



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 24117. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024117 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024117
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hua Ma1( ), Changqing Li1, Pinfeng Yu1, Jie Chen1, Tianyao He1, Kehong Wang1,2,*(
), Changqing Li1, Pinfeng Yu1, Jie Chen1, Tianyao He1, Kehong Wang1,2,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-03-26
Accepted:2024-05-16
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-07-02
Contact:
*E-mail: wang018837@hotmail.com
Supported by:Hua Ma, Changqing Li, Pinfeng Yu, Jie Chen, Tianyao He, Kehong Wang. Distribution patterns and impact factors of soil macrofauna communities in the riparian zone of the Pengxi River[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24117.
| 项目 Items | 样点 Site | 高程(样点) Elevation (Site) |
|---|---|---|
| 丰度 Richness | 1.059 | 3.867*** |
| 多度 Abundance | 1.662 | 1.814* |
| 多样性指数 Diversity index (H′) | 1.051 | 2.326** |
| 优势度指数 Dominance index (C) | 0.969 | 2.451** |
| 捕食者相对多度 Relative abundance of predator | 0.807 | 3.925*** |
| 杂食者相对多度 Relative abundance of omnivore | 0.845 | 2.761*** |
| 腐食者相对多度 Relative abundance of detritivore | 0.357 | 9.377*** |
| 植食者相对多度 Relative abundance of herbivore | 1.109 | 2.997*** |
Table 1 Nested two-way ANOVA results of site and elevation on riparian soil macrofauna community structure
| 项目 Items | 样点 Site | 高程(样点) Elevation (Site) |
|---|---|---|
| 丰度 Richness | 1.059 | 3.867*** |
| 多度 Abundance | 1.662 | 1.814* |
| 多样性指数 Diversity index (H′) | 1.051 | 2.326** |
| 优势度指数 Dominance index (C) | 0.969 | 2.451** |
| 捕食者相对多度 Relative abundance of predator | 0.807 | 3.925*** |
| 杂食者相对多度 Relative abundance of omnivore | 0.845 | 2.761*** |
| 腐食者相对多度 Relative abundance of detritivore | 0.357 | 9.377*** |
| 植食者相对多度 Relative abundance of herbivore | 1.109 | 2.997*** |
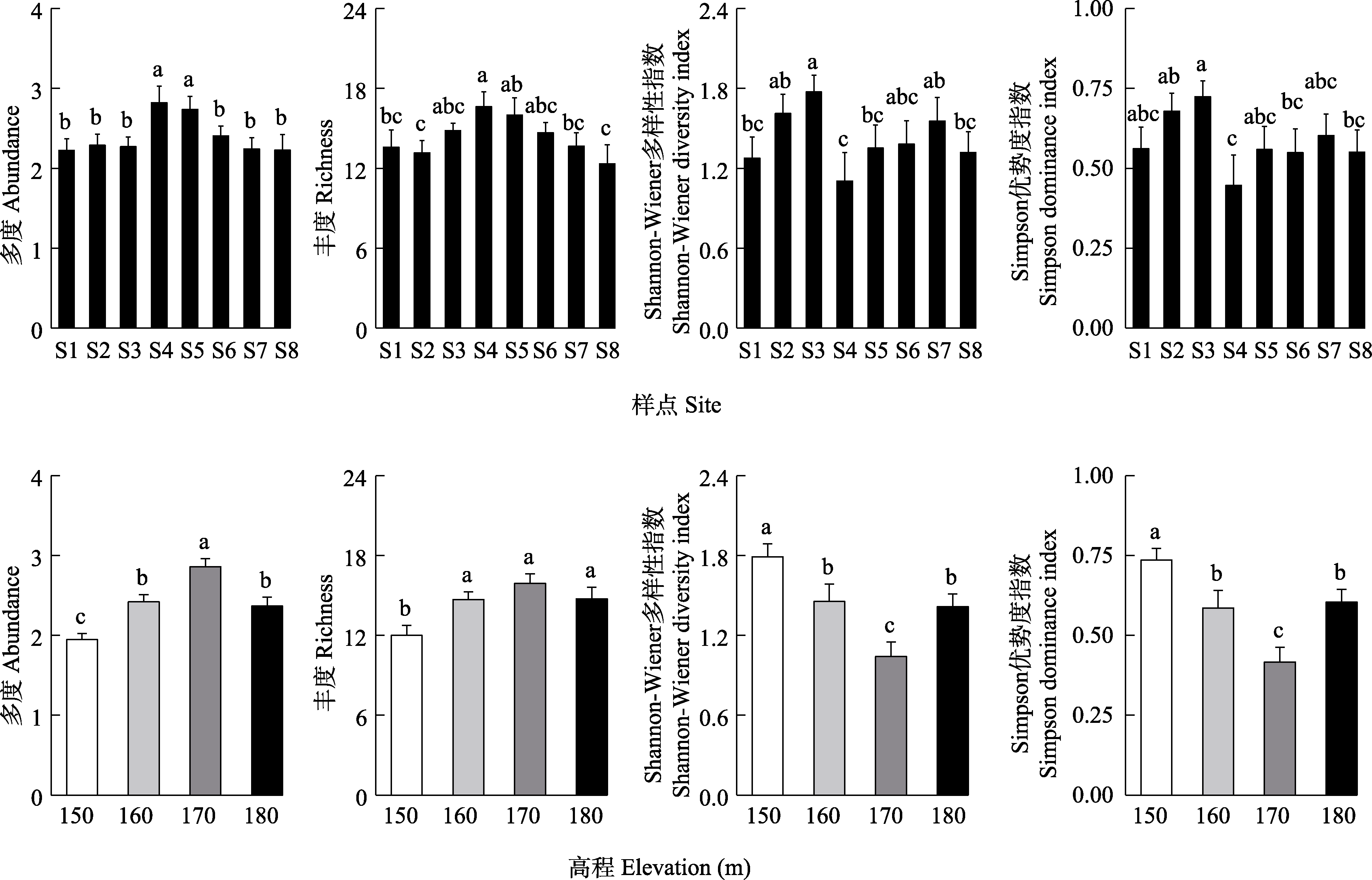
Fig. 2 Soil fauna community structure of different sites and elevations in riparian zone of the Pengxi River. Different letters indicate significant differences among different groups (P < 0.05).
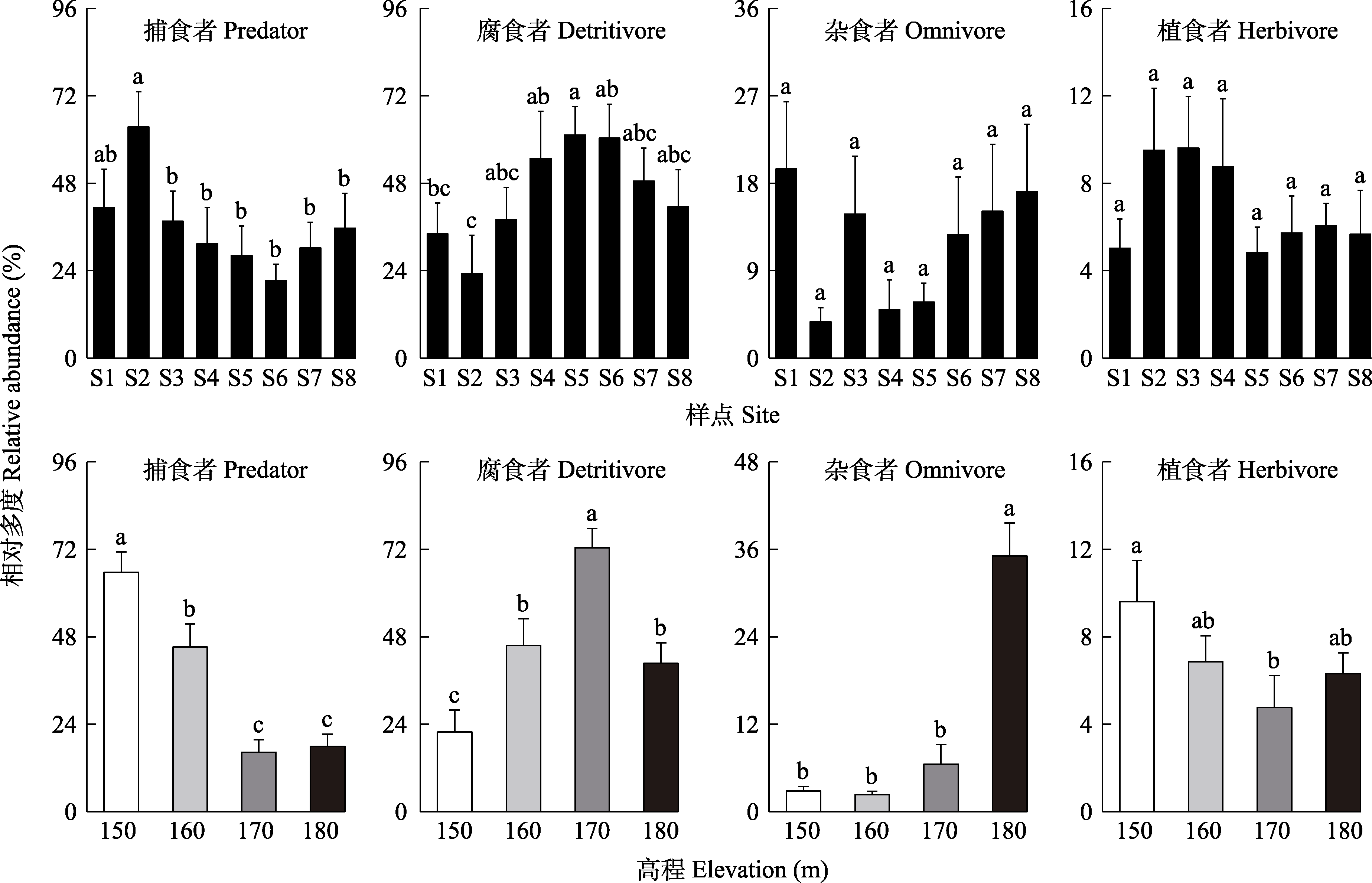
Fig. 3 Relative abundance of functional groups of soil macrofauna in riparian zone of the Pengxi River. Different letters indicate significant differences among different groups (P < 0.05).
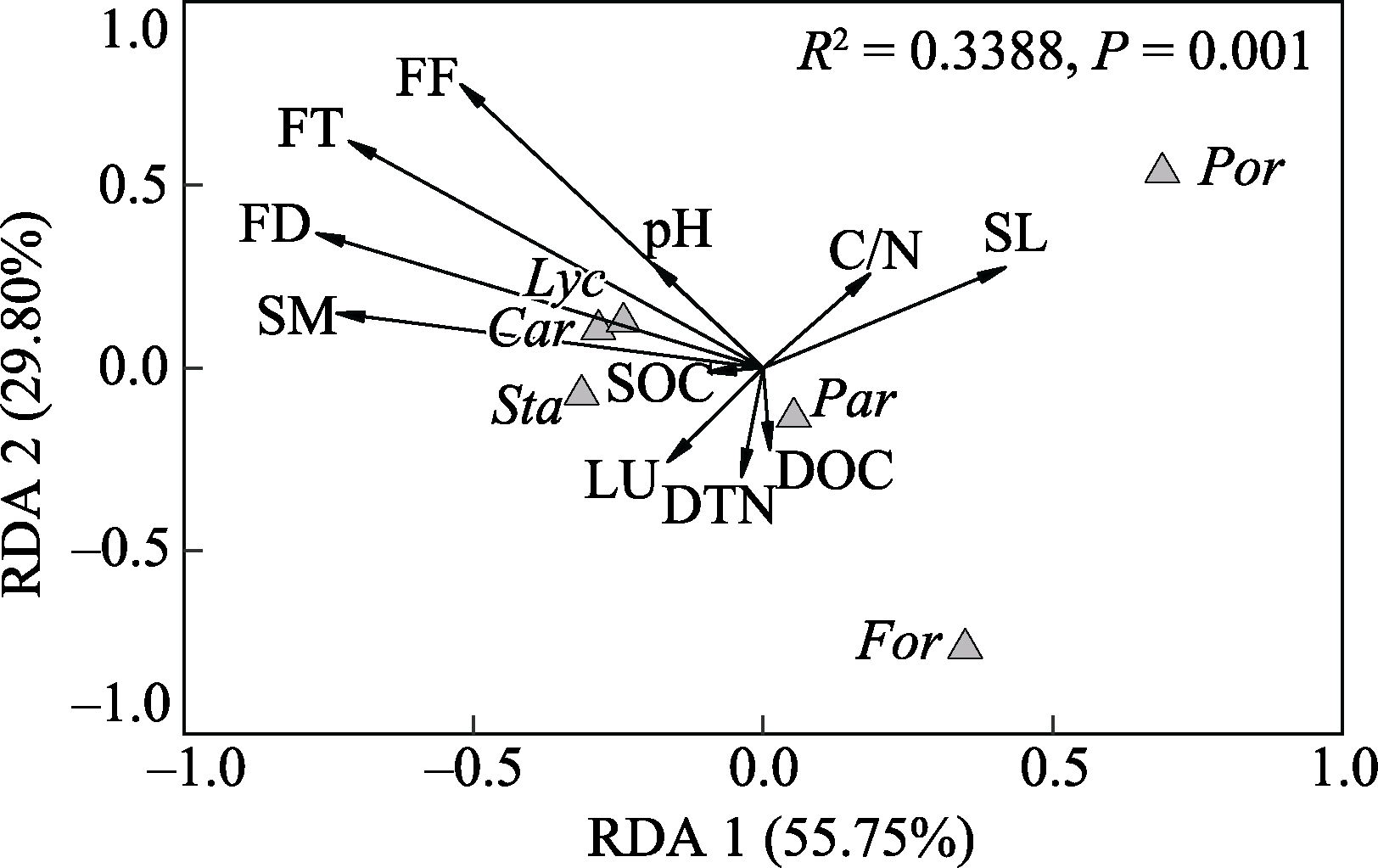
Fig. 4 RDA ordination of soil macrofauna community and environmental factors in riparian zone of the Pengxi River. Lyc, Lycosidae; Car, Carabidae; Sta, Staphylinidae; Por, Porcellionidae; Par, Paradoxosomatidae; For, Formicidae. Other abbreviations infer the environmental factors in Table 2.
| 因素 Factors | 解释量 Explanatory (%) | Monte Carlo’s P |
|---|---|---|
| 淹水时间 Flood time (FT) | 6.96 | 0.001 |
| 淹水深度 Flood depth (FD) | 4.57 | 0.001 |
| 淹水频率 Flood frequency (FF) | 5.31 | 0.001 |
| 土壤含水率 Soil moisture (SM) | 12.17 | 0.001 |
| 坡度 Slope (SL) | 3.29 | 0.001 |
| 土地利用类型 Land use (LU) | 1.67 | 0.048 |
| 土壤碳氮比 Soil C-N ratio (C/N) | 2.52 | 0.007 |
| 溶解性总氮 Dissolved total nitrogen (DTN) | 1.43 | 0.024 |
| 溶解性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) | 1.36 | 0.095 |
| pH | 1.80 | 0.027 |
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (SOC) | 0.54 | 0.549 |
Table 2 Explanatory of environmental factors to riparian soil macrofauna community composition
| 因素 Factors | 解释量 Explanatory (%) | Monte Carlo’s P |
|---|---|---|
| 淹水时间 Flood time (FT) | 6.96 | 0.001 |
| 淹水深度 Flood depth (FD) | 4.57 | 0.001 |
| 淹水频率 Flood frequency (FF) | 5.31 | 0.001 |
| 土壤含水率 Soil moisture (SM) | 12.17 | 0.001 |
| 坡度 Slope (SL) | 3.29 | 0.001 |
| 土地利用类型 Land use (LU) | 1.67 | 0.048 |
| 土壤碳氮比 Soil C-N ratio (C/N) | 2.52 | 0.007 |
| 溶解性总氮 Dissolved total nitrogen (DTN) | 1.43 | 0.024 |
| 溶解性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) | 1.36 | 0.095 |
| pH | 1.80 | 0.027 |
| 土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (SOC) | 0.54 | 0.549 |
| 水文情势 Hydrological regime | 土壤理化性质 Soil properties | 其他 Others | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 单独效应 Unique effects (%) | 16.10 | 0.31 | 1.51 |
| 共同效应 Common effects (%) | 15.43 | 14.05 | 4.26 |
| 总效应 Total effects (%) | 31.53 | 14.36 | 5.77 |
| P | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.007 |
Table 3 Explanatory of environmental factor groups to riparian soil macrofauna community composition
| 水文情势 Hydrological regime | 土壤理化性质 Soil properties | 其他 Others | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 单独效应 Unique effects (%) | 16.10 | 0.31 | 1.51 |
| 共同效应 Common effects (%) | 15.43 | 14.05 | 4.26 |
| 总效应 Total effects (%) | 31.53 | 14.36 | 5.77 |
| P | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.007 |
| [1] | Allen DC (2016) Microclimate modification by riparian vegetation affects the structure and resource limitation of arthropod communities. Ecosphere, 7, e01200. |
| [2] | Arif M, Zheng J, Tahir M, Hu X, Li CX (2022) The impact of stress factors on riparian and drawdown zones degradation around dams and reservoirs. Land Degradation & Development, 33, 2127-2141. |
| [3] | Babenko A, Touletaev S, Temnikova I (2015) Bio-diversity and population structure of rove beetles (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae) in the flood plain habitats of the Ob and Irtysh Basin. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 72, 516-520. |
| [4] | Baruch EM, Bateman HL, Lytle DA, Merritt DM, Sabo JL (2021) Integrated ecosystems: Linking food webs through reciprocal resource reliance. Ecology, 102, e03450. |
| [5] | Batzer DP, Noe GB, Lee L, Galatowitsch M (2018) A floodplain continuum for Atlantic coast rivers of the southeastern US: Predictable changes in floodplain biota along a river’s length. Wetlands, 38, 1-13. |
| [6] |
Batzer DP, Wu HT (2020) Ecology of terrestrial arthropods in freshwater wetlands. Annual Review of Entomology, 65, 101-119.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Benke AC, Chaubey I, Ward GM, Dunn EL (2000) Flood pulse dynamics of an unregulated river floodplain in the southeastern U.S. coastal plain. Ecology, 81, 2730-2741. |
| [8] | Brosofske KD, Chen J, Naiman RJ, Franklin JF (1997) Harvesting effects on microclimatic gradients from small streams to uplands in Western Washington. Ecological Applications, 7, 1188-1200. |
| [9] | Butler OM, Ye C, Zhang QF (2022) Dynamics of insect communities across a unique network of hydrologically altered riparian habitats in central China. Ecohydrology, 15, e2462. |
| [10] | Cai BH (2017) Insect Taxonomy (Revised Edition). Chemical Industry Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [蔡邦华 (2017) 昆虫分类学(修订版). 化学工业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [11] | Chen C, Wu S, Meurk CD, Ma M, Zhao J, Lü M, Tong X (2017) Effects of local and landscape factors on exotic vegetation in the riparian zone of a regulated river: Implications for reservoir conservation. Landscape and Urban Planning, 157, 45-55. |
| [12] |
Chu CJ, Wang YS, Liu Y, Jiang L, He FL (2017) Advances in species coexistence theory. Biodiversity Science, 25, 345-354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[储诚进, 王酉石, 刘宇, 蒋林, 何芳良 (2017) 物种共存理论研究进展. 生物多样性, 25, 345-354.]
DOI |
|
| [13] | Corti R, Datry T (2014) Drying of a temperate, intermittent river has little effect on adjacent riparian arthropod communities. Freshwater Biology, 59, 666-678. |
| [14] | Dixon P (2003) VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 927-930. |
| [15] | Dong ZR, Zhang J (2009) Ecological effect of flood pulses. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 40, 281-288. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董哲仁, 张晶 (2009) 洪水脉冲的生态效应. 水利学报, 40, 281-288.] | |
| [16] | Dong ZR, Zhao JY, Zhang J (2019) Three types flows via four dimensional connectivity ecological model. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 50(6), 134-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董哲仁, 赵进勇, 张晶 (2019) 3流4D连通性生态模型. 水利水电技术, 50(6), 134-141.] | |
| [17] | Edmonds JW, King KBS, Neely MB, Hensley RT, Goodman KJ, Cawley KM (2022) Using large, open datasets to understand spatial and temporal patterns in lotic ecosystems: NEON case studies. Ecosphere, 13, e4102. |
| [18] |
Feng YL, Wang YZ, Lin YY, Zhao WZ, Gao JW, Liu JL (2022) Effects of ant nest microhabitats on the diversity of soil macrofauna in Gobi ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22282. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[冯怡琳, 王永珍, 林永一, 赵文智, 高俊伟, 刘继亮 (2022) 戈壁生态系统蚁穴微生境对大型土壤动物多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 30, 22282.]
DOI |
|
| [19] | Fonseca A, Zina V, Fernandes MR, Froidevaux JSP, Ferreira MT, Duarte G (2023) Can the habitat Ecological Infrastructure’s Diversity Index predict ant and bat biodiversity in Mediterranean agricultural floodplains? A multi-taxon approach using hierarchical modelling. Ecological Indicators, 153, 110446. |
| [20] | Framenau VW, Manderbach R, Baehr M (2002) Riparian gravel banks of upland and lowland rivers in Victoria (Southeast Australia): Arthropod community structure and life-history patterns along a longitudinal gradient. Australian Journal of Zoology, 50, 103-123. |
| [21] | Gerisch M, Dziock F, Schanowski A, Ilg C, Henle K (2012) Community resilience following extreme disturbances: The response of ground beetles to a severe summer flood in a Central European lowland stream. River Research and Applications, 28, 81-92. |
| [22] | Huang ZY, Pan BZ (2020) Research on the impact of flood process on aquatic ecosystem. Journal of Xi’an University of Technology, 36, 300-306. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄振宇, 潘保柱 (2020) 洪水过程对水生态系统影响的研究进展. 西安理工大学学报, 36, 300-306.] | |
| [23] | Januschke K, Brunzel S, Haase P, Hering D (2011) Effects of stream restorations on riparian mesohabitats, vegetation and carabid beetles. Biodiversity and Conservation, 20, 3147-3164. |
| [24] | Kato C, Iwata T, Nakano S, Kishi D (2003) Dynamics of aquatic insect flux affects distribution of riparian web-building spiders. Oikos, 103, 113-120. |
| [25] | Kędzior R, Skalski T, Radecki-Pawlik A (2016) The effect of channel restoration on ground beetle communities in the floodplain of a channelized mountain stream. Periodicum Biologorum, 118, 171-184. |
| [26] | Lambeets K, Maelfait JP, Bonte D (2008) Plasticity in flood-avoiding behaviour in two congeneric riparian wolf spiders. Animal Biology, 58, 389-400. |
| [27] |
Larsen S, Muehlbauer JD, Marti E (2016) Resource subsidies between stream and terrestrial ecosystems under global change. Global Change Biology, 22, 2489-2504.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Leigh C, Reis TM, Sheldon F (2013) High potential subsidy of dry-season aquatic fauna to consumers in riparian zones of wet-dry tropical rivers. Inland Waters, 3, 411-420. |
| [29] | Malmqvist B (2002) Aquatic invertebrates in riverine landscapes. Freshwater Biology, 47, 679-694. |
| [30] | Mendelssohn IA, Batzer DP, Holt CR, Graham SA (2014) Abiotic constraints for wetland plants and animals. In: Ecology of Freshwater and Estuarine Wetlands (eds Batzer DP, Sharitz RR), pp. 61-86. University of California Press, Berkeley. |
| [31] | Paetzold A, Yoshimura C, Tockner K (2008) Riparian arthropod responses to flow regulation and river channelization. Journal of Applied Ecology, 45, 894-903. |
| [32] | Qiu J (2012) Trouble on the Yangtze. Science, 336, 288-291. |
| [33] | Raitif J, Roussel JM, Olmos M, Piscart C, Plantegenest M (2022) Assessing spatial deposition of aquatic subsidies by insects emerging from agricultural streams. Science of the Total Environment, 837, 155686. |
| [34] | Ralston BE, Cobb NS, Brantley SL, Higgins J, Yackulic CB (2017) Taxonomic and compositional differences of ground-dwelling arthropods in riparian habitats in Glen Canyon, Arizona, USA. Western North American Naturalist, 77, 369-384. |
| [35] | Ramey TL, Richardson JS (2017) Terrestrial invertebrates in the riparian zone: Mechanisms underlying their unique diversity. BioScience, 67, 808-819. |
| [36] | Sabo JL, Sponseller R, Dixon M, Gade K, Harms T, Heffernan J, Jani A, Katz G, Soykan C, Watts J, Welter J (2005) Riparian zones increase regional species richness by harboring different, not more, species. Ecology, 86, 56-62. |
| [37] | Sadler JP, Bell D, Fowles A (2004) The hydroecological controls and conservation value of beetles on exposed riverine sediments in England and Wales. Biological Conservation, 118, 41-56. |
| [38] |
Sánchez-Hernández J (2023) Fresh perspectives on the River Continuum Concept require trophic ecology approaches focused on food web structure and energy mobilisation routes. Journal of Animal Ecology, 92, 957-964.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Taylor AN, Batzer DP (2010) Spatial and temporal variation in invertebrate consumer diets in forested and herbaceous wetlands. Hydrobiologia, 651, 145-159. |
| [40] | Tockner K, Lorang MS, Stanford JA (2010) River flood plains are model ecosystems to test general hydrogeomorphic and ecological concepts. River Research and Applications, 26, 76-86. |
| [41] | Tong XX, Chen CD, Wu SJ, Jia ZY, Yi XM, Ma MH (2018) Spatial distribution pattern of plant community and habitat impact analysis of the drawdown zone of Pengxi River in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 571-580. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [童笑笑, 陈春娣, 吴胜军, 贾振毅, 易雪梅, 马茂华 (2018) 三峡库区澎溪河消落带植物群落分布格局及生境影响. 生态学报, 38, 571-580.] | |
| [42] |
Uno H (2016) Stream thermal heterogeneity prolongs aquatic-terrestrial subsidy and enhances riparian spider growth. Ecology, 97, 2547-2553.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Vannote RL, Minshall GW, Cummins KW, Sedell JR, Cushing CE (1980) The River Continuum Concept. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 37, 130-137. |
| [44] | Vilmi A, Gibert C, Escarguel G, Happonen K, Heino J, Jamoneau A, Passy SI, Picazo F, Soininen J, Tison-Rosebery J, Wang JJ (2021) Dispersal-Niche Continuum Index: A new quantitative metric for assessing the relative importance of dispersal versus niche processes in community assembly. Ecography, 44, 370-379. |
| [45] | Wang KH, Yuan XZ, Zhang GX, Wu SK, Liu SS, Zhang MJ (2020) Maintaining mechanisms of riparian invertebrate biodiversity: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31, 1043-1054. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[王可洪, 袁兴中, 张冠雄, 武帅楷, 刘双爽, 张梦婕 (2020) 河岸无脊椎动物多样性维持机制研究进展. 应用生态学报, 31, 1043-1054.]
DOI |
|
| [46] |
Wang S, Faeflen SJ, Wright AL, Zhu-Barker X, Jiang X (2019) Redox-driven shifts in soil microbial community structure in the drawdown zone after construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Soil Ecology Letters, 1, 114-125.
DOI |
| [47] | Xiao HY, Du CL, Yuan XZ, Li B (2020) Multiple floods affect composition and community structure of the ground-dwelling arthropods in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106220. |
| [48] | Xiao HY, Li B, Willison JHM, Wang YF (2022) Habitat change and interspecific associations mediate the response of riparian ground-dwelling arthropod assemblages to flooding in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecological Engineering, 185, 106812. |
| [49] | Yao L, Gong Y, Ye C, Shi W, Zhang K, Du M, Zhang Q (2022) Soil denitrification rates are more sensitive to hydrological changes than restoration approaches in a unique riparian zone. Functional Ecology, 36, 2056-2068. |
| [50] | Yin WY (1998) Pictorical Keys to Soil Animals of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (1998) 中国土壤动物检索图鉴. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [51] | Zhang A, Xie Z (2021) C4 herbs dominate the reservoir flood area of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Science of the Total Environment, 755, 142479. |
| [52] |
Zhang SN, Tong CF, Wang T, Wang YW (2023) Effects of flooding and vegetation mowing on soil macrofauna community in the Qingcaosha Reservoir beach. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 42, 361-367. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [张胜楠, 童春富, 王涛, 王毅伟 (2023) 淹水和植被刈割对青草沙水库边滩大型土壤动物群落的影响. 生态学杂志, 42, 361-367.] | |
| [53] | Zhu K, Ma MH, Ran YG, Liu ZM, Wu SJ, Huang P (2020) In mitigating CO2 emission in the reservoir riparian: The influences of land use and the dam-triggered flooding on soil respiration. Soil and Tillage Research, 197, 104522. |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn