



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 340-349. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019112 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019112
收稿日期:2019-04-01
接受日期:2019-11-04
出版日期:2020-03-20
发布日期:2019-11-25
通讯作者:
郭忠玲
基金资助:
Dan Liu1,2,Zhongling Guo1,2,*( ),Xiaoyang Cui2,Chunnan Fan1
),Xiaoyang Cui2,Chunnan Fan1
Received:2019-04-01
Accepted:2019-11-04
Online:2020-03-20
Published:2019-11-25
Contact:
Zhongling Guo
摘要:
东北红豆杉(Taxus cuspidata)是我国数量极少的珍贵濒危树种, 了解其天然群落的组成和特征对东北红豆杉种群的保护利用和恢复有重要意义。本文对吉林省天然东北红豆杉群落进行调查, 根据物种组成进行系统聚类分析。将20块40 m × 40 m样地划分为5种群丛类型, 分别以优势种进行命名, 即: Ⅰ. 舞鹤草-五味子+狗枣猕猴桃-紫椴+臭冷杉群丛; II. 东北羊角芹-狗枣猕猴桃-臭冷杉群丛; III. 盾叶唐松草-狗枣猕猴桃-臭冷杉群丛; IV. 舞鹤草-软枣猕猴桃-红松+紫椴+臭冷杉群丛; V. 舞鹤草-软枣猕猴桃-紫椴+臭冷杉群丛。对群丛的物种组成、群落结构和群丛类型、物种多样性进行了分析。物种多样性选用Menhinick丰富度指数、Pielou均匀度指数、Simpson优势度指数以及Shannon-Wiener多样性指数, 对比分析不同群丛特征。结果显示: 东北红豆杉植物群落组成中蔷薇科的种和属数所占比例最大; 5个群丛的多样性指数顺序为群丛V > 群丛III > 群丛IV > 群丛II > 群丛Ⅰ; 群丛Ⅰ和II具有较低的多样性和较高的优势度, 群丛II和群丛III的乔木层的多样性指数差异不明显, 但其丰富度指数和优势度指数却呈现了相反的特征; 群丛II丰富度低而优势度高, 而群丛III丰富度高而优势度低; 群丛III中的草本层的多样性高于乔木层, 群落郁闭度较低; 群丛IV和群丛V均位于和龙市荒沟林场, 随着海拔上升, 其物种多样性随之下降。结果表明, 不同物种组成的东北红豆杉植物群丛的群落特征存在显著差异。
刘丹, 郭忠玲, 崔晓阳, 范春楠 (2020) 5种东北红豆杉植物群丛及其物种多样性的比较. 生物多样性, 28, 340-349. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019112.
Dan Liu, Zhongling Guo, Xiaoyang Cui, Chunnan Fan (2020) Comparison of five associations of Taxus cuspidata and their species diversity. Biodiversity Science, 28, 340-349. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019112.
| 层次 Layer | 物种名 Species | 拉丁名 Latin name | 相对多度 Relative abundance | 相对盖度 Relative coverage | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Arbor | 色木槭 | Acer mono | 1.37% | 78.73% | 2.15% | 27.42% |
| 臭冷杉 | Abies nephrolepis | 22.39% | 4.35% | 20.57% | 15.77% | |
| 紫椴 | Tilia amurensis | 12.14% | 4.27% | 11.05% | 9.15% | |
| 髭脉槭 | Acer barbinerve | 12.33% | 0.51% | 9.40% | 7.41% | |
| 花楷槭 | Acer ukurunduense | 11.64% | 0.54% | 9.55% | 7.24% | |
| 东北红豆杉 | Taxus cuspidata | 6.79% | 1.80% | 8.64% | 5.74% | |
| 青楷槭 | Acer tegmentosum | 8.06% | 0.66% | 7.04% | 5.25% | |
| 红松 | Pinus koraiensis | 4.08% | 2.55% | 5.60% | 4.08% | |
| 硕桦 | Betula costata | 4.90% | 1.50% | 5.66% | 4.02% | |
| 鱼鳞云杉 | Picea jezoensis | 3.41% | 2.06% | 4.95% | 3.47% | |
| 杉松 | Abies holophylla | 2.88% | 0.55% | 3.71% | 2.38% | |
| 灌木层 Shrub | 软枣猕猴桃 | Actinidia arguta | 17.09% | 30.29% | 15.67% | 21.02% |
| 狗枣猕猴桃 | Actinidia kolomikta | 18.18% | 18.60% | 11.04% | 15.94% | |
| 刺五加 | Acanthopanax senticosus | 9.02% | 8.40% | 11.48% | 9.63% | |
| 长白忍冬 | Lonicera ruprechtiana | 11.60% | 6.29% | 9.05% | 8.98% | |
| 东北溲疏 | Deutzia parviflora | 5.70% | 9.01% | 8.17% | 7.63% | |
| 瘤枝卫矛 | Euonymus verrucosus | 4.61% | 2.70% | 7.51% | 4.94% | |
| 五味子 | Schisandra chinensis | 6.38% | 5.55% | 2.43% | 4.78% | |
| 长白茶藨 | Ribes komarovii | 5.36% | 2.30% | 6.18% | 4.61% | |
| 栓翅卫矛 | Euonymus phellomanus | 6.21% | 1.82% | 4.86% | 4.30% | |
| 卫矛 | Euonymus alatus | 3.26% | 1.29% | 5.74% | 3.43% | |
| 东北山梅花 | Philadelphus schrenkii | 2.68% | 4.36% | 3.09% | 3.38% | |
| 辽东楤木 | Aralia elata | 1.80% | 2.99% | 3.09% | 2.62% | |
| 草本层 Herbage | 盾叶唐松草 | Thalictrum ichangense | 11.46% | 9.62% | 17.82% | 12.97% |
| 东北羊角芹 | Aegopodium alpestre | 11.83% | 8.34% | 14.50% | 11.56% | |
| 舞鹤草 | Maianthemum bifolium | 12.47% | 11.24% | 9.75% | 11.15% | |
| 白花酢浆草 | Oxalis acetosella | 14.00% | 9.83% | 9.07% | 10.97% | |
| 丝引薹草 | Carex remotiuscula | 9.95% | 6.06% | 5.40% | 7.14% | |
| 稀羽鳞毛蕨 | Dryopteris sparsa | 4.83% | 4.64% | 9.25% | 6.24% | |
| 华西龙头草 | Meehania fargesii | 2.85% | 3.97% | 2.50% | 3.11% | |
| 东北蹄盖蕨 | Athyrium brevifrons | 0.88% | 1.41% | 4.16% | 2.15% | |
| 毛缘薹草 | Carex pilosa | 2.24% | 1.75% | 2.16% | 2.05% |
表1 东北红豆杉群落优势种群的重要值(重要值 > 2%)
Table 1 Importance value (IV) of dominant populations in Taxus cuspidata communities (IV > 2%)
| 层次 Layer | 物种名 Species | 拉丁名 Latin name | 相对多度 Relative abundance | 相对盖度 Relative coverage | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Arbor | 色木槭 | Acer mono | 1.37% | 78.73% | 2.15% | 27.42% |
| 臭冷杉 | Abies nephrolepis | 22.39% | 4.35% | 20.57% | 15.77% | |
| 紫椴 | Tilia amurensis | 12.14% | 4.27% | 11.05% | 9.15% | |
| 髭脉槭 | Acer barbinerve | 12.33% | 0.51% | 9.40% | 7.41% | |
| 花楷槭 | Acer ukurunduense | 11.64% | 0.54% | 9.55% | 7.24% | |
| 东北红豆杉 | Taxus cuspidata | 6.79% | 1.80% | 8.64% | 5.74% | |
| 青楷槭 | Acer tegmentosum | 8.06% | 0.66% | 7.04% | 5.25% | |
| 红松 | Pinus koraiensis | 4.08% | 2.55% | 5.60% | 4.08% | |
| 硕桦 | Betula costata | 4.90% | 1.50% | 5.66% | 4.02% | |
| 鱼鳞云杉 | Picea jezoensis | 3.41% | 2.06% | 4.95% | 3.47% | |
| 杉松 | Abies holophylla | 2.88% | 0.55% | 3.71% | 2.38% | |
| 灌木层 Shrub | 软枣猕猴桃 | Actinidia arguta | 17.09% | 30.29% | 15.67% | 21.02% |
| 狗枣猕猴桃 | Actinidia kolomikta | 18.18% | 18.60% | 11.04% | 15.94% | |
| 刺五加 | Acanthopanax senticosus | 9.02% | 8.40% | 11.48% | 9.63% | |
| 长白忍冬 | Lonicera ruprechtiana | 11.60% | 6.29% | 9.05% | 8.98% | |
| 东北溲疏 | Deutzia parviflora | 5.70% | 9.01% | 8.17% | 7.63% | |
| 瘤枝卫矛 | Euonymus verrucosus | 4.61% | 2.70% | 7.51% | 4.94% | |
| 五味子 | Schisandra chinensis | 6.38% | 5.55% | 2.43% | 4.78% | |
| 长白茶藨 | Ribes komarovii | 5.36% | 2.30% | 6.18% | 4.61% | |
| 栓翅卫矛 | Euonymus phellomanus | 6.21% | 1.82% | 4.86% | 4.30% | |
| 卫矛 | Euonymus alatus | 3.26% | 1.29% | 5.74% | 3.43% | |
| 东北山梅花 | Philadelphus schrenkii | 2.68% | 4.36% | 3.09% | 3.38% | |
| 辽东楤木 | Aralia elata | 1.80% | 2.99% | 3.09% | 2.62% | |
| 草本层 Herbage | 盾叶唐松草 | Thalictrum ichangense | 11.46% | 9.62% | 17.82% | 12.97% |
| 东北羊角芹 | Aegopodium alpestre | 11.83% | 8.34% | 14.50% | 11.56% | |
| 舞鹤草 | Maianthemum bifolium | 12.47% | 11.24% | 9.75% | 11.15% | |
| 白花酢浆草 | Oxalis acetosella | 14.00% | 9.83% | 9.07% | 10.97% | |
| 丝引薹草 | Carex remotiuscula | 9.95% | 6.06% | 5.40% | 7.14% | |
| 稀羽鳞毛蕨 | Dryopteris sparsa | 4.83% | 4.64% | 9.25% | 6.24% | |
| 华西龙头草 | Meehania fargesii | 2.85% | 3.97% | 2.50% | 3.11% | |
| 东北蹄盖蕨 | Athyrium brevifrons | 0.88% | 1.41% | 4.16% | 2.15% | |
| 毛缘薹草 | Carex pilosa | 2.24% | 1.75% | 2.16% | 2.05% |
| 科名 Family | 属数 No. of genus | 属的百分比 % of genus | 种数 No. of species | 种的百分比 % of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 9 | 9.09 | 11 | 7.64 |
| 槭树科 Aceraceae | 1 | 1.01 | 9 | 6.25 |
| 松科 Pinaceae | 4 | 4.04 | 9 | 6.25 |
| 百合科 Liliaceae | 8 | 8.08 | 8 | 5.56 |
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 6 | 6.06 | 8 | 5.56 |
| 虎耳草科 Saxifragaceae | 6 | 6.06 | 7 | 4.86 |
| 桦木科 Betulaceae | 3 | 3.03 | 6 | 4.17 |
| 伞形科 Umbelliferae | 6 | 6.06 | 6 | 4.17 |
| 堇菜科 Violaceae | 1 | 1.01 | 5 | 3.47 |
| 菊科 Compositae | 4 | 4.04 | 5 | 3.47 |
| 其他 Other families | 51 | 51.52 | 70 | 48.61 |
表2 东北红豆杉群落重要科、属和种的组成
Table 2 Composition of important species, genera and families in Taxus cuspidata communities
| 科名 Family | 属数 No. of genus | 属的百分比 % of genus | 种数 No. of species | 种的百分比 % of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 9 | 9.09 | 11 | 7.64 |
| 槭树科 Aceraceae | 1 | 1.01 | 9 | 6.25 |
| 松科 Pinaceae | 4 | 4.04 | 9 | 6.25 |
| 百合科 Liliaceae | 8 | 8.08 | 8 | 5.56 |
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 6 | 6.06 | 8 | 5.56 |
| 虎耳草科 Saxifragaceae | 6 | 6.06 | 7 | 4.86 |
| 桦木科 Betulaceae | 3 | 3.03 | 6 | 4.17 |
| 伞形科 Umbelliferae | 6 | 6.06 | 6 | 4.17 |
| 堇菜科 Violaceae | 1 | 1.01 | 5 | 3.47 |
| 菊科 Compositae | 4 | 4.04 | 5 | 3.47 |
| 其他 Other families | 51 | 51.52 | 70 | 48.61 |
| 编号 Number | 群丛名称 Association | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 坡度 Slope | 土壤水分 Soil humidity | 分布林场 Forest farm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 舞鹤草-五味子+狗枣猕猴桃-紫椴+臭冷杉群丛 Maianthemum bifolium-Schisandra chinensis+Actinidia kolomikta-Tilia amurensis+Abies nephrolepis | 800-940 | 13°-24° | 10%-25% | 杜荒子林场 Duhuangzi Forest Farm |
| II | 东北羊角芹-狗枣猕猴桃-臭冷杉群丛 Aegopodium alpestre-Actinidia kolomikta-Abies nephrolepis | 745 | 20° | 28% | 马滴答林场 Madida Forest Farm |
| III | 盾叶唐松草-狗枣猕猴桃-臭冷杉群丛 Thalictrum ichangense-Actinidia kolomikta-Abies nephrolepis | 680-900 | 3°-27° | 20%-40% | 金钩岭林场、兰家、荒沟林场 Jingouling, Lanjia, and Huanggou Forest Farms |
| IV | 舞鹤草-软枣猕猴桃-红松+紫椴+臭冷杉群丛 Maianthemum bifolium-Actinidia arguta-Pinus koraiensis + Tilia amurensis + Abies nephrolepis | 970-1,200 | 10°-35° | 12.6%-40% | 和龙市荒沟林场 Helong Forest Farm |
| V | 舞鹤草-软枣猕猴桃-紫椴+臭冷杉群丛 Maianthemum bifolium-Actinidia arguta-Tilia amurensis + Abies nephrolepis | 800-890 | 25°-30° | 15%-25% | 和龙市荒沟林场 Helong Forest Farm |
表3 东北红豆杉植物群丛特点 Table 3 The character of Taxus cuspidata association
| 编号 Number | 群丛名称 Association | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 坡度 Slope | 土壤水分 Soil humidity | 分布林场 Forest farm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 舞鹤草-五味子+狗枣猕猴桃-紫椴+臭冷杉群丛 Maianthemum bifolium-Schisandra chinensis+Actinidia kolomikta-Tilia amurensis+Abies nephrolepis | 800-940 | 13°-24° | 10%-25% | 杜荒子林场 Duhuangzi Forest Farm |
| II | 东北羊角芹-狗枣猕猴桃-臭冷杉群丛 Aegopodium alpestre-Actinidia kolomikta-Abies nephrolepis | 745 | 20° | 28% | 马滴答林场 Madida Forest Farm |
| III | 盾叶唐松草-狗枣猕猴桃-臭冷杉群丛 Thalictrum ichangense-Actinidia kolomikta-Abies nephrolepis | 680-900 | 3°-27° | 20%-40% | 金钩岭林场、兰家、荒沟林场 Jingouling, Lanjia, and Huanggou Forest Farms |
| IV | 舞鹤草-软枣猕猴桃-红松+紫椴+臭冷杉群丛 Maianthemum bifolium-Actinidia arguta-Pinus koraiensis + Tilia amurensis + Abies nephrolepis | 970-1,200 | 10°-35° | 12.6%-40% | 和龙市荒沟林场 Helong Forest Farm |
| V | 舞鹤草-软枣猕猴桃-紫椴+臭冷杉群丛 Maianthemum bifolium-Actinidia arguta-Tilia amurensis + Abies nephrolepis | 800-890 | 25°-30° | 15%-25% | 和龙市荒沟林场 Helong Forest Farm |
| 群丛 Assoc | 林分密度 Stand density (inds./ha) | 平均胸 径 Mean DBH (cm) | 主要物种组成(重要值%) Dominant species composition (Importance Value%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木 Arbor | 灌木 Shrub | 草本 Herbage | |||
| I | 2,446 | 11.45 | 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (24.19) | 五味子 Schisandra chinensis (25.01) | 舞鹤草 Maianthemum bifolium (21.57) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (16.23) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (22.69) | 丝引薹草 Carex remotiuscula (17.78) | |||
| 髭脉槭 Acer barbinerve (10.03) | 软枣猕猴桃 Actinidia arguta (13.09) | 白花酢浆草 Oxalis acetosella (13.39) | |||
| 硕桦 Betula costata (7.69) | 长白忍冬 Lonicera ruprechtiana (11.95) | 盾叶唐松草 Thalictrum ichangense (12.29) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (7.68) | 瘤枝卫矛 Euonymus verrucosus (9.71) | 东北羊角芹 Aegopodium alpestre (11.46) | |||
| II | 1,288 | 14.29 | 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (29.72) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (27.37) | 东北羊角芹 Aegopodium alpestre (28.95) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (13.11) | 东北山梅花 Philadelphus schrenkii (22.03) | 白花酢浆草 Oxalis acetosella (18.11) | |||
| 紫花槭 Acer pseudosieboldianum (10.15) | 栓翅卫矛 Euonymus phellomanus (14.66) | 辽细辛 Asarum heterotropoides (11.73) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (9.15) | 五味子 Schisandra chinensis (11.84) | 丝引薹草 Carex remotiuscula (10.49) | |||
| 鱼鳞云杉 Picea jezoensis (8.35) | 卫矛 Euonymus alatus (8.49) | 稀羽鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris sparsa (8.29) | |||
| III | 1,567 | 12.6 | 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (25) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (22.38) | 盾叶唐松草 Thalictrum ichangense (20.75) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (14.54) | 东北溲疏 Deutzia parviflora (15.73) | 东北羊角芹 Aegopodium alpestre (9.4) | |||
| 髭脉槭 Acer barbinerve (10.54) | 长白忍冬 Lonicera ruprechtiana (14.56) | 白花酢浆草 Oxalis acetosella (8.04) | |||
| 红松 Pinus koraiensis (8.65) | 长白茶藨 Ribes komarovii (11.77) | 稀羽鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris sparsa (7.59) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (7.17) | 刺五加 Acanthopanax senticosus (9.66) | 舞鹤草 Maianthemum bifolium (6.57) | |||
| IV | 1,520 | 12.49 | 花楷槭 Acer ukurunduense (18.4) | 软枣猕猴桃 Actinidia arguta (50.74) | 舞鹤草 Maianthemum bifolium (19.55) |
| 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (14.36) | 刺五加 Acanthopanax senticosus (17.1) | 华西龙头草 Meehania fargesii (11.58) | |||
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (10.66) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (9.26) | 稀羽鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris sparsa (10.62) | |||
| 红松 Pinus koraiensis (10.27) | 卫矛 Euonymus alatus (7) | 卵果蕨 Phegopteris connectilis (5.88) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (9.05) | 瘤枝卫矛 Euonymus verrucosus (5.37) | 玉竹 Polygonatum odoratum (4.65) | |||
| V | 1,278 | 11.93 | 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (16.3) | 软枣猕猴桃 Actinidia arguta (39.11) | 舞鹤草 Maianthemum bifolium (17.31) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (13.27) | 瘤枝卫矛 Euonymus verrucosus (13.23) | 东北蹄盖蕨 Athyrium brevifrons (12.4) | |||
| 鱼鳞云杉 Picea jezoensis (12.41) | 木通 Akebia quinata (10.57) | 丝引薹草 Carex remotiuscula (11.46) | |||
| 紫花槭 Acer pseudosieboldianum (11.57) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (8.28) | 宽叶薹草 Carex siderosticta (11.38) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (10.7) | 辽东楤木 Aralia elata (7.56) | 白毛羊胡子草 Eriophorum vaginatum (9.8) | |||
表4 东北红豆杉植物群丛物种组成
Table 4 The species composition of Taxus cuspidata associations
| 群丛 Assoc | 林分密度 Stand density (inds./ha) | 平均胸 径 Mean DBH (cm) | 主要物种组成(重要值%) Dominant species composition (Importance Value%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木 Arbor | 灌木 Shrub | 草本 Herbage | |||
| I | 2,446 | 11.45 | 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (24.19) | 五味子 Schisandra chinensis (25.01) | 舞鹤草 Maianthemum bifolium (21.57) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (16.23) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (22.69) | 丝引薹草 Carex remotiuscula (17.78) | |||
| 髭脉槭 Acer barbinerve (10.03) | 软枣猕猴桃 Actinidia arguta (13.09) | 白花酢浆草 Oxalis acetosella (13.39) | |||
| 硕桦 Betula costata (7.69) | 长白忍冬 Lonicera ruprechtiana (11.95) | 盾叶唐松草 Thalictrum ichangense (12.29) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (7.68) | 瘤枝卫矛 Euonymus verrucosus (9.71) | 东北羊角芹 Aegopodium alpestre (11.46) | |||
| II | 1,288 | 14.29 | 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (29.72) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (27.37) | 东北羊角芹 Aegopodium alpestre (28.95) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (13.11) | 东北山梅花 Philadelphus schrenkii (22.03) | 白花酢浆草 Oxalis acetosella (18.11) | |||
| 紫花槭 Acer pseudosieboldianum (10.15) | 栓翅卫矛 Euonymus phellomanus (14.66) | 辽细辛 Asarum heterotropoides (11.73) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (9.15) | 五味子 Schisandra chinensis (11.84) | 丝引薹草 Carex remotiuscula (10.49) | |||
| 鱼鳞云杉 Picea jezoensis (8.35) | 卫矛 Euonymus alatus (8.49) | 稀羽鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris sparsa (8.29) | |||
| III | 1,567 | 12.6 | 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (25) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (22.38) | 盾叶唐松草 Thalictrum ichangense (20.75) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (14.54) | 东北溲疏 Deutzia parviflora (15.73) | 东北羊角芹 Aegopodium alpestre (9.4) | |||
| 髭脉槭 Acer barbinerve (10.54) | 长白忍冬 Lonicera ruprechtiana (14.56) | 白花酢浆草 Oxalis acetosella (8.04) | |||
| 红松 Pinus koraiensis (8.65) | 长白茶藨 Ribes komarovii (11.77) | 稀羽鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris sparsa (7.59) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (7.17) | 刺五加 Acanthopanax senticosus (9.66) | 舞鹤草 Maianthemum bifolium (6.57) | |||
| IV | 1,520 | 12.49 | 花楷槭 Acer ukurunduense (18.4) | 软枣猕猴桃 Actinidia arguta (50.74) | 舞鹤草 Maianthemum bifolium (19.55) |
| 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (14.36) | 刺五加 Acanthopanax senticosus (17.1) | 华西龙头草 Meehania fargesii (11.58) | |||
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (10.66) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (9.26) | 稀羽鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris sparsa (10.62) | |||
| 红松 Pinus koraiensis (10.27) | 卫矛 Euonymus alatus (7) | 卵果蕨 Phegopteris connectilis (5.88) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (9.05) | 瘤枝卫矛 Euonymus verrucosus (5.37) | 玉竹 Polygonatum odoratum (4.65) | |||
| V | 1,278 | 11.93 | 臭冷杉 Abies nephrolepis (16.3) | 软枣猕猴桃 Actinidia arguta (39.11) | 舞鹤草 Maianthemum bifolium (17.31) |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis (13.27) | 瘤枝卫矛 Euonymus verrucosus (13.23) | 东北蹄盖蕨 Athyrium brevifrons (12.4) | |||
| 鱼鳞云杉 Picea jezoensis (12.41) | 木通 Akebia quinata (10.57) | 丝引薹草 Carex remotiuscula (11.46) | |||
| 紫花槭 Acer pseudosieboldianum (11.57) | 狗枣猕猴桃 Actinidia kolomikta (8.28) | 宽叶薹草 Carex siderosticta (11.38) | |||
| 东北红豆杉 Taxus cuspidata (10.7) | 辽东楤木 Aralia elata (7.56) | 白毛羊胡子草 Eriophorum vaginatum (9.8) | |||
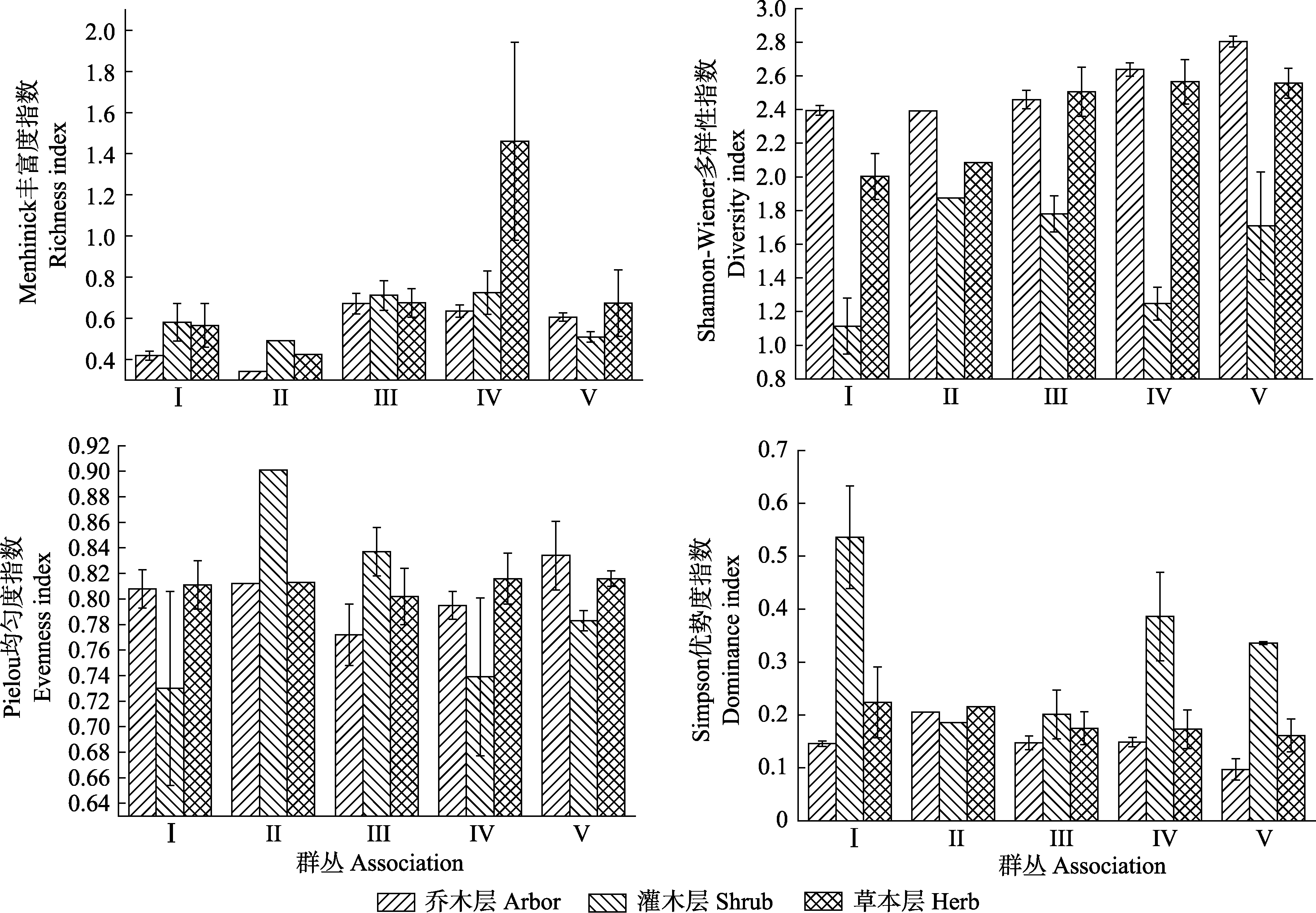
图2 东北红豆杉各群丛不同层次物种多样性。图中误差线代表的是标准误。群丛Ⅰ-V的含义同表3。
Fig. 2 Species diversity of different layers of Taxus cuspidata associations. The error bars in the figure represent standard errors. Associations Ⅰ-V are the same as Table 3.
| 群丛 Association | Menhinick丰富度指数 Menhinick richness index | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index | Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 0.521 ± 0.03 | 1.837 ± 0.018 | 0.783 ± 0.021 | 0.302 ± 0.02 |
| II | 0.419 | 2.117 | 0.842 | 0.202 |
| III | 0.686 ± 0.023 | 2.248 ± 0.051 | 0.804 ± 0.013 | 0.174 ± 0.019 |
| IV | 0.940 ± 0.162 | 2.149 ± 0.057 | 0.783 ± 0.02 | 0.236 ± 0.028 |
| V | 0.596 ± 0.069 | 2.356 ± 0.147 | 0.811 ± 0.013 | 0.198 ± 0.016 |
表5 东北红豆杉不同群丛物种多样性指数差异
Table 5 The difference of species diversity of five Taxus cuspidata associations
| 群丛 Association | Menhinick丰富度指数 Menhinick richness index | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index | Simpson优势度指数 Simpson dominance index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 0.521 ± 0.03 | 1.837 ± 0.018 | 0.783 ± 0.021 | 0.302 ± 0.02 |
| II | 0.419 | 2.117 | 0.842 | 0.202 |
| III | 0.686 ± 0.023 | 2.248 ± 0.051 | 0.804 ± 0.013 | 0.174 ± 0.019 |
| IV | 0.940 ± 0.162 | 2.149 ± 0.057 | 0.783 ± 0.02 | 0.236 ± 0.028 |
| V | 0.596 ± 0.069 | 2.356 ± 0.147 | 0.811 ± 0.013 | 0.198 ± 0.016 |
| 1 |
Chen J, Guo YL, Lu XL, Ding SY, Su S, Guo JJ, Li QX ( 2012) Species diversity of herbaceous communities in the Yiluo River Basin. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 3021-3030. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 陈杰, 郭屹立, 卢训令, 丁圣彦, 苏思, 郭静静, 李乾玺 ( 2012) 伊洛河流域草本植物群落物种多样性. 生态学报, 32, 3021-3030.]
DOI URL |
|
| 2 | Chen J, Long T, Yang L, Wang Y, Xu C, Li JW ( 2019) Habitat suitability assessment of Taxus cuspidata. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 41(4), 51-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈杰, 龙婷, 杨蓝, 王寅, 徐超, 李景文 ( 2019) 东北红豆杉生境适宜性评价. 北京林业大学学报, 41(4), 51-59.] | |
| 3 | Chen TG, Zhang JT ( 2000) Plant species diversity of Shenweigou in Guandi Mountains (Shanxi, China) I. Richness, evenness and diversity indexes. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 6, 406-411. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈廷贵, 张金屯 ( 2000) 山西关帝山神尾沟植物群落物种多样性与环境关系的研. I. 丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数. 应用与环境生物学报, 6, 406-411.] | |
| 4 |
Diao YF, Jin GZ, Tian SY, Liu YK, Liu YL, Han LD, Li YH ( 2016) Species composition and community structure of a Taxus cuspidata forest in Muling Nature Reserve of Heilongjiang Province, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 52(5), 26-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 刁云飞, 金光泽, 田松岩, 刘延坤, 刘玉龙, 韩丽冬, 李云红 ( 2016) 黑龙江省穆棱东北红豆杉林物种组成与群落结构. 林业科学, 52(5), 26-36.]
DOI URL |
|
| 5 | Ji RF, Zhou SX, Huang CD, Zhang J, Li XW, He CL ( 2015) Effects of different thinning intensity on the understory diversity within Cupressus funebris low-efficiency plan- tation. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 43(5), 68-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 季荣飞, 周世兴, 黄从德, 张建, 李宪伟, 何传龙 ( 2015) 间伐强度对柏木低效人工林灌草多样性的影响. 东北林业大学学报, 43(5), 68-74.] | |
| 6 | Li WL, Yu Q, Guo XY, Da LJ ( 2014) Community dynamics in different successional stages of secondary Pinus massoniana forest in south Anhui Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33, 1997-2004. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李伟立, 余倩, 郭雪艳, 达良俊 ( 2014) 皖南次生马尾松林自然演替进程中的群落动态. 生态学杂志, 33, 1997-2004.] | |
| 7 | Li XH, Deng YL, Zhang F, Dong G, Li SG ( 2013) Species diversity of forest communities in Pangquangou Nature Reserve, Shanxi of China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32, 1667-1673. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李旭华, 邓永利, 张峰, 董刚, 李世广 ( 2013) 山西庞泉沟自然保护区森林群落物种多样性. 生态学杂志, 32, 1667-1673.] | |
| 8 | Liu L, Zhang F ( 2010) Species diversity of plant community in Baiyundong Scenic Spot, Lishan Mountains, Shanxi. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition), 33, 468-472. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘蕾, 张峰 ( 2010) 历山白云洞景区植物群落物种多样性研究. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 33, 468-472.] | |
| 9 | Liu T ( 2007) Population Ecology of Natural Japanese Yew. PhD dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘彤 ( 2007) 天然东北红豆杉种群生态学研究. 博士学位论文, 东北林业大学, 哈尔滨.] | |
| 10 |
Lomolino MV ( 2001) Elevation gradients of species-density: Historical and prospective views. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 10, 3-13.
DOI URL |
| 11 | Ma XY, Shangguan TL ( 2004) Species diversity of the forest communities in Taiyue Mountain, Shanxi. Journal of Mountain Science, 22, 606-612. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马晓勇, 上官铁梁 ( 2004) 太岳山森林群落物种多样性. 山地学报, 22, 606-612.] | |
| 12 |
Nascimento LMD, Everardo VSB, Rodal MJN, Lins-E-Silva ACB ( 2014) Secondary succession in a fragmented Atlantic forest landscape: Evidence of structural and diversity convergence along a chronosequence. Journal of Forest Research, 19, 501-513.
DOI URL |
| 13 | Ren BB, Li SH, Zhu CY, Zhang XT ( 2010) Numerical classification and ordination of forest vegetation communities in Yushan Mountain, Changshu. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 34(3), 45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任斌斌, 李树华, 朱春阳, 张晓彤 ( 2010) 常熟虞山森林植被群落的数量分类与排序. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 34(3), 45-50.] | |
| 14 | Ren GX, Liu JF, Xu DW, Hong W, Zheng SQ, Huang ZS ( 2011) Analysis on classification and species diversity of Pinus taiwanensis community in Daiyun Mountain National Nature Reserve. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 20(3), 82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任国学, 刘金福, 徐道炜, 洪伟, 郑世群, 黄志森 ( 2011) 戴云山国家级自然保护区黄山松群落类型与物种多样性分析. 植物资源与环境学报, 20(3), 82-88.] | |
| 15 | Wang DD, Zhang YW ( 2019) Identification and genetic diversity analysis of Taxus cuspidata hybrid. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 51(1), 113-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王丹丹, 张彦文 ( 2019) 东北红豆杉杂交种鉴定及遗传多样性分析. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 51(1), 113-118.] | |
| 16 | Wang L ( 2010) SPSS Statistical Analysis Foundation, Application and Practice. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [ 王璐 ( 2010) SPSS统计分析基础、应用与实践. 化学工业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 17 | Wang YP, Hong X, Liu K, Li JH, Zhou SB, Zhang DL, Chen WH ( 2018) Floristic analysis of seed plants and altitudinal patterns of plant species diversity on the northern slope of Guniujiang National Nature Reserve in Anhui. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 54(4), 165-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王育鹏, 洪欣, 刘坤, 李建辉, 周守标, 张丁来, 陈文豪 ( 2018) 安徽牯牛降北坡种子植物区系特征及其多样性的海拔梯度变化. 林业科学, 54(4), 165-173.] | |
| 18 | Wu SX, Liu YH, Zhang LM, Shang FQ, Tan CQ ( 2018) Growth stability analysis of ex situ conservation of Taxus cuspidata seedlings from different sources. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 40(12), 27-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴世雄, 刘艳红, 张利民, 尚福强, 谭成权 ( 2018) 不同产地东北红豆杉幼苗迁地保护的生长稳定性分析. 北京林业大学学报, 40(12), 27-37.] | |
| 19 | Xu YM, Lv SH ( 2011) Effects of wind desertification on the biodiversity of grassland vegetation of Hulunbeir steppe. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 25(4), 133-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐永明, 吕世海 ( 2011) 风蚀沙化对草原植被生物多样性的影响——以呼伦贝尔草原为例. 干旱区资源与环境, 25(4), 133-137.] | |
| 20 | Yuan WJ, Lu XL, Zhang WR, Wang ZH, Zhang LM, Ding SY ( 2015) Plant’s diversity of different vegetation types. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 4651-4657. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁王俊, 卢训令, 张维瑞, 王智慧, 张灵敏, 丁圣彦 ( 2015) 不同植被类型植物物种多样性. 生态学报, 35, 4651-4657.] | |
| 21 | Zhao P, Xu XY, Jin HX, Zhang JH, Tang WD, Chai CW, Dong ZL ( 2014) Quantitative classification and ordination analysis on vegetation in the Minqin Oasis-Desert ecotone. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 34, 364-371. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵鹏, 徐先英, 金红喜, 张进虎, 唐卫东, 柴成武, 董志玲 ( 2014) 民勤绿洲荒漠过渡带植物群落数量分类和排序研究. 西北植物学报, 34, 364-371.] | |
| 22 | Zhao TL ( 2017) Species diversity of Larix principis rupprechtii communities in Shanxi Province of northern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 39(6), 45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵天梁 ( 2017) 山西华北落叶松群落物种多样性. 北京林业大学学报, 39(6), 45-50.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [13] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [14] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [15] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn