



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 24264. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024264 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024264
• Original Papers: Biosafety and Nature Conservation • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-06-28
Accepted:2024-08-28
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:CLC Number:
Xinmeng Tang, Tao Qin. Chinese enterprises’ biodiversity disclosure index construction and financing effects[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24264.
| 行业 Industries | 报告数 No. of reports | 行业 Industries | 报告数 No. of reports |
|---|---|---|---|
| A 农、林、牧、渔业 Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fisheries industry | 153 | K 房地产业 Real estate industry | 359 |
| B 采矿业 Mining industry | 311 | L 租赁和商务服务业 Leasing and business services industry | 69 |
| C 制造业 Manufacturing industry | 6,525 | M 科学研究、技术服务和地质勘查业 Scientific research, technical services, and geological exploration industry | 65 |
| D 电力、燃气及水的生产和供应业 Electricity, gas, and water production and supply industry | 1,215 | N 水利、环境和公共设施管理业 Water conservancy, environmental protection, and public facilities management industry | 96 |
| E 建筑业 Construction industry | 324 | O 居民服务和其他服务业 Residential services and other service industries | 33 |
| F 交通运输、仓储和邮政业 Transportation, warehousing, and postal industry | 416 | P 教育业 Education industries | 2 |
| G 信息传输、计算机服务和软件业 Information transmission, computer services, and software industry | 557 | Q 卫生、社会保障和社会福利业 Health, social security, and social welfare services industries | 18 |
| H 批发和零售业 Wholesale and retail industry | 20 | R 文化、体育和娱乐业 Culture, sports, and entertainment industries | 137 |
| I 住宿和餐饮业 Accommodation and catering industry | 576 | S 公共管理和社会组织 Public administration and social organizations industries | 285 |
| J 金融业 Financial industry | 706 | 总计 Total | 11,867 |
Table 1 Sample pool of observed enterprise report
| 行业 Industries | 报告数 No. of reports | 行业 Industries | 报告数 No. of reports |
|---|---|---|---|
| A 农、林、牧、渔业 Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fisheries industry | 153 | K 房地产业 Real estate industry | 359 |
| B 采矿业 Mining industry | 311 | L 租赁和商务服务业 Leasing and business services industry | 69 |
| C 制造业 Manufacturing industry | 6,525 | M 科学研究、技术服务和地质勘查业 Scientific research, technical services, and geological exploration industry | 65 |
| D 电力、燃气及水的生产和供应业 Electricity, gas, and water production and supply industry | 1,215 | N 水利、环境和公共设施管理业 Water conservancy, environmental protection, and public facilities management industry | 96 |
| E 建筑业 Construction industry | 324 | O 居民服务和其他服务业 Residential services and other service industries | 33 |
| F 交通运输、仓储和邮政业 Transportation, warehousing, and postal industry | 416 | P 教育业 Education industries | 2 |
| G 信息传输、计算机服务和软件业 Information transmission, computer services, and software industry | 557 | Q 卫生、社会保障和社会福利业 Health, social security, and social welfare services industries | 18 |
| H 批发和零售业 Wholesale and retail industry | 20 | R 文化、体育和娱乐业 Culture, sports, and entertainment industries | 137 |
| I 住宿和餐饮业 Accommodation and catering industry | 576 | S 公共管理和社会组织 Public administration and social organizations industries | 285 |
| J 金融业 Financial industry | 706 | 总计 Total | 11,867 |
| 面板A: 生物多样性概念体系 Panel A: Conceptual framework of biodiversity | ||
|---|---|---|
| 一级维度 Primary dimension | 二级维度 Secondary dimension | 三级维度 Tertiary dimension |
| 生物多样性保护概念 Biodiversity conservation concept | 生物多样性 Biodiversity | |
| 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | ||
| 物种多样性 Species diversity | ||
| 基因多样性 Genetic diversity | ||
| 生物多样性影响因素 Factors influencing biodiversity | 土地和海洋利用改变 Changes in land and ocean use | 土地利用改变 Land use changes |
| 海洋利用改变 Ocean use changes | ||
| 生物资源过度利用 Biological resources overexploitation | ||
| 外来入侵物种 Invasive alien species | ||
| 生物遗传资源与惠益分享 Genetic resources and benefit sharing | 生物遗传资源 Genetic resources | |
| 惠益分享 Benefit sharing | ||
| 面板B: 生物多样性词典 Panel B: Biodiversity dictionary | ||
| 概念维度 Conceptual dimension | 关键词 Keywords | |
| 生物多样性概念 Concept of biodiversity | 生物、生物多样性 Biology and biodiversity | |
| 生态系统、生态系统多样性 Ecosystem and ecosystem diversity | ||
| 物种、物种多样性 Species and species diversity | ||
| 基因、基因多样性 Genes and genetic diversity | ||
| 土地和海洋利用改变 Changes in land and ocean use | 土地、栖息地、湿地、森林、野生动物廊道 Land, habitat, wetlands, forests, and wildlife corridors | |
| 海洋、海洋生态 Ocean and marine ecology | ||
| 生物资源过度利用 Biological resources overexploitation | 生物资源、生物体、生物资源过度利用、直接利用生物体 Biological resources, organisms, overexploitation of biological resources, and direct utilization of organisms | |
| 外来入侵物种 Invasive alien species | 入侵物种、外来入侵物种 Invasive species and invasive alien species | |
| 生物遗传资源与惠益分享 Genetic resources and benefit sharing | 生物遗传资源、基因信息、基因资源 Genetic resources, genetic information, and genetic material | |
Table 2 Enterprise biodiversity dictionary from the perspective of information disclosure in this study
| 面板A: 生物多样性概念体系 Panel A: Conceptual framework of biodiversity | ||
|---|---|---|
| 一级维度 Primary dimension | 二级维度 Secondary dimension | 三级维度 Tertiary dimension |
| 生物多样性保护概念 Biodiversity conservation concept | 生物多样性 Biodiversity | |
| 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | ||
| 物种多样性 Species diversity | ||
| 基因多样性 Genetic diversity | ||
| 生物多样性影响因素 Factors influencing biodiversity | 土地和海洋利用改变 Changes in land and ocean use | 土地利用改变 Land use changes |
| 海洋利用改变 Ocean use changes | ||
| 生物资源过度利用 Biological resources overexploitation | ||
| 外来入侵物种 Invasive alien species | ||
| 生物遗传资源与惠益分享 Genetic resources and benefit sharing | 生物遗传资源 Genetic resources | |
| 惠益分享 Benefit sharing | ||
| 面板B: 生物多样性词典 Panel B: Biodiversity dictionary | ||
| 概念维度 Conceptual dimension | 关键词 Keywords | |
| 生物多样性概念 Concept of biodiversity | 生物、生物多样性 Biology and biodiversity | |
| 生态系统、生态系统多样性 Ecosystem and ecosystem diversity | ||
| 物种、物种多样性 Species and species diversity | ||
| 基因、基因多样性 Genes and genetic diversity | ||
| 土地和海洋利用改变 Changes in land and ocean use | 土地、栖息地、湿地、森林、野生动物廊道 Land, habitat, wetlands, forests, and wildlife corridors | |
| 海洋、海洋生态 Ocean and marine ecology | ||
| 生物资源过度利用 Biological resources overexploitation | 生物资源、生物体、生物资源过度利用、直接利用生物体 Biological resources, organisms, overexploitation of biological resources, and direct utilization of organisms | |
| 外来入侵物种 Invasive alien species | 入侵物种、外来入侵物种 Invasive species and invasive alien species | |
| 生物遗传资源与惠益分享 Genetic resources and benefit sharing | 生物遗传资源、基因信息、基因资源 Genetic resources, genetic information, and genetic material | |
| 变量名称 Variable names | 符号 Symbols | 数据来源 Data sources |
|---|---|---|
| 企业生物多样性信息披露指数 Enterprise biodiversity information disclosure index | Information disclosure | 上市企业年报、上市企业社会责任报告、上市企业ESG报告 Annual reports of listed enterprises, enterprise social responsibility reports of listed enterprises, ESG reports of listed enterprises |
| 融资约束KZ指数 KZ index of financing constraints | Financing constraints_KZ | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 融资约束WW指数 WW index of financing constraints | Financing constraints_WW | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 债权融资成本 Cost of debt financing | Financing cost_debt | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 股权融资成本 Cost of equity financing | Financing cost_equity | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 债权融资占比 Proportion of debt financing | Financing structure_debt | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 股权融资占比 Proportion of equity financing | Financing structure_ equity | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业规模 Enterprise size | Size | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业经理是否具有金融背景 Whether the enterprise manager has a financial background | Finback | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业资产流动性 Enterprise asset liquidity | Liquid | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业托宾Q Enterprise Tobin’s Q | TobinQ | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业账面市值比 Enterprise book to market ratio | Bm | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业董事会持股比例 Enterprise board ownership proportion | Chairholdr | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
Table 3 Summary of empirical variables
| 变量名称 Variable names | 符号 Symbols | 数据来源 Data sources |
|---|---|---|
| 企业生物多样性信息披露指数 Enterprise biodiversity information disclosure index | Information disclosure | 上市企业年报、上市企业社会责任报告、上市企业ESG报告 Annual reports of listed enterprises, enterprise social responsibility reports of listed enterprises, ESG reports of listed enterprises |
| 融资约束KZ指数 KZ index of financing constraints | Financing constraints_KZ | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 融资约束WW指数 WW index of financing constraints | Financing constraints_WW | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 债权融资成本 Cost of debt financing | Financing cost_debt | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 股权融资成本 Cost of equity financing | Financing cost_equity | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 债权融资占比 Proportion of debt financing | Financing structure_debt | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 股权融资占比 Proportion of equity financing | Financing structure_ equity | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业规模 Enterprise size | Size | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业经理是否具有金融背景 Whether the enterprise manager has a financial background | Finback | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业资产流动性 Enterprise asset liquidity | Liquid | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业托宾Q Enterprise Tobin’s Q | TobinQ | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业账面市值比 Enterprise book to market ratio | Bm | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
| 企业董事会持股比例 Enterprise board ownership proportion | Chairholdr | Wind数据库 Wind database ( |
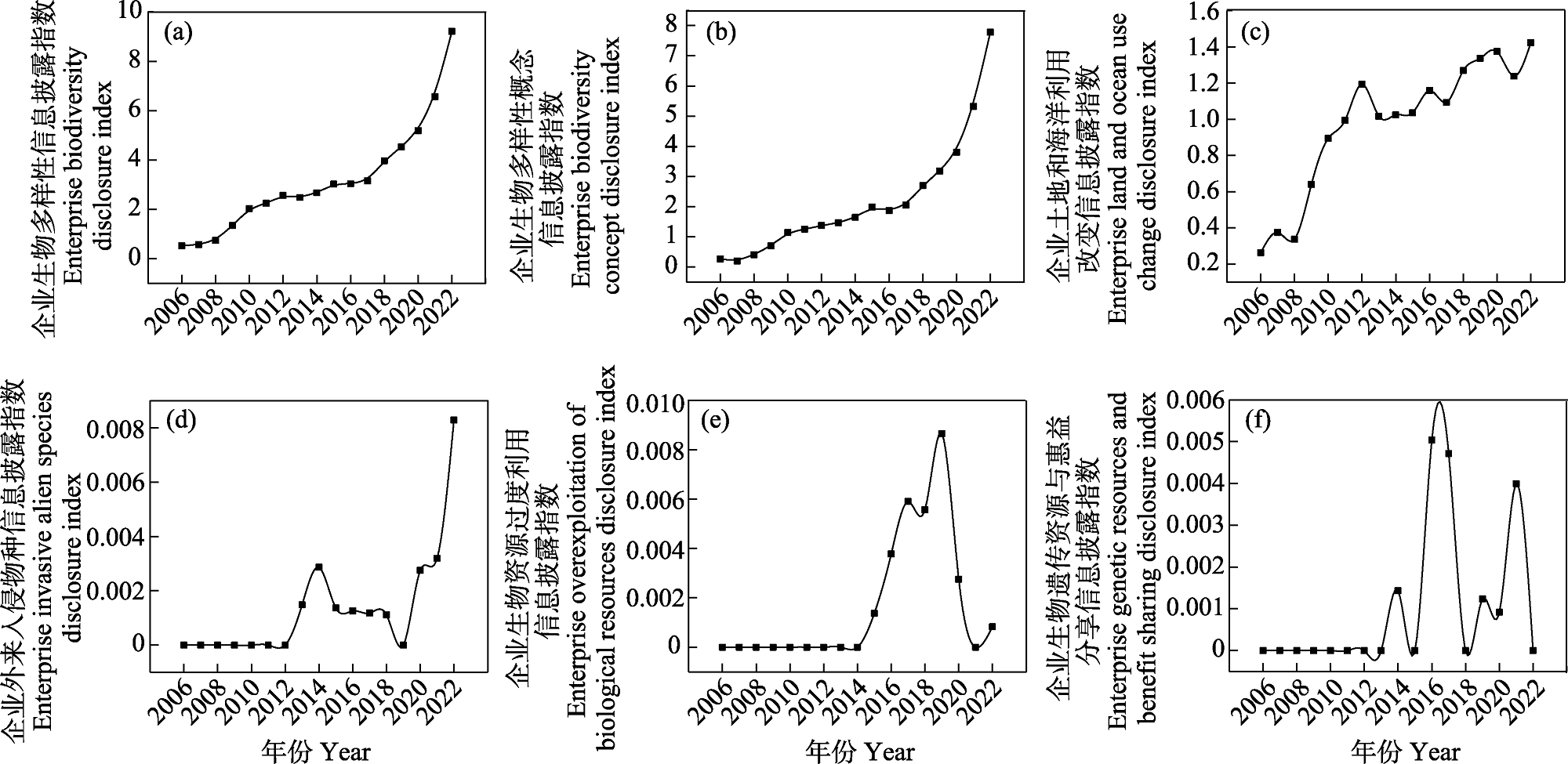
Fig. 3 Temporal development of the enterprise biodiversity information disclosure index. (a) Enterprise biodiversity disclosure index; (b) Enterprise biodiversity concept disclosure index; (c) Enterprise land and ocean use change disclosure index; (d) Enterprise invasive alien species disclosure index; (e) Enterprise overexploitation of biological resources disclosure index; (f) Enterprise genetic resources and benefit sharing disclosure index.
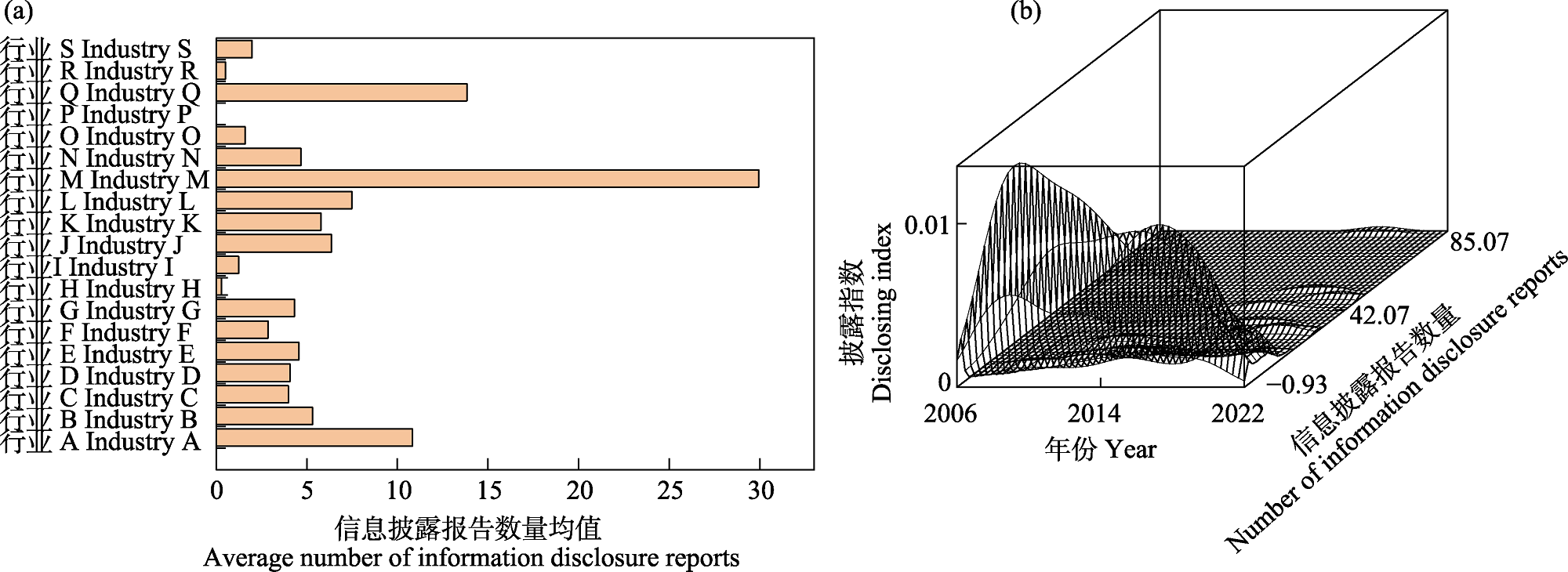
Fig. 4 Industry distribution of enterprise biodiversity information disclosure. (a) Enterprise average of the enterprise biodiversity information disclosure index; (b) Kernel density distribution of the enterprise biodiversity information disclosure index. The letters A to Z represent enterprise codes, which are detailed in Table 1.
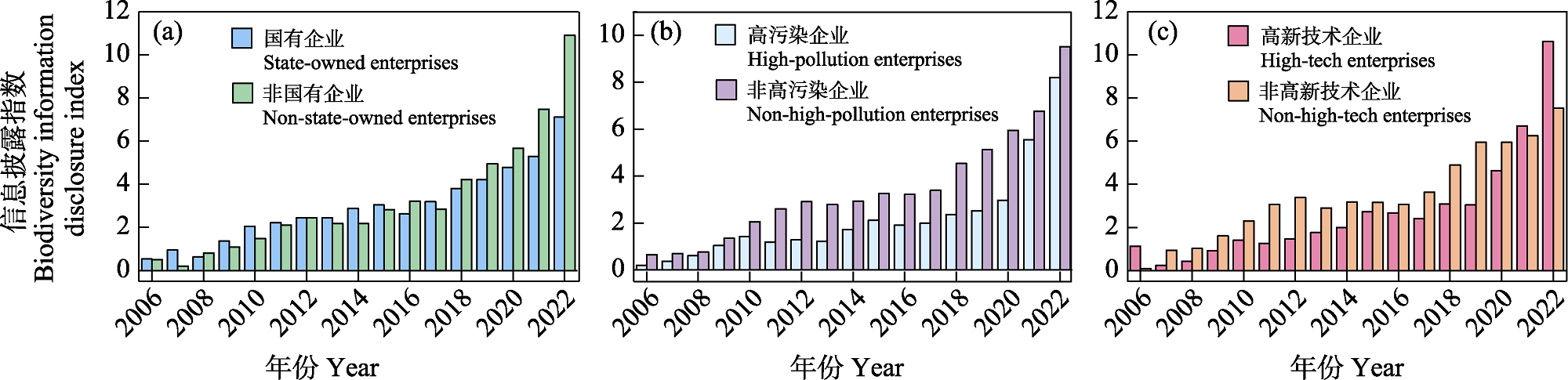
Fig. 5 Differences in biodiversity information disclosure index by enterprise ownership type. (a) State-owned enterprises and Non-state-owned enterprises biodiversity information disclosure index; (b) High-pollution enterprises and Non-high-pollution enterprises biodiversity information disclosure index; (c) High-tech enterprises and Non-high-tech enterprises biodiversity information disclosure index.
| 模型1 Model 1 Financing constraints_KZ | 模型2 Model 2 Financing constraints_KZ | 模型3 Model 3 Financing constraints_WW | 模型4 Model 4 Financing constraints_WW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Information disclosure | -0.0248 (-2.78)*** | -0.02217 (-2.64)*** | -0.0507 (-6.21)*** | -0.0202 (-2.61)*** |
| TobinQ | 0.1406 (10.89)*** | -2.61 (1.60) | ||
| Bm | 0.1599 (9.93)*** | 0.0085 (0.66) | ||
| Chairholdr | -0.0955 (-10.51)*** | -0.0034 (-0.41) | ||
| Size | 0.0046 (0.40) | -0.3271 (-30.50)*** | ||
| Finback | -0.0009 (-0.10) | 0.0056 (0.62) | ||
| Liquid | -0.3073 (-34.31)*** | 0.0554 (6.72)*** | ||
| 常数 Constant | 1.2378 (5.07)*** | 1.1321 (4.99)*** | 0.7020 (3.15)*** | 0.1839 (0.88) |
| 行业固定效应 Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 时间固定效应 Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| F-stata. | 30.14 | 49.96 | 15.84 | 31.66 |
| Prob > F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Adj R-squared | 0.2156 | 0.3297 | 0.1216 | 0.2336 |
Table 4 Empirical results on the effect of enterprise biodiversity information disclosure on alleviating financing constraints
| 模型1 Model 1 Financing constraints_KZ | 模型2 Model 2 Financing constraints_KZ | 模型3 Model 3 Financing constraints_WW | 模型4 Model 4 Financing constraints_WW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Information disclosure | -0.0248 (-2.78)*** | -0.02217 (-2.64)*** | -0.0507 (-6.21)*** | -0.0202 (-2.61)*** |
| TobinQ | 0.1406 (10.89)*** | -2.61 (1.60) | ||
| Bm | 0.1599 (9.93)*** | 0.0085 (0.66) | ||
| Chairholdr | -0.0955 (-10.51)*** | -0.0034 (-0.41) | ||
| Size | 0.0046 (0.40) | -0.3271 (-30.50)*** | ||
| Finback | -0.0009 (-0.10) | 0.0056 (0.62) | ||
| Liquid | -0.3073 (-34.31)*** | 0.0554 (6.72)*** | ||
| 常数 Constant | 1.2378 (5.07)*** | 1.1321 (4.99)*** | 0.7020 (3.15)*** | 0.1839 (0.88) |
| 行业固定效应 Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 时间固定效应 Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| F-stata. | 30.14 | 49.96 | 15.84 | 31.66 |
| Prob > F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Adj R-squared | 0.2156 | 0.3297 | 0.1216 | 0.2336 |
| 模型5 Model 5 Financing cost_debt | 模型6 Model 6 Financing cost_debt | 模型7 Model 7 Financing cost_equity | 模型8 Model 8 Financing cost_equity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Information disclosure | -0.0251 (-2.50)** | -0.0278 (-2.75)*** | -0.0183 (-2.51)** | -0.0155 (-2.16)** |
| TobinQ | 0.0400 (2.84)*** | -0.0255 (-2.53)** | ||
| Bm | -0.0273 (-1.61) | 0.1411 (10.81)*** | ||
| Chairholdr | -0.0113 (-1.03) | 0.0416 (5.12)*** | ||
| Size | 0.0156 (1.11) | 0.0266 (2.40)** | ||
| Finback | -0.0126 (-1.06) | -0.0086 (-0.96) | ||
| Liquid | -0.0640 (-5.91)*** | -0.0340 (-4.19)*** | ||
| 常数 Constant | -0.0149 (-0.05) | -0.0658 (-0.24) | -0.2602 (-1.17) | -0.1235 (-0.57) |
| 行业固定效应 Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 时间固定效应 Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| F-stata. | 3.46 | 3.84 | 26.65 | 30.13 |
| Prob > F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Adj R-squared | 0.0225 | 0.0277 | 0.2442 | 0.2810 |
Table 5 Empirical results on the effect of corporate biodiversity information disclosure on reducing financing costs
| 模型5 Model 5 Financing cost_debt | 模型6 Model 6 Financing cost_debt | 模型7 Model 7 Financing cost_equity | 模型8 Model 8 Financing cost_equity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Information disclosure | -0.0251 (-2.50)** | -0.0278 (-2.75)*** | -0.0183 (-2.51)** | -0.0155 (-2.16)** |
| TobinQ | 0.0400 (2.84)*** | -0.0255 (-2.53)** | ||
| Bm | -0.0273 (-1.61) | 0.1411 (10.81)*** | ||
| Chairholdr | -0.0113 (-1.03) | 0.0416 (5.12)*** | ||
| Size | 0.0156 (1.11) | 0.0266 (2.40)** | ||
| Finback | -0.0126 (-1.06) | -0.0086 (-0.96) | ||
| Liquid | -0.0640 (-5.91)*** | -0.0340 (-4.19)*** | ||
| 常数 Constant | -0.0149 (-0.05) | -0.0658 (-0.24) | -0.2602 (-1.17) | -0.1235 (-0.57) |
| 行业固定效应 Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 时间固定效应 Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| F-stata. | 3.46 | 3.84 | 26.65 | 30.13 |
| Prob > F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Adj R-squared | 0.0225 | 0.0277 | 0.2442 | 0.2810 |
| 模型9 Model 9 Financing structure_debt | 模型10 Model 10 Financing structure_debt | 模型11 Model 11 Financing structure_equity | 模型12 Model 12 Financing structure_equity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Information disclosure | 0.0009 (0.13)*** | -0.0219 (-3.53)*** | 0.1028 (0.46) | 0.0219 (3.52)*** |
| TobinQ | -0.0263 (-3.03)*** | 0.0262 (3.01)*** | ||
| Bm | 0.0837 (7.95)*** | -0.0837 (-7.93)*** | ||
| Chairholdr | -0.0387 (-5.65)*** | 0.0386 (5.62)*** | ||
| Size | 0.2947 (33.67)*** | -0.2950 (-33.63)*** | ||
| Finback | -0.0114 (-1.57) | 0.0116 (1.59) | ||
| Liquid | -0.2955 (-44.58)*** | 0.2954 (44.47)*** | ||
| 常数 Constant | -0.5027 (-2.35)** | -0.0684 (-0.40) | 0.5022 (2.34)** | 0.0675 (0.39) |
| 行业固定效应 Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 时间固定效应 Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| F-stata. | 46.49 | 126.70 | 46.83 | 126.07 |
| Prob > F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Adj R-squared | 0.3021 | 0.5603 | 0.3014 | 0.5591 |
Table 6 Empirical results on the effect of enterprise biodiversity information disclosure on improving financing structure
| 模型9 Model 9 Financing structure_debt | 模型10 Model 10 Financing structure_debt | 模型11 Model 11 Financing structure_equity | 模型12 Model 12 Financing structure_equity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Information disclosure | 0.0009 (0.13)*** | -0.0219 (-3.53)*** | 0.1028 (0.46) | 0.0219 (3.52)*** |
| TobinQ | -0.0263 (-3.03)*** | 0.0262 (3.01)*** | ||
| Bm | 0.0837 (7.95)*** | -0.0837 (-7.93)*** | ||
| Chairholdr | -0.0387 (-5.65)*** | 0.0386 (5.62)*** | ||
| Size | 0.2947 (33.67)*** | -0.2950 (-33.63)*** | ||
| Finback | -0.0114 (-1.57) | 0.0116 (1.59) | ||
| Liquid | -0.2955 (-44.58)*** | 0.2954 (44.47)*** | ||
| 常数 Constant | -0.5027 (-2.35)** | -0.0684 (-0.40) | 0.5022 (2.34)** | 0.0675 (0.39) |
| 行业固定效应 Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 时间固定效应 Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| F-stata. | 46.49 | 126.70 | 46.83 | 126.07 |
| Prob > F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Adj R-squared | 0.3021 | 0.5603 | 0.3014 | 0.5591 |
| [1] | Ahmad MF, Karpuz A (2024) Beyond climate change risk: Biodiversity and corporate cash holdings. Economics Letters, 236, 111608. |
| [2] | Blanco-Zaitegi G, Álvarez Etxeberria I, Moneva JM (2024) Impression management of biodiversity reporting in the energy and utilities sectors: An assessment of transparency in the disclosure of negative events. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 42, 100942. |
| [3] |
Cai YL, Zhu HG, Li JX (2024) Biodiversity conservation in China: Policy evolution, main measures and development trends. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23386. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[蔡颖莉, 朱洪革, 李家欣 (2024) 中国生物多样性保护政策演进、主要措施与发展趋势. 生物多样性, 32, 23386.]
DOI |
|
| [4] | Costanza R, d’Arge R, De Groot R, Farber S, Grasso M, Hannon B, Limburg K, Naeem S, O’neill RV, Paruelo J (1997) The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature, 387, 253-260. |
| [5] | Cui CY, Hou YL, Wang TY, Wen YL (2022) Financial support for biodiversity conservation: Global practices and policy implications. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22326. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[崔楚云, 侯一蕾, 王天一, 温亚利 (2022) 金融支持生物多样性保护: 全球实践及政策启示. 生物多样性, 30, 22326.]
DOI |
|
| [6] | Elliot V, Jonäll K, Paananen M, Bebbington J, Michelon G (2024) Biodiversity reporting: Standardization, materiality, and assurance. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 68, 101435. |
| [7] | Feng YQ, Hu Y (2024) Has digital finance optimized the financing structure of enterprises in the real economy? Financial Economics Research, 39(3), 59-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯永琦, 胡玥 (2024) 数字金融是否优化了实体企业融资结构. 金融经济学研究, 39(3), 59-76.] | |
| [8] | Fenichel EP, Dean MF (2024) Blended academic insights for biodiversity and conservation finance. Ecological Economics, 223, 108258. |
| [9] | Giglio S, Kuchler T, Stroebel J, Zeng XR (2023) Biodiversity Risk. https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w31137/w31137.pdf. (accessed on 2024-06-11) |
| [10] | Hadji-Lazaro P, Salin M, Svartzman R, Espagne E, Gauthey J, Berger J, Calas J, Godin A, Vallier A (2024) Biodiversity loss and financial stability as a new frontier for central banks: An exploration for France. Ecological Economics, 223, 108246. |
| [11] | Hutchinson MC, Lucey B (2024) A bibliometric and systemic literature review of biodiversity finance. Finance Research Letters, 64, 105377. |
| [12] | Jiang FX, Cai WJ, Cai XN, Li XT (2019) Microeconomic effects of bank competition: Evidence from corporate financial constraints. Economic Research Journal, 54(6), 72-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜付秀, 蔡文婧, 蔡欣妮, 李行天 (2019) 银行竞争的微观效应: 来自融资约束的经验证据. 经济研究, 54(6), 72-88.] | |
| [13] | Kalhoro MR, Kyaw K (2024) Manage biodiversity risk exposure? Finance Research Letters, 61, 104989. |
| [14] | Kaplan SN, Zingales L (1997) Do investment-cash flow sensitives provide useful measures of financing constraints. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 112, 169-216. |
| [15] | Kopnina H, Zhang SR, Anthony S, Hassan A, Maroun W (2024) The inclusion of biodiversity into Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework: A strategic integration of ecocentric extinction accounting. Journal of Environmental Management, 351, 119808. |
| [16] | Liu ZY, Hu KL, Hussain A (2023) R&D disclosure and corporate innovation: Mediating role of financing structure. Finance Research Letters, 56, 104106. |
| [17] | Lorente DB, Joof F, Samour A, Türsoy T (2023) Renewable energy, economic complexity and biodiversity risk: New insights from China. Environmental and Sustainability Indicators, 18, 100244. |
| [18] | Marco-Fondevila M, Álvarez-Etxeberría I (2023) Trends in private sector engagement with biodiversity: EU listed companies’ disclosure and indicators. Ecological Economics, 210, 107864. |
| [19] | Moreno AI, Caminero T (2022) Application of text mining to the analysis of climate-related disclosures. International Review of Financial Analysis, 83, 102307. |
| [20] | Narain D, Teo HC, Lechner AM, Watson JEM, Maron M (2022) Biodiversity risks and safeguards of China’s hydropower financing in Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) countries. One Earth, 5, 1019-1029. |
| [21] | Sun JK, Zhu XP (2024) The market reaction to carbon disclosure of listed companies—Evidence from heavily polluting industries. Accounting Research, (2), 53-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙甲奎, 朱小平 (2024) 上市公司碳信息披露的市场反应——来自重污染行业的证据. 会计研究, (2), 53-73.] | |
| [22] | Sun MH, Li YS, Zhao FW (2021) Current status and challenges of protection, access to and benefit sharing of bio-genetic resources of China. Environmental Protection, 49(21), 30-34. (in Chinese) |
| [孙名浩, 李颖硕, 赵富伟 (2021) 生物遗传资源保护、获取与惠益分享现状和挑战. 环境保护, 49(21), 30-34.] | |
| [23] | Talbot D, Barbat G, Boiral O, Ordonez-Ponce E (2023) Failure to consider environmental risk: The case for biodiversity impact disclosure in the electricity sector. Utilities Policy, 85, 101672. |
| [24] | Torreggiani G, De Giacomo MR (2022) CSR representation in the public discourse and corporate environmental disclosure strategies in the context of Brexit. A cross-country study of France, Germany, and the United Kingdom. Journal of Cleaner Production, 367, 132783. |
| [25] | Wang Y, Wang JX (2024) ‘Deterrence’ or ‘reliance’: Impact of geographical distance on the quality of corporate environmental information disclosure. China Population, Resources and Environment, 34(4), 91-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王钰, 王建新 (2024) “震慑”还是“依靠”: 地理距离对企业环境信息披露质量的影响. 中国人口·资源与环境, 34(4), 91-102.] | |
| [26] | Wang YQ, Xie M (2022) The impact of ESG information disclosure on corporate financing costs: Based on the empirical evidence of listed companies in China. Nankai Economic Studies, (11), 75-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王翌秋, 谢萌 (2022) ESG信息披露对企业融资成本的影响——基于中国A股上市公司的经验证据. 南开经济研究, (11), 75-94.] | |
| [27] | Whited TM, Wu G (2006) Financial constraints risk. The Review of Financial Studies, 19, 531-559. |
| [28] | Wu HJ, Liu QR, Wu SN (2017) Corporate environmental disclosure and financing constraints. The Journal of World Economy, 40(5), 124-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴红军, 刘啟仁, 吴世农 (2017) 公司环保信息披露与融资约束. 世界经济, 40(5), 124-147.] | |
| [29] | Yang Q, Liu GY, Yang ZF (2024) A new framework for biodiversity system analysis driven by climate change and land use change. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44, 871-884. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨青, 刘耕源, 杨志峰 (2024) 气候变化和土地利用变化驱动下的生物多样性系统分析新框架. 生态学报, 44, 871-884.] | |
| [30] | Zeng ZX, Wang FY, Yang R (2024) The concept of representativeness and research progress in the field of biodiversity conservation research. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (Social Sciences), 23(2), 18-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾子轩, 王方邑, 杨锐 (2024) 生物多样性保护研究领域的代表性概念及研究进展. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版), 23(2), 18-27.] | |
| [31] | Zhang XY, Feng PP, Wei X (2023) The signal effect of corporate targeted poverty alleviation disclosure on fund investment. Economic Research Journal, 58(4), 152-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张学勇, 冯盼盼, 魏旭 (2023) 上市公司精准扶贫信息披露对基金投资的信号作用. 经济研究, 58(4), 152-170.] | |
| [32] |
Zhao Y, Li HT (2022) Corporate biodiversity disclosure: Investigation, analysis and recommendation. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22049. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [赵阳, 李宏涛 (2022) 企业生物多样性信息披露: 调查、分析与建议. 生物多样性, 30, 22049.] |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()
