



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 25027. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025027 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025027
Special Issue: 昆蒙框架目标12下的中国城市生物多样性研究专辑
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang*( ), Yujun Zhang*(
), Yujun Zhang*( )
)
Received:2025-01-16
Accepted:2025-04-14
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-06-23
Contact:
Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang
Supported by:Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027.
| 年份 Year | 缔约方大会 COP | 地点 Location | 关于城市绿地生物多样性的决定 Decisions related to urban green space biodiversity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | COP1 | 巴哈马拿骚 Nassau, Bahamas | 无专门针对城市绿地生物多样性的决定, 主要集中在总体生物多样性保护目标和策略。 There are no dedicated decisions specifically targeting urban green space biodiversity; current efforts are primarily concentrated on overarching biodiversity conservation goals and strategies. |
| 1995 | COP2 | 印度尼西亚雅加达 Jakarta, Indonesia | |
| 1996 | COP3 | 阿根廷布宜诺斯艾利斯 Buenos Aires, Argentina | |
| 1998 | COP4 | 斯洛伐克布拉迪斯拉发 Bratislava, Slovakia | |
| 2000 | COP5 | 肯尼亚内罗毕 Nairobi, Kenya | |
| 2002 | COP6 | 荷兰海牙 Hague, the Netherlands | |
| 2004 | COP7 | 马来西亚吉隆坡 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia | |
| 2006 | COP8 | 巴西库里提巴 Curitiba, Brazil | |
| 2008 | COP9 | 德国波恩 Bonn, Germany | 决定IX/28: 首次明确提出“城市生物多样性”, 呼吁加强对城市生态系统的关注, 并制定和实施城市生物多样性战略和行动计划。Decision IX/28: Explicitly introduced the concept of “urban biodiversity” for the first time, calling for increased attention to urban ecosystems and the development and implementation of urban biodiversity strategies and action plans. |
| 2010 | COP10 | 日本名古屋 Nagoya, Japan | 决定X/22: 认可“城市生物多样性指数” (新加坡指数)作为衡量和监控工具, 鼓励将生物多样性纳入城市规划。Decision X/22: Endorsed the “City Biodiversity Index” (Singapore Index) as a monitoring and evaluation tool, encouraging the integration of biodiversity considerations into urban planning processes. |
| 2012 | COP11 | 印度海德拉巴 Hyderabad, India | 决定XI/8: 强调在城市规划中整合生物多样性保护措施, 促进生态系统服务供给, 确保城市居民的福祉。Decision XI/8: Highlighted the need to integrate biodiversity conservation measures into urban planning to promote ecosystem service provision and ensure the well-being of urban residents. |
| 2014 | COP12 | 韩国平昌 Pyeongchang, South Korea | 决定XII/9: 支持并推广城市生物多样性指数, 强调通过绿色基础设施和生态走廊提高城市生态系统连通性。Decision XII/9: Supported the adoption and promotion of the City Biodiversity Index, emphasizing the enhancement of urban ecosystem connectivity through green infrastructure and ecological corridors. |
| 2016 | COP13 | 墨西哥坎昆 Cancun, Mexico | 决定XIII/3: 在城市化、基础设施和土地利用规划中主流化生物多样性, 呼吁各国在政策制定中考虑纳入生物多样性。Decision XIII/3: Mainstreamed biodiversity into urbanization, infrastructure, and land-use planning frameworks, urging member states to incorporate biodiversity into national and local policy development. |
| 2018 | COP14 | 埃及沙姆沙伊赫 Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt | 决定XIV/8: 加强城市和地方生物多样性保护, 推广基于自然的解决方案, 应对气候变化和生物多样性丧失等挑战。Decision XIV/8: Strengthened urban and local biodiversity conservation efforts, advocating for nature-based solutions to address challenges such as climate change and biodiversity loss. |
| 2021-2022 | COP15 | 中国昆明和加拿大蒙特利尔 Kunming, China & Montreal, Canada | 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》: 目标12提出确保所有城市和地方采取措施增强生物多样性, 促进绿色基础设施建设, 强调通过自然解决方案提高生态系统服务和居民福祉。Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: Target 12 mandates all cities and local governments to implement measures that enhance biodiversity, advance green infrastructure development, and emphasize nature-based solutions to improve ecosystem services and resident well-being. |
Table 1 Decisions related to urban green space biodiversity adopted by the Conferences of the Parties (COP) to the Convention on Biological Diversity
| 年份 Year | 缔约方大会 COP | 地点 Location | 关于城市绿地生物多样性的决定 Decisions related to urban green space biodiversity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | COP1 | 巴哈马拿骚 Nassau, Bahamas | 无专门针对城市绿地生物多样性的决定, 主要集中在总体生物多样性保护目标和策略。 There are no dedicated decisions specifically targeting urban green space biodiversity; current efforts are primarily concentrated on overarching biodiversity conservation goals and strategies. |
| 1995 | COP2 | 印度尼西亚雅加达 Jakarta, Indonesia | |
| 1996 | COP3 | 阿根廷布宜诺斯艾利斯 Buenos Aires, Argentina | |
| 1998 | COP4 | 斯洛伐克布拉迪斯拉发 Bratislava, Slovakia | |
| 2000 | COP5 | 肯尼亚内罗毕 Nairobi, Kenya | |
| 2002 | COP6 | 荷兰海牙 Hague, the Netherlands | |
| 2004 | COP7 | 马来西亚吉隆坡 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia | |
| 2006 | COP8 | 巴西库里提巴 Curitiba, Brazil | |
| 2008 | COP9 | 德国波恩 Bonn, Germany | 决定IX/28: 首次明确提出“城市生物多样性”, 呼吁加强对城市生态系统的关注, 并制定和实施城市生物多样性战略和行动计划。Decision IX/28: Explicitly introduced the concept of “urban biodiversity” for the first time, calling for increased attention to urban ecosystems and the development and implementation of urban biodiversity strategies and action plans. |
| 2010 | COP10 | 日本名古屋 Nagoya, Japan | 决定X/22: 认可“城市生物多样性指数” (新加坡指数)作为衡量和监控工具, 鼓励将生物多样性纳入城市规划。Decision X/22: Endorsed the “City Biodiversity Index” (Singapore Index) as a monitoring and evaluation tool, encouraging the integration of biodiversity considerations into urban planning processes. |
| 2012 | COP11 | 印度海德拉巴 Hyderabad, India | 决定XI/8: 强调在城市规划中整合生物多样性保护措施, 促进生态系统服务供给, 确保城市居民的福祉。Decision XI/8: Highlighted the need to integrate biodiversity conservation measures into urban planning to promote ecosystem service provision and ensure the well-being of urban residents. |
| 2014 | COP12 | 韩国平昌 Pyeongchang, South Korea | 决定XII/9: 支持并推广城市生物多样性指数, 强调通过绿色基础设施和生态走廊提高城市生态系统连通性。Decision XII/9: Supported the adoption and promotion of the City Biodiversity Index, emphasizing the enhancement of urban ecosystem connectivity through green infrastructure and ecological corridors. |
| 2016 | COP13 | 墨西哥坎昆 Cancun, Mexico | 决定XIII/3: 在城市化、基础设施和土地利用规划中主流化生物多样性, 呼吁各国在政策制定中考虑纳入生物多样性。Decision XIII/3: Mainstreamed biodiversity into urbanization, infrastructure, and land-use planning frameworks, urging member states to incorporate biodiversity into national and local policy development. |
| 2018 | COP14 | 埃及沙姆沙伊赫 Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt | 决定XIV/8: 加强城市和地方生物多样性保护, 推广基于自然的解决方案, 应对气候变化和生物多样性丧失等挑战。Decision XIV/8: Strengthened urban and local biodiversity conservation efforts, advocating for nature-based solutions to address challenges such as climate change and biodiversity loss. |
| 2021-2022 | COP15 | 中国昆明和加拿大蒙特利尔 Kunming, China & Montreal, Canada | 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》: 目标12提出确保所有城市和地方采取措施增强生物多样性, 促进绿色基础设施建设, 强调通过自然解决方案提高生态系统服务和居民福祉。Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: Target 12 mandates all cities and local governments to implement measures that enhance biodiversity, advance green infrastructure development, and emphasize nature-based solutions to improve ecosystem services and resident well-being. |
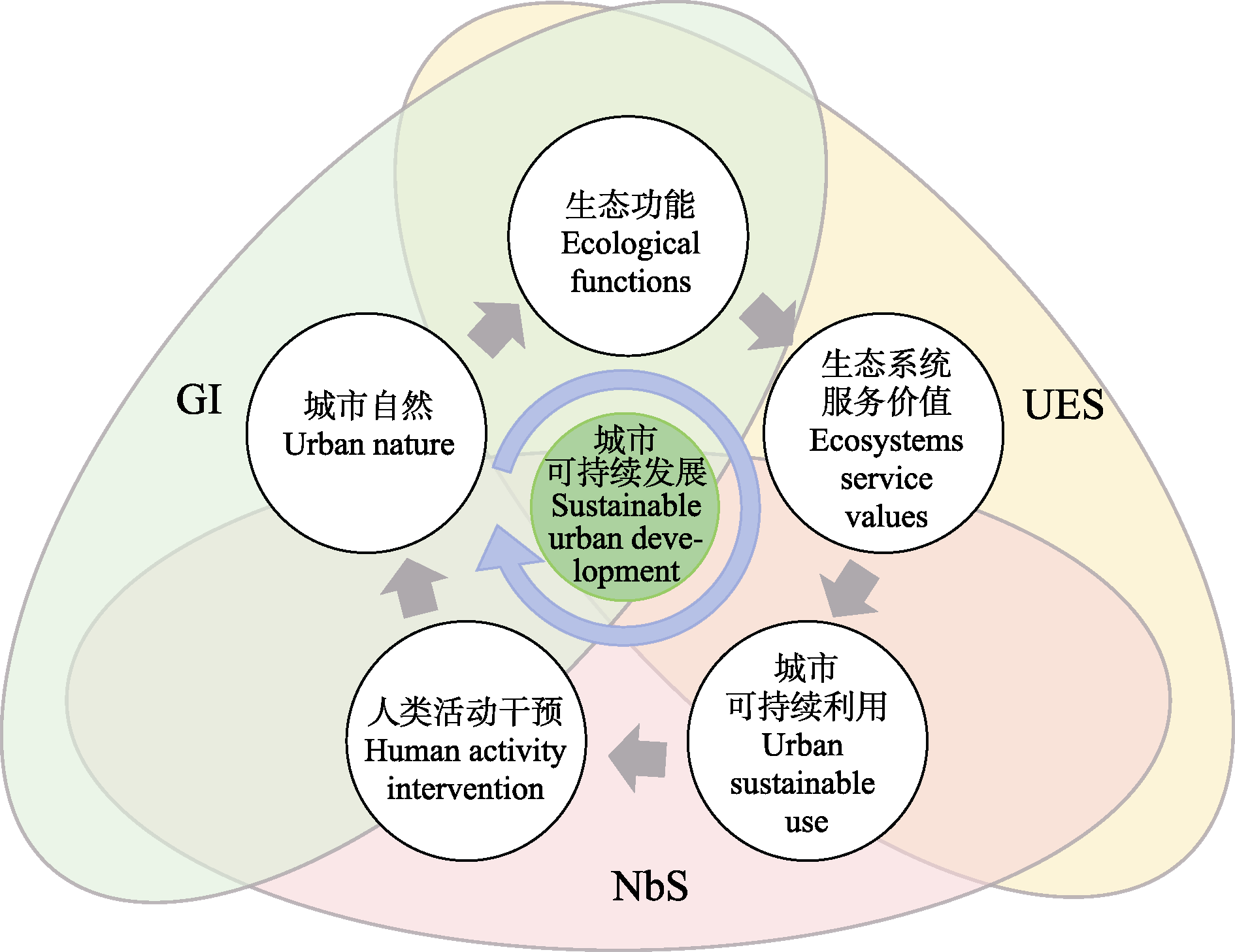
Fig. 4 Conceptual framework integrating three ecosystem- based approaches for urban sustainability. UES, Urban ecosystem services; GI, Green infrastructure; NbS, Nature- based solutions. Adapted from Fang et al, 2023.
| [1] |
Andersson-Sköld Y, Klingberg J, Gunnarsson B, Cullinane K, Gustafsson I, Hedblom M, Knez I, Lindberg F, Sang ÅO, Pleijel H, Thorsson P, Thorsson S (2018) A framework for assessing urban greenery’s effects and valuing its ecosystem services. Journal of Environmental Management, 205, 274-285.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Aznarez C, Svenning JC, Taveira G, Baró F, Pascual U (2022) Wildness and habitat quality drive spatial patterns of urban biodiversity. Landscape and Urban Planning, 228, 104570. |
| [3] | Banks-Leite C, Ewers RM, Folkard-Tapp H, Fraser A (2020) Countering the effects of habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation through habitat restoration. One Earth, 3, 672-676. |
| [4] | Behm JE, Bélouard N, Gleditsch JM, Phillips PM, Swartz TM (2022) Trait-based approaches for understanding how biodiversity generates sustainable benefits in urban vegetated green infrastructure. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 57, 101204. |
| [5] | Berthon K, Thomas F, Bekessy S (2021) The role of ‘nativeness’ in urban greening to support animal biodiversity. Landscape and Urban Planning, 205, 103959. |
| [6] | Brink E, Aalders T, Ádám D, Feller R, Henselek Y, Hoffmann A, Ibe K, Matthey-Doret A, Meyer M, Negrut NL, Rau AL, Riewerts B, von Schuckmann L, Törnros S, von Wehrden H, Abson DJ, Wamsler C (2016) Cascades of green: A review of ecosystem-based adaptation in urban areas. Global Environmental Change, 36, 111-123. |
| [7] | Cai YL, Zhu HG, Li JX (2024) Biodiversity conservation in China: Policy evolution, main measures, and development trends. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23386. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[蔡颖莉, 朱洪革, 李家欣 (2024) 中国生物多样性保护政策演进、主要措施与发展趋势. 生物多样性, 32, 23386.]
DOI |
|
| [8] | Castelli KR, Silva AM, Dunning JB (2021) Improving the biodiversity in urban green spaces: A nature based approach. Ecological Engineering, 173, 106398. |
| [9] | Chen YY, Men HL, Ke XL (2023) Optimizing urban green space patterns to improve spatial equity using location-allocation model: A case study in Wuhan. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 84, 127922. |
| [10] | Cheshmehzangi A, Butters C, Xie LJ, Dawodu A (2021) Green infrastructures for urban sustainability: Issues, implications, and solutions for underdeveloped areas. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 59, 127028. |
| [11] | Cui QY, Tan L, Ma HR, Wei XL, Yi SG, Zhao D, Lu HY, Lin PQ (2024) Effective or useless? Assessing the impact of park entrance addition policy on green space services from the 15-min city perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production, 467, 142951. |
| [12] | Dai F, Jiang JY, Yang B (2017) Research frontiers of GIS application in foreign landscape architecture field. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 33(8), 52-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴菲, 姜佳怡, 杨波 (2017) GIS在国外风景园林领域研究前沿. 中国园林, 33(8), 52-58.] | |
| [13] |
Deng J, Li Y, Hou YL (2023) Urban biodiversity conservation: Experience from the comparative perspective of China and Europe. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23070. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[邓晶, 李艺, 侯一蕾 (2023) 城市生物多样性保护: 基于中欧对比视角下的经验借鉴. 生物多样性, 31, 23070.]
DOI |
|
| [14] | Deng LL, Chen TY, Xu Y, Shen J, Gong HY, Weng P, Guo JL, Huang ML, Wu H, Yan W (2024) Promotion of urban biodiversity conservation through natural education by botanical gardens. Landscape Architecture Academic Journal, 41(S1), 127-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邓玲丽, 陈婷媛, 许源, 沈菁, 宫鹤忆, 翁沛, 郭江莉, 黄梅林, 吴鸿, 严巍 (2024) 浅析植物园自然教育促进城市生物多样性保护. 园林, 41(S1), 127-134.] | |
| [15] | Fahrig L (2003) Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 34, 487-515. |
| [16] | Fang XN, Li JW, Ma Q (2023) Integrating green infrastructure, ecosystem services and nature-based solutions for urban sustainability: A comprehensive literature review. Sustainable Cities and Society, 98, 104843. |
| [17] | Fisher JC, Dallimer M, Irvine KN, Aizlewood SG, Austen GE, Fish RD, King PM, Davies ZG (2023) Human well-being responses to species’ traits. Nature Sustainability, 6, 1219-1227. |
| [18] | Gan J (2018) Built environment factors affecting urban biodiversity and planning optimization approaches. Urban Planning International, 33(4), 67-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [干靓 (2018) 城市建成环境对生物多样性的影响要素与优化路径. 国际城市规划, 33(4), 67-73.] | |
| [19] | Gaston KJ (2010) Biodiversity and ecosystem services in a changing world. Science, 327, 1425-1430. |
| [20] | Gong C, Yang RT, Li SH (2024) The role of urban green space in promoting health and well-being is related to nature connectedness and biodiversity: Evidence from a two-factor mixed-design experiment. Landscape and Urban Planning, 245, 105020. |
| [21] | Grilo F, McPhearson T, Santos-Reis M, Branquinho C (2022) A trait-based conceptual framework to examine urban biodiversity, socio-ecological filters, and ecosystem services linkages. NPJ Urban Sustainability, 2, 32. |
| [22] |
Guo QH, Hu TY, Jiang YX, Jin SC, Wang R, Guan HC, Yang QL, Li YM, Wu FF, Zhai QP, Liu J, Su YJ (2018) Advances in remote sensing application for biodiversity research. Biodiversity Science, 26, 789-806. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[郭庆华, 胡天宇, 姜媛茜, 金时超, 王瑞, 关宏灿, 杨秋丽, 李玉美, 吴芳芳, 翟秋萍, 刘瑾, 苏艳军 (2018) 遥感在生物多样性研究中的应用进展. 生物多样性, 26, 789-806.]
DOI |
|
| [23] | Hansen R, Mattes A, Meier M, Kurths A (2023) Reorienting urban green infrastructure planning towards biodiversity—Perspectives and ongoing debates from Germany. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 90, 128155. |
| [24] | Hu XL, Lima MF (2024) The association between maintenance and biodiversity in urban green spaces: A review. Landscape and Urban Planning, 251, 105153. |
| [25] | Huang XX, Wang HJ, Shan LY, Xiao FT (2021) Constructing and optimizing urban ecological network in the context of rapid urbanization for improving landscape connectivity. Ecological Indicators, 132, 108319. |
| [26] | Huang YL, Fu WC, Chen ZR, Ren W, Dong JW (2024) Research progress in the biodiversity of urban green space based on citizen science. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 22(4), 84-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄雅凌, 傅伟聪, 陈梓茹, 任维, 董建文 (2024) 基于公众科学的城市绿地生物多样性研究进展. 中国城市林业, 22(4), 84-91.] | |
| [27] |
Huovila A, Bosch P, Airaksinen M (2019) Comparative analysis of standardized indicators for smart sustainable cities: What indicators and standards to use and when? Cities, 89, 141-153.
DOI |
| [28] | Huynh LTM, Gasparatos A, Su J, Dam Lam R, Grant EI, Fukushi K (2022) Linking the nonmaterial dimensions of human-nature relations and human well-being through cultural ecosystem services. Science Advances, 8, eabn8042. |
| [29] | Javed AR, Shahzad F, Rehman SU, Bin Zikria Y, Razzak I, Jalil Z, Xu GD (2022) Future smart cities: Requirements, emerging technologies, applications, challenges, and future aspects. Cities, 129, 103794. |
| [30] | Jia G, Lin WP, Xu RJ, Li LB (2022) Calculation and analysis of SDG 15.1.2 biodiversity index based on remote sensing: A case study of demonstration zone of green and integrated ecological development of the Yangtze River Delta. Research of Environmental Sciences, 35, 1025-1036. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [伽光, 林文鹏, 徐润浇, 李鲁冰 (2022) 基于遥感的SDG 15.1.2生物多样性指标计算与分析: 以长三角生态绿色一体化发展示范区为例. 环境科学研究, 35, 1025-1036.] | |
| [31] | Kowarik I (2023) Urban biodiversity, ecosystems and the city. Insights from 50 years of the Berlin School of urban ecology. Landscape and Urban Planning, 240, 104877. |
| [32] | Lambert MR, Donihue CM (2020) Urban biodiversity management using evolutionary tools. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 903-910. |
| [33] | Lepczyk CA, Aronson MFJ, Evans KL, Goddard MA, Lerman SB, MacIvor JS (2017) Biodiversity in the city: Fundamental questions for understanding the ecology of urban green spaces for biodiversity conservation. BioScience, 67, 799-807. |
| [34] | Li F, Ma Y (2021) Research progress of urban ecosystem restoration. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 9144-9153. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李锋, 马远 (2021) 城市生态系统修复研究进展. 生态学报, 41, 9144-9153.] | |
| [35] | Li L, Zhang CY, Pei NC, Gao BT, Wang N, Li JR, Wu RC, Hao ZZ (2024) Correlation analysis of urban green space landscape patterns and bird diversity based on passive acoustic monitoring technology. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24296. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[李乐, 张承云, 裴男才, 高丙涛, 王娜, 李嘉睿, 武瑞琛, 郝泽周 (2024) 基于被动声学监测技术的城市绿地景观格局与鸟类多样性关联分析. 生物多样性, 32, 24296.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Li XH, Mu S, Zhang X, Xi ZH, Jiang B, Wang S, Qiu L, Gao T (2024) Comparison of the reduction effects of green space on atmospheric particulate matter concentration in northern cities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44, 4051-4063. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李笑寒, 穆森, 张祥, 席子菡, 姜博, 王森, 邱玲, 高天 (2024) 北方城市绿地对大气颗粒物浓度的削减作用对比研究. 生态学报, 44, 4051-4063.] | |
| [37] | Li XX, Ou XY, Sun XY, Li HR, Li YX, Zheng X (2024) Urban biodiversity conservation: A framework for ecological network construction and priority areas identification considering habit differences within species. Journal of Environmental Management, 365, 121512. |
| [38] | Liu Y, Ou XY, Zheng X (2022) Urban biodiversity conservation planning integrating green space structure and functional connectivity analysis. Landscape Architecture, 29(1), 26-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘阳, 欧小杨, 郑曦. (2022) 整合绿地结构与功能性连接分析的城市生物多样性保护规划. 风景园林, 29(1), 26-33. ] | |
| [39] | Liu ZH, Wei L, Zhou Y (2024) Constructing sustainable landscape patterns for enhancing urban biodiversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44, 5905-5913. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘珍环, 魏莱, 周义 (2024) 面向城市生物多样性提升的可持续景观格局构建机理与途径. 生态学报, 44, 5905-5913.] | |
| [40] | Liu ZQ, Wang XY, Yang F, Li FZ (2023) Advances in informal green space digital recognition technology based on deep learning in the context of urban renewal. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 39(6), 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘子晴, 王薪宇, 杨锋, 李方正 (2023) 城市更新背景下融合深度学习的非正式绿地数字识别技术研究进展. 中国园林, 39(6), 33-38.] | |
| [41] | Ma KP, Qian YQ (1998) Biodiversity conservation and its research progress. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 4, 95-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克平, 钱迎倩 (1998) 生物多样性保护及其研究进展. 应用与环境生物学报, 4, 95-99.] | |
| [42] | Mao QZ, Ma KM, Wu JG, Tang RL, Zhang YX, Luo SH, Bao L, Cai XH (2013) An overview of advances in distributional pattern of urban biodiversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 1051-1064. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [毛齐正, 马克明, 邬建国, 唐荣莉, 张育新, 罗上华, 宝乐, 蔡小虎 (2013) 城市生物多样性分布格局研究进展. 生态学报, 33, 1051-1064.] | |
| [43] | Martins GB, La Rosa LEC, Happ PN, Coelho Filho LCT, Santos CJF, Feitosa RQ, Ferreira MP (2021) Deep learning-based tree species mapping in a highly diverse tropical urban setting. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 64, 127241. |
| [44] | McPhearson T, Pickett STA, Grimm NB, Niemelä J, Alberti M, Elmqvist T, Weber C, Haase D, Breuste J, Qureshi S (2016) Advancing urban ecology toward a science of cities. BioScience, 66, 198-212. |
| [45] |
Meeus S, Silva-Rocha I, Adriaens T, Brown PMJ, Chartosia N, Claramunt-López B, Martinou AF, Pocock MJO, Preda C, Roy HE, Tricarico E, Groom QJ (2023) More than a bit of fun: The multiple outcomes of a bioblitz. BioScience, 73, 168-181.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Mi XC, Feng G, Hu YB, Zhang J, Chen L, Corlett RT, Hughes AC, Pimm S, Schmid B, Shi SH, Svenning JC, Ma KP (2021) The global significance of biodiversity science in China: An overview. National Science Review, 8, nwab032. |
| [47] | Mihalakakou G, Souliotis M, Papadaki M, Menounou P, Dimopoulos P, Kolokotsa D, Paravantis JA, Tsangrassoulis A, Panaras G, Giannakopoulos E, Papaefthimiou S (2023) Green roofs as a nature-based solution for improving urban sustainability: Progress and perspectives. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 180, 113306. |
| [48] | Neeson TM, Emmons SC, Mullenbach LE (2024) Tradeoffs and synergies between social equity and environmental benefits in conservation. Global Ecology and Conservation, 55, e03219. |
| [49] | Noe EE, Stolte O (2023) Dwelling in the city: A qualitative exploration of the human-nature relationship in three types of urban greenspace. Landscape and Urban Planning, 230, 104633. |
| [50] |
Nørgaard L, Olesen CR, Trøjelsgaard K, Pertoldi C, Nielsen JL, Taberlet P, Ruiz-González A, De Barba M, Iacolina L (2021) eDNA metabarcoding for biodiversity assessment, generalist predators as sampling assistants. Scientific Reports, 11, 6820.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Paudel S, States SL (2023) Urban green spaces and sustainability: Exploring the ecosystem services and disservices of grassy lawns versus floral meadows. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 84, 127932. |
| [52] |
Peng YY, Jin T, Zhang XQ (2024) Biodiversity credits: Concepts, principles, transactions and challenges. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[彭昀月, 靳彤, 张小全 (2024) 生物多样性信用的概念、原则、交易和挑战. 生物多样性, 32, 23300.]
DOI |
|
| [53] | Reyes-Riveros R, Altamirano A, De La Barrera F, Rozas-Vásquez D, Vieli L, Meli P (2021) Linking public urban green spaces and human well-being: A systematic review. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 61, 127105. |
| [54] |
Shen XH, Zhu XY, Shi HF, Wang CZ (2023) Research progress of birdsong recognition algorithms based on machine learning. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23272. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[申小虎, 朱翔宇, 史洪飞, 王传之 (2023) 基于机器学习鸟声识别算法研究进展. 生物多样性, 31, 23272.]
DOI |
|
| [55] | Shen Z, Yin HW, Kong FH, Wu W, Sun H, Su J, Tian SQ (2024) Enhancing ecological network establishment with explicit species information and spatially coordinated optimization for supporting urban landscape planning and management. Landscape and Urban Planning, 248, 105079. |
| [56] | Shwartz A, Tzunz M, Gafter L, Colléony A (2023) One size does not fit all: The complex relationship between biodiversity and psychological well-being. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 86, 128008. |
| [57] | Southon GE, Jorgensen A, Dunnett N, Hoyle H, Evans KL (2018) Perceived species-richness in urban green spaces: Cues, accuracy and well-being impacts. Landscape and Urban Planning, 172, 12.002 |
| [58] | Tzoulas K, Korpela K, Venn S, Yli-Pelkonen V, Kaźmierczak A, Niemelä J, James P (2007) Promoting ecosystem and human health in urban areas using green infrastructure: A literature review. Landscape and Urban Planning, 81, 167-178. |
| [59] | Uchida K, Blakey RV, Burger JR, Cooper DS, Niesner CA, Blumstein DT (2021) Urban biodiversity and the importance of scale. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 36, 123-131. |
| [60] | Wan YY, Li HY, He MX, Zhao N (2017) Influences of habitat fragmentation on natural regeneration of Ailanthus altissima in urban greenland based on different pavement conditions. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 23, 1110-1116. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [万媛媛, 李洪远, 贺梦璇, 赵娜 (2017) 基于不同铺装条件下的生境片断化对城市绿地中臭椿幼苗自然更新的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 23, 1110-1116.] | |
| [61] | Wang HY, Wang HQ, Chen XY, Han BL, Shu CJ, Zhang T, Ding SY (2023) Review on evaluation and enhancement of urban biodiversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 2995-3006. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王海洋, 王浩琪, 陈禧悦, 韩宝龙, 束承继, 张童, 丁仕宇 (2023) 国内外城市生物多样性评价与提升研究综述. 生态学报, 43, 2995-3006.] | |
| [62] | Wang J, Wang Y, Guan L, Chen B, Cao GH, Kong YP (2019) A review of the impacts of highway construction on wild animals and protection in tropical rainforest. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38, 3183-3188. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王冀, 王云, 关磊, 陈兵, 曹广华, 孔亚平 (2019) 热带雨林公路建设对野生动物的影响及保护研究进展. 生态学杂志, 38, 3183-3188.] | |
| [63] | Wei Y, He JY (2022) Beijing has continuously improved its natural belt protection system. Greening and Life, (6), 2. (in Chinese) |
| [魏瑶, 何建勇 (2022) 北京不断完善自然带保护体系. 绿化与生活, (6), 2.] | |
| [64] | Weiskopf SR, Rubenstein MA, Crozier LG, Gaichas S, Griffis R, Halofsky JE, Hyde KJW, Morelli TL, Morisette JT, Muñoz RC, Pershing AJ, Peterson DL, Poudel R, Staudinger MD, Sutton-Grier AE, Thompson L, Vose J, Weltzin JF, Whyte KP (2020) Climate change effects on biodiversity, ecosystems, ecosystem services, and natural resource management in the United States. Science of The Total Environment, 733, 137782. |
| [65] |
Wen Z, Zheng H, Ouyang ZY (2020) Research progress on the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem services. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31, 340-348. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[文志, 郑华, 欧阳志云 (2020) 生物多样性与生态系统服务关系研究进展. 应用生态学报, 31, 340-348.]
DOI |
|
| [66] | Wu F, Li SH, Liu JM (2007) Research on the relationship between urban green spaces of different areas and the temperature and humidity benefit. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 23(6), 71-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴菲, 李树华, 刘娇妹 (2007) 城市绿地面积与温湿效益之间关系的研究. 中国园林, 23(6), 71-74.] | |
| [67] | Xia F, Guo ZL, Zhang MY, Yan LL, Li W, Wang DA, Cui LJ (2024) Urban biodiversity conservation and management: Exploration and progress. World Forestry Research, 37(3), 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏舫, 郭子良, 张曼胤, 闫亮亮, 李伟, 王大安, 崔丽娟 (2024) 城市生物多样性保育管理的探索及进展. 世界林业研究, 37(3), 33-39.] | |
| [68] | Xiao X, Wang QZ, Guan QY, Zhang ZP, Yan Y, Mi JM, Yang EQ (2023) Quantifying the nonlinear response of vegetation greening to driving factors in Longnan of China based on machine learning algorithm. Ecological Indicators, 151, 110277. |
| [69] | Xu XH, Wang WW, Mi XC, Chen L, Ma KP (2023) The Chinese forest biodiversity monitoring network (CForBio): 20-year achievements and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23354. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[徐学红, 王巍伟, 米湘成, 陈磊, 马克平 (2023) 中国森林生物多样性监测网络(CForBio): 二十年进展与展望. 生物多样性, 31, 23354.]
DOI |
|
| [70] | Xu YR, Zhang MY, Fan SX, Li XL, Dong L, Zeng ZQ (2023) Niche and community characteristics of spontaneous herbs in community parks: A case study of Xicheng District of Beijing City. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 50, 784-791. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐幼榕, 张梦园, 范舒欣, 李晓璐, 董丽, 曾赞青 (2023) 城市社区公园自生草本生态位及群落特征——以北京市西城区为例. 安徽农业大学学报, 50, 784-791.] | |
| [71] | Xue JH, Wang YC, Chen CD (2021) Reference and enlightenment of city biodiversity index in Singapore and Japan. Jounal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 19(1), 31-35, 100. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [薛竣桓, 王云才, 陈春谛 (2021) 新加坡和日本城市生物多样性指标的借鉴与启示. 中国城市林业, 19(1), 31-35, 100.] | |
| [72] | Yang B, Guo TR, Zheng SJ, Xu ZF, Wu YC, Zhang L (2021) A practical exploration on plant diversity monitoring in urban areas based on the public participation & artificial intelligent technology—A case study on native herbaceous plants diversity monitoring in Shanghai. Landscape Architecture Academic Journal, 38(12), 112-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨博, 郭陶然, 郑思俊, 徐洲锋, 吴奕辰, 张浪 (2021) 基于公众参与和人工智能技术的上海草本植物多样性监测实践探索. 园林, 38(12), 112-118.] | |
| [73] | Yang C, Jiang TT, Li X, Li XM (2024) Effects of percent green cover on the relationship between greenspace fragmentation and land surface temperature: A case study in Changsha, China. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33, 242-248. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[杨纯, 蒋恬田, 李欣, 李小马 (2024) 绿化覆盖率对城市绿地破碎度与地表温度的关系的影响. 生态环境学报, 33, 242-248.]
DOI |
|
| [74] | Yin LH, Gong SN, Li L, Shen ZH, Qiu S, Deng XY, Han YW (2024) Progress and thoughts on establishment of urban insect pollination habitats. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 22(1), 77-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [殷利华, 巩思凝, 李良, 沈正豪, 邱爽, 邓心怡, 韩依纹 (2024) 城市昆虫传粉生境营建研究进展及思考. 中国城市林业, 22(1), 77-86.] | |
| [75] | Yu JL, Li J, Sheng Y, Liu B (2021) Study on the influence of urban green space on the satisfaction of residents. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 37(7), 95-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [俞佳俐, 李健, 盛莹, 刘斌 (2021) 城市绿地对居民身心健康福祉满意度影响研究. 中国园林, 37(7), 95-100.] | |
| [76] | Zeng HC, Li CL, Zhang JY, Zhang J, Zheng AD, Wu ZJ, Wang JN (2023) Research on influencing factors to biodiversity in urban green spaces. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 21(5), 171-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾海聪, 李晨亮, 张君瑶, 张健, 郑安迪, 吴子敬, 王嘉楠 (2023) 城市绿地生物多样性影响因素研究概述. 中国城市林业, 21(5), 171-178.] | |
| [77] | Zhang DM, Luo YL, Zhang L, Fu RJ, You XL, Yin LJ (2024) A study on the investigation method of plant species biodiversity in several urban green spaces: Taking Shanghai as an example. Journal of Landscape Architecture, 41(4), 4-10, 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张冬梅, 罗玉兰, 张浪, 傅仁杰, 有祥亮, 尹丽娟 (2024) 几种城市绿地植物物种生物多样性调查方法研究——以上海为例. 园林, 41(4), 4-10, 51.] | |
| [78] | Zhang H, He J, Yang TY, Cao SY (2023) Research on vitality characteristics and influence factors of urban parks in Tianjin under the perception of dynamic population distribution. Landscape Architecture, 30(7), 36-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张赫, 贺晶, 杨天宇, 曹舒仪 (2023) 人群动态分布感知下的天津市公园活力特征及影响因素研究. 风景园林, 30(7), 36-42.] | |
| [79] | Zhao QG, Huang GQ, Ma YQ (2016) The ecological environment conditions and construction of an ecological civilization construction in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 6328-6335. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵其国, 黄国勤, 马艳芹 (2016) 中国生态环境状况与生态文明建设. 生态学报, 36, 6328-6335.] | |
| [80] | Zheng YC, Lin T, Hamm NAS, Liu J, Zhou TY, Geng HK, Zhang JM, Ye H, Zhang GQ, Wang XT, Chen TY (2024) Quantitative evaluation of urban green exposure and its impact on human health: A case study on the 3-30- 300 green space rule. Science of the Total Environment, 924, 171461. |
| [81] | Zhong L, Yang R, Xue F (2021) State of art on urban biodiversity conservation research. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 37(5), 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [钟乐, 杨锐, 薛飞 (2021) 城市生物多样性保护研究述评. 中国园林, 37(5), 25-30.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()