617(11,195)* | 2.10(1.86) | 6.70 | 0.38147 | 10.50(14.24) |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 2,142(2,362) | 7.73(7.27) | 59.00 | 2.43008 | 8.25(7.23) |
| 刺五加 Acanthopanax senticosus | 1,937(3,328) | 1.57(1.52) | 5.00 | 0.07297 | 5.07(5.31) |
| 瘤枝卫矛 Euonymus pauciflorus | 1,279(1,730) | 1.85(1.78) | 7.40 | 0.05428 | 4.14(3.84) |
| 花楷槭 Acer ukurunduense | 1,262(2,573) | 4.26(3.50) | 30.40 | 0.43052 | 4.38(4.93) |
| 红松 Pinus koraiensis | 1,200(1,219) | 42.81(42.40) | 108.10 | 24.15018 | 23.33(22.65) |
| 青楷槭 Acer tegmentosum | 988(1,416) | 5.10(5.55) | 26.80 | 0.49454 | 3.58(3.43) |
| 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata | 971(1,166) | 7.73(6.88) | 64.60 | 1.47732 | 4.65(4.27) |
| 冷杉 Abies nephrolepis | 905(911) | 16.17(16.08) | 48.30 | 3.00860 | 5.77(5.25) |
| 东北山梅花 Philadelphus schrenkii | 800(1,103) | 1.70(1.66) | 4.00 | 0.02938 | 2.96(2.80) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis | 728(1,017) | 13.35(11.34) | 94.40 | 3.00901 | 5.13(4.99) |
| 枫桦 Betula costata | 601(634) | 13.02(12.66) | 83.20 | 2.04383 | 3.73(3.41) |
| 暴马丁香 Syringa reticulate var. mandshurica | 598(898) | 4.78(4.13) | 32.00 | 0.23008 | 2.42(2.37) |
| 光萼溲疏 Deutzia gladata | 446(683) | 1.35(1.33) | 2.60 | 0.01099 | 1.73(1.71) |
| 水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica | 407(423) | 12.54(12.27) | 68.70 | 1.26995 | 2.61(2.39) |
| 稠李 Prunus padus | 402(741) | 3.71(3.33) | 14.70 | 0.11077 | 1.28(1.38) |
| 春榆 Ulmus japonica | 392(447) | 5.11(4.79) | 81.50 | 0.29190 | 1.42(1.24) |
| 黄花忍冬 Lonicera chrysantha | 379(534) | 1.56(1.56) | 4.90 | 0.01266 | 1.52(1.45) |
| 糠椴 Tilia mandshurica | 220(323) | 7.18(5.95) | 64.30 | 0.25451 | 0.85(0.82) |
| 龙牙楤木 Aralia elata | 196(235) | 3.08(2.97) | 12.70 | 0.02442 | 0.71(0.63) |
| 红皮云杉 Picea koraiensis | 126(127) | 20.51(20.35) | 81.00 | 0.82988 | 1.30(1.23) |
| 花楸 Sorbus pohuashanensis | 91(110) | 6.65(6.14) | 30.20 | 0.06735 | 0.50(0.47) |
| 早花忍冬 Lonicera praeflorens | 87(123) | 1.66(1.64) | 3.30 | 0.00313 | 0.36(0.35) |
| 大青杨 Populus ussuriensis | 77(78) | 19.73(19.49) | 133.00 | 0.89629 | 0.97(0.93) |
| 暖木条荚蒾 Viburnum burejaeticum | 69(133) | 1.62(1.58) | 3.00 | 0.00311 | 0.32(0.35) |
| 山槐 Maackia amurensis | 61(71) | 6.03(5.70) | 14.70 | 0.02984 | 0.26(0.23) |
| 鱼鳞云杉 Picea jezoensis | 58(59) | 15.70(15.46) | 63.00 | 0.22544 | 0.49(0.46) |
| 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 42(48) | 13.02(12.17) | 55.50 | 0.14238 | 0.33(0.31) |
| 东北茶藨子 Ribes mandschuricum | 41(68) | 1.42(1.45) | 3.10 | 0.00135 | 0.21(0.21) |
| 黄菠萝 Phellodendron amurense | 29(32) | 14.84(14.13) | 33.10 | 0.07537 | 0.21(0.20) |
| 大黄柳 Salix raddeana | 29(32) | 13.34(12.68) | 24.70 | 0.04971 | 0.16(0.14) |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 28(28) | 14.63(14.63) | 31.00 | 0.06837 | 0.19(0.17) |
| 毛赤杨 Alnus sibirica | 26(33) | 12.79(12.47) | 31.7 | 0.05828 | 0.15(0.14) |
| 鸡树条荚蒾 Viburnum sargenti | 24(25) | 1.83(1.85) | 3.50 | 0.00084 | 0.12(0.10) |
| 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta | 16(20) | 2.03(1.91) | 4.00 | 0.00073 | 0.09(0.09) |
| 白桦 Betula platyphylla | 15(15) | 13.59(13.59) | 22.20 | 0.02730 | 0.09(0.08) |
| 大叶小檗 Berberis poiretii | 12(16) | 1.33(1.35) | 1.80 | 0.00026 | 0.06(0.06) |
| 鼠李 Rhamnus davarica | 11(11) | 4.24(4.24) | 15.30 | 0.00333 | 0.06(0.05) |
| 香杨 Populus koreana | 11(11) | 10.41(10.41) | 18.00 | 0.01152 | 0.05(0.04) |
| 接骨木 Sambucus williamsii | 8(14) | 2.10(2.18) | 4.20 | 0.00069 | 0.05(0.05) |
| 山桃稠李 Prunus maackii | 6(7) | 10.77(10.41) | 19.00 | 0.00837 | 0.04(0.04) |
| 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 4(4) | 10.73(10.73) | 26.70 | 0.00731 | 0.03(0.03) |
| 刺玫果 Rosa acicularis | 3(6) | 1.17(1.15) | 1.50 | 0.00007 | 0.02(0.02) |
| 蒿柳 Salix viminalis | 3(3) | 8.63(8.63) | 12.20 | 0.00214 | 0.02(0.02) |
| 谷柳 Salix starkeana var. livida | 3(3) | 7.80(7.80) | 9.80 | 0.00165 | 0.02(0.02) |
| 五味子 Schisandra chinensis | 3(3) | 2.80(2.80) | 3.70 | 0.00022 | 0.01(0.01) |
| 伪粉枝柳 Salix rorida var. roridaeformis | 1(2) | 1.20(1.20) | 1.20 | 0.00003 | 0.01(0.01) |
| 珍珠梅 Sorbaria sorbifolia | 1(1) | 1.00(1.00) | 1.00 | 0.00001 | 0.01(0.01) |
| 总计 Total | 21,355(34,021) | 7.41(5.43) | 42.30241 |
表1 凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地的物种组成
Table 1 Species composition of a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest plot in Liangshui Nature Reserve
| 树种 Species | 多度 Abundance | 平均胸径 Mean DBH (cm) | 最大胸径 Max. DBH (cm) | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2/ha) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 毛榛子 Corylus mandshurica | 4,617(11,195)* | 2.10(1.86) | 6.70 | 0.38147 | 10.50(14.24) |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 2,142(2,362) | 7.73(7.27) | 59.00 | 2.43008 | 8.25(7.23) |
| 刺五加 Acanthopanax senticosus | 1,937(3,328) | 1.57(1.52) | 5.00 | 0.07297 | 5.07(5.31) |
| 瘤枝卫矛 Euonymus pauciflorus | 1,279(1,730) | 1.85(1.78) | 7.40 | 0.05428 | 4.14(3.84) |
| 花楷槭 Acer ukurunduense | 1,262(2,573) | 4.26(3.50) | 30.40 | 0.43052 | 4.38(4.93) |
| 红松 Pinus koraiensis | 1,200(1,219) | 42.81(42.40) | 108.10 | 24.15018 | 23.33(22.65) |
| 青楷槭 Acer tegmentosum | 988(1,416) | 5.10(5.55) | 26.80 | 0.49454 | 3.58(3.43) |
| 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata | 971(1,166) | 7.73(6.88) | 64.60 | 1.47732 | 4.65(4.27) |
| 冷杉 Abies nephrolepis | 905(911) | 16.17(16.08) | 48.30 | 3.00860 | 5.77(5.25) |
| 东北山梅花 Philadelphus schrenkii | 800(1,103) | 1.70(1.66) | 4.00 | 0.02938 | 2.96(2.80) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis | 728(1,017) | 13.35(11.34) | 94.40 | 3.00901 | 5.13(4.99) |
| 枫桦 Betula costata | 601(634) | 13.02(12.66) | 83.20 | 2.04383 | 3.73(3.41) |
| 暴马丁香 Syringa reticulate var. mandshurica | 598(898) | 4.78(4.13) | 32.00 | 0.23008 | 2.42(2.37) |
| 光萼溲疏 Deutzia gladata | 446(683) | 1.35(1.33) | 2.60 | 0.01099 | 1.73(1.71) |
| 水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshurica | 407(423) | 12.54(12.27) | 68.70 | 1.26995 | 2.61(2.39) |
| 稠李 Prunus padus | 402(741) | 3.71(3.33) | 14.70 | 0.11077 | 1.28(1.38) |
| 春榆 Ulmus japonica | 392(447) | 5.11(4.79) | 81.50 | 0.29190 | 1.42(1.24) |
| 黄花忍冬 Lonicera chrysantha | 379(534) | 1.56(1.56) | 4.90 | 0.01266 | 1.52(1.45) |
| 糠椴 Tilia mandshurica | 220(323) | 7.18(5.95) | 64.30 | 0.25451 | 0.85(0.82) |
| 龙牙楤木 Aralia elata | 196(235) | 3.08(2.97) | 12.70 | 0.02442 | 0.71(0.63) |
| 红皮云杉 Picea koraiensis | 126(127) | 20.51(20.35) | 81.00 | 0.82988 | 1.30(1.23) |
| 花楸 Sorbus pohuashanensis | 91(110) | 6.65(6.14) | 30.20 | 0.06735 | 0.50(0.47) |
| 早花忍冬 Lonicera praeflorens | 87(123) | 1.66(1.64) | 3.30 | 0.00313 | 0.36(0.35) |
| 大青杨 Populus ussuriensis | 77(78) | 19.73(19.49) | 133.00 | 0.89629 | 0.97(0.93) |
| 暖木条荚蒾 Viburnum burejaeticum | 69(133) | 1.62(1.58) | 3.00 | 0.00311 | 0.32(0.35) |
| 山槐 Maackia amurensis | 61(71) | 6.03(5.70) | 14.70 | 0.02984 | 0.26(0.23) |
| 鱼鳞云杉 Picea jezoensis | 58(59) | 15.70(15.46) | 63.00 | 0.22544 | 0.49(0.46) |
| 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 42(48) | 13.02(12.17) | 55.50 | 0.14238 | 0.33(0.31) |
| 东北茶藨子 Ribes mandschuricum | 41(68) | 1.42(1.45) | 3.10 | 0.00135 | 0.21(0.21) |
| 黄菠萝 Phellodendron amurense | 29(32) | 14.84(14.13) | 33.10 | 0.07537 | 0.21(0.20) |
| 大黄柳 Salix raddeana | 29(32) | 13.34(12.68) | 24.70 | 0.04971 | 0.16(0.14) |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 28(28) | 14.63(14.63) | 31.00 | 0.06837 | 0.19(0.17) |
| 毛赤杨 Alnus sibirica | 26(33) | 12.79(12.47) | 31.7 | 0.05828 | 0.15(0.14) |
| 鸡树条荚蒾 Viburnum sargenti | 24(25) | 1.83(1.85) | 3.50 | 0.00084 | 0.12(0.10) |
| 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta | 16(20) | 2.03(1.91) | 4.00 | 0.00073 | 0.09(0.09) |
| 白桦 Betula platyphylla | 15(15) | 13.59(13.59) | 22.20 | 0.02730 | 0.09(0.08) |
| 大叶小檗 Berberis poiretii | 12(16) | 1.33(1.35) | 1.80 | 0.00026 | 0.06(0.06) |
| 鼠李 Rhamnus davarica | 11(11) | 4.24(4.24) | 15.30 | 0.00333 | 0.06(0.05) |
| 香杨 Populus koreana | 11(11) | 10.41(10.41) | 18.00 | 0.01152 | 0.05(0.04) |
| 接骨木 Sambucus williamsii | 8(14) | 2.10(2.18) | 4.20 | 0.00069 | 0.05(0.05) |
| 山桃稠李 Prunus maackii | 6(7) | 10.77(10.41) | 19.00 | 0.00837 | 0.04(0.04) |
| 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 4(4) | 10.73(10.73) | 26.70 | 0.00731 | 0.03(0.03) |
| 刺玫果 Rosa acicularis | 3(6) | 1.17(1.15) | 1.50 | 0.00007 | 0.02(0.02) |
| 蒿柳 Salix viminalis | 3(3) | 8.63(8.63) | 12.20 | 0.00214 | 0.02(0.02) |
| 谷柳 Salix starkeana var. livida | 3(3) | 7.80(7.80) | 9.80 | 0.00165 | 0.02(0.02) |
| 五味子 Schisandra chinensis | 3(3) | 2.80(2.80) | 3.70 | 0.00022 | 0.01(0.01) |
| 伪粉枝柳 Salix rorida var. roridaeformis | 1(2) | 1.20(1.20) | 1.20 | 0.00003 | 0.01(0.01) |
| 珍珠梅 Sorbaria sorbifolia | 1(1) | 1.00(1.00) | 1.00 | 0.00001 | 0.01(0.01) |
| 总计 Total | 21,355(34,021) | 7.41(5.43) | 42.30241 |
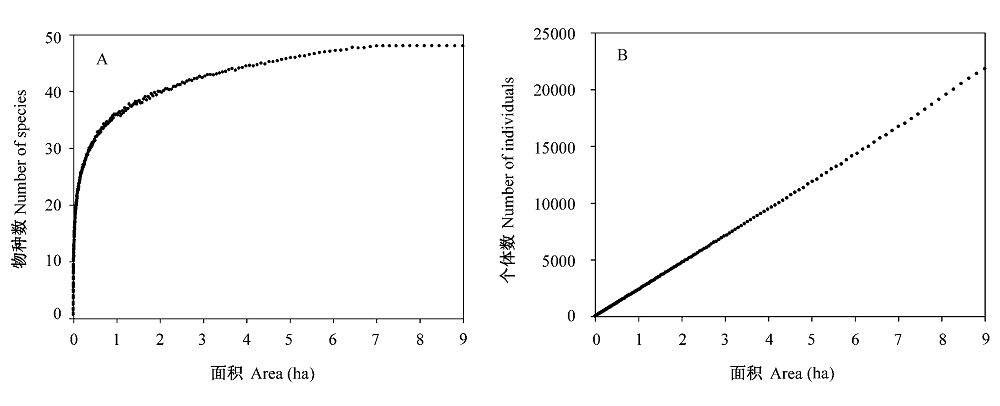
图2 凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地种-面积曲线和个体数-面积曲线
Fig. 2 Species-area curve and individual-area curve of a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest plot in Liangshui Nature Reserve
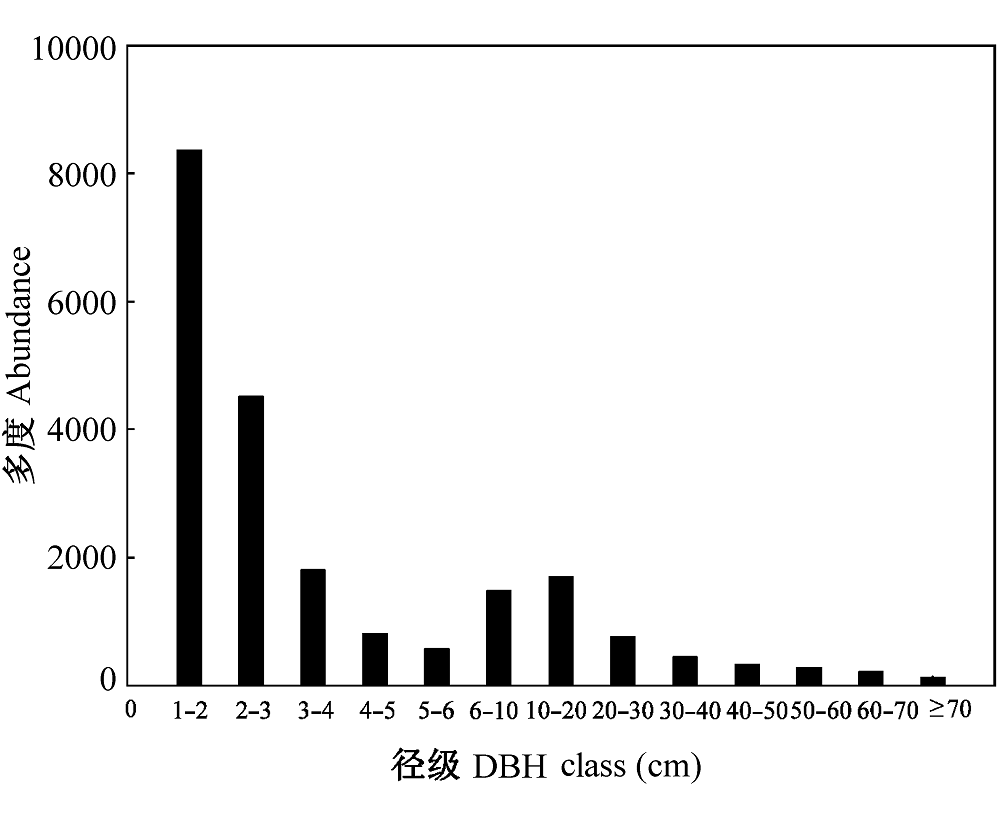
图3 凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地木本植物径级分布
Fig. 3 Distributional patterns of DBH class of woody species of a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest plot in Liangshui Nature Reserve
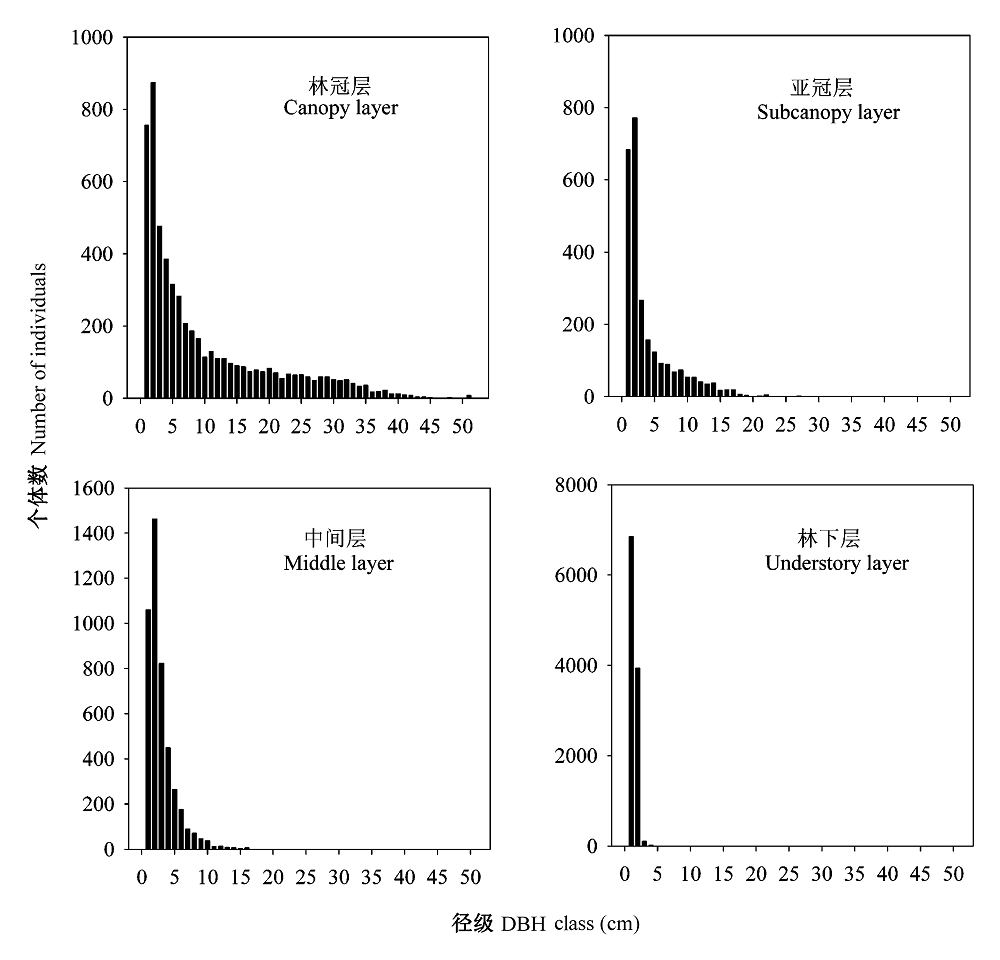
图4 凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地4个林层物种的径级结构
Fig. 4 Size-class distribution of four vertical layers of a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest plot in Liangshui Nature Reserve
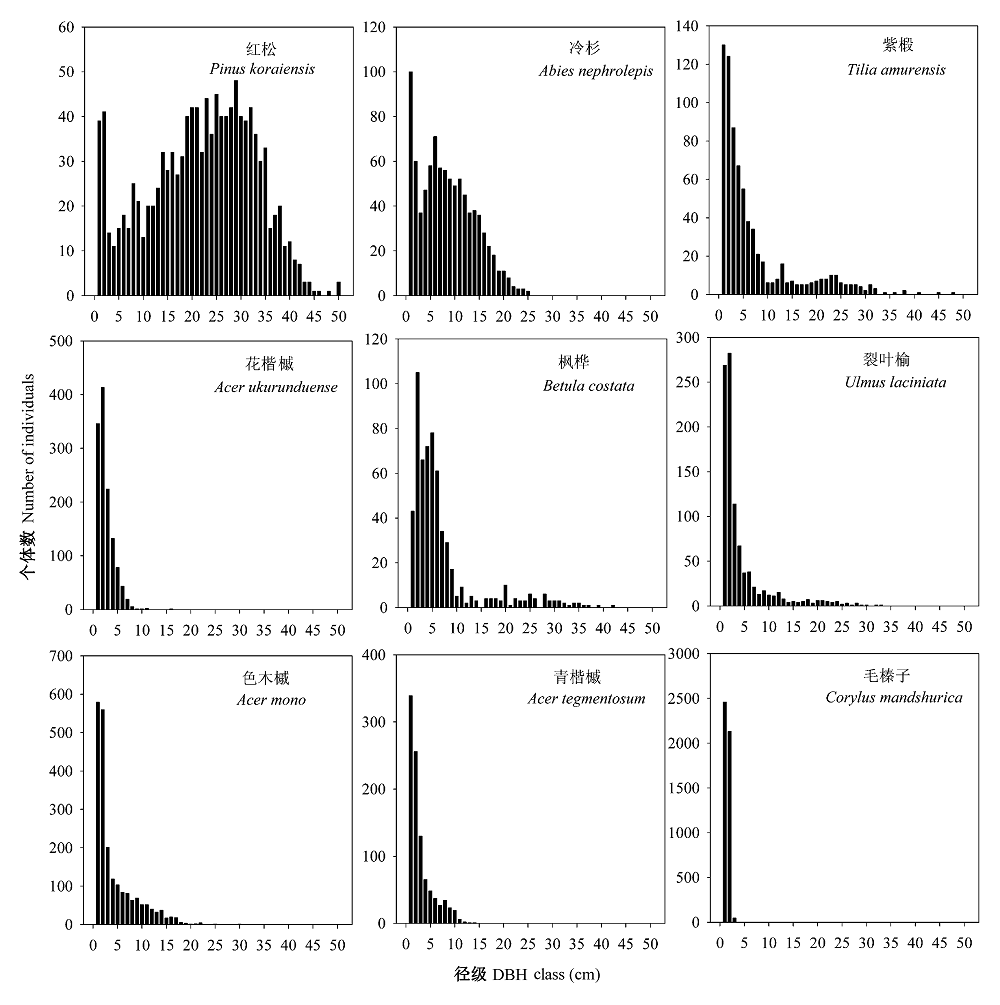
图5 凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地9个主要物种的径级结构
Fig. 5 Size-class distribution of nine major species of a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest plot in Liangshui Nature Reserve
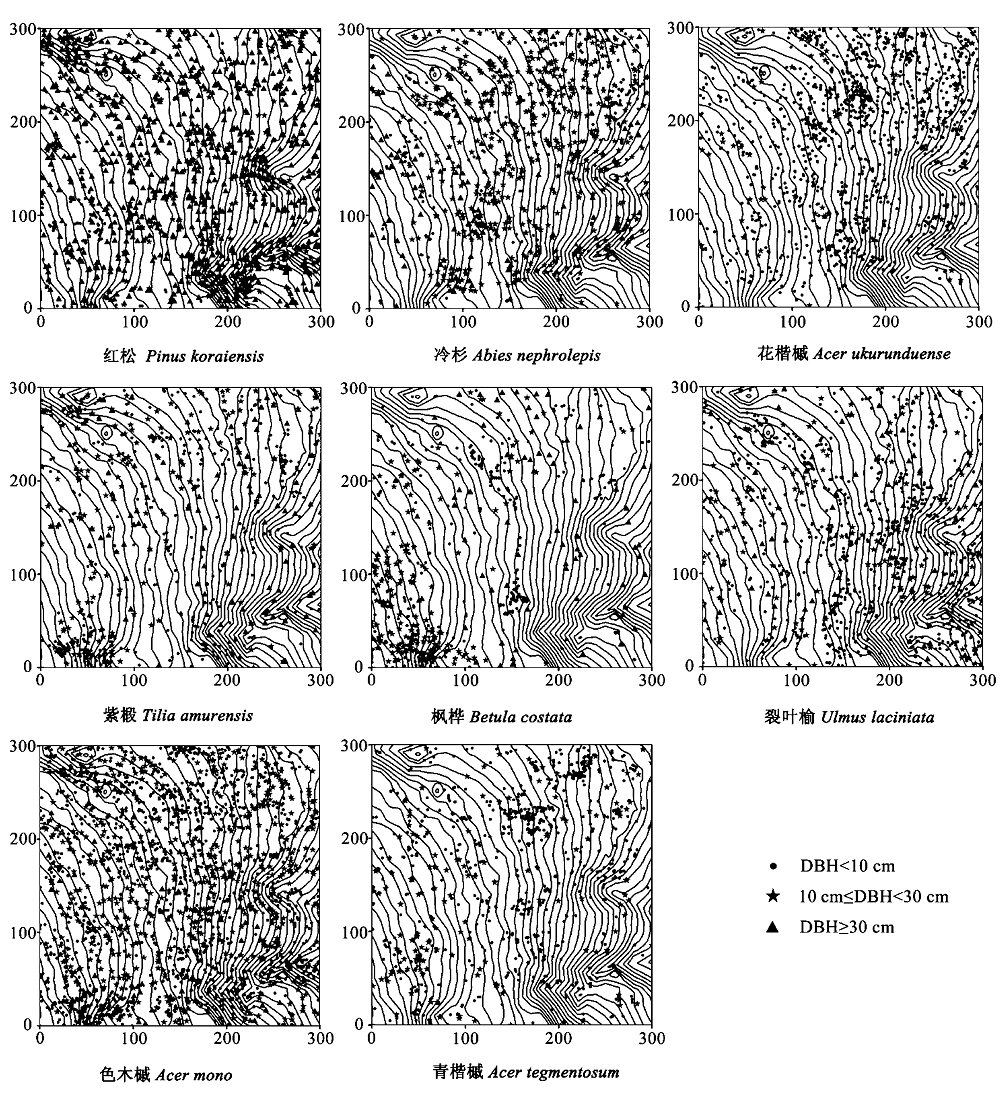
图6 凉水典型阔叶红松林动态监测样地8个主要乔木树种在3个不同径级的空间分布
Fig. 6 Spatial distribution of eight major tree species at three DBH classes of a typical mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest plot in Liangshui Nature Reserve
| [1] |
Berkley HA, Kendall BE, Mitarai S, Siegel DA (2010) Turbulent dispersal promotes species coexistence. Ecology Letters, 13, 360-371.
URL PMID |
| [2] | Chen L, Mi XC, Comita LS, Zhang LW, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Community-level consequences of density depen- dence and habitat association in a subtropical broad-leaved forest. Ecology Letters, 13, 695-704. |
| [3] | Condit R (1995) Research in large, long-term tropical forest plots. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 18-22. |
| [4] |
Condit R, Ashton P, Baker P, Bunyavejchewin S, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Hubbell SP, Foster RB, Itoh A, LaFrankie JV, Lee HS, Losos E, Manokaran N, Sukumar R, Yamakura T (2000) Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species. Science, 288, 1414-1418.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Condit R, Ashton P, Bunyavejchewin S, Dattaraja HS, Davies S, Esufali S, Ewango C, Foster R, Gunatilleke IA, Gunatil- leke CV, Hall P, Harms KE, Hart T, Hernandez C, Hubbell S, Itoh A, Kiratiprayoon S, LaFrankie J, de Lao SL, Makana JR, Noor MN, Kassim AR, Russo S, Sukumar R, Samper C, Suresh HS, Tan S, Thomas S, Valencia R, Vallejo M, Villa G, Zillio T (2006) The importance of demographic niches to tree diversity. Science, 313, 98-101. |
| [6] | Ellum DS, Ashton MS, Siccama TG (2010) Spatial pattern in herb diversity and abundance of second growth mixed deciduous-evergreen forest of southern New England, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 259, 1416-1426. |
| [7] | Hao ZQ (郝占庆), Li BH (李步杭), Zhang J (张健), Wang XG (王绪高), Ye J (叶吉), Yao XL (姚晓琳) (2008) Broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest plot in Changbaishan of China: community composition and structure. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 238-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Harms K, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (2001) Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot. Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959. |
| [9] | Hubbell SP (2001) The United Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [10] | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1986) Commonness and rarity in a neotropical forest: implications for tropical tree conservation. In: Conservation Biology: Science of Scarcity and Diversity (ed. Soulé ME), pp. 205-231. Sinauer Press, Sunderland. |
| [11] | Lan GY (兰国玉), Hu YH (胡跃华), Cao M (曹敏), Zhu H (朱华), Wang H (王洪), Zhou SS (周仕顺), Deng XB (邓晓保), Cui JY (崔景云), Huang JG (黄建国), Liu LY (刘林云), Xu HL (许海龙), Song JP (宋军平), He YC (何有才) (2008) Establishment of Xishuangbanna tropical forest dynamics plot: species composition and spatial distribution patterns. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 287-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
Lengendre P, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP, Yu MJ, Sun IF, He FL (2009) Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad- leaved forest of China. Ecology, 90, 663-674.
URL PMID |
| [13] |
Liu HF (刘海丰), Li L (李亮), Sang WG (桑卫国) (2011) Species composition and community structure of the Donglingshan forest dynamic plot in a warm temperate deciduous broad- leaved secondary forest, China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 19, 232-242. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [14] | Liu YY (刘妍妍), Jin GZ (金光泽) (2009) Influence of topography on coarse woody debris in a mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest in Xiaoxing′an Mountains, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 29, 1398-1407. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Liu YY (刘妍妍), Jin GZ (金光泽) (2010) Spatial point pattern analysis for coarse woody debris in a mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest in Xiaoxing'an Mountains, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 30, 6072-6081. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] |
Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: current knowledge and future challenge. Science, 294, 804-808.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] | Ma KP (马克平) (2011) Assessing progress of biodiversity conservation with monitoring approach. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 19, 125-126. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | Martinez I, Wiegand T, Gonzalez-Taboada F, Obeso JR (2010) Spatial associations among tree species in a temperate forest community in North-western Spain. Forest Ecology and Management, 260, 456-465. |
| [19] | Ricklefs RE (2004) A comprehensive framework for global patterns in biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 7, 1-15. |
| [20] | Sapkota IP, Tigabu M, Oden PC (2009) Spatial distribution, advanced regeneration and stand structure of Nepalese Sal (Shorea robusta) forests subject to disturbances of different intensities. Forest Ecology and Management, 257, 1966-1975. |
| [21] |
Shen GC, Yu MJ, Hu XS, Mi XC, Ren HB, Sun IF, Ma KP (2009) Species-area relationships explained by the joint effects of dispersal limitation and habitat heterogeneity. Ecology, 90, 3033-3041.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] | Wang XG, Hao ZQ, Ye J, Zhang J, Li BH, Yao XL (2008) Spatial pattern of diversity in an old-growth temperate forest in Northeastern China. Acta Oecologica, 33, 345-354. |
| [23] | Wang XG, Hao ZQ, Zhang J, Lian JY, Li BH, Ye J, Yao XL (2009) Tree size distributions in an old-growth temperate forest. Oikos, 118, 25-36. |
| [24] | Wang XG, Ye J, Li BH, Zhang J, Lin F, Hao ZQ (2010) Spatial distributions of species in an old-growth temperate forest, northeastern China. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 40, 1011-1019. |
| [25] | Wang LW (王利伟), Li BH (李步航), Ye J (叶吉), Bai XJ (白雪娇), Yuan ZQ (原作强), Xing DL (刑丁亮), Lin F (蔺菲), Shi S (师帅), Wang XG (王绪高), Hao ZQ (郝占庆) (2011) Dynamics of short-term tree mortality in broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest in the Changbai Mountains. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 19, 260-270. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Wang YH (王义弘), Chen DK (陈大珂), Zhu N (祝宁) (1995) The occurrence and formation of broad-leaved Korean pine forest. In: Korean Pine Forest (阔叶红松林) (ed. Wang YC (王业蘧)), pp. 32-74. Northeast Forestry University Press, Harbin. (in Chinese) |
| [27] | Wang YH (汪殷华), Mi XC (米湘成), Chen SW (陈声文), Li MH (李铭红), Yu MJ (于明坚) (2011) Regeneration dynamics of major tree species during 2002-2007 in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve in East China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 19, 178-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Ye WH (叶万辉), Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Lian JY (练琚愉), Wang ZG (王志高), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Wang ZM (王章明) (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China . Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Zhang J, Hao ZQ, Song B, Li BH, Wang XG, Ye J (2009) Fine-scale species co-occurrence patterns in an old-growth temperate forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 257, 2115-2120. |
| [30] | Zhang J, Hao ZQ, Sun IF, Song B, Ye J, Li BH, Wang XG (2009) Density dependence on tree survival in an old-growth temperate forest in Northeastern China. Annals of Forest Science, 66, 204. |
| [31] | Zhang J, Song B, Li BH, Ye J, Wang XG, Hao ZQ (2010) Spatial patterns and associations of six congeneric species in an old-growth temperate forest. Acta Oecologica, 36, 29-38. |
| [32] | Zhu Y (祝燕), Mi XC (米湘成), Ma KP (马克平) (2009) A mechanism of plant species coexistence: the negative density-dependent hypothesis. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 594-604. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Zhu Y, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2010) Density dependence is prevalent in a heterogeneous subtropical forest. Oikos, 119, 109-119. |
| [34] | Zhu Y (祝燕), Zhao GF (赵谷风), Zhang LW (张俪文), Shen GC (沈国春), Mi XC (米湘成), Ren HB (任海保), Yu MJ (于明坚), Chen JH (陈建华), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 舒为杰, 何花, 曾罗, 谷志容, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 雌雄异株物种一把伞南星雌雄株空间分布及性别二态性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24084-. |
| [2] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [3] | 林迪, 陈双林, 杜榷, 宋文龙, 饶固, 闫淑珍. 大别山黏菌的物种多样性调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [4] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [5] | 陈哲涵, 尹进, 叶吉, 刘冬伟, 毛子昆, 房帅, 蔺菲, 王绪高. 增温对东北温带次生林草本群落季节动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [6] | 林木青, 张应明, 欧阳芳, 束祖飞, 朱朝东, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区独栖性胡蜂多样性空间分布特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22310-. |
| [7] | 杨涛, 沈泽昊, 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘倩, 钱恒君, 解宇阳, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 张玉坤, 侯波, 李建斌, 欧晓昆. 滇中高原亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| [8] | 王晓凤, 米湘成, 王希华, 江明喜, 杨涛, 张健, 沈泽昊. 中国中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23296-. |
| [9] | 刘文聪, 田希, 杨涛, 饶杰生, 王晓凤, 钱恒君, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林优势树种的种群结构与更新特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23251-. |
| [10] | 崔家鹤, 李智勇, 王宇池, 孙蔷, 莎娜, 李紫晶, 武艳涛, 史亚博, 韩瀛, 李明乐, 王立新, 赵利清, 梁存柱. 垫状驼绒藜群落特征及地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23172-. |
| [11] | 李正飞, 蒋小明, 王军, 孟星亮, 张君倩, 谢志才. 雅鲁藏布江中下游底栖动物物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21431-. |
| [12] | 鲁梦珍, 曾馥平, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 苏樑, 刘坤平, 谭卫宁, 杜虎. 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林死亡个体空间分布格局及生境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21340-. |
| [13] | 王雅婷, 张定海, 张志山. 古尔班通古特沙漠固定沙丘上白梭梭和梭梭的空间分布及种间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21280-. |
| [14] | 王重阳, 赵联军, 孟世勇. 王朗国家级自然保护区滑坡体兰科植物分布格局及其保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21313-. |
| [15] | 赵琦, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 金清, 李佳丽, 邱江平. 海南岛蚯蚓物种组成及其系统发育分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22224-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
