



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 24128. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024128 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024128
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yihui Jiang1, Yue Liu1, Xu Zeng1, Zheying Lin1, Nan Wang1, Jihao Peng1, Ling Cao2( ), Cong Zeng1,2,*(
), Cong Zeng1,2,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-04-05
Accepted:2024-05-14
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-05-16
Contact:
* E-mail: congzeng@sjtu.edu.cnCLC Number:
Yihui Jiang, Yue Liu, Xu Zeng, Zheying Lin, Nan Wang, Jihao Peng, Ling Cao, Cong Zeng. Fish diversity and connectivity in six national marine protected areas in the East China Sea[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24128.
| 海洋保护区 MPA | 所在地 Location | 建立时间 Establishment time | 主要保护对象 Main objects of protection | 面积 Area (km2) | 保护区类型 MPA type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城洲岛国家级海洋公园Chengzhou Island National Marine Park | 福建省漳州市 Zhangzhou City, Fujian Province | 2012.12 | 海岛生态系统 Island ecosystems | 3.03 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 深沪湾海底古森林遗迹国家级自然保护区 Shenhu Bay National Nature Reserve | 福建省泉州市 Quanzhou City, Fujian Province | 1992.10 | 海洋自然遗迹和非生物资源; 海底古森林遗迹、古牡蛎礁遗迹 Marine natural remains and non- living resources; Remains of ancient forests on the seabed and ancient oyster reefs | 31.00 | 自然保护区 Nature reserve |
| 湄洲岛国家级海洋公园Meizhou Island National Marine Park | 福建省莆田市 Putian City, Fujian Province | 2012.12 | 海岛生态系统及砂质岸线 Island ecosystems and sandy shorelines | 69.11 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 平潭综合实验区海坛湾国家级海洋公园 Haitan Bay National Marine Park in Pingtan | 福建省福州市 Fuzhou City, Fujian Province | 2016.08 | 滨海沙滩、海岸景观、海域生境、仙女蛤种质资源 Coastal beaches and landscapes, marine habitats, Callista chinensis germplasm resources | 34.90 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 洞头国家级海洋公园 Dongtou National Marine Park | 浙江省温州市 Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province | 2012.12 | 海洋公园/典型海岛生态系统, 海洋景观、生物资源、鸟类资源 Marine park/typical island ecosystem, marine landscape, biological resources, bird resources | 311.04 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 玉环国家级海洋公园 Yuhuan National Marine Park | 浙江省台州市 Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province | 2016.12 | 鱼类、贝类和大型藻类、红树林群落及湿地鸟类, 重要渔业品种及生境、乐清湾茅埏岛湿地红树林生态系统生境的多样性 Fish, shellfish, macroalgae, mangrove communities, wetland birds, important fishery species and habitats, diversity of mangrove ecosystem habitats in the wetland of Maotao Island in Yueqing Bay | 306.69 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
Table 1 Basic information on the marine protected areas (MPAs) surveyed in this study
| 海洋保护区 MPA | 所在地 Location | 建立时间 Establishment time | 主要保护对象 Main objects of protection | 面积 Area (km2) | 保护区类型 MPA type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城洲岛国家级海洋公园Chengzhou Island National Marine Park | 福建省漳州市 Zhangzhou City, Fujian Province | 2012.12 | 海岛生态系统 Island ecosystems | 3.03 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 深沪湾海底古森林遗迹国家级自然保护区 Shenhu Bay National Nature Reserve | 福建省泉州市 Quanzhou City, Fujian Province | 1992.10 | 海洋自然遗迹和非生物资源; 海底古森林遗迹、古牡蛎礁遗迹 Marine natural remains and non- living resources; Remains of ancient forests on the seabed and ancient oyster reefs | 31.00 | 自然保护区 Nature reserve |
| 湄洲岛国家级海洋公园Meizhou Island National Marine Park | 福建省莆田市 Putian City, Fujian Province | 2012.12 | 海岛生态系统及砂质岸线 Island ecosystems and sandy shorelines | 69.11 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 平潭综合实验区海坛湾国家级海洋公园 Haitan Bay National Marine Park in Pingtan | 福建省福州市 Fuzhou City, Fujian Province | 2016.08 | 滨海沙滩、海岸景观、海域生境、仙女蛤种质资源 Coastal beaches and landscapes, marine habitats, Callista chinensis germplasm resources | 34.90 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 洞头国家级海洋公园 Dongtou National Marine Park | 浙江省温州市 Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province | 2012.12 | 海洋公园/典型海岛生态系统, 海洋景观、生物资源、鸟类资源 Marine park/typical island ecosystem, marine landscape, biological resources, bird resources | 311.04 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 玉环国家级海洋公园 Yuhuan National Marine Park | 浙江省台州市 Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province | 2016.12 | 鱼类、贝类和大型藻类、红树林群落及湿地鸟类, 重要渔业品种及生境、乐清湾茅埏岛湿地红树林生态系统生境的多样性 Fish, shellfish, macroalgae, mangrove communities, wetland birds, important fishery species and habitats, diversity of mangrove ecosystem habitats in the wetland of Maotao Island in Yueqing Bay | 306.69 | 特别保护区 Special protection area |
| 分组 Group | 温度 Temperature (℃) | 盐度 Salinity | 溶解氧 DO (mg/L) | 酸碱度 pH | 浊度 Turbidity (NTU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城洲岛 CZD | 22.11 ± 5.30a | 32.65 ± 1.24b | 7.05 ± 0.58b | 7.79 ± 0.21a | 10.99 ± 6.28a |
| 深沪湾 SHW | 23.19 ± 7.96a | 32.84 ± 1.56b | 6.43 ± 0.37a | 7.88 ± 0.18a | 40.52 ± 43.86ab |
| 湄洲岛 MZD | 20.69 ± 5.98a | 31.80 ± 1.46b | 7.12 ± 0.86b | 8.13 ± 0.45a | 32.82 ± 18.00b |
| 平潭岛 PTD | 20.43 ± 7.53a | 31.91 ± 1.68b | 7.05 ± 0.85b | 7.95 ± 0.17a | 26.10 ± 25.73ab |
| 洞头岛 DTD | 20.36 ± 6.41a | 28.34 ± 0.73a | 7.14 ± 0.71b | 8.50 ± 1.06a | 65.98 ± 36.21b |
| 玉环 YH | 20.80 ± 7.24a | 28.65 ± 0.74a | 7.35 ± 0.96b | 7.87 ± 0.27a | 405.73 ± 656.86b |
| 冬季 Winter | 14.46 ± 1.93a | 30.24 ± 1.51a | 6.73 ± 1.01a | 8.12 ± 0.09c | 49.86 ± 37.92b |
| 春季 Spring | 15.71 ± 1.50b | 30.26 ± 1.61a | 7.63 ± 0.78b | 8.47 ± 0.89c | 28.66 ± 27.92a |
| 夏季 Summer | 29.88 ± 2.57d | 32.19 ± 3.16a | 6.81 ± 0.54a | 7.86 ± 0.10b | 258.26 ± 568.82c |
| 秋季 Autumn | 24.56 ± 1.05c | 31.31 ± 1.75a | 6.90 ± 0.29a | 7.65 ± 0.10a | 53.49 ± 31.56b |
Table 2 Comparison of environmental parameters between different marine protected areas (MPAs) and seasons
| 分组 Group | 温度 Temperature (℃) | 盐度 Salinity | 溶解氧 DO (mg/L) | 酸碱度 pH | 浊度 Turbidity (NTU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城洲岛 CZD | 22.11 ± 5.30a | 32.65 ± 1.24b | 7.05 ± 0.58b | 7.79 ± 0.21a | 10.99 ± 6.28a |
| 深沪湾 SHW | 23.19 ± 7.96a | 32.84 ± 1.56b | 6.43 ± 0.37a | 7.88 ± 0.18a | 40.52 ± 43.86ab |
| 湄洲岛 MZD | 20.69 ± 5.98a | 31.80 ± 1.46b | 7.12 ± 0.86b | 8.13 ± 0.45a | 32.82 ± 18.00b |
| 平潭岛 PTD | 20.43 ± 7.53a | 31.91 ± 1.68b | 7.05 ± 0.85b | 7.95 ± 0.17a | 26.10 ± 25.73ab |
| 洞头岛 DTD | 20.36 ± 6.41a | 28.34 ± 0.73a | 7.14 ± 0.71b | 8.50 ± 1.06a | 65.98 ± 36.21b |
| 玉环 YH | 20.80 ± 7.24a | 28.65 ± 0.74a | 7.35 ± 0.96b | 7.87 ± 0.27a | 405.73 ± 656.86b |
| 冬季 Winter | 14.46 ± 1.93a | 30.24 ± 1.51a | 6.73 ± 1.01a | 8.12 ± 0.09c | 49.86 ± 37.92b |
| 春季 Spring | 15.71 ± 1.50b | 30.26 ± 1.61a | 7.63 ± 0.78b | 8.47 ± 0.89c | 28.66 ± 27.92a |
| 夏季 Summer | 29.88 ± 2.57d | 32.19 ± 3.16a | 6.81 ± 0.54a | 7.86 ± 0.10b | 258.26 ± 568.82c |
| 秋季 Autumn | 24.56 ± 1.05c | 31.31 ± 1.75a | 6.90 ± 0.29a | 7.65 ± 0.10a | 53.49 ± 31.56b |
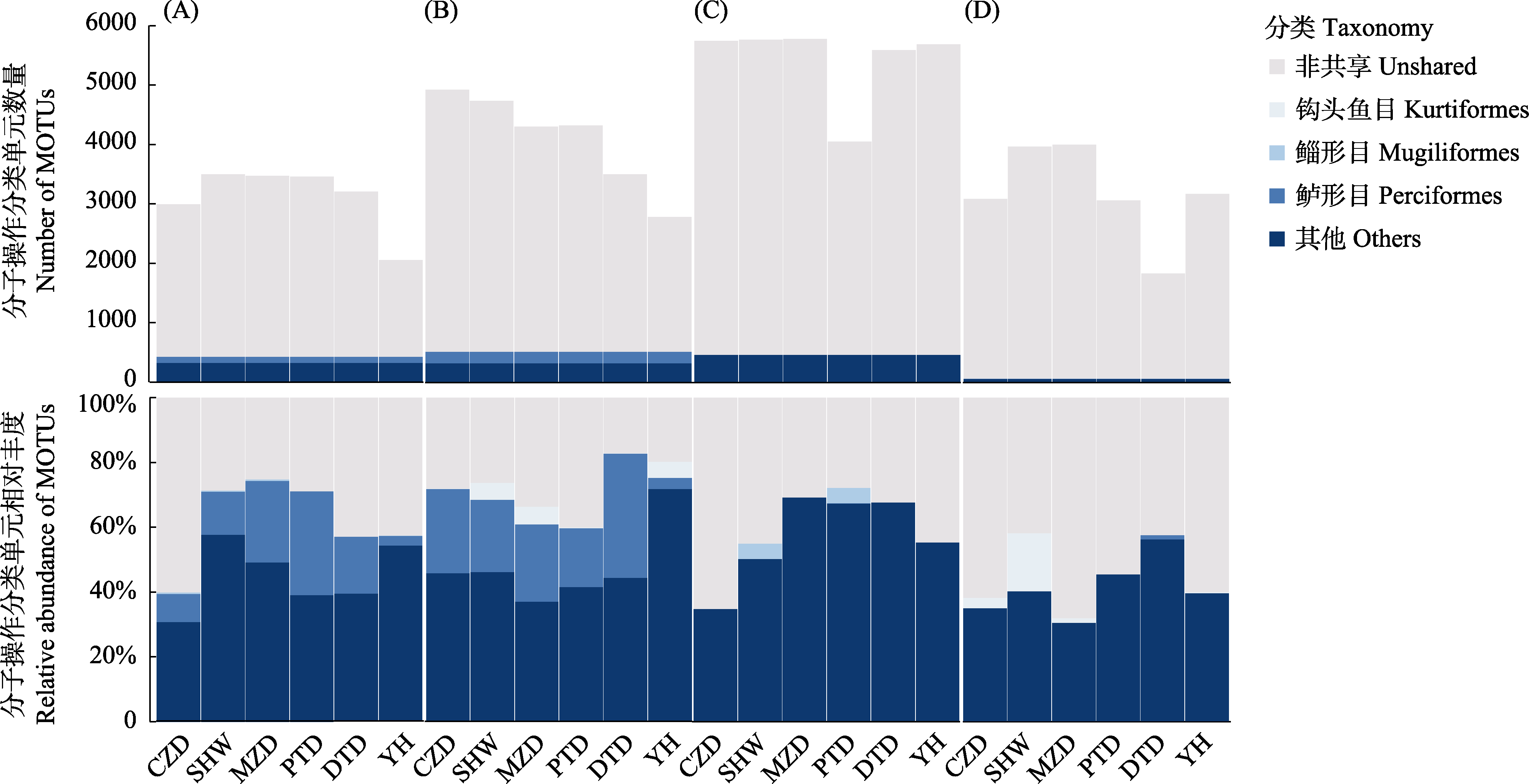
Fig. 1 Molecular operational taxonomic units (MOTUs) composition (top) and its relative abundance (bottom) in marine protected areas (MPAs) in different seasons. A, B, C and D are winter, spring, summer and autumn, respectively. CZD, Chengzhou Island National Marine Park; SHW, Shenhu Bay National Nature Reserve; MZD, Meizhou Island National Marine Park; PTD, Haitan Bay National Marine Park in Pingtan; DTD, Dongtou National Marine Park; YH, Yuhuan National Marine Park.
| 分组 Group | Chao 1指数 Chao 1 index | 观测MOTUs数 Observed MOTUs | Pielou均匀度 Pielou evenness | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城洲岛 CZD | 3,670.65 ± 1,412.54a | 2,069.31 ± 679.58a | 0.54 ± 0.10a | 5.96 ± 1.38a | 0.88 ± 0.11a |
| 深沪湾 SHW | 3,549.04 ± 1,189.05a | 2,124.28 ± 720.24a | 0.52 ± 0.10a | 5.78 ± 1.28a | 0.87 ± 0.11a |
| 湄洲岛 MZD | 3,552.78 ± 1,296.09a | 2,030.64 ± 561.76a | 0.51 ± 0.04a | 5.54 ± 0.66a | 0.88 ± 0.04a |
| 平潭岛 PTD | 2,976.05 ± 785.15a | 1,700.30 ± 404.86a | 0.47 ± 0.07a | 5.05 ± 0.91a | 0.83 ± 0.12a |
| 洞头岛 DTD | 2,882.04 ± 1,382.58a | 1,744.87 ± 805.76a | 0.48 ± 0.09a | 5.19 ± 1.34a | 0.84 ± 0.10a |
| 玉环 YH | 2,714.99 ± 1,110.37a | 1,624.95 ± 684.92a | 0.45 ± 0.11a | 4.76 ± 1.47a | 0.79 ± 0.15a |
| 冬季 Winter | 2,846.51 ± 603.43bc | 1,643.15 ± 274.04ab | 0.48 ± 0.07b | 5.13 ± 0.82b | 0.86 ± 0.08bc |
| 春季 Spring | 3,289.03 ± 873.69ab | 1,906.99 ± 508.71ab | 0.48 ± 0.08ab | 5.27 ± 0.98ab | 0.85 ± 0.12ab |
| 夏季 Summer | 4,481.35 ± 1,289.66a | 2,557.84 ± 739.96a | 0.57 ± 0.11a | 6.51 ± 1.43a | 0.89 ± 0.12a |
| 秋季 Autumn | 2,234.35 ± 755.41c | 1,397.91 ± 371.07b | 0.44 ± 0.05b | 4.56 ± 0.70b | 0.78 ± 0.08c |
Table 3 Comparison of diversity indices between different marine protected areas (MPAs) and seasons
| 分组 Group | Chao 1指数 Chao 1 index | 观测MOTUs数 Observed MOTUs | Pielou均匀度 Pielou evenness | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城洲岛 CZD | 3,670.65 ± 1,412.54a | 2,069.31 ± 679.58a | 0.54 ± 0.10a | 5.96 ± 1.38a | 0.88 ± 0.11a |
| 深沪湾 SHW | 3,549.04 ± 1,189.05a | 2,124.28 ± 720.24a | 0.52 ± 0.10a | 5.78 ± 1.28a | 0.87 ± 0.11a |
| 湄洲岛 MZD | 3,552.78 ± 1,296.09a | 2,030.64 ± 561.76a | 0.51 ± 0.04a | 5.54 ± 0.66a | 0.88 ± 0.04a |
| 平潭岛 PTD | 2,976.05 ± 785.15a | 1,700.30 ± 404.86a | 0.47 ± 0.07a | 5.05 ± 0.91a | 0.83 ± 0.12a |
| 洞头岛 DTD | 2,882.04 ± 1,382.58a | 1,744.87 ± 805.76a | 0.48 ± 0.09a | 5.19 ± 1.34a | 0.84 ± 0.10a |
| 玉环 YH | 2,714.99 ± 1,110.37a | 1,624.95 ± 684.92a | 0.45 ± 0.11a | 4.76 ± 1.47a | 0.79 ± 0.15a |
| 冬季 Winter | 2,846.51 ± 603.43bc | 1,643.15 ± 274.04ab | 0.48 ± 0.07b | 5.13 ± 0.82b | 0.86 ± 0.08bc |
| 春季 Spring | 3,289.03 ± 873.69ab | 1,906.99 ± 508.71ab | 0.48 ± 0.08ab | 5.27 ± 0.98ab | 0.85 ± 0.12ab |
| 夏季 Summer | 4,481.35 ± 1,289.66a | 2,557.84 ± 739.96a | 0.57 ± 0.11a | 6.51 ± 1.43a | 0.89 ± 0.12a |
| 秋季 Autumn | 2,234.35 ± 755.41c | 1,397.91 ± 371.07b | 0.44 ± 0.05b | 4.56 ± 0.70b | 0.78 ± 0.08c |
| 基于Jaccard距离 Based on Jaccard distance | 基于Bray-Curtis距离 Based on Bray-Curtis distance | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自由度 df | 总方差 SS | R2 | F | Pr (> F) | 自由度 df | 总方差 SS | R2 | F | Pr (> F) | ||
| 保护区 MPA | 5 | 1.33 | 0.09 | 1.30 | 0.09 | 5 | 1.10 | 0.10 | 1.52 | 0.054 | |
| 残差 Residual | 65 | 13.29 | 0.91 | 65 | 9.36 | 0.90 | |||||
| 总和 Total | 70 | 14.61 | 1 | 70 | 10.46 | 1 | |||||
| 季节 Season | 3 | 1.89 | 0.13 | 3.31 | 0.001*** | 3 | 1.49 | 0.14 | 3.70 | 0.001*** | |
| 残差 Residual | 67 | 12.72 | 0.87 | 67 | 8.97 | 0.86 | |||||
| 总和 Total | 70 | 14.61 | 1 | 70 | 10.46 | 1 | |||||
Table 4 Tests of variability in fish community composition among different marine protected areas (MPAs) and seasons
| 基于Jaccard距离 Based on Jaccard distance | 基于Bray-Curtis距离 Based on Bray-Curtis distance | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自由度 df | 总方差 SS | R2 | F | Pr (> F) | 自由度 df | 总方差 SS | R2 | F | Pr (> F) | ||
| 保护区 MPA | 5 | 1.33 | 0.09 | 1.30 | 0.09 | 5 | 1.10 | 0.10 | 1.52 | 0.054 | |
| 残差 Residual | 65 | 13.29 | 0.91 | 65 | 9.36 | 0.90 | |||||
| 总和 Total | 70 | 14.61 | 1 | 70 | 10.46 | 1 | |||||
| 季节 Season | 3 | 1.89 | 0.13 | 3.31 | 0.001*** | 3 | 1.49 | 0.14 | 3.70 | 0.001*** | |
| 残差 Residual | 67 | 12.72 | 0.87 | 67 | 8.97 | 0.86 | |||||
| 总和 Total | 70 | 14.61 | 1 | 70 | 10.46 | 1 | |||||
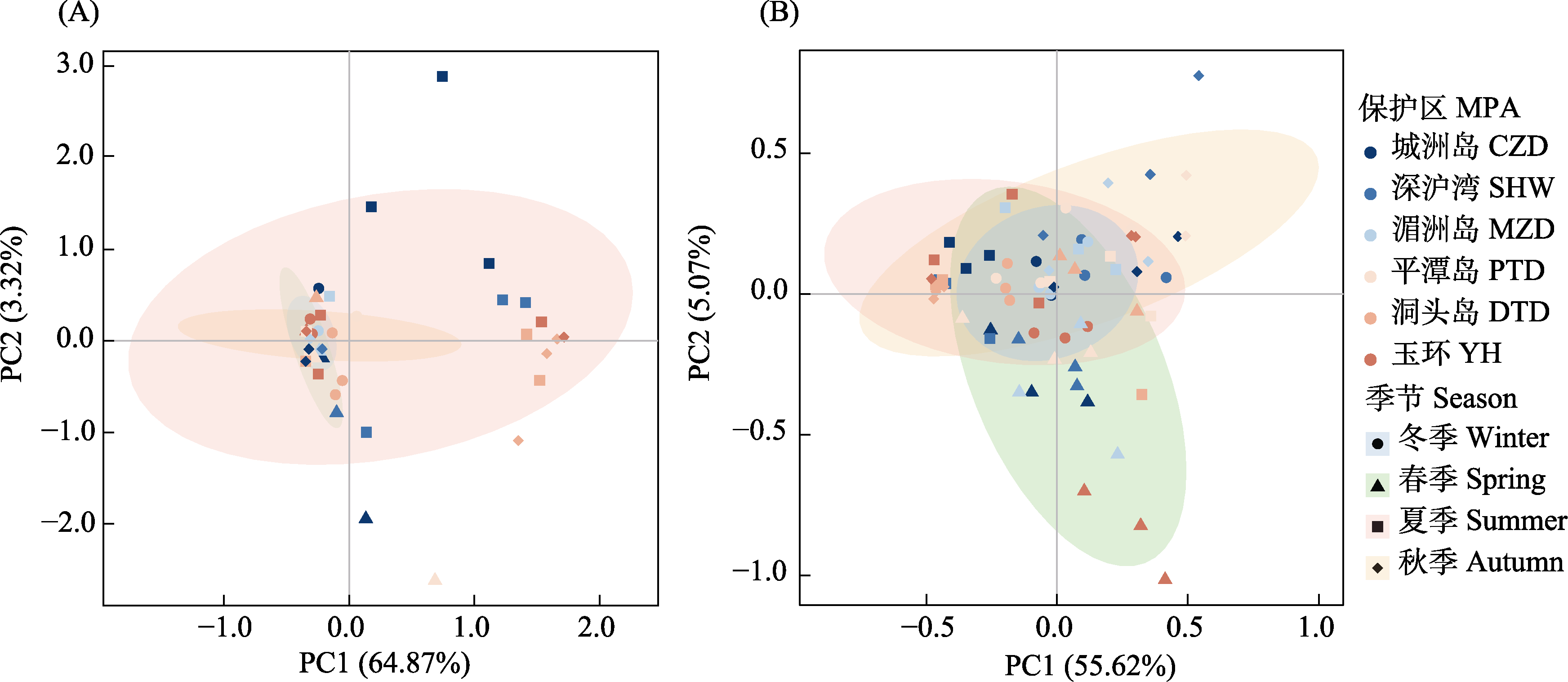
Fig. 2 Principal component analysis of fish community composition in marine protected areas (MPAs) based on presence/absence data (A) and Hellinge transformed abundance data (B). CZD, Chengzhou Island National Marine Park; SHW, Shenhu Bay National Nature Reserve; MZD, Meizhou Island National Marine Park; PTD, Haitan Bay National Marine Park in Pingtan; DTD, Dongtou National Marine Park; YH, Yuhuan National Marine Park.
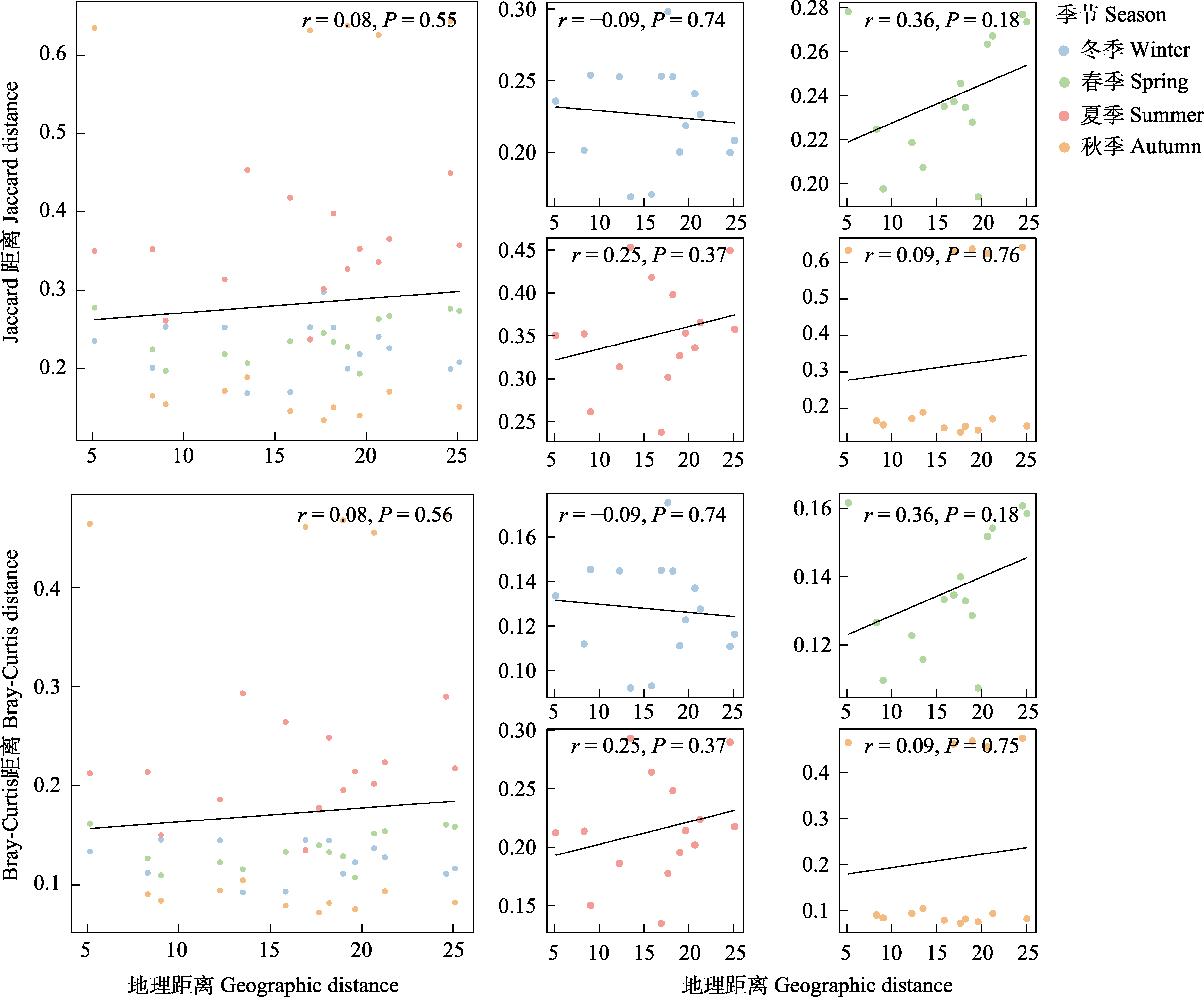
Fig. 3 Correlation analysis between differences in community composition and geographic distance. Geographic distance is the shortest straight-line distance between two sampling converted to a logarithmic scale. r, Correlation coefficient; P, P-value.
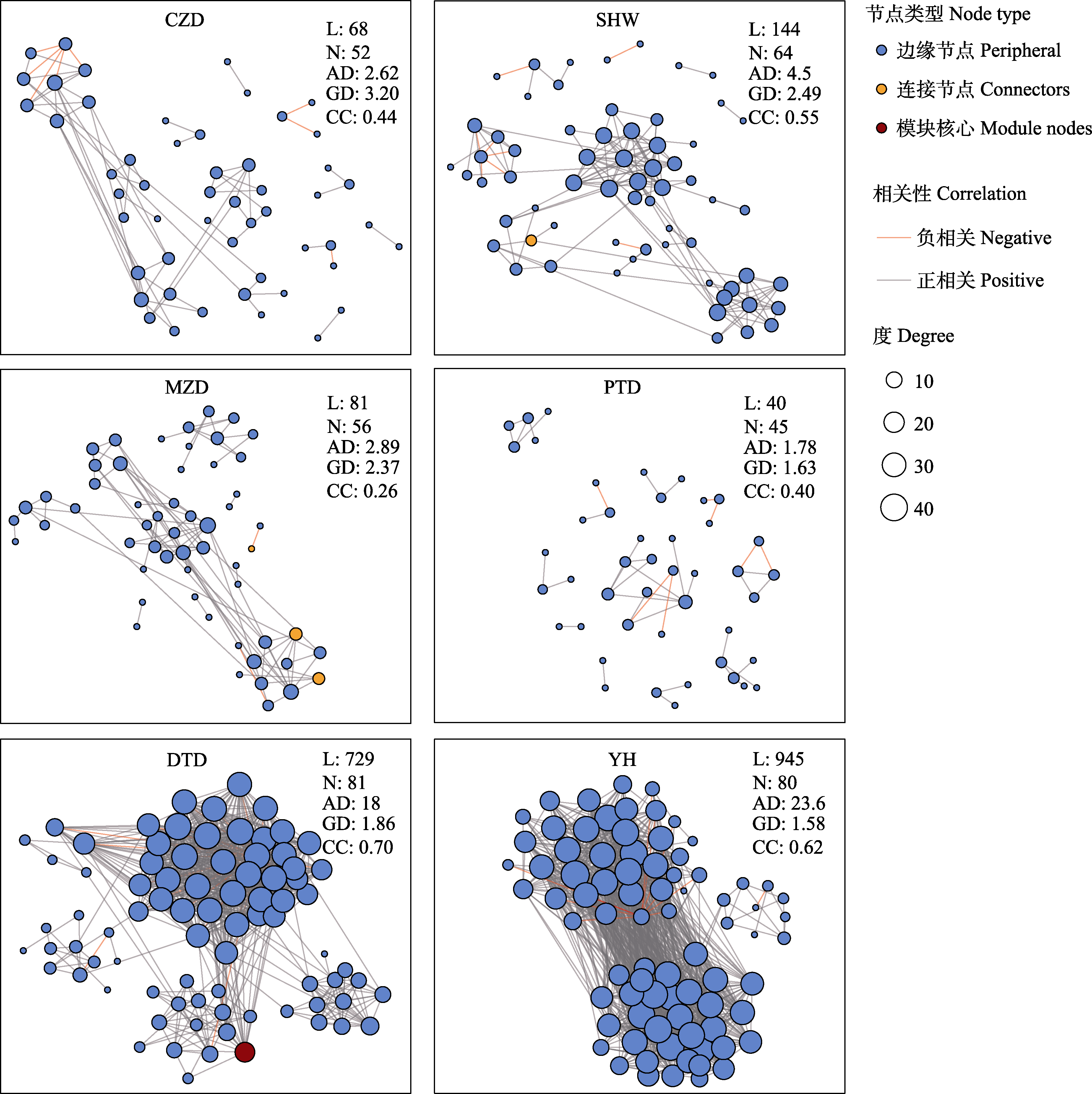
Fig. 4 Network analysis of associations in protected areas. L, N, AD, GD and CC stand for the number of edges, number of nodes, mean degree, mean path length and mean clustering coefficient respectively, and degree stands for the number of nodes connected to a node. CZD, Chengzhou Island National Marine Park; SHW, Shenhu Bay National Nature Reserve; MZD, Meizhou Island National Marine Park; PTD, Haitan Bay National Marine Park in Pingtan; DTD, Dongtou National Marine Park; YH, Yuhuan National Marine Park.
| [1] | Airamé S, Dugan JE, Lafferty KD, Leslie H, McArdle DA, Warner RR (2003) Applying ecological criteria to marine reserve design: A case study from the California channel islands. Ecological Applications, 13, 170-184. |
| [2] | Alberdi A, Aizpurua O, Gilbert MTP, Bohmann K (2017) Scrutinizing key steps for reliable metabarcoding of environmental samples. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 134-147. |
| [3] | Altermatt F, Bieger A, Carrara F, Rinaldo A, Holyoak M (2011) Effects of connectivity and recurrent local disturbances on community structure and population density in experimental metacommunities. PLoS ONE, 6, e19525. |
| [4] |
Avolio ML, Forrestel EJ, Chang CC, LaPierre KJ, Burghardt KT, Smith MD (2019) Demystifying dominant species. New Phytologist, 223, 1106-1126.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Balbar AC, Metaxas A (2019) The current application of ecological connectivity in the design of marine protected areas. Global Ecology and Conservation, 17, e00569. |
| [6] | Barnes MA, Turner CR, Jerde CL, Renshaw MA, Chadderton WL, Lodge DM (2014) Environmental conditions influence eDNA persistence in aquatic systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 48, 1819-1827. |
| [7] | Chen MY, Zeng C, Zeng X, Liu Y, Wang ZH, Shi XJ, Cao L (2023) Assessment of marine protected areas in the East China Sea using a management effectiveness tracking tool. Frontiers in Marine Science, 10, 1081036. |
| [8] | Christie MR, Tissot BN, Albins MA, Beets JP, Jia YL, Ortiz DM, Thompson SE, Hixon MA (2010) Larval connectivity in an effective network of marine protected areas. PLoS ONE, 5, e15715. |
| [9] |
Costello MJ, Tsai P, Wong PS, Cheung AKL, Basher Z, Chaudhary C (2017) Marine biogeographic realms and species endemicity. Nature Communications, 8, 1057.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Du JG, Xie ML, Wang YY, Chen ZH, Liu WH, Liao JJ, Chen B (2020) Connectivity of fish assemblages along the mangrove-seagrass-coral reef continuum in Wenchang, China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 39, 43-52. |
| [11] | Du PJ, Zhang H, Xiao WJ, Kang X, Guan QL (2011) Analysis of thermohaline and current distribution characteristics of Zhejiang and Fujian waters in summer. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 30, 71-83. |
| [12] |
Freeland JR (2017) The importance of molecular markers and primer design when characterizing biodiversity from environmental DNA. Genome, 60, 358-374.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Guan BX (1994) Patterns and structures of the currents in Bohai, Huanghai and East China Seas. In: Oceanology of China Seas (eds Zhou D, Liang YB, Zeng CK), pp.17-26. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [14] | He XB, Zhang FJ, Lin L, Chen WD, Cai HC, Yu CG (2013) Species composition and quantitative distribution of fishes in island-reef water of Nanji Islands. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 44, 453-460. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何贤保, 章飞军, 林利, 陈万东, 蔡厚才, 俞存根 (2013) 南麂列岛岛礁区域鱼类种类组成和数量分布. 海洋与湖沼, 44, 453-460.] | |
| [15] | Hellinger E (1909) Neue Begründung der Theorie quadratischer Formen von unendlichvielen Veränderlichen. Journal Für Die Reine Und Angewandte Mathematik, 1909, 210-271. |
| [16] | Jiang PW, Li M, Zhang S, Chen ZZ, Xu SN (2022) Investigating the fish diversity in Pearl River Estuary based on environmental DNA matebarcoding and bottom trawling. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 46, 1701-1711. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋佩文, 李敏, 张帅, 陈作志, 徐姗楠 (2022) 基于环境DNA宏条码和底拖网的珠江河口鱼类多样性. 水生生物学报, 46, 1701-1711.] | |
| [17] | Jing ZY, Qi YQ, Hua ZL (2007) Numerical study on upwelling and its seasonal variation along Fujian and Zhejiang coast. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 35, 464-470. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [经志友, 齐义泉, 华祖林 (2007) 闽浙沿岸上升流及其季节变化的数值研究. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 35, 464-470.] | |
| [18] | Kelleher G, Kenchington RA (1992) Guidelines for Establishing Marine Protected Areas. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. |
| [19] | Lester SE, Costello C, Halpern BS, Gaines SD, White C, Barth JA (2013) Evaluating tradeoffs among ecosystem services to inform marine spatial planning. Marine Policy, 38, 80-89. |
| [20] | Li SF (2005) The Ecological Study for Fish Community in the East China Sea Continental Shelf: The Spatial Pattern and Diversity. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李圣法 (2005) 东海大陆架鱼类群落生态学研究——空间格局及其多样性. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [21] | Li SF, Cheng JH, Yan LP (2007) Spatial structures of fish communities on the continental shelf of the East China Sea. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27, 4377-4386. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李圣法, 程家骅, 严利平 (2007) 东海大陆架鱼类群落的空间结构. 生态学报, 27, 4377-4386.] | |
| [22] | Li XL, Liu Y, Wang CC, Yu YW, Li G (2022) Study on fish species diversity in the East China Sea in summer based on environmental DNA technology. Haiyang Xuebao, 44(4), 74-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李晓玲, 刘洋, 王丛丛, 俞晔伟, 李纲 (2022) 基于环境DNA技术的夏季东海鱼类物种多样性研究. 海洋学报, 44(4), 74-84.] | |
| [23] | Li YZ, Fluharty DL (2017) Marine protected area networks in China: Challenges and prospects. Marine Policy, 85, 8-16. |
| [24] | Lim SJ, Thompson LR (2021) Mitohelper: A mitochondrial reference sequence analysis tool for fish eDNA studies. Environmental DNA, 3, 706-715. |
| [25] |
Liu CL, Xu Q, Wang LL, Xing YK, Song JH, Lin BA, Kang B, Liu M (2023) Nekton diversity, density, and community structure of spring and autumn in coastal waters of eastern Fujian Province. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22635. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘彩莲, 许庆, 王林龙, 邢衍阔, 宋稼豪, 林柏岸, 康斌, 刘敏 (2023) 闽东近海春秋季游泳动物多样性、密度及群落特征. 生物多样性, 31, 22635.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Liu Y, Li SF, Cheng JH (2006) A study on seasonal changes of the fish communities in the East China Sea and the Huanghai Sea. Haiyang Xuebao, 28(4), 108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘勇, 李圣法, 程家骅 (2006) 东海、黄海鱼类群落结构的季节变化研究. 海洋学报, 28(4), 108-114.] | |
| [27] | Liu ZL, Yang LL, Yan LP, Yuan XW, Cheng JH (2016) Fish assemblages and environmental interpretation in the northern Taiwan Strait and its adjacent waters in summer. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 23, 1399-1416. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘尊雷, 杨林林, 严利平, 袁兴伟, 程家骅 (2016) 夏季台湾海峡北部及邻近海域鱼类群落结构及环境解释. 中国水产科学, 23, 1399-1416.] | |
| [28] | Liu ZQ, Gan JP, Hu JY, Wu H, Cai ZY, Deng YF (2021) Progress on circulation dynamics in the East China Sea and southern Yellow Sea: Origination, pathways, and destinations of shelf currents. Progress in Oceanography, 193, 102553. |
| [29] | Loke LHL, Chisholm RA (2023) Unveiling the transition from niche to dispersal assembly in ecology. Nature, 618, 537-542. |
| [30] | Lu JY, Chen YJ, Wang ZH, Zhao F, Zhong YS, Zeng C, Cao L (2023) Larval dispersal modeling reveals low connectivity among national marine protected areas in the Yellow and East China seas. Biology, 12, 396. |
| [31] |
Luboeinski J, Claro L, Pomi A, Mizraji E (2023) Stabilization through self-coupling in networks of small-world and scale-free topology. Scientific Reports, 13, 1089.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Mathieu C, Hermans SM, Lear G, Buckley TR, Lee KC, Buckley HL (2020) A systematic review of sources of variability and uncertainty in eDNA data for environmental monitoring. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 8, 135. |
| [33] | Miya M, Gotoh RO, Sado T (2020) MiFish metabarcoding: A high-throughput approach for simultaneous detection of multiple fish species from environmental DNA and other samples. Fisheries Science, 86, 939-970. |
| [34] | Miya M, Sato Y, Fukunaga T, Sado T, Poulsen JY, Sato K, Minamoto T, Yamamoto S, Yamanaka H, Araki H, Kondoh M, Iwasaki W (2015) MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. Royal Society Open Science, 2, 150088. |
| [35] | Paris CB, Murawski SA, Olascoaga MJ, Vaz AC, Berenshtein I, Miron P, Beron-Vera FJ (2020) Connectivity of the Gulf of Mexico continental shelf fish populations and implications of simulated oil spills. In: Scenarios and Responses to Future Deep Oil Spills (eds Murawski S, Ainsworth CH, Gilbert S, Hollander DJ, Paris CB, Schlüter M, Wetzel DL), pp.369-389. Springer, Cham. |
| [36] | Porebski S, Bailey LG, Baum BR (1997) Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 15, 8-15. |
| [37] |
Port JA, O’Donnell JL, Romero-Maraccini OC, Leary PR, Litvin SY, Nickols KJ, Yamahara KM, Kelly RP (2016) Assessing vertebrate biodiversity in a kelp forest ecosystem using environmental DNA. Molecular Ecology, 25, 527-541.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | Ross RE, Nimmo-Smith WAM, Howell KL (2017) Towards ‘ecological coherence’: Assessing larval dispersal within a network of existing Marine Protected Areas. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 126, 128-138. |
| [39] | Selkoe KA, D’Aloia CC, Crandall ED, Iacchei M, Liggins L, Puritz JB, von der Heyden S, Toonen RJ (2016) A decade of seascape genetics: Contributions to basic and applied marine connectivity. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 554, 1-19. |
| [40] | Smith J, Metaxas A (2018) A decision tree that can address connectivity in the design of Marine Protected Area Networks (MPAn). Marine Policy, 88, 269-278. |
| [41] | Tang FL (2020) Features and paths of building unique Chinese National Park system. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (Social Sciences), 19(2), 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [唐芳林 (2020) 中国特色国家公园体制建设的特征和路径. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版), 19(2), 33-39.] | |
| [42] | Treml EA, Halpin PN, Urban DL, Pratson LF (2008) Modeling population connectivity by ocean currents, a graph-theoretic approach for marine conservation. Landscape Ecology, 23, 19-36. |
| [43] |
Uroy L, Ernoult A, Mony C (2019) Effect of landscape connectivity on plant communities: A review of response patterns. Landscape Ecology, 34, 203-225.
DOI |
| [44] | Wang B (2018) The outlook for the establishment and management of marine protected area network in China. International Journal of Geoheritage and Parks, 6, 32-42. |
| [45] | Wang PK, Li SF, Liu ZL, Jin Y, Jiang YZ, Zhang H, Zhang Y (2022) Spatial connectivity in juvenile Larimichthys polyactis from otolith microchemistry in coastal areas of southern Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Marine Fisheries, 44, 140-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王鹏凯, 李圣法, 刘尊雷, 金艳, 姜亚洲, 张辉, 张翼 (2022) 基于耳石微化学的东海和黄海南部近海小黄鱼幼鱼的空间连通性研究. 海洋渔业, 44, 140-151.] | |
| [46] | Wang ZH, Zeng C, Cao L (2023) Mapping the biodiversity conservation gaps in the East China Sea. Journal of Environmental Management, 336, 117667. |
| [47] |
Wang ZH, Zeng C, Jiang ZY, Cao L (2023) Conservation gap analysis of threatened fish in the East China Sea and adjacent sea areas. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 42, 66-86. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王子涵, 曾聪, 姜子禺, 曹玲 (2023) 东海及其邻近海域受胁鱼类保护空缺分析. 热带海洋学报, 42, 66-86.]
DOI |
|
| [48] |
Watson JR, Hays CG, Raimondi PT, Mitarai S, Dong C, McWilliams JC, Blanchette CA, Caselle JE, Siegel DA (2011) Currents connecting communities: Nearshore community similarity and ocean circulation. Ecology, 92, 1193-1200.
PMID |
| [49] | Weng SX, Wu JF (2021) Pingtan International Tourism Island receives over 24 million tourists in 5 years. China Tourism News, 2021-08-10, 002. (in Chinese) |
| [翁书歆, 吴健芳 (2021) 平潭国际旅游岛5年接待游客超2400万人次. 中国旅游报, 2021-08-10, 002.] | |
| [50] | White C, Selkoe KA, Watson J, Siegel DA, Zacherl DC, Toonen RJ (2010) Ocean currents help explain population genetic structure. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 277, 1685-1694. |
| [51] | Wilhelm T, Sheppard CRC, Sheppard ALS, Gaymer CF, Parks J, Wagner D, Lewis N (2014) Large marine protected areas—Advantages and challenges of going big. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 24, 24-30. |
| [52] | Xiong Y, Zheng YJ, Tang JH, Zhong XM, Yang J, Cui ZH, Wu L (2018) Advances in survey methods for population identification in marine fishes and their application to small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis). Marine Fisheries, 40, 117-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [熊瑛, 郑元甲, 汤建华, 仲霞铭, 杨健, 崔正贺, 吴磊 (2018) 海洋鱼类种群划分的研究方法及其在小黄鱼上的应用进展. 海洋渔业, 40, 117-128.] | |
| [53] | Xu ZL, Chen JJ (2009) Analysis on migratory routine of Larimichthy polyactis. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 16, 931-940. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐兆礼, 陈佳杰 (2009) 小黄鱼洄游路线分析. 中国水产科学, 16, 931-940.] | |
| [54] | Zaiko A, Pochon X, Garcia-Vazquez E, Olenin S, Wood SA (2018) Advantages and limitations of environmental DNA/RNA tools for marine biosecurity: Management and surveillance of non-indigenous species. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5, 322. |
| [55] | Zeng JN, Zeng X, Ye GQ, Deng BP (2021) The development process and future trend of marine protected areas in Yangtze River Delta based on the integration strategy. Natural Protected Areas, 1, 60-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾江宁, 曾旭, 叶观琼, 邓邦平 (2021) 基于一体化战略的长三角海洋保护地建设历程与未来趋势. 自然保护地, 1, 60-71.] | |
| [56] | Zhang JS, Su FZ, Du YY (2004) Relationship between pelagic fishery resources and sea surface temperature in East China Sea. Resources Science, (5), 147-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张甲珅, 苏奋振, 杜云艳 (2004) 东海区中上层鱼类资源与海表温度关系. 资源科学, (5), 147-152.] | |
| [57] | Zhang S, Zhao JD, Yao M, Gilbert M (2020) A comprehensive and comparative evaluation of primers for metabarcoding eDNA from fish. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 11, 1609-1625. |
| [58] | Zhang ZH, Zhou J, Lü JB, Ding DW (2007) Connotation and characteristics of marine ecosystem services. Marine Environmental Research, 26, 259-263. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张朝晖, 周骏, 吕吉斌, 丁德文 (2007) 海洋生态系统服务的内涵与特点. 海洋环境科学, 26, 259-263.] | |
| [59] | Zhao F, Liu Y, Wang ZH, Lu JY, Cao L, Zeng C (2023) Genetic diversity and connectivity of Ocypode ceratophthalmus in the East and South China Seas and its implications for conservation. Biology, 12, 437. |
| [60] | Zheng YJ, Li JS, Zhang QY, Hong WS (2014) Research progresses of resource biology of important marine pelagic food fishes in China. Journal of Fisheries of China, 38, 149-160. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑元甲, 李建生, 张其永, 洪万树 (2014) 中国重要海洋中上层经济鱼类生物学研究进展. 水产学报, 38, 149-160.] |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn