



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 24150. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024150 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024150
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xueyuan Li1,2, Zhixian Sun1,3( ), Fengzhen Wang4, Rui Xi1,3, Yutian Fang1,2, Junyuan Hao1,3, Dong Sheng1, Shuya Sun1, Yahui Zhao1,2,*(
), Fengzhen Wang4, Rui Xi1,3, Yutian Fang1,2, Junyuan Hao1,3, Dong Sheng1, Shuya Sun1, Yahui Zhao1,2,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-04-21
Accepted:2024-09-06
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-12
Contact:
*E-mail: zhaoyh@ioz.ac.cn
Supported by:Xueyuan Li, Zhixian Sun, Fengzhen Wang, Rui Xi, Yutian Fang, Junyuan Hao, Dong Sheng, Shuya Sun, Yahui Zhao. Impacts of urban development on functional diversity in fish: A case study of Beijing, a megacity[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24150.
| 功能性状 Functional traits | 测量方法 Measuring methods |
|---|---|
| 标准体长 Standard length | 吻端至尾柄最后一枚尾椎骨的距离 The distance from the snout to the last vertebra of caudal peduncle |
| 体高 Body depth | 背鳍起点至体下端的垂直距离 The vertical distance from the origin of dorsal fin to the lower end of body |
| 体宽 Body width | 背鳍起点身体两侧的最大宽度 The maximum width on either side of the body at the origin of the dorsal fin |
| 头长 Head length | 吻端至鳃盖骨后缘的距离 The distance from the snout to the posterior margin of operculum |
| 下颌长 Lower jaw length | 口角处到下颌顶点的距离 The distance from the corner of mouth to the tip of lower jaw |
| 口裂宽 Mouth width | 左右口角间的距离 The distance between corners of mouth |
| 口高 Mouth height | 口裂上下中点垂直距离 The vertical distance from the midpoint of mouth cleft |
| 眼径 Eye diameter | 眼睛的横向直径 Horizontal diameter of eye |
| 眼间距 Interorbital width | 眼眶间的最短距离 The minimum distance between the edges of the orbits |
| 胸鳍长 Pectoral-fin length | 胸鳍基至胸鳍末端距离 The distance from the base to tip of pectoral fin |
| 臀鳍长 Anal-fin length | 臀鳍起点至臀鳍末端距离 The distance from the origin to tip of anal fin |
| 尾柄长 Caudal peduncle length | 臀鳍基末端至最后一枚尾椎骨的距离 The distance from the end of anal-fin base to the last vertebra |
| 尾柄高 Caudal peduncle depth | 尾柄最窄处的垂直高度 The vertical height at the narrowest point of caudal peduncle |
| 尾柄宽 Caudal peduncle width | 尾柄在直线面上的宽度 The width of caudal peduncle in linear profile |
Table 1 Functional traits and measuring methods of fish
| 功能性状 Functional traits | 测量方法 Measuring methods |
|---|---|
| 标准体长 Standard length | 吻端至尾柄最后一枚尾椎骨的距离 The distance from the snout to the last vertebra of caudal peduncle |
| 体高 Body depth | 背鳍起点至体下端的垂直距离 The vertical distance from the origin of dorsal fin to the lower end of body |
| 体宽 Body width | 背鳍起点身体两侧的最大宽度 The maximum width on either side of the body at the origin of the dorsal fin |
| 头长 Head length | 吻端至鳃盖骨后缘的距离 The distance from the snout to the posterior margin of operculum |
| 下颌长 Lower jaw length | 口角处到下颌顶点的距离 The distance from the corner of mouth to the tip of lower jaw |
| 口裂宽 Mouth width | 左右口角间的距离 The distance between corners of mouth |
| 口高 Mouth height | 口裂上下中点垂直距离 The vertical distance from the midpoint of mouth cleft |
| 眼径 Eye diameter | 眼睛的横向直径 Horizontal diameter of eye |
| 眼间距 Interorbital width | 眼眶间的最短距离 The minimum distance between the edges of the orbits |
| 胸鳍长 Pectoral-fin length | 胸鳍基至胸鳍末端距离 The distance from the base to tip of pectoral fin |
| 臀鳍长 Anal-fin length | 臀鳍起点至臀鳍末端距离 The distance from the origin to tip of anal fin |
| 尾柄长 Caudal peduncle length | 臀鳍基末端至最后一枚尾椎骨的距离 The distance from the end of anal-fin base to the last vertebra |
| 尾柄高 Caudal peduncle depth | 尾柄最窄处的垂直高度 The vertical height at the narrowest point of caudal peduncle |
| 尾柄宽 Caudal peduncle width | 尾柄在直线面上的宽度 The width of caudal peduncle in linear profile |
| 功能类型 Function type | 功能性状 Functional traits | 计算方法 Method | 生态学意义 Ecological meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 栖息 Habitat | 体型指标 Body shape | 体高/标准体长 Body depth/Standard length | 在水体中的栖息位置及游泳能力 Position and swimming ability in water |
| 运动 Sport | 胸鳍相对长度 Relative pectoral-fin length | 胸鳍长/标准体长 Pectoral-fin length/Standard length | 比值越大, 则转向越强, 灵活性越高 The higher the ratio, the stronger the turning ability and greater flexibility |
| 臀鳍相对长度 Relative anal-fin length | 臀鳍长/标准体长 Anal-fin length/Standard length | 比值越大, 则平衡力越强 The higher the ratio, the stronger the balance | |
| 尾柄相对面积 Relative area of caudal peduncle | (尾柄长 × 尾柄高)/(标准体长 × 体高) (Caudal peduncle length × Caudal peduncle depth)/(Standard length × Body depth) | 比值越高, 则游泳能力越强 The higher the ratio, the stronger the swimming ability | |
| 尾柄相对高度 Relative depth of caudal peduncle | 尾柄高/体高 Caudal peduncle depth/Body depth | 比值越高, 尾鳍摆动能力越强 The higher the ratio, the stronger the caudal fin oscillation ability | |
| 尾柄相对宽度 Relative width of caudal peduncle | 尾柄宽/体宽 Caudal peduncle width/Body width | 较高的值表示具有更好持续游泳能力 Higher values indicate better sustained swimming ability | |
| 摄食 Feeding | 口裂相对大小1 Relative mouth opening 1 | (口裂宽 × 口高)/(体宽 × 体高) (Mouth width × Mouth height)/(Body width × Body depth) | 最大捕食能力, 比值越高, 能力越强 Maximum feeding capacity, higher ratio indicates stronger ability |
| 口裂相对大小2 Relative mouth opening 2 | 口裂宽 × 口高/下颌长 Mouth width × Mouth height/Lower jaw length | 比值越高, 表示其摄食体型更大食物的能力越强 Higher ratio indicates ability to consume larger food items | |
| 口裂形状 Mouth opening shape | 口高/口裂宽 Mouth height/Mouth width | 食物形状 Shape of food | |
| 眼睛相对长度 Relative eye length | 眼径/头长 Eye diameter/Head length | 对食物的可视范围 Visual range of food | |
| 相对眼径 Relative eye diameter | 眼间距/眼径 Interorbital width/Eye diameter | 比值越高, 对食物的可视范围越大 The higher the ratio, the greater the visual range of food | |
| 口位 Mouth position | 端位、上位、下位 Termina, superior, inferior | 不同位置表示获得食物组成不一样 Different location means different food composition | |
| 繁殖 Breed | 鱼卵生态类型 Ecological types of fish eggs | 沉黏性、黏性、浮性、漂流性 Pelagic, adhesive, buoyant, drift | 不同产卵类型表示生长发育和繁衍方式不一样 Different spawning types indicate varied methods of growth, development, and reproduction |
Table 2 Calculation methods and ecological meaning of fish functional traits
| 功能类型 Function type | 功能性状 Functional traits | 计算方法 Method | 生态学意义 Ecological meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 栖息 Habitat | 体型指标 Body shape | 体高/标准体长 Body depth/Standard length | 在水体中的栖息位置及游泳能力 Position and swimming ability in water |
| 运动 Sport | 胸鳍相对长度 Relative pectoral-fin length | 胸鳍长/标准体长 Pectoral-fin length/Standard length | 比值越大, 则转向越强, 灵活性越高 The higher the ratio, the stronger the turning ability and greater flexibility |
| 臀鳍相对长度 Relative anal-fin length | 臀鳍长/标准体长 Anal-fin length/Standard length | 比值越大, 则平衡力越强 The higher the ratio, the stronger the balance | |
| 尾柄相对面积 Relative area of caudal peduncle | (尾柄长 × 尾柄高)/(标准体长 × 体高) (Caudal peduncle length × Caudal peduncle depth)/(Standard length × Body depth) | 比值越高, 则游泳能力越强 The higher the ratio, the stronger the swimming ability | |
| 尾柄相对高度 Relative depth of caudal peduncle | 尾柄高/体高 Caudal peduncle depth/Body depth | 比值越高, 尾鳍摆动能力越强 The higher the ratio, the stronger the caudal fin oscillation ability | |
| 尾柄相对宽度 Relative width of caudal peduncle | 尾柄宽/体宽 Caudal peduncle width/Body width | 较高的值表示具有更好持续游泳能力 Higher values indicate better sustained swimming ability | |
| 摄食 Feeding | 口裂相对大小1 Relative mouth opening 1 | (口裂宽 × 口高)/(体宽 × 体高) (Mouth width × Mouth height)/(Body width × Body depth) | 最大捕食能力, 比值越高, 能力越强 Maximum feeding capacity, higher ratio indicates stronger ability |
| 口裂相对大小2 Relative mouth opening 2 | 口裂宽 × 口高/下颌长 Mouth width × Mouth height/Lower jaw length | 比值越高, 表示其摄食体型更大食物的能力越强 Higher ratio indicates ability to consume larger food items | |
| 口裂形状 Mouth opening shape | 口高/口裂宽 Mouth height/Mouth width | 食物形状 Shape of food | |
| 眼睛相对长度 Relative eye length | 眼径/头长 Eye diameter/Head length | 对食物的可视范围 Visual range of food | |
| 相对眼径 Relative eye diameter | 眼间距/眼径 Interorbital width/Eye diameter | 比值越高, 对食物的可视范围越大 The higher the ratio, the greater the visual range of food | |
| 口位 Mouth position | 端位、上位、下位 Termina, superior, inferior | 不同位置表示获得食物组成不一样 Different location means different food composition | |
| 繁殖 Breed | 鱼卵生态类型 Ecological types of fish eggs | 沉黏性、黏性、浮性、漂流性 Pelagic, adhesive, buoyant, drift | 不同产卵类型表示生长发育和繁衍方式不一样 Different spawning types indicate varied methods of growth, development, and reproduction |
| 亚科 Subfamily | 建成区物种数 Species numbers of built-up area | 生态涵养区物种数 Species numbers of ecological conservation area |
|---|---|---|
| 鲑亚科 Salmoninae | 0 | 1 |
| 马口鱼亚科 Opsariichthyinae | 2 | 2 |
| 雅罗鱼亚科 Leuciscinae | 1 | 3 |
| 鲌亚科 Culterinae | 4 | 5 |
| 鲴亚科 Xenocyprinae | 0 | 2 |
| 鱊亚科 Acheilognathinae | 7 | 6 |
| 鮈亚科 Gobioninae | 8 | 12 |
| 鲤亚科 Cyprininae | 2 | 2 |
| 条鳅亚科 Nemacheilinae | 0 | 3 |
| 花鳅亚科 Cobitinae | 1 | 3 |
| 青鳉亚科 Oryziinae | 1 | 1 |
| 刺鳅亚科 Mastacembelinae | 1 | 1 |
| 斗鱼亚科 Macropodinae | 1 | 1 |
Table 3 Comparison of species numbers of native fish subfamilies between built-up area and ecological conservation area in Beijing
| 亚科 Subfamily | 建成区物种数 Species numbers of built-up area | 生态涵养区物种数 Species numbers of ecological conservation area |
|---|---|---|
| 鲑亚科 Salmoninae | 0 | 1 |
| 马口鱼亚科 Opsariichthyinae | 2 | 2 |
| 雅罗鱼亚科 Leuciscinae | 1 | 3 |
| 鲌亚科 Culterinae | 4 | 5 |
| 鲴亚科 Xenocyprinae | 0 | 2 |
| 鱊亚科 Acheilognathinae | 7 | 6 |
| 鮈亚科 Gobioninae | 8 | 12 |
| 鲤亚科 Cyprininae | 2 | 2 |
| 条鳅亚科 Nemacheilinae | 0 | 3 |
| 花鳅亚科 Cobitinae | 1 | 3 |
| 青鳉亚科 Oryziinae | 1 | 1 |
| 刺鳅亚科 Mastacembelinae | 1 | 1 |
| 斗鱼亚科 Macropodinae | 1 | 1 |
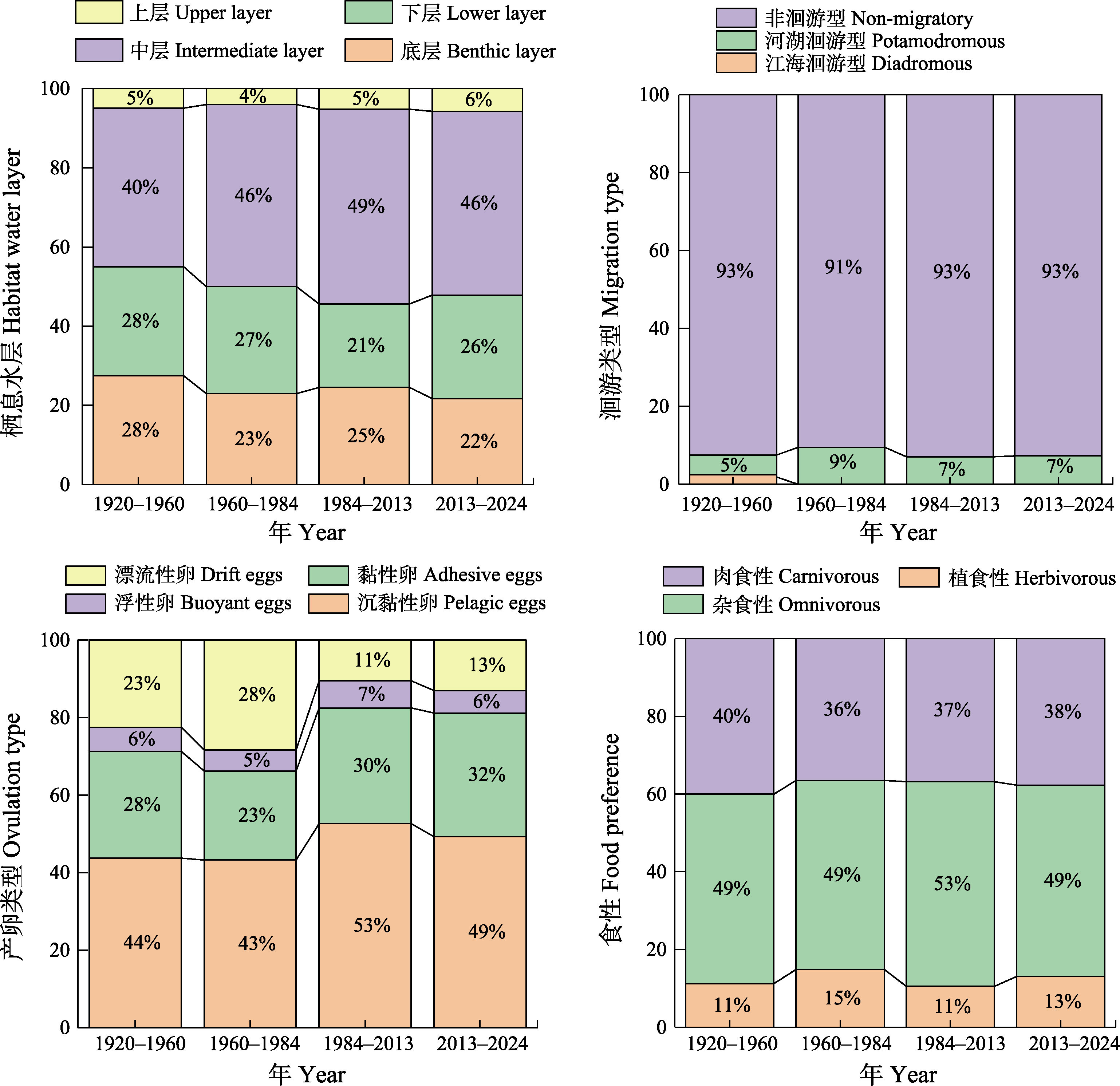
Fig. 7 Ecological distribution of fishes in Beijing in four periods according to habitat water layer, migration type, ovulation type and food preference
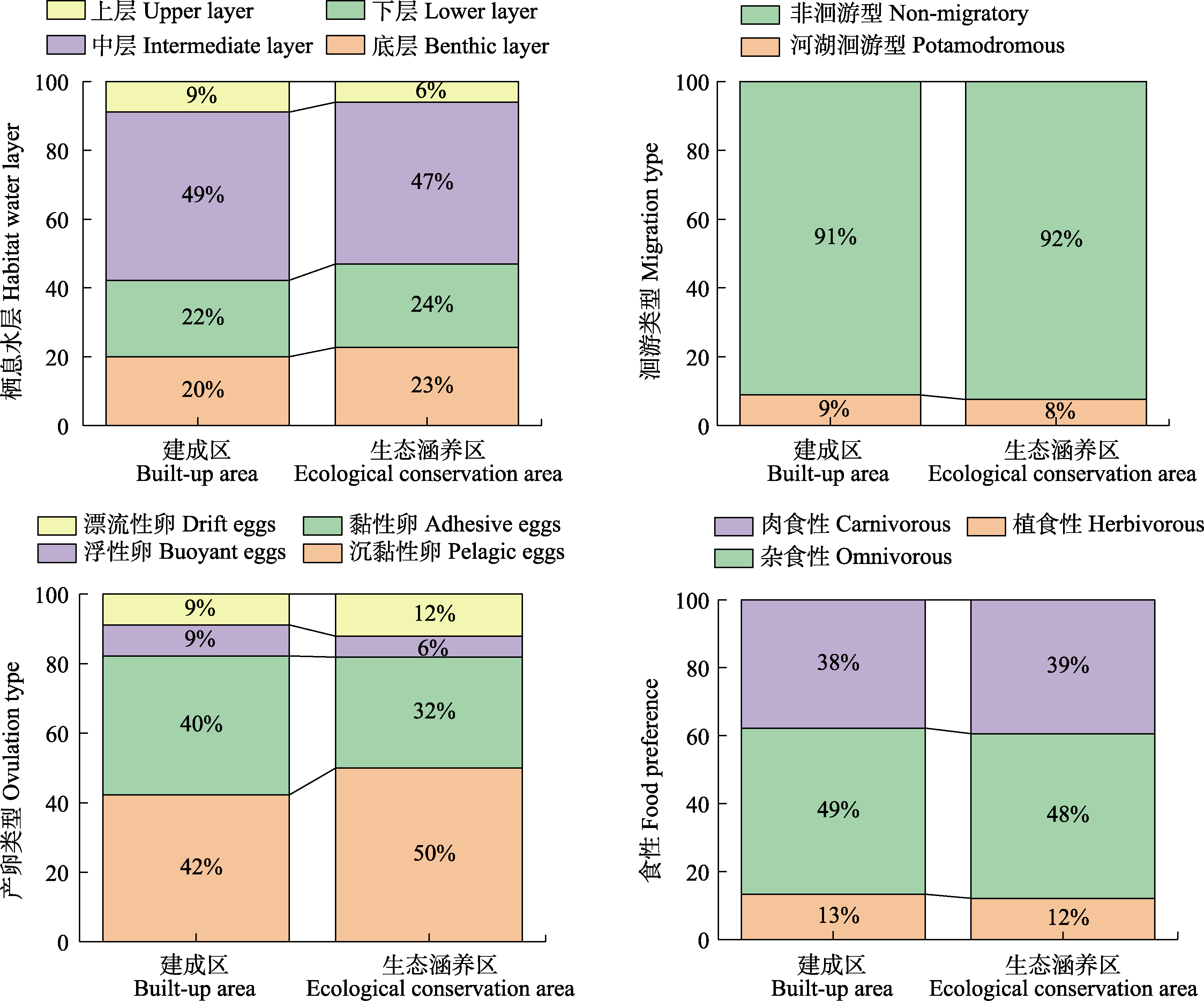
Fig. 8 Ecological distribution of fish in built-up areas and ecological conservation areas of Beijing by habitat water layer, migration type, ovulation type and food preference
| [1] | Boët P, Belliard J, Berrebi-dit-Thomas R, Tales E (1999) Man and River Systems. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [2] |
Chen QJ, Sun ZX, Li XJ, Zhang R, Xi R, Tian C, Wang X, Xing YC, Zhao YH (2022) Fish diversity of Wuyishan National Park and its adjacent areas. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22260. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈秋菊, 孙智闲, 李雪健, 张睿, 席蕊, 田晨, 王鑫, 邢迎春, 赵亚辉 (2022) 武夷山国家公园及其周边鱼类多样性. 生物多样性, 30, 22260.]
DOI |
|
| [3] | Chen YY (1998) Fauna Sinica∙Osteichthyes∙Cypriniformes.II. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈宜瑜 (1998) 中国动物志∙硬骨鱼纲∙鲤形目(中卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [4] | Chu XL (1999) Fauna Sinica∙Osteichthyes∙Siluriformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [褚新洛 (1999) 中国动物志∙硬骨鱼纲∙鲇形目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Chua KWJ, Tan HH, Yeo DCJ (2019) Loss of endemic fish species drives impacts on functional richness, redundancy and vulnerability in freshwater ecoregions of Sundaland. Biological Conservation, 234, 72-81. |
| [6] | Gou SJ, Qiu WS, Li S, Yang MY, Li XL, Wang H, Li GH (2023) Effect of large-scale ecological water replenishment on infiltration capacity of Beijing section of long-term cut-off river Yongding River. Water Resources and Power, 41(8), 35-38, 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苟少杰, 仇文顺, 李述, 杨默远, 李晓琳, 王赫, 黎光和 (2023) 大规模生态补水对长期断流河道永定河北京段入渗能力的影响. 水电能源科学, 41(8), 35-38, 26.] | |
| [7] | Hao L, Sun G (2021) Impacts of urbanization on watershed ecohydrological processes: Progresses and perspectives. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 13-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郝璐, 孙阁 (2021) 城市化对流域生态水文过程的影响研究综述. 生态学报, 41, 13-26.] | |
| [8] |
Haubrock PJ, Pilotto F, Innocenti G, Cianfanelli S, Haase P (2021) Two centuries for an almost complete community turnover from native to non-native species in a riverine ecosystem. Global Change Biology, 27, 606-623.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R: A language for data analysis and graphics. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 5, 299314. |
| [10] | Jia WQ, Ren GY, Yu XJ, Zhang YQ, Zhang PF (2021) Difference of urban heat island effect among representative cities of different climatic zones over eastern China monsoon region. Climatic and Environmental Research, 26, 569-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贾文茜, 任国玉, 于秀晶, 张永强, 张盼峰 (2021) 中国东部季风区不同气候带城市热岛效应的差异. 气候与环境研究, 26, 569-582.] | |
| [11] |
Laliberté E, Legendre P (2010) A distance-based framework for measuring functional diversity from multiple traits. Ecology, 91, 299-305.
PMID |
| [12] | Li XJ, Sun ZX, Tang WQ, Zhao YH (2022) Revalidation and redescription of Sarcocheilichthys sciistius (Abbott, 1901) (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) from the northern China. Zootaxa, 5141, 341-357. |
| [13] | Liang ZS, Yi BL, Yu ZT (2019) A Photographic Guide to Early Development of Fish in Rivers. Guangdong Science & Technology Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [梁秩燊, 易伯鲁, 余志堂 (2019) 江河鱼类早期发育图志. 广东科技出版社, 广州.] | |
| [14] | Liu M, Lin AW, Gu JN, Cao XK, Jin H (2016) Evaluation on water quality of north water delivery line of water diversion project from Yellow River to Beijing. Journal of Water Resources Research, 5, 510-515. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘苗, 林爱武, 顾军农, 曹新恺, 金红 (2016) “引黄入京”工程北输水线水源水质评价. 水资源研究, 5, 510-515.] | |
| [15] | Liu X, Wang HR, Yu S, Ma DC, Liang Y, Lai WL, Gao YY (2015) Study on water resources risk in Beijing after “South-north Water Transfer” Project. Journal of China Hydrology, 35(4), 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晓, 王红瑞, 俞淞, 马东春, 梁媛, 来文立, 高媛媛 (2015) 南水北调进京后的北京市水资源短缺风险研究. 水文, 35(4), 55-61.] | |
| [16] | Lü YL, Wang CC, Cao XH (2018) Ecological risk of urbanization and risk management. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 359-370. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吕永龙, 王尘辰, 曹祥会 (2018) 城市化的生态风险及其管理. 生态学报, 38, 359-370.] | |
| [17] | Mao ZG, Gu XH, Cao Y, Luo JH, Zeng QF, Chen HH, Jeppesen E (2021) How does fish functional diversity respond to environmental changes in two large shallow lakes? Science of the Total Environment, 753, 142158. |
| [18] | Massicotte P, Frenette JJ, Proulx R, Pinel-Alloul B, Bertolo A (2014) Riverscape heterogeneity explains spatial variation in zooplankton functional evenness and biomass in a large river ecosystem. Landscape Ecology, 29, 67-79. |
| [19] | Meng QY, Ouyang ZY, Ma DC (2012) Water Ecosystem Service Assessment and Valuation in Beijing. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [孟庆义, 欧阳志云, 马东春 (2012) 北京水生态服务功能与价值. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Pease AA, González-Díaz AA, Rodiles-Hernández R, Winemiller KO (2012) Functional diversity and trait-environment relationships of stream fish assemblages in a large tropical catchment. Freshwater Biology, 57, 1060-1075. |
| [21] | Peng SL, Zhou K, Ye YH, Su J (2005) Research progress in urban heat island. Ecology and Environment, 14, 574-579. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [彭少麟, 周凯, 叶有华, 粟娟 (2005) 城市热岛效应研究进展. 生态环境, 14, 574-579.] | |
| [22] | Piao Y, Ma KM (2006) Economic driving force of urban built-up area expansion in Beijing. Natural Resource Economics of China, 19(7), 34-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朴妍, 马克明 (2006) 北京城市建成区扩张的经济驱动: 1978-2002. 中国国土资源经济, 19(7), 34-37.] | |
| [23] |
Prada-Salcedo LD, Wambsganss J, Bauhus J, Buscot F, Goldmann K (2021) Low root functional dispersion enhances functionality of plant growth by influencing bacterial activities in European forest soils. Environmental Microbiology, 23, 1889-1906.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Qiao JL, Liu Y, Fu HX, Chu L, Yan YZ (2022) Urbanization affects the taxonomic and functional alpha and beta diversity of fish assemblages in streams of subtropical China. Ecological Indicators, 144, 109441. |
| [25] | Qu X, Liu H, Yang M, Xin W, Wang WM, Chen YS (2022) Characteristics of fish communities and driving factors under urbanization in typical river basins in Shenzhen City, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 10029-10040. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [屈霄, 刘晗, 阳敏, 辛未, 王伟民, 陈宇顺 (2022) 城镇化背景下深圳典型流域鱼类群落特征及驱动因子. 生态学报, 42, 10029-10040.] | |
| [26] | Shuai FM, Li XH, Chen FC, Li YF, Yang JP, Li J, Wu Z (2017) Functional diversity of freshwater fishes and methods of measurement. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 5228-5237. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [帅方敏, 李新辉, 陈方灿, 李跃飞, 杨计平, 李捷, 武智 (2017) 淡水鱼类功能多样性及其研究方法. 生态学报, 37, 5228-5237.] | |
| [27] | Sun R, Pan XY, Wang JW, Ren Y, Du P, Ma Y, Xing Y (2021) An analysis and evaluation of ecological water replenishment benefit of Yongding River (Beijing Section). China Rural Water and Hydropower, (6), 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙冉, 潘兴瑶, 王俊文, 任宇, 杜鹏, 马尧, 邢渊 (2021) 永定河(北京段)河道生态补水效益分析与方案评估. 中国农村水利水电, (6), 19-24.] | |
| [28] | Sun ZX, Kawase S, Zhang R, Zhao YH (2021) Taxonomic revision and redescription of Microphysogobio hsinglungshanensis, the type species of Microphysogobio Mori, 1934 (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Journal of Fish Biology, 99, 373-383. |
| [29] | UN (2018) The world’s cities in 2018. The World’s Cities in 2018- Data Booklet (ST/ESA/SER.A/417). https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/content/worlds-cities-2018-data-booklet. (accessed on 2024-04-02) |
| [30] |
Villéger S, Mason NWH, Mouillot D (2008) New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology, 89, 2290-2301.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Villéger S, Miranda JR, Hernández DF, Mouillot D (2010) Contrasting changes in taxonomic vs. functional diversity of tropical fish communities after habitat degradation. Ecological Applications, 20, 1512-1522.
PMID |
| [32] | Wang HY (1984) Beijing Fish Records. Beijing Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [王鸿媛 (1984) 北京鱼类志. 北京出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Wu HL, Zhong JS (2008) Fauna Sinica∙Osteichthyes∙Perciformes (V)∙Gobioidei. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [伍汉霖, 钟俊生 (2008) 中国动物志∙硬骨鱼纲∙鲈形目(五)∙虾虎鱼亚目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | Xia ZJ, Liu F, Yu FD, Tang R, Wang JW (2022) Species, functional and taxonomic diversity of fish in the Chishui River basin. Journal of Hydroecology, 43(5), 89-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏治俊, 刘飞, 余梵冬, 唐瑞, 王剑伟 (2022) 赤水河流域鱼类物种、功能和分类多样性研究. 水生态学杂志, 43(5), 89-98.] | |
| [35] | Yang B, Qu X, Liu H, Yang M, Xin W, Wang W, Chen Y (2024) Urbanization reduces fish taxonomic and functional diversity while increases phylogenetic diversity in subtropical rivers. Science of the Total Environment, 908, 168178. |
| [36] | Yang H (2013) Analysis on climate change feature of Beijing during 1951 to 2006. Beijing Water, (3), 36-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨浩 (2013) 1951-2006年北京气候变化特征分析. 北京水务, (3), 36-40.] | |
| [37] | Yang S (2018) Analysis on evolution of water consumption structure and driving forces in Beijing. Pearl River, 39(5), 50-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨硕 (2018) 北京市用水结构演变分析及驱动因子研究. 人民珠江, 39(5), 50-53.] | |
| [38] | Yu RH, Wu QQ, Li F, Zhan AB, Zhou JX, Li S (2024) Risk screening of invasive aquatic species and a survey of fish diversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding analysis in Shanghai. Diversity, 16, 29. |
| [39] | Yue PQ (2000) Fauna Sinica∙Osteichthyes∙Cypriniformes (III). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [乐佩琦 (2000) 中国动物志∙硬骨鱼纲∙鲤形目(下卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] | Zhang CG, Shao GZ, Wu HL, Zhao YH, Xing YC, Niu CY (2020) Species Catalogue of China (Vol. 2): Animals∙Vertebrates (V)∙Fish (I). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春光, 邵广昭, 伍汉霖, 赵亚辉, 邢迎春, 牛诚祎 (2020) 中国生物物种名录(第二卷): 动物∙脊椎动物(V)∙鱼类(上卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [41] | Zhang CG, Zhao YH (2013) Fishes in Beijing and Adjacent Area. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春光, 赵亚辉 (2013) 北京及其邻近地区的鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] | Zhang CG, Zhao YH (2016) Species Diversity and Distribution of Inland Fishes in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春光, 赵亚辉 (2016) 中国内陆鱼类物种与分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] | Zhang E, Cao WX (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity∙Vertebrates (V)∙Freshwater Fishes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [张鹗, 曹文宣 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录∙脊椎动物(第五卷)∙淡水鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [44] | Zhang S, Zheng YT, Zhan AB, Dong CX, Zhao JD, Yao M (2022) Environmental DNA captures native and non-native fish community variations across the lentic and lotic systems of a megacity. Science Advances, 8, eabk0097. |
| [45] | Zhu ZF, Zhang XH, Liu RJ (2012) Expectation on “super city”—Tianjin urban traffic mode. Urban Roads, Bridges & Flood Control, (8), 1-9, 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱兆芳, 张欣红, 刘锐晶 (2012) “超级城市”——天津城市交通方式的展望. 城市道桥与防洪, (8), 1-9, 15.] |
| [1] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [2] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [3] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [4] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [5] | Ma Shangfei, Gong Xin, Shangguan Huayuan, Yao Haifeng, Wang Bin, Li Zhipeng, Sun Xin. Effects of urbanization and different land use types on soil eukaryotic biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24540-. |
| [6] | Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| [7] | Zhou Zhihua, Jin Xiaohua, Luo Ying, Li Diqiang, Yue Jianbing, Liu Fang, He Tuo, Li Xi, Dong Hui, Luo Peng. Analyses and suggestions on mechanisms of forestry and grassland administrations in China to achieve targets of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [8] | Liu Li, Zang Mingyue, Ma Yue, Wan Yaqiong, Hu Feilong, Lu Xiaoqiang, Liu Yan. Measures, progress and prospects of central-local cooperation in the implementation of the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24532-. |
| [9] | Yang Song, Jun Liu, Shaolin He, Wei Xu, Chen Cheng, Bo Liu, Jiqing Yu. Mainstreaming path of biodiversity conservation for Chinese energy enterprises [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24345-. |
| [10] | Zhiqing Hu, Lu Dong. Effects of urbanization on interspecific interactions involving birds [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24048-. |
| [11] | Fei Duan, Mingzhang Liu, Hongliang Bu, Le Yu, Sheng Li. Effects of urbanization on bird community composition and functional traits: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23473-. |
| [12] | Jiayu Lu, Xiaoyi Shi, Li’an Duo, Tianming Wang, Zhilin Li. Circadian rhythms of urban terrestrial mammals in Tianjin based on camera trapping method [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [13] | Jiangtian Geng, Fei Wang, Huabin Zhao. Research progress on the impacts of urbanization on bats in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24109-. |
| [14] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [15] | Rongfei Su, Ruishan Chen, Linlin Yu, Jingbin Wu, Yan Kang. Biodiversity in community habitat gardens in Changning District, Shanghai based on camera trapping [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 24068-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn