



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 24525. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024525 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024525
• Special Feature: How the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework Becomes a Mainstream Work Objective in the China’s System • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhao Weiyang1,2( ), Wang Wei1,2,*(
), Wang Wei1,2,*( )(
)( ), Ma Bingran1,2(
), Ma Bingran1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-01
Accepted:2025-03-04
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-04
Contact:
*E-mail: wang.wei@craes.org.cn
Supported by:Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs)[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525.
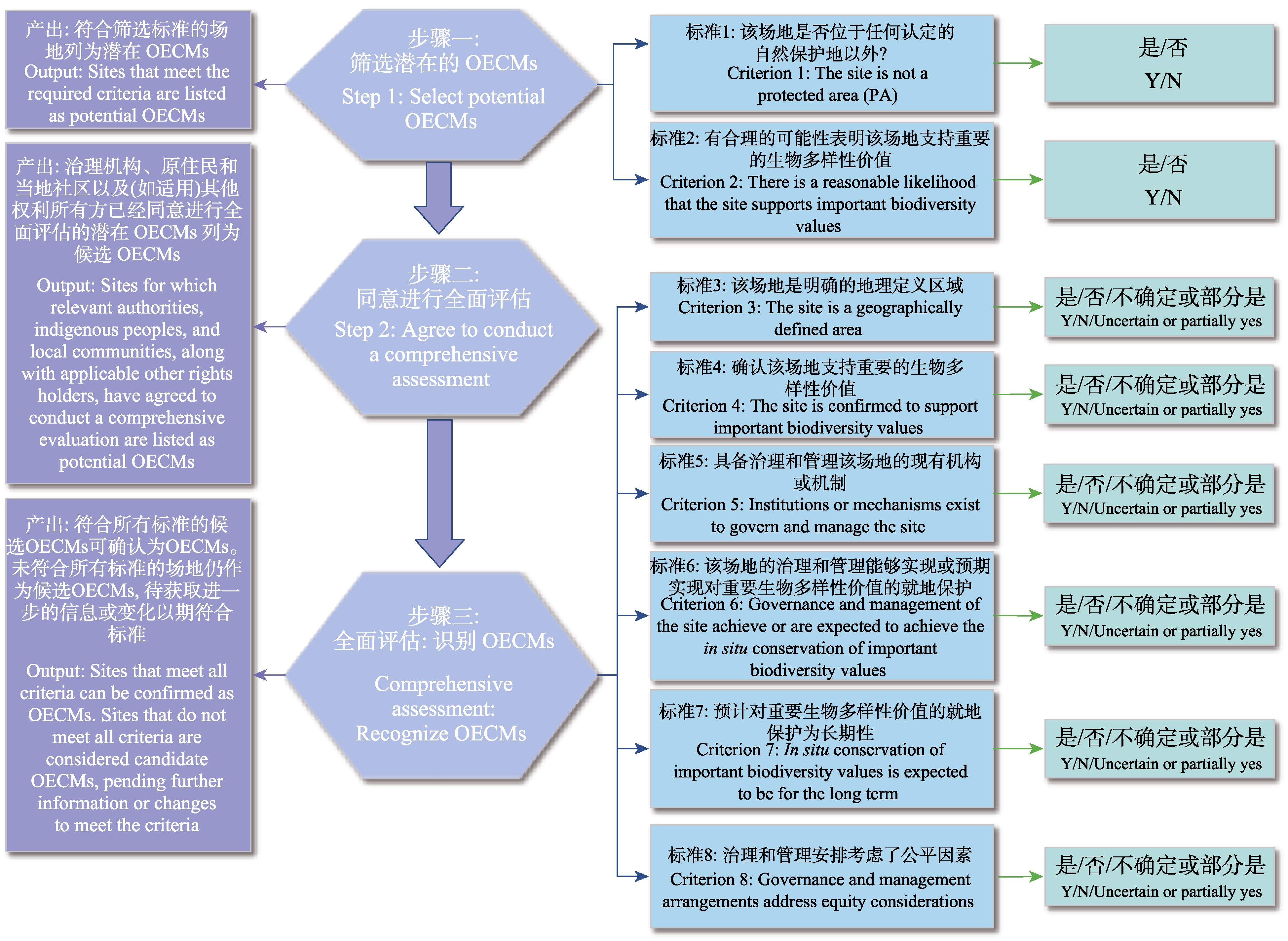
Fig. 1 The process for recognizing other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs). “Y” indicates a positive evaluation result, while “N” indicates a negative evaluation result. Sites for which all criteria receive a “Y” response are confirmed as OECMs, subject to stakeholder consent and approval by the governing body. Sites with a combination of “Y” and “uncertain or partially yes” responses, or those with entirely “uncertain or partially yes” responses, remain candidate OECMs until further information or changes confirm their recognition as OECMs. Sites with one or more “N” responses cannot currently be considered OECMs, but may be re-evaluated in the future if changes occur that enable them to meet all criteria (adapted from IUCN, 2023a).
| [1] | Beazley L, Kenchington E, Korabik M, Fenton D, King M(2021) Other effective area-based conservation measure promotes recovery in a cold-water coral reef. Global Ecology and Conservation, 26, e01485. |
| [2] | Bhola N, Klimmek H, Kingston N, Burgess ND, van Soesbergen A, Corrigan C, Harrison J, Kok MTJ(2021) Perspectives on area-based conservation and its meaning for future biodiversity policy. Conservation Biology, 35, 168-178. |
| [3] | Chen X, Tian TT, Pan H, Jin YY, Zhang XD, Yang B, Zhang L(2024) Establishing a protected area network in Xinlong with other effective area-based conservation measures. Conservation Biology, 38, e14297. |
| [4] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2018) CBD/COP/DEC/14/8:Decision Adopted by the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity. (accessed on 2024-10-08) https://www.cbd.int/doc/decisions/cop-14/cop-14-dec-08-en.pdf. |
| [5] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2020) Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020, Including Aichi Biodiversity Targets. (accessed on 2024-10-08) https://www.cbd.int/sp/. |
| [6] | CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity) (2022) Kunming Declaration “Ecological Civilization: Building a Shared Future for All Life on Earth”. (accessed on 2024-10-08) https://www.cbd.int/doc/c/c2db/972a/fb32e0a277bf1ccfff742be5/cop-15-05-add1-en.pdf. |
| [7] | Cook CN(2024a) Diverse approaches to protecting biodiversity: The different conservation measures discussed as possible other effective area-based conservation measures. Conservation Letters, 17, e13027. |
| [8] | Cook CN(2024b) Progress developing the concept of other effective area-based conservation measures. Conservation Biology, 38, e14106. |
| [9] | Donald PF, Buchanan GM, Balmford A, Bingham H, Couturier AR, de la Rosa GE Jr, Gacheru P, Herzog SK, Jathar G, Kingston N, Marnewick D, Maurer G, Reaney L, Shmygaleva T, Sklyarenko S, Stevens CMD, Butchart SHM(2019) The prevalence, characteristics and effectiveness of Aichi Target 11’s “other effective area-based conservation measures” (OECMs) in key biodiversity areas. Conservation Letters, 12, e12659. |
| [10] | Dudley N, Jonas H, Nelson F, Parrish J, Pyhälä A, Stolton S, Watson JEM(2018) The essential role of other effective area-based conservation measures in achieving big bold conservation targets. Global Ecology and Conservation, 15, e00424. |
| [11] | Earth Journalism Network (2022) Morocco’s Biodiversity Suffers as Rich Locals and Foreign Tourists Hunt for Fun. (accessed on 2024-02-20) https://earthjournalism.net/stories/moroccos-biodiversity-suffers-as-rich-locals-and-foreign-tourists-hunt-for-fun. |
| [12] | Fitzsimons JA, Stolton S, Rafa M(2024) Advances in privately protected areas. Frontiers in Conservation Science, 5, 1441046. |
| [13] | Government of Canada (2019) List of Marine Refuges: Bay of Islands Salmon Migration Closure. (accessed on 2024-10-28) https://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/oceans/oecm-amcepz/refuges/lophelia-eng.html. |
| [14] | Gurney GG, Darling ES, Ahmadia GN, Agostini VN, Ban NC, Blythe J, Claudet J, Epstein G, Estradivari, Himes-Cornell A, Jonas HD, Armitage D, Campbell SJ, Cox C, Friedman WR, Gill D, Lestari P, Mangubhai S, McLeod E, Muthiga NA, Naggea J, Ranaivoson R, Wenger A, Yulianto I, Jupiter SD(2021) Biodiversity needs every tool in the box: Use OECMs. Nature, 595, 646-649. |
| [15] | Haase P, Tonkin JD, Stoll S, Burkhard B, Frenzel M, Geijzendorffer IR, Häuser C, Klotz S, Kühn I, McDowell WH, Mirtl M, Müller F, Musche M, Penner J, Zacharias S, Schmeller DS(2018) The next generation of site-based long-term ecological monitoring: Linking essential biodiversity variables and ecosystem integrity. Science of the Total Environment, 613, 1376-1384. |
| [16] | Hockings M, Leverington F, Cook C(2015) Protected area management effectiveness. In: Protected Area Governance and Management (eds WorboysGL, LockwoodM, KothariA, FearyS, PulsfordI),pp.889-928. ANU Press, Canberra. |
| [17] | Hoesen J, Bagshaw D, Elliott J, Haas CA, Kelly J, Lazaruk H, MacKinnon D, Lemieux CJ(2023) Assessing the effectiveness of potential protected areas and OECMs in conserving biodiversity against subsurface resource extraction impacts. Biological Conservation, 283, 110134. |
| [18] | International Land Conservation Network News (2024a) China Announces Its First OECMs at COP16, Advancing Its “30×30” Conservation Target. (accessed on 2024-11-20) https://landconservationnetwork.org/china-announces-its-first-oecms-at-cop16-advancing-its-30x30-conservation-target/. |
| [19] | International Land Conservation Network News (2024b) Australia Grapples with New Draft National OECM Framework That Falls Short of Conservationists’ Expectations. (accessed on 2025-03-02)https://landconservationnetwork.org/australia-grapples-with-new-draft-national-oecm-framework-that-falls-short-of-conservationists-expectations/. |
| [20] | IUCN (2019) Recognising and Reporting Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures. (accessed on 2024-11-20) https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/PATRS-003-En.pdf. |
| [21] | IUCN (2020a) Algeria and Morocco Acknowledge Biodiversity Value of Cultural Parks, Biosphere and Hunting Reserves Through OECMs. (accessed on 2024-11-20)https://www.iucn.org/news/mediterranean/202009/algeria-and-morocco-acknowledge-biodiversity-value-cultural-parks-biosphere-and-hunting-reserves-through-oecms. |
| [22] | IUCN (2020b) Tapping OECMs Potential to Advance Aichi Target 11 in Southern and Eastern Mediterranean Countries. (accessed on 2024-10-20) https://iucn.org/news/mediterranean/202006/tapping-oecms-potential-advance-aichi-target-11-southern-and-eastern-mediterranean-countries. |
| [23] | IUCN (2023a) Site-Level Tool for Identifying Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures (OECMs). (accessed on 2024-10-28) https://portals.iucn.org/library/node/51296. |
| [24] | IUCN (2023b) Nature, Culture and Community Commitment to Effective Area-based Conservation—Recognising What is an ‘OECM’ in Korea. (accessed on 2025-02-17) https://iucn.org/story/202302/nature-culture-and-community-commitment-effective-area-based-conservation-recognising. |
| [25] | IUCN (2024a) Global OECMs Practice: Insights from China and International Case Studies Contribute to Common Pathways for Definition. (accessed on 2024-11-28) https://iucn.org/blog/202411/global-oecms-practice-insights-china-and-international-case-studies-contribute-common-1. |
| [26] | IUCN (2024b) A Stocktaking Report on Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures in China. (accessed on 2024-11-18) https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2024-027-En.pdf. |
| [27] | IUCN (2024c) IUCN and Korea Work towards Effective Protected and Conserved Areas. (accessed on 2025-02-17) https://iucn.org/news/202403/iucn-and-korea-work-towards-effective-protected-and-conserved-areas. |
| [28] | Jin T, Bu JY, Ma JZ(2022) Other effective area-based conservation measures of global experiences and implications for post-2020 biodiversity conservation in China. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 51(1), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 靳彤, 卜君玉, 马建忠 (2022) 其他有效的区域保护措施的国际经验及对中国2020年后生物多样性保护的启示. 西部林业科学, 51(1), 1-8. ] | |
| [29] | Jonas HD, Barbuto V, Jonas, Kothari A, Nelson F(2014) New steps of change: Looking beyond protected areas to consider other effective area-based conservation measures. PARKS, 20, 111-128. |
| [30] | Jonas HD, Bingham HC, Bennett NJ, Woodley S, Zlatanova R, Howland E, Belle E, Upton J, Gottlieb B, Kamath V, Lessmann J, Delli G, Dubois G, Ahmadia G, Claudet J, Cook C, Deza J, Grorud-Colvert K, Gurney G, Lemieux CJ, Ruiz L(2024) Global status and emerging contribution of other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) towards the ‘30×30’ biodiversity Target 3. Frontiers in Conservation Science, 5, 1447434. |
| [31] | Jonas HD, MacKinnon K, Dudley N, Hockings M, Jessen S, Dan L, MacKinnon D, Matallana-Tobón CL, Sandwith T, Waithaka J, Woodley S(2018) Other effective area-based conservation measures: From Aichi Target 11 to the Post-2020 Biodiversity Framework. PARKS, 24, 9-16. |
| [32] | Laffoley D, Dudley N, Jonas H, MacKinnon D, MacKinnon K, Hockings M, Woodley S(2017) An introduction to ‘other effective area-based conservation measures’ under Aichi Target 11 of the Convention on Biological Diversity: Origin, interpretation and emerging ocean issues. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 27, 130-137. |
| [33] | Lü Z(2022) Meeting China’s “3030 goal” on biodiversity conservation. Frontiers, (4), 24-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吕植 (2022) 中国生物多样性保护与“3030目标”. 人民论坛 · 学术前沿, (4), 24-34.] | |
| [34] | Maini B, Blythe JL, Darling ES, Gurney GG(2023) Charting the value and limits of other effective conservation measures (OECMs) for marine conservation: A Delphi study. Marine Policy, 147, 105350. |
| [35] | Marnewick D, Stevens CMD, Jonas H, Antrobus-Wuth R, Wilson N, Theron N(2021) Assessing the extent and contribution of OECMs in South Africa. PARKS, 27, 57-70. |
| [36] | Maxwell SL, Cazalis V, Dudley N, Hoffmann M, Rodrigues ASL, Stolton S, Visconti P, Woodley S, Kingston N, Lewis E, Maron M, Strassburg BBN, Wenger A, Jonas HD, Venter O, Watson JEM(2020) Area-based conservation in the twenty-first century. Nature, 586, 217-227. |
| [37] | Ministry of the Environment of the Government of Japan (2024a) Japan’s 30by30 roadmap. (accessed on 2025-03-02) https://policies.env.go.jp/nature/biodiversity/30by30alliance/documents/3030emap.pdf. |
| [38] | Ministry of the Environment of the Government of Japan (2024b) Registration of Japan’s first OECMs on the World Database on OECMs. (accessed on 2025-03-02) https://www.env.go.jp/en/press/press_02886.html. |
| [39] | Mitchell BA, Fitzsimons JA, Stevens CMD, Wright DR(2018) PPA or OECM? Differentiating between privately protected areas and other effective area-based conservation measures on private land. PARKS, 24, 49-60. |
| [40] | Palomo I, Montes C, Martín-López B, González JA, García-Llorente M, Alcorlo P, Mora MRG(2014) Incorporating the social-ecological approach in protected areas in the Anthropocene. BioScience, 64, 181-191. |
| [41] | Raquino MER, Pajaro M, Enaje JE, Tercero RB, Torio TG, Watts P(2023) Capacitating Philippine indigenous and local institutions and actualising local synergies on restorative ridge-to-reef biodiversity conservation for food security and livelihoods. Maiko Nishi, p. 247. |
| [42] | Rayner L, Lindenmayer DB, Wood JT, Gibbons P, Manning AD(2014) Are protected areas maintaining bird diversity? Ecography, 37, 43-53. |
| [43] | Renn C, Rees S, Rees A, Davies BF, Cartwright AY, Fanshawe S, Attrill MJ, Holmes LA, Sheehan EV(2024) Lessons from Lyme Bay (UK) to inform policy, management, and monitoring of marine protected areas. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 81, 276-292. |
| [44] | Rodríguez-Rodríguez D, Sánchez-Espinosa A, Abdul Malak D,(2021) Potential contribution of OECMs to international area-based conservation targets in a biodiversity rich country, Spain. Journal for Nature Conservation, 62, 126019. |
| [45] | Stolpe G, Howland E, Upton J(2024) OECMS in Europe: The way forward for Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures. (accessed on 2024-11-15) https://iucn.org/sites/default/files/2024-05/oecms-in-europe-final.pdf. |
| [46] | Troupin D, Carmel Y(2014) Canagro-ecosystems efficiently complement protected area networks? Biological Conservation, 169, 158-166. |
| [47] | UNEP-WCMC (2023) December 2023 Update of the WDPA and WD-OECM. (accessed on 2024-10-28) https://www.protectedplanet.net/en/resources/december-2023-update-of-the-wdpa-and-wd-oecm. |
| [48] | UNEP-WCMC (2025) February 2025 Update of the WDPA, WD-OECM and GD-PAME. (accessed on 2025-02-16) https://www.protectedplanet.net/en/resources/february-2025-update-of-the-wdpa-and-wd-oecm. |
| [49] | UNEP-WCMC, IUCN (2024) Protected Planet Report 2024. (accessed on 2024-11-15) https://pp-digital-report-files.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/Protected+Planet+Report+2024.pdf. |
| [50] | UNEP-WCMC, IUCN (2025) Discover the World’s Protected and Conserved Areas-Global Statistics. (accessed on 2025-02-15) https://www.protectedplanet.net/en. |
| [51] | Wang J, Seyler BC, Phuntsok TS, Lu YL, Tsomo L(2022) Traditional beliefs, culture, and local biodiversity protection: An ethnographic study in the Shaluli Mountains Region, Sichuan Province, China. Journal for Nature Conservation, 68, 126213. |
| [52] | Wang W, Gao JX(2024) Progress and prospects of the construction of protected area system with national parks as the main body in China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 37, 2100-2109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王伟, 高吉喜 (2024) 我国以国家公园为主体的自然保护地体系建设进展与展望. 环境科学研究, 37, 2100-2109.] | |
| [53] | Wang W, Li JS(2021) In-situ conservation of biodiversity in China: Advances and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 29, 133-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王伟, 李俊生 (2021) 中国生物多样性就地保护成效与展望. 生物多样性, 29, 133-149.] | |
| [54] | Woodley S, Locke H, Laffoley D, MacKinnon K, Sandwith T, Smart J(2019) A review of evidence for area-based conservation targets for the post-2020 global biodiversity framework. PARKS, 25, 31-46. |
| [55] | Woodley S, MacKinnon K, McCanny S, Pither R, Prior K, Salafsky N, Lindenmayer D(2015) Managing protected areas for biological diversity and ecosystem functions. In: Protected Area Governance and Management (eds WorboysGL, LockwoodM, KothariA, FearyS, PulsfordI),pp.651-684. ANU Press, Canberra. |
| [56] | Yang R, Hou SY, Zhang Y, Zhao ZC(2024) The necessity and feasibility of establishing conservation compatible land in China. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23454. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 杨锐, 侯姝彧, 张引, 赵智聪 (2024) 论建立中国自然保护兼用地的必要性和可行性. 生物多样性, 32, 23454.]
DOI |
|
| [57] |
Zhang K, Zou CX, Zhang Y, Liu XM, Gao JX(2022) Understanding the connotation of the ecological conservation redline from its delineation process and attribute characteristics. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21464. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 张琨, 邹长新, 张怡, 刘晓曼, 高吉喜 (2022) 从划定历程与属性特征正确认识生态保护红线内涵. 生物多样性, 30, 21464.]
DOI |
|
| [58] |
Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhu CQ(2015) IUCN green list of protected areas: Introduction, progress, opportunities and challenges for protected areas in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 437-439. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 张琰, 刘静, 朱春全 (2015) 自然保护地绿色名录: 内容、进展及为中国自然保护地带来的机遇和挑战. 生物多样性, 23, 437-439.]
DOI |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()