



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 1229-1235. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021020 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021020
• Original Papers: Microbial Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Miao Yang1, Jie Zhang1, Jiawei Bai1, Jiangang Guo2, Yahui Qu2, Huiping Li1,3,*( )
)
Received:2021-01-14
Accepted:2021-04-12
Online:2021-09-20
Published:2021-05-28
Contact:
Huiping Li
Miao Yang, Jie Zhang, Jiawei Bai, Jiangang Guo, Yahui Qu, Huiping Li. Species diversity of macrofungi in the Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1229-1235.
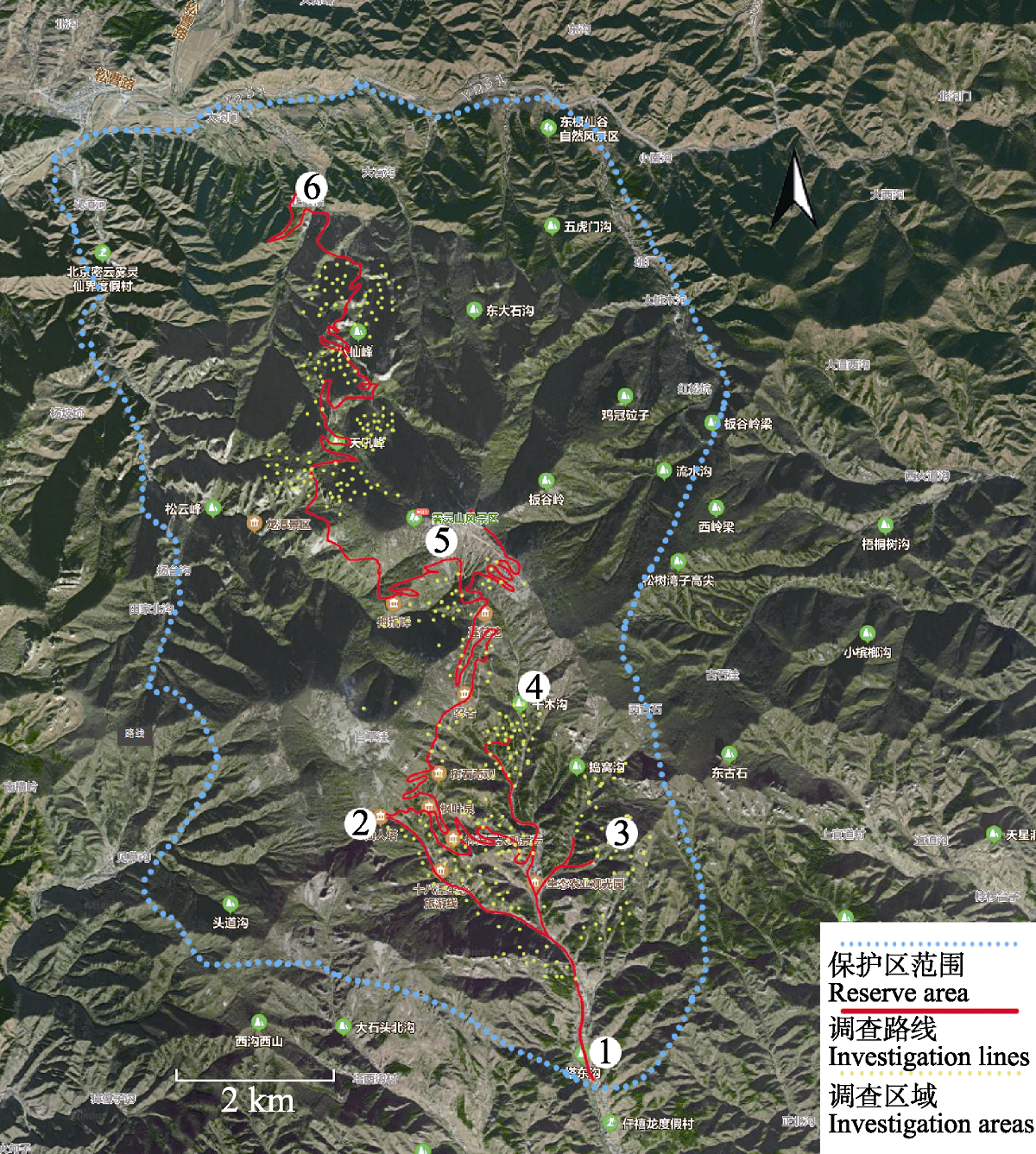
Fig. 1 Investigation lines of macrofungi in the Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve. (1) South gate of the reserve; (2) Fairy Tower; (3) Niangniangwa Valley; (4) Wucha Valley; (5) Lianhuachi; (6) North gate of the reserve.
| 科 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species | 科 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绿杯盘菌科 Chlorociboriaceae | 1 | 1 | 球盖菇科 Strophariaceae | 4 | 6 |
| 地锤菌科 Cudoniaceae | 1 | 1 | 口蘑科 Tricholomataceae | 2 | 4 |
| 马鞍菌科 Helvellaceae | 1 | 4 | 木耳科 Auriculariaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 羊肚菌科 Morchellaceae | 1 | 1 | 牛肝菌科 Boletaceae | 3 | 7 |
| 盘菌科 Pezizaceae | 1 | 2 | 铆钉菇科 Gomphidiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 火丝盘菌科 Pyronemataceae | 3 | 3 | 硬皮马勃科 Sclerodermataceae | 1 | 1 |
| 肉杯菌科 Sarcoscyphaceae | 1 | 1 | 黏盖牛肝菌科 Suillaceae | 1 | 3 |
| 疣杯盘菌科 Tarzettaceae | 1 | 1 | 桩菇科 Paxillaceae | 1 | 4 |
| 炭球菌科 Hypoxylaceae | 1 | 1 | 齿菌科 Hydnaceae | 4 | 5 |
| 蘑菇科 Agaricaceae | 5 | 17 | 地星科 Geastraceae | 1 | 4 |
| 鹅膏菌科 Amanitaceae | 1 | 6 | 钉菇科 Gomphaceae | 1 | 3 |
| 碘伏革菌科 Amylocorticiaceae | 1 | 1 | 刺革菌科 Hymenochaetaceae | 2 | 3 |
| 珊瑚菌科 Clavariaceae | 1 | 1 | 藓菇科 Rickenellaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 丝膜菌科 Cortinariaceae | 1 | 10 | 革菌科 Thelephoraceae | 1 | 2 |
| 锈耳科 Crepidotaceae | 1 | 3 | 鬼笔科 Phallaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 粉褶菌科 Entolomataceae | 2 | 4 | 拟层孔菌科 Fomitopsidaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 轴腹菌科 Hydnangiaceae | 1 | 3 | 干皮菌科 Incrustoporiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 蜡伞科 Hygrophoraceae | 2 | 4 | 耙齿菌科 Irpicaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 层腹菌科 Hymenogastraceae | 1 | 2 | 硫磺菌科 Laetiporaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 丝盖伞科 Inocybaceae | 1 | 5 | 平革菌科 Phanerochaetaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 马勃科 Lycoperdaceae | 2 | 6 | 多孔菌科 Polyporaceae | 8 | 14 |
| 小皮伞科 Marasmiaceae | 1 | 5 | 齿耳菌科 Steccherinaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 小菇科 Mycenaceae | 2 | 6 | 红菇科 Russulaceae | 2 | 21 |
| 光茸菌科 Omphalotaceae | 2 | 5 | 韧革菌科 Stereaceae | 2 | 4 |
| 膨瑚菌科 Physalacriaceae | 3 | 5 | 耳匙菌科 Auriscalpiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 侧耳科 Pleurotaceae | 1 | 5 | 花耳科 Dacrymycetaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 光柄菇科 Pluteaceae | 1 | 7 | 银耳科 Tremellaceae | 1 | 2 |
| 小脆柄菇科 Psathyrellaceae | 3 | 6 | 未定科 Incertae sedis | 14 | 21 |
| 裂褶菌科 Schizophyllaceae | 1 | 1 | 总计 Total | 107 | 236 |
Table 1 Number of families, genera and species of macrofungi in Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve
| 科 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species | 科 Family | 属数 No. of genera | 种数 No. of species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绿杯盘菌科 Chlorociboriaceae | 1 | 1 | 球盖菇科 Strophariaceae | 4 | 6 |
| 地锤菌科 Cudoniaceae | 1 | 1 | 口蘑科 Tricholomataceae | 2 | 4 |
| 马鞍菌科 Helvellaceae | 1 | 4 | 木耳科 Auriculariaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 羊肚菌科 Morchellaceae | 1 | 1 | 牛肝菌科 Boletaceae | 3 | 7 |
| 盘菌科 Pezizaceae | 1 | 2 | 铆钉菇科 Gomphidiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 火丝盘菌科 Pyronemataceae | 3 | 3 | 硬皮马勃科 Sclerodermataceae | 1 | 1 |
| 肉杯菌科 Sarcoscyphaceae | 1 | 1 | 黏盖牛肝菌科 Suillaceae | 1 | 3 |
| 疣杯盘菌科 Tarzettaceae | 1 | 1 | 桩菇科 Paxillaceae | 1 | 4 |
| 炭球菌科 Hypoxylaceae | 1 | 1 | 齿菌科 Hydnaceae | 4 | 5 |
| 蘑菇科 Agaricaceae | 5 | 17 | 地星科 Geastraceae | 1 | 4 |
| 鹅膏菌科 Amanitaceae | 1 | 6 | 钉菇科 Gomphaceae | 1 | 3 |
| 碘伏革菌科 Amylocorticiaceae | 1 | 1 | 刺革菌科 Hymenochaetaceae | 2 | 3 |
| 珊瑚菌科 Clavariaceae | 1 | 1 | 藓菇科 Rickenellaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 丝膜菌科 Cortinariaceae | 1 | 10 | 革菌科 Thelephoraceae | 1 | 2 |
| 锈耳科 Crepidotaceae | 1 | 3 | 鬼笔科 Phallaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 粉褶菌科 Entolomataceae | 2 | 4 | 拟层孔菌科 Fomitopsidaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 轴腹菌科 Hydnangiaceae | 1 | 3 | 干皮菌科 Incrustoporiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 蜡伞科 Hygrophoraceae | 2 | 4 | 耙齿菌科 Irpicaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 层腹菌科 Hymenogastraceae | 1 | 2 | 硫磺菌科 Laetiporaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 丝盖伞科 Inocybaceae | 1 | 5 | 平革菌科 Phanerochaetaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 马勃科 Lycoperdaceae | 2 | 6 | 多孔菌科 Polyporaceae | 8 | 14 |
| 小皮伞科 Marasmiaceae | 1 | 5 | 齿耳菌科 Steccherinaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 小菇科 Mycenaceae | 2 | 6 | 红菇科 Russulaceae | 2 | 21 |
| 光茸菌科 Omphalotaceae | 2 | 5 | 韧革菌科 Stereaceae | 2 | 4 |
| 膨瑚菌科 Physalacriaceae | 3 | 5 | 耳匙菌科 Auriscalpiaceae | 1 | 1 |
| 侧耳科 Pleurotaceae | 1 | 5 | 花耳科 Dacrymycetaceae | 2 | 2 |
| 光柄菇科 Pluteaceae | 1 | 7 | 银耳科 Tremellaceae | 1 | 2 |
| 小脆柄菇科 Psathyrellaceae | 3 | 6 | 未定科 Incertae sedis | 14 | 21 |
| 裂褶菌科 Schizophyllaceae | 1 | 1 | 总计 Total | 107 | 236 |
| 属 Genus | 种数 No. species | 占总种数比例 % | 营养类型 Nutritional type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 红菇属 Russula | 12 | 5.08 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 蘑菇属 Agaricus | 10 | 4.24 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 丝膜菌属 Cortinarius | 10 | 4.24 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 乳菇属 Lactarius | 9 | 3.81 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 光柄菇属 Pluteus | 7 | 2.97 | 木生 Lignicolous |
| 鹅膏菌属 Amanita | 6 | 2.54 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 马勃属 Lycoperdon | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 小皮伞属 Marasmius | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 小菇属 Mycena | 5 | 2.12 | 木生、土生 Lignicolous & geophilous |
| 丝盖伞属 Inocybe | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 侧耳属 Pleurotus | 5 | 2.12 | 木生 Lignicolous |
| 共计 Total | 79 | 33.47 |
Table 2 Dominant genera of macrofungi in Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve (≥ 5 species)
| 属 Genus | 种数 No. species | 占总种数比例 % | 营养类型 Nutritional type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 红菇属 Russula | 12 | 5.08 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 蘑菇属 Agaricus | 10 | 4.24 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 丝膜菌属 Cortinarius | 10 | 4.24 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 乳菇属 Lactarius | 9 | 3.81 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 光柄菇属 Pluteus | 7 | 2.97 | 木生 Lignicolous |
| 鹅膏菌属 Amanita | 6 | 2.54 | 共生 Symbiotic |
| 马勃属 Lycoperdon | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 小皮伞属 Marasmius | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 小菇属 Mycena | 5 | 2.12 | 木生、土生 Lignicolous & geophilous |
| 丝盖伞属 Inocybe | 5 | 2.12 | 土生 Geophilous |
| 侧耳属 Pleurotus | 5 | 2.12 | 木生 Lignicolous |
| 共计 Total | 79 | 33.47 |
| [1] | Bao HY (2006) Studies on Chemical Compositions and Pharmacological Action of Some Toadstools. Inner Mongolia Education Press, Huhhot. (in Chinese) |
| [包海鹰 (2006) 毒蘑菇化学成分与药理活性的研究. 内蒙古教育出版社, 呼和浩特.] | |
| [2] | Bau T (2018) Mushroom Taxonomy. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [图力古尔 (2018) 蕈菌分类学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [3] | Bau T, Bao HY, Li Y (2014) A revised checklist of poisonous mushrooms in China. Mycosystema, 33, 517-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [图力古尔, 包海鹰, 李玉 (2014) 中国毒蘑菇名录. 菌物学报, 33, 517-548.] | |
| [4] | Bau T, Li Y (2000) Fungal community diversity in Daqinggou Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 20, 986-991. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [图力古尔, 李玉 (2000) 大青沟自然保护区大型真菌群落多样性研究. 生态学报, 20, 986-991.] | |
| [5] | Bau T, Li Y (2000) Study on fungal flora diversity in Daqinggou Nature Reserve. Chinese Biodiversity, 8, 73-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [图力古尔, 李玉 (2000) 大青沟自然保护区大型真菌区系多样性的研究. 生物多样性, 8, 73-80.] | |
| [6] |
Bau T, Wang XS, Zhang P (2019) Floristic of agarics and boletus in the Greater and Lesser Khinggan Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 27, 867-873. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[图力古尔, 王雪珊, 张鹏 (2019) 大小兴安岭地区伞菌和牛肝菌类区系. 生物多样性, 27, 867-873.]
DOI |
|
| [7] | Chen ZH, Yang ZL, Bau T, Li TH (2016) Poisonous Mushrooms:Recognition and Poisoning Treatment. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈作红, 杨祝良, 图力古尔, 李泰辉 (2016) 毒蘑菇识别与中毒防治. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Dai YC, Bau T (2007) Illustrations of Edible and Medicinal Fungi in Northeastern China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴玉成, 图力古尔 (2007) 中国东北食药用真菌图志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Dai YC, Yang ZL (2008) A revised checklist of medicinal fungi in China. Mycosystema, 27, 801-824. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴玉成, 杨祝良 (2008) 中国药用真菌名录及部分名称的修订. 菌物学报, 27, 801-824.] | |
| [10] | Dai YC, Zhou LW, Yang ZL, Wen HA, Bau T, Li TH (2010) A revised checklist of edible fungi in China. Mycosystema, 29, 1-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴玉成, 周丽伟, 杨祝良, 文华安, 图力古尔, 李泰辉 (2010) 中国食用菌名录. 菌物学报, 29, 1-21.] | |
| [11] | Li Y, Li TH, Yang ZL, Bau T, Dai YC (2015) Resources of Macrofungi in China. Central Plain Farmers Press, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [李玉, 李泰辉, 杨祝良, 图力古尔, 戴玉成 (2015) 中国大型菌物资源图鉴. 中原农民出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [12] | Lu WL, Wei TZ, Wang XL, Li Y, Lü HM, Yang L, Yang WJ, Yao YJ (2015) Species diversity of macrofungi in Beijing, China. Mycosystema, 34, 982-995. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢维来, 魏铁铮, 王晓亮, 李熠, 吕红梅, 杨柳, 杨文婧, 姚一建 (2015) 北京地区大型真菌多样性分析. 菌物学报, 34, 982-995.] | |
| [13] | Mao XL (2000) Chinese Macrofungi. Henan Science and Technology Press, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [卯晓岚 (2000) 中国大型真菌. 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [14] | Mao XL (1998) Economic Fungi of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [卯晓岚 (1998) 中国经济真菌. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [15] | Mao XL (2006) Poisonous mushrooms and their toxins in China. Mycosystema, 25, 345-363. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卯晓岚 (2006) 中国毒菌物种多样性及其毒素. 菌物学报, 25, 345-363.] | |
| [16] | Shao LP, Xiang CD (2017) Forest Mushrooms in China. Northeast Forestry University Press, Harbin. (in Chinese) |
| [邵力平, 项存悌 (2017) 中国森林蘑菇. 东北林业大学出版社, 哈尔滨.] | |
| [17] | Wang Q, Liu HX, Zhang JG, Lu J, Liu YX, Yang LH, Ji H, Chen WJ (2005) Investigation of wild edible and medical fungi of Wuling Mountain area. Journal of Hebei University (Natural Science Edition), 25, 523-525. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王谦, 刘会欣, 张俊刚, 卢婕, 刘玉霞, 杨立华, 冀宏, 陈文杰 (2005) 雾灵山地区野生食药用真菌资源调查. 河北大学学报(自然科学版), 25, 523-525.] | |
| [18] | Wang XS, Bau T, Bao JS, Bao H, Feng J (2020) Macrofungal diversity in Hanwula National Nature Reserve, Inner Mongolia. Mycosystema, 39, 695-706. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王雪珊, 图力古尔, 宝金山, 宝虎, 丰洁 (2020) 内蒙古罕山国家级自然保护区大型真菌多样性. 菌物学报, 39, 695-706.] | |
| [19] |
Wu F, Zhou LW, Yang ZL, Bau T, Li TH, Dai YC (2019) Resource diversity of Chinese macrofungi: Edible, medicinal and poisonous species. Fungal Diversity, 98, 1-76.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Wu JG, Zhou H, Hou CL (2020) Diversity of poisonous macrofungi in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 41(4), 52-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴记贵, 周昊, 侯成林 (2020) 北京松山国家级自然保护区有毒大型真菌物种多样性研究. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 41(4), 52-56.] | |
| [21] | Yuan MS, Sun PQ (2013) Color Atlas of Large Fungus in China. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [袁明生, 孙佩琼 (2013) 中国大型真菌彩色图谱. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [22] | Zhang JH, Yang XB, Lu SW, Bai CL, Tan HX (2014) Study on shrub-grass diversity and influence factors of different forests in Wuling Mountain of Hebei Province. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 37, 27-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张建华, 杨新兵, 鲁绍伟, 白翠玲, 谭海霞 (2014) 河北雾灵山不同林分灌草多样性及影响因素研究. 河北农业大学学报, 37, 27-32.] | |
| [23] | Zhao HZ, Xu YY, Fu XY, Fan L (2007) The progress of food and medical values of puff-balls. Microbiology, 34, 367-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵会珍, 胥艳艳, 付晓燕, 范黎 (2007) 马勃的食药用价值及其研究进展. 微生物学通报, 34, 367-369.] |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [10] | Yanli Wang, Ying Zhang, Chunlin Qi, Changda Zhang, Youhai Shi, Yanjun Du, Qiong Ding. Identifying biodiversity hotspots and conservation gaps in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park based on macrofungi and plants perspectives [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [11] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [14] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [15] | Weiqiang Xu, Qiang Su. Exploring the interplay of fractal model and species abundance distribution: A case study of shellfish and insect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn