



Biodiv Sci ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 21549. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021549 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021549
• Forum • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yang Wu, Yu Tian( ), Fengbin Dai, Ziyuan Li
), Fengbin Dai, Ziyuan Li
Received:2021-12-30
Accepted:2022-01-23
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-04-11
Contact:
Yu Tian
Yang Wu, Yu Tian, Fengbin Dai, Ziyuan Li. Realization, development trend and enlightenment of Nature’s contributions to people[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21549.
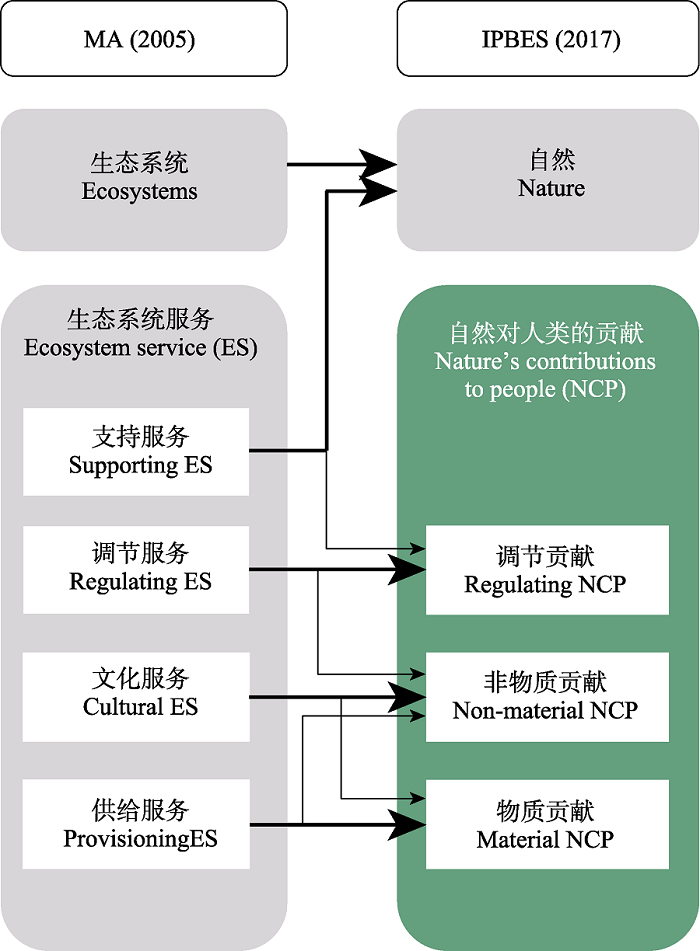
Fig. 1 The relationship between Nature’s contributions to people (NCP) and ecosystem services (ES). The arrow represents the evolution of concepts, the thick arrow indicates a strong correlation and the thin arrow indicates a weak correlation between NCP and ES.
| 类别 Categories | 序号 Number | 子类别 Subcategories |
|---|---|---|
| 调节贡献 Regulating NCP | 1 | 生境形成和维持 Habitat creation and maintenance |
| 2 | 种子和其他繁殖体的传粉和传播 Pollination and dispersal of seeds and other propagules | |
| 3 | 空气质量调节 Regulation of air quality | |
| 4 | 气候调节 Regulation of climate | |
| 5 | 海洋酸化调节 Regulation of ocean acidification | |
| 6 | 淡水水量、水位和流速调节 Regulation of freshwater quantity, location and timing | |
| 7 | 淡水和沿海水质调节 Regulation of freshwater and coastal water quality | |
| 8 | 土壤和沉淀物的形成、保护和去污 Formation, protection and decontamination of soils and sediments | |
| 9 | 各种危害和极端事件调节 Regulation of hazards and extreme events | |
| 10 | 有害生物和生物过程调节 Regulation of detrimental organisms and biological processes | |
| 物质贡献 Material NCP | 11 | 能源 Energy |
| 12 | 粮食和饲料 Food and feed | |
| 13 | 物质和辅助 Materials and assistance | |
| 14 | 医学、生物化学和遗传资源 Medicinal, biochemical and genetic resources | |
| 非物质贡献 Non-material NCP | 15 | 学习和启发 Learning and inspiration |
| 16 | 身心体验 Physical and psychological experiences | |
| 17 | 支持身份认同 Supporting identities | |
| 18 | 保持各种选择 Maintenance of options |
Table 1 Classification of Nature’s contributions to people (NCP) including 3 categories and 18 subcategories
| 类别 Categories | 序号 Number | 子类别 Subcategories |
|---|---|---|
| 调节贡献 Regulating NCP | 1 | 生境形成和维持 Habitat creation and maintenance |
| 2 | 种子和其他繁殖体的传粉和传播 Pollination and dispersal of seeds and other propagules | |
| 3 | 空气质量调节 Regulation of air quality | |
| 4 | 气候调节 Regulation of climate | |
| 5 | 海洋酸化调节 Regulation of ocean acidification | |
| 6 | 淡水水量、水位和流速调节 Regulation of freshwater quantity, location and timing | |
| 7 | 淡水和沿海水质调节 Regulation of freshwater and coastal water quality | |
| 8 | 土壤和沉淀物的形成、保护和去污 Formation, protection and decontamination of soils and sediments | |
| 9 | 各种危害和极端事件调节 Regulation of hazards and extreme events | |
| 10 | 有害生物和生物过程调节 Regulation of detrimental organisms and biological processes | |
| 物质贡献 Material NCP | 11 | 能源 Energy |
| 12 | 粮食和饲料 Food and feed | |
| 13 | 物质和辅助 Materials and assistance | |
| 14 | 医学、生物化学和遗传资源 Medicinal, biochemical and genetic resources | |
| 非物质贡献 Non-material NCP | 15 | 学习和启发 Learning and inspiration |
| 16 | 身心体验 Physical and psychological experiences | |
| 17 | 支持身份认同 Supporting identities | |
| 18 | 保持各种选择 Maintenance of options |
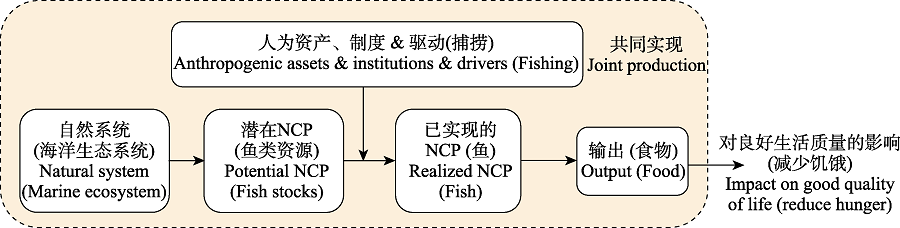
Fig. 2 The mechanism of co-production of Nature’s contributions to people (NCP) by people and nature. An example of co-production of NCP by people and marine ecosystems are presented in parentheses.
| [1] | Braat LC (2018) Five reasons why the Science publication “Assessing nature’s contributions to people” (Diaz et al. 2018) would not have been accepted in Ecosystem Services. Ecosystem Services, 30, A1-A2. |
| [2] | Chaplin-Kramer R, Sharp RP, Weil C, Bennett EM, Pascual U, Arkema KK, Brauman KA, Bryant BP, Guerry AD, Haddad NM, Hamann M, Hamel P, Johnson JA, Mandle L, Pereira HM, Polasky S, Ruckelshaus M, Shaw MR, Silver JM, Vogl AL, Daily GC (2019) Global modeling of nature’s contributions to people. Science, 366, 255-258. |
| [3] |
Díaz S, Demissew S, Carabias J, Joly C, Lonsdale M, Ash N, Larigauderie A, Adhikari JR, Arico S, Báldi A, Bartuska A, Baste IA, Bilgin A, Brondizio E, Chan KM, Figueroa VE, Duraiappah A, Fischer M, Zlatanova D (2015) The IPBES Conceptual Framework—connecting nature and people. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 14, 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Díaz S, Pascual U, Stenseke M, Martín-López B, Watson RT, Molnár Z, Hill R, Chan KMA, Baste IA, Brauman KA, Polasky S, Church A, Lonsdale M, Larigauderie A, Leadley PW, van der Plaat F, Schröter M, Lavorel S, Aumeeruddy-Thomas Y, Bukvareva E, Davies K, Demissew S, Erpul G, Failler P, Guerra CA, Hewitt CL, Keune H, Lindley S, Shirayama Y (2018) Assessing nature’s contributions to people. Science, 359, 270-272.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Fu BJ, Yu DD, Lü N (2017) An indicator system for biodiversity and ecosystem services evaluation in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 341-348. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [傅伯杰, 于丹丹, 吕楠 (2017) 中国生物多样性与生态系统服务评估指标体系. 生态学报, 37, 341-348.] | |
| [6] | Hou YZ, Zhao WW, Liu YX (2019) “Unprecedented” natural recession and “accelerated” species extinction rate: A summary of the IPBES global assessment report. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 6943-6949. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [侯焱臻, 赵文武, 刘焱序 (2019) 自然衰退“史无前例”, 物种灭绝率“加速”——IPBES全球评估报告简述. 生态学报, 39, 6943-6949.] | |
| [7] | IPBES (2013) Recommended Conceptual Framework of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES/2/4). https://ipbes.net/events/ipbes-2-plenary. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [8] | IPBES (2016) The Methodological Assessment Report on Scenarios and Models of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. https://ipbes.net/assessment-reports/scenarios. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [9] | IPBES (2017) Update on the classification of nature’s contributions to people by the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES/5/INF/24). https://ipbes.net/events/ipbes-5-plenary#pills-information. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [10] | IPBES (2018a) The Regional Assessment Report on Biodiver-sity and Ecosystem Services for Asia and the Pacific. https://ipbes.net/assessment-reports/asia-pacific. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [11] | IPBES (2018b) The Regional Assessment Report on Biodi-versity and Ecosystem Services for the Americas. https://ipbes.net/assessment-reports/americas. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [12] | IPBES (2018c) The Regional Assessment Report on Bio- diversity and Ecosystem Services for Africa. https://ipbes.net/assessment-reports/africa. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [13] | IPBES (2018d) The Regional Assessment Report on Biodiver- sity and Ecosystem Services for Europe and Central Asia. https://ipbes.net/assessment-reports/eca. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [14] | IPBES (2019) Global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. https://zenodo.org/record/5657041. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [15] |
Kenter JO (2018) IPBES: Don’t throw out the baby whilst keeping the bathwater; Put People’s values central, not nature’s contributions. Ecosystem Services, 33, 40-43.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Lan CZ, Tian Y, Xu J, Li JS (2015) Conceptual framework and operational model of Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Biodiversity Science, 23, 681-688. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[兰存子, 田瑜, 徐靖, 李俊生 (2015) 生物多样性和生态系统服务政府间科学-政策平台的概念框架和运作模式. 生物多样性, 23, 681-688.]
DOI |
|
| [17] | Li SC (2020) On how to measure the contribution of nature to human beings scientifically—A social-ecosystem analysis framework based on ecosystem services and its application. Frontiers, (11), 28-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李双成 (2020) 如何科学衡量自然对人类的贡献——一个基于生态系统服务的社会-生态系统分析框架及其应用. 人民论坛·学术前沿, (11), 28-35.] | |
| [18] | Li X, Wu JH, Li B (2019) The battle for biodiversity and human future. Chinese Science Bulletin, 64, 2374-2378. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李骁, 吴纪华, 李博 (2019) 为生物多样性与人类未来而战. 科学通报, 64, 2374-2378.] | |
| [19] | Liu YP, Shi PR, Zhang ZR, Wan HW, Peng Y, Wang YC (2021) Study on the indicator system for quantitatively measuring the biodiversity contributions to human well-being. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 37, 1242-1248. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘玉平, 施佩荣, 张志如, 万华伟, 彭羽, 王永财 (2021) 定量测度生物多样性对人类福祉贡献的指标体系研究. 生态与农村环境学报, 37, 1242-1248.] | |
| [20] | MA Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis. Island Press, Washington DC. |
| [21] | Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (2020) Global Biodiversity Outlook 5. Montreal. https://www.cbd.int/gbo/gbo5/publication/gbo-5-en.pdf. (accessed on 2021-06-06) |
| [22] | Stenseke M, Larigauderie A (2018) The role, importance and challenges of social sciences and humanities in the work of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES). Innovation: The European Journal of Social Science Research, 31, S10-S14. |
| [23] |
Wu Y, Pan YX, Zhang BY, Dai FB, Tian Y (2020) Regional assessment on biodiversity and ecosystem services and policy experience within the IPBES framework. Biodiversity Science, 28, 913-919. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[吴杨, 潘玉雪, 张博雅, 戴逢斌, 田瑜 (2020) IPBES框架下的生物多样性和生态系统服务区域评估及政策经验. 生物多样性, 28, 913-919.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | Yu DD, Lü N, Fu BJ (2017) Indicator systems and methods for evaluating biodiversity and ecosystem services. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 349-357. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于丹丹, 吕楠, 傅伯杰 (2017) 生物多样性与生态系统服务评估指标与方法. 生态学报, 37, 349-357.] | |
| [25] | Yue TX, Fan ZM, Shi WJ, Zhao N (2020) Models and scenarios for nature and nature’s contribution. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 22, 743-750. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[岳天祥, 范泽孟, 史文娇, 赵娜 (2020) 自然和自然贡献情景模型研究综述. 地球信息科学学报, 22, 743-750.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Zhang YM, Zhao SD (2010) The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment follow-up: A global strategy for turning knowledge into action. Journal of Natural Resources, 25, 522-528. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张永民, 赵士洞 (2010) 千年生态系统评估项目的后续计划——将知识转化为行动的全球战略. 自然资源学报, 25, 522-528.] | |
| [27] | Zhao SD, Zhang YM (2004) Concepts, contents and challenges of ecosystem assessment—Introduction to “Ecosystems and Human Well-being: A Framework for Assessment”. Advance in Earth Sciences, 19, 650-657. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵士洞, 张永民 (2004) 生态系统评估的概念、内涵及挑战——介绍《生态系统与人类福利: 评估框架》. 地球科学进展, 19, 650-657.] |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | Zhao Weiyang, Wang Wei, Ma Bingran. Advances and prospects in research on other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn