



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 25181. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025181 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025181
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zichen Hong1, Yuanguang Yang1, Xinhao Huang1, Zi Wang1( ), Xiao Zheng2, Xu Zhou2, Yan Zhou3, Shipin Chen1(
), Xiao Zheng2, Xu Zhou2, Yan Zhou3, Shipin Chen1( ), Wenjun Lin1,*(
), Wenjun Lin1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2025-05-16
Accepted:2025-10-20
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-12-26
Contact:
Wenjun Lin
Zichen Hong, Yuanguang Yang, Xinhao Huang, Zi Wang, Xiao Zheng, Xu Zhou, Yan Zhou, Shipin Chen, Wenjun Lin. Changes and driving mechanism of biomass in evergreen broad-leaved forests in Wuyishan National Park[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(11): 25181.
| 指标 Index | 范围 Range | 平均值 Mean | 标准偏差 SD | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构多样性 Structural diversity | ||||
| 胸径Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index of DBH (H°d) | 0.58-1.83 | 0.84 | 0.14 | 16.43 |
| 胸径Simpson多样性指数 Simpson diversity index of DBH (Dd) | 0.05-0.93 | 0.70 | 0.15 | 21.62 |
| 胸径标准偏差 Standard deviation of DBH (DSD) | 2.37-16.86 | 6.86 | 1.98 | 28.90 |
| 胸径Gini系数 Gini index of DBH (CG) | 0.15-0.92 | 0.78 | 0.10 | 12.50 |
| 物种多样性 Species diversity | ||||
| Margalef物种丰富度指数 Margalef species richness index (R) | 1.67-8.34 | 5.07 | 1.14 | 22.52 |
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H°) | 1.33-3.27 | 2.63 | 0.33 | 12.75 |
| Simpson多样性指数 Simpson diversity index (D) | 0.63-0.95 | 0.89 | 0.05 | 5.68 |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (E) | 0.64-1.00 | 0.86 | 0.06 | 7.03 |
| 叶功能性状 Leaf functional traits | ||||
| 叶片全碳含量 Leaf total carbon content (mg/g) | 473.46-507.74 | 491.56 | 5.91 | 1.20 |
| 叶片全氮含量 Leaf total nitrogen content (mg/g) | 11.59-18.04 | 15.12 | 1.24 | 8.23 |
| 叶片全磷含量 Leaf total phosphorus content (mg/g) | 0.30-0.51 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 10.32 |
| 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content (mg/g) | 348.88-753.09 | 497.08 | 117.86 | 23.71 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 68.36-123.69 | 93.90 | 11.29 | 12.02 |
| 土壤元素含量 Soil element content | ||||
| 土壤全碳含量 Soil total carbon content (mg/g) | 30.12-86.28 | 52.53 | 12.24 | 23.29 |
| 土壤全氮含量 Soil total nitrogen content (mg/g) | 2.36-6.43 | 3.82 | 0.85 | 22.37 |
| 土壤全磷含量 Soil total phosphorus content (mg/g) | 0.00-0.40 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 112.84 |
Table 1 Basic situation of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyishan National Park
| 指标 Index | 范围 Range | 平均值 Mean | 标准偏差 SD | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构多样性 Structural diversity | ||||
| 胸径Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index of DBH (H°d) | 0.58-1.83 | 0.84 | 0.14 | 16.43 |
| 胸径Simpson多样性指数 Simpson diversity index of DBH (Dd) | 0.05-0.93 | 0.70 | 0.15 | 21.62 |
| 胸径标准偏差 Standard deviation of DBH (DSD) | 2.37-16.86 | 6.86 | 1.98 | 28.90 |
| 胸径Gini系数 Gini index of DBH (CG) | 0.15-0.92 | 0.78 | 0.10 | 12.50 |
| 物种多样性 Species diversity | ||||
| Margalef物种丰富度指数 Margalef species richness index (R) | 1.67-8.34 | 5.07 | 1.14 | 22.52 |
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H°) | 1.33-3.27 | 2.63 | 0.33 | 12.75 |
| Simpson多样性指数 Simpson diversity index (D) | 0.63-0.95 | 0.89 | 0.05 | 5.68 |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index (E) | 0.64-1.00 | 0.86 | 0.06 | 7.03 |
| 叶功能性状 Leaf functional traits | ||||
| 叶片全碳含量 Leaf total carbon content (mg/g) | 473.46-507.74 | 491.56 | 5.91 | 1.20 |
| 叶片全氮含量 Leaf total nitrogen content (mg/g) | 11.59-18.04 | 15.12 | 1.24 | 8.23 |
| 叶片全磷含量 Leaf total phosphorus content (mg/g) | 0.30-0.51 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 10.32 |
| 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content (mg/g) | 348.88-753.09 | 497.08 | 117.86 | 23.71 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 68.36-123.69 | 93.90 | 11.29 | 12.02 |
| 土壤元素含量 Soil element content | ||||
| 土壤全碳含量 Soil total carbon content (mg/g) | 30.12-86.28 | 52.53 | 12.24 | 23.29 |
| 土壤全氮含量 Soil total nitrogen content (mg/g) | 2.36-6.43 | 3.82 | 0.85 | 22.37 |
| 土壤全磷含量 Soil total phosphorus content (mg/g) | 0.00-0.40 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 112.84 |
| 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 生活型 Life form | 变化 Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 木姜子属 Litsea | 石木姜子 Litsea elongata var. faberi | 常绿 Evergreen | 进入种 Entering species |
| 清风藤科 Sabiaceae | 清风藤属 Sabia | 灰背清风藤 Sabia discolor | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 红豆属 Ormosia | 小叶红豆 Ormosia microphylla | 常绿 Evergreen | 进入种 Entering species |
| 杜英科 Elaeocarpaceae | 猴欢喜属 Sloanea | 猴欢喜 Sloanea sinensis | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 白木乌桕属 Neoshirakia | 白木乌桕 Neoshirakia japonica | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 省沽油科 Staphyleaceae | 野鸦椿属 Euscaphis | 野鸦椿 Euscaphis japonica | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 无患子科 Sapindaceae | 槭属 Acer | 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 落叶 Deciduous | 进入种 Entering species |
| 无患子科 Sapindaceae | 槭属 Acer | 岭南槭 Acer tutcheri | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 楝科 Meliaceae | 香椿属 Toona | 红椿 Toona ciliata | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 山茱萸科 Cornaceae | 八角枫属 Alangium | 八角枫 Alangium chinense | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 报春花科 Primulaceae | 铁仔属 Myrsine | 光叶铁仔 Myrsine stolonifera | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 杜鹃花属 Rhododendron | 弯蒴杜鹃 Rhododendron henryi | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 粗叶木属 Lasianthus | 日本粗叶木 Lasianthus japonicus | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 冬青科 Aquifoliaceae | 冬青属 Ilex | 大叶冬青 Ilex latifolia | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
Table 2 Species change of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyishan National Park
| 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 生活型 Life form | 变化 Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 木姜子属 Litsea | 石木姜子 Litsea elongata var. faberi | 常绿 Evergreen | 进入种 Entering species |
| 清风藤科 Sabiaceae | 清风藤属 Sabia | 灰背清风藤 Sabia discolor | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 红豆属 Ormosia | 小叶红豆 Ormosia microphylla | 常绿 Evergreen | 进入种 Entering species |
| 杜英科 Elaeocarpaceae | 猴欢喜属 Sloanea | 猴欢喜 Sloanea sinensis | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 白木乌桕属 Neoshirakia | 白木乌桕 Neoshirakia japonica | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 省沽油科 Staphyleaceae | 野鸦椿属 Euscaphis | 野鸦椿 Euscaphis japonica | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 无患子科 Sapindaceae | 槭属 Acer | 青榨槭 Acer davidii | 落叶 Deciduous | 进入种 Entering species |
| 无患子科 Sapindaceae | 槭属 Acer | 岭南槭 Acer tutcheri | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 楝科 Meliaceae | 香椿属 Toona | 红椿 Toona ciliata | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 山茱萸科 Cornaceae | 八角枫属 Alangium | 八角枫 Alangium chinense | 落叶 Deciduous | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 报春花科 Primulaceae | 铁仔属 Myrsine | 光叶铁仔 Myrsine stolonifera | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 杜鹃花科 Ericaceae | 杜鹃花属 Rhododendron | 弯蒴杜鹃 Rhododendron henryi | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 粗叶木属 Lasianthus | 日本粗叶木 Lasianthus japonicus | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 冬青科 Aquifoliaceae | 冬青属 Ilex | 大叶冬青 Ilex latifolia | 常绿 Evergreen | 退出种 Exiting species |
| 树种 Species | 生活型 Life form | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 生物量 Biomass (t/ha) | 生产力 Productivity (t·ha-1·yr-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2023 | 2018 | 2023 | |||
| 甜槠 Castanopsis eyrei | 常绿 Evergreen | 8.53 | 8.36 | 89.85 | 95.76 | 1.18 |
| 马银花 Rhododendron ovatum | 常绿 Evergreen | 7.79 | 8.22 | 7.35 | 10.41 | 0.61 |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 常绿 Evergreen | 5.72 | 6.08 | 23.79 | 28.30 | 0.90 |
| 小叶青冈 Quercus myrsinifolia | 常绿 Evergreen | 3.66 | 3.72 | 33.78 | 37.35 | 0.72 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 常绿 Evergreen | 3.51 | 3.53 | 18.32 | 19.70 | 0.28 |
| 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 常绿 Evergreen | 3.37 | 3.40 | 2.68 | 2.85 | 0.03 |
| 树参 Dendropanax dentiger | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.87 | 2.96 | 9.88 | 10.85 | 0.20 |
| 华南蒲桃 Syzygium austrosinense | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.58 | 2.90 | 2.49 | 3.43 | 0.19 |
| 罗浮锥 Castanopsis faberi | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.51 | 2.22 | 14.80 | 14.38 | -0.08 |
| 港柯 Lithocarpus harlandii | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.41 | 2.21 | 16.34 | 15.18 | -0.23 |
| 日本杜英 Elaeocarpus japonicus | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.20 | 2.22 | 9.48 | 10.33 | 0.17 |
| 大萼杨桐 Adinandra glischroloma var. macrosepala | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.13 | 2.19 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.01 |
| 白背瑞木 Corylopsis multiflora var. nivea | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.76 | 1.71 | 2.83 | 2.88 | 0.01 |
| 乌冈栎 Quercus phillyraeoides | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.68 | 1.58 | 10.05 | 10.15 | 0.02 |
| 黄山松 Pinus hwangshanensis | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.50 | 1.49 | 8.00 | 8.39 | 0.08 |
| 薄叶山矾 Symplocos anomala | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.49 | 1.55 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.02 |
| 凤凰润楠 Machilus phoenicis | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.44 | 1.37 | 0.54 | 0.68 | 0.03 |
| 桃叶石楠 Photinia prunifolia | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.37 | 1.36 | 1.34 | 1.45 | 0.02 |
| 虎皮楠 Daphniphyllum oldhamii | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.26 | 1.34 | 3.90 | 4.49 | 0.12 |
| 峨眉鼠刺 Itea omeiensis | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.25 | 1.04 | 0.48 | 0.37 | -0.02 |
| 冬青 Ilex chinensis | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.16 | 1.19 | 1.40 | 1.65 | 0.05 |
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.14 | 1.21 | 1.38 | 1.68 | 0.06 |
| 尾叶冬青 Ilex wilsonii | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.11 | 1.12 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.00 |
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.11 | 1.03 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.00 |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | 常绿 Evergreen | 0.98 | 1.09 | 0.58 | 0.72 | 0.03 |
Table 3 Biomass changes of main species of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyishan National Park
| 树种 Species | 生活型 Life form | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 生物量 Biomass (t/ha) | 生产力 Productivity (t·ha-1·yr-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2023 | 2018 | 2023 | |||
| 甜槠 Castanopsis eyrei | 常绿 Evergreen | 8.53 | 8.36 | 89.85 | 95.76 | 1.18 |
| 马银花 Rhododendron ovatum | 常绿 Evergreen | 7.79 | 8.22 | 7.35 | 10.41 | 0.61 |
| 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 常绿 Evergreen | 5.72 | 6.08 | 23.79 | 28.30 | 0.90 |
| 小叶青冈 Quercus myrsinifolia | 常绿 Evergreen | 3.66 | 3.72 | 33.78 | 37.35 | 0.72 |
| 木荷 Schima superba | 常绿 Evergreen | 3.51 | 3.53 | 18.32 | 19.70 | 0.28 |
| 鹿角杜鹃 Rhododendron latoucheae | 常绿 Evergreen | 3.37 | 3.40 | 2.68 | 2.85 | 0.03 |
| 树参 Dendropanax dentiger | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.87 | 2.96 | 9.88 | 10.85 | 0.20 |
| 华南蒲桃 Syzygium austrosinense | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.58 | 2.90 | 2.49 | 3.43 | 0.19 |
| 罗浮锥 Castanopsis faberi | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.51 | 2.22 | 14.80 | 14.38 | -0.08 |
| 港柯 Lithocarpus harlandii | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.41 | 2.21 | 16.34 | 15.18 | -0.23 |
| 日本杜英 Elaeocarpus japonicus | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.20 | 2.22 | 9.48 | 10.33 | 0.17 |
| 大萼杨桐 Adinandra glischroloma var. macrosepala | 常绿 Evergreen | 2.13 | 2.19 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.01 |
| 白背瑞木 Corylopsis multiflora var. nivea | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.76 | 1.71 | 2.83 | 2.88 | 0.01 |
| 乌冈栎 Quercus phillyraeoides | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.68 | 1.58 | 10.05 | 10.15 | 0.02 |
| 黄山松 Pinus hwangshanensis | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.50 | 1.49 | 8.00 | 8.39 | 0.08 |
| 薄叶山矾 Symplocos anomala | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.49 | 1.55 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.02 |
| 凤凰润楠 Machilus phoenicis | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.44 | 1.37 | 0.54 | 0.68 | 0.03 |
| 桃叶石楠 Photinia prunifolia | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.37 | 1.36 | 1.34 | 1.45 | 0.02 |
| 虎皮楠 Daphniphyllum oldhamii | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.26 | 1.34 | 3.90 | 4.49 | 0.12 |
| 峨眉鼠刺 Itea omeiensis | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.25 | 1.04 | 0.48 | 0.37 | -0.02 |
| 冬青 Ilex chinensis | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.16 | 1.19 | 1.40 | 1.65 | 0.05 |
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.14 | 1.21 | 1.38 | 1.68 | 0.06 |
| 尾叶冬青 Ilex wilsonii | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.11 | 1.12 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.00 |
| 窄基红褐柃 Eurya rubiginosa var. attenuata | 常绿 Evergreen | 1.11 | 1.03 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.00 |
| 尖连蕊茶 Camellia cuspidata | 常绿 Evergreen | 0.98 | 1.09 | 0.58 | 0.72 | 0.03 |
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 生活型 Life form | 物种数 No. of species | 个体数 No. of individual | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 生物量 Biomass (t/ha) | 生产力 Productivity (t·ha-1·yr-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2023 | 2018 | 2023 | 2018 | 2023 | 2018 | 2023 | |||
| 800 | 常绿 Evergreen | 112 | 107 | 3,986 | 3,287 | 77.72 | 78.03 | 283.04 | 315.25 | 6.44 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 19 | 19 | 701 | 559 | 22.28 | 21.97 | 17.00 | 16.94 | -0.01 | |
| 900 | 常绿 Evergreen | 91 | 92 | 2,886 | 2,681 | 80.97 | 81.33 | 344.38 | 358.69 | 2.86 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 12 | 12 | 283 | 231 | 19.03 | 18.67 | 3.92 | 3.96 | 0.01 | |
| 1,000 | 常绿 Evergreen | 86 | 85 | 3,827 | 3,150 | 81.65 | 82.04 | 265.29 | 281.73 | 3.29 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 32 | 28 | 232 | 147 | 18.35 | 17.96 | 14.67 | 16.29 | 0.33 | |
| 1,100 | 常绿 Evergreen | 76 | 76 | 2,655 | 2,316 | 83.24 | 83.47 | 304.44 | 340.29 | 7.17 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 20 | 18 | 203 | 151 | 16.76 | 16.53 | 4.19 | 5.83 | 0.33 | |
| 1,200 | 常绿 Evergreen | 82 | 78 | 3,341 | 2,953 | 82.43 | 82.72 | 328.85 | 356.31 | 5.49 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 27 | 23 | 161 | 113 | 17.57 | 17.28 | 6.27 | 7.17 | 0.18 | |
| 平均 Mean | 常绿 Evergreen | 89 ± 12 | 88 ± 11 | 3,339 ± 516 | 2,877 ± 347 | 81.20 ± 1.90 | 81.52 ± 1.88 | 305.20 ± 28.91 | 330.45 ± 28.87 | 5.05 ± 1.70 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 22 ± 7 | 20 ± 5 | 316 ± 197 | 240 ± 164 | 18.80 ± 1.90 | 18.48 ± 1.88 | 9.21 ± 5.52 | 10.04 ± 5.47 | 0.17 ± 0.15 | |
Table4 Biomass changes of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyishan National Park
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 生活型 Life form | 物种数 No. of species | 个体数 No. of individual | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 生物量 Biomass (t/ha) | 生产力 Productivity (t·ha-1·yr-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2023 | 2018 | 2023 | 2018 | 2023 | 2018 | 2023 | |||
| 800 | 常绿 Evergreen | 112 | 107 | 3,986 | 3,287 | 77.72 | 78.03 | 283.04 | 315.25 | 6.44 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 19 | 19 | 701 | 559 | 22.28 | 21.97 | 17.00 | 16.94 | -0.01 | |
| 900 | 常绿 Evergreen | 91 | 92 | 2,886 | 2,681 | 80.97 | 81.33 | 344.38 | 358.69 | 2.86 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 12 | 12 | 283 | 231 | 19.03 | 18.67 | 3.92 | 3.96 | 0.01 | |
| 1,000 | 常绿 Evergreen | 86 | 85 | 3,827 | 3,150 | 81.65 | 82.04 | 265.29 | 281.73 | 3.29 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 32 | 28 | 232 | 147 | 18.35 | 17.96 | 14.67 | 16.29 | 0.33 | |
| 1,100 | 常绿 Evergreen | 76 | 76 | 2,655 | 2,316 | 83.24 | 83.47 | 304.44 | 340.29 | 7.17 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 20 | 18 | 203 | 151 | 16.76 | 16.53 | 4.19 | 5.83 | 0.33 | |
| 1,200 | 常绿 Evergreen | 82 | 78 | 3,341 | 2,953 | 82.43 | 82.72 | 328.85 | 356.31 | 5.49 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 27 | 23 | 161 | 113 | 17.57 | 17.28 | 6.27 | 7.17 | 0.18 | |
| 平均 Mean | 常绿 Evergreen | 89 ± 12 | 88 ± 11 | 3,339 ± 516 | 2,877 ± 347 | 81.20 ± 1.90 | 81.52 ± 1.88 | 305.20 ± 28.91 | 330.45 ± 28.87 | 5.05 ± 1.70 |
| 落叶 Deciduous | 22 ± 7 | 20 ± 5 | 316 ± 197 | 240 ± 164 | 18.80 ± 1.90 | 18.48 ± 1.88 | 9.21 ± 5.52 | 10.04 ± 5.47 | 0.17 ± 0.15 | |
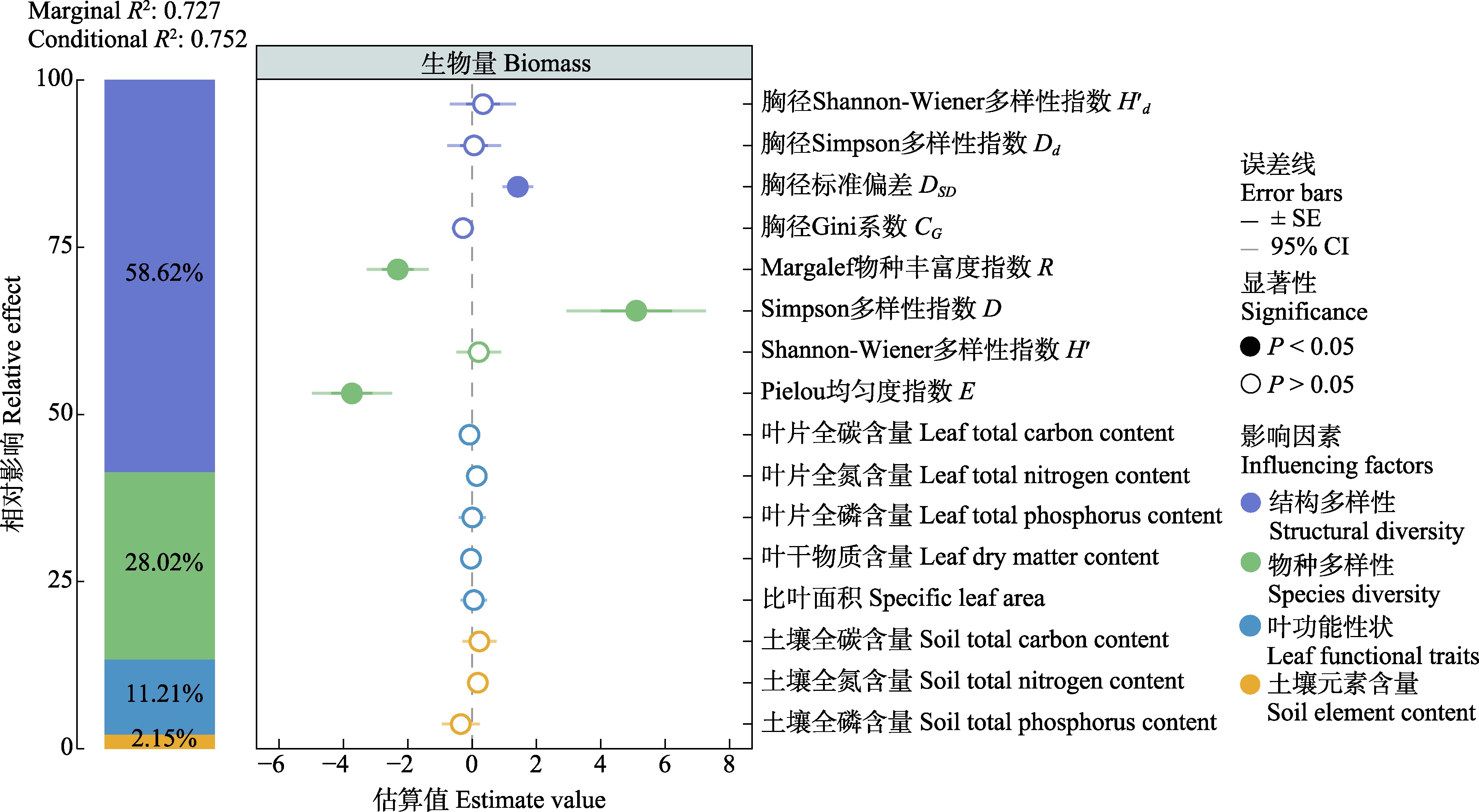
Fig. 2 Correlation analysis between the biomass of evergreen broad-leaved forest and influencing factors in Wuyishan National Park. SE, Standard error; CI, Confidence interval; H′d, Shannon-Wiener diversity index of DBH; Dd, Simpson diversity index of DBH; DSD, Standard deviation of DBH; CG, Gini index of DBH; R, Margalef species richness index; D, Simpson diversity index; H′, Shannon-Wiener diversity index; E, Pielou evenness index.
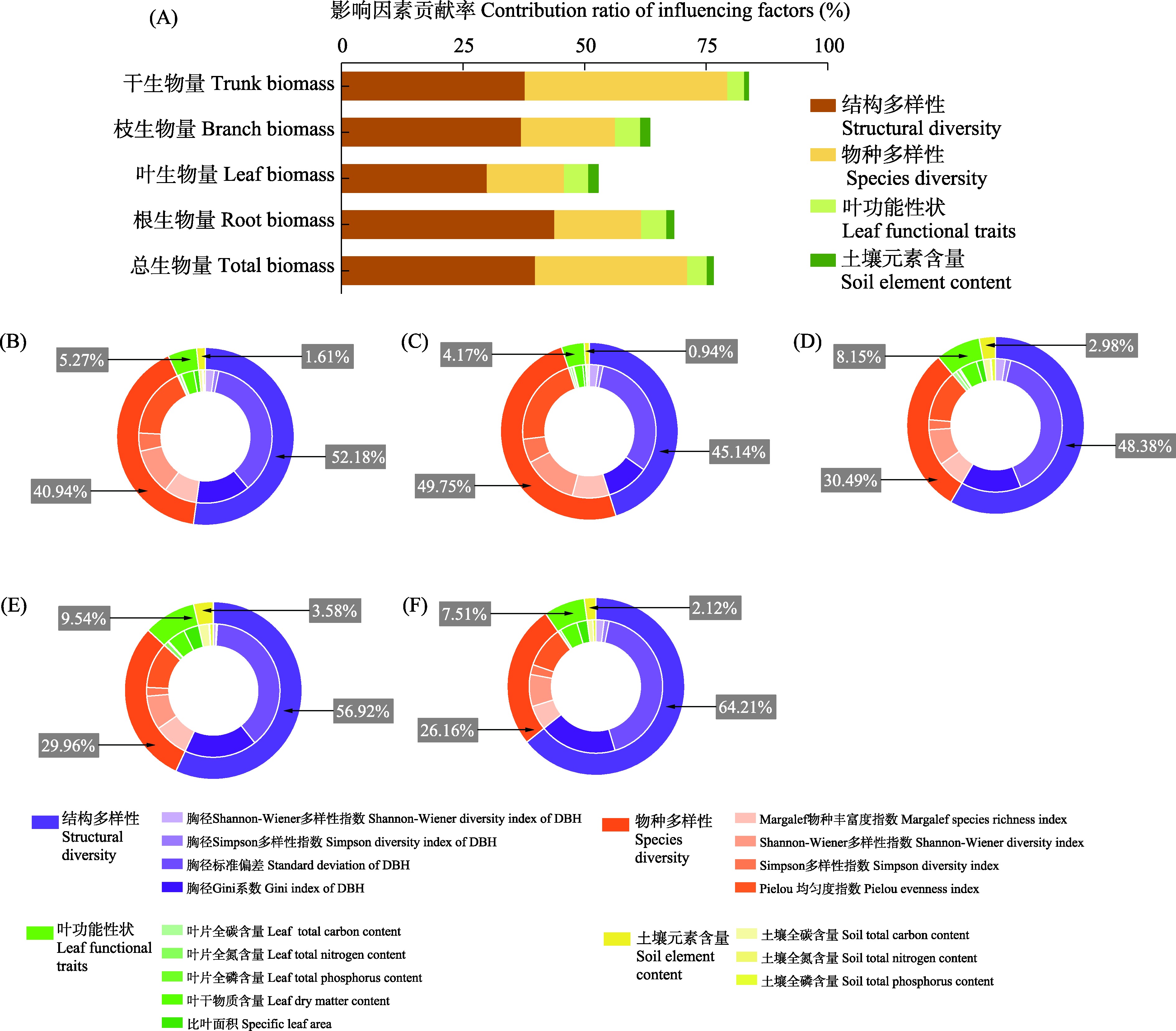
Fig. 3 Contribution rate of influencing factors of evergreen broad-leaved forest biomass in Wuyishan National Park. (A) Cumulative contribution rate of combined factors; (B) Contribution rate of influencing factors to total biomass; (C) Contribution rate of influencing factors to trunk biomass; (D) Contribution rate of influencing factors to branch biomass; (E) Contribution rate of influencing factors to leaf biomass; (F) Contribution rate of influencing factors to root biomass.
| [1] |
Ali A (2019) Forest stand structure and functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Ecological Indicators, 98, 665-677.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Bohn FJ, Huth A (2017) The importance of forest structure to biodiversity-productivity relationships. Royal Society Open Science, 4, 160521.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bruelheide H, Böhnke M, Both S, Fang T, Assmann T, Baruffol M, Bauhus J, Buscot F, Chen XY, Ding BY, Durka W, Erfmeier A, Fischer M, Geißler C, Guo DL, Guo LD, Härdtle W, He JS, Hector A, Kröber W, Kühn P, Lang AC, Nadrowski K, Pei KQ, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Shi XZ, Scholten T, Schuldt A, Trogisch S, von Oheimb G, Welk E, Wirth C, Wu YT, Yang XF, Zeng XQ, Zhang SR, Zhou HZ, Ma KP, Schmid B (2011) Community assembly during secondary forest succession in a Chinese subtropical forest. Ecological Monographs, 81, 25-41.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Bruelheide H, Dengler J, Purschke O, Lenoir J, Jiménez-Alfaro B, Hennekens SM, Botta-Dukát Z, Chytry M, Field R, Jansen F, …, Tsiripidis I, Vassilev K, Violle C, Virtanen R, Weiher E, Welk E, Wesche K, Winter M, Wirth C, Jandt U (2018) Global trait-environment relationships of plant communities. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2, 1906-1917. |
| [5] | Chen JS, Guo QJ, Yao L, Zhu J, Liu XY, Xiang Q, Zhao HD, Ai XR (2024) Interspecific associations and community stability changes of dominant woody species of natural forest communities in Mulinzi National Nature Reserve. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 32, 601-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈锦世, 郭秋菊, 姚兰, 朱江, 刘西尧, 向钦, 赵奂敦, 艾训儒 (2024) 木林子国家级自然保护区天然林群落优势木本植物种间联结和稳定性. 热带亚热带植物学报, 32, 601-610.] | |
| [6] | Chen SF, Xu H, Lin WJ, Zheng X, Xu XJ, Liu WF, Ding H, Chen SP (2023) Variation analysis on species diversity of plant communities along the elevation gradient in Wuyishan National Park. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 32(1), 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈水飞, 徐辉, 林文俊, 郑笑, 徐鲜钧, 刘文芳, 丁晖, 陈世品 (2023) 武夷山国家公园植物群落物种多样性沿海拔梯度的变化分析. 植物资源与环境学报, 32(1), 1-9.] | |
| [7] | Chen XP, Wang MT, Li M, Sun J, Lyu M, Zhong QL, Cheng DL (2020) Convergent nitrogen-phosphorus scaling relationships in different plant organs along an elevational gradient. AoB Plants, 12, plaa021. |
| [8] | Cheng ZH, Zhang JC, Jiang J, Meng MJ, Li JY, Luo M, Fang XH (2025) Spatial distribution pattern and correlation of dominant species at different vertical levels in Baishanzu mid-mountain evergreen broad-leaved forest. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 61(3), 72-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程子翰, 张金池, 姜姜, 孟苗婧, 李珈印, 罗梅, 方向华 (2025) 百山祖中山常绿阔叶林不同垂直层次优势种空间分布格局及关联性. 林业科学, 61(3), 72-85.] | |
| [9] |
Chisholm RA, Muller-Landau HC, Abdul Rahman K, Bebber DP, Bin Y, Bohlman SA, Bourg NA, Brinks J, Bunyavejchewin S, Butt N, Cao HL, Cao M, Cárdenas D, Chang L-W, Chiang JM, Chuyong G, Condit R, Dattaraja HS, Davies S, Duque A, Fletcher C, Gunatilleke N, Gunatilleke S, Hao ZQ, Harrison RD, Howe R, Hsieh CF, Hubbell SP, Itoh A, Kenfack D, Kiratiprayoon S, Larson AJ, Lian JY, Lin DM, Liu HF, Lutz JA, Ma KP, Malhi Y, McMahon S, McShea W, Meegaskumbura M, Mohd Razman S, Morecroft MD, Nytch CJ, Oliveira A, Parker GG, Pulla S, Punchi-Manage R, Romero-Saltos H, Sang WG, Schurman J, Su SH, Sukumar R, Sun IF, Suresh HS, Tan S, Thomas D, Thomas S, Thompson J, Valencia R, Wolf A, Yap S, Ye WH, Yuan ZQ, Zimmerman JK (2013) Scale-dependent relationships between tree species richness and ecosystem function in forests. Journal of Ecology, 101, 1214-1224.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Chu CJ, Weiner J, Maestre FT, Xiao S, Wang YS, Li Q, Yuan JL, Zhao LQ, Ren ZW, Wang G (2009) Positive interactions can increase size inequality in plant populations. Journal of Ecology, 97, 1401-1407.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| [12] |
Dănescu A, Albrecht AT, Bauhus J (2016) Structural diversity promotes productivity of mixed, uneven-aged forests in southwestern Germany. Oecologia, 182, 319-333.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Du QQ, Ren SY, Yuan NTS, Zhu Y (2024) Factors affecting the productivity of sapling and adult trees in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24284. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕 (2024) 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素. 生物多样性, 32, 24284.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Dyola N, Liang EY, Peñuelas J, Camarero JJ, Sigdel SR, Aryal S, Lin WT, Liu X, Liu YW, Xu XL, Rossi S (2024) Linking leaf elemental traits to biomass across forest biomes in the Himalayas. Science China Earth Sciences, 67, 1518-1528.
DOI |
| [15] |
Fahey RT, Fotis AT, Woods KD (2015) Quantifying canopy complexity and effects on productivity and resilience in late-successional hemlock-hardwood forests. Ecological Applications, 25, 834-847.
PMID |
| [16] | Fang JY, Li YD, Zhu B, Liu GH, Zhou GY (2004) Community structures and species richness in the montane rain forest of Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Biodiversity Science, 12, 29-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 方精云, 李意德, 朱彪, 刘国华, 周光益 (2004) 海南岛尖峰岭山地雨林的群落结构、物种多样性以及在世界雨林中的地位. 生物多样性, 12, 29-43.]
DOI |
|
| [17] |
Forrester DI, Bauhus J (2016) A review of processes behind diversity-productivity relationships in forests. Current Forestry Reports, 2, 45-61.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Fotis AT, Murphy SJ, Ricart DR, Krishnadas M, Whitacre J, Wenzel JW, Queenborough SA, Comita LS (2017) Above-ground biomass is driven by mass-ratio effects and stand structural attributes in a temperate deciduous forest. Journal of Ecology, 106, 561-570.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Fox JW (2005) Interpreting the “selection effect” of biodiversity on ecosystem function. Ecology Letters, 8, 846-856.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Gamfeldt L, Snäll T, Bagchi R, Jonsson M, Gustafsson L, Kjellander P, Ruiz-Jaen MC, Fröberg M, Stendahl J, Philipson CD, Mikusiński G, Andersson E, Westerlund B, Andrén H, Moberg F, Moen J, Bengtsson J (2013) Higher levels of multiple ecosystem services are found in forests with more tree species. Nature Communications, 4, 1340.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Gao L, Jiang ZH, Hong ZC, Zheng X, Zhou Y, Chen SF, Chen SP, Lin WJ (2024) Analysis on niche and interspecific association of main tree species in Castanopsis eyrei forests in Wuyishan National Park. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 33(6), 65-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高亮, 江子涵, 洪子辰, 郑笑, 周艳, 陈水飞, 陈世品, 林文俊 (2024) 武夷山国家公园甜槠林主要树种生态位与种间联结分析. 植物资源与环境学报, 33(6), 65-73.] | |
| [22] | Ge XM, Chen SF, Zhou X, Xu H, Hu YP, Jiang BX, Ding H (2019) Seasonal dynamics of soil nitrogen mineralization in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyi Mountains, Fujian Province, China. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28, 1351-1360. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 葛晓敏, 陈水飞, 周旭, 徐辉, 胡亚萍, 江宝兴, 丁晖 (2019) 武夷山中亚热带常绿阔叶林土壤氮矿化的季节动态. 生态环境学报, 28, 1351-1360.]
DOI |
|
| [23] | Givnish TJ (2002) Adaptive significance of evergreen vs. deciduous leaves: Solving the triple paradox. Silva Fennica 36, 703-743. |
| [24] |
Hardiman BS, Bohrer G, Gough CM, Vogel CS, Curtis PS (2011) The role of canopy structural complexity in wood net primary production of a maturing northern deciduous forest. Ecology, 92, 1818-1827.
PMID |
| [25] |
Hardiman BS, Gough CM, Halperin A, Hofmeister KL, Nave LE, Bohrer G, Curtis PS (2013) Maintaining high rates of carbon storage in old forests: A mechanism linking canopy structure to forest function. Forest Ecology and Management, 298, 111-119.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
He NP, Li Y, Liu CC, Xu L, Li MX, Zhang JH, He JS, Tang ZY, Han XG, Ye Q, Xiao CW, Yu Q, Liu SR, Sun W, Niu SL, Li SG, Sack L, Yu GR (2020) Plant trait networks: Improved resolution of the dimensionality of adaptation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35, 908-918.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Hofhansl F, Chacón-Madrigal E, Fuchslueger L, Jenking D, Morera-Beita A, Plutzar C, Silla F, Andersen KM, Buchs DM, Dullinger S, Fiedler K, Franklin O, Hietz P, Huber W, Quesada CA, Rammig A, Schrodt F, Vincent AG, Weissenhofer A, Wanek W (2020) Climatic and edaphic controls over tropical forest diversity and vegetation carbon storage. Scientific Reports, 10, 5066.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Hordijk I, Maynard DS, Hart SP, Mo LD, ter Steege H, Liang JJ, de-Miguel S, Nabuurs GJ, Reich PB, Abegg M, …, Wittmann F, Wortel V, Zagt R, Zawila-Niedzwiecki T, Zhang CY, Zhao XH, Zhou M, Zhu ZX, Zo-Bi IC, Crowther TW (2023) Evenness mediates the global relationship between forest productivity and richness. Journal of Ecology, 111, 1308-1326.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Huang CS, Xu Y, Zang RG (2024) Low functional redundancy revealed high vulnerability of the subtropical evergreen broadleaved forests to environmental change. Science of the Total Environment, 935, 173307.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Jin Y, Russo SE, Yu MJ (2018) Effects of light and topography on regeneration and coexistence of evergreen and deciduous tree species in a Chinese subtropical forest. Journal of Ecology, 106, 1634-1645.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Jonsson M, Bengtsson J, Moen J, Gamfeldt L, Snäll T (2020) Stand age and climate influence forest ecosystem service delivery and multifunctionality. Environmental Research Letters, 15, 0940a8. |
| [32] | Kröber W, Böhnke M, Welk E, Wirth C, Bruelheide H (2012) Leaf trait-environment relationships in a subtropical broadleaved forest in South-East China. PLoS ONE, 7, e35742. |
| [33] | Lai JS, Zhu WJ, Cui DF, Mao LF (2023) Extension of the glmm. hp package to zero-inflated generalized linear mixed models and multiple regression. Journal of Plant Ecology, 16, rtad038. |
| [34] |
Lai JS, Zou Y, Zhang JL, Peres-Neto PR (2022) Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 13, 782-788.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Lan J, Lei XD, He X, Gao WQ, Guo H (2023) Stand density, climate and biodiversity jointly regulate the multifunctionality of natural forest ecosystems in Northeast China. European Journal of Forest Research, 142, 493-507.
DOI |
| [36] | Lan SR (2003) Plant species diversity in Wuyishan National Nature Reserve. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 39(1), 36-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 兰思仁 (2003) 武夷山国家级自然保护区植物物种多样性研究. 林业科学, 39(1), 36-43.] | |
| [37] |
Levine JM, HilleRisLambers J (2009) The importance of niches for the maintenance of species diversity. Nature, 461, 254-257.
DOI |
| [38] |
Li J, Hao MH, Fan CY, Zhang CY, Zhao XH (2023) Effect of tree species and functional diversity on ecosystem multifunctionality in temperate forests of Northeast China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 47, 1507-1522. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 李杰, 郝珉辉, 范春雨, 张春雨, 赵秀海 (2023) 东北温带森林树种和功能多样性对生态系统多功能性的影响. 植物生态学报, 47, 1507-1522.]
DOI |
|
| [39] |
Linger E, Asefa M, Zhang T, Lin LL, Long WX (2025) Phosphorus stress disrupts leaf-root trait relationships and reduces biomass in a tropical cloud forest: Evidence from a two-year phosphorus addition experiment. Forest Ecology and Management, 586, 122726.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Liu J, Liu QJ, Dong CC, Shi K, Qian NP, Sun Z, Meng DC, Li GD (2025) Effects of species and structural diversity in different forest layers on community growth in broadleaved Korean pine forests in Changbai Mountain, northeastern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 47(8), 64-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘健, 刘琪璟, 董淳超, 石宽, 钱尼澎, 孙震, 孟德琛, 李港墩 (2025) 长白山阔叶红松林不同林层物种与结构多样性对群落生长的影响. 北京林业大学学报, 47(8), 64-76.] | |
| [41] |
Loreau M, de Mazancourt C (2013) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability: A synthesis of underlying mechanisms. Ecology Letters, 16, 106-115.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science, 294, 804-808.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Lu RK (1999) Methods for Agricultural Chemical Analysis of Soil. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 鲁如坤 (1999) 土壤农业化学分析方法. 中国农业科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [44] | Lugli LF, Rosa JS, Andersen KM, Di Ponzio R, Almeida RV, Pires M, Cordeiro AL, Cunha HFV, Martins NP, Assis RL, Moraes ACM, Souza ST, Aragão LEOC, Camargo JL, Fuchslueger L, Schaap KJ, Valverde-Barrantes OJ, Meir P, Quesada CA, Mercado LM, Hartley IP (2021) Rapid responses of root traits and productivity to phosphorus and cation additions in a tropical lowland forest in Amazonia. New Phytologist, 230, 116-128. |
| [45] |
Lü SJ, Huang JJ, Liu HM, Ma SY (2024) Grazing effects on species diversity across different scales are related to grassland types. BMC Plant Biology, 24, 1103.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Ma F, Wang SZ, Feng JC, Sang WG (2018) The study of the effect of tree death on spatial pattern and habitat associations in dominant populations of Dongling Mountains in Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 7669-7678. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马芳, 王顺忠, 冯金朝, 桑卫国 (2018) 北京东灵山优势种群树木死亡对空间格局与生境的影响. 生态学报, 38, 7669-7678.] | |
| [47] |
Mensah S, Veldtman R, Assogbadjo AE, Glèlè Kakaï R, Seifert T (2016) Tree species diversity promotes aboveground carbon storage through functional diversity and functional dominance. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 7546-7557.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Ouyang S, Gou MM, Lei PF, Liu Y, Chen L, Deng XW, Zhao ZH, Zeng YL, Hu YT, Peng CH, Xiang WH (2023) Plant functional trait diversity and structural diversity co-underpin ecosystem multifunctionality in subtropical forests. Forest Ecosystems, 10, 100093.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Ouyang S, Xiang WH, Wang XP, Zeng ZL, Lei Pf, Deng XW, Peng CH (2016) Significant effects of biodiversity on forest biomass during the succession of subtropical forest in South China. Forest Ecology and Management, 372, 291-302.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Peet PK (1974) The measurement of species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 5, 285-307. |
| [51] | Peñuelas J, Fernández-Martínez M, Ciais P, Jou D, Piao SL, Obersteiner M, Vicca S, Janssens IA, Sardans J (2019) The bioelements, the elementome, and the biogeochemical niche. Ecology, 100, e02652. |
| [52] | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. John Wiley and Sons, New York. |
| [53] |
Poorter L, van der Sande MT, Thompson J, Arets EJMM, Alarcón A, Alvarez-Sánchez J, Ascarrunz N, Balvanera P, Barajas-Guzmán G, Boit A, …, Stropp J, ter Steege H, Swenson NG, Thonicke K, Toledo M, Uriarte M, van der Hout P, Walker P, Zamora N, Peña-Claros M (2015) Diversity enhances carbon storage in tropical forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 24, 1314-1328.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Prado-Junior JA, Schiavini I, Vale VS, Arantes CS, van der Sande MT, Lohbeck M, Poorter L (2016) Conservative species drive biomass productivity in tropical dry forests. Journal of Ecology, 104, 817-827.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Reich PB, Walters MB, Ellsworth DS (1997) From tropics to tundra: Global convergence in plant functioning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 94, 13730-13734 |
| [56] |
Ryan MG, Stape JL, Binkley D, Fonseca S, Loos RA, Takahashi EN, Silva CR, Silva SR, Hakamada RE, Ferreira JM, Lima AMN, Gava JL, Leite FP, Andrade HB, Alves JM, Silva GGC (2010) Factors controlling Eucalyptus productivity: How water availability and stand structure alter production and carbon allocation. Forest Ecology and Management, 259, 1695-1703.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Tan LZ, Fan CY, Fan XH (2017) Relationships between species diversity or community structure and productivity of woody-plants in a broad-leaved Korean pine forest in Jiaohe, Jilin, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 41, 1149-1156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 谭凌照, 范春雨, 范秀华 (2017) 吉林蛟河阔叶红松林木本植物物种多样性及群落结构与生产力的关系. 植物生态学报, 41, 1149-1156.]
DOI |
|
| [58] | Vitousek PM, Howarth RW (1991) Nitrogen limitation on land and in the sea: How can it occur? Biogeochemistry, 13, 87-15. |
| [59] | Wang L, Ju YL, Ji YJ, Marino A, Zhang WF, Jing Q (2024) Estimation of forest above-ground biomass in the study area of Greater Khingan Ecological Station with integration of airborne LiDAR, Landsat 8 OLI, and hyperspectral remote sensing data. Forests, 15, 1861. |
| [60] |
Wang XY, Meng JH, Ren SY, Zhu Y (2024) Relationship between biodiversity and aboveground biomass in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24230. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕 (2024) 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系. 生物多样性, 32, 24230.]
DOI |
|
| [61] |
Weemstra M, Freschet GT, Stokes A, Roumet C (2021) Patterns in intraspecific variation in root traits are species-specific along an elevation gradient. Functional Ecology, 35, 342-356.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M, Ackerly DD, Baruch Z, Bongers F, Cavender-Bares J, Chapin T, Cornelissen JHC, Diemer M, Flexas J, Garnier E, Groom PK, Gulias J, Hikosaka K, Lamont BB, Lee TL, Lee W, Lusk C, Midgley JJ, Navas ML, Niinemets Ü, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Poot P, Prior L, Pyankov VI, Roumet C, Thomas SC, Tjoelker MG, Veneklaas EJ, Villar R (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature, 428, 821-827.
DOI |
| [63] |
Wu X, Wang XP, Tang ZY, Shen ZH, Zheng CY, Xia XL, Fang JY (2015) The relationship between species richness and biomass changes from boreal to subtropical forests in China. Ecography, 38, 602-613.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Yachi S, Loreau M (2007) Does complementary resource use enhance ecosystem functioning? A model of light competition in plant communities. Ecology Letters, 10, 54-62.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
Yang J, Cao M, Swenson NG (2018) Why functional traits do not predict tree demographic rates. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 33, 326-336.
DOI URL |
| [66] | Yu YQ, Lin WJ, Chen SP, Fan DJ, Fu RR, You WB (2023) Comparison of population quantity characteristics and spatial point pattern of dominant tree species in typical coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest in Wuyi Mountain. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 52, 649-659. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 余云钦, 林文俊, 陈世品, 范敦锦, 傅榕榕, 游巍斌 (2023) 武夷山不同海拔针阔混交林种群数量特征及优势树种空间点格局比较. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 52, 649-659.] | |
| [67] |
Zhang Y, Chen HYH (2015) Individual size inequality links forest diversity and above-ground biomass. Journal of Ecology, 103, 1245-1252.
DOI URL |
| [68] | Zhao Q, Liu S, Chen K, Wang SJ, Wu CZ, Li J, Lin YM (2021) Change characteristics and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in Castanopsis eyrei natural forests at different altitudes in Wuyishan Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 5328-5339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵青, 刘爽, 陈凯, 王世君, 吴承祯, 李键, 林勇明 (2021) 武夷山自然保护区不同海拔甜槠天然林土壤有机碳变化特征及影响因素. 生态学报, 41, 5328-5339.] | |
| [69] |
Zhao WZ, Xiao CW, Li MX, Xu L, He NP (2022) Variation and adaptation in leaf sulfur content across China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 15, 743-755.
DOI |
| [70] | Zhu J, Wu AC, Zou S, Xiong X, Liu SZ, Chu GW, Zhang QM, Liu JX, Tang XL, Yan JH, Zhang DQ, Zhou GY (2021) Relationships between tree diversity and biomass/productivity and their influence factors in a lower subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1435-1446. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 朱杰, 吴安驰, 邹顺, 熊鑫, 刘世忠, 褚国伟, 张倩媚, 刘菊秀, 唐旭利, 闫俊华, 张德强, 周国逸 (2021) 南亚热带常绿阔叶林树木多样性与生物量和生产力的关联及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 29, 1435-1446.]
DOI |
|
| [71] |
Zou S, Zhou GY, Zhang MQ, Xu S, Xiong X, Xia YJ, Liu SZ, Meng Z, Chu GW (2018) Long-term (1992-2015) dynamics of community composition and structure in a monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42, 442-452. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 邹顺, 周国逸, 张倩媚, 徐姗, 熊鑫, 夏艳菊, 刘世忠, 孟泽, 褚国伟 (2018) 1992-2015年鼎湖山季风常绿阔叶林群落结构动态. 植物生态学报, 42, 442-452.]
DOI |
| [1] | Shiyun Yang, Lujie Hu, Qinxiu Huang, Shiqi Zeng, Jiajun Wang, Tong Zhang, Cancan Zhang, Wensheng Bu. Post-snowstorm community dynamics in an evergreen broad-leaved forest of Jiulian Mountains, Jiangxi Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(9): 25005-. |
| [2] | Yang Yang, Rui Zou, Yaqin Qiao, Xiang Meng, Feiyun Tu. The species diversity of terrestrial mammals in Hainan Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(8): 25044-. |
| [3] | Qilong Yu, Minhui Hao, Huaijiang He, Chunyu Zhang, Xiuhai Zhao. Relationships of biodiversity and productivity change with forest succession in Changbai Mountains: Insights from species, traits, and phylogeny [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(8): 25060-. |
| [4] | Ying Feng, Feng Song, Guangzhao Jin, Komiljon Tojibaev, Xuejun Ge. Distribution patterns and species diversity of the genus Calligonum in the desert regions of Central Asia [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(8): 25086-. |
| [5] | Xinbo Hou, Xiuhai Zhao, Huaijiang He, Chunyu Zhang, Juan Wang, Xueying Ren, Xinna Zhang. Responses of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere microbial communities to the soil carbon and nitrogen in Quercus mongolica pure forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(7): 25119-. |
| [6] | Yang Zhang, Yanping Wang. A review of the SLOSS debate: Analysis methods, theoretical mechanisms and conservation practices [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(7): 25081-. |
| [7] | Zhengdong Pan, Xirong Lin, Hua Xue, Zhiying Hu, Hongyi Guo, Ya Zhang, Enuo Wu, Wenqiao Tang. Fish species diversity background and community structure in the main inland water bodies of Shanghai [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24290-. |
| [8] | Wen Peng, Zeshuai Deng, Wenbao Zheng, Lingxuan Gong, Yufeng Zeng, Hao Meng, Jun Chen, Daode Yang. Application of eDNA technology in amphibian surveys: A case study of Hunan Mangshan National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24552-. |
| [9] | Lulu Zhang, Zhaojie Ren, Ningning Yu, Fengxi Zhao, Zuntian Zhao. List of bryophytes in Gansu Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24451-. |
| [10] | Xiaoqing Wu, Meihui Zhang, Suting Ge, Manshu Li, Liangjun Da, Kun Song, Guochun Shen, Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal dynamics of woody plant species diversity and aboveground biomass during near-nature forest reconstruction in Shanghai: A case study from the eco-island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [11] | Wang Tai, Song Fujun, Zhang Yongsheng, Lou Zhongyu, Zhang Yanping, Du Yanyan. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [12] | Zhang Jingjing, Huang Wenbin, Chen Yiting, Yang Zepeng, Ke Weiye, Peng Zhaojie, Wei Shichao, Zhang Zhiwei, Hu Yisi, Yu Wenhua, Zhou Wenliang. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [13] | Zhang Mingyi, Wang Xiaomei, Zheng Yanxin, Wu Nan, Li Donghao, Fan Enyuan, Li Na, Shan Xiujuan, Yu Tao, Zhao Chunnuan, Li Bo, Xu Shuai, Wu Yuping, Ren Liqun. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [14] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [15] | Jia Zhenni, Zhang Yicen, Du Yanjun, Ren Haibao. Influences of disturbances on successional dynamics of species diversity in mid- subtropical forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn