



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 24553. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024553 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024553
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhang Haobin1,2, Xiao Lu1,*( )(
)( ), Liu Yanjie1,*(
), Liu Yanjie1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-12-09
Accepted:2025-02-18
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-03-27
Contact:
*E-mail: xiaolu@iga.ac.cn;
liuyanjie@iga.ac.cn
Supported by:Zhang Haobin, Xiao Lu, Liu Yanjie. Effects of artificial light at night on the diversity and growth of invasive alien and native plants[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24553.
| 外来入侵植物 Invasive alien plants | 本地植物 Native plants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种 Species | 频度 Frequency (%) | 物种 Species | 频度 Frequency (%) | |
| 全部植物 All plants | 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 39.13 | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 69.57 |
| 三裂叶豚草 Ambrosia trifida | 31.88 | 稗 Echinochloa crus-galli | 50.72 | |
| 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 18.84 | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 47.83 | |
| 牛膝菊 Galinsoga parviflora | 17.39 | 萹蓄 Polygonum aviculare | 40.58 | |
| 一年蓬 Erigeron annuus | 11.59 | 苦荬菜 Ixeris polycephala | 39.13 | |
| 有路灯(亮) LIT POLES | 三裂叶豚草 Ambrosia trifida | 40.74 | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 74.07 |
| 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 33.33 | 萹蓄 Polygonum aviculare | 55.56 | |
| 牛膝菊 Galinsoga parviflora | 25.93 | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 51.85 | |
| 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 22.22 | 稗 Echinochloa crus-galli | 48.15 | |
| 小蓬草 Erigeron canadensis | 14.81 | 苦荬菜 Ixeris polycephala | 44.44 | |
| 有路灯(不亮) UNLIT POLES | 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 80.00 | 稗 Echinochloa crus-galli | 60.00 |
| 三裂叶豚草 Ambrosia trifida | 40.00 | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 60.00 | |
| 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 20.00 | 藜 Chenopodium album | 50.00 | |
| 苘麻 Abutilon theophrasti | 10.00 | 野大豆 Glycine soja | 50.00 | |
| / | / | 金色狗尾草 Setaria pumila | 40.00 | |
| 无路灯 NO POLES | 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 31.25 | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 68.75 |
| 三裂叶豚草 Ambrosia trifida | 21.88 | 稗 Echinochloa crus-galli | 50.00 | |
| 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 15.63 | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 46.88 | |
| 牛膝菊 Galinsoga parviflora | 15.63 | 蒲公英 Taraxacum mongolicum | 46.88 | |
| 一年蓬 Erigeron annuus | 12.50 | 大籽蒿 Artemisia sieversiana | 37.50 | |
Table 1 Average frequency of main invasive alien and native plants under different levels of artificial light at night
| 外来入侵植物 Invasive alien plants | 本地植物 Native plants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种 Species | 频度 Frequency (%) | 物种 Species | 频度 Frequency (%) | |
| 全部植物 All plants | 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 39.13 | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 69.57 |
| 三裂叶豚草 Ambrosia trifida | 31.88 | 稗 Echinochloa crus-galli | 50.72 | |
| 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 18.84 | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 47.83 | |
| 牛膝菊 Galinsoga parviflora | 17.39 | 萹蓄 Polygonum aviculare | 40.58 | |
| 一年蓬 Erigeron annuus | 11.59 | 苦荬菜 Ixeris polycephala | 39.13 | |
| 有路灯(亮) LIT POLES | 三裂叶豚草 Ambrosia trifida | 40.74 | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 74.07 |
| 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 33.33 | 萹蓄 Polygonum aviculare | 55.56 | |
| 牛膝菊 Galinsoga parviflora | 25.93 | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 51.85 | |
| 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 22.22 | 稗 Echinochloa crus-galli | 48.15 | |
| 小蓬草 Erigeron canadensis | 14.81 | 苦荬菜 Ixeris polycephala | 44.44 | |
| 有路灯(不亮) UNLIT POLES | 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 80.00 | 稗 Echinochloa crus-galli | 60.00 |
| 三裂叶豚草 Ambrosia trifida | 40.00 | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 60.00 | |
| 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 20.00 | 藜 Chenopodium album | 50.00 | |
| 苘麻 Abutilon theophrasti | 10.00 | 野大豆 Glycine soja | 50.00 | |
| / | / | 金色狗尾草 Setaria pumila | 40.00 | |
| 无路灯 NO POLES | 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 31.25 | 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 68.75 |
| 三裂叶豚草 Ambrosia trifida | 21.88 | 稗 Echinochloa crus-galli | 50.00 | |
| 反枝苋 Amaranthus retroflexus | 15.63 | 马唐 Digitaria sanguinalis | 46.88 | |
| 牛膝菊 Galinsoga parviflora | 15.63 | 蒲公英 Taraxacum mongolicum | 46.88 | |
| 一年蓬 Erigeron annuus | 12.50 | 大籽蒿 Artemisia sieversiana | 37.50 | |
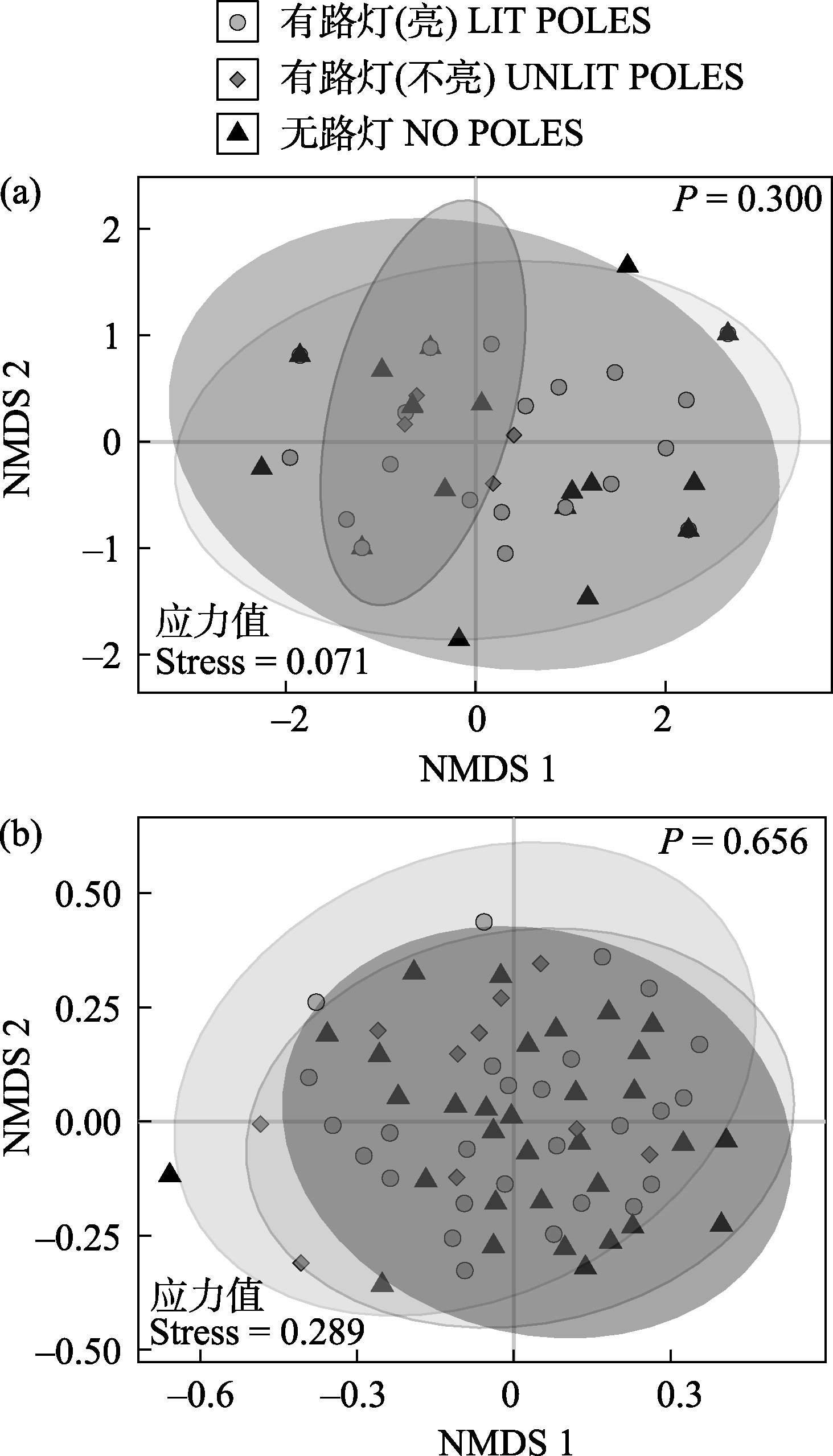
Fig. 1 NMDS analysis results of β diversity differences between the communities of invasive alien plants (a) and native plants (b), based on the Bray-Curtis distance. The areas lacking direct illumination from streetlights (NO POLES); The areas where streetlights on poles are not lit (UNLIT POLES); The areas where streetlights on poles are lit (LIT POLES).
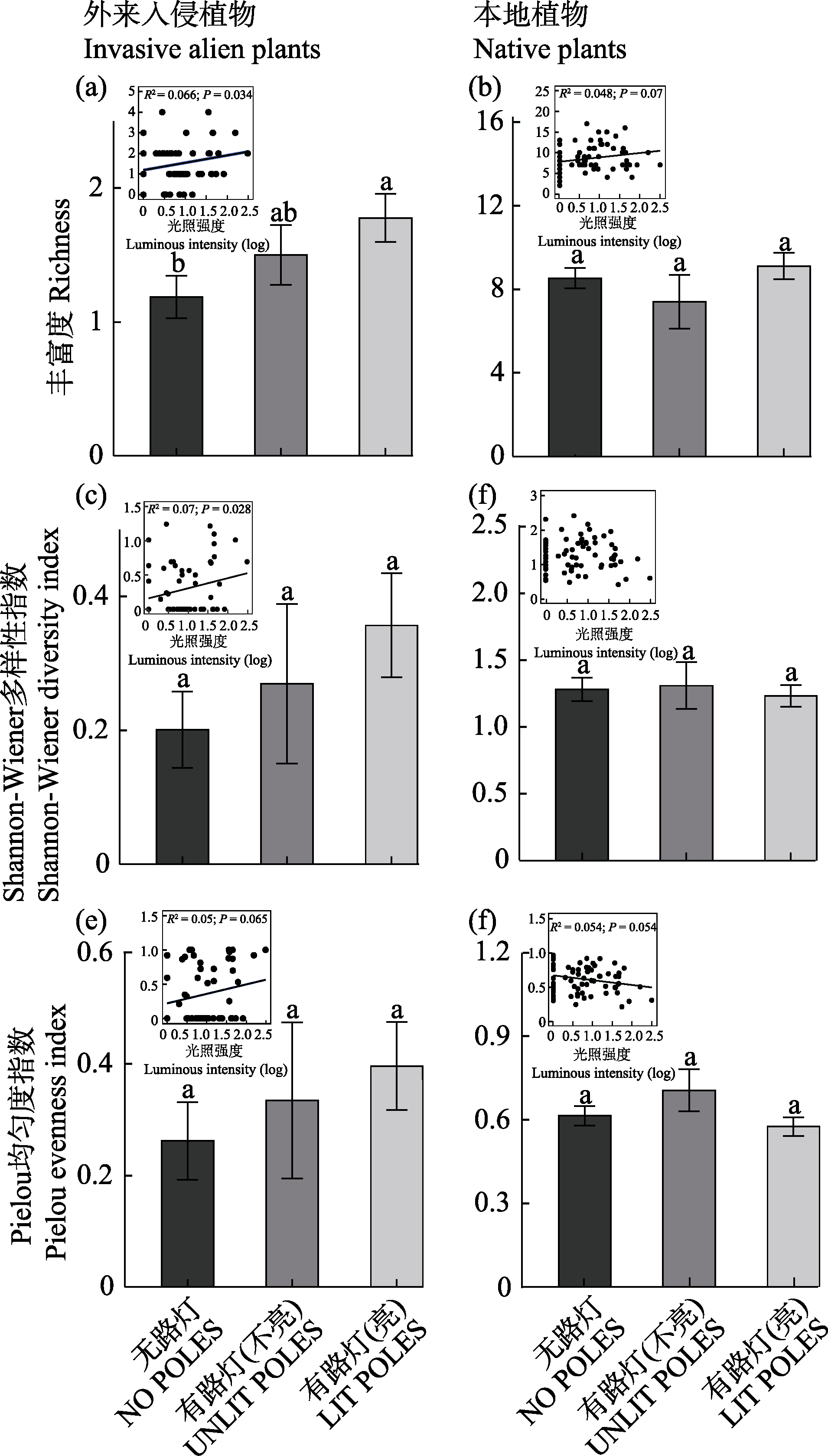
Fig. 2 The impacts of artificial light at night on α-diversity indices (richness, Shannon-Wiener diversity index, and Pielou evenness index) of invasive alien plants and native plants. The areas lacking direct illumination from streetlights (NO POLES); The areas where streetlights on poles are not lit (UNLIT POLES); The areas where streetlights on poles are lit (LIT POLES). The values are the mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant differences in the same index among different levels of artificial light at night (P < 0.05). The regression plots in the upper left corner illustrate the relationships between the α-diversity indices of invasive alien plants or native plants and the intensity of artificial light at night. For models showing significant and marginally significant relationships, the R², P values, and regression fit lines are displayed.
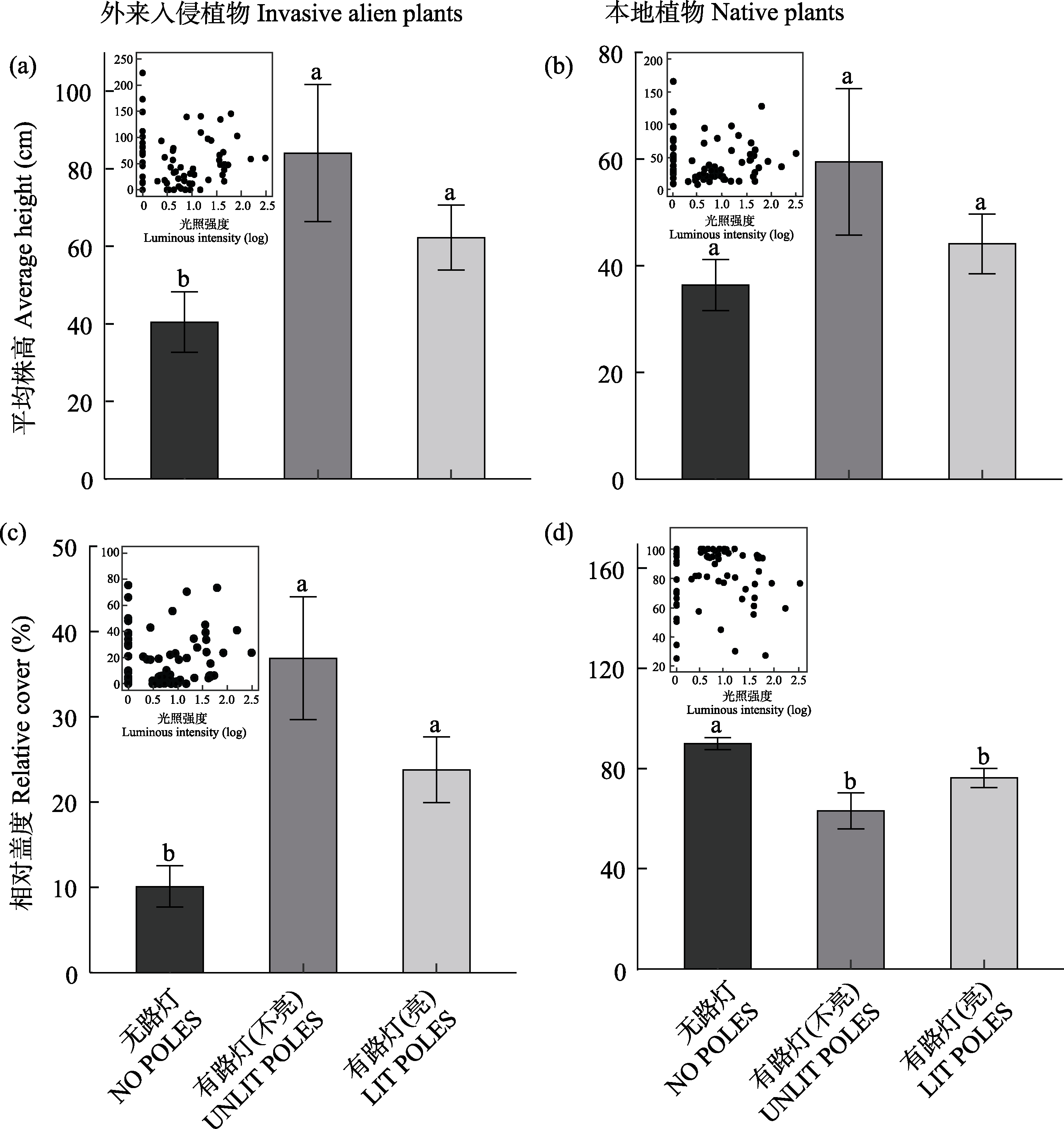
Fig. 3 The impacts of artificial light at night on the average plant height and relative cover of invasive alien plants and native plants. The areas lacking direct illumination from streetlights (NO POLES). The areas where streetlights on poles are not lit (UNLIT POLES). The areas where streetlights on poles are lit (LIT POLES). The values are the mean ± SE. Different letters indicate significant differences in the same index among different levels of artificial light at night (P < 0.05). The regression plots in the upper left corner illustrate the relationships between the growth indices of invasive alien plants or native plants and the intensity of artificial light at night. For models showing significant and marginally significant relationships, the R², P values, and regression fit lines are displayed.
| [1] | Abonyo CRK, Oduor AMO (2024) Artificial night-time lighting and nutrient enrichment synergistically favour the growth of alien ornamental plant species over co-occurring native plants. Journal of Ecology, 112, 319-337. |
| [2] | Allan E, Manning P, Alt F, Binkenstein J, Blaser S, Blüthgen N, Böhm S, Grassein F, Hölzel N, Klaus VH, Kleinebecker T, Morris EK, Oelmann Y, Prati D, Renner SC, Rillig MC, Schaefer M, Schloter M, Schmitt B, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Solly E, Sorkau E, Steckel J, Steffen-Dewenter I, Stempfhuber B, Tschapka M, Weiner CN, Weisser WW, Werner M, Westphal C, Wilcke W, Fischer M (2015) Land use intensification alters ecosystem multifunctionality via loss of biodiversity and changes to functional composition. Ecology Letters, 18, 834-843. |
| [3] | Azeem A, Mai WX, Tian CY, Javed Q, Abbas A (2021) Competition and plant trait plasticity of invasive (Wedelia trilobata) and native species (Wedelia chinensis, WC) under nitrogen enrichment and flooding condition. Water, 13, 3472. |
| [4] | Bao SD (2000) Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis, 3rd edn. China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [鲍士旦 (2000) 土壤农化分析, 第三版. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Bennie J, Davies TW, Cruse D, Gaston KJ (2016) Ecological effects of artificial light at night on wild plants. Journal of Ecology, 104, 611-620. |
| [6] | Bennie J, Davies TW, Cruse D, Inger R, Gaston KJ (2018) Artificial light at night causes top-down and bottom-up trophic effects on invertebrate populations. Journal of Applied Ecology, 55, 2698-2706. |
| [7] | Boscutti F, Lami F, Pellegrini E, Buccheri M, Busato F, Martini F, Sibella R, Sigura M, Marini L (2022) Urban sprawl facilitates invasions of exotic plants across multiple spatial scales. Biological Invasions, 24, 1497-1510. |
| [8] | Bucher SF, Uhde L, Weigelt A, Cesarz S, Eisenhauer N, Gebler A, Kyba C, Römermann C, Shatwell T, Hines J (2023) Artificial light at night decreases plant diversity and performance in experimental grassland communities. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 378, 20220358. |
| [9] | Cao Y, Zhang S, Ma KM (2024) Artificial light at night decreases leaf herbivory in typical urban areas. Frontiers in Plant Science, 15, 1392262. |
| [10] | Crump MC, Brown C, Griffin-Nolan RJ, Angeloni L, Lemoine NP, Seymoure BM (2021) Effects of low-level artificial light at night on Kentucky bluegrass and an introduced herbivore. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 732959. |
| [11] |
Davidson AM, Jennions M, Nicotra AB (2011) Do invasive species show higher phenotypic plasticity than native species and, if so, is it adaptive? A meta-analysis. Ecology Letters, 14, 419-431.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Davies TW, Smyth T (2018) Why artificial light at night should be a focus for global change research in the 21st century. Global Change Biology, 24, 872-882.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Davis MA, Grime JP, Thompson K (2000) Fluctuating resources in plant communities: A general theory of invasibility. Journal of Ecology, 88, 528-534. |
| [14] |
Derryberry EP (2017) Dawn song in natural and artificial continuous day: Light pollution affects songbirds at high latitudes. Journal of Animal Ecology, 86, 1283-1285.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Diagne C, Leroy B, Vaissière AC, Gozlan RE, Roiz D, Jarić I, Salles JM, Bradshaw CJA, Courchamp F (2021) High and rising economic costs of biological invasions worldwide. Nature, 592, 571-576. |
| [16] | Díaz S, Kattge J, Cornelissen JHC, Wright IJ, Lavorel S, Dray S, Reu B, Kleyer M, Wirth C, Colin Prentice I, Garnier E, Bönisch G, Westoby M, Poorter H, Reich PB, Moles AT, Dickie J, Gillison AN, Zanne AE, Chave J, Joseph Wright S, Sheremet′ev SN, Jactel H, Baraloto C, Cerabolini B, Pierce S, Shipley B, Kirkup D, Casanoves F, Joswig JS, Günther A, Falczuk V, Rüger N, Mahecha MD, Gorné LD (2016) The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature, 529, 167-171. |
| [17] | Dubois J, Cheptou PO (2017) Effects of fragmentation on plant adaptation to urban environments. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 372, 20160038. |
| [18] | Editorial Committee of Flora of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences(2004) Flora of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会 (2004) 中国植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [19] | El-Barougy RF, Dakhil MA, Abdelaal M, El-Keblawy A, Bersier LF (2021) Trait-environment relationships reveal the success of alien plants invasiveness in an urbanized landscape. Plants, 10, 1519. |
| [20] | Falchi F, Cinzano P, Duriscoe D, Kyba CCM, Elvidge CD, Baugh K, Portnov BA, Rybnikova NA, Furgoni R (2016) The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Science Advances, 2, e1600377. |
| [21] | Ffrench-Constant RH, Somers-Yeates R, Bennie J, Economou T, Hodgson D, Spalding A, McGregor PK (2016) Light pollution is associated with earlier tree budburst across the United Kingdom. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 283, 20160813. |
| [22] | Forero LE, Grenzer J, Heinze J, Schittko C, Kulmatiski A (2019) Greenhouse- and field-measured plant-soil feedbacks are not correlated. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 7, 184. |
| [23] | Gaston KJ, Bennie J, Davies TW, Hopkins J (2013) The ecological impacts of nighttime light pollution: A mechanistic appraisal. Biological Reviews, 88, 912-927. |
| [24] |
Giavi S, Blösch S, Schuster G, Knop E (2020) Artificial light at night can modify ecosystem functioning beyond the lit area. Scientific Reports, 10, 11870.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Gioria M, Hulme PE, Richardson DM, Pyšek P (2023) Why are invasive plants successful? Annual Review of Plant Biology, 74, 635-670.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Grenis K, Murphy SM (2019) Direct and indirect effects of light pollution on the performance of an herbivorous insect. Insect Science, 26, 770-776.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Haeuser E, Dawson W, van Kleunen M (2017) The effects of climate warming and disturbance on the colonization potential of ornamental alien plant species. Journal of Ecology, 105, 1698-1708. |
| [28] |
Heinen R (2021) A spotlight on the phytobiome: Plant-mediated interactions in an illuminated world. Basic and Applied Ecology, 57, 146-158.
DOI |
| [29] | Hopkins GR, Gaston KJ, Visser ME, Elgar MA, Jones TM (2018) Artificial light at night as a driver of evolution across urban-rural landscapes. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 16, 472-479. |
| [30] |
Jägerbrand AK, Spoelstra K (2023) Effects of anthropogenic light on species and ecosystems. Science, 380, 1125-1130.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Kyba CCM, Kuester T, Miguel ASD, Baugh K, Jechow A, Hölker F, Bennie J, Elvidge CD, Gaston KJ, Guanter L (2017) Artificially lit surface of Earth at night increasing in radiance and extent. Science Advances, 3, e1701528. |
| [32] | Liu YJ, Heinen R (2024) Plant invasions under artificial light at night. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 39, 703-705. |
| [33] | Liu YJ, Huang W, Yang Q, Zheng YL, Li SP, Wu H, Ju RT, Sun Y, Ding JQ (2022) Research advances of plant invasion ecology over the past 10years. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22438. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[刘艳杰, 黄伟, 杨强, 郑玉龙, 黎绍鹏, 吴昊, 鞠瑞亭, 孙燕, 丁建清 (2022) 近十年植物入侵生态学重要研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22438.]
DOI |
|
| [34] |
Liu YJ, Liu M, Xu XL, Tian YQ, Zhang Z, van Kleunen M (2018) The effects of changes in water and nitrogen availability on alien plant invasion into a stand of a native grassland species. Oecologia, 188, 441-450.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Liu YJ, Oduor AMO, Zhang Z, Manea A, Tooth IM, Leishman MR, Xu XL, van Kleunen M (2017) Do invasive alien plants benefit more from global environmental change than native plants? Global Change Biology, 23, 3363-3370.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Liu YJ, Speißer B, Knop E, van Kleunen M (2022) The Matthew effect: Common species become more common and rare ones become more rare in response to artificial light at night. Global Change Biology, 28, 3674-3682. |
| [37] | Liu YJ, Zhang DD, Yang LY, Dong YH, Liang GM, Philip D, Ren GW, Xu PJ, Wu KM (2021) Analysis of phototactic responses in Spodoptera frugiperda using Helicoverpa armigera as control. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 20, 821-828. |
| [38] | Lukács K, Valkó O (2021) Human-vectored seed dispersal as a threat to protected areas: Prevention, mitigation and policy. Global Ecology and Conservation, 31, e01851. |
| [39] | Ma JS, Li HR (2018) The Checklist of Alien Invasive Plants in China. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [马金双, 李惠茹 (2018) 中国外来入侵植物名录. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] | Maggi E, Serôdio J (2020) Artificial light at night: A new challenge in microphytobenthos research. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 329. |
| [41] | Marques PS, Manna LR, Frauendorf TC, Zandonà E, Mazzoni R, El-Sabaawi R (2020) Urbanization can increase the invasive potential of alien species. Journal of Animal Ecology, 89, 2345-2355. |
| [42] | Mazza G, Tricarico E, Genovesi P, Gherardi F (2014) Biological invaders are threats to human health: An overview. Ethology, Ecology & Evolution, 26, 112-129. |
| [43] |
Meng L (2021) Green with phenology. Science, 374, 1065-1066.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (2021) 2020 State of Ecology and Environment Report. (in Chinese) |
| [中华人民共和国生态环境部 (2021) 2020中国生态环境状况公报.] https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202305/P020230529570623593284.pdf. (accessed on 2024-12-18) | |
| [45] | Mondy N, Boisselet C, Poussineau S, Vallier F, Lengagne T, Secondi J, Romestaing C, Geay M, Puijalon S (2021) Herbivory increases on freshwater plants exposed to artificial light at night. Aquatic Botany, 175, 103447. |
| [46] | Mozdzer TJ, Caplan JS (2018) Complementary responses of morphology and physiology enhance the stand-scale production of a model invasive species under elevated CO2 and nitrogen. Functional Ecology, 32, 1784-1796. |
| [47] |
Murphy SM, Vyas DK, Hoffman JL, Jenck CS, Washburn BA, Hunnicutt KE, Davidson A, Andersen JM, Bennet RK, Gifford A, Herrera M, Lawler B, Lorman S, Peacock V, Walker L, Watkins E, Wilkinson L, Williams Z, Tinghitella RM (2021) Streetlights positively affect the presence of an invasive grass species. Ecology and Evolution, 11, 10320-10326.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Murphy SM, Vyas DK, Sher AA, Grenis K (2022) Light pollution affects invasive and native plant traits important to plant competition and herbivorous insects. Biological Invasions, 24, 599-602. |
| [49] |
Owens ACS, Lewis SM (2018) The impact of artificial light at night on nocturnal insects: A review and synthesis. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 11337-11358.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Poulin C, Bruyant F, Laprise MH, Cockshutt AM, Vandenhecke JMR, Huot Y (2014) The impact of light pollution on diel changes in the photophysiology of Microcystis aeruginosa. Journal of Plankton Research, 36, 286-291. |
| [51] | Qin WC, Tao ZB, Wang YJ, Liu YJ, Huang W (2021) Research progress and prospect on the impacts of resource pulses on alien plant invasion. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45, 573-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [秦文超, 陶至彬, 王永健, 刘艳杰, 黄伟 (2021) 资源脉冲对外来植物入侵影响的研究进展和展望. 植物生态学报, 45, 573-582.] | |
| [52] | Qu TB, Meng FY, Wang Y (2015) Species composition and flora analysis of alien invasive plants in Changchun. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 907-911. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曲同宝, 孟繁勇, 王豫 (2015) 长春地区入侵植物种类组成及区系分析. 生态学杂志, 34, 907-911.] | |
| [53] | Ratcliffe H, Kendig A, Vacek S, Carlson D, Ahlering M, Dee LE (2024) Extreme precipitation promotes invasion in managed grasslands. Ecology, 105, e4190. |
| [54] |
Richards CL, Bossdorf O, Muth NZ, Gurevitch J, Pigliucci M (2006) Jack of all trades, master of some? On the role of phenotypic plasticity in plant invasions. Ecology Letters, 9, 981-993.
PMID |
| [55] | Sanders D, Gaston KJ (2018) How ecological communities respond to artificial light at night. Journal of Experimental Zoology Part A: Ecological and Integrative Physiology, 329, 394-400. |
| [56] | Shan LP, Oduor AMO, Liu YJ (2023) Herbivory and elevated levels of CO2 and nutrients separately, rather than synergistically, impacted biomass production and allocation in invasive and native plant species. Global Change Biology, 29, 6741-6755. |
| [57] |
Singhal RK, Kumar M, Bose B (2019) Eco-physiological responses of artificial night light pollution in plants. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 66, 190-202.
DOI |
| [58] | Sodani R, Nandan Mishra U, Chand S, Indu, Anuragi H, Chandra K, Chauhan J, Bose B, Kumar V, Shankar Singh G, Lenka D, Kumar Singhal R (2021) Artificial Light at Night: A Global Threat to Plant Biological Rhythms and Eco-Physiological Processes. Light Pollution, Urbanization and Ecology (ed. Hufnagel L) pp.11-28. IntechOpen, Rijeka. |
| [59] | Speißer B, Liu YJ, van Kleunen M (2021) Biomass responses of widely and less-widely naturalized alien plants to artificial light at night. Journal of Ecology, 109, 1819-1827. |
| [60] |
van Kleunen M, Weber E, Fischer M (2010) A meta-analysis of trait differences between invasive and non-invasive plant species. Ecology Letters, 13, 235-245.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Xiao L, Wang WJ, He XY, Lv HL, Wei CH, Zhou W, Zhang B (2016) Urban-rural and temporal differences of woody plants and bird species in Harbin City, northeastern China. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 20, 20-31. |
| [62] |
Ye XH, Tang SL, Cornwell WK, Gao SQ, Huang ZY, Dong M, Cornelissen JHC (2015) Impact of land-use on carbon storage as dependent on soil texture: Evidence from a desertified dryland using repeated paired sampling design. Journal of Environmental Management, 150, 489-498.
DOI PMID |
| [63] | Yuan JJ, Ding WX, Liu DY, Kang H, Freeman C, Xiang J, Lin YX (2015) Exotic Spartina alterniflora invasion alters ecosystem-atmosphere exchange of CH4 and N2O and carbon sequestration in a coastal salt marsh in China. Global Change Biology, 21, 1567-1580. |
| [64] | Zhu B, Wei CQ, Zhou H, Chen W, Siemann E, Lu XM (2025) Traits estimated when grown alone may underestimate the competitive advantage and invasiveness of exotic species. New Phytologist, 245, 2202-2213. |
| [65] | Zou D, Zhou YK, Lin JT, Chen TY, Wu ZJ, Wang H (2022) Analysis of inequality of socioeconomic development on both sides of Hu Huanyong Line using nighttime light. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 37, 929-937. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[邹丹, 周玉科, 林金堂, 陈天宇, 吴志杰, 王洪 (2022) 利用夜间灯光分析胡焕庸线两侧社会经济发展不均衡状况. 遥感技术与应用, 37, 929-937.]
DOI |
| [1] | Quanfeng Yang, Yanjie Tang, Haijun Xiao, Ying Wang, Rong Zhang, Fang Ouyang, Shuhua Wei. The cascading effects of plant diversity-grasshoppers-carabids and their impacts on primary productivity in different grassland types of Ningxia [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 25021-. |
| [2] | Song Wei, Cheng Cai, Wang Jiawei, Wu Jihua. Soil microbes regulate the relationships between plant diversity and ecosystem functions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [3] | Yuan Jingyi, Zhang Xu, Tian Zhenpeng, Wang Zizhe, Gao Yongping, Yao Dizhao, Guan Hongcan, Li Wenkai, Liu Jing, Zhang Hong, Ma Qin. A comparison of methods for extracting tree species composition and quantitative characteristics in urban plant communities using UAV high-resolution RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [4] | Jiali Lian, Jing Chen, Xueqin Yang, Ying Zhao, Xu Luo, Cui Han, Yaxin Zhao, Jianping Li. Responses of desert steppe plant diversity and microbial diversity to precipitation change [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24044-. |
| [5] | Fengming Wan, Huawei Wan, Zhiru Zhang, Jixi Gao, Chenxi Sun, Yongcai Wang. The application potential of unmanned aerial vehicle surveys in grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| [6] | Naipeng Zhang, Hongru Liang, Yan Zhang, Chao Sun, Yong Chen, Lulu Wang, Jiangbao Xia, FangLei Gao. Effects of soil type and groundwater depth on spatial differentiation of typical salt marsh plant communities in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [7] | Chen-Kun Jiang, Wen-Bin Yu, Guang-Yuan Rao, Huaicheng Li, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. Plant Phylogeny Posters—An educational project on plant diversity from an evolutionary perspective [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [8] | Yun Han, Xiaofeng Chi, Jingya Yu, Xujie Ding, Shilong Chen, Faqi Zhang. A checklist of wild vascular plants in Qinghai, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [9] | Yousheng Chen, Zhuqiu Song, Ran Wei, Yan Luo, Wenli Chen, Fusheng Yang, Lianming Gao, Yuan Xu, Zhuoxin Zhang, Pengcheng Fu, Chunlei Xiang, Huanchong Wang, Jiachen Hao, Shiyong Meng, Lei Wu, Bo Li, Shengxiang Yu, Shuren Zhang, Li He, Xinqiang Guo, Wenguang Wang, Yihua Tong, Qi Gao, Wenqun Fei, Youpai Zeng, Lin Bai, Zichao Jin, Xingjie Zhong, Buyun Zhang, Siyi Du. A dataset on inventory and geographical distribution of vascular plants in Xizang, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23188-. |
| [10] | Zhuqiu Song, Wen Ye, Shiyong Dong, Zichao Jin, Xingjie Zhong, Zhen Wang, Buyun Zhang, Yechun Xu, Wenli Chen, Shijin Li, Gang Yao, Zhoufeng Xu, Shuai Liao, Yihua Tong, Youpai Zeng, Yunbao Zeng, Yousheng Chen. A dataset on inventory and geographical distributions of higher plants in Guangdong, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23177-. |
| [11] | Caiqun Liang, Yukai Chen, Xiaobo Yang, Kai Zhang, Donghai Li, Yuexin Jiang, Jinghan Li, Chongyang Wang, Shunwei Zhang, Zicheng Zhu. A dataset on inventory and geographical distributions of wild vascular plants in Hainan Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 23067-. |
| [12] | Shiyu Li, Yiqi Zhang, Pu Zou, Zulin Ning, Jingping Liao. Ex situ conservation of plant diversity status and suggestions for the development of botanical gardens in Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22647-. |
| [13] | Hao Wu, Yurong Yu, Jiayu Wang, Yuanbo Zhao, Yafei Gao, Xiaoling Li, Guijun Bu, Dan Xue, Lin Wu. Lower water table increase shrub plant diversity and biomass but decrease soil organic carbon content: A case study of oligotrophic peatland in the Southwestern Hubei Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22600-. |
| [14] | Yixin Jiang, Yingying Shi, Shuo Gao, Supen Wang. The impact of anthropogenic noise, artificial light at night and road kills on amphibians [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22427-. |
| [15] | Cui Xiao, Bing Liu, Chaoran Wu, Jinshuang Ma, Jianfei Ye, Xiaofei Xia, Qinwen Lin. A dataset on inventory and geographical distributions of vascular plants in Beijing, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 22064-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()