



Biodiv Sci ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 321-331. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014145 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014145
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
You Nong1,2,*, Lu Zheng1,2, Hongyan Jia1,2, Lihua Lu1,2, Dewei Huang1,2, Bohua Huang1,2, Liqun Lei1,2
Received:2014-07-10
Accepted:2015-01-26
Online:2015-06-08
Published:2015-06-12
Contact:
Nong You
You Nong, Lu Zheng, Hongyan Jia, Lihua Lu, Dewei Huang, Bohua Huang, Liqun Lei. Community characteristics and spatial distribution of dominant tree species in a secondary forest of Daqing Mountains, southwestern Guangxi, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(3): 321-331.
| 层次 Stratification | 物种丰富度指数 Species richness (S) | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H′) | Simpson指数 Simpson index (D) | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (Jsw) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Tree Layer | 58 | 2.95 | 0.91 | 0.73 |
| 灌木层 Shrub Layer | 29 | 2.25 | 0.82 | 0.70 |
| 草本层 Herb Layer | 22 | 2.02 | 0.78 | 0.65 |
Table 1 Forest stratification and diversity in the 1-ha secondary forest plot of Daqing Mountains
| 层次 Stratification | 物种丰富度指数 Species richness (S) | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H′) | Simpson指数 Simpson index (D) | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (Jsw) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乔木层 Tree Layer | 58 | 2.95 | 0.91 | 0.73 |
| 灌木层 Shrub Layer | 29 | 2.25 | 0.82 | 0.70 |
| 草本层 Herb Layer | 22 | 2.02 | 0.78 | 0.65 |
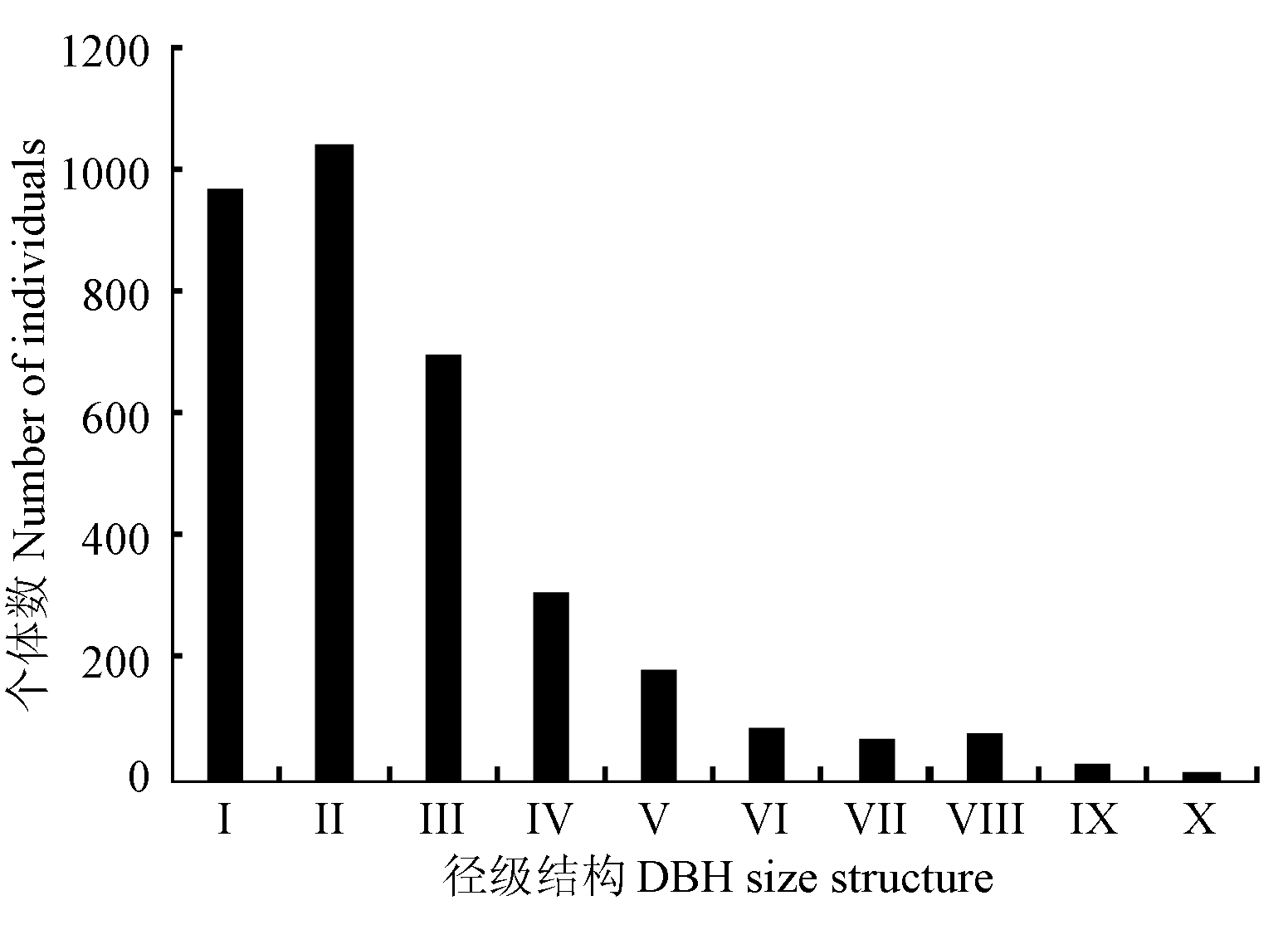
Fig. 1 DBH size structure of trees in the 1-ha secondary forest plot of Daqing Mountains I: 1.0-2.5 cm; II: 2.5-5.0 cm; III: 5.0-10.0 cm; IV: 10.0-15.0 cm; V: 15.0-20.0 cm; VI: 20.0-25.0 cm; VII: 25.0-30.0 cm; VIII: 30.0-40.0 cm; IX: 40.0-50.0 cm; X: ≥50.0 cm.
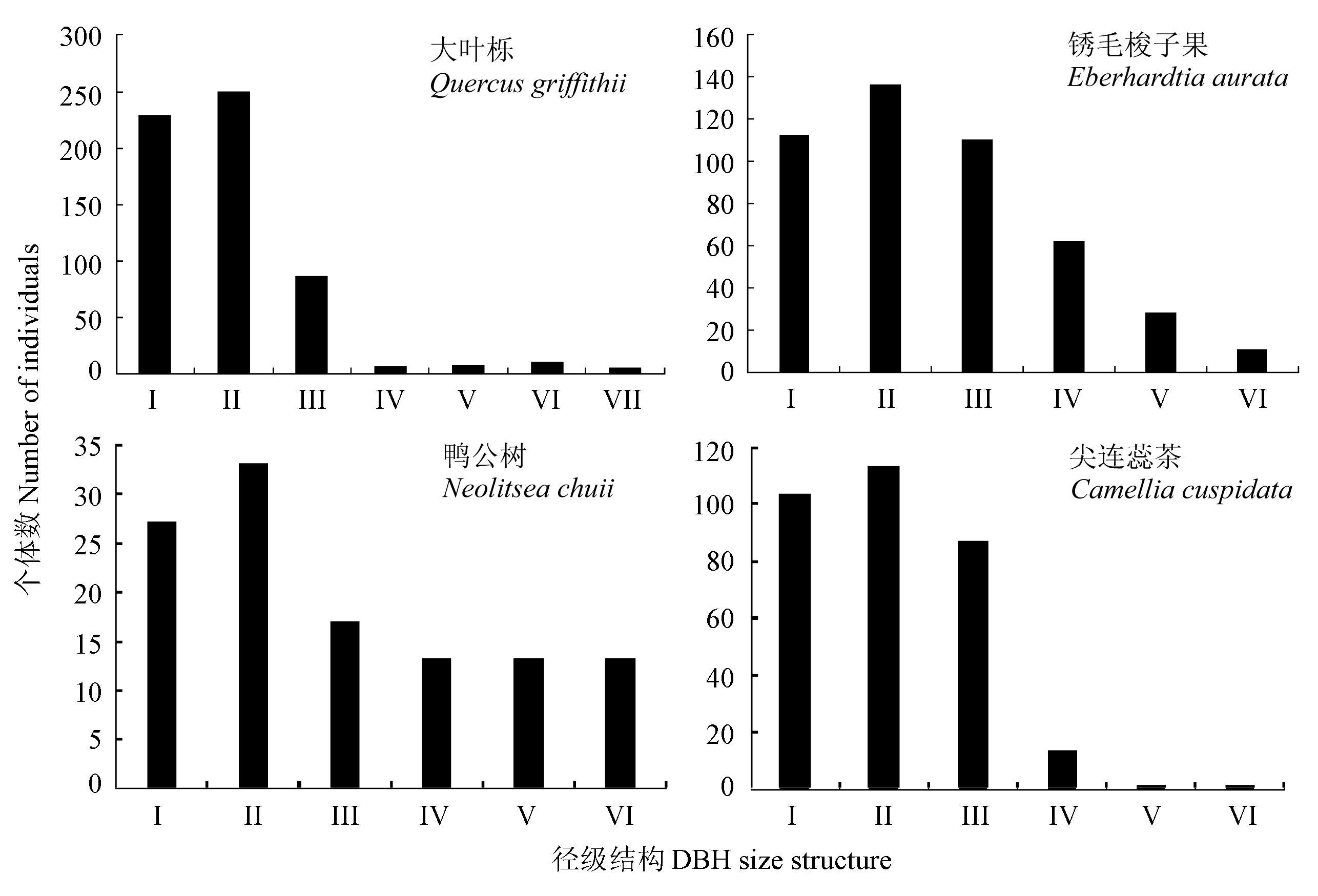
Fig. 2 DBH size structure of main tree species in the 1-ha secondary forest plot of Daqing Mountains I: 1.0-2.5 cm; II: 2.5-5.0 cm; III: 5.0-10.0 cm; IV: 10.0-15.0 cm; V: 15.0-20.0 cm; VI: 20.0-25.0 cm; VII: 25.0-30.0 cm.
| 种名 Species | 个体数 Individuals | 胸高断面积 Basal area (cm2) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大叶栎 Quercus griffithii | 594 | 29,800.92 | 33.59 |
| 锈毛梭子果 Eberhardtia aurata | 459 | 26,591.51 | 28.83 |
| 鹿角锥 Castanopsis lamontii | 107 | 44,791.11 | 21.98 |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | 318 | 10,046.76 | 17.69 |
| 木姜子 Litsea pungens | 75 | 22,724.85 | 13.58 |
| 鸭公树 Neolitsea chuii | 123 | 16,414.89 | 13.50 |
| 广东琼楠 Beilschmiedia fordii | 121 | 13,834.18 | 13.34 |
| 罗浮锥 Castanopsis faberi | 39 | 27,981.65 | 13.16 |
| 环鳞烟斗柯 Lithocarpus corneus | 127 | 15,114.14 | 13.02 |
| 桂南木莲 Manglietia chingii | 75 | 20,219.74 | 12.77 |
| 柠檬金花茶 Camellia limonia | 142 | 6,196.79 | 11.00 |
| 海南山龙眼 Helicia hainanensis | 129 | 5,881.87 | 10.28 |
Table 2 The importance value of main tree species in the 1-ha secondary forest plot of Daqing Mountains
| 种名 Species | 个体数 Individuals | 胸高断面积 Basal area (cm2) | 重要值 Importance value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 大叶栎 Quercus griffithii | 594 | 29,800.92 | 33.59 |
| 锈毛梭子果 Eberhardtia aurata | 459 | 26,591.51 | 28.83 |
| 鹿角锥 Castanopsis lamontii | 107 | 44,791.11 | 21.98 |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | 318 | 10,046.76 | 17.69 |
| 木姜子 Litsea pungens | 75 | 22,724.85 | 13.58 |
| 鸭公树 Neolitsea chuii | 123 | 16,414.89 | 13.50 |
| 广东琼楠 Beilschmiedia fordii | 121 | 13,834.18 | 13.34 |
| 罗浮锥 Castanopsis faberi | 39 | 27,981.65 | 13.16 |
| 环鳞烟斗柯 Lithocarpus corneus | 127 | 15,114.14 | 13.02 |
| 桂南木莲 Manglietia chingii | 75 | 20,219.74 | 12.77 |
| 柠檬金花茶 Camellia limonia | 142 | 6,196.79 | 11.00 |
| 海南山龙眼 Helicia hainanensis | 129 | 5,881.87 | 10.28 |
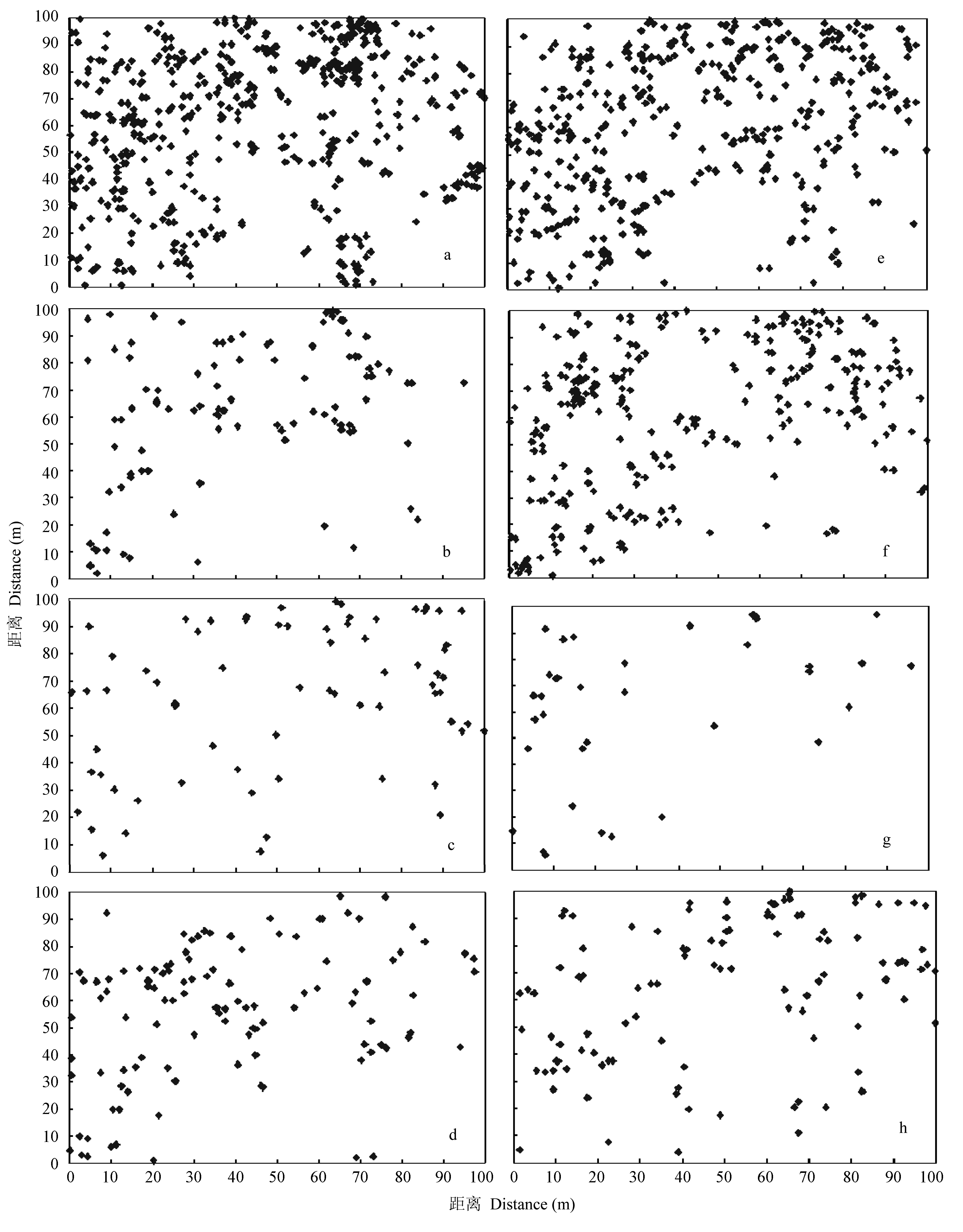
Fig. 3 The distribution of main species in the 1-ha secondary forest plot of Daqing Mountains. (a) Quercus griffithii; (b) Castanopsis lamontii; (c) Litsea pungens; (d) Neolitsea chuii; (e) Eberhardtia aurata; (f) Camellia cuspidata; (g) Castanopsis faberi; (h) Beilschmiedia fordii.
| 种名 Species | 尺度 Scale (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-50 | |
| 大叶栎 Quercus griffithii | a | a | a | a | a |
| 广东琼楠 Beilschmiedia fordii | a | a | a | a | a |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | a | a | a | a | a |
| 鹿角锥 Castanopsis lamontii | a | a | a | a | a |
| 罗浮锥 Castanopsis faberi | a | a | a | a | a |
| 木姜子 Litsea pungens | a (+) | a (0) | a | a | a (+) |
| 锈毛梭子果 Eberhardtia aurata | a | a | a | a | a |
| 鸭公树 Neolitsea chuii | a | a | a | a | a |
Table 3 Effects of habitat heterogeneity on the spatial distribution pattern of main tree species
| 种名 Species | 尺度 Scale (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-50 | |
| 大叶栎 Quercus griffithii | a | a | a | a | a |
| 广东琼楠 Beilschmiedia fordii | a | a | a | a | a |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | a | a | a | a | a |
| 鹿角锥 Castanopsis lamontii | a | a | a | a | a |
| 罗浮锥 Castanopsis faberi | a | a | a | a | a |
| 木姜子 Litsea pungens | a (+) | a (0) | a | a | a (+) |
| 锈毛梭子果 Eberhardtia aurata | a | a | a | a | a |
| 鸭公树 Neolitsea chuii | a | a | a | a | a |
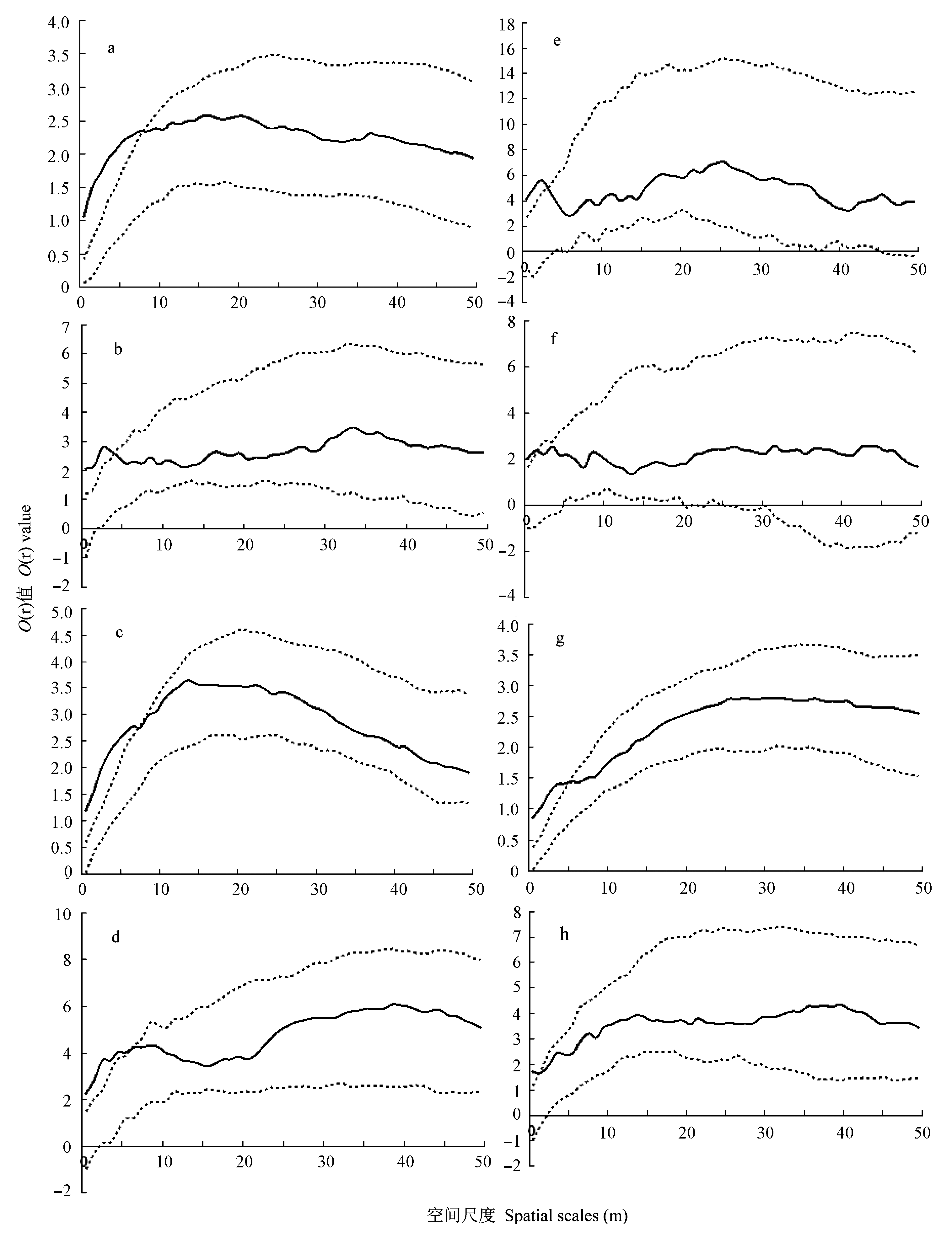
Fig. 4 Spatial distribution pattern of the main populations without environmental heterogeneity effect. The solid line is the analysis of the data of O(r), the dotted line is the envelope curve, representing the 99% confidence intervals of the simulation. (a) Quercus griffithii; (b) Beilschmiedia fordii; (c) Camellia cuspidata; (d) Castanopsis lamontii; (e) Castanopsis faberi; (f) Litsea pungens; (g) Eberhardtia aurata; (h) Neolitsea chuii.
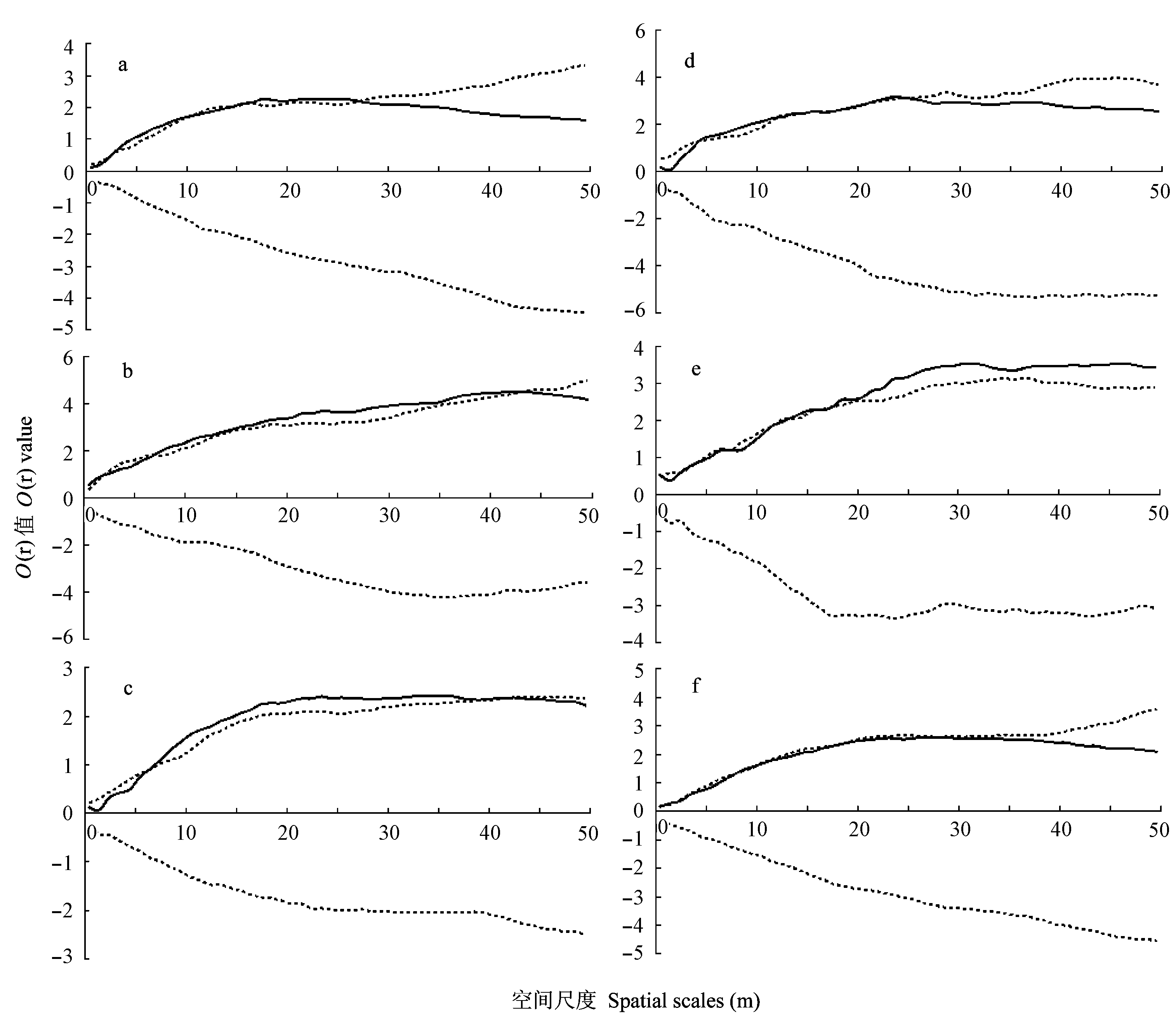
Fig. 5 Interspecific analysis of main populations in the secondary forest of Daqing Mountains. The solid line is the analysis of the data of O12(r), the dotted line is the envelope curve, representing the 99% confidence interval of the simulation. (a) Quercus griffithii-Camellia cuspidata; (b) Quercus griffithii-Castanopsis lamontii; (c) Quercus griffithii-Eberhardtia aurata; (d) Castanopsis lamontii-Camellia cuspidata; (e) Castanopsis lamontii-Eberhardtia aurata; (f) Eberhardtia aurata-Camellia cuspidata.
| 1 | An HJ (安惠君) (2003) Study on the Spatial Structure of the Broad-leaved Korean Pine Forest (阔叶红松林空间结构研究). PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 2 | Cao GX (操国兴), Zhong ZC (钟章成), Liu Y (刘芸), Xie DT (谢德体) (2003) The study of distribution pattern of Camellia rosthorniana population in Jinyun Mountain.Journal of Biology(生物学杂志), 20(1), 10-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Method and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plot. Springer Verlag, Berlin. |
| 4 | Condit R, Ashton PS, Baker P, Bunyavejchewin S, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Hubbell SP, Foster RB, Itoh A, LaFrankie JV, Lee HS, Losos E, Manokaran N, Sukumar R, Yamakura T (2000) Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species.Science, 288, 1414-1418. |
| 5 | Getzin S, Wiegand T, Wiegand K, He F (2008) Heterogeneity influences spatial patterns and demographics in forest stands.Journal of Ecology, 96, 807-820. |
| 6 | Grubb P (1977) Maintenance of species-richness in plant communities: importance of regeneration niche.Biological Reviews, 52, 107-145. |
| 7 | Gunatilleke S (2004) Ecology of Sinharaja Rain Forest and the Forest Dynamics Plot in Sri Lanka’s Natural World Heritage Site. WHT Publications , Sri Lanka. |
| 8 | Guo YX (郭垚鑫), Kang B (康冰), Li G (李刚), Wang DY (王得祥), Yang GH (杨改河), Wang DW (王大伟) (2011) Species composition and point pattern analysis of standing trees in secondary Betula albosinensis forest in Xiaolongshan of west Qinling Mountains.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 22, 2799-2806. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 9 | Guo ZL (郭忠玲), Ma YD (马元丹), Zheng JP (郑金萍), Liu WD (刘万德), Jin ZF (金哲峰) (2004) Biodiversity of tree species, their populations’ spatial distribution pattern and interspecific association in mixed deciduous broadleaved forest in Changbai Mountain.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 15, 2013-2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 10 | Hao ZQ, Zhang J, Song B, Ye J, Li BH (2007) Vertical structure and spatial associations of dominant tree species in an old growth temperate forest.Forest Ecology and Management, 252, 1-11. |
| 11 | Harms KE, Wright JS, Calderón O, Hernandez A, Herre EA (2000) Pervasive density-dependent recruitment enhances seedling diversity in a tropical forest.Nature, 404, 493-495. |
| 12 | Harms KE, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (2001) Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha neotropical forest plot. Journal of Ecology, 89, 947-959. |
| 13 | He F, Legendre P, LaFrankie JV (1997) Distribution patterns of tree species in a Malaysian tropical rain forest.Journal of Vegetation Science, 8, 105-114. |
| 14 | He F, Duncan RP (2000) Density-dependent effects on tree survival in an old-growth Douglas fir forest. Journal of Ecology, 88, 676-688. |
| 15 | Hu YB (胡艳波), Hui GY (惠刚盈), Qi JZ (戚继忠), An HJ (安慧君), Hao GM (郝广明) (2003) Analysis of the spatial structure of nature Korean pine broadleaved forest.Forest Research(林业科学研究), 16, 523-530. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 16 | Huang CB (黄承标), Lu LH (卢立华), Wen YG (温远光), Cai DX (蔡道雄), Lü GY (吕广阳), Huang J (黄竞) (2011) Vertical distribution of main meteorological elements in Daqingshan forest zone of Guangxi.Guizhou Agricultural Sciences(贵州农业科学), 39, 90-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 17 | Hubbell SP (1979) Tree dispersion, abundance and diversity in a tropical dry forest.Science, 203, 1299-1309. |
| 18 | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| 19 | John R, Dalling JW, Harms KE, Yavitt JB, Stallard RF, Mirabello M, Hubbell SP, Valencia R, Navarrete H, Vallejo M (2007) Soil nutrients influence spatial distributions of tropical tree species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 864-869. |
| 20 | Kang B (康冰), Liu SR (刘世荣), Wen YG (温远光), Zhang YJ (张跃进), Jiang ZM (姜在民), Chang JG (常建国) (2006) Population dynamics during succession of secondary natural forest in Daqingshan, Guangxi, China.Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 30, 931-940. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 21 | Knight DH (1975) A phytosociological analysis of species-rich tropical forest on Barro Colorado Island, Panama.Ecological Monographs, 45, 259-284. |
| 22 | Legendre P, Mi X, Ren H, Ma K, Yu M, Sun IF, He F (2009) Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China.Ecology, 90, 663-674. |
| 23 | Liao CZ (廖成章), Hong W (洪伟), Wu CZ (吴承祯), Wang XG (王新功), Cheng Y (程煜), Feng L (封磊) (2003) Study on the spatial of species diversity for the subtropical evergreen broadleaf forest in Fujian Province.Guihaia(广西植物), 23, 517-522. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 24 | Lin YC, Chang LW, Yang KC, Wang HH, Sun IF (2011) Point patterns of tree distribution determined by habitat heterogeneity and dispersal limitation.Oecologia, 165, 175-184. |
| 25 | Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: current knowledge and future challenges.Science, 294, 804-808. |
| 26 | Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Large scale permanent plots: impor- tant platform for long term research on biodiversity in forest ecosystem. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 237. (in Chinese) |
| 27 | Magurran AE (1988) Ecological Diversity and Its Measure- ment. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| 28 | Manokaran N, LaFrankie JV Jr (1990) Stand structure of Pasoh Forest Reserve, a lowland rain forest in Peninsular Malaysia.Journal of Tropical Forest Science, 3, 14-24. |
| 29 | Meng FH (孟繁华) (2006) Study on Species Diversity and Conservation the Flora of Yuanbaoshan Nature Reserve (元宝山植物物种多样性及其保护研究). PhD dissertation, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 30 | Murrell DJ (2009) On the emergent spatial structure of size-structured populations: when does self-thinning lead to a reduction in clustering.Journal of Ecology, 97, 256-266. |
| 31 | Queenborough SA, Burslem DFRP, Garwood NC, Valencia R (2007) Habitat niche partitioning by 16 species of Myristicaceae in Amazonian Ecuador.Plant Ecology, 192, 193-207. |
| 32 | Sterner RW, Ribic CA, Schatz GE (1986) Testing for life historical changes in spatial patterns of four tropical tree species.Journal of Ecology, 74, 621-633. |
| 33 | Stoyan D, Penttinen A (2000) Recent applications of point process methods in forestry statistics.Statistical Science, 15, 61-78. |
| 34 | Tang MP (汤孟平), Zhou GM (周国模), Shi YJ (施拥军), Chen YG (陈永刚), Wu YQ (吴亚琪), Zhao MS (赵明水) (2006) Spatial patterns in evergreen broadleaved forest in Tianmu Mountain, China.Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 30, 743-752. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature, 441, 629-632. |
| 36 | Wang L (王磊), Sun QW (孙启武), Hao CY (郝朝运), Tian SN (田胜尼), Zhang SS (张姗姗), Chen YK (陈一锟), Zhang XP (张小平) (2010) Point pattern analysis of different age-class Taxus chinensis var. mairei individuals in mountainous area of southern Anhui Province.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 21, 272-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 37 | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Rings circles and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology.Oikos, 104, 209-229. |
| 38 | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2014) A Handbook of Spatial Point Pattern Analysis in Ecology. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. |
| 39 | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1991) The areal-types of Chinese genera of seed plants.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 13(Suppl.4), 1-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 40 | Xie ZS (谢正生), Gu YK (古炎坤), Chen BG (陈北光), Su ZY (苏志尧) (1998) Species diversity of the natural forest communities in Nanling National Nature Reserve, Guang dong.Journal of South China Agricultural University(华南农业大学学报), 19(3), 61-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 41 | Ye WH (叶万辉), Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Lian JY (练琚愉), Wang ZG (王志高), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Wang ZM (王章明) (2008) Community structure of a 20 hm2 lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 42 | Yue YJ (岳永杰), Yu XX (余新晓), Li GT (李钢铁), Fan DX (樊登星), Ye JD (叶俊道) (2009) Spatial structure of Quercus mongolica forest in Beijing Songshan Mountain Nature Reserve.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 20, 1811-1816. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 43 | Zhang JT (张金屯), Meng DP (孟东平) (2004) Spatial pattern analysis of individuals in different age-classes of Larix gmelinii in Luyashan Mountain, China.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 24, 35-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 44 | Zhang J, Song B, Li BH, Ye J, Wang XG, Hao ZQ (2010) Spatial patterns and associations of six congeneric species in an old-growth temperate forest.Acta Oecologica, 36, 29-38. |
| 45 | Zhang YT (张毓涛), Li JZ (李吉政), Chang SL (常顺利), Li X (李翔), Lu JJ (芦建江) (2011) Spatial distribution pattern of Picea schrenkiana var. tianshanica population and its relationships with topographic factors in middle part of Tianshan Mountain.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 22, 2799-2806. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Jingyi Yuan, Xu Zhang, Zhenpeng Tian, Zizhe Wang, Yongping Gao, Dizhao Yao, Hongcan Guan, Wenkai Li, Jing Liu, Hong Zhang, Qin Ma. A comparison of methods for extracting tree species composition and quantitative characteristics in urban plant communities using UAV high-resolution RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [2] | Jia Zhenni, Zhang Yicen, Du Yanjun, Ren Haibao. Influences of disturbances on successional dynamics of species diversity in mid- subtropical forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [3] | Ma Wenjun, Liu Sijia, Li Kemao, Jian Shenglong, Xue Chang’an, Han Qingxiango, Wei Jinliang, Chen Shengxue, Niu Yimeng, Cui Zhouping, Sui Ruichen, Tian Fei, Zhao Kai. Fish diversity and distribution in the source region of the Yangtze River in Qinghai Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [4] | Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [5] | Zerong He, Peng Ye, Shuting Wang, Yongxin Guan, Shujun Yan, Xinru Hong. Composition and spatial distribution of dominant weed species in urban lawns of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [6] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [7] | Weijie Shu, Hua He, Luo Zeng, Zhirong Gu, Dunyan Tan, Xiaochen Yang. Spatial distribution and sexual dimorphism of dioecious Arisaema erubescens [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24084-. |
| [8] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [9] | Di Lin, Shuanglin Chen, Que Du, Wenlong Song, Gu Rao, Shuzhen Yan. Investigation of species diversity of myxomycetes in Dabie Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [10] | Fangfang Wu, Na Liu, Chunmei He, Zuoqiang Yuan, Zhanqing Hao, Qiulong Yin. Elevational gradient pattern of woody plant community structure and diversity in the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [11] | Jia Yao, Congling Zhang, Shixuan Li, Yang Lin, Zhen Wang, Yuhan Zhang, Weilong Zhou, Xinhe Pan, Shan Zhu, Yiqing Wu, Dan Wang, Jinliang Liu, Shanshan Tan, Guochun Shen, Mingjian Yu. Characteristics of plant communities in the Baishanzu continuous elevational transect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [12] | Junyi Yang, Xiao Guan, Junsheng Li, Jingjing Liu, Haojing Hao, Huairui Wang. Spatial patterns and interrelationships between biodiversity and ecosystem services in the Wujiang River Basin [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [13] | Zhehan Chen, Jin Yin, Ji Ye, Dongwei Liu, Zikun Mao, Shuai Fang, Fei Lin, Xugao Wang. Effects of simulated warming on seasonal dynamics of herbaceous diversity in temperate secondary forests in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [14] | Muqing Lin, Yingming Zhang, Fang Ouyang, Zufei Shu, Chaodong Zhu, Zhishu Xiao. Spatial distribution of species diversity of solitary wasps (Vespidae) and its responses to environmental factors in the Chebaling National Nature Reserve, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22310-. |
| [15] | Tao Yang, Zehao Shen, Xiaofeng Wang, Jiesheng Rao, Wencong Liu, Xi Tian, Xi Chen, Qiuyu Zhang, Qian Liu, Hengjun Qian, Yuyang Xie, Qiming Liu, Yanxiao Xu, Mengling Tu, Ziming Shan, Yukun Zhang, Bo Hou, Jianbin Li, Xiaokun Ou. Characteristics of plant community diversity in a subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Central Yunnan Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn