



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 25382. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025382 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025382
• CITES 50th Anniversary: Integrating Science, Policy, and International Action • Previous Articles
Wenqi Wang1, Yongchuan Yang1,*( )(
)( ), Wei Chang1, Siwei Hu1, Wenbo Mu1, Yan Zeng2,3(
), Wei Chang1, Siwei Hu1, Wenbo Mu1, Yan Zeng2,3( )
)
Received:2025-09-29
Accepted:2025-12-23
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-12-26
Contact:
Yongchuan Yang
Supported by:Wenqi Wang, Yongchuan Yang, Wei Chang, Siwei Hu, Wenbo Mu, Yan Zeng. Community structure, growth characteristics, and potential resource assessment of Nardostachys jatamansi in varied habitats[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(11): 25382.
| 样地编号 Sample plot number | 经度 Longitude (°E) | 纬度 Latitude (°N) | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 地形 Topography | 土壤湿度 Soil water content (%) | 生境类型 Habitat type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HY-1 | 103.25 | 32.93 | 3,750 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 32.90 ± 2.34 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-2 | 102.60 | 33.09 | 3,539 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 26.93 ± 2.22 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-3 | 102.61 | 33.00 | 3,487 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 23.37 ± 3.32 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-4 | 102.96 | 33.08 | 3,721 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 35.9 ± 7.04 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-5 | 102.31 | 32.66 | 3,495 | 山谷洼地 Valley bottom | 39.03 ± 4.52 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-6 | 102.61 | 32.75 | 3,621 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 25.23 ± 4.24 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-7 | 102.64 | 32.68 | 3,814 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 26.13 ± 3.54 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-8 | 102.46 | 32.95 | 3,685 | 河漫滩 Floodplain | 50.43 ± 4.33 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-9 | 102.61 | 32.87 | 3,495 | 山谷洼地 Valley bottom | 46.40 ± 8.19 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-10 | 102.61 | 33.03 | 3,481 | 河漫滩 Floodplain | 55.63 ± 3.99 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-11 | 102.23 | 32.39 | 3,637 | 河漫滩 Floodplain | 48.03 ± 8.02 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-12 | 102.08 | 32.50 | 3,482 | 河漫滩 Floodplain | 50.46 ± 4.04 | 湿润 Humid |
Table 1 Field survey data sheet for Nardostachys jatamansi in Hongyuan County, Sichuan Province
| 样地编号 Sample plot number | 经度 Longitude (°E) | 纬度 Latitude (°N) | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 地形 Topography | 土壤湿度 Soil water content (%) | 生境类型 Habitat type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HY-1 | 103.25 | 32.93 | 3,750 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 32.90 ± 2.34 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-2 | 102.60 | 33.09 | 3,539 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 26.93 ± 2.22 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-3 | 102.61 | 33.00 | 3,487 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 23.37 ± 3.32 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-4 | 102.96 | 33.08 | 3,721 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 35.9 ± 7.04 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-5 | 102.31 | 32.66 | 3,495 | 山谷洼地 Valley bottom | 39.03 ± 4.52 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-6 | 102.61 | 32.75 | 3,621 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 25.23 ± 4.24 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-7 | 102.64 | 32.68 | 3,814 | 山坡坡地 Hillside | 26.13 ± 3.54 | 中生 Mesic |
| HY-8 | 102.46 | 32.95 | 3,685 | 河漫滩 Floodplain | 50.43 ± 4.33 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-9 | 102.61 | 32.87 | 3,495 | 山谷洼地 Valley bottom | 46.40 ± 8.19 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-10 | 102.61 | 33.03 | 3,481 | 河漫滩 Floodplain | 55.63 ± 3.99 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-11 | 102.23 | 32.39 | 3,637 | 河漫滩 Floodplain | 48.03 ± 8.02 | 湿润 Humid |
| HY-12 | 102.08 | 32.50 | 3,482 | 河漫滩 Floodplain | 50.46 ± 4.04 | 湿润 Humid |
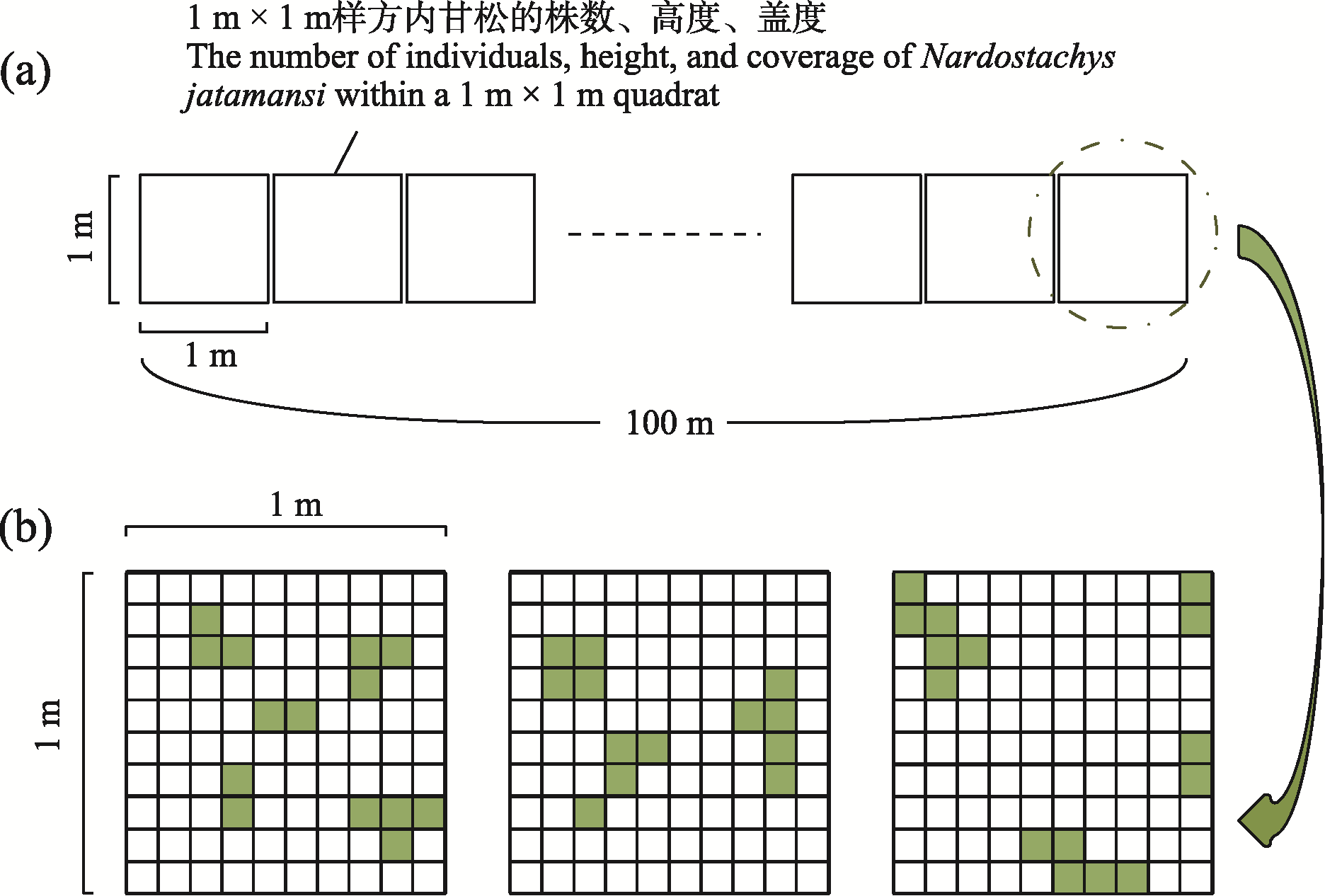
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of transect survey of Nardostachys jatamansi community (a) and its common distribution pattern within a single sample plot (b). Green grids indicate the presence of N. jatamansi, with each grid representing 1% coverage.
| 物种 Species | 频次 Count | 频率 Frequency (%) | 是否药用 Medicinal/Non-medicinal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 甘松 Nardostachys jatamansi | 36 | 3.85 | 是 Medicinal |
| 嵩草 Carex myosuroides | 36 | 3.85 | 否 Non-medicinal |
| 早熟禾 Poa annua | 34 | 3.64 | 是 Medicinal |
| 委陵菜 Potentilla chinensis | 32 | 3.42 | 是 Medicinal |
| 条叶银莲花 Anemone coelestina var. linearis | 30 | 3.21 | 是 Medicinal |
| 喜湿龙胆 Gentiana helophila | 29 | 3.10 | 否 Non-medicinal |
| 老鹳草 Geranium wilfordii | 27 | 2.89 | 是 Medicinal |
| 川西风毛菊 Saussurea dzeurensis | 26 | 2.78 | 是 Medicinal |
| 狼毒 Stellera chamaejasme | 25 | 2.67 | 是 Medicinal |
| 卵萼花锚 Halenia elliptica | 25 | 2.67 | 是 Medicinal |
| 高原唐松草 Thalictrum cultratum | 23 | 2.46 | 是 Medicinal |
| 矮金莲花 Trollius farreri | 22 | 2.35 | 是 Medicinal |
| 珠芽蓼 Bistorta vivipara | 22 | 2.35 | 是 Medicinal |
| 草玉梅 Anemone rivularis | 19 | 2.03 | 是 Medicinal |
| 高原毛茛 Ranunculus tanguticus | 19 | 2.03 | 是 Medicinal |
| 深红龙胆 Gentiana rubicunda | 18 | 1.93 | 是 Medicinal |
| 火绒草 Leontopodium leontopodioides | 17 | 1.82 | 是 Medicinal |
| 米口袋 Gueldenstaedtia verna | 16 | 1.71 | 是 Medicinal |
| 羊茅 Festuca ovina | 16 | 1.71 | 否 Non-medicinal |
| 虉草 Phalaris arundinacea | 16 | 1.71 | 是 Medicinal |
Table 2 Top 20 most frequently encountered species in natural Nardostachys jatamansi communities
| 物种 Species | 频次 Count | 频率 Frequency (%) | 是否药用 Medicinal/Non-medicinal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 甘松 Nardostachys jatamansi | 36 | 3.85 | 是 Medicinal |
| 嵩草 Carex myosuroides | 36 | 3.85 | 否 Non-medicinal |
| 早熟禾 Poa annua | 34 | 3.64 | 是 Medicinal |
| 委陵菜 Potentilla chinensis | 32 | 3.42 | 是 Medicinal |
| 条叶银莲花 Anemone coelestina var. linearis | 30 | 3.21 | 是 Medicinal |
| 喜湿龙胆 Gentiana helophila | 29 | 3.10 | 否 Non-medicinal |
| 老鹳草 Geranium wilfordii | 27 | 2.89 | 是 Medicinal |
| 川西风毛菊 Saussurea dzeurensis | 26 | 2.78 | 是 Medicinal |
| 狼毒 Stellera chamaejasme | 25 | 2.67 | 是 Medicinal |
| 卵萼花锚 Halenia elliptica | 25 | 2.67 | 是 Medicinal |
| 高原唐松草 Thalictrum cultratum | 23 | 2.46 | 是 Medicinal |
| 矮金莲花 Trollius farreri | 22 | 2.35 | 是 Medicinal |
| 珠芽蓼 Bistorta vivipara | 22 | 2.35 | 是 Medicinal |
| 草玉梅 Anemone rivularis | 19 | 2.03 | 是 Medicinal |
| 高原毛茛 Ranunculus tanguticus | 19 | 2.03 | 是 Medicinal |
| 深红龙胆 Gentiana rubicunda | 18 | 1.93 | 是 Medicinal |
| 火绒草 Leontopodium leontopodioides | 17 | 1.82 | 是 Medicinal |
| 米口袋 Gueldenstaedtia verna | 16 | 1.71 | 是 Medicinal |
| 羊茅 Festuca ovina | 16 | 1.71 | 否 Non-medicinal |
| 虉草 Phalaris arundinacea | 16 | 1.71 | 是 Medicinal |
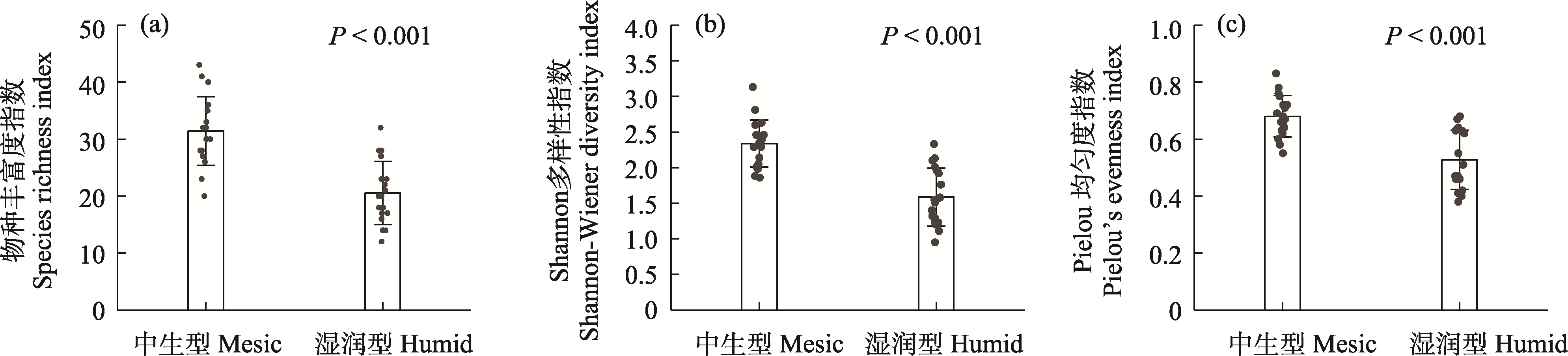
Fig. 3 Diversity characteristics of Nardostachys jatamansi communities across varied habitats. A P-value of < 0.001 indicates that the difference was statistically significant.
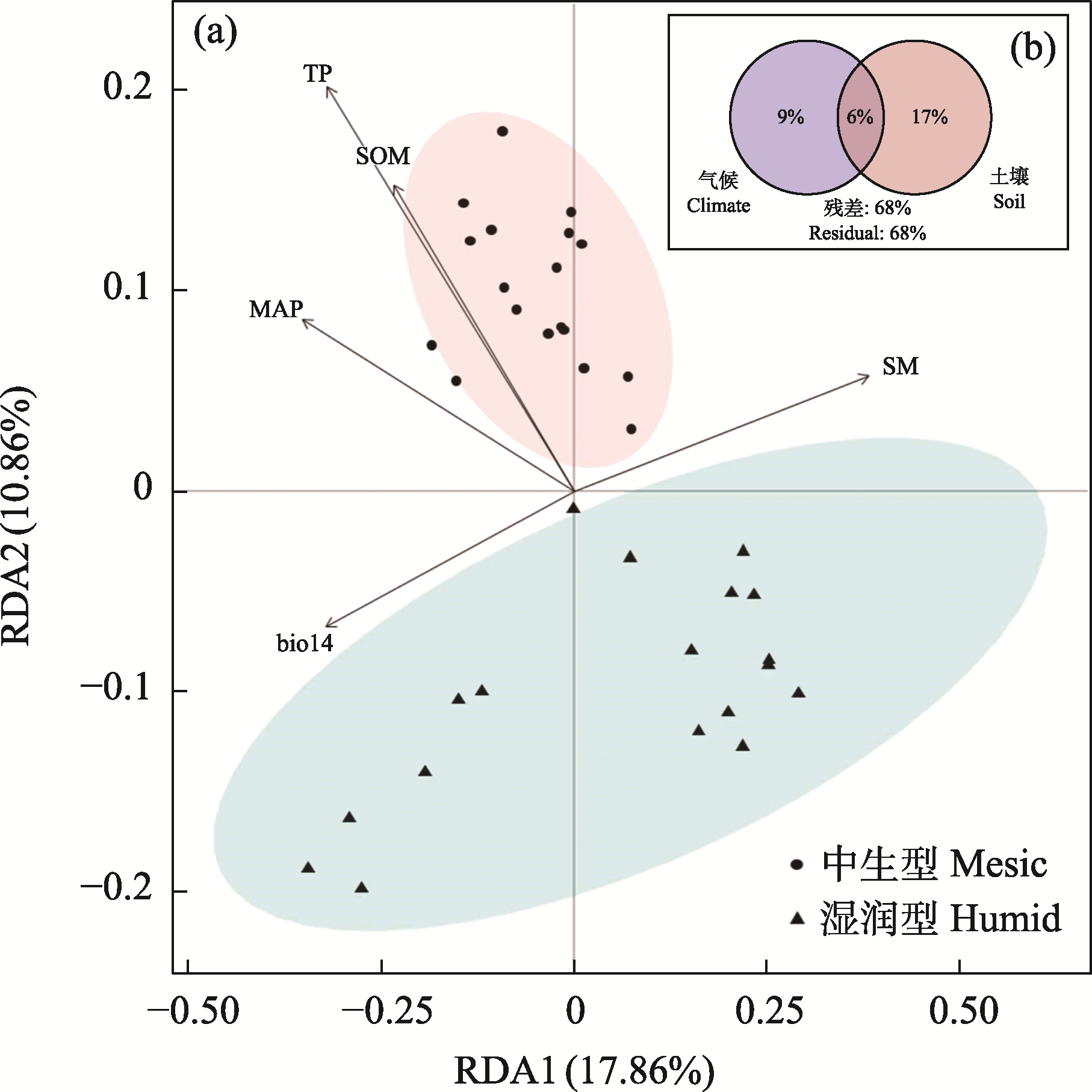
Fig. 4 RDA ranking diagram of species composition in natural Nardostachys jatamansi communities (a) and variation partitioning of environmental factors affecting species composition (b). TP, Total phosphorus; SOM, Soil organic matter; SM, Soil water content; MAP, Mean annual precipitation; bio4, Precipitation of driest month.

Fig. 5 Comparison of biomass (a), root-to-shoot ratio (b), and fresh weight to dry weight ratio (c) of Nardostachys jatamansi in varied habitats. A P-value of < 0.05 indicates that the difference was statistically significant.
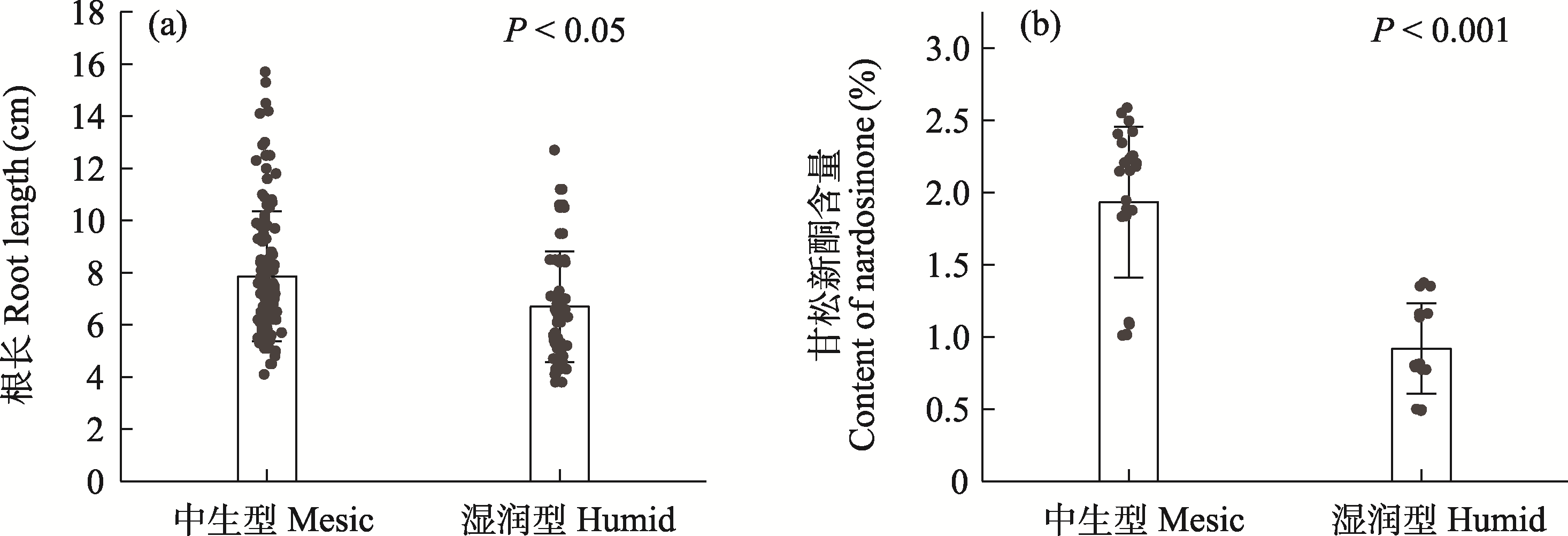
Fig. 6 Comparison of root length of Nardostachys jatamansi (a) and nardosinone content (b) in varied habitats. A P-value of < 0.05 indicates that the difference was statistically significant.
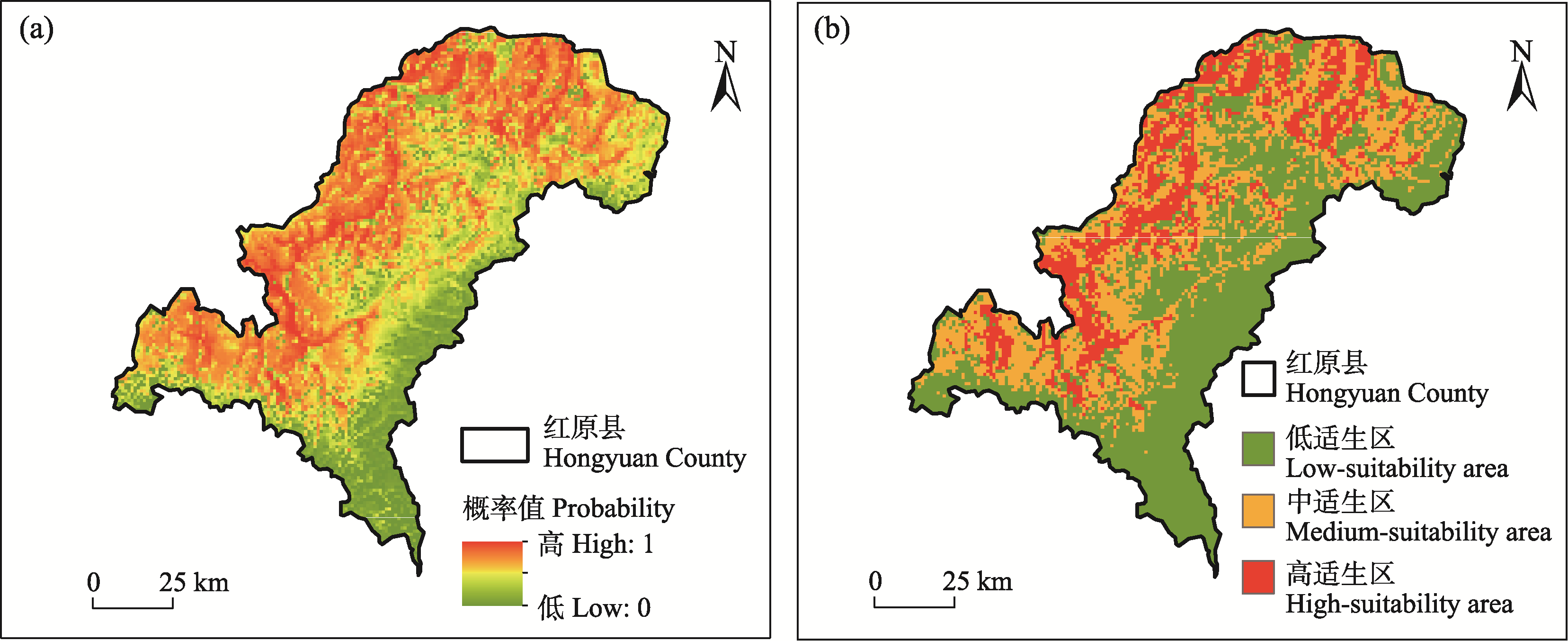
Fig. 7 Potential habitat suitability probability map (a) and potential habitat distribution map (b) of the natural Nardostachys jatamansi population in Hongyuan County
| 变量 Independent variable | 估计值 Estimate | 标准误 Std. error | t | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1389.38 | 441.78 | 3.145 | <0.001 |
| altitude | -0.20 | 0.12 | -1.691 | 0.094 |
| MAT | 291.93 | 86.42 | 3.378 | <0.001 |
| bio3 | -22.78 | 9.97 | -2.284 | 0.024 |
| bio6 | -306.33 | 67.71 | -4.524 | <0.001 |
| bio7 | -180.91 | 43.40 | -4.168 | <0.001 |
| MAP | 0.83 | 0.47 | 1.761 | 0.081 |
| aspect | -0.16 | 0.05 | -3.293 | <0.001 |
| SM | 365.24 | 263.41 | 1.387 | 0.169 |
Table 3 Multivariate linear regression equation for biomass per unit area of Nardostachys jatamansi in Hongyuan County
| 变量 Independent variable | 估计值 Estimate | 标准误 Std. error | t | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1389.38 | 441.78 | 3.145 | <0.001 |
| altitude | -0.20 | 0.12 | -1.691 | 0.094 |
| MAT | 291.93 | 86.42 | 3.378 | <0.001 |
| bio3 | -22.78 | 9.97 | -2.284 | 0.024 |
| bio6 | -306.33 | 67.71 | -4.524 | <0.001 |
| bio7 | -180.91 | 43.40 | -4.168 | <0.001 |
| MAP | 0.83 | 0.47 | 1.761 | 0.081 |
| aspect | -0.16 | 0.05 | -3.293 | <0.001 |
| SM | 365.24 | 263.41 | 1.387 | 0.169 |
| [1] |
Aarts G, Fieberg J, Matthiopoulos J (2012) Comparative interpretation of count, presence-absence and point methods for species distribution models. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 3, 177-187.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Aiello-Lammens ME, Boria RA, Radosavljevic A, Vilela B, Anderson RP (2015) spThin: An R package for spatial thinning of species occurrence records for use in ecological niche models. Ecography, 38, 541-545.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Astutik S, Pretzsch J, Kimengsi JN, Astutik S, Pretzsch J, Kimengsi JN (2019) Asian medicinal plants’ production and utilization potentials: A review. Sustainability, 11, 5483.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Bai WF, Yu L, Li JH, Nie DL, Yan JW, Wu SZ, Li JC, Xiao JD (2021) Structure and species diversity of Cerasus community in Dawei Mountain of Hunan, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32, 1201-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 柏文富, 禹霖, 李建挥, 聂东伶, 严佳文, 吴思政, 李继承, 肖金顶 (2021) 大围山樱属植物群落结构及物种多样性. 应用生态学报, 32, 1201-1212.]
DOI |
|
| [5] |
Bose B, Kumaria S, Choudhury H, Tandon P (2016) Assessment of genetic homogeneity and analysis of phytomedicinal potential in micropropagated plants of Nardostachys jatamansi, a critically endangered, medicinal plant of alpine Himalayas. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 124, 331-349.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Chai TT, Li ZW, Zhang L, Qin JM (2019) Multivariate statistical regression model to forecast the break-up date of Mohe Station. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 49(4), 124-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 柴婷婷, 李卓伟, 张丽, 秦建敏 (2019) 多元线性回归模型的漠河站开河预测. 数学的实践与认识, 49(4), 124-128.] | |
| [7] | Chauhan HK (2021) Nardostachys jatamansi. The lUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021. e. T50126627A88304158. (accessed on 2025-09-23) |
| [8] |
Chauhan HK, Bisht AK, Bhatt ID, Bhatt A, Gallacher D, Santo A (2018) Population change of Trillium govanianum (Melanthiaceae) amid altered indigenous harvesting practices in the Indian Himalayas. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 213, 302-310.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Chauhan HK, Oli S, Bisht AK, Meredith C, Leaman D (2021) Review of the biology, uses and conservation of the critically endangered endemic Himalayan species Nardostachys jatamansi (Caprifoliaceae). Biodiversity and Conservation, 30, 3315-3333.
DOI |
| [10] | Chauhan RS, Nautiyal MC (2005) Commercial viability of cultivation of an endangered medicinal herb Nardostachys jatamansi at three different agroclimatic zones. Current Science, 89, 1481-1488. |
| [11] | Chauhan RS, Nautiyal MC, Kumar A (2011) Analysis of variabilities in populations of Nardostachys jatamansi DC. in Garhwal Himalaya, India. International Journal of Plant Breeding and Genetics, 3, 190-194. |
| [12] | Chen YL, Dai W, Ma JH, Ma L (2019) Thoughts on the status quo and countermeasures of the development of Chinese-Tibetan medicine industry in Hongyuan County. South China Agriculture, 13(28), 56-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈玉林, 戴维, 马家骅, 马林 (2019) 红原县中藏药产业发展现状及对策思考. 南方农业, 13(28), 56-59.] | |
| [13] | China Pharmacopoeia Committee (2020) Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Part 1. China Medical Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家药典委员会 (2020) 中华人民共和国药典(一部). 中国医药科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [14] | Deng YC, Jiang Z, Zhu YQ, Yang CT, Cheng MJ, Wu WD, Tang WQ, Rong J, He PP, Li HQ (2023) Countermeasures of soil testing and fertilization for artificially planted gramineous grasses in pastoral areas of northwest Sichuan—A case study of Hongyuan County, Sichuan Province. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, (2), 52-56. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邓榆川, 姜臻, 朱永群, 杨春桃, 程明军, 伍文丹, 唐玮琦, 荣璟, 何佩佩, 李洪泉 (2023) 川西北牧区人工种植禾本科牧草测土施肥对策——以四川省红原县为例. 草学, (2), 52-56.] | |
| [15] | Department of Forests and Soil Conservation Forestry Complex (2019) National Quota Fixation for Jatamansi (Nardostachys jatamansi DC) Ensuring Sustainable Management and Conservation in Nepal. https://cites.org/sites/default/files/eng/com/sc/71/E-SC71-12-A5.pdf. (accessed on 2025-09-23) |
| [16] | Department of Plant Resources (2025) Non-Detriment Findings for Nardostachys jatamansi (D. Don) DC. from Nepal. https://cites.org/sites/default/files/ndf_material/NDF%20Nardostachys%20jatamansi.pdf. (accessed on 2025-09-23) |
| [17] |
Dhiman N, Bhattacharya A (2020) Nardostachys jatamansi (D. Don) DC. Challenges and opportunities of harnessing the untapped medicinal plant from the Himalayas. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 246, 112211.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Farooquee NA, Saxena KG (1996) Conservation and utilization of medicinal plants in high hills of the central Himalayas. Environmental Conservation, 23, 75-80.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Fu WK (1993) History of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Bashu Publication, Chengdu, China. (in Chinese) |
| [ 傅维康 (1993) 中药学史. 巴蜀书社, 成都.] | |
| [20] |
Ghimire SK, Gimenez O, Pradel R, McKey D, Aumeeruddy-Thomas Y (2008) Demographic variation and population viability in a threatened Himalayan medicinal and aromatic herb Nardostachys grandiflora: Matrix modelling of harvesting effects in two contrasting habitats. Journal of Applied Ecology, 45, 41-51.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Ghimire SK, McKey D, Aumeeruddy-Thomas Y (2005) Conservation of Himalayan medicinal plants: Harvesting patterns and ecology of two threatened species, Nardostachys grandiflora DC. and Neopicrorhiza scrophulariiflora (Pennell) Hong. Biological Conservation, 124, 463-475.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Hamilton AC (2004) Medicinal plants, conservation and livelihoods. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13, 1477-1517.
DOI |
| [23] | He BH, Zhong ZC (2003) Study on variation dynamics of modular population of Ginkgo biloba under different conditions of environmental stress. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University, 25, 7-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何丙辉, 钟章成 (2003) 不同环境胁迫下银杏构件种群药用成分变化的研究. 西南农业大学学报, 25, 7-10.] | |
| [24] | Huai HY, Liu AZ (2013) Effects of selective harvesting on target plants and the related ecosystems. Plant Diversity and Resources, 35, 180-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 淮虎银, 刘爱忠 (2013) 选择性采集对植物及生态系统的效应. 植物分类与资源学报, 35, 180-186.] | |
| [25] | Jin Q, Li Y, Xiao F, Ke YX, Liu Z, Liu Y (2018) Multidimensional statistical analysis of inorganic elements in above ground parts of Nardostachs jatamansi from different producing areas and different elevations. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 24(13), 54-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 金乾, 李莹, 肖芳, 克永霞, 刘哲, 刘圆 (2018) 不同产地、不同海拔地区的甘松地上部分无机元素的多维统计分析. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 24(13), 54-61.] | |
| [26] | Kabacoff RI (2015) R in Action: Data Analysis and Graphics with R, 2nd edn. Manning Publications, Greenwich. |
| [27] |
Lei GC (2025) Goals of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and solutions by China’s Biosphere Reserve Network. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 40, 1536-1545. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 雷光春 (2025) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》目标及中国生物圈保护区网络解决方案. 中国科学院院刊, 40, 1536-1545.] | |
| [28] | Li Q (2011) Species accumulation curves and its application. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 48, 1882-1888. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李巧 (2011) 物种累积曲线及其应用. 应用昆虫学报, 48, 1882-1888.] | |
| [29] | Li YF, Li S, Zhao WJ, Li J, Yang XW, Jia GF, Chen YH (2023) Content analysis and antioxidant activity of chemical components in Nardostachys jatamansi DC. from different sources. Journal of Chengdu Medical College, 18, 545-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李雨繁, 李双, 赵文吉, 黎剑, 杨兴无, 贾国夫, 陈宇航 (2023) 不同来源甘松化学成分含量分析与抗氧化活性研究. 成都医学院学报, 18, 545-548.] | |
| [30] | Li YM, Liu GL, Qiao J, Liu S, Zhang Y, Qin ZX, Liu Y (2015) Simultaneous determination of chlorogenic acid and nardosinone in Nardostachys chinensis DC. from different producing areas by HPLC. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 32(6), 27-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李艳忙, 刘国林, 乔晶, 刘爽, 张瑜, 秦振娴, 刘勇 (2015) HPLC同时测定不同产地甘松中绿原酸和甘松新酮的含量. 中医药信息, 32(6), 27-30.] | |
| [31] | Liao HX, Zhou T, Chen BM, Chen EJ, Zhang HJ, Peng SL (2021) Ecological control of exotic invasive plants. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 60(4), 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 廖慧璇, 周婷, 陈宝明, 陈恩健, 张海杰, 彭少麟 (2021) 外来入侵植物的生态控制. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 60(4), 1-11.] | |
| [32] | Liu W, Yin DX, Li N, Hou XG, Wang DM, Li DW, Liu JJ (2016) Influence of environmental factors on the active substance production and antioxidant activity in Potentilla fruticosa L. and its quality assessment. Scientific Reports, 6, 28591. |
| [33] | Liu YM, Dong XZ, Li XY, Zhu ZM, Li YY (2024) Spatial pattern of degraded alpine communities invaded by Stellera chamaejasme and environmental interpretation in the central Qilian Mountain. Journal of Plant Protection, 51, 1248-1258. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘咏梅, 董幸枝, 李潇雨, 朱志梅, 李艳莹 (2024) 祁连山中段狼毒入侵退化草甸群落格局及环境解释. 植物保护学报, 51, 1248-1258.] | |
| [34] |
Lou KE, Qu WJ, Wang L, Wang X, Gao YG, Zhang B, You WX, Yang XG (2024) Root architecture characteristics of four dominant annual herbs in Tengger Desert, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 35, 3015-3022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 楼科尔, 曲文杰, 王磊, 王兴, 郜永贵, 张波, 尤万学, 杨新国 (2024) 腾格里沙漠地区4种优势一年生草本植物根构型特征. 应用生态学报, 35, 3015-3022.]
DOI |
|
| [35] | Maitinuer MWLJ, Dong TX, Zhan HQ, Aisa AJAKBE (2017) Analysis of HPLC fingerprints and determination of nardosinone of Nardostachyos Radix et Rhizoma from Nardostachys jatamansi DC. Herald of Medicine, 36, 1298-1302. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 买吾兰江·买提努尔, 董婷霞, 詹华强, 阿吉艾克拜尔·艾萨, (2017) 甘松药材高效液相色谱指纹图谱及甘松新酮含量测定. 医药导报, 36, 1298-1302.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Mulliken T, Crofton P (2008) Review of the status, harvest, trade and management of seven Asian CITES-listed medicinal and aromatic plant species. BfN-Skripten, 227. |
| [37] | Nautiyal BP, Chauhan R, Prakash V, Purohit H, Nautiyal MC (2003) Population studies for the evaluation of germplasm and threat status of the alpine medicinal herb Nardostachys jatamansi. Plant Genetic Resources Newsletter, 136, 34-39. |
| [38] | Niu TZ, Wang YL, Hou QW, Xiao SX, Luo HM, Liu AK (2022) Correlation between functional components in Codonopsis pilosula roots and soil factors. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 28(11), 164-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 牛天增, 王玉龙, 侯沁文, 肖淑贤, 骆红梅, 刘阿克 (2022) 党参功效成分含量与土壤因子相关性分析. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 28(11), 164-172.] | |
| [39] |
Olsen CS, Larsen HO (2003) Alpine medicinal plant trade and Himalayan Mountain livelihood strategies. The Geographical Journal, 169, 243-254.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Özüpek B, Pekacar S, Orhan DD (2023) Evaluation of phytochemical contents and biological activities of Salvia offcinalis and Salvia triloba grown with organic farming. Fabad Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 48, 125-138. |
| [41] | Pei XJ (2024) Mechanisms of geological environment disturbance and ecological restoration technical systems for major engineering projects on the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Engineering Geology, 32, 1737-1758. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 裴向军 (2024) 青藏高原重大工程地质环境扰损机制及生态修复技术体系. 工程地质学报, 32, 1737-1758.] | |
| [42] |
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Pitman NCA, Jørgensen PM (2002) Estimating the size of the world’s threatened flora. Science, 298, 989.
PMID |
| [44] |
Rai LK, Prasad P, Sharma E (2000) Conservation threats to some important medicinal plants of the Sikkim Himalaya. Biological Conservation, 93, 27-33.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Rehman T, Ahmad S (2019) Nardostachys chinensis Batalin: A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. Phytotherapy Research, 33, 2622-2648.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Shao FF, Chen YH, Cui Y, Liu HB, Yang LP, Chen XZ, Huang WJ, Luo FL (2023) Plant community characteristics under low and high soil moisture conditions in typical marsh wetlands in northern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 8692-8703. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邵非凡, 陈禹含, 崔圆, 刘华兵, 杨梨萍, 陈炫铮, 黄文军, 罗芳丽 (2023) 北方典型沼泽湿地高低土壤水分下植物群落特征. 生态学报, 43, 8692-8703.] | |
| [47] | Sun J, Du Z, Lin YZ, Wang J (2023) Inversion of aboveground biomass of grassland on the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau combined with Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data. Pratacultural Science, 40, 1977-1987. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙剑, 杜忠, 林用智, 王杰 (2023) 联合Sentinel-1与Sentinel-2数据的青藏高原东缘草地地上生物量反演. 草业科学, 40, 1977-1987.] | |
| [48] | Sun J, Weng LL, Xiao CP, Zhou XL, Jiang YX (2021) Effects of drought stress on accumulation of three sesquiterpenoids and gene expression of key enzymes in biosynthesis of Atractylodes chinensis. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 44, 812-817. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙金, 翁丽丽, 肖春萍, 周秀丽, 姜雨昕 (2021) 干旱胁迫对北苍术3种倍半萜类成分积累及生物合成关键酶基因表达的影响. 中药材, 44, 812-817.] | |
| [49] | Tang SQ, Suo ZW, Lai ZS, Shi YT, Zhou XQ, Xue MX, Li XJ (2023) Community structural characteristics and species diversity of endangered medicinal plant Striga asiatica. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 46, 2958-2963. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐思琪, 索宗武, 赖政松, 施咏滔, 周秀芹, 薛梦鑫, 李小军 (2023) 濒危药用植物独脚金群落结构特征及物种多样性. 中药材, 46, 2958-2963.] | |
| [50] | Tang XF, Liu DM, Wan T, Xi H, Tu WG, Li YD, Yang YC (2013) Research on soil characteristics of alpine desertification grassland and treatment model in Hongyuan County, northwest Sichuan. Sichuan Environment, 32(6), 11-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐学芳, 刘冬梅, 万婷, 席欢, 涂卫国, 李裕东, 杨一川 (2013) 川西北高寒草地沙化土壤特征及治理模式探讨——以阿坝州红原县为例. 四川环境, 32(6), 11-15.] | |
| [51] | Ved D, Saha D, Ravikumar K, Haridasan K (2015) Nardostachys jatamansi. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015. e. T50126627A50131395. (accessed on 2025-09-23) |
| [52] | Wang JL, Zhong ZM, Wang ZH, Yu CQ, Zhang XZ, Hu XX, Shen ZX, Daci ZG (2014) Distribution characteristics and influence factors of vegetation phosphorus content of alpine grassland ecosystem in Qinhai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, (1), 27-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 王建林, 钟志明, 王忠红, 余成群, 张宪洲, 胡兴祥, 沈振西, 大次卓嘎 (2014) 青藏高原高寒草原生态系统植被磷含量分布特征及其影响因素. 草地学报, (1), 27-38.]
DOI |
|
| [53] | Wang L, Hu JM, Song CC, Yang T (2008) Influences of water gradients on the aboveground biomass of a typical wetland plant (Calamagrostis angustifolia) in the Sanjiang Plain. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 17(4), 19-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王丽, 胡金明, 宋长春, 杨涛 (2008) 水分梯度对三江平原典型湿地植物小叶章地上生物量的影响. 草业学报, 17(4), 19-25.] | |
| [54] | Wang LN, Gesang Q, Luo JF, Wu XL, Rebi A, You YG, Zhou JX (2024) Drivers of plant diversification along an altitudinal gradient in the alpine desert grassland, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Global Ecology and Conservation, 53, e02987. |
| [55] | Wang M, Gao XH, Chen SY, Feng QS, Liang TG (2015) The land use classification based on Landsat 8 remote sensing image—A case study of Anqu demonstration community in Hongyuan County of Sichuan Province. Pratacultural Science, 32, 694-701. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王敏, 高新华, 陈思宇, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚 (2015) 基于Landsat 8遥感影像的土地利用分类研究——以四川省红原县安曲示范区为例. 草业科学, 32, 694-701.] | |
| [56] |
Wang M, Yang TT, Rao Y, Wang ZM, Dong XQ, Zhang LH, Han LF, Zhang Y, Wang T, Zhu Y, Gao XM, Li TX, Wang HY, Xu YT, Wu HH (2021) A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and the analytical methods of the genus Nardostachys. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 280, 114446.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Wang XF, Yao WJ, Feng XM, Jia ZX, Zhang XR, Ma JH, Zhou JT, Tu Y, Sun ZC (2023) Changes and driving factors of ecosystem services supply and demand on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 6968-6982. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王晓峰, 尧文洁, 冯晓明, 贾子续, 张欣蓉, 马嘉豪, 周继涛, 涂又, 孙泽冲 (2023) 青藏高原生态系统服务供需变化及其驱动因素. 生态学报, 43, 6968-6982.] | |
| [58] | Wangchuk S, Shacha N, Gyeltshen N, Wangmo K, Dukpa K, Sangay, Tshering T, Tshering D (2025) Non-Detrimental Findings of Nardostachys jatamansi (D. Don) DC. https://cites.org/sites/default/files/ndf_material/NJ_NDF_Web.pdf. (accessed on 2025-09-23) |
| [59] | Xu L (2001) Cultivation of Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plants. Guizhou Science and Technology Publishing House, Guiyang. (in Chinese) |
| [ 徐良 (2001) 中药栽培学. 贵州科技出版社, 贵阳.] | |
| [60] | Yang YC, Wang EH, Wang JQ, Dang YN, Sun ZZ, An L, Liu TT, Ma CD (2022) The history of Chinese medicine Nardostachyos Radix et Rhizoma. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 31(14), 45-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨祎辰, 王二欢, 王继强, 党艳妮, 孙珍珍, 安莉, 刘腾恬, 马存德 (2022) 中药甘松的历史沿革. 中国民族民间医药, 31(14), 45-52.] | |
| [61] | Yu SL, Ye X, Jia GF, He ZJ, Sun P, Zhang CB, Zhao WJ (2021) Nardostachys jatamansi, a medicinal plant from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: A review. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 27(19), 243-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于素玲, 叶霄, 贾国夫, 何正军, 孙佩, 张昌兵, 赵文吉 (2021) 青藏高原药用植物甘松研究进展. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 27(19), 243-250.] | |
| [62] | Zhang JT (2018) Quantitative Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张金屯 (2018) 数量生态学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [63] | Zhang JT, Zhao FX, Chen JH, Li Y, Sun J (2023) Correlations of species diversity and biomass with environmental factors in alpine grasslands across the Qingzang Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 40, 616-626. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张锦涛, 赵峰侠, 陈俊合, 李洋, 孙建 (2023) 青藏高原不同类型高寒草地物种多样性与生物量的关系及影响要素. 草业科学, 40, 616-626.] | |
| [64] | Zhang MJ, Chen LH, Hu XW, Xu R, Zhang J (2015) Effects of water and fertilizer on growth and photosynthetic pigments of Puelia sinense. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 24(5), 75-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 张明锦, 陈良华, 胡相伟, 徐睿, 张健 (2015) 水肥耦合对巨能草生长和光合色素的影响. 草业学报, 24(5), 75-83.]
DOI |
|
| [65] | Zhang SZ (2014) Effect of drought stress on growing development and physiological characteristics of Pennisetum setaceum. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 29, 752-756. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张苏州 (2014) 干旱胁迫对‘紫叶’狼尾草生长发育及生理特性的影响. 福建农业学报, 29, 752-756.] | |
| [66] | Zhang X, Feng HW, Wang J, Lin L, Wang YH (2024) Ethnobotanical survey and research on bsang plants in Xizang Autonomous Region. Guihaia, 44, 1961-1975. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张雄, 冯浩文, 王瑾, 蔺蕾, 王雨华 (2024) 西藏煨桑植物的民族植物学调查研究. 广西植物, 44, 1961-1975.] | |
| [67] | Zhao JR, Wang PS, Gou Y, Zeng Y, Jin XM, Liu G, Qimei LM, Zhou JQ (2025) Prediction of the near-modern and future potential distribution of Poa pratensis L. in response to climate change based on the MaxEnt model. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 33, 2992-3002. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 赵佳芮, 王鹏森, 苟扬, 曾园, 金雪梅, 刘刚, 其美拉姆, 周冀琼 (2025) 基于MaxEnt模型预测近现代和未来草地早熟禾的适宜分布区. 草地学报, 33, 2992-3002.]
DOI |
|
| [68] | Zheng DS, Liu QJ (2023) Effects of environmental factors on forest community distribution in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve of northeastern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 45(8), 57-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑东升, 刘琪璟 (2023) 环境因子对长白山自然保护区森林群落分布的影响. 北京林业大学学报, 45(8), 57-64.] | |
| [69] | Zhou CL, Lin L, Peng CJ, Li YK, Cao GM (2020) Differentiation characteristics of plant functional groups in alpine Kobresia meadow under different succession states. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 55(1), 136-144, 152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周春丽, 林丽, 朋措吉, 李以康, 曹广民 (2020) 不同演替状态下高寒嵩草草甸植物功能群分异特征. 甘肃农业大学学报, 55(1), 136-144, 152.] | |
| [70] | Zhu GL, Li J, Wei XH, He NP (2017) Longitudinal patterns of productivity and plant diversity in Tibetan alpine grasslands. Journal of Natural Resources, 32, 210-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 朱桂丽, 李杰, 魏学红, 何念鹏 (2017) 青藏高寒草地植被生产力与生物多样性的经度格局. 自然资源学报, 32, 210-222.]
DOI |
| [1] | Xinbo Hou, Xiuhai Zhao, Huaijiang He, Chunyu Zhang, Juan Wang, Xueying Ren, Xinna Zhang. Responses of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere microbial communities to the soil carbon and nitrogen in Quercus mongolica pure forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(7): 25119-. |
| [2] | Zhengdong Pan, Xirong Lin, Hua Xue, Zhiying Hu, Hongyi Guo, Ya Zhang, Enuo Wu, Wenqiao Tang. Fish species diversity background and community structure in the main inland water bodies of Shanghai [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24290-. |
| [3] | Zhang Mingyi, Wang Xiaomei, Zheng Yanxin, Wu Nan, Li Donghao, Fan Enyuan, Li Na, Shan Xiujuan, Yu Tao, Zhao Chunnuan, Li Bo, Xu Shuai, Wu Yuping, Ren Liqun. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [4] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [5] | Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [6] | Jihong Huang, Erfan Akberjan, Ruiming Cheng, Wendong Wang, Yue Xu, Jie Yao, Yi Ding. Dynamics of the Picea schrenkiana community in the west Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang and their influencing factors [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(11): 25275-. |
| [7] | Zichen Hong, Yuanguang Yang, Xinhao Huang, Zi Wang, Xiao Zheng, Xu Zhou, Yan Zhou, Shipin Chen, Wenjun Lin. Changes and driving mechanism of biomass in evergreen broad-leaved forests in Wuyishan National Park [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(11): 25181-. |
| [8] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [9] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [10] | Yanmei Ni, Li Chen, Zhiyuan Dong, Debin Sun, Baoquan Li, Xumin Wang, Linlin Chen. Community structure of macrobenthos and ecological health evaluation in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta wetland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [11] | Jiaxin Wei, Zhiguo Jiang, Linsen Yang, Huanhuan Xiong, Jiaojiao Jin, Fanglin Luo, Jiehua Li, Hao Wu, Yaozhan Xu, Xiujuan Qiao, Xinzeng Wei, Hui Yao, Huiliang Yu, Jingyuan Yang, Mingxi Jiang. Community composition and structure in a 25 ha mid-subtropical mountain deciduous broad-leaved forest dynamics plot in Shennongjia, Hubei, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [12] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [13] | Qingqing Du, Siyuan Ren, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, Yan Zhu. Factors affecting the productivity of sapling and adult trees in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [14] | Xingyu Wang, Jinghui Meng, Siyuan Ren, Yan Zhu. Relationship between biodiversity and aboveground biomass in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [15] | Jiayi Feng, Juyu Lian, Yujun Feng, Dongxu Zhang, Honglin Cao, Wanhui Ye. Effects of vertical stratification on community structure and functions in a subtropical, evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Dinghushan National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn