



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 23410. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023410 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023410
• Technology and Methodology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-10-31
Accepted:2024-01-17
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-03-06
Contact:
* E-mail: CLC Number:
Weiqiang Xu, Qiang Su. Exploring the interplay of fractal model and species abundance distribution: A case study of shellfish and insect[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23410.
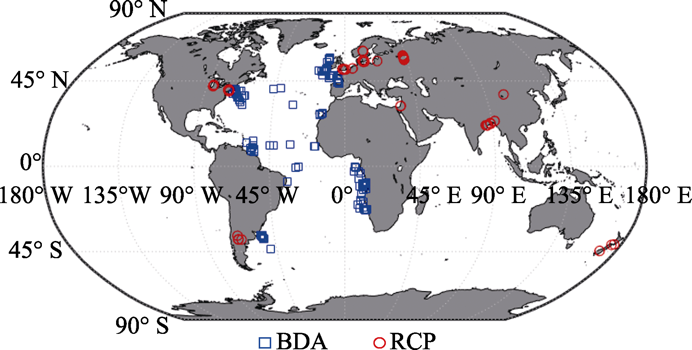
Fig. 1 Global distribution of research stations in Bivalvia of the Deep-sea Atlantic Database (BDA) and Reading University Crop Pollinator Database (RCP)
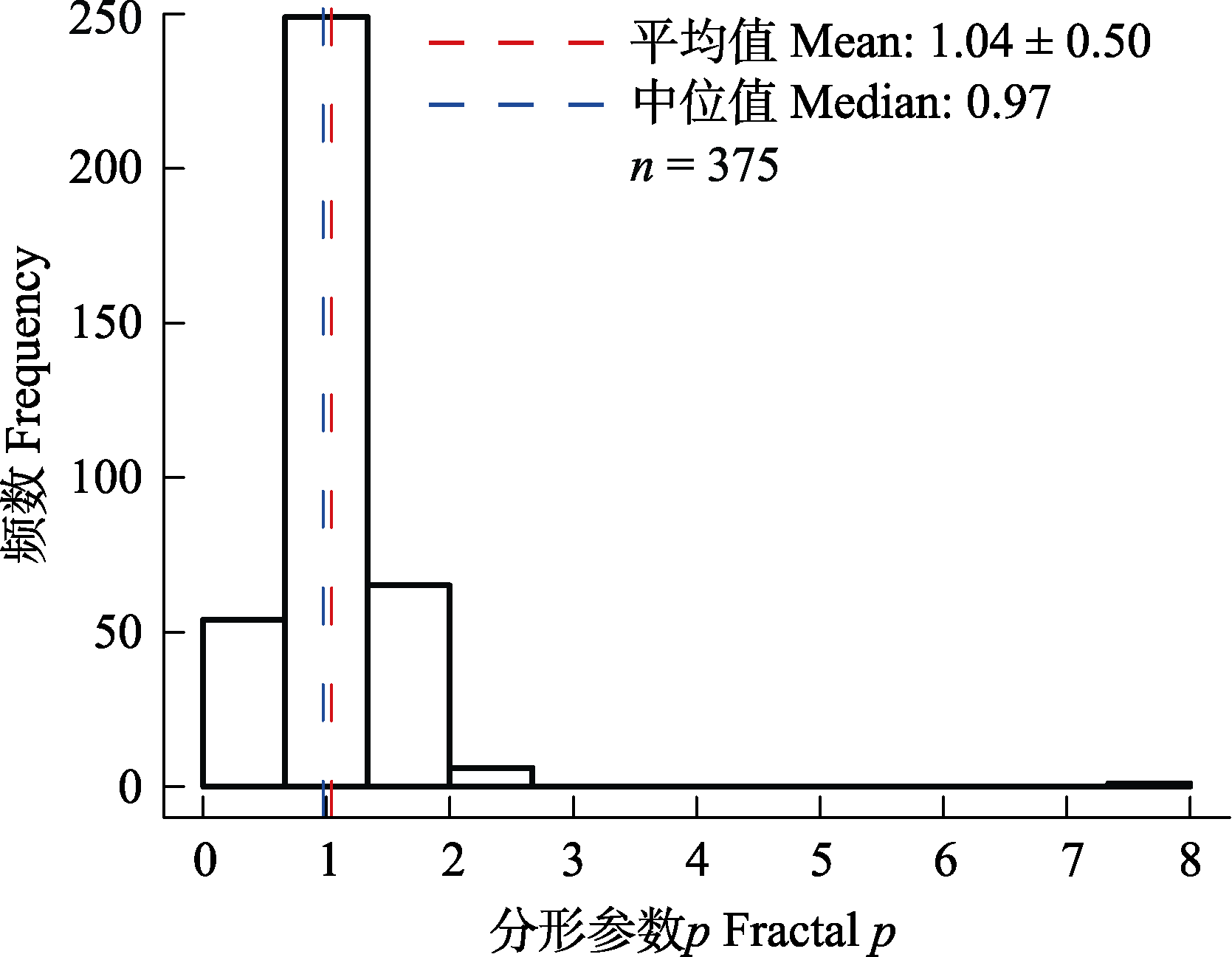
Fig. 2 Frequency distribution of the fractal p of community samples in Reading University Crop Pollinator Database (RCP) without a 30-day time interval post-sampling
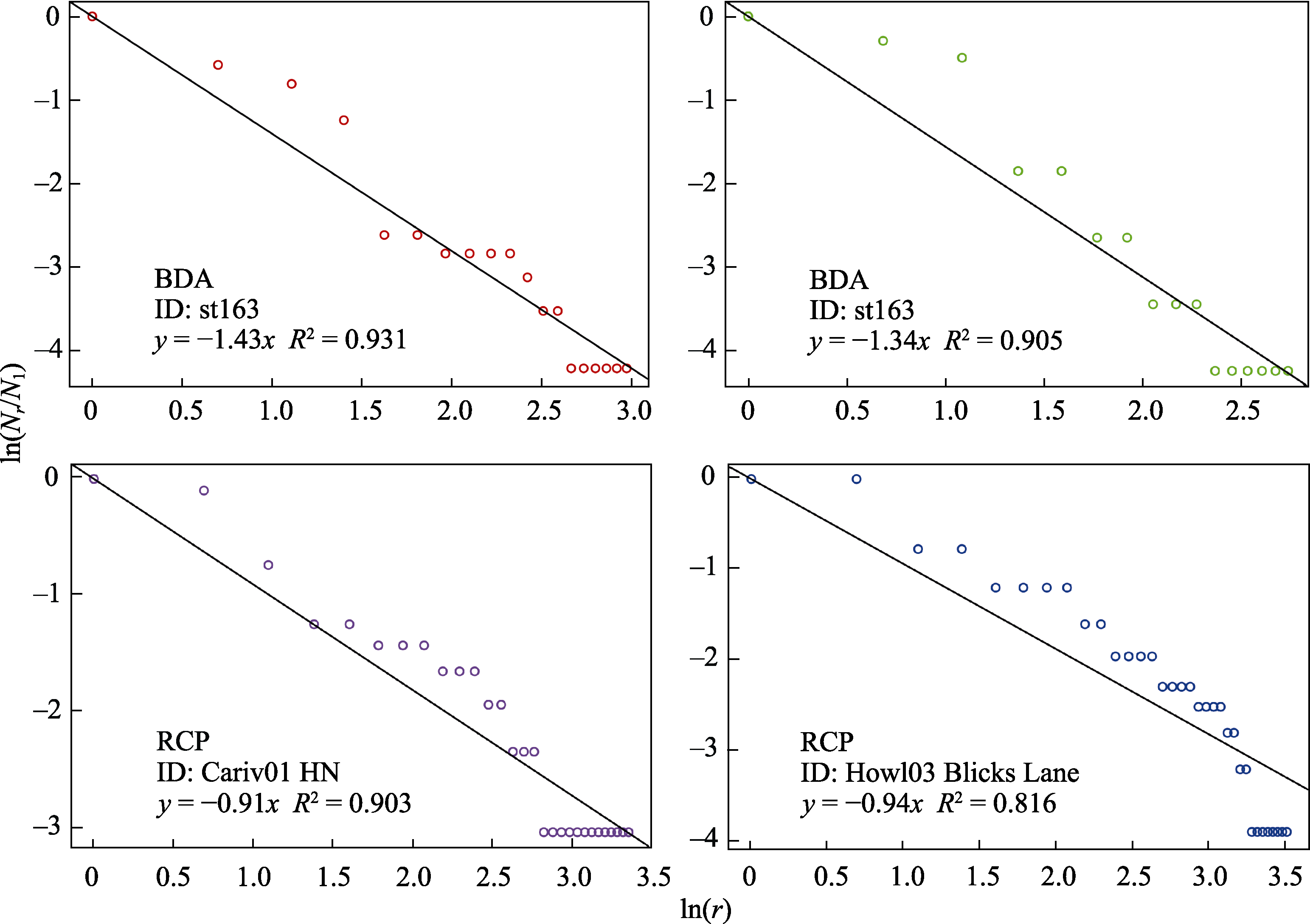
Fig. 3 The p-model fits four natural communities randomly selected from Bivalvia of the Deep-sea Atlantic Database (BDA) and Reading University Crop Pollinator Database (RCP)
| 数据库 Dataset | 最大值 Max. | 最小值 Min. | 中位值 Median | 平均值 Mean | 样本数量 No. of sample | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDA | 5.66 | 0.00 | 1.57 | 1.62 ± 0.66 | 242 | 本研究 This study |
| RCP | 4.92 | 0.00 | 1.11 | 1.19 ± 0.58 | 926 | 本研究 This study |
| BFD | 6.03 | 0.81 | 1.53 | 1.65 ± 0.03 | 1,265 | Gao & Su, |
| DIN | 5.46 | 0.26 | 1.66 | 1.74 ± 0.01 | 2,402 | Gao & Su, |
| DEV | 11.39 | 0.05 | 1.77 | 2.09 ± 0.02 | 2,179 | Gao & Su, |
| DINC | 5.11 | 0.29 | 1.61 | 1.67 ± 0.02 | 602 | Gao & Su, |
| Diatom | 5.83 | 0.34 | 1.27 | 1.34 ± 0.01 | 3,224 | Su, |
| Fish | 4.56 | 0.76 | 1.59 | 1.70 ± 0.02 | 761 | Su, |
| BBS | 2.38 | 0.55 | 0.94 | 0.98 ± 0.004 | 2,769 | Su, |
| CBC | 3.74 | 0.73 | 1.49 | 1.56 ± 0.01 | 1,999 | Su, |
| FIA | 2.23 | 0.24 | 0.91 | 0.93 ± 0.003 | 10,355 | Su, |
| Gentry | 1.85 | 0.35 | 0.83 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 222 | Su, |
| MCDB | 3.27 | 0.50 | 1.55 | 1.59 ± 0.05 | 103 | Su, |
| NABC | 3.11 | 0.54 | 1.24 | 1.28 ± 0.02 | 400 | Su, |
| Total | 11.39 | 0.00 | 1.51 | 1.46 ± 0.10 | 27,449 |
Table 1 Comparison of fractal p calculation results in Bivalvia of the Deep-sea Atlantic Database (BDA), Reading University Crop Pollinator Database (RCP) and previous studies
| 数据库 Dataset | 最大值 Max. | 最小值 Min. | 中位值 Median | 平均值 Mean | 样本数量 No. of sample | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDA | 5.66 | 0.00 | 1.57 | 1.62 ± 0.66 | 242 | 本研究 This study |
| RCP | 4.92 | 0.00 | 1.11 | 1.19 ± 0.58 | 926 | 本研究 This study |
| BFD | 6.03 | 0.81 | 1.53 | 1.65 ± 0.03 | 1,265 | Gao & Su, |
| DIN | 5.46 | 0.26 | 1.66 | 1.74 ± 0.01 | 2,402 | Gao & Su, |
| DEV | 11.39 | 0.05 | 1.77 | 2.09 ± 0.02 | 2,179 | Gao & Su, |
| DINC | 5.11 | 0.29 | 1.61 | 1.67 ± 0.02 | 602 | Gao & Su, |
| Diatom | 5.83 | 0.34 | 1.27 | 1.34 ± 0.01 | 3,224 | Su, |
| Fish | 4.56 | 0.76 | 1.59 | 1.70 ± 0.02 | 761 | Su, |
| BBS | 2.38 | 0.55 | 0.94 | 0.98 ± 0.004 | 2,769 | Su, |
| CBC | 3.74 | 0.73 | 1.49 | 1.56 ± 0.01 | 1,999 | Su, |
| FIA | 2.23 | 0.24 | 0.91 | 0.93 ± 0.003 | 10,355 | Su, |
| Gentry | 1.85 | 0.35 | 0.83 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 222 | Su, |
| MCDB | 3.27 | 0.50 | 1.55 | 1.59 ± 0.05 | 103 | Su, |
| NABC | 3.11 | 0.54 | 1.24 | 1.28 ± 0.02 | 400 | Su, |
| Total | 11.39 | 0.00 | 1.51 | 1.46 ± 0.10 | 27,449 |
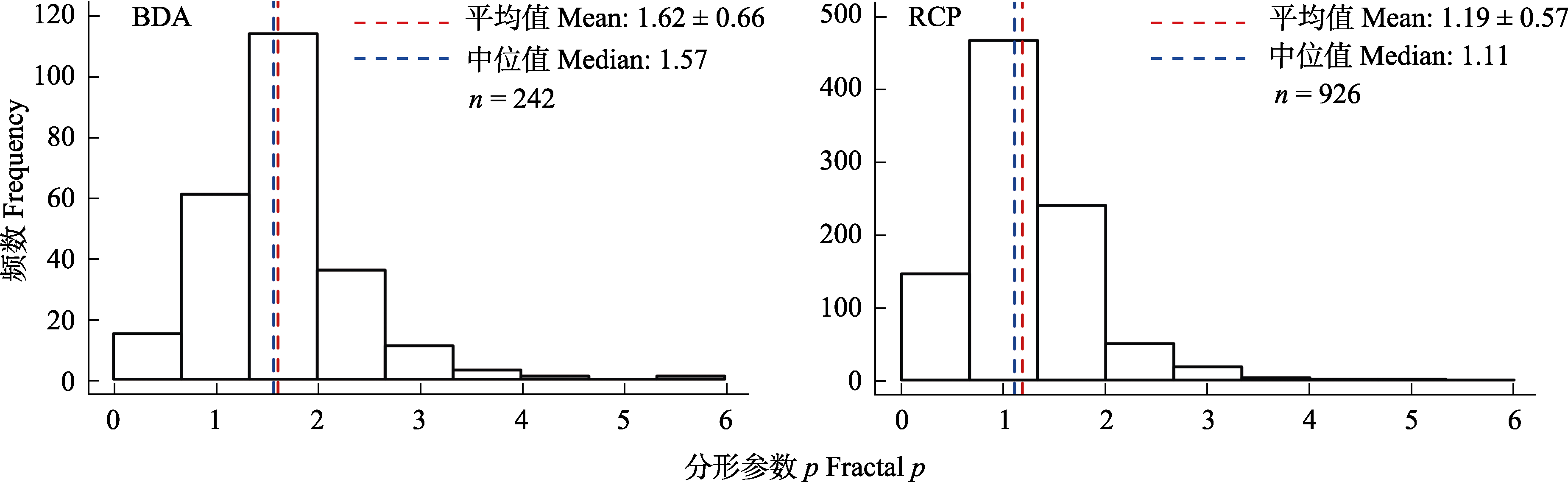
Fig. 4 The frequency distribution of the fractal p of community samples in Bivalvia of the Deep-sea Atlantic Database (BDA) and Reading University Crop Pollinator Database (RCP)
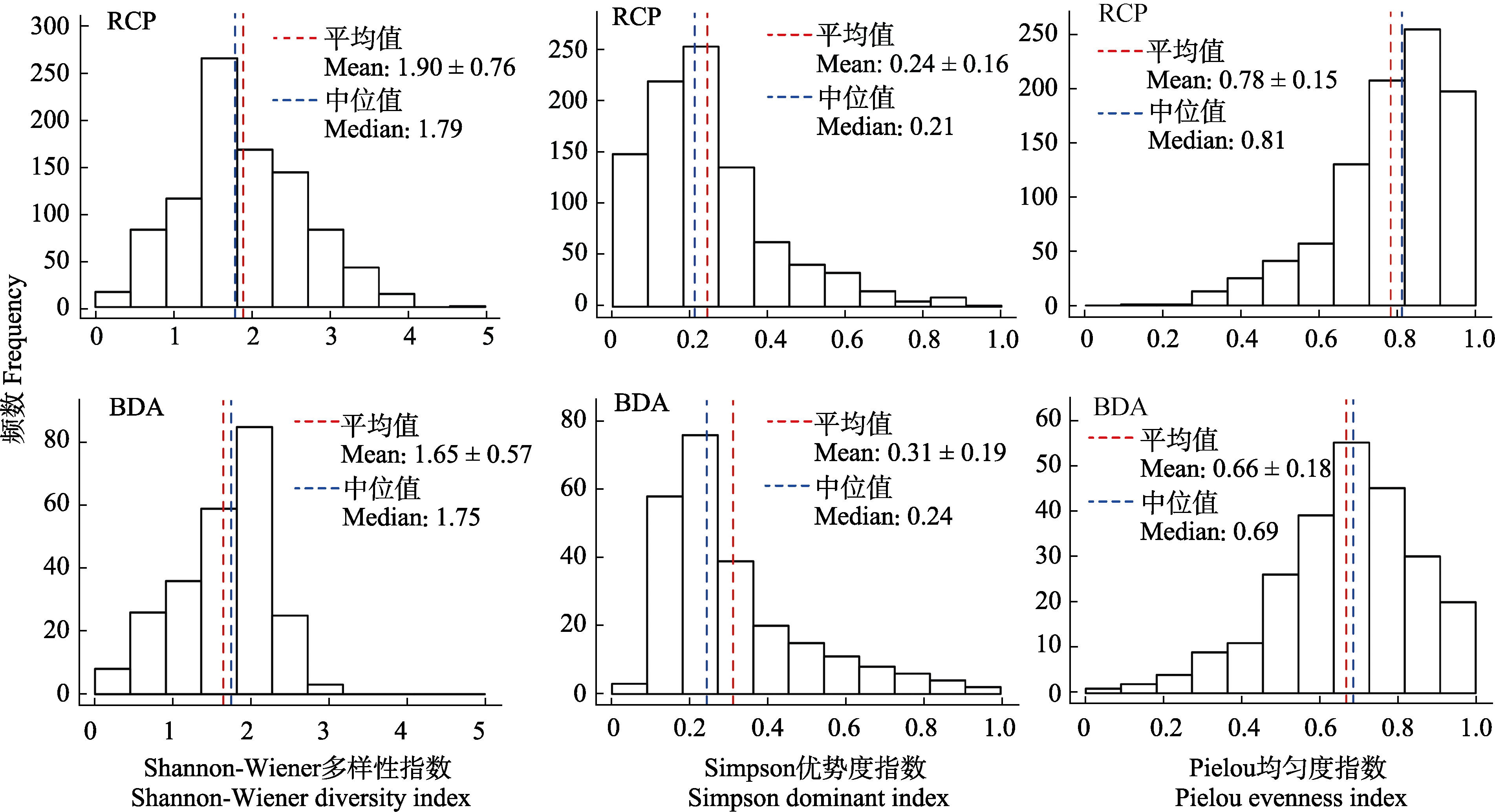
Fig. 5 The frequency distribution of diversity index of community samples in Bivalvia of the Deep-sea Atlantic Database (BDA, n = 242) and Reading University Crop Pollinator Database (RCP, n = 926)
| [1] | Alexander JM, Diez JM, Hart SP, Levine JM (2016) When climate reshuffles competitors: A call for experimental macroecology. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 831-841. |
| [2] | Allen JA (2008) Bivalvia of the deep Atlantic. Malacologia, 50, 57-173. |
| [3] | Antão LH, Bates AE, Blowes SA, Waldock C, Supp SR, Magurran AE, Dornelas M, Schipper AM (2020) Temperature-related biodiversity change across temperate marine and terrestrial systems. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 927-933. |
| [4] | Arellano G, Umaña MN, Macía MJ, Loza MI, Fuentes A, Cala V, Jørgensen PM (2017) The role of niche overlap, environmental heterogeneity, landscape roughness and productivity in shaping species abundance distributions along the Amazon-Andes gradient. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 26, 191-202. |
| [5] | Avolio ML, Komatsu KJ, Collins SL, Grman E, Koerner SE, Tredennick AT, Wilcox KR, Baer S, Boughton EH, Britton AJ, Foster B, Gough L, Hovenden M, Isbell F, Jentsch A, Johnson DS, Knapp AK, Kreyling J, Langley JA, Lortie C, McCulley RL, McLaren JR, Reich PB, Seabloom EW, Smith MD, Suding KN, Suttle KB, Tognetti PM (2021) Determinants of community compositional change are equally affected by global change. Ecology Letters, 24, 1892-1904. |
| [6] | Baldridge E, Harris DJ, Xiao X, White EP (2016) An extensive comparison of species-abundance distribution models. PeerJ, 4, e2823. |
| [7] | Baula IU, Azanza RV, Fukuyo Y, Siringan FP (2011) Dinoflagellate cyst composition, abundance and horizontal distribution in Bolinao, Pangasinan, Northern Philippines. Harmful Algae, 11, 33-44. |
| [8] | Bedford BL, Walbridge MR, Aldous A (1999) Patterns in nutrient availability and plant diversity of temperate North American wetlands. Ecology, 80, 2151-2169. |
| [9] | Benitez J, Pizarro JC, Blazina AP, Lencinas MV (2021) Response of bird communities to native forest urbanization in one of the southernmost city of the world. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 58, 126887. |
| [10] |
Brown JH (2014) Why are there so many species in the tropics? Journal of Biogeography, 41, 8-22.
PMID |
| [11] | Cerezer FO, Almeida de Azevedo R, Nascimento MAS, Franklin E, de Morais JW, de Sales Dambros C (2020) Latitudinal gradient of termite diversity indicates higher diversification and narrower thermal niches in the tropics. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29, 1967-1977. |
| [12] | Connolly S, Dornelas M (2011) Fitting and empirical evaluation of models for species abundance distributions. In: Biological Diversity: Frontiers in Measurement and Assessment (eds MagurranAE, McGill BJ), pp. 123-140. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [13] | Fisher RA, Corbet AS, Williams CB (1943) The relation between the number of species and the number of individuals in a random sample of an animal population. Journal of Animal Ecology, 12, 42-58. |
| [14] | Frontier S (1985) Diversity and structure in aquatic ecosystems. In: Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review (ed. Rnes M), pp. 253-312. Aberdeen University Press, Aberdeen. |
| [15] | Frontier S (1987) Applications of fractal theory to ecology. In: Develoments in Numerical Eecology (eds. Legendre P, Legendre L), pp. 335-378. Springer-Verlag, Berlin |
| [16] | Frontier S (1994) Species diversity as a fractal property of biomass. In: Fractals in the Natural and Applied Sciences (ed. Novak M), pp. 119-127. North-Holland Publishing, Amsterdam. |
| [17] |
Gao JF, Su Q (2021) Verification and discussion on fractal model and the general pattern on species abundance in community. Advances in Earth Science, 36, 625-631. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[高俊峰, 苏强 (2021) 群落物种多度的分形模型和一般性分布规律的验证与探讨. 地球科学进展, 36, 625-631.]
DOI |
|
| [18] | Gao JF, Su Q (2022a) A comprehensive analysis of the relationship between temperature and species diversity: The case of planktonic foraminifera. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9, 1069276. |
| [19] | Gao JF, Su Q (2022b) A multi-level exploration of the relationship between temperature and species diversity: Two cases of marine phytoplankton. Ecology and Evolution, 12, e9584. |
| [20] | Gao JF, Su Q (2023) The relationship between inorganic nutrients and diversity of dinoflagellate cysts: An evaluation from the perspective of species abundance distribution. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9, 1089331. |
| [21] | Hill MO (1973) Diversity and evenness: A unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology, 54, 427-432. |
| [22] | Hutchinson GE (1959) Homage to Santa Rosalia or why are there so many kinds of animals? The American Naturalist, 93, 145-159. |
| [23] | Lee-Yaw JA, McCune JL, Pironon S, Sheth SN (2022) Species distribution models rarely predict the biology of real populations. Ecography, 16, e05877. |
| [24] | Li H, Chen YX, Yu GL, Rossi F, Huo D, de Philippis R, Cheng XL, Wang WB, Li RH (2021) Multiple diversity facets of crucial microbial groups in biological soil crusts promote soil multifunctionality. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30, 1204-1217. |
| [25] | Loke LHL, Chisholm RA (2023) Unveiling the transition from niche to dispersal assembly in ecology. Nature, 618, 537-542. |
| [26] | Ma KM (2003) Advances of the study on species abundance pattern. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 27, 412-426. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[马克明 (2003) 物种多度格局研究进展. 植物生态学报, 27, 412-426.]
DOI |
|
| [27] | Ma KP (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. Measurement of α diversity (Part 1). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 162-168. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(上). 生物多样性, 2, 162-168.] | |
| [28] | Ma KP, Liu YM (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. Measurement of α diversity (Part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 刘玉明 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I. α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| [29] | MacArthur RH (1957) On the relative abundance of bird species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 43, 293-295. |
| [30] | Mandelbrot B (1953) An informational theory of the statistical structure of language. Communication Theory, 84, 486-502. |
| [31] | Matthews TJ, Whittaker RJ (2015) On the species abundance distribution in applied ecology and biodiversity manage- ment. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52, 443-454. |
| [32] | McClain CR (2021) The commonness of rarity in a deep-sea taxon. Oikos, 130, 863-878. |
| [33] | McGill BJ, Etienne RS, Gray JS, Alonso D, Anderson MJ, Benecha HK, Dornelas M, Enquist BJ, Green JL, He FL, Hurlbert AH, Magurran AE, Marquet PA, Maurer BA, Ostling A, Soykan CU, Ugland KI, White EP (2007) Species abundance distributions: Moving beyond single prediction theories to integration within an ecological framework. Ecology Letters, 10, 995-1015. |
| [34] |
Passy SI, Larson CA, Jamoneau A, Budnick W, Heino J, Leboucher T, Tison-Rosebery J, Soininen J (2018) Biogeographical patterns of species richness and abundance distribution in stream diatoms are driven by climate and water chemistry. The American Naturalist, 192, 605-617.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. Wiley, New York. |
| [36] | Preston FW (1948) The commonness, and rarity, of species. Ecology, 29, 254-283. |
| [37] |
Rinas CL, McMullin RT, Rousseu F, Vellend M (2023) Diversity and assembly of lichens and bryophytes on tree trunks along a temperate to boreal elevation gradient. Oecologia, 202, 55-67.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | Sankaran M, McNaughton SJ (1999) Determinants of biodiversity regulate compositional stability of communities. Nature, 401, 691-693. |
| [39] | Senapathi D (2021) Temporal Variation in Global Crop Pollinator Communities. University of Reading. http://dx.doi.org/10.17864/1947.291/. (accessed on 2023-05-30) |
| [40] | Senapathi D, Fründ J, Albrecht M, Garratt MPD, Kleijn D, Pickles BJ, Potts SG, An JD, Andersson GKS, Bänsch S, Basu P, Benjamin F, Bezerra ADM, Bhattacharya R, Biesmeijer JC, Blaauw B, Blitzer EJ, Brittain CA, Carvalheiro LG, Cariveau DP, Chakraborty P, Chatterjee A, Chatterjee S, Cusser S, Danforth BN, Degani E, Freitas BM, Garibaldi LA, Geslin B, de Groot GA, Harrison T, Howlett B, Isaacs R, Jha S, Klatt BK, Krewenka K, Leigh S, Lindström SAM, Mandelik Y, McKerchar M, Park M, Pisanty G, Rader R, Reemer M, Rundlöf M, Smith B, Smith HG, Silva PN, Steffan-Dewenter I, Tscharntke T, Webber S, Westbury DB, Westphal C, Wickens JB, Wickens VJ, Winfree R, Zhang H, Klein AM (2021) Wild insect diversity increases inter-annual stability in global crop pollinator communities. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 288, 20210212. |
| [41] |
Smith MD, Koerner SE, Avolio ML, Komatsu KJ, Eby S, Forrestel EJ, Collins SL, Wilcox KR, Ahumada R, Morgan JW, Oliva G, Oñatibia GR, Overbeck GE, Peter G, Quiroga E, Sankaran M, Wu JS, Yahdjian L, Yu Q (2022) Richness, not evenness, varies across water availability gradients in grassy biomes on five continents. Oecologia, 199, 649-659.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Su Q (2015) Analyzing fractal property of species abundance distribution in a community. Advances in Earth Science, 30, 1144-1150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[苏强 (2015) 群落物种多度格局的分形解析. 地球科学进展, 30, 1144-1150.]
DOI |
|
| [43] |
Su Q (2016) Analyzing fractal property of species abundance distribution and diversity indexes. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 392, 107-112.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Su Q (2018) A general pattern of the species abundance distribution. PeerJ, 6, e5928. |
| [45] | Tang ZY, Qiao XJ, Fang JY (2009) Species-area relationship in biological communities. Biodiversity Science, 17, 549-559. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[唐志尧, 乔秀娟, 方精云 (2009) 生物群落的种-面积关系. 生物多样性, 17, 549-559.]
DOI |
|
| [46] | Thein MM, Wu LM, Corlett RT, Quan RC, Wang B (2021) Changes in seed predation along a 2300-m elevational gradient on a tropical mountain in Myanmar: A standardized test with 32 non-native plant species. Ecography, 44, 602-611. |
| [47] | Tilman D, Isbell F, Cowles JM (2014) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 45, 471-493. |
| [48] | Tokeshi M (1993) Species abundance patterns and community structure. Advances in Ecological Research, 24, 111-186. |
| [49] | Ulrich W, Ollik M, Ugland KI (2010) A meta-analysis of species-abundance distributions. Oikos, 119, 1149-1155. |
| [50] |
Villéger S, Mason NWH, Mouillot D (2008) New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology, 89, 2290-2301.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Wang QY (2006) Comparison between estimated standard error and coefficient of determination of regression. Statistics and Decision, 23, 141-141. (in Chinese) |
| [王巧英 (2006) 回归估计标准误差与可决系数的比较. 统计与决策, 23, 141-141.] | |
| [52] |
Yang QC, Zhang HH, Wang LH, Ling F, Wang ZX, Li TT, Huang JL (2021) Topography and soil content contribute to plant community composition and structure in subtropical evergreen-deciduous broadleaved mixed forests. Plant Diversity, 43, 264-274.
DOI |
| [53] |
Zhang S, Lin F, Yuan ZQ, Kuang X, Jia SH, Wang YY, Suo YY, Fang S, Wang XG, Ye J, Hao ZQ (2015) Herb layer species abundance distribution patterns in different seasons in an old-growth temperate forest in Changbai Mountain, China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 641-648. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张姗, 蔺菲, 原作强, 匡旭, 贾仕宏, 王芸芸, 索炎炎, 房帅, 王绪高, 叶吉, 郝占庆 (2015) 长白山阔叶红松林草本层物种多度分布格局及其季节动态. 生物多样性, 23, 641-648.]
DOI |
|
| [54] | Zillio T, Condit R (2007) The impact of neutrality, niche differentiation and species input on diversity and abundance distributions. Oikos, 116, 931-940. |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [7] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [8] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [9] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [10] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [11] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [12] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [13] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [14] | Hui Ran, Tianyou Yang, Xiaoqi Mi. The updated checklist of reptiles in Guizhou Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23348-. |
| [15] | Qifan Wang, Xiaohui Liu, Ziwei Zhu, Lei Liu, Xinxue Wang, Xuyang Ji, Shaochun Zhou, Zidong Zhang, Hongyu Dong, Minghai Zhang. Mammal and avian diversity in Beijicun National Nature Reserve, Heilongjiang Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
