



Biodiv Sci ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (1): 24-31. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.08092 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.08092
Special Issue: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jie Ji, Yanxuan Zhang( ), Xia Chen, Jianzhen Lin, Li Sun
), Xia Chen, Jianzhen Lin, Li Sun
Received:2011-06-07
Accepted:2011-09-13
Online:2012-01-20
Published:2012-02-14
Contact:
Yanxuan Zhang
Jie Ji, Yanxuan Zhang, Xia Chen, Jianzhen Lin, Li Sun. The effect of repeated release of the predatory mite Neoseiulus(Amblyseius) cucumeris on arthropod communities in citrus ecosystems[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(1): 24-31.
Fig. 1 The schematic diagram of the experimental design for studying the species composition and diversity of arthropod community of different management orchard in Mawei and Jin’an citrus experimental field of Fuzhou, China. There were four replicates in every orchard, and there were five experimental plots in every replicate.
| 马尾试验区 Mawei citrus experimental field | 晋安试验区 Jin’an citrus experimental field | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生防园 Biocontrol orchard | 自然园 Natural orchard | 化防园 Chemical control orchard | 生防园 Biocontrol orchard | 自然园 Natural orchard | 化防园 Chemical control orchard | ||
| 同翅目 Homoptera | 27 | 28 | 24 | 29 | 32 | 28 | |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 22 | 16 | 21 | 31 | 32 | 29 | |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 19 | 16 | 11 | 18 | 19 | 18 | |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 32 | 27 | 29 | 24 | 23 | 23 | |
| 双翅目 Diptera | 49 | 43 | 48 | 32 | 33 | 32 | |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 26 | 24 | 23 | 38 | 40 | 38 | |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 12 | 7 | 7 | 21 | 16 | 20 | |
| 缨翅目 Thysanoptera | 2 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 脉翅目 Neuroptera | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 竹节虫目 Phasmida | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 蜈蚣目 Scolopendromorpha | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 螳螂目 Mantedea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 蜻蜓目 Odonata | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 弹尾目 Collembola | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 啮虫目 Psocoptera | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 蜚蠊目 Blattodea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 盲蛛目 Opiliones | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 31 | 34 | 29 | 38 | 35 | 38 | |
| 蝎目 Scorpiones | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 伪蝎目 Pseudoscorpionida | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| 缨尾目 Thysanura | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 等足目 Isopoda | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 绒螨目 Trombidiformes | 12 | 12 | 11 | 15 | 14 | 13 | |
| 中气门目 Mesostigmata | 5 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 9 | 10 | |
| 疥螨目 Sarcoptiformes | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 蜱目 Ixodida | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 合计 Total | 252 | 230 | 221 | 276 | 270 | 266 | |
Table 1 The species number of arthropods in different management orchard of Mawei and Jin’an citrus experimental field
| 马尾试验区 Mawei citrus experimental field | 晋安试验区 Jin’an citrus experimental field | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生防园 Biocontrol orchard | 自然园 Natural orchard | 化防园 Chemical control orchard | 生防园 Biocontrol orchard | 自然园 Natural orchard | 化防园 Chemical control orchard | ||
| 同翅目 Homoptera | 27 | 28 | 24 | 29 | 32 | 28 | |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 22 | 16 | 21 | 31 | 32 | 29 | |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 19 | 16 | 11 | 18 | 19 | 18 | |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 32 | 27 | 29 | 24 | 23 | 23 | |
| 双翅目 Diptera | 49 | 43 | 48 | 32 | 33 | 32 | |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 26 | 24 | 23 | 38 | 40 | 38 | |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 12 | 7 | 7 | 21 | 16 | 20 | |
| 缨翅目 Thysanoptera | 2 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 脉翅目 Neuroptera | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 竹节虫目 Phasmida | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 蜈蚣目 Scolopendromorpha | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 螳螂目 Mantedea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 蜻蜓目 Odonata | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 弹尾目 Collembola | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 啮虫目 Psocoptera | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 蜚蠊目 Blattodea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 盲蛛目 Opiliones | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 31 | 34 | 29 | 38 | 35 | 38 | |
| 蝎目 Scorpiones | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 伪蝎目 Pseudoscorpionida | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| 缨尾目 Thysanura | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 等足目 Isopoda | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 绒螨目 Trombidiformes | 12 | 12 | 11 | 15 | 14 | 13 | |
| 中气门目 Mesostigmata | 5 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 9 | 10 | |
| 疥螨目 Sarcoptiformes | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 蜱目 Ixodida | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 合计 Total | 252 | 230 | 221 | 276 | 270 | 266 | |
| 试验区 Experimental field | 处理 Managements | 物种数 Species number (S) | 个体数 Individual number (N) | 多样性指数 Diversity index (H') | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (E) | 优势度指数 Dominance index (C) | 群落稳定性 Community stability Ss/St |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马尾 Mawei | 生防园 Biocontrol orchard | 249.77a | 70,252.96b | 1.6188a | 0.2928a | 0.3381c | 0.0036 |
| 化防园 Chemical control orchard | 220.58b | 75,289.12a | 1.0833c | 0.2007c | 0.5631a | 0.0029 | |
| 自然园 Natural orchard | 229.27b | 64,429.89c | 1.3349b | 0.2455b | 0.4202b | 0.0036 | |
| 晋安 Jin’an | 生防园 Biocontrol orchard | 277.68a | 60,762.62a | 1.0216b | 0.1817ab | 0.6917a | 0.0046 |
| 化防园 Chemical control orchard | 267.84b | 63,991.68a | 0.8660c | 0.1548b | 0.7619a | 0.0042 | |
| 自然园 Natural orchard | 270.36b | 51,213.27b | 1.3083a | 0.2337a | 0.6101b | 0.0053 |
Table 2 Community diversity of arthropods in different management orchard of Mawei and Jin’an citrus experimental field after Neoseiulus(Amblyseius) cucumeris was released.
| 试验区 Experimental field | 处理 Managements | 物种数 Species number (S) | 个体数 Individual number (N) | 多样性指数 Diversity index (H') | 均匀度指数 Evenness index (E) | 优势度指数 Dominance index (C) | 群落稳定性 Community stability Ss/St |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马尾 Mawei | 生防园 Biocontrol orchard | 249.77a | 70,252.96b | 1.6188a | 0.2928a | 0.3381c | 0.0036 |
| 化防园 Chemical control orchard | 220.58b | 75,289.12a | 1.0833c | 0.2007c | 0.5631a | 0.0029 | |
| 自然园 Natural orchard | 229.27b | 64,429.89c | 1.3349b | 0.2455b | 0.4202b | 0.0036 | |
| 晋安 Jin’an | 生防园 Biocontrol orchard | 277.68a | 60,762.62a | 1.0216b | 0.1817ab | 0.6917a | 0.0046 |
| 化防园 Chemical control orchard | 267.84b | 63,991.68a | 0.8660c | 0.1548b | 0.7619a | 0.0042 | |
| 自然园 Natural orchard | 270.36b | 51,213.27b | 1.3083a | 0.2337a | 0.6101b | 0.0053 |
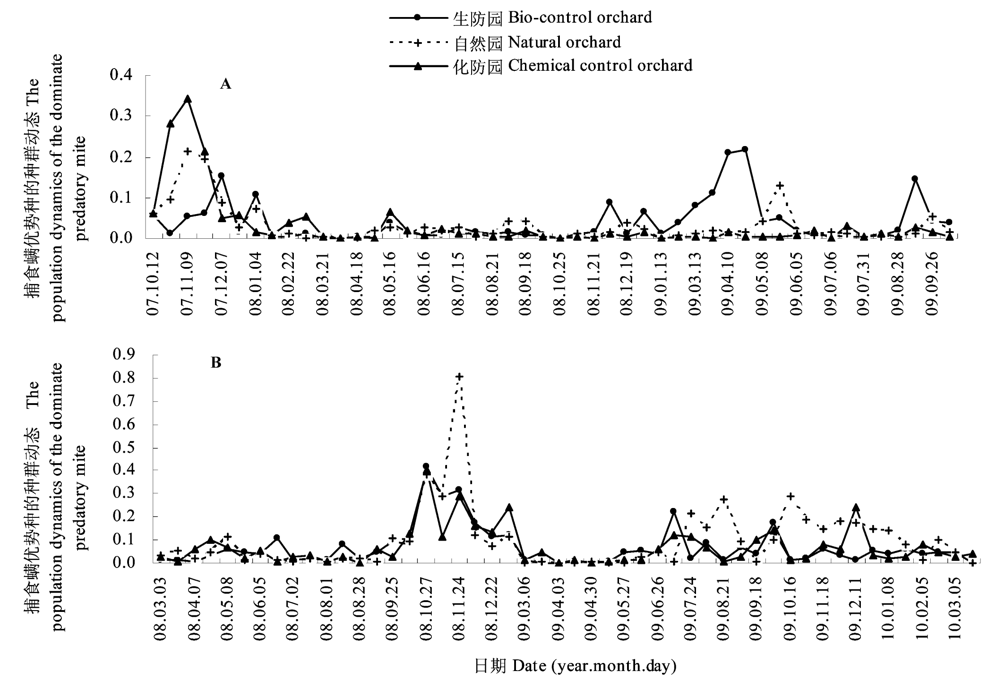
Fig. 3 The population dynamics of the dominant predatory mite in different management orchard of Mawei (A) and Jin’an (B) citrus experimental field. The dominate predatory mite of biocontrol orchard or natural orchard wasAmblyseius eharai, but that of the chemical control orchard was A. imbricatusin Mawei. And those of different management orchard was Amblyseius eharai in Jin’an. The every data in the fig. 3 was the mean of population number of the dominant predatory mite on every leaf.
| [1] | Buitenhuis RSL, Scott-Dupree C (2010) Intra-guild vs extra-guild prey: effect on predator fitness and preference of Amblyseius swirskii (Athias-Henriot) and Neoseiulus cucumeris (Oudemans)(Acari: Phytoseiidae). Bulletin of Entomological Research, 2,167-173. |
| [2] | Chen X (陈霞), Zhang YX (张艳璇), Ji J (季洁), Lin JZ (林坚贞) (2007) Acute toxicity of four insecticides against adult mite of Neoseiulus cucumeris (Oudemans). Natural Enemies of Insects (昆虫天敌), 29(2),60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] | He YR (何余容), Lü LH (吕利华), Chen KW (陈科伟) (2005) Parasitizing ability and interspecific competition of Trichogramma confusum Viggiani and T. pretiosum Riley on the eggs of Plutella xylostella (L.) in the laboratory. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 25,837-841. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Ji J (季洁), Zhang YX (张艳璇), Hong XY (洪晓月), Kang YM (康玉妹), Yu DY (余德亿), Lin JZ (林坚贞) (2004) Community structure and dynamics of arthropods in the bio-control orchard released by Amblyseius cucumeris (Oudemans) and the chemical control orchard in citrus ecosystem. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University (南京农业大学学报), 27(4),45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Lange E, Trautmann M (1994) Competitive behaviour of the predatory mite species Amblyseius andersoni (Chant) and Typhlodromus pyri (Scheuten). Erwerbsobstbau, 3,63-65. |
| [6] | Li JM (李佳敏), Lü JL (吕佳乐), Qu YF (屈云芳), Yang YY (杨琰云), Wu QH (吴千红) (2003) Effect of temperature on developmental duration of Amblyseius cucumeris. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 14,2255-2257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Li ZQ (李志强), Liang GW (梁广文), Cen YJ (岑伊静), Zeng L (曾玲) (2009) Roles of organic management in restoration of arthropod community diversity in citrus orchard. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 28,1515-1519. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Liu DG (刘德广), Xiong JJ (熊锦君), Tan BL (谭炳林), Huang MD (黄明度), Zhang RJ (张润杰) (2001) Diversity and stability analyses of arthropod community in litchi-herbage complex system. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 21,1596-1601. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Margalef R (1958) Information theory in ecology. General Systems, 3,36-71. |
| [10] | Messelink G, van Steenpaal S, van Wensveen W (2005) Typhlodromips swirskii (Athias-Henriot) (Acari: Phytoseiidae): a new predator for thrips control in greenhouse cucumber. Bulletin IOBC/wprs Bulletin, 28 (1),183-186. |
| [11] | Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 13,131-144. |
| [12] | Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature, 163,688. |
| [13] | Zhang HY (张辉元), Ma M (马明), Dong T (董铁), Liu XY (刘小勇), Zhang K (张坤), Wang FL (王发林) (2010) Biological control efficiency of Amblyseius cucumeris (Oudemans) on Panonychus ulmi (Koch). Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 21,191-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Zhang YX (张艳璇), Lin JZ (林坚贞), Ji J (季洁), Chen CP (陈传培), Lin Z (林璋) (2003) Studies on Amblyseius cucumeris Oudemans for controlling the pest mites on citrus trees. Plant Protection (植物保护), 29(2),31-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Zhang YX (张艳璇), Zhang ZQ (张智强), Yutaka S, Liu QY (刘巧云), Ji J (季洁) (2004) On the causes of mite pest outbreaks in mono- and poly-cultured moso bamboo forests. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报), 15,1161-1165. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()