



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 854-866. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019040 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019040
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bin Cao,Guojie Li,Ruilin Zhao( )
)
Received:2019-02-19
Accepted:2019-04-10
Online:2019-08-20
Published:2019-09-25
Contact:
Zhao Ruilin
Bin Cao, Guojie Li, Ruilin Zhao. Species diversity and geographic components of Russula from the Greater and Lesser Khinggan Mountains[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(8): 854-866.
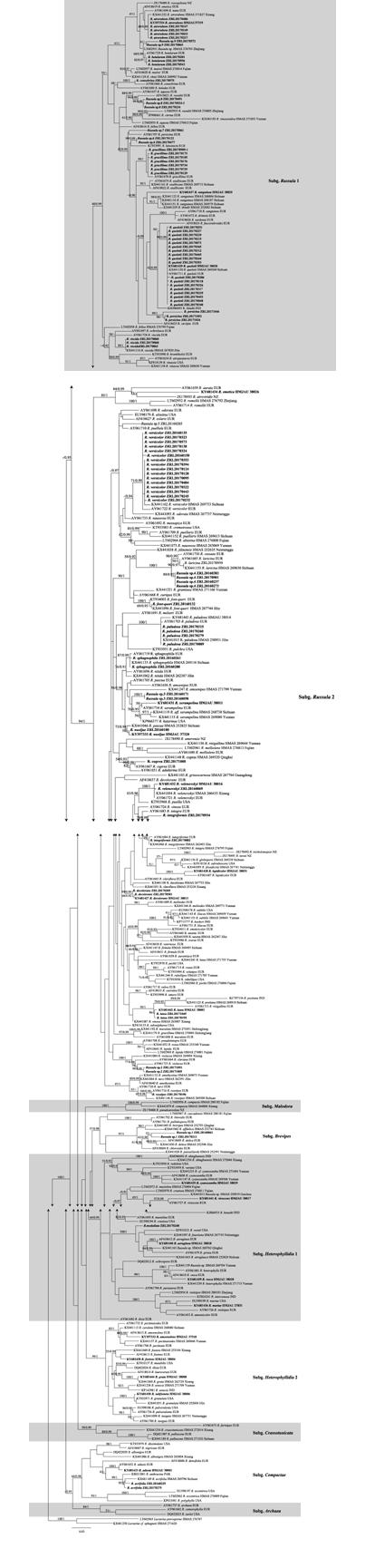
Fig. 1 ITS phylogenetic tree of Russula, generated by maximum likelihood and Bayesian methods. Numbers above the branches are presented as: bootstrap values (BS) ≥ 50 and posterior probabilities (PP) ≥ 0.90. The bold fonts represent the specimen in the Greater and Lesser Khinggan Mountains. Abbreviations correspond to the geographic origins of the collections: Europe (EUR), India (IND), New Zealand (NZ), Pakistan (PAK), the United States (USA).

Fig. 2 The species of Russula in the Greater and Lesser Khinggan Mountains. (A) R. decolorans (ZRL20170581); (B) R. font-queri (ZRL20160132); (C) R. gracillim (ZRL20170734); (D) R. lutea (ZRL20170195); (E) R. medullata (ZRL20170248); (F) R. paludosa (ZRL20170315); (G) R. persicina (ZRL20171046); (H) R. queletii (ZRL20170215); (I) R. roseipes (ZRL20170196); (J) R. velenovskyi (ZRL20160069); (K) R. viscida (ZRL20170860); (L) R. sphagnophila (ZRL20160288).

Fig. 3 The species of Russula in the Greater and Lesser Khinggan Mountains. (A) R. betularum (ZRL20170201); (B) R. acrifolia (ZRL20160225); (C) R. atrorubens (ZRL20170486); (D) R. consobrina (ZRL20170575); (E) R. cuprea (ZRL20171000); (F) R. integriformis (ZRL20170934); (G) R. laricina (ZRL20170959); (H) R. nuoljae (ZRL20160100); (I) R. versicolor (ZRL20170232).
| 编号 Number | 物种 Species | 生境 Ecological habitat | 本研究标本来源( Specimen sources ( | 其他分布地区 Other distribution areas | 文献 References | 地理成分 Geographical elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 尖褶红菇 R. acrifolia | 阔叶林 Broadleaf forest | 大小兴安岭、四川 GLHM, Sichuan | 欧洲 Europe | Sarnari, 2005 | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 2 | 烟色红菇 R. adusta | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲、大洋洲、非洲 North America, Oceania, Africa | Singer, 1986; Buyck, 1989 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 3 | 铜绿红菇 R. aeruginea | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 4 | 怡人红菇 R. amoenolens | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 刘晓亮等, 2017 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 5 | 黑紫红菇 R. atropurpurea | 阔叶林/针叶林 Broadleaf/ coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、大洋洲、非洲、欧洲 North America, Oceania, Africa, Europe | Buyck, 1989; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 6 | 暗红红菇 R. atrorubens | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、西藏 GLHM, Xizang | 欧洲 Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 刘晓亮等, 2017 | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 7 | 桦红菇 R. betularum | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲、非洲 North America, Africa | Buyck, 1989; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
Table 1 Species diversity, ecological habitats and geographical elements of Russula in the Greater and Lesser Khinggan Mountains (GLHM)
| 编号 Number | 物种 Species | 生境 Ecological habitat | 本研究标本来源( Specimen sources ( | 其他分布地区 Other distribution areas | 文献 References | 地理成分 Geographical elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 尖褶红菇 R. acrifolia | 阔叶林 Broadleaf forest | 大小兴安岭、四川 GLHM, Sichuan | 欧洲 Europe | Sarnari, 2005 | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 2 | 烟色红菇 R. adusta | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲、大洋洲、非洲 North America, Oceania, Africa | Singer, 1986; Buyck, 1989 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 3 | 铜绿红菇 R. aeruginea | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 4 | 怡人红菇 R. amoenolens | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 刘晓亮等, 2017 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 5 | 黑紫红菇 R. atropurpurea | 阔叶林/针叶林 Broadleaf/ coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、大洋洲、非洲、欧洲 North America, Oceania, Africa, Europe | Buyck, 1989; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 6 | 暗红红菇 R. atrorubens | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、西藏 GLHM, Xizang | 欧洲 Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 刘晓亮等, 2017 | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 7 | 桦红菇 R. betularum | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲、非洲 North America, Africa | Buyck, 1989; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 编号 Number | 物种 Species | 生境 Ecological habitat | 本研究标本来源( Specimen sources ( | 其他分布地区 Other distribution areas | 文献 References | 地理成分 Geographical elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 解毒红菇 R. consobrina | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 9 | 铜色红菇 R. cuprea | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 10 | 蓝黄红菇 R. cyanoxantha | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、云南、欧洲 GLHM, Yunnan, Europe | 北美洲、大洋洲 North America, Oceania | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 11 | 褪色红菇 R. decolorans | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 12 | 美味红菇 R. delica | 针叶林/阔叶林 Broadleaf/ coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、大洋洲、欧洲 North America, Oceania, Europe | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 13 | 毒红菇 R. emetica | 阔叶林/针叶林 Broadleaf/ coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、大洋洲、欧洲 North America, Oceania, Europe | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 14 | 臭红菇 R. foetens | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、西藏、欧洲 GLHM, Xizang, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 15 | 冯特奎尔氏红菇 R. font-queri | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、吉林、欧洲 GLHM, Jilin, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 16 | 灰褐红菇 R. gracillima | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 17 | 可爱红菇 R. grata | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、西藏 GLHM, Xizang | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 18 | 全缘形红菇 R. integriformis | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、吉林、欧洲 GLHM, Jilin, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 19 | 落叶松红菇 R. laricina | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、四川 GLHM, Sichuan | 欧洲 Europe | Sarnari, 2005 | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 20 | 怡人色红菇 R. lepidicolor | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 21 | 黄红菇 R. lutea | 阔叶林/针叶林 Broadleaf/ coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; Sarnari, 2005 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 22 | 绒紫红菇 R. mariae | 阔叶林 Broadleaf forest | 大小兴安岭、北美洲 GLHM, North America | 大洋洲 Oceania | Singer, 1986 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 23 | 髓质红菇 R. medullata | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; Sarnari, 2005 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 24 | 诺尔亚红菇 R. nuoljae | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 欧洲 Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 刘晓亮等, 2017 | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 25 | 沼泽红菇 R. paludosa | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、吉林、欧洲 GLHM, Jilin, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 26 | 桃红菇 R. persicina | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; Sarnari, 2005 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 27 | 凯莱红菇 R. queletii | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、四川、欧洲 GLHM, Sichuan, Europe | 北美洲 North America | 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 28 | 玫瑰柄红菇 R. roseipes | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
Table 1 (continued)
| 编号 Number | 物种 Species | 生境 Ecological habitat | 本研究标本来源( Specimen sources ( | 其他分布地区 Other distribution areas | 文献 References | 地理成分 Geographical elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 解毒红菇 R. consobrina | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 9 | 铜色红菇 R. cuprea | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 10 | 蓝黄红菇 R. cyanoxantha | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、云南、欧洲 GLHM, Yunnan, Europe | 北美洲、大洋洲 North America, Oceania | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 11 | 褪色红菇 R. decolorans | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 12 | 美味红菇 R. delica | 针叶林/阔叶林 Broadleaf/ coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、大洋洲、欧洲 North America, Oceania, Europe | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 13 | 毒红菇 R. emetica | 阔叶林/针叶林 Broadleaf/ coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、大洋洲、欧洲 North America, Oceania, Europe | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 14 | 臭红菇 R. foetens | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、西藏、欧洲 GLHM, Xizang, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 15 | 冯特奎尔氏红菇 R. font-queri | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、吉林、欧洲 GLHM, Jilin, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 16 | 灰褐红菇 R. gracillima | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 17 | 可爱红菇 R. grata | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、西藏 GLHM, Xizang | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 18 | 全缘形红菇 R. integriformis | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、吉林、欧洲 GLHM, Jilin, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 19 | 落叶松红菇 R. laricina | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、四川 GLHM, Sichuan | 欧洲 Europe | Sarnari, 2005 | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 20 | 怡人色红菇 R. lepidicolor | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 21 | 黄红菇 R. lutea | 阔叶林/针叶林 Broadleaf/ coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; Sarnari, 2005 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 22 | 绒紫红菇 R. mariae | 阔叶林 Broadleaf forest | 大小兴安岭、北美洲 GLHM, North America | 大洋洲 Oceania | Singer, 1986 | 世界广布 Cosmopolitan |
| 23 | 髓质红菇 R. medullata | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; Sarnari, 2005 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 24 | 诺尔亚红菇 R. nuoljae | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 欧洲 Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 刘晓亮等, 2017 | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 25 | 沼泽红菇 R. paludosa | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、吉林、欧洲 GLHM, Jilin, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 26 | 桃红菇 R. persicina | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; Sarnari, 2005 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 27 | 凯莱红菇 R. queletii | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、四川、欧洲 GLHM, Sichuan, Europe | 北美洲 North America | 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 28 | 玫瑰柄红菇 R. roseipes | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 编号 Number | 物种 Species | 生境 Ecological habitat | 本研究标本来源( Specimen sources ( | 其他分布地区 Other distribution areas | 文献 References | 地理成分 Geographical elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 | 血红菇 R. sanguinea | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 30 | 泥炭藓红菇 R. sphagnophila | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、四川、欧洲 GLHM, Sichuan, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; | 北温带 North temperate |
| 31 | 亚臭红菇 R. subfoetens | 阔叶林 Broadleaf forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; Sarnari, 2005 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 32 | 细皮囊体红菇 R. velenovskyi | 阔叶林 Broadleaf forest | 大小兴安岭、西藏、欧洲 GLHM, Xizang, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 33 | 多色红菇 R. versicolor | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、四川、欧洲 GLHM, Sichuan, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 34 | 菱红菇 R. vesca | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 35 | 变绿红菇 R. virescens | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 36 | 粘质红菇 R. viscida | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、吉林 GLHM, Jilin | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 37 | 黄孢红菇 R. xerampelina | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
Table 1 (continued)
| 编号 Number | 物种 Species | 生境 Ecological habitat | 本研究标本来源( Specimen sources ( | 其他分布地区 Other distribution areas | 文献 References | 地理成分 Geographical elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 | 血红菇 R. sanguinea | 针叶林/混交林 Coniferous/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Sarnari, 2005; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 30 | 泥炭藓红菇 R. sphagnophila | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、四川、欧洲 GLHM, Sichuan, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; | 北温带 North temperate |
| 31 | 亚臭红菇 R. subfoetens | 阔叶林 Broadleaf forest | 大小兴安岭 GLHM | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; Sarnari, 2005 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 32 | 细皮囊体红菇 R. velenovskyi | 阔叶林 Broadleaf forest | 大小兴安岭、西藏、欧洲 GLHM, Xizang, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 33 | 多色红菇 R. versicolor | 混交林 Mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、四川、欧洲 GLHM, Sichuan, Europe | - | - | 欧亚 Eurasian |
| 34 | 菱红菇 R. vesca | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 35 | 变绿红菇 R. virescens | 阔叶林/混交林 Broadleaf/ mixed forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 温带-热带 Temperate- Tropical |
| 36 | 粘质红菇 R. viscida | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、吉林 GLHM, Jilin | 北美洲、欧洲 North America, Europe | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 37 | 黄孢红菇 R. xerampelina | 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 大小兴安岭、欧洲 GLHM, Europe | 北美洲 North America | Singer, 1986; 李国杰, 2014 | 北温带 North temperate |
| 1 | Avis PG, Mclaughlin DJ, Dentinger BC, Reich PB (2003) Long-term increase in nitrogen supply alters above- and below-ground ectomycorrhizal communities and increases the dominance of Russula spp. in a temperate oak savanna. New Phytologist, 160, 239-253. |
| 2 | Ba T, Oyongowa, Bau T (2005) Statistics of mycobiota of macrofungi in Gogostai Haan Nature Reserve of Inner Mongolia. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 29, 34-42.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 巴图, 乌云高娃, 图力古尔 ( 2005) 内蒙古高格斯台罕乌拉自然保护区大型真菌区系调查. 吉林农业大学学报, 29, 34-42.] | |
| 3 | Bau T, Bao HY, Li Y ( 2014) A revised checklist of poisonous mushrooms in China. Mycosystema, 33, 517-548.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 图力古尔, 包海鹰, 李玉 (2014) 中国毒蘑菇名录. 菌物学报, 33, 517-548.] | |
| 4 | Bazzicalupo AL, Buyck B, Saar I, Vauras J, Carmean D, Berbee ML (2017) Troubles with mycorrhizal mushroom identification where morphological identification lags behind barcode sequence divergence. Taxon, 66, 791-810. |
| 5 | Bian LS, Dai YC (2015) Mycota and ecology of polypores in eastern Himalayas. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 1554-1563.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 边禄森, 戴玉成 ( 2015) 东喜马拉雅地区多孔菌区系和生态习性. 生态学报, 35, 1554-1563.] | |
| 6 | Buyck B ( 1989) Révision du Genre Russula Persoon en Afrique Centrale. PhD dissertation, Ghent University, Ghent. |
| 7 | Buyck B, Thoen D, Watling R ( 1996) Ectomycorrhizal Fungi of the Guinea-Congo Region. The Royal Society of Edinburgh, Edinburgh. |
| 8 | Buyck B, Hofstetter V, Eberhardt U, Verbeken A, Kauff F ( 2008) Walking the thin line between Russula and Lactarius: The dilemma of Russula subsect Ochricompactae. Fungal Diversity, 28, 15-40. |
| 9 | Buyck B, Hofstetter V, Verbeken A, Walleyn R ( 2010) Proposal to conserve Lactarius nom. cons. (Basidiomycota) with a conserved type. Taxon, 59, 295-296. |
| 10 | Buyck B, Zoller S, Hofstetter V (2018) Walking the thin line… ten years later: The dilemma of above- versus below-ground features to support phylogenies in the Russulaceae (Basidiomycota). Fungal Diversity, 89, 267-292. |
| 11 | Cai Q, Tulloss RE, Tang LP, Bau T, Zhang P, Chen ZH, Yang ZL (2014) Multi-locus phylogeny of lethal amanitas: Implications for species diversity and historical biogeography. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 14, 1-16. |
| 12 | Chen ZH, Yang ZL, Bau T, Li TH (2016) Poisonous Mushrooms: Recognition and Poisoning Treatment. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [ 陈作红, 杨祝良, 图力古尔, 李泰辉 (2016) 毒蘑菇识别与中毒预防. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 13 | Cui BK, Yu CJ (2011) Fungal flora and population structure of polypores in the Greater Hinggan Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 3700-3709.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 崔宝凯, 余长军 (2011) 大兴安岭林区多孔菌的区系组成与种群结构. 生态学报, 31, 3700-3709.] | |
| 14 | Dai YC, Yang ZL ( 2008) A revised checklist of medicinal fungi in China. Mycosystema, 27, 801-824.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴玉成, 杨祝良 ( 2008) 中国药用真菌名录及部分名称的修订. 菌物学报, 27, 801-824.] | |
| 15 | Dai YC, Zhou LW, Yang ZL, Wen HA, Bau T, Li TH ( 2010) A revised checklist of edible fungi in China. Mycosystema, 29, 1-21. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [ 戴玉成, 周丽伟, 杨祝良, 文华安, 图力古尔, 李泰辉 ( 2010) 中国食用菌名录. 菌物学报, 29, 1-21.] | |
| 16 | Eberhardt U (2002) Molecular kinship analyses of the agaricoid Russulaceae: Correspondence with mycorrhizal anatomy and sporocarp features in the genus Russula. Mycological Progress, 1, 201-223. |
| 17 | Feng B, Xu J, Wu G, Hosen MI, Zeng NK, Li YC, Bau T, Kost GW, Yang ZL ( 2012) DNA sequence analyses reveal abundant diversity, endemism and evidence for Asian origin of the porcini mushrooms. PLoS ONE, 7, e37567. |
| 18 | Han LH, Feng B, Wu G, Halling RE, Buyck B, Yorou NS, Ebika STN, Yang ZL ( 2018) African origin and global distribution patterns: Evidence inferred from phylogenetic and biogeographical analyses of ectomycorrhizal fungal genus Strobilomyces. Journal of Biogeography, 45, 201-212. |
| 19 | Hibbett DS, Binder M, Bischoff JF (2007) A higher-level phylogenetic classification of the Fungi. Mycological Research, 111, 509-547. |
| 20 | Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA (2008) Dictionary of the Fungi, 10th edn. Cromwell Press, Trowbridge. |
| 21 | Li GJ (2014) The Taxonomy of Russula in China. PhD dissertation, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李国杰 (2014) 中国红菇属的分类研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院微生物研究所, 北京.] | |
| 22 | Li GJ, Li SF, Zhao D, Wen HA ( 2015) Recent research progress of Russula (Russulales, Agaricomycetes): A review. Mycosystema, 34, 821-848.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李国杰, 李赛飞, 赵东, 文华安 ( 2015) 红菇属研究进展. 菌物学报, 34, 821-848.] | |
| 23 | Liu XL, Bau T, Wang XH ( 2017) Species diversity of Russula from the Greater and Lesser Hinggan Mountains in Northeast China. Mycosystema, 36, 1355-1368.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘晓亮, 图力古尔, 王向华 ( 2017) 东北大小兴安岭地区的红菇属物种多样性. 菌物学报, 36, 1355-1368.] | |
| 24 | Looney BP, Ryberg M, Hampe F, Sánchez-García M, Matheny PB ( 2016) Into and out of the tropics: Global diversification patterns in a hyperdiverse clade of ectomycorrhizal fungi. Molecular Ecology, 25, 630-647. |
| 25 | Mao XL (2000) The Macrofungi in China. Henan Science and Technology Press, Zhengzhou.(in Chinese) |
| [ 卯晓岚 (2000) 中国大型真菌. 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| 26 | Miller SL, Buyck B (2002) Molecular phylogeny of the genus Russula in Europe with a comparison of modern infrageneric classifications. Mycological Research, 106, 259-276. |
| 27 | Sánchez-Ramírez S, Tulloss RE, Amalfi M, Moncalvo J ( 2015) Palaeotropical origins, boreotropical distribution and increased rates of diversification in a clade of edible ectomycorrhizal mushrooms (Amanita section Caesareae). Journal of Biogeography, 42, 351-363. |
| 28 | Sarnari M (2005) Monografia illustrate de genere Russula in Europa. Tomo Secondo, AMB, Centro Studi Micologici, Trento. |
| 29 | Singer R (1986) The Agaricales in Modern Taxonomy, 4th edn. Koeltz Scientific Books, Koenigstein. |
| 30 | Song B, Li TH, Wu XL, Li JJ, Shen YH, Lin QY ( 2007) Known species of Russula from China and their distribution. Journal of Fungal Research, 5, 20-42. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [ 宋斌, 李泰辉, 吴兴亮, 黎静静, 沈亚恒, 林群英 ( 2007) 中国红菇属种类及其分布. 菌物研究, 5, 20-42.] | |
| 31 | Xie XD, Liu PG, Yu FQ (2010) Species diversity of russuloid mycorrhizae-forming fungi on Pinus yunnanensis seedlings and the mycorrhizal morphology. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 32, 211-220.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢雪丹, 刘培贵, 于富强 ( 2010) 云南松幼苗上红菇类菌根真菌的物种多样性及其菌根形态. 云南植物研究, 32, 211-220.] | |
| 32 | Xu HC (1998) Greater Hinggan Mountains Forests in China. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [ 徐化成 ( 1998) 中国大兴安岭森林. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 33 | Yang ZL ( 2013) Fungal taxonomy in the genomics era: Opportunities and challenges. Mycosystema, 32, 931-946.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨祝良 ( 2013) 基因组学时代的真菌分类学: 机遇与挑战. 菌物学报, 32, 931-946.] | |
| 34 | Ying JZ, Zang M (1994) Economic Macrofungi from Southwestern China. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [ 应建浙, 臧穆 ( 1994) 西南地区大型经济真菌. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 35 | Yuan K, Cao ZM ( 2008) Primary analysis on polypores flora in Huoditang Forest Farm in Qinling Mountains. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 23, 117-121.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁坤, 曹支敏 ( 2008) 秦岭火地塘林区多孔菌区系地理成分初步分析. 西北林学院学报, 23, 117-121.] | |
| 36 | Zhang JW, Ma SY, Qi LL, Li Y ( 2017) Macrofungal flora diversity in Liangshui Nature Reserve, Heilongjiang Province. Journal of Fungal Research, 15, 170-176.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张进武, 马世玉, 祁亮亮, 李玉 ( 2017) 黑龙江凉水自然保护区大型真菌的区系多样性. 菌物研究, 15, 170-176.] | |
| 37 | Zhao RL, Li GJ, Sánchez-Ramírez S, Stata M, Yang ZL, Wu G, Dai YC, He SH, Cui BK, Zhou JL, Wu F, He MQ, Moncalvo J, Hyde KD ( 2017) A six-gene phylogenetic overview of Basidiomycota, and allied phyla with estimated divergence times of higher taxa and a phyloproteomics perspective. Fungal Diversity, 84, 1-32. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn