



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 1658-1672. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021199 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021199
Special Issue: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全; 生物入侵
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhaosong Chen1,2, Bei An2,3, Ziwang Wang4,5, Faning Wu1, Zhangyun Sun1, Lixun Zhang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-05-19
Accepted:2021-07-10
Online:2021-12-20
Published:2021-11-12
Contact:
Lixun Zhang
Zhaosong Chen, Bei An, Ziwang Wang, Faning Wu, Zhangyun Sun, Lixun Zhang. Fish diversity and conservation in the Lanzhou reach of the Yellow River[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(12): 1658-1672.
| 河流 River | 河流级别 Order | 代号 Code | 断面名称 Section name | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄河 Yellow River | 一级 First | S1 | 榆中县园子岔乡 Yuanzicha Town, Yuzhong County | 36°22′ | 104°20′ | 1,404 |
| S2 | 皋兰县什川镇1 Shichuan Town 1, Gaolan County | 36°17′ | 104°09′ | 1,501 | ||
| S3 | 皋兰县什川镇2 Shichuan Town 2, Gaolan County | 36°12′ | 104°03′ | 1,513 | ||
| S4 | 安宁区刘家堡街道 Liujiabao Street, Anning District | 36°06′ | 103°40′ | 1,529 | ||
| S5 | 西固区河口镇 Hekou Town, Xigu District | 36°10′ | 103°26′ | 1,508 | ||
| 大通河 Datong River | 四级 Fourth | S6 | 永登县连城镇1 Liancheng Town 1, Yongdeng County | 36°45′ | 102°43′ | 1,966 |
| S7 | 永登县连城镇2 Liancheng Town 2, Yongdeng County | 36°39′ | 102°46′ | 1,904 | ||
| S8 | 永登县连城镇3 Liancheng Town 3, Yongdeng County | 36°32′ | 102°52′ | 1,867 | ||
| S9 | 永登县河桥镇 Heqiao Town, Yongdeng County | 36°27′ | 102°51′ | 1,822 | ||
| 湟水河 Huangshui River | 四级 Fourth | S10 | 红古区海石湾镇 Haishiwan Town, Honggu District | 36°20′ | 102°50′ | 1,680 |
| S11 | 红古区红古镇 Honggu Town, Honggu District | 36°13′ | 103°01′ | 1,624 | ||
| S12 | 红古区达川乡 Dachuan Town, Honggu District | 36°07′ | 103°21′ | 1,547 | ||
| 庄浪河 Zhuanglang River | 五级 Fifth | S13 | 永登县武胜驿镇 Wushengyi Town, Yongdeng County | 36°55′ | 103°08′ | 2,280 |
| S14 | 永登县柳树镇 Liushu Town, Yongdeng County | 36°44′ | 103°14′ | 2,025 | ||
| S15 | 永登县龙泉寺镇 Longquansi Town, Yongdeng County | 36°36′ | 103°21′ | 1,894 | ||
| S16 | 永登县苦水镇 Kushui Town, Yongdeng County | 36°22′ | 103°23′ | 1,695 | ||
| 宛川河 Wanchuan River | 五级 Fifth | S17 | 榆中县马坡乡 Mapo Town, Yuzhong County | 35°46′ | 104°01′ | 2,465 |
| S18 | 榆中县小康营乡 Xiaokangying Town, Yuzhong County | 35°44′ | 104°08′ | 2,186 | ||
| S19 | 榆中县龙泉乡 Longquan Town, Yuzhong County | 35°38′ | 104°14′ | 2,092 | ||
| S20 | 榆中县甘草店镇 Gancaodian Town, Yuzhong County | 35°46′ | 104°18′ | 1,853 | ||
| S21 | 榆中县夏官营镇 Xiaguanying Town, Yuzhong County | 35°57′ | 104°11′ | 1,723 | ||
| S22 | 榆中县金崖镇 Jinya Town, Yuzhong County | 36°00′ | 104°06′ | 1,627 | ||
| S23 | 榆中县来紫堡乡 Laizibao Town, Yuzhong County | 36°03′ | 104°00′ | 1,461 |
Table 1 The coordinates of sections in the Lanzhou reach of the Yellow River
| 河流 River | 河流级别 Order | 代号 Code | 断面名称 Section name | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 海拔 Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄河 Yellow River | 一级 First | S1 | 榆中县园子岔乡 Yuanzicha Town, Yuzhong County | 36°22′ | 104°20′ | 1,404 |
| S2 | 皋兰县什川镇1 Shichuan Town 1, Gaolan County | 36°17′ | 104°09′ | 1,501 | ||
| S3 | 皋兰县什川镇2 Shichuan Town 2, Gaolan County | 36°12′ | 104°03′ | 1,513 | ||
| S4 | 安宁区刘家堡街道 Liujiabao Street, Anning District | 36°06′ | 103°40′ | 1,529 | ||
| S5 | 西固区河口镇 Hekou Town, Xigu District | 36°10′ | 103°26′ | 1,508 | ||
| 大通河 Datong River | 四级 Fourth | S6 | 永登县连城镇1 Liancheng Town 1, Yongdeng County | 36°45′ | 102°43′ | 1,966 |
| S7 | 永登县连城镇2 Liancheng Town 2, Yongdeng County | 36°39′ | 102°46′ | 1,904 | ||
| S8 | 永登县连城镇3 Liancheng Town 3, Yongdeng County | 36°32′ | 102°52′ | 1,867 | ||
| S9 | 永登县河桥镇 Heqiao Town, Yongdeng County | 36°27′ | 102°51′ | 1,822 | ||
| 湟水河 Huangshui River | 四级 Fourth | S10 | 红古区海石湾镇 Haishiwan Town, Honggu District | 36°20′ | 102°50′ | 1,680 |
| S11 | 红古区红古镇 Honggu Town, Honggu District | 36°13′ | 103°01′ | 1,624 | ||
| S12 | 红古区达川乡 Dachuan Town, Honggu District | 36°07′ | 103°21′ | 1,547 | ||
| 庄浪河 Zhuanglang River | 五级 Fifth | S13 | 永登县武胜驿镇 Wushengyi Town, Yongdeng County | 36°55′ | 103°08′ | 2,280 |
| S14 | 永登县柳树镇 Liushu Town, Yongdeng County | 36°44′ | 103°14′ | 2,025 | ||
| S15 | 永登县龙泉寺镇 Longquansi Town, Yongdeng County | 36°36′ | 103°21′ | 1,894 | ||
| S16 | 永登县苦水镇 Kushui Town, Yongdeng County | 36°22′ | 103°23′ | 1,695 | ||
| 宛川河 Wanchuan River | 五级 Fifth | S17 | 榆中县马坡乡 Mapo Town, Yuzhong County | 35°46′ | 104°01′ | 2,465 |
| S18 | 榆中县小康营乡 Xiaokangying Town, Yuzhong County | 35°44′ | 104°08′ | 2,186 | ||
| S19 | 榆中县龙泉乡 Longquan Town, Yuzhong County | 35°38′ | 104°14′ | 2,092 | ||
| S20 | 榆中县甘草店镇 Gancaodian Town, Yuzhong County | 35°46′ | 104°18′ | 1,853 | ||
| S21 | 榆中县夏官营镇 Xiaguanying Town, Yuzhong County | 35°57′ | 104°11′ | 1,723 | ||
| S22 | 榆中县金崖镇 Jinya Town, Yuzhong County | 36°00′ | 104°06′ | 1,627 | ||
| S23 | 榆中县来紫堡乡 Laizibao Town, Yuzhong County | 36°03′ | 104°00′ | 1,461 |
| 物种 Species | 黄河 Yellow River | 大通河 Datong River | 湟水河 Huang- shui River | 庄浪河 Zhuang- lang River | 宛川河 Wan- chuan River | 土著物种的特有性 Endemic species | 生态类型 Ecological types | 濒危状况 Endangered status | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 食性 Feeding habits | 栖息水层 Habit characteristics | 生活习性 Life habits | |||||||||||||||
| 中国特有种 Endemic species to China | 黄河特有种 Endemic species to the Yellow River | Jiang et al ( | IUCN ( | ||||||||||||||
| 一 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | |||||||||||||||||
| (一)花鳅科 Cobitidae | |||||||||||||||||
| 1. 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | + | + | + | O | DE | SE | LC | LC | |||||||||
| 2. 大鳞副泥鳅 Paramisgurnus dabryanus* | + | + | + | O | DE | SE | LC | ||||||||||
| (二)条鳅科 Nemacheilidae | |||||||||||||||||
| 3. 东方高原鳅 Triplophysa orientalis | + | + | + | + | C | DE | MS | LC | LC | ||||||||
| 4. 黄河高原鳅 Triplophysa pappenheimi | + | + | + | + | + | C | DE | MS | EN | ||||||||
| 5. 硬刺高原鳅 Triplophysa scleroptera | + | + | + | + | C | DE | MS | LC | |||||||||
| 6. 似鲇高原鳅 Triplophysa siluroides | + | + | + | C | DE | MS | VU | ||||||||||
| 7. 斯氏高原鳅 Triplophysa stoliczkae | + | + | O | DE | MS | LC | |||||||||||
| 8. 粗壮高原鳅 Triplophysa robusta | + | + | + | O | DE | MS | LC | ||||||||||
| (三)鲤科 Cyprinidae | |||||||||||||||||
| 9. ? Hemiculter leucisculus* | + | O | U | DE | LC | LC | |||||||||||
| 10. 鳙 Hypophthalmichthys nobilis* | + | C | U | M | LC | DD | |||||||||||
| 11. 高体鳑鲏 Rhodeus ocellatus* | + | O | L | SE | LC | DD | |||||||||||
| 12. 棒花鱼 Abbottina rivularis* | + | O | DE | SE | LC | ||||||||||||
| 13. 黄河鮈 Gobio huanghensis | + | + | + | C | DE | M | EN | ||||||||||
| 14. 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva* | + | + | + | + | + | O | L | MS | LC | LC | |||||||
| 15. 鲫 Carassius auratus* | + | + | + | + | O | DE | SE | LC | LC | ||||||||
| 16. 鲤 Cyprinus rubrofuscus | + | + | O | DE | SE | LC | LC | ||||||||||
| 17. 黄河裸裂尻鱼 Schizopygopsis pylzovi | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | O | L | MS | VU | ||||||
| 二 鲇形目 Siluriformes | |||||||||||||||||
| (四)鲇科 Siluridae | |||||||||||||||||
| 18. 鲇 Silurus asotus | + | C | L | SE | LC | LC | |||||||||||
| 三 胡瓜鱼目 Osmeriformes | |||||||||||||||||
| (五)胡瓜鱼科 Osmeridae | |||||||||||||||||
| 19. 池沼公鱼 Hypomesus olidus* | + | C | U | M | LC | LC | |||||||||||
| 四 鲈形目 Perciformes | |||||||||||||||||
| (六)沙塘鳢科 Odontobutidae | |||||||||||||||||
| 20. 小黄黝鱼 Micropercops swinhonis* | + | + | C | DE | SE | LC | LC | ||||||||||
Table 2 Species composition, distribution, ecological types and endangered status of fish in the Lanzhou reach of the Yellow River
| 物种 Species | 黄河 Yellow River | 大通河 Datong River | 湟水河 Huang- shui River | 庄浪河 Zhuang- lang River | 宛川河 Wan- chuan River | 土著物种的特有性 Endemic species | 生态类型 Ecological types | 濒危状况 Endangered status | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 食性 Feeding habits | 栖息水层 Habit characteristics | 生活习性 Life habits | |||||||||||||||
| 中国特有种 Endemic species to China | 黄河特有种 Endemic species to the Yellow River | Jiang et al ( | IUCN ( | ||||||||||||||
| 一 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | |||||||||||||||||
| (一)花鳅科 Cobitidae | |||||||||||||||||
| 1. 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | + | + | + | O | DE | SE | LC | LC | |||||||||
| 2. 大鳞副泥鳅 Paramisgurnus dabryanus* | + | + | + | O | DE | SE | LC | ||||||||||
| (二)条鳅科 Nemacheilidae | |||||||||||||||||
| 3. 东方高原鳅 Triplophysa orientalis | + | + | + | + | C | DE | MS | LC | LC | ||||||||
| 4. 黄河高原鳅 Triplophysa pappenheimi | + | + | + | + | + | C | DE | MS | EN | ||||||||
| 5. 硬刺高原鳅 Triplophysa scleroptera | + | + | + | + | C | DE | MS | LC | |||||||||
| 6. 似鲇高原鳅 Triplophysa siluroides | + | + | + | C | DE | MS | VU | ||||||||||
| 7. 斯氏高原鳅 Triplophysa stoliczkae | + | + | O | DE | MS | LC | |||||||||||
| 8. 粗壮高原鳅 Triplophysa robusta | + | + | + | O | DE | MS | LC | ||||||||||
| (三)鲤科 Cyprinidae | |||||||||||||||||
| 9. ? Hemiculter leucisculus* | + | O | U | DE | LC | LC | |||||||||||
| 10. 鳙 Hypophthalmichthys nobilis* | + | C | U | M | LC | DD | |||||||||||
| 11. 高体鳑鲏 Rhodeus ocellatus* | + | O | L | SE | LC | DD | |||||||||||
| 12. 棒花鱼 Abbottina rivularis* | + | O | DE | SE | LC | ||||||||||||
| 13. 黄河鮈 Gobio huanghensis | + | + | + | C | DE | M | EN | ||||||||||
| 14. 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva* | + | + | + | + | + | O | L | MS | LC | LC | |||||||
| 15. 鲫 Carassius auratus* | + | + | + | + | O | DE | SE | LC | LC | ||||||||
| 16. 鲤 Cyprinus rubrofuscus | + | + | O | DE | SE | LC | LC | ||||||||||
| 17. 黄河裸裂尻鱼 Schizopygopsis pylzovi | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | O | L | MS | VU | ||||||
| 二 鲇形目 Siluriformes | |||||||||||||||||
| (四)鲇科 Siluridae | |||||||||||||||||
| 18. 鲇 Silurus asotus | + | C | L | SE | LC | LC | |||||||||||
| 三 胡瓜鱼目 Osmeriformes | |||||||||||||||||
| (五)胡瓜鱼科 Osmeridae | |||||||||||||||||
| 19. 池沼公鱼 Hypomesus olidus* | + | C | U | M | LC | LC | |||||||||||
| 四 鲈形目 Perciformes | |||||||||||||||||
| (六)沙塘鳢科 Odontobutidae | |||||||||||||||||
| 20. 小黄黝鱼 Micropercops swinhonis* | + | + | C | DE | SE | LC | LC | ||||||||||
| 河流 River | 采样断面 Sampling sections | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou指数 Pielou index | Simpson指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄河 Yellow River | S1 | 1.101 | 0.459 | 0.430 |
| S2 | 1.300 | 0.808 | 0.679 | |
| S3 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| S4 | 2.343 | 0.888 | 0.882 | |
| S5 | 0.548 | 0.395 | 0.248 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 1.058 ± 0.879 | 0.637 ± 0.246 | 0.448 ± 0.347 | |
| 大通河 Datong River | S6 | 1.048 | 0.954 | 0.631 |
| S7 | 0.837 | 0.761 | 0.478 | |
| S8 | 0.349 | 0.503 | 0.198 | |
| S9 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 0.559 ± 0.474 | 0.740 ± 0.226 | 0.327 ± 0.282 | |
| 湟水河 Huangshui River | S10 | 0.826 | 0.596 | 0.415 |
| S11 | 1.099 | 1.000 | 0.667 | |
| S12 | 0.305 | 0.439 | 0.165 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 0.743 ± 0.403 | 0.678 ± 0.289 | 0.416 ± 0.251 | |
| 庄浪河 Zhuanglang River | S13 | 1.431 | 0.798 | 0.729 |
| S14 | 0.994 | 0.905 | 0.605 | |
| S15 | 1.183 | 0.735 | 0.652 | |
| S16 | 0.451 | 0.650 | 0.278 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 1.015 ± 0.416 | 0.772 ± 0.107 | 0.566 ± 0.199 | |
| 宛川河 Wanchuan River | S17 | 0.689 | 0.994 | 0.496 |
| S18 | 1.027 | 0.494 | 0.536 | |
| S19 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| S20 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | |
| S21 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | |
| S22 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | |
| S23 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 0.245 ± 0.430 | 0.298 ± 0.444 | 0.576 ± 0.449 |
Table 3 Spatial distribution of diversity indices in the Lanzhou reach of the Yellow River. Sampling sections code in accordance with Table 1.
| 河流 River | 采样断面 Sampling sections | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou指数 Pielou index | Simpson指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄河 Yellow River | S1 | 1.101 | 0.459 | 0.430 |
| S2 | 1.300 | 0.808 | 0.679 | |
| S3 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| S4 | 2.343 | 0.888 | 0.882 | |
| S5 | 0.548 | 0.395 | 0.248 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 1.058 ± 0.879 | 0.637 ± 0.246 | 0.448 ± 0.347 | |
| 大通河 Datong River | S6 | 1.048 | 0.954 | 0.631 |
| S7 | 0.837 | 0.761 | 0.478 | |
| S8 | 0.349 | 0.503 | 0.198 | |
| S9 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 0.559 ± 0.474 | 0.740 ± 0.226 | 0.327 ± 0.282 | |
| 湟水河 Huangshui River | S10 | 0.826 | 0.596 | 0.415 |
| S11 | 1.099 | 1.000 | 0.667 | |
| S12 | 0.305 | 0.439 | 0.165 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 0.743 ± 0.403 | 0.678 ± 0.289 | 0.416 ± 0.251 | |
| 庄浪河 Zhuanglang River | S13 | 1.431 | 0.798 | 0.729 |
| S14 | 0.994 | 0.905 | 0.605 | |
| S15 | 1.183 | 0.735 | 0.652 | |
| S16 | 0.451 | 0.650 | 0.278 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 1.015 ± 0.416 | 0.772 ± 0.107 | 0.566 ± 0.199 | |
| 宛川河 Wanchuan River | S17 | 0.689 | 0.994 | 0.496 |
| S18 | 1.027 | 0.494 | 0.536 | |
| S19 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| S20 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | |
| S21 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | |
| S22 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 | |
| S23 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| 河流 River (mean ± SD) | 0.245 ± 0.430 | 0.298 ± 0.444 | 0.576 ± 0.449 |
| 黄河 Yellow River | 大通河 Datong River | 湟水河 Huangshui River | 庄浪河 Zhuanglang River | 宛川河 Wanchuan River | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄河 Yellow River | 12.5 | 10.6 | 13.3 | 9.1 | |
| 大通河 Datong River | 7.5 | 3.0 | 2.6 | 8.0 | |
| 湟水河 Huangshui River | 6.5 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.8 | |
| 庄浪河 Zhuanglang River | 8.0 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 5.5 | |
| 宛川河 Wanchuan River | 5.5 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 3.5 |
Table 4 βc (below diagonal) and βr (above diagonal) diversity in the Lanzhou reach of the Yellow River
| 黄河 Yellow River | 大通河 Datong River | 湟水河 Huangshui River | 庄浪河 Zhuanglang River | 宛川河 Wanchuan River | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄河 Yellow River | 12.5 | 10.6 | 13.3 | 9.1 | |
| 大通河 Datong River | 7.5 | 3.0 | 2.6 | 8.0 | |
| 湟水河 Huangshui River | 6.5 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.8 | |
| 庄浪河 Zhuanglang River | 8.0 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 5.5 | |
| 宛川河 Wanchuan River | 5.5 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 3.5 |
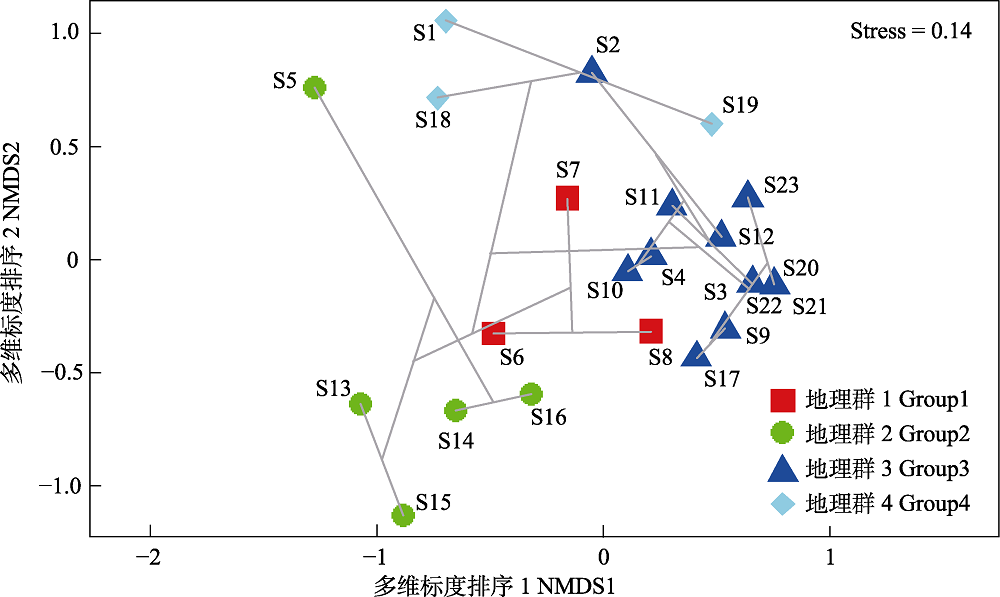
Fig. 3 Ordination of sampling sites in a two-dimensional NMDS in the Lanzhou reach of the Yellow River. Sampling sections code in accordance with Table 1.
| [1] |
Albert JS, Destouni G, Duke-Sylvester SM, Magurran AE, Oberdorff T, Reis RE, Winemiller KO, Ripple WJ (2021) Scientists’ warning to humanity on the freshwater biodiversity crisis. Ambio, 50, 85-94.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Babbitt KJ, Tanner GW (1998) Effects of cover and predator size on survival and development of Rana utricularia tadpoles. Oecologia, 114, 258-262.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Barbarossa V, Schmitt RJP, Huijbregts MAJ, Zarfl C, King H, Schipper AM (2020) Impacts of current and future large dams on the geographic range connectivity of freshwater fish worldwide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 117, 3648-3655. |
| [4] |
Cao L, Zhang E, Zang CX, Cao WX (2016) Evaluating the status of China’s continental fish and analyzing their causes of endangerment through the red list assessment. Biodiversity Science, 24, 598-609. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 曹亮, 张鹗, 臧春鑫, 曹文宣 (2016) 通过红色名录评估研究中国内陆鱼类受威胁现状及其成因. 生物多样性, 24, 598-609.]
DOI |
|
| [5] | Carvajal-Quintero J, Villalobos F, Oberdorff T, Grenouillet G, Brosse S, Hugueny B, Jézéquel C, Tedesco PA (2019) Drainage network position and historical connectivity explain global patterns in freshwater fishes’ range size. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 13434-13439. |
| [6] | Chen YY (1998) Fauna Sinica, Osteichthyes, Cypriniformes. II. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈宜瑜 (1998) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(中卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Chen YY, Chen YF, Liu HZ (1996) Studies on the position of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau region in zoogeographic divisions and its eastern demarcation line. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 20, 97-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈宜瑜, 陈毅峰, 刘焕章 (1996) 青藏高原动物地理区划的地位和东部界线问题. 水生生物学报, 20, 97-103.] | |
| [8] | Cody ML, Diamond JM (1975) Towards a theory of continental species diversities:Bird distributions over Mediterranean habitat gradients. In: Ecology and Evolution of Communities (eds Cody ML, Diamond JM), pp. 214-257. Harvard University Press, Cambridge. |
| [9] | Ding RH (1994) The Fishes of Sichuan. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [ 丁瑞华 (1994) 四川鱼类志. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [10] |
Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata ZI, Knowler DJ, Lévêque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biological Reviews, 81, 163-182.
PMID |
| [11] | Feng CG, Tong C, Zhang RY, Li GG, Wang HKY, Tang YT, Zhang CF, Zhao K (2017) Biodiversity and distribution patterns of Triplophysa species in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 25, 53-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 冯晨光, 童超, 张仁意, 李国刚, 王贺崐元, 汤永涛, 张存芳, 赵凯 (2017) 青藏高原东北部边缘高原鳅属鱼类的多样性与分布格局. 生物多样性, 25, 53-61.]
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Haubrock PJ, Pilotto F, Innocenti G, Cianfanelli S, Haase P (2021) Two centuries for an almost complete community turnover from native to non-native species in a riverine ecosystem. Global Change Biology, 27, 606-623.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | He CL, Song ZB, Zhang E (2011) Triplophysa fishes in China and the status of its taxonomic studies. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 30, 150-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何春林, 宋昭彬, 张鹗 (2011) 中国高原鳅属鱼类及其分类研究现状. 四川动物, 30, 150-155.] | |
| [14] |
He DK, Sui XY, Sun HY, Tao J, Ding CZ, Chen YF, Chen YY (2020) Diversity, pattern and ecological drivers of freshwater fish in China and adjacent areas. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 30, 387-404.
DOI URL |
| [15] | IUCN International Union for Conservation of Nature (2021) The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. http://www. iucnredlist.org . (accessed on 2021-03-30) |
| [16] | Jia QH, Chen XX, Gao HW, Bai HF, Shen HB, Wang YC, Wen SE, Li WX (2015) Investigation of fish resources in autumn in Lanzhou urban section of the Yellow River. Hebei Fisheries, (9), 21-23. (in Chinese) |
| [ 贾秋红, 陈晓霞, 高宏伟, 白海锋, 沈红保, 王益昌, 问思恩, 李文香 (2015) 黄河兰州市区段秋季鱼类资源现状调查. 河北渔业, (9), 21-23.] | |
| [17] |
Jiang XM, Wang J, Tang WJ, Sun ZW, Pan BZ (2021) Non-native freshwater fish species in the Yellow River Basin: Origin, distribution and potential risk. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 104, 253-264.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG (2016) Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24, 500-551. (in Chinese and in English)
DOI URL |
|
[ 蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 (2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性, 24, 500-551.]
DOI |
|
| [19] | Li F, Zhang JJ, Yuan YF, Feng H, Zhang JY, Yang XZ (2008) Present situation and problems on fish introduction in Yellow River system. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 36, 15024-15026. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李芳, 张建军, 袁永锋, 冯慧, 张军燕, 杨兴中 (2008) 黄河流域鱼类引种现状及存在问题. 安徽农业科学, 36, 15024-15026.] | |
| [20] |
Li JX, Wang Y, Jin HF, Li WJ, Yan CC, Yan PF, Zhang XY, He SP, Song ZB (2017) Identification of Triplophysa species from the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (QTP) and its adjacent regions through DNA barcodes. Gene, 605, 12-19.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Li SZ (2017) Fishes of the Yellow River. China Ocean University Press, Qingdao. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李思忠 (2017) 黄河鱼类志. 中国海洋大学出版社, 青岛.] | |
| [22] |
Li XJ, Jia PY, Niu CY, Xing YC, Li HL, Liu HB, Tang WQ, Zhao YH (2020) Species diversity of freshwater fish and assessment on watershed health in the Irtysh River and Ulungur River basins in Xinjiang, China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 422-434. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李雪健, 贾佩尧, 牛诚祎, 邢迎春, 李浩林, 刘海波, 唐文乔, 赵亚辉 (2020) 新疆阿勒泰地区额尔齐斯河和乌伦古河流域鱼类多样性演变和流域健康评价. 生物多样性, 28, 422-434.]
DOI |
|
| [23] | Liao JQ, Huang Y (2013) Research progress on using index of biological integrity to assess aquatic ecosystem health. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 295-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 廖静秋, 黄艺 (2013) 应用生物完整性指数评价水生态系统健康的研究进展. 应用生态学报, 24, 295-302.] | |
| [24] |
Liu XJ, Hu XY, Ao XF, Wu XP, Ouyang S (2018) Community characteristics of aquatic organisms and management implications after construction of Shihutang Dam in the Gangjiang River, China. Lake and Reservoir Management, 34, 42-57.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Oberdorff T, Dias MS, Jézéquel C, Albert JS, Arantes CC, Bigorne R, Carvajal-Valleros FM, De Wever A, Frederico RG, Hidalgo M, Hugueny B, Leprieur F, Maldonado M, Maldonado-Ocampo J, Martens K, Ortega H, Sarmiento J, Tedesco PA, Torrente-Vilara G, Winemiller KO, Zuanon J (2019) Unexpected fish diversity gradients in the Amazon basin. Science Advances, 5, eaav8681.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. Wiley, New York. |
| [27] |
Prokovfiev AM (2007) Materials towards the revision of the genus Triplophysa rendahl, 1933 (Cobitoidea: Balitoridae: Nemacheilinae): A revision of nominal taxa of Herzenstein (1888) described within the species “Nemachilus” stoliczkae and “N.” dorsonotatus, with the description of the new species T. scapanognatha sp. nova. Journal of Ichthyology, 47, 1-20.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Ren JS, Zhang J, Gao XY (2018) Study on transplantation, multiplication and stable yield of Hypomesus olidus in canyon-type reservoir. China Fisheries, (1), 86-89. (in Chinese) |
| [ 任锦帅, 张静, 郜晓瑜 (2018) 峡谷型水库池沼公鱼移植增殖与稳产技术研究. 中国水产, (1), 86-89.] | |
| [29] |
Routledge RD (1977) On Whittaker’s components of diversity. Ecology, 58, 1120-1127.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Ru HJ, Liu XQ, Huang XR, Ning YZ, Wang HZ (2008) Diversity of fish species and its spatio-temporal variations in Lake Dongting, a large Yangtze-connected lake. Journal of Lake Sciences, 20, 93-99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 茹辉军, 刘学勤, 黄向荣, 宁应之, 王洪铸 (2008) 大型通江湖泊洞庭湖的鱼类物种多样性及其时空变化. 湖泊科学, 20, 93-99.] | |
| [31] |
Ru HJ, Wang HJ, Zhao WH, Shen YQ, Wang Y, Zhang XK (2010) Fishes in the mainstream of the Yellow River: Assemblage characteristics and historical changes. Biodiversity Science, 18, 179-186. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 茹辉军, 王海军, 赵伟华, 沈亚强, 王勇, 张晓可 (2010) 黄河干流鱼类群落特征及其历史变化. 生物多样性, 18, 179-186.] | |
| [32] | Shannon EC, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. Urbana University of Illinois Press, Illinois. |
| [33] | Shen HB, Li KS, Zhang M (2007) Investigation and analysis of fish resources in the upper reaches of the Yellow River. Hebei Fisheries, (6), 37-41. (in Chinese) |
| [ 沈红保, 李科社, 张敏 (2007) 黄河上游鱼类资源现状调查与分析. 河北渔业, (6), 37-41.] | |
| [34] |
Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature, 163, 688.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Su GH, Logez M, Xu J, Tao SL, Villéger S, Brosse S (2021) Human impacts on global freshwater fish biodiversity. Science, 371, 835-838.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Tang WJ, Chen YF, Ding CZ (2013) The current situation and protection of fish resources in Huangshui River in Qinghai Province. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 28, 307-313. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐文家, 陈毅峰, 丁城志 (2013) 青海省湟水鱼类资源现状及保护对策. 大连海洋大学学报, 28, 307-313.] | |
| [37] |
Tang ZY, Qiao XJ, Fang JY (2009) Species-area relationship in biological communities. Biodiversity Science, 17, 549-559. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 唐志尧, 乔秀娟, 方精云 (2009) 生物群落的种-面积关系. 生物多样性, 17, 549-559.]
DOI |
|
| [38] |
Villéger S, Brosse S, Mouchet M, Mouillot D, Vanni MJ (2017) Functional ecology of fish: Current approaches and future challenges. Aquatic Sciences, 79, 783-801.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Wang T, Zhang YP, Yang ZY, Liu Z, Du YY (2020) DNA barcoding reveals cryptic diversity in the underestimated genus Triplophysa (Cypriniformes: Cobitidae, Nemacheilinae) from the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 20, 151.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wang T, Zhang YP, Guan LH, Du YY, Lou ZY, Jiao WL (2015) Current freshwater fish resources and the application of DNA barcoding in species identification in Gansu Province. Biodiversity Science, 23, 306-313. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 王太, 张艳萍, 管丽红, 杜岩岩, 娄忠玉, 焦文龙 (2015) 甘肃省鱼类资源现状及DNA条形码在鱼类物种鉴定中的应用. 生物多样性, 23, 306-313.]
DOI |
|
| [41] | Wang XT (1991) Vertebrate Fauna of Gansu. Gansu Science and Technology Press, Lanzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王香亭 (1991) 甘肃脊椎动物志. 甘肃科学技术出版社, 兰州.] | |
| [42] | Wang XT (1996) Local Investigation on Resources of Xinglong Mountains National Nature Reserve in Gansu Province. Gansu Nationalities Press, Lanzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王香亭 (1996) 甘肃兴隆山国家级自然保护区资源本地调查研究. 甘肃民族出版社, 兰州.] | |
| [43] | Wang XT, He RL, Zhao HM (1956) Fishes in the Yellow River near Lanzhou. Bulletin of Biology, (8), 16-21. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王香亭, 贺汝良, 赵宏谟 (1956) 兰州附近黄河的鱼类. 生物学通报, (8), 16-21.] | |
| [44] | Wang Z, Song C, Yan WL, Zhu LF (2019) Biodiversity and spatial pattern of fish in the Pingchuan segment of the upper reaches of Hanjiang River. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 28, 1675-1681. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王卓, 宋策, 闫文龙, 朱来福 (2019) 汉江上游平川段鱼类群落多样性及空间格局分析. 长江流域资源与环境, 28, 1675-1681.] | |
| [45] |
Ward RD, Zemlak TS, Innes BH, Last PR, Hebert PDN (2005) DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 360, 1847-1857.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Wu QJ, Zhao YJ, Xiao ZQ (2021) Comparative analysis of temperature and precipitation change trend between Lanzhou and Longnan. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, (4), 173-175. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴巧娟, 赵育俊, 肖志强 (2021) 兰州市和陇南市温度降水变化趋势对比分析. 现代农业科技, (4), 173-175.] | |
| [47] |
Xie JY, Tang WJ, Yang YH (2018) Fish assemblage changes over half a century in the Yellow River, China. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 4173-4182.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Xu FK, He L, Wang YF, He C, Niu Y, Liu WJ, Song WH (2021) Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of water quality in Lanzhou and Baiyin section of the Yellow River main stream from 2010 to 2019. Water Resources Protection, 37, 44-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐发凯, 何丽, 王一帆, 何昌, 牛毓, 刘文君, 宋伟宏 (2021) 2010-2019年黄河干流兰州和白银段水质时空变化特征. 水资源保护, 37, 44-50.] | |
| [49] | Xu RM, Ye WH (2004) Biological Invasion:Theory and Practice. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 徐汝梅, 叶万辉 (2004) 生物入侵:理论与实践. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [50] | Yang YT, Tang YQ (1995) Resources and geographical distribution of the fishes in Gansu Province, China. Journal of Gansu Sciences, (3), 72-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨友桃, 唐迎秋 (1995) 甘肃鱼类资源及其地理分布. 甘肃科学学报, (3), 72-75.] | |
| [51] | Ye FL, Zhang JD (2002) Fish Ecology. Guangdong Higher Education Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 叶富良, 张健东 (2002) 鱼类生态学. 广东高等教育出版社, 广州.] | |
| [52] | Yu GQ (2007) Biodiversity Inventory and Assessment. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [ 喻国庆 (2007) 生物多样性调查与评价. 云南科学技术出版社, 昆明.] | |
| [53] | Yuan YF, Li YD, Zhang LL, Yu B, Qi XR, Han MX, Zhang JJ (2009) Investigation & research on hydrobios resources in the middle and upper reaches of main Yellow River. Journal of Hydroecology, 30, 15-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁永锋, 李引娣, 张林林, 余斌, 齐喜荣, 韩明轩, 张建军 (2009) 黄河干流中上游水生生物资源调查研究. 水生态学杂志, 30, 15-19.] | |
| [54] | Yue PQ (2000) Fauna Sinica, Osteichthyes, Cypriniformes. III. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 乐佩琦 (2000) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(下卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [55] | Zhang CG, Zhao YH (2016) Species Diversity and Distribution of Inland Fishes in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张春光, 赵亚辉 (2016) 中国内陆鱼类物种与分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [56] |
Zhao YH, Xing YC, Lü BB, Zhou CJ, Yang WB, Zhao K (2020) Species diversity and conservation of freshwater fishes in the Yellow River Basin. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1496-1510. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 赵亚辉, 邢迎春, 吕彬彬, 周传江, 杨文波, 赵凯 (2020) 黄河流域淡水鱼类多样性和保护. 生物多样性, 28, 1496-1510.] | |
| [57] | Zhu SQ (1989) The Loaches of the Subfamily Nemacheilinae in China. Jiangsu Science and Technology Publishing House, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 朱松泉 (1989) 中国条鳅志. 江苏科学技术出版社, 南京.] |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn